Contents
- IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- Information About IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Trust Models and Threats
- SeND Protocol
- Cryptographically Generated Addresses in SeND
- Authorization Delegation Discovery
- SeND Deployment Models
- Host-to-Host Deployment Without a Trust Anchor
- Neighbor Solicitation Flow
- Host-Device Deployment Model
- RAs and Certificate Path Flows
- Single CA Deployment Model
- How to Configure IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- Configuring Certificate Servers to Enable SeND
- Configuring a Host to Enable SeND
- Configuring a Device to Enable SeND
- Generating the RSA Key Pair and CGA Modifier for the Key Pair
- Configuring Certificate Enrollment for a PKI
- Configuring a Cryptographically Generated Address
- Configuring General CGA Parameters
- Configuring CGA Address Generation on an Interface
- Configuring SeND Parameters
- Configuring the SeND Trustpoint
- Configuring SeND Trust Anchors on the Interface
- Configuring Secured and Nonsecured Neighbor Discovery Message Coexistence Mode
- Customizing SeND Parameters
- Configuring the SeND Time Stamp
- Configuration Examples for IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- Example: Configuring Certificate Servers
- Example: Configuring a Host to Enable SeND
- Example: Configuring a Device to Enable SeND
- Example: Configuring a SeND Trustpoint
- Example: Configuring SeND Trust Anchors
- Example: Configuring CGA Address Generation on an Interface
- Additional References
- Feature Information for IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- Glossary
IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery for Cisco software is one of several features that comprise first-hop security functionality in IPv6.
IPv6 nodes use the Neighbor Discovery (ND) protocol to discover other nodes on the link, to determine their link-layer addresses to find devices, and to maintain reachability information about the paths to active neighbors. If not secured, the Neighbor Discovery protocol is vulnerable to various attacks.
Secure neighbor discovery (SeND) is designed to counter possible threats of the Neighbor Discovery protocol. SeND defines a set of neighbor discovery options and two neighbor discovery messages. SeND also defines a new autoconfiguration mechanism to establish address ownership.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- Information About IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- How to Configure IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- Configuration Examples for IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- Additional References
- Feature Information for IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- Glossary
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
The SeND feature is available on crypto images because it involves using cryptographic libraries.
Configure the following before you implement SeND on a host:
- An Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman (RSA) key pair used to generate cryptographically generated addresses (CGAs) addresses on the interface.
- A SeND modifier that is computed using the RSA key pair.
- A key on the SeND interface.
- CGAs on the SeND interface.
- A Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) trustpoint with minimum content, such as the URL of the certificate server. A trust anchor certificate must be provisioned on the host.
Complete the following tasks before you configure SeND on a host or device:
- Configure the host with one or more trust anchors.
- Configure the host with an RSA key pair or configure the host with the capability to generate an RSA key pair locally. For hosts that do not establish their own authority using a trust anchor, these keys are not certified by any certificate authority (CA).
- Configure devices with RSA keys and corresponding certificate chains, or the capability to obtain certificate chains that match the host trust anchor at some level of the chain.
Information About IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Trust Models and Threats
There are three IPv6 neighbor discovery trust models:
- All authenticated nodes trust each other to behave correctly at the IP layer and not to send any neighbor discovery or router discovery (RD) messages that contain false information. This model represents a situation in which the nodes are under a single administration and form a closed or semiclosed group. A corporate intranet is an example of this model.
- A device is trusted by the other nodes in the network to be a legitimate device that routes packets between the local network and any connected external networks. This device is trusted to behave correctly at the IP layer and not to send any neighbor discovery or RD messages that contain false information. This model represents a public network run by an operator. The clients pay the operator, have the operator's credentials, and trust the operator to provide the IP forwarding service. The clients do not trust each other to behave correctly; any other client node must be considered able to send falsified neighbor discovery and RD messages.
- Nodes do not trust each other at the IP layer. This model is considered suitable when a trusted network operator is not available.
Nodes on the same link use neighbor discovery to detect each other's presence and link-layer addresses, to find devices, and to maintain reachability information about paths to active neighbors. Neighbor discovery is used by both hosts and devices.
SeND Protocol
The SeND protocol counters ND threats. It defines a set of ND options, and two ND messages, Certification Path Solicitation (CPS) and Certification Path Answer (CPA). It also defines an autoconfiguration mechanism to be used in conjunction with these ND options to establish address ownership.
SeND defines the mechanisms defined in the following sections for securing ND:
Cryptographically Generated Addresses in SeND
CGAs are IPv6 addresses generated from the cryptographic hash of a public key and auxiliary parameters. CGAs securely associate a cryptographic public key with an IPv6 address in the SeND protocol.
The node generating a CGA address must first obtain an RSA key pair (SeND uses an RSA public/private key pair). The node then computes the interface identifier of the IPv6 address and appends the result to the prefix to form the CGA address.
CGA address generation is a one-time event. A valid CGA cannot be spoofed, and the message must be signed with the private key that matches the public key used for CGA generation. A user cannot replay the complete SeND message (including the CGA address, CGA parameters, and CGA signature) because the signature has only a limited lifetime.
Authorization Delegation Discovery
Authorization delegation discovery is used to certify the authority of devices by using a trust anchor. A trust anchor is a third party that the host trusts and to which the device has a certification path. At a basic level, the device is certified by the trust anchor. In a more complex environment, the device is certified by a user that is certified by the trust anchor. In addition to certifying the device identity (or the right for a node to act as a device), the certification path contains information about prefixes that a device is allowed to advertise in RAs. Authorization delegation discovery enables a node to adopt a device as its default device.
SeND Deployment Models
- Host-to-Host Deployment Without a Trust Anchor
- Neighbor Solicitation Flow
- Host-Device Deployment Model
- RAs and Certificate Path Flows
- Single CA Deployment Model
Host-to-Host Deployment Without a Trust Anchor
Deployment for SeND between hosts is straightforward. The hosts can generate a pair of RSA keys locally, autoconfigure their CGA addresses, and use them to validate their sender authority, rather than using a trust anchor to establish sender authority. The figure below illustrates this model.
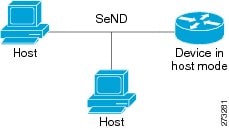
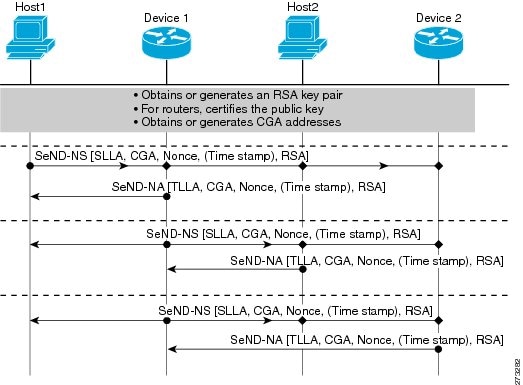
Neighbor Solicitation Flow
In a neighbor solicitation scenario, hosts and devices in host mode exchange neighbor solicitations and neighbor advertisements. These neighbor solicitations and neighbor advertisements are secured with CGA addresses and CGA options, and have nonce, time stamp, and RSA neighbor discovery options. The figure below illustrates this scenario.
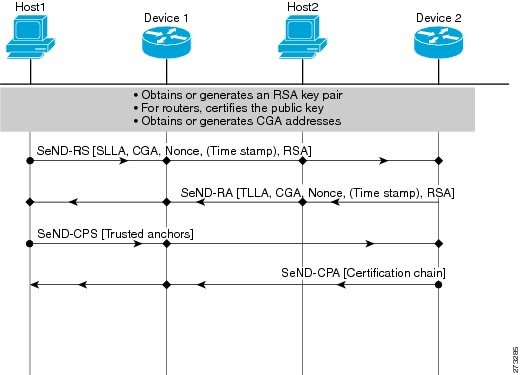
Host-Device Deployment Model
In many cases, hosts will not have access to the infrastructure that enables them to obtain and announce their certificates. In these situations, hosts secure their relationships using CGA, and secure their relationships with devices using trusted anchors. When using RAs, devices must be authenticated through a trust anchor. The figure below illustrates this scenario.
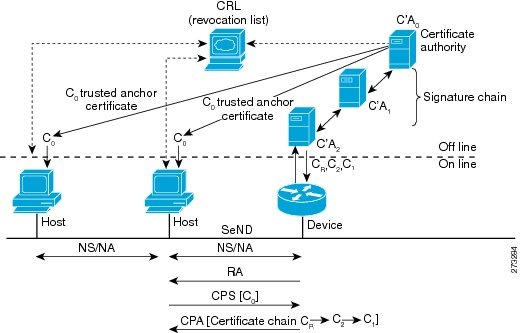
RAs and Certificate Path Flows
The figure below shows the certificate exchange performed using certification path solicitation CPS/CPA SeND messages. In the illustration, Router 1 is certified (using an X.509 certificate) by its own certification authority (CA). The CA itself (CA2) is certified by its own CA (certificates C2), and so on, up to a CA (CA0) that the hosts trusts. The certificate CR contains IP extensions per RFC 3779, which describes which prefix ranges the Router 1 is allowed to announce (in RAs). This prefix range, certified by CA2, is a subset of CA2's own range, certified by CA1, and so on. Part of the validation process when a certification chain is received consists of validating the certification chain and the consistency of nested prefix ranges.
How to Configure IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
Certificate servers are used to grant certificates after validating or certifying key pairs. A tool for granting certificates is mandatory in any SeND deployment. However, few certificate servers support granting certificates that contain IP extensions. Cisco certificate servers support every kind of certificate, including certificates containing IP extensions.
SeND is available in host mode. The set of available functions on a host are a subset of SeND functionality. CGA is fully available, and the prefix authorization delegation is supported on the host side (the sending CPS and receiving CPA).
SeND is also available in device mode. Use the ipv6 unicast-routing command to configure a node to a device. To implement SeND, configure devices with the same elements as that of the host. The devices will need to retrieve certificates of their own from a certificate server. The RSA key and subject name of the trustpoint are used to retrieve certificates from a certificate server. Once the certificate has been obtained and uploaded, the device generates a certificate request to the certificate server and installs the certificate.
Hosts and devices must either retrieve or generate their CGAs when they are booted. Typically, devices autoconfigure their CGAs once and save them (along with the key pair used in the CGA operation) in their permanent storage. At a minimum, link-local addresses on a SeND interface should be CGAs. Additionally, global addresses can be CGAs.
- Configuring Certificate Servers to Enable SeND
- Configuring a Host to Enable SeND
- Configuring a Device to Enable SeND
- Generating the RSA Key Pair and CGA Modifier for the Key Pair
- Configuring Certificate Enrollment for a PKI
- Configuring a Cryptographically Generated Address
- Configuring SeND Parameters
Configuring Certificate Servers to Enable SeND
Hosts and devices must be configured with RSA key pairs and corresponding certificate chains before the SeND parameters are configured. Perform the following task to configure the certificate server to grant certificates. Once the certificate server is configured, other parameters for the certificate server can be configured.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a Host to Enable SeND
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a Device to Enable SeND
DETAILED STEPS
Generating the RSA Key Pair and CGA Modifier for the Key Pair
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Certificate Enrollment for a PKI
Certificate enrollment, which is the process of obtaining a certificate from a CA, occurs between the end host that requests the certificate and the CA. Each peer that participates in the PKI must enroll with a CA. In IPv6, you can autoenroll or manually enroll the device certificate.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a Cryptographically Generated Address
Configuring General CGA Parameters
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring CGA Address Generation on an Interface
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring SeND Parameters
- Configuring the SeND Trustpoint
- Configuring SeND Trust Anchors on the Interface
- Configuring Secured and Nonsecured Neighbor Discovery Message Coexistence Mode
- Customizing SeND Parameters
- Configuring the SeND Time Stamp
Configuring the SeND Trustpoint
The key pair used to generate the CGA addresses on an interface must be certified by the CA and the certificate sent on demand over the SeND protocol. One RSA key pair and associated certificate is enough for SeND to operate; however, users may use several keys, identified by different labels. SeND and CGA refer to a key directly by label or indirectly by trustpoint.
Multiple steps are required to bind SeND to a trustpoint. First, a key pair is generated. Then the device refers to it in a trustpoint, and next the SeND interface configuration points to the trustpoint. There are two reasons for the multiple steps:
- The same key pair can be used on several SeND interfaces.
- The trustpoint contains additional information, such as the certificate, required for SeND to perform authorization delegation.
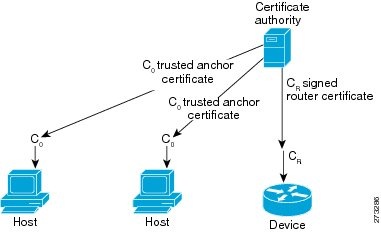
A CA certificate must be uploaded for the referred trustpoint, which is a trusted anchor.
Several trustpoints, pointing to the same RSA keys, can be configured on a given interface. This function is useful if different hosts have different trusted anchors (that is, CAs that they trust). The device can then provide each host with the certificate signed by the CA it trusts.
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
crypto
key
generate
rsa
[general-keys |
usage-keys |
signature |
encryption] [label
key-label] [exportable] [modulus
modulus-size] [storage
devicename:] [on
devicename:]
Example: Device(config)# crypto key generate rsa label SEND |
Generates RSA key pairs. |
Step 4 |
ipv6
cga
modifier
rsakeypair
key-label
sec-level
{0 |
1}
Example: Device(config)# ipv6 cga modifier rsakeypair SEND sec-level 1 |
Generates the CGA modifier for a specified RSA key, which enables the key to be used by SeND. |
Step 5 |
crypto
pki
trustpoint
name
Example: Device(config)# crypto pki trustpoint trustpoint1 |
Defines the trustpoint that the device should use, and enters ca-trustpoint configuration mode. |
Step 6 |
subject-name
[x.500-name]
Example: Device(ca-trustpoint)# subject-name name1 |
Specifies the subject name in the certificate request. |
Step 7 |
rsakeypair
key-label
[
key-size
[encryption-key-size]]
Example: Device(ca-trustpoint)# rsakeypair SEND |
Specifies which key pair to associate with the certificate. |
Step 8 |
enrollment
terminal
[pem]
Example: Device(ca-trustpoint)# enrollment terminal |
Specifies manual cut-and-paste certificate enrollment. |
Step 9 |
ip-extension
[multicast |
unicast] {inherit [ipv4 |
ipv6] |
prefix
ipaddress |
range
min-ipaddress
max-ipaddress}
Example: Device(ca-trustpoint)# ip-extension unicast prefix 2001:100:1://48 |
Adds IP extensions to the device certificate request. |
Step 10 |
exit
Example: Device(ca-trustpoint)# exit |
Exits ca-trustpoint configuration mode, and returns to global configuration mode. |
Step 11 |
crypto
pki
authenticate
name
Example: Device(config)# crypto pki authenticate trustpoint1 |
Authenticates the certification authority by getting the certificate of the CA. |
Step 12 |
crypto
pki
enroll
name
Example: Device(config)# crypto pki enroll trustpoint1 |
Obtains the certificates for your device from the CA. |
Step 13 |
crypto
pki
import
name
certificate
Example: Device(config)# crypto pki import trustpoint1 certificate |
Imports a certificate manually using TFTP or the cut-and-paste method at the terminal. |
Step 14 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Ethernet 0/0 |
Specifies an interface type and number, and places the device in interface configuration mode. |
Step 15 |
ipv6
nd
secured
trustpoint
trustpoint-name
Example: Device(config-if)# ipv6 nd secured trustpoint trustpoint1 |
Enables SeND on an interface, and specifies which trustpoint should be used. |
Configuring SeND Trust Anchors on the Interface
As soon as SeND is bound to a trustpoint on an interface, this trustpoint is also a trust anchor. A trust anchor configuration consists of the following items:
- A public key signature algorithm and associated public key, which may include parameters
- A name
- An optional public key identifier
- An optional list of address ranges for which the trust anchor is authorized
The trust anchor configuration is accomplished by binding SeND to one or several PKI trustpoints. PKI is used to upload the corresponding certificates, which contain the required parameters, such as name and key.
This optional task allows you to select trust anchors listed in the CPS when requesting for a certificate.
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
crypto
pki
trustpoint
name
Example: Device(config)# crypto pki trustpoint anchor1 |
Defines the trustpoint for the device to use, and enters ca-trustpoint configuration mode. |
Step 4 |
enrollment
terminal
[pem]
Example: Device(ca-trustpoint)# enrollment terminal |
Specifies manual cut-and-paste certificate enrollment. |
Step 5 |
exit
Example: Device(ca-trustpoint)# exit |
Returns to global configuration. |
Step 6 |
crypto
pki
authenticate
name
Example: Device(config)# crypto pki authenticate anchor1 |
Authenticates the certification authority by getting the certificate of the CA. |
Step 7 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Ethernet 0/0 |
Specifies an interface type and number, and places the device in interface configuration mode. |
Step 8 |
ipv6
nd
secured
trustanchor
trustanchor-name
Example: Device(config-if)# ipv6 nd secured trustanchor anchor1 |
Configures a trusted anchor on an interface, and binds SeND to a trustpoint. |
Configuring Secured and Nonsecured Neighbor Discovery Message Coexistence Mode
During the transition to SeND secured interfaces, network operators may want to run a particular interface with a mixture of nodes accepting secured and unsecured neighbor discovery messages. Perform this task to configure the coexistence mode for secure and nonsecure ND messages on the same interface.
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Ethernet 0/0 |
Specifies an interface type and number, and places the device in interface configuration mode. |
Step 4 |
ipv6
nd
secured
trustpoint
trustpoint-name
Example: Device(config-if)# ipv6 nd secured trustpoint trustpoint1 |
Enables SeND on an interface and specifies which trustpoint should be used. |
Step 5 |
no
ipv6
nd
secured
full-secure
Example: Device(config-if)# no ipv6 nd secured full-secure |
Provides the coexistence mode for secure and nonsecure ND messages on the same interface. |
Customizing SeND Parameters
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
ipv6
nd
secured
key-length
[[minimum |
maximum]
value]
Example: Device(config)# ipv6 nd secured key-length minimum 512 |
Configures the SeND key-length options. |
Step 4 |
ipv6
nd
secured
sec-level
minimum
value
Example: Device(config)# ipv6 nd secured sec-level minimum 2 |
Configures the minimum security level value that can be accepted from peers. |
Configuring the SeND Time Stamp
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Ethernet 0/0 |
Specifies an interface type and number, and places the device in interface configuration mode. |
Step 4 |
ipv6
nd
secured
timestamp
{delta
value
|
fuzz
value}
Example: Device(config-if)# ipv6 nd secured timestamp delta 600 |
Configures the SeND time stamp. |
Configuration Examples for IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
- Example: Configuring Certificate Servers
- Example: Configuring a Host to Enable SeND
- Example: Configuring a Device to Enable SeND
- Example: Configuring a SeND Trustpoint
- Example: Configuring SeND Trust Anchors
- Example: Configuring CGA Address Generation on an Interface
Example: Configuring Certificate Servers
crypto pki server CA issuer-name C=FR, ST=fr, L=example, O=cisco, OU=nsstg, CN=CA0 lifetime ca-certificate 700 ! crypto pki trustpoint CA ip-extension prefix 2001::/16 revocation-check crl rsakeypair CA no shutdown
To display the certificate servers with IP extensions, use the show crypto pki certificates verbose command:
Device# show crypto pki certificates verbose
CA Certificate
Status: Available
Version: 3
Certificate Serial Number (hex): 01
Certificate Usage: Signature
Issuer:
c=FR
st=fr
l=example
o=cisco
ou=nsstg
cn=CA0
Subject:
c=FR
st=fr
l=example
o=cisco
ou=nsstg
cn=CA0
Validity Date:
start date: 09:50:52 GMT Feb 5 2009
end date: 09:50:52 GMT Jan 6 2011
Subject Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
RSA Public Key: (1024 bit)
Signature Algorithm: MD5 with RSA Encryption
Fingerprint MD5: 87DB764F 29367A65 D05CEE3D C12E0AC3
Fingerprint SHA1: 04A06602 86AA72E9 43F2DB33 4A7D40A2 E2ED3325
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: 86000000
Digital Signature
Key Cert Sign
CRL Signature
X509v3 Subject Key ID: 75B477C6 B2CA7BBE C7866657 57C84A32 90CEFB5A
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA: TRUE
X509v3 Authority Key ID: 75B477C6 B2CA7BBE C7866657 57C84A32 90CEFB5A
Authority Info Access:
X509v3 IP Extension:
IPv6:
2001::/16
Associated Trustpoints: CA
Example: Configuring a Host to Enable SeND
crypto key generate rsa label SEND modulus 1024 The name for the keys will be: SEND % The key modulus size is 1024 bits % Generating 1024 bit RSA keys, keys will be non-exportable...[OK] ipv6 cga modifier rsakeypair SEND sec-level 1 crypto pki trustpoint SEND enrollment url http://10.165.200.254 revocation-check none exit crypto pki authenticate SEND Certificate has the following attributes: Fingerprint MD5: FC99580D 0A280EB4 2EB9E72B 941E9BDA Fingerprint SHA1: 22B10EF0 9A519177 145EA4F6 73667837 3A154C53 % Do you accept this certificate? [yes/no]: yes Trustpoint CA certificate accepted. ipv6 nd secured sec-level minimum 1 interface fastethernet 0/0 ipv6 cga rsakeypair SEND ipv6 address FE80::260:3EFF:FE11:6770 link-local cga ipv6 nd secured trustanchor SEND ipv6 nd secured timestamp delta 300 exit ipv6 nd secured full-secure
Use the show running-config command to verify the configuration:
Device# show running-config
Building configuration...
[snip]
crypto pki trustpoint SEND
enrollment url http://10.165.200.225
revocation-check none
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 10.165.202.129 255.255.255.0
duplex half
ipv6 cga rsakeypair SEND
ipv6 address 2001:100::/64 cga
Example: Configuring a Device to Enable SeND
crypto key generate rsa label SEND modulus 1024 ipv6 cga modifier rsakeypair SEND sec-level 1 crypto pki trustpoint SEND subject-name C=FR, ST=PACA, L=Example, O=Cisco, OU=NSSTG, CN=device rsakeypair SEND revocation-check none exit crypto pki authenticate key1 Certificate has the following attributes: Fingerprint MD5: FC99580D 0A280EB4 2EB9E72B 941E9BDA Fingerprint SHA1: 22B10EF0 9A519177 145EA4F6 73667837 3A154C53 % Do you accept this certificate? [yes/no]: yes Trustpoint CA certificate accepted. crypto pki enroll SEND % Start certificate enrollment .. % Create a challenge password. You will need to verbally provide this password to the CA Administrator in order to revoke your certificate. For security reasons your password will not be saved in the configuration. Please make a note of it. Password: Re-enter password: % The subject name in the certificate will include: C=FR, ST=fr, L=example, O=cisco, OU=nsstg, CN=device % The subject name in the certificate will include: Device % Include the device serial number in the subject name? [yes/no]: no % Include an IP address in the subject name? [no]: Request certificate from CA? [yes/no]: yes % Certificate request sent to Certificate Authority % The 'show crypto pki certificate SEND verbose' commandwill show the fingerprint. *Feb 5 09:40:37.171: CRYPTO_PKI: Certificate Request Fingerprint MD5: A6892F9F 23561949 4CE96BB8 CBC85 E64 *Feb 5 09:40:37.175: CRYPTO_PKI: Certificate Request Fingerprint SHA1: 30832A66 E6EB37DF E578911D 383F 96A0 B30152E7 *Feb 5 09:40:39.843: %PKI-6-CERTRET: Certificate received from Certificate Authority interface fastethernet 0/0 ipv6 nd secured sec-level minimum 1 ipv6 cga rsakeypair SEND ipv6 address fe80:: link-local cga ipv6 nd secured trustanchor SEND ipv6 nd secured timestamp delta 300 exit ipv6 nd secured full-secure
To verify that the certificates are generated, use the show crypto pki certificates command:
Device# show crypto pki certificates
Certificate
Status: Available
Certificate Serial Number: 0x15
Certificate Usage: General Purpose
Issuer:
cn=CA
Subject:
Name: Device
hostname=Device
c=FR
st=fr
l=example
o=cisco
ou=nsstg
cn=device
Validity Date:
start date: 09:40:38 UTC Feb 5 2009
end date: 09:40:38 UTC Feb 5 2010
Associated Trustpoints: SEND
CA Certificate
Status: Available
Certificate Serial Number: 0x1
Certificate Usage: Signature
Issuer:
cn=CA
Subject:
cn=CA
Validity Date:
start date: 10:54:53 UTC Jun 20 2008
end date: 10:54:53 UTC Jun 20 2011
Associated Trustpoints: SEND
To verify the configuration, use the show running-config command:
Device# show running-config
Building configuration...
[snip]
crypto pki trustpoint SEND
enrollment url http://209.165.201.1
subject-name C=FR, ST=fr, L=example, O=cisco, OU=nsstg, CN=device
revocation-check none rsakeypair SEND !
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.0
duplex half
ipv6 cga rsakeypair SEND
ipv6 address FE80:: link-local cga
ipv6 address 2001:100::/64 cga
Example: Configuring a SeND Trustpoint
crypto key generate rsa label SEND Choose the size of the key modulus in the range of 360 to 2048 for your General Purpose Keys. Choosing a key modulus greater than 512 may take a few minutes. How many bits in the modulus [512]: 778 % Generating 778 bit RSA keys, keys will be non-exportable...[OK] ipv6 cga modifier rsakeypair SEND sec-level 1 crypto pki trustpoint trustpoint1 subject-name C=FR, ST=fr, L=example, O=cisco, OU=nsstg, CN=sa14-72b rsakeypair SEND enrollment terminal ip-extension unicast prefix 2001:100:1://48 exit crypto pki authenticate trustpoint1 crypto pki enroll trustpoint1 crypto pki import trustpoint1 certificate interface Ethernet 0/0 ipv6 nd secured trustpoint trustpoint1
Example: Configuring SeND Trust Anchors
! Configure the location of the CS we trust ! crypto pki trustpoint B1 enrollment terminal crypto pki authenticate anchor1 exit ! Only Query a certificate signed by the CS at B2 on this interface ! interface Ethernet 0/0 ip address 204.209.1.54 255.255.255.0 ipv6 cga rsakeypair SEND ipv6 address 2001:100::/64 cga ipv6 nd secured trustanchor anchor1
Additional References
Related Documents
MIBs
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery |
| Feature Name | Releases | Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
IPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery |
12.4(24)T |
The SeND protocol is designed to counter the threats of the ND protocol. SeND defines a set of neighbor discovery options and two neighbor discovery messages. SeND also defines a new autoconfiguration mechanism to establish address ownership. The following commands were introduced or modified: auto-enroll, crypto key generate rsa, crypto pki authenticate, crypto pki enroll, crypto pki import, enrollment terminal (ca-trustpoint), enrollment url (ca-trustpoint), fingerprint, ip-extension, ip http server, ipv6 address, ipv6 address link-local, ipv6 cga modifier rsakeypair, ipv6 cga modifier rsakeypair (interface), ipv6 nd secured certificate-db, ipv6 nd secured full-secure, ipv6 nd secured full-secure (interface), ipv6 nd secured key-length, ipv6 nd secured sec-level, ipv6 nd secured timestamp, ipv6 nd secured timestamp-db, ipv6 nd secured trustanchor, ipv6 nd secured trustpoint, password (ca-trustpoint), revocation-check, rsakeypair, serial-number (ca-trustpoint), show ipv6 cga address-db, show ipv6 cga modifier-db, show ipv6 nd secured certificates, show ipv6 nd secured counters interface, show ipv6 nd secured nonce-db, show ipv6 nd secured timestamp-db, subject-name. |
Glossary
- CA--certification authority.
- CGA--cryptographically generated address.
- CPA--certificate path answer.
- CPR--certificate path response.
- CPS--certification path solicitation. The solicitation message used in the addressing process.
- CRL--certificate revocation list.
- CS--certification server.
- CSR--certificate signing request.
- DAD--duplicate address detection. A mechanism that ensures two IPv6 nodes on the same link are not using the same address.
- DER--distinguished encoding rules. An encoding scheme for data values.
- nonce--An unpredictable random or pseudorandom number generated by a node and used once. In SeND, nonces are used to assure that a particular advertisement is linked to the solicitation that triggered it.
- non-SeND node--An IPv6 node that does not implement SeND but uses only the Neighbor Discovery protocol without security.
- NUD--neighbor unreachability detection. A mechanism used for tracking neighbor reachability.
- PACL--port-based access list.
- PKI--public key infrastructure.
- RA--router advertisement.
- RD--Router discovery allows the hosts to discover what devices exist on the link and what subnet prefixes are available. Router discovery is a part of the Neighbor Discovery protocol.
- Router Authorization Certificate--A public key certificate.
- SeND node--An IPv6 node that implements SeND.
- trust anchor--An entity that the host trusts to authorize devices to act as devices. Hosts are configured with a set of trust anchors to protect device discovery.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.

 Feedback
Feedback