Contents
- Configuration Examples for IOS SLB
- Example How to Configure a Basic IOS SLB Network
- Server Farm Configuration
- Virtual Server Configuration
- Restricted Client Configuration
- Example How to Configure a Complete IOS SLB Network
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Firewall Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Basic Firewall Load Balancing
- Internal Firewall Load-Balancing Device
- External Firewall Load-Balancing Device
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Server Load Balancing and Firewall Load Balancing
- Internal Server and Firewall Load-Balancing Device
- External Firewall Load-Balancing Device
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Multiple Firewall Farms
- Internal Firewall Load-Balancing Device
- External Firewall Load-Balancing Device
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Dual Firewall Load Balancing "Sandwich"
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Probes
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Ping and HTTP Probes
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Routed Probe
- Example How to Configure a Layer 3 Switch with IOS SLB
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with NAT and Static NAT
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with NAT
- Switch A Configuration Statements
- Switch B Configuration Statements
- Switch C Configuration Statements
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Static NAT
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Redundancy
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Stateless Backup
- Example How to Configure Dynamic Routing and Trunking
- SLB 1 Configuration Statements
- SLB 2 Configuration Statements
- Example How to Configure Dynamic Routing and No Trunking
- SLB 1 Configuration Statements
- SLB 2 Configuration Statements
- Example How to Configure Static Routing and Trunking
- SLB 1 Configuration Statements
- SLB 2 Configuration Statements
- Distribution Device Configuration Statements
- Example How to Configure Static Routing and No Trunking
- SLB 1 Configuration Statements
- SLB 2 Configuration Statements
- Distribution Device Configuration Statements
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Stateful Backup
- Switch SLB1 Configuration Statements
- Switch SLB2 Configuration Statements
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Stateful Backup of Redundant Route Processors
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Active Standby
- SLB 1 Configuration Statements
- SLB 2 Configuration Statements
- Access Router Configuration Statements
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Redistribution of Static Routes
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
- Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (Enhanced IGRP)
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with WAP and UDP Load Balancing
- Example How to Balance WAP Flows on UDP Port 9201
- Example How to Balance WAP Flows on UDP Port 9203
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Route Health Injection
- Example How to Configure Two Distributed Sites with One Web Server Each
- Example How to Configure Two Distributed Sites with Two Web Servers Each
- Example How to Configure Two Distributed Sites with One Web Server and a Backup IOS SLB Switch Each
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing Without GTP Cause Code Inspection
- IOS SLB Configuration Statements
- GGSN1 Configuration Statements
- GGSN2 Configuration Statements
- GGSN3 Configuration Statements
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing and NAT
- IOS SLB Configuration Statements
- GGSN1 Configuration Statements
- GGSN2 Configuration Statements
- GGSN3 Configuration Statements
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing NAT and GTP Cause Code Inspection
- IOS SLB Configuration Statements
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing Maps
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Dual-Stack Addresses for GTP Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with VPN Server Load Balancing
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for a GPRS Network
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for a Simple IP CDMA2000 Network
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for a Mobile IP CDMA2000 Network
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for Multiple Service Gateway Farms
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing Firewall Load Balancing "Sandwich"
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing Maps
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing Accelerated Data Plane Forwarding
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Home Agent Director
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Sticky Connections
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GTP IMSI Sticky Database
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with ASN Sticky Database
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Transparent Web Cache Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with KAL-AP Agent
- GSS
- Site-1 IOS SLB - CHICAGO
- GGSN-1
- GGSN-2
- Site-2 IOS SLB - NEWYORK
- GGSN-1
- GGSN-2
- Example How to Configure Combined IOS SLB
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB IPv6 Configuration
- Example How to Configure Combined IOS SLB
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB IPv6 Configuration
Configuration Examples for IOS SLB
This section provides real-world examples of IOS SLB configurations. For a complete description of the IOS SLB commands in this section, refer to the Cisco IOS IP Application Services Command Reference. To locate documentation of other commands that appear in this section, search online using Cisco.com.
This section includes the following examples:
 Note | The IP and network addresses in these examples are generic; you must replace them with the actual addresses for your network. |
- Example How to Configure a Basic IOS SLB Network
- Example How to Configure a Complete IOS SLB Network
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Firewall Load Balancing
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Probes
- Example How to Configure a Layer 3 Switch with IOS SLB
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with NAT and Static NAT
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Redundancy
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Redistribution of Static Routes
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with WAP and UDP Load Balancing
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Route Health Injection
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with VPN Server Load Balancing
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Home Agent Director
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Sticky Connections
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GTP IMSI Sticky Database
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with ASN Sticky Database
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Transparent Web Cache Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with KAL-AP Agent
- Example How to Configure Combined IOS SLB
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB IPv6 Configuration
- Example How to Configure Combined IOS SLB
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB IPv6 Configuration
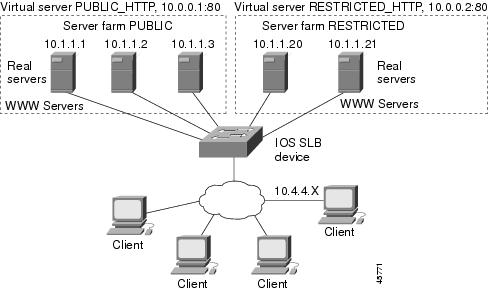
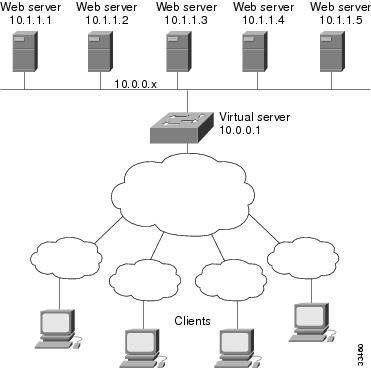
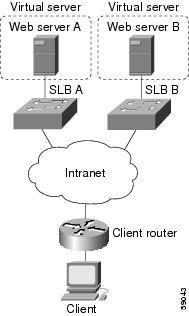
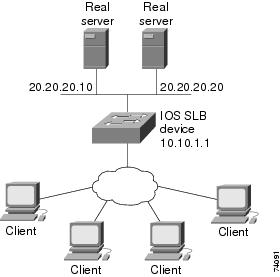
Example How to Configure a Basic IOS SLB Network
The figure below shows a sample IOS SLB network with the following components:
- Two server farms--one configured to allow access by the public and named PUBLIC, one configured to allow limited access and named RESTRICTED.
- Five real servers configured as follows:
- Two virtual servers--one configured to allow access by the public and named PUBLIC_HTTP and one configured to allow limited access and named RESTRICTED_HTTP.
- Virtual server PUBLIC_HTTP is configured with IP address 10.0.0.1 load balancing TCP connections on the WWW port (80).
- Virtual server RESTRICTED_HTTP is configured with IP address 10.0.0.2 load balancing TCP connections on the WWW port (80) and allows access only from clients from network 10.4.4.0 255.255.255.0.
The following sections include examples of the configuration commands used to configure and verify the IOS SLB network shown in the figure above.
Server Farm Configuration
The following example shows the configuration for the server farm PUBLIC, associated with three real servers:
ip slb serverfarm PUBLIC
real 10.1.1.1
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4 numclients 2
retry 20
inservice
exit
real 10.1.1.2
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
exit
real 10.1.1.3
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
end
The following example shows the configuration for the server farm RESTRICTED, associated with two real servers:
ip slb serverfarm RESTRICTED
real 10.1.1.20
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
exit
real 10.1.1.21
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
end
Virtual Server Configuration
The following example shows the configuration for the virtual servers PUBLIC_HTTP and RESTRICTED_HTTP:
ip slb vserver PUBLIC_HTTP virtual 10.0.0.1 tcp www serverfarm PUBLIC idle 120 delay 5 inservice exit ip slb vserver RESTRICTED_HTTP virtual 10.0.0.2 tcp www serverfarm RESTRICTED idle 120 delay 5 inservice end
Example How to Configure a Complete IOS SLB Network
The following example provides a complete configuration using many of the commands described in this feature document:
ip slb probe PROBE2 http request method POST url /probe.cgi?all header HeaderName HeaderValue ! ip slb serverfarm PUBLIC nat server real 10.1.1.1 reassign 4 faildetect numconns 16 retry 120 inservice real 10.1.1.2 reassign 4 faildetect numconns 16 retry 120 inservice probe PROBE2 ! ip slb serverfarm RESTRICTED predictor leastconns bindid 309 real 10.1.1.1 weight 32 maxconns 1000 reassign 4 faildetect numconns 16 retry 120 inservice real 10.1.1.20 reassign 4 faildetect numconns 16 retry 120 inservice real 10.1.1.21 reassign 4 faildetect numconns 16 retry 120 inservice ! ip slb vserver PUBLIC_HTTP virtual 10.0.0.1 tcp www serverfarm PUBLIC ! ip slb vserver RESTRICTED_HTTP virtual 10.0.0.2 tcp www serverfarm RESTRICTED no advertise sticky 60 group 1 idle 120 delay 5 client 10.4.4.0 255.255.255.0 synguard 3600000 inservice
Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Firewall Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Basic Firewall Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Server Load Balancing and Firewall Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Multiple Firewall Farms
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Dual Firewall Load Balancing "Sandwich"
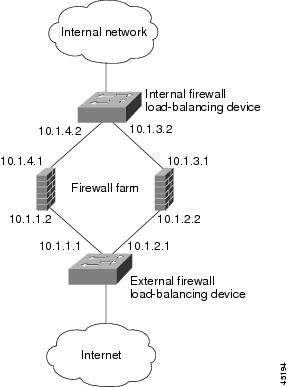
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Basic Firewall Load Balancing
The figure below shows a sample IOS SLB firewall load-balancing network with the following components:
- Two firewalls with IP addresses as shown
- An internal firewall load-balancing device on the secure side of the firewalls
- An external firewall load-balancing device on the Internet side of the firewalls
- One firewall farm named FIRE1, containing both firewalls
When you configure IOS SLB firewall load balancing, the load-balancing devices use route lookup to recognize flows destined for the firewalls. To enable route lookup, you must configure each device with the IP address of each firewall that will route flows to that device.
In the following firewall farm configuration samples:
Internal Firewall Load-Balancing Device
The following example shows the configuration for ping probe PROBE1, HTTP probe PROBE2, and firewall farm FIRE1, associated with the two real servers for the load-balancing device on the internal (secure) side of the firewall:
!-----Ping probe
ip slb probe PROBE1 ping
!-----IP address of other load-balancing device
address 10.1.1.1
faildetect 4
!-----HTTP probe
ip slb probe PROBE2 http
!-----IP address of other load-balancing device
address 10.1.2.1
expect status 401
!-----Firewall farm FIRE1
ip slb firewallfarm FIRE1
!-----First firewall
real 10.1.4.1
probe PROBE1
!-----Enable first firewall
inservice
!-----Second firewall
real 10.1.3.1
probe PROBE2
!-----Enable second firewall
inservice
External Firewall Load-Balancing Device
The following example shows the configuration for ping probe PROBE1, HTTP probe PROBE2, and firewall farm FIRE1, associated with the two real servers for the load-balancing device on the external (Internet) side of the firewall:
!-----Ping probe
ip slb probe PROBE1 ping
!-----IP address of other load-balancing device
address 10.1.4.2
faildetect 4
!-----HTTP probe
ip slb probe PROBE2 http
!-----IP address of other load-balancing device
address 10.1.3.2
expect status 401
!-----Firewall farm FIRE1
ip slb firewallfarm FIRE1
!-----First firewall
real 10.1.1.2
probe PROBE1
!-----Enable first firewall
inservice
!-----Second firewall
real 10.1.2.2
probe PROBE2
!-----Enable second firewall
inservice
exit
inservice
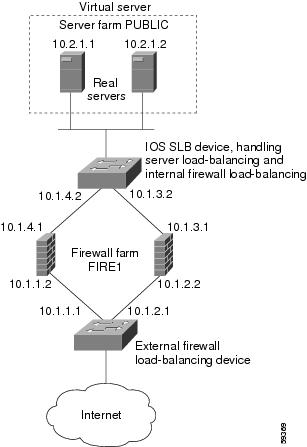
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Server Load Balancing and Firewall Load Balancing
The figure below shows a sample IOS SLB load-balancing network with server load balancing and firewall load balancing running together, and the following components:
- Two real servers with IP addresses as shown
- One server farm named PUBLIC, containing both real servers
- Two firewalls with IP addresses as shown
- One firewall farm named FIRE1, containing both firewalls
- An internal IOS SLB device on the secure side of the firewalls, performing server load balancing and firewall load balancing
- An external firewall load-balancing device on the Internet side of the firewalls
In the following firewall farm configuration samples:
Internal Server and Firewall Load-Balancing Device
The following example shows the configuration for ping probes ABCPROBE and XYZPROBE, firewall farm FIRE1, and server farm PUBLIC for the load-balancing device on the internal (secure) side of the firewalls:
ip slb probe ABCPROBE ping
address 10.1.1.1
ip slb probe XYZPROBE ping
address 10.1.2.1
!
ip slb firewallfarm FIRE1
real 10.1.4.1
probe ABCPROBE
inservice
real 10.1.3.1
probe XYZPROBE
inservice
inservice
!
ip slb serverfarm PUBLIC
nat server
real 10.2.1.1
inservice
real 10.2.1.2
inservice
!
ip slb vserver HTTP1
virtual 128.1.0.1 tcp www
serverfarm PUBLIC
idle 120
delay 5
inservice
External Firewall Load-Balancing Device
The following example shows the configuration for ping probes ABCPROBE and XYZPROBE and firewall farm FIRE1 for the load-balancing device on the external (Internet) side of the firewalls:
ip slb probe ABCPROBE ping
address 10.1.4.2
ip slb probe XYZPROBE ping
address 10.1.3.2
ip slb firewallfarm FIRE1
real 10.1.1.2
probe ABCPROBE
inservice
probe XYZPROBE
inservice
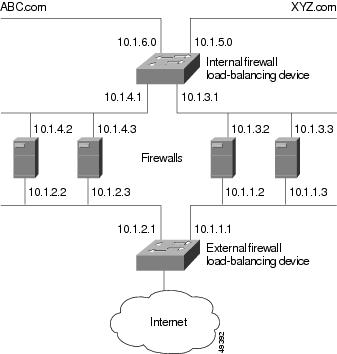
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Multiple Firewall Farms
The figure below shows a sample IOS SLB load-balancing network with multiple firewall farms and the following components:
- Four firewalls with IP addresses as shown
- An internal firewall load-balancing device on the secure side of the firewalls
- An external firewall load-balancing device on the Internet side of the firewalls
- One firewall farm named ABCFARM, containing the two firewalls on the left.
- One firewall farm named XYZFARM, containing the two firewalls on the right.
In the following firewall farm configuration samples:
Internal Firewall Load-Balancing Device
The following example shows the configuration for ping probes ABCPROBE and XYZPROBE and firewall farms ABCFARM and XYZFARM for the load-balancing device on the internal (secure) side of the firewalls:
ip slb probe ABCPROBE ping
address 10.1.2.1
ip slb probe XYZPROBE ping
address 10.1.1.1
ip slb firewallfarm ABCFARM
access source 10.1.6.0 255.255.255.0
inservice
real 10.1.4.2
probe ABCPROBE
inservice
real 10.1.4.3
probe ABCPROBE
inservice
ip slb firewallfarm XYZFARM
access source 10.1.5.0 255.255.255.0
inservice
real 10.1.3.2
probe XYZPROBE
inservice
real 10.1.3.3
probe XYZPROBE
inservice
External Firewall Load-Balancing Device
The following example shows the configuration for ping probes ABCPROBE and XYZPROBE and firewall farms ABCFARM and XYZFARM for the load-balancing device on the external (Internet) side of the firewalls:
ip slb probe ABCPROBE ping
address 10.1.4.1
ip slb probe XYZPROBE ping
address 10.1.3.1
ip slb firewallfarm ABCFARM
access destination 10.1.6.0 255.255.255.0
inservice
real 10.1.2.2
probe ABCPROBE
inservice
real 10.1.2.3
probe ABCPROBE
inservice
ip slb firewallfarm XYZFARM
access destination 10.1.5.0 255.255.255.0
inservice
real 10.1.1.2
probe XYZPROBE
inservice
real 10.1.1.3
probe XYZPROBE
inservice
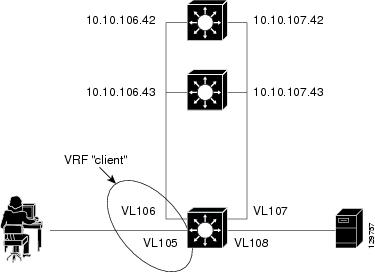
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Dual Firewall Load Balancing "Sandwich"
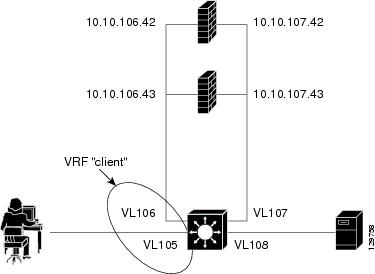
The figure below illustrates a basic dual firewall load balancing "sandwich" configuration hosted on one IOS SLB device, including Virtual Private Network (VPN) routing and forwarding (VRF) and access interface configuration. VL105, VL106, VL107, and VL108 are VLANs.
 Note | The client and server in this configuration are directly connected; in a more typical deployment, additional routes would be needed inside and outside the VRF. |
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
ip vrf client rd 0:1 ! ip slb probe P642 ping address 10.10.106.42 interval 120 ip slb probe P643 ping address 10.10.106.43 interval 120 ip slb probe P742 ping address 10.10.107.42 interval 120 ip slb probe P743 ping address 10.10.107.43 interval 120 ! ip slb firewallfarm CLIENT access inbound Vlan105 access outbound Vlan106 no inservice ! real 10.10.106.42 probe P642 inservice real 10.10.106.43 probe P643 inservice protocol tcp sticky 180 source protocol datagram sticky 180 source predictor hash address port ! ip slb firewallfarm SERVER access inbound Vlan108 access outbound Vlan107 inservice ! real 10.10.107.42 probe P742 inservice real 10.10.107.43 probe P743 inservice protocol tcp sticky 180 destination protocol datagram sticky 180 destination predictor hash address port ! mls flow ip interface-full ! !************************************************* !* Switchports, port channels and trunks * !* added to vlans 105-108 (left out for brevity) * !************************************************* ! interface Vlan105 ip vrf forwarding client ip address 10.10.105.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Vlan106 ip vrf forwarding client ip address 10.10.106.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Vlan107 ip address 10.10.107.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Vlan108 ip address 10.10.108.2 255.255.255.0 ! ip route 10.10.105.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.107.42 ip route vrf client 10.10.108.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.106.42
Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Probes
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Ping and HTTP Probes
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Routed Probe
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Ping and HTTP Probes
The figure below shows a sample configuration with IOS SLB real server connections configured as part of a server farm, focusing on using ping and HTTP probes to monitor applications that are server load-balanced.
The topology shown in the figure above is a heterogeneous server farm servicing one virtual server. Following are the configuration statements for this topology, including a ping probe named PROBE1 and an HTTP probe named PROBE2:
! Configure ping probe PROBE1, change CLI to IOS SLB probe configuration mode ip slb probe PROBE1 ping ! Configure probe to receive responses from IP address 13.13.13.13 address 13.13.13.13 ! Configure unacknowledged ping threshold to 16 faildetect 16 ! Configure ping probe timer interval to send every 11 seconds interval 11 ! Configure HTTP probe PROBE2 ip slb probe PROBE2 http ! Configure request method as POST, set URL as /probe.cgi?all request method post url /probe.cgi?all ! Configure header HeaderName header HeaderName HeaderValue ! Configure basic authentication username and password credentials Semisweet chips ! Exit to global configuration mode exit ! Enter server farm configuration mode for server farm PUBLIC ip slb serverfarm PUBLIC ! Configure NAT server and real servers on the server farm nat server real 10.1.1.1 inservice real 10.1.1.2 inservice real 10.1.1.3 inservice real 10.1.1.4 inservice real 10.1.1.5 inservice ! Configure ping probe on the server farm probe PROBE1 ! Configure HTTP probe on the server farm probe PROBE2 end
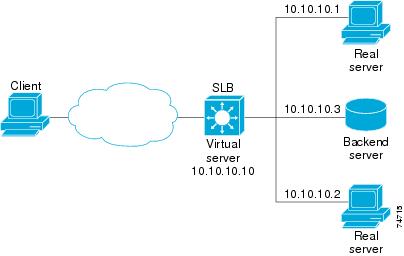
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Routed Probe
The figure below shows a typical datacenter and IOS SLB configuration. Virtual server ACME_VSERVER is configured with two real servers (10.10.10.1 and 10.10.10.2) in server farm ACME_FARM. The user wants the real servers to fail based on the health of the backend server (10.10.10.3). To accomplish this configuration without sending health checks through the real servers, the user defines BACKEND, a routed ping probe to the backend server's IP address.
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
ip slb probe BACKEND ping address 10.10.10.3 routed ip slb serverfarm ACME_SFARM nat server probe BACKEND real 10.10.10.1 inservice real 10.10.10.2 inservice ip slb vserver ACME_VSERVER virtual 10.10.10.10 tcp 80 serverfarm ACME_SFARM inservice
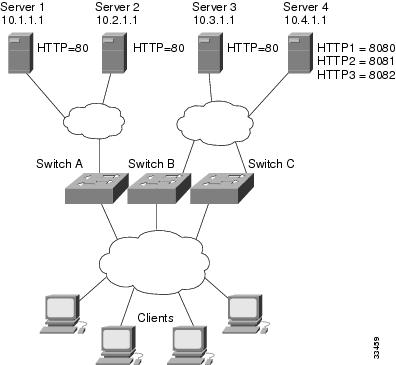
Example How to Configure a Layer 3 Switch with IOS SLB
The figure below shows a sample configuration with IOS SLB server connections configured as part of a server farm.
As shown in the following sample configuration, the example topology has three public web servers and two restricted web servers for privileged clients in subnet 10.4.4.0. The public web servers are weighted according to their capacity, with server 10.1.1.2 having the lowest capacity and having a connection limit imposed on it. The restricted web servers are configured as members of the same sticky group, so that HTTP connections and Secure Socket Layer (SSL) connections from the same client use the same real server.
The network configuration to provide the previously described IOS SLB functionality follows:
ip slb probe PROBE2 http
request method POST url /probe.cgi?all
header HeaderName HeaderValue
header Authorization Basic U2VtaXN3ZWV0OmNoaXBz
!
ip slb serverfarm PUBLIC
nat server
predictor leastconns
! First real server
real 10.1.1.1
reassign 4
faildetect numconns 16
retry 120
inservice
! Second real server
real 10.1.1.2
reassign 4
faildetect numconns 16
retry 120
inservice
! Third real server
real 10.1.1.3
reassign 4
faildetect numconns 16
retry 120
inservice
! Probe
probe PROBE2
! Restricted web server farm
ip slb serverfarm RESTRICTED
predictor leastconns
! First real server
real 10.1.1.20
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
! Second real server
real 10.1.1.21
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
!
! Unrestricted web virtual server
ip slb vserver PUBLIC_HTTP
virtual 10.0.0.1 tcp www
serverfarm PUBLIC
idle 120
delay 5
inservice
!
! Restricted HTTP virtual server
ip slb vserver RESTRICTED_HTTP
virtual 10.0.0.1 tcp www
serverfarm RESTRICTED
client 10.4.4.0 255.255.255.0
sticky 60 group 1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice
!
! Restricted SSL virtual server
ip slb vserver RESTRICTED_SSL
virtual 10.0.0.1 tcp https
serverfarm RESTRICTED
client 10.4.4.0 255.255.255.0
sticky 60 group 1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/1
switchport
switchport access vlan 3
switchport mode access
no ip address
!
interface FastEthernet2/1
switchport
switchport access vlan 2
switchport mode access
no ip address
!
interface FastEthernet2/2
switchport
switchport access vlan 2
switchport mode access
no ip address
!
interface FastEthernet2/3
switchport
switchport access vlan 2
switchport mode access
no ip address
!
interface Vlan2
ip address 10.1.1.100 255.255.255.0
!
interface Vlan3
ip address 40.40.40.1 255.255.255.0
Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with NAT and Static NAT
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with NAT
The figure below shows a sample configuration with IOS SLB real server connections configured as part of a server farm, focusing on the configuration of the NAT server and address pool of clients.
The topology in the figure above has four web servers, configured as follows:
- Servers 1, 2, and 3 are running single HTTP server applications listening on port 80.
- Server 4 has multiple HTTP server applications listening on ports 8080, 8081, and 8082.
Server 1 and Server 2 are load-balanced using Switch A, which is performing server address translation.
Server 3 and Server 4 are load-balanced using Switch B and Switch C. These two switches are performing both server and client address translation since there are multiple paths between the clients and the servers. These switches also must perform server port translation for HTTP packets to and from Server 4.
Switch A Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm FARM1
! Translate server addresses
nat server
! Server 1 port 80
real 10.1.1.1
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4 numclients 2
retry 20
inservice
! Server 2 port 80
real 10.2.1.1
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
!
ip slb vserver HTTP1
! Manage HTTP (port 80) requests
virtual 128.1.0.1 tcp www
serverfarm FARM1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice
Switch B Configuration Statements
ip slb natpool web-clients 128.3.0.1 128.3.0.254
! NAT address pool for clients
ip slb serverfarm FARM2
! Translate server addresses
nat server
! Translate client addresses
nat client web-clients
! Server 3 port 80
real 10.3.1.1
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
! Server 4 port 8080
real 10.4.1.1 port 8080
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
! Server 4 port 8081
real 10.4.1.1 port 8081
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
! Server 4 port 8082
real 10.4.1.1 port 8082
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
!
ip slb vserver HTTP2
! Manage HTTP (port 80) requests
virtual 128.2.0.1 tcp www
serverfarm FARM2
idle 120
delay 5
inservice
Switch C Configuration Statements
ip slb natpool web-clients 128.5.0.1 128.5.0.254
! NAT address pool for clients
ip slb serverfarm FARM2
! Translate server addresses
nat server
! Translate client addresses
nat client web-clients
! Server 3 port 80
real 10.3.1.1
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
! Server 4 port 8080
real 10.4.1.1 port 8080
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
! Server 4 port 8081
real 10.4.1.1 port 8081
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
! Server 4 port 8082
real 10.4.1.1 port 8082
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
!
ip slb vserver HTTP2
! Manage HTTP (port 80) requests
virtual 128.4.0.1 tcp www
serverfarm FARM2
idle 120
delay 5
inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Static NAT
The following example shows configuration statements for the following items:
- A DNS probe, PROBE4, configured to supply real server IP address 13.13.13.13 in response to domain name resolve requests.
- A server farm, DNS, that is configured to use server NAT and PROBE4.
- An all-port virtual server, 10.11.11.11, associated with server farm DNS, that performs per-packet server load balancing for UDP connections.
- A real server, 10.1.1.3, associated with server farm DNS, configured for static NAT and per-packet server load balancing.
ip slb probe PROBE4 dns lookup 13.13.13.13 ! ip slb serverfarm DNS nat server probe PROBE4 real 10.1.1.3 inservice ! ip slb vserver DNS virtual 10.11.11.11 UDP 0 service per-packet serverfarm DNS ! ip slb static nat 10.11.11.11 per-packet real 10.1.1.3
Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Redundancy
- Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Stateless Backup
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Stateful Backup
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Stateful Backup of Redundant Route Processors
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Active Standby
Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Stateless Backup
There are several different ways in which you can configure IOS SLB stateless backup. The differences between the configurations depend on the networking capabilities of your load balancing devices, and on the capabilities of the distribution devices that direct client traffic to those load balancing devices.
- If a load balancing device is not capable of both Layer 2 switching and VLAN trunking, you must connect it and its real servers to a Layer 2 switch. This configuration is required in order to use HSRP on the server-side VLANs.
- If a distribution device is capable of Layer 3 switching, it can use route redistribution to direct flows to the active load balancing device.
- If a distribution device is capable of Layer 2 switching, it can use client-side HSRP on the load balancing device to direct flows to the active load balancing device.
- While HSRP offers faster failover times, routing converges quickly enough for most configurations. If you use both client-side and server-side HSRP on the load balancing devices, you must use HSRP interface tracking and priorities to synchronize the client-side and server-side HSRP groups.
This section contains the following examples, illustrating several different IOS SLB stateless backup configurations:
- Example How to Configure Dynamic Routing and Trunking
- Example How to Configure Dynamic Routing and No Trunking
- Example How to Configure Static Routing and Trunking
- Example How to Configure Static Routing and No Trunking
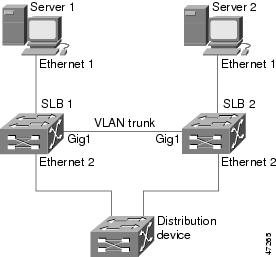
Example How to Configure Dynamic Routing and Trunking
The figure below shows a sample IOS SLB stateless backup configuration with the following characteristics:
- The IP address for real server 1 is 10.10.1.3, and for real server 2 is 10.10.1.4, routed to clients through 10.10.1.100.
- The IP address for the virtual server is 10.10.14.1.
- The IP address for VLAN 1 is 10.10.1.0, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- The IP address for Subnet 2 is 10.10.2.0, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- The IP address for Subnet 3 is 10.10.3.0, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- The distribution device uses EIGRP to learn the route to 10.10.14.1 through either 10.10.2.1 or 10.10.3.1, depending on which IOS SLB is active.
SLB 1 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm SF1
real 10.10.1.3
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4 numclients 2
retry 20
inservice
real 10.10.1.4
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
ip slb vserver VS1
virtual 10.10.14.1 tcp www
serverfarm SF1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice standby SERVER
!
interface Ethernet1
switchport
switchport vlan 1
interface Ethernet2
ip address 10.10.2.1 255.255.255.0
interface vlan 1
ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.1.100
standby priority 10 preempt delay sync 20
standby name SERVER
standby track Ethernet2
standby timers 1 3
router eigrp 666
redistribute static
network 10.0.0.0
SLB 2 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm SF1
real 10.10.1.3
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
real 10.10.1.4
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
ip slb vserver VS1
virtual 10.10.14.1 tcp www
serverfarm SF1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice standby SERVER
!
interface GigabitEthernet1
no ip address
switchport
switchport trunk encapsulation isl
interface Ethernet1
switchport
switchport vlan 1
interface Ethernet2
ip address 10.10.3.1 255.255.255.0
interface vlan 1
ip address 10.10.1.2 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.1.100
standby priority 5 preempt delay sync 20
standby name SERVER
standby track Ethernet2
standby timers 1 3
router eigrp 666
redistribute static
network 10.0.0.0
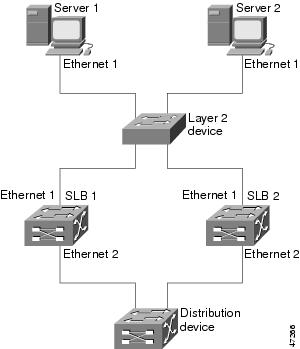
Example How to Configure Dynamic Routing and No Trunking
The figure below shows a sample IOS SLB stateless backup configuration with the following characteristics:
- The IP address for real server 1 is 10.10.1.3, and for real server 2 is 10.10.1.4, routed to clients through 10.10.1.100.
- The IP address for the virtual server is 10.10.14.1.
- The IP address for Subnet 2 is 10.10.2.0, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- The IP address for Subnet 3 is 10.10.3.0, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- The distribution device uses EIGRP to learn the route to 10.10.14.1 through either 10.10.2.2 or 10.10.3.2, depending on which IOS SLB is active.
SLB 1 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm SF1
real 10.10.1.3
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
real 10.10.1.4
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
ip slb vserver VS1
virtual 10.10.14.1 tcp www
serverfarm SF1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice standby SERVER
!
interface Ethernet1
ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.1.100
standby priority 10 preempt delay sync 20
standby name SERVER
standby track Ethernet2
standby timers 1 3
interface Ethernet2
ip address 10.10.2.1 255.255.255.0
router eigrp 666
redistribute static
network 10.0.0.0
SLB 2 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm SF1
real 10.10.1.3
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
real 10.10.1.4
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
ip slb vserver VS1
virtual 10.10.14.1 tcp www
serverfarm SF1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice standby SERVER
!
interface Ethernet1
ip address 10.10.1.2 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.1.100
standby priority 5 preempt delay sync 20
standby name SERVER
standby track Ethernet2
standby timers 1 3
interface Ethernet2
ip address 10.10.3.1 255.255.255.0
router eigrp 666
redistribute static
network 10.0.0.0
Example How to Configure Static Routing and Trunking
The figure below shows a sample IOS SLB stateless backup configuration with the following characteristics:
- The IP address for real server 1 is 10.10.1.3, and for real server 2 is 10.10.1.4, routed to clients through 10.10.1.100.
- The IP address for the virtual server is 10.10.14.1.
- The IP address for VLAN 1 is 10.10.1.0, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- The IP address for Subnet 2 is 10.10.2.0, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- The IP address for Subnet 3 is 10.10.3.0, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- The configuration uses static routing to the HSRP route on the distribution device.
- SLB 1 Configuration Statements
- SLB 2 Configuration Statements
- Distribution Device Configuration Statements
SLB 1 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm SF1
real 10.10.1.3
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
real 10.10.1.4
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
ip slb vserver VS1
virtual 10.10.14.1 tcp www
serverfarm SF1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice standby SERVER
!
interface Ethernet1
switchport
switchport vlan 1
interface Ethernet2
ip address 10.10.2.1 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.2.100
standby priority 10 preempt delay sync 20
standby track vlan1
standby timers 1 3
interface vlan 1
ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.1.100
standby priority 10 preempt delay sync 20
standby name SERVER
standby track Ethernet2
standby timers 1 3
SLB 2 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm SF1
real 10.10.1.3
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
real 10.10.1.4
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
ip slb vserver VS1
virtual 10.10.14.1 tcp www
serverfarm SF1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice standby SERVER
!
interface GigabitEthernet1
no ip address
switchport
switchport trunk encapsulation isl
interface Ethernet1
switchport
switchport vlan 1
interface Ethernet2
ip address 10.10.2.2 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.2.100
standby priority 5 preempt delay sync 20
standby track vlan 1
standby timers 1 3
interface vlan 1
ip address 10.10.1.2 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.1.100
standby priority 5 preempt delay sync 20
standby name SERVER
standby track Ethernet2
standby timers 1 3
Example How to Configure Static Routing and No Trunking
The figure below shows a sample IOS SLB stateless backup configuration with the following characteristics:
- The IP address for real server 1 is 10.10.1.3, and for real server 2 is 10.10.1.4, routed to clients through 10.10.1.100.
- The IP address for the virtual server is 10.10.14.1.
- The IP address for Subnet 2 is 10.10.2.0, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- The IP address for Subnet 3 is 10.10.3.0, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- The configuration uses static routing to the HSRP route on the distribution device.
- SLB 1 Configuration Statements
- SLB 2 Configuration Statements
- Distribution Device Configuration Statements
SLB 1 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm SF1
real 10.10.1.3
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
real 10.10.1.4
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
ip slb vserver VS1
virtual 10.10.14.1 tcp www
serverfarm SF1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice standby SERVER
!
interface Ethernet1
ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.1.100
standby priority 10 preempt delay sync 20
standby name SERVER
standby track Ethernet2
standby timers 1 3
interface Ethernet2
ip address 10.10.2.1 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.2.100
standby priority 10 preempt delay sync 20
standby track Ethernet1
standby timers 1 3
SLB 2 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm SF1
real 10.10.1.3
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
real 10.10.1.4
reassign 2
faildetect numconns 4
retry 20
inservice
ip slb vserver VS1
virtual 10.10.14.1 tcp www
serverfarm SF1
idle 120
delay 5
inservice standby SERVER
!
interface Ethernet1
ip address 10.10.1.2 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.1.100
standby priority 5 preempt delay sync 20
standby name SERVER
standby track Ethernet2
standby timers 1 3
!
interface Ethernet2
ip address 10.10.2.2 255.255.255.0
standby ip 10.10.2.100
standby priority 5 preempt delay sync 20
standby track Ethernet1
standby timers 1 3
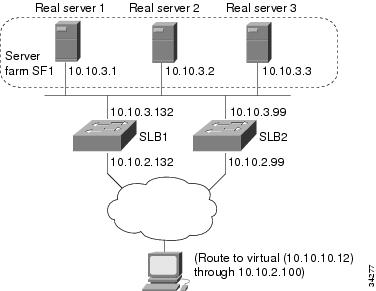
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Stateful Backup
This sample configuration focuses on the IOS SLB real server connections configured as part of a server farm, with real and virtual servers over Fast Ethernet interfaces configured with stateful backup standby connections.
The figure below is an example of a stateful backup configuration, using HSRP on both the client and server sides to manage failover. The real servers route outbound flows to 10.10.3.100, which is the HSRP address on the server side interfaces. The client (or access router), routes to the virtual IP address (10.10.10.12) through 10.10.2.100, HSRP address on the client side.
Notice the loopback interfaces configured on both devices for the exchange of these messages. Each IOS SLB should also be given duplicate routes to the other switch loopback address. This configuration allows replication messages to flow despite an interface failure.
 Note | To allow HSRP to function properly, the set spantree portfast command must be configured on any Layer 2 device between the IOS SLB switches. |
Switch SLB1 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm SF1 nat server real 10.10.3.1 inservice real 10.10.3.2 inservice real 10.10.3.3 inservice ! ip slb vserver VS1 virtual 10.10.10.12 tcp telnet serverfarm SF1 replicate casa 10.10.99.132 10.10.99.99 1024 password PASS inservice standby virt ! interface loopback 1 ip address 10.10.99.132 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet1 ip address 10.10.3.132 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects no ip mroute-cache standby priority 5 preempt standby name out standby ip 10.10.3.100 standby track FastEthernet2 standby timers 1 3 interface FastEthernet2 ip address 10.10.2.132 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects standby priority 5 standby name virt standby ip 10.10.2.100 standby timers 1 3
Switch SLB2 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm SF1 nat server real 10.10.3.1 inservice real 10.10.3.2 inservice real 10.10.3.3 inservice ! ip slb vserver VS1 virtual 10.10.10.12 tcp telnet serverfarm SF1 replicate casa 10.10.99.99 10.10.99.132 1024 password PASS inservice standby virt ! interface loopback 1 ip address 10.10.99.99 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet2 ip address 10.10.2.99 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache standby priority 10 preempt delay sync 20 standby name virt standby ip 10.10.2.100 standby track FastEthernet3 standby timers 1 3 ! interface FastEthernet3 ip address 10.10.3.99 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache standby priority 10 preempt delay 20 standby name out standby ip 10.10.3.100 standby track FastEthernet2 standby timers 1 3
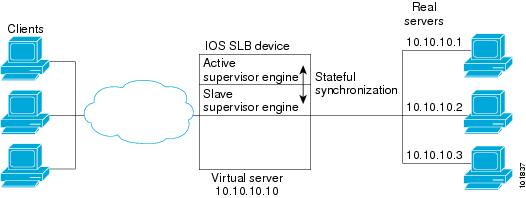
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Stateful Backup of Redundant Route Processors
In the figure below, the IOS SLB device includes two Supervisor engines configured for stateful backup. If the active Supervisor engine fails, the backup Supervisor engine takes over through RPR+ with IOS SLB synchronization information already populated. IOS SLB replicates state information for virtual server ACME_VSERVER (10.10.10.10) from the active Supervisor engine to the backup every 20 seconds. The real servers (10.10.10.1, 10.10.10.2, and 10.10.10.3) are configured in server farm ACME_SFARM.
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
ip slb replicate slave rate 300 ip slb serverfarm ACME_SFARM nat server real 10.10.10.1 inservice real 10.10.10.2 inservice real 10.10.10.3 inservice ip slb vserver ACME_VSERVER virtual 10.10.10.10 tcp 80 replicate interval 20 replicate slave serverfarm ACME_SFARM inservice
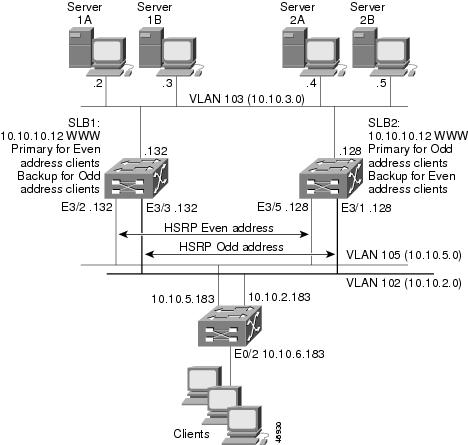
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Active Standby
The figure below shows an IOS SLB network configured for active standby, with two IOS SLB devices load-balancing the same virtual IP address while backing up each other. If either device fails, the other takes over its load through normal HSRP failover and IOS SLB stateless redundancy.
The sample network configuration in the figure above has the following characteristics:
- SLB 1 balances servers 1A and 1B and SLB 2 balances 2A and 2B.
- One virtual IP address (10.10.10.12 for web) is supported across the two IOS SLB devices.
- Client traffic is divided in an access router, sending clients with even IP addresses to HSRP1 (10.10.5.100) and clients with odd IP addresses to HSRP2 (10.10.2.100). SLB 1 is configured as primary for clients with odd IP addresses, and SLB 2 is primary for clients with even IP addresses.
- The IOS SLB devices balance the traffic to disjoint sets of real servers. (If client NAT was used in this example, this characteristic would not be a requirement).
- Each set of real servers has a default gateway configured to its IOS SLB device.
- The HSRP address on VLAN 105 is 10.10.5.100. The HSRP address on VLAN 102 is 10.10.2.100.
SLB 1 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm EVEN nat server real 10.10.3.2 reassign 2 faildetect numconns 4 numclients 2 retry 20 inservice real 10.10.3.3 reassign 2 faildetect numconns 4 retry 20 inservice ! ip slb serverfarm ODD nat server real 10.10.3.2 reassign 2 faildetect numconns 4 retry 20 inservice real 10.10.3.3 reassign 2 faildetect numconns 4 retry 20 inservice !-----Same EVEN virtual server as in SLB 2 ip slb vserver EVEN virtual 10.10.10.12 tcp www serverfarm EVEN client 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.1 idle 120 delay 5 !-----See standby name in Ethernet 3/3 below inservice standby STANDBY_EVEN !-----Same ODD virtual server as in SLB 2 ip slb vserver ODD virtual 10.10.10.12 tcp www serverfarm ODD client 0.0.0.1 0.0.0.1 idle 120 delay 5 !-----See standby name in Ethernet 3/2 below inservice standby STANDBY_ODD ! interface Ethernet3/2 ip address 10.10.5.132 255.255.255.0 standby priority 20 preempt delay sync 20 !-----See standby name in SLB 2, Ethernet 3/5 standby name STANDBY_ODD standby ip 10.10.5.100 standby track Ethernet3/3 standby timers 1 3 ! interface Ethernet3/3 ip address 10.10.2.132 255.255.255.0 standby priority 10 !-----See standby name in SLB 2, Ethernet 3/1 standby name STANDBY_EVEN standby ip 10.10.2.100 standby track Ethernet3/2 standby timers 1 3
SLB 2 Configuration Statements
ip slb serverfarm EVEN nat server real 10.10.3.4 reassign 2 faildetect numconns 4 retry 20 inservice real 10.10.3.5 reassign 2 faildetect numconns 4 retry 20 inservice ! ip slb serverfarm ODD nat server real 10.10.3.4 reassign 2 faildetect numconns 4 retry 20 inservice real 10.10.3.5 reassign 2 faildetect numconns 4 retry 20 inservice !-----Same EVEN virtual server as in SLB 1 ip slb vserver EVEN virtual 10.10.10.12 tcp www serverfarm EVEN client 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.1 idle 120 delay 5 !-----See standby name in Ethernet 3/1 below inservice standby STANDBY_EVEN !-----Same ODD virtual server as in SLB 1 ip slb vserver ODD virtual 10.10.10.12 tcp www serverfarm ODD client 0.0.0.1 0.0.0.1 idle 120 delay 5 !-----See standby name in Ethernet 3/5 below inservice standby STANDBY_ODD ! interface Ethernet3/1 ip address 10.10.2.128 255.255.255.0 standby priority 20 preempt delay sync 20 !-----See standby name in SLB 1, Ethernet 3/3 standby name STANDBY_EVEN standby ip 10.10.2.100 standby track Ethernet3/5 standby timers 1 3 ! interface Ethernet3/5 ip address 10.10.5.128 255.255.255.0 standby priority 10 preempt delay sync 20 !-----See standby name in SLB 1, Ethernet 3/2 standby name STANDBY_ODD standby ip 10.10.5.100 standby track Ethernet3/1 standby timers 1 3
Access Router Configuration Statements
interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.10.5.183 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 10.10.2.183 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache ! interface Ethernet0/2 ip address 10.10.6.183 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache ip policy route-map virts ! access-list 100 permit ip 0.0.0.1 255.255.255.254 host 10.10.10.12 access-list 101 permit ip 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.254 host 10.10.10.12 route-map virts permit 10 match ip address 100 set ip next-hop 10.10.5.100 ! route-map virts permit 15 match ip address 101 set ip next-hop 10.10.2.100
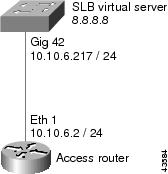
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Redistribution of Static Routes
The figure below shows an IOS SLB network configured to distribute static routes to a virtual server's IP address. The route to the address is added to the routing table as static if you advertise the address when you bring the virtual server into service (using the inservice command). See the description of the advertisecommand in the Cisco IOS IP Application Services Command Reference for more details about advertising virtual server IP addresses.
Because the routing configuration varies from protocol to protocol, sample configurations for several different routing protocols are given.
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
- Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (Enhanced IGRP)
Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Following is the RIP static route redistribution configuration for the IOS SLB switch shown in the figure above:
router rip redistribute static network 10.0.0.0 network 8.0.0.0
Following is the RIP static route redistribution configuration for the access router that is listening for routing updates shown in the figure above:
router rip network 10.0.0.0 network 8.0.0.0
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
Following is the OSPF static route redistribution configuration for the IOS SLB switch shown in the figure above:
router ospf 1 redistribute static subnets network 10.10.6.217 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 8.8.8.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Following is the OSPF static route redistribution configuration for the access router that is listening for routing updates shown in the figure above:
router ospf 1 network 10.10.6.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 8.8.8.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
Following is the IGRP static route redistribution configuration for the IOS SLB switch shown in the figure above:
router igrp 1 redistribute connected redistribute static network 8.0.0.0 network 10.0.0.0
Following is the IGRP static route redistribution configuration for the access router that is listening for routing updates shown in the figure above:
router igrp 1 network 8.0.0.0 network 10.0.0.0
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (Enhanced IGRP)
Following is the Enhanced IGRP static route redistribution configuration for the IOS SLB switch shown in the figure above:
router eigrp 666 redistribute static network 10.0.0.0 network 8.0.0.0
Following is the Enhanced IGRP static route redistribution configuration for the access router that is listening for routing updates shown in the figure above:
router eigrp 666 network 10.0.0.0 network 8.0.0.0
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with WAP and UDP Load Balancing
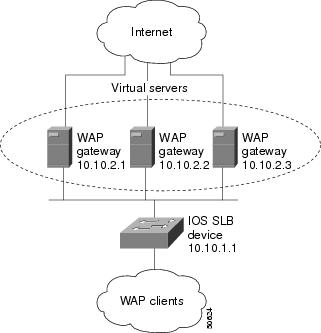
The figure below shows an IOS SLB network configured to balance WAP flows. In this example:
- WAP flows are balanced between WAP gateways 10.10.2.1, 10.10.2.2, and 10.10.2.3.
- The clients connect to 10.10.1.1, the IOS SLB virtual server address.
- For a given session, load-balancing decisions change if the connection idles longer than the virtual server's idle connection timer (3000 seconds in this example).
There are two ways to configure IOS SLB load balancing for WAP:
- To load-balance sessions running in connection-oriented WSP mode, define a WSP probe and use WAP load balancing. WAP load balancing requires a WAP virtual server configured on one of the WAP ports.
- To load-balance sessions running in connectionless WSP, connectionless secure WSP, and connection-oriented secure WSP modes, define a ping or WSP probe and use standard UDP load balancing with a low idle timer.
Example How to Balance WAP Flows on UDP Port 9201
The following example shows the configuration for the IOS SLB device shown in the figure above, which balances WAP flows on UDP port 9201 (WSP/WTP/UDP):
ip slb probe PROBE3 wsp url http://localhost/test.txt ! ip slb serverfarm WAPFARM nat server real 10.10.2.1 inservice real 10.10.2.2 inservice real 10.10.2.3 inservice probe PROBE3 ! ip slb vserver VSERVER virtual 10.10.1.1 udp 9201 serverfarm WAPFARM idle 3000 inservice
Example How to Balance WAP Flows on UDP Port 9203
The following example shows the configuration for the IOS SLB device shown in the figure above, which balances WAP flows on UDP port 9203 (WSP/WTP/WTLS/UDP):
ip slb probe PROBE1 ping ! ip slb serverfarm WAPFARM nat server real 10.10.2.1 inservice real 10.10.2.2 inservice real 10.10.2.3 inservice probe PROBE1 ! ip slb vserver VSERVER virtual 10.10.1.1 udp 9203 serverfarm WAPFARM idle 3000 inservice
Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with Route Health Injection
- Example How to Configure Two Distributed Sites with One Web Server Each
- Example How to Configure Two Distributed Sites with Two Web Servers Each
- Example How to Configure Two Distributed Sites with One Web Server and a Backup IOS SLB Switch Each
Example How to Configure Two Distributed Sites with One Web Server Each
The figure below shows an IOS SLB network configured with route health injection with the following characteristics:
- Both IOS SLB devices are configured with the same virtual IP address.
- Each IOS SLB device has a server farm containing only the locally attached web server as a real server.
- The path to SLB A has the lower weight.
When both web servers in the figure above are operational, the client router receives the host route from both IOS SLB devices.
If Web Server A fails, the virtual server for the virtual IP address on SLB A enters FAILED state and stops advertising the host route for the virtual IP address. The client router then begins using the route to SLB B.
When Web Server A is again available, the virtual server again advertises the host route for the virtual IP address, and the client router begins using SLB A.
Example How to Configure Two Distributed Sites with Two Web Servers Each
The figure below shows an IOS SLB network configured with route health injection with the following characteristics:
- Both IOS SLB devices are configured with the same virtual IP address.
- Each IOS SLB device has a server farm containing two locally attached web servers as real servers.
- The path to SLB A has the lower weight.
When all web servers in the figure above are operational, the client router receives the host route from both IOS SLB devices.
If one web server in either server farm fails, the route continues to be advertised by the given IOS SLB device.
If both Web Server A1 and Web Server A2 fail, the virtual server for the virtual IP address on SLB A enters FAILED state and stops advertising the host route for the virtual IP address. The client router then begins using the route to SLB B.
When either Web Server A1 or Web Server A2 is again available, the virtual server again advertises the host route for the virtual IP address, and the client router begins using SLB A.
Example How to Configure Two Distributed Sites with One Web Server and a Backup IOS SLB Switch Each
The figure below shows an IOS SLB network configured with route health injection with the following characteristics:
- Both IOS SLB devices are configured with the same virtual IP address.
- Each IOS SLB device has a server farm containing only the locally attached web server as a real server.
- Each site has a primary IOS SLB device and a backup IOS SLB device.
- The path to SLB A has the lower weight.
When both web servers in the figure above are operational, the client router receives the host route from both SLB A Primary and SLB B Primary.
If SLB A Primary fails, SLB A Backup begins advertising the host route to the virtual IP address. If SLB A Backup also fails, the virtual server for the virtual IP address on SLB A Primary and SLB A Backup enters FAILED state and stops advertising the host route for the virtual IP address. The client router then begins using the route to SLB B Primary (or to SLB B Backup, if SLB B Primary is not available).
When either SLB A Primary or SLB A Backup is again available, the virtual server again advertises the host route for the virtual IP address, and the client router begins using SLB A Primary or SLB A Backup.
Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing Without GTP Cause Code Inspection
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing and NAT
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing NAT and GTP Cause Code Inspection
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing Maps
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Dual-Stack Addresses for GTP Load Balancing
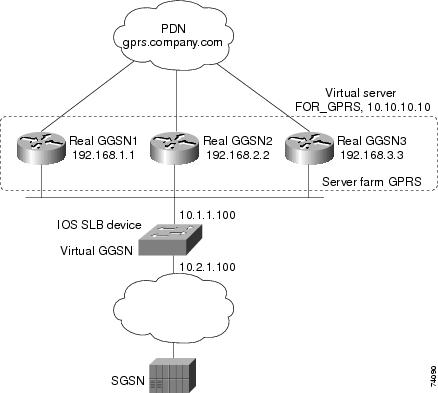
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing Without GTP Cause Code Inspection
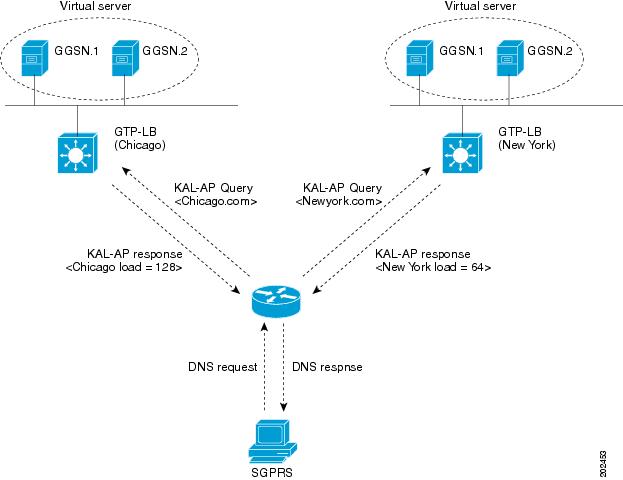
The figure below shows a typical GPRS load-balancing configuration without GTP cause code inspection enabled. In this configuration:
- IOS SLB can balance GPRS flows across multiple real GGSNs. The SGSN "sees" the real GGSNs as one virtual GGSN. This configuration increases the flow-handling capability of the real GGSNs and increases the reliability and availability.
- The virtual template address of the SGSN is 10.111.111.111.
- The virtual template address of GGSN1 is 192.168.1.1.
- The virtual template address of GGSN2 is 192.168.2.2.
- The virtual template address of GGSN3 is 192.168.3.3.
Following are the configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
For more detailed GGSN configuration examples, refer to the Cisco IOS Mobile Wireless Configuration Guide .
- IOS SLB Configuration Statements
- GGSN1 Configuration Statements
- GGSN2 Configuration Statements
- GGSN3 Configuration Statements
IOS SLB Configuration Statements
hostname GTP_SLB ! ip domain-name gprs.com ! ip slb serverfarm GPRS real 192.168.1.1 weight 1 faildetect numconns 1 numclients 1 inservice ! real 192.168.2.2 weight 1 faildetect numconns 1 numclients 1 inservice ! real 192.168.3.3 weight 1 faildetect numconns 1 numclients 1 inservice ! ip slb vserver FOR_GPRS virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 3386 service gtp serverfarm GPRS inservice ! ip slb dfp password Password1 0 agent 10.1.1.201 1111 30 0 10 agent 10.1.1.202 1111 30 0 10 agent 10.1.1.203 1111 30 0 10 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 description TO SERVERFARM GPRS ip address 10.1.1.100 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects duplex half ! interface FastEthernet3/0 description TO SGSN ip address 10.2.1.100 255.255.255.0 no ip mroute-cache duplex half ! ip route 10.111.111.111 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet1/0 ip route 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.1.1.201 ip route 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.1.1.202 ip route 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.255 10.1.1.203
GGSN1 Configuration Statements
service gprs ggsn ! hostname GGSN1 ! ip dfp agent gprs port 1111 password Password1 0 inservice ! ip domain-name gprs.com ! interface loopback 1 description LOOPBACK SAME AS IOS SLB VSERVER ADDRESS ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255 no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache ! interface FastEthernet1/0 description TO SLB ip address 10.1.1.201 255.255.255.0 ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache duplex half ! interface Virtual-Template1 description GTP VIRTUAL TEMPLATE ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 encapsulation gtp gprs access-point-list gprs1 ! ip route 10.111.111.111 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet1/0 ! gprs access-point-list gprs1 access-point 1 access-point-name gprs.company.com access-mode non-transparent ip-address-pool dhcp-proxy-client dhcp-server 10.100.0.5 10.100.0.6 dhcp-gateway-address 10.27.3.1 exit ! gprs maximum-pdp-context-allowed 45000 gprs qos map canonical-qos gprs gtp path-echo-interval 0 gprs dfp max-weight 32 gprs slb cef 10.10.10.10
GGSN2 Configuration Statements
service gprs ggsn ! hostname GGSN2 ! ip dfp agent gprs port 1111 password Password1 0 inservice ! ip domain-name gprs.com ! interface loopback 1 description LOOPBACK SAME AS IOS SLB VSERVER ADDRESS ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255 no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache ! interface FastEthernet1/0 description TO SLB ip address 10.1.1.202 255.255.255.0 ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache duplex half ! interface Virtual-Template1 description GTP VIRTUAL TEMPLATE ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 encapsulation gtp gprs access-point-list gprs1 ! ip route 10.111.111.111 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet1/0 ! gprs access-point-list gprs1 access-point 1 access-point-name gprs.company.com access-mode non-transparent ip-address-pool dhcp-proxy-client dhcp-server 10.100.0.5 10.100.0.6 dhcp-gateway-address 10.27.3.1 exit ! gprs maximum-pdp-context-allowed 45000 gprs qos map canonical-qos gprs gtp path-echo-interval 0 gprs dfp max-weight 32 gprs slb cef 10.10.10.10
GGSN3 Configuration Statements
service gprs ggsn ! hostname GGSN3 ! ip dfp agent gprs port 1111 password Password1 0 inservice ! ip domain-name gprs.com ! interface loopback 1 description LOOPBACK SAME AS IOS SLB VSERVER ADDRESS ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255 no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache ! interface FastEthernet1/0 description TO SLB ip address 10.1.1.203 255.255.255.0 ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache duplex half ! interface Virtual-Template1 description GTP VIRTUAL TEMPLATE ip address 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.0 encapsulation gtp gprs access-point-list gprs1 ! ip route 10.111.111.111 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet1/0 ! gprs access-point-list gprs1 access-point 1 access-point-name gprs.company.com access-mode non-transparent ip-address-pool dhcp-proxy-client dhcp-server 10.100.0.5 10.100.0.6 dhcp-gateway-address 10.27.3.1 exit ! gprs maximum-pdp-context-allowed 45000 gprs qos map canonical-qos gprs gtp path-echo-interval 0 gprs dfp max-weight 32 gprs slb cef 10.10.10.10
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing and NAT
The following example uses the same basic configuration as in the "Example: How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing Without GTP Cause Code Inspection", including the network shown in the figure above, but with the addition of NAT:
For more detailed GGSN configuration examples, refer to the Cisco IOS Mobile Wireless Configuration Guide.
- IOS SLB Configuration Statements
- GGSN1 Configuration Statements
- GGSN2 Configuration Statements
- GGSN3 Configuration Statements
IOS SLB Configuration Statements
hostname GTP_SLB ! ip domain-name gprs.com ! ip slb serverfarm GPRS nat server real 192.168.1.1 weight 1 faildetect numconns 1 numclients 1 inservice ! real 192.168.2.2 weight 1 faildetect numconns 1 numclients 1 inservice ! real 192.168.3.3 weight 1 faildetect numconns 1 numclients 1 inservice ! ip slb vserver FOR_GPRS virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 3386 service gtp serverfarm GPRS inservice ! ip slb dfp password Password1 0 agent 10.1.1.201 1111 30 0 10 agent 10.1.1.202 1111 30 0 10 agent 10.1.1.203 1111 30 0 10 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 description TO SERVERFARM GPRS ip address 10.1.1.100 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects duplex half ! interface FastEthernet3/0 description TO SGSN ip address 10.2.1.100 255.255.255.0 no ip mroute-cache duplex half ! ip route 10.111.111.111 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet1/0 ip route 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.1.1.201 ip route 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.1.1.202 ip route 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.255 10.1.1.203
GGSN1 Configuration Statements
service gprs ggsn ! hostname GGSN1 ! ip dfp agent gprs port 1111 password Password1 0 inservice ! ip domain-name gprs.com ! interface FastEthernet1/0 description TO SLB ip address 10.1.1.201 255.255.255.0 ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache duplex half ! interface Virtual-Template1 description GTP VIRTUAL TEMPLATE ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 encapsulation gtp gprs access-point-list gprs1 ! ip route 10.111.111.111 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet1/0 ! gprs access-point-list gprs1 access-point 1 access-point-name gprs.company.com access-mode non-transparent ip-address-pool dhcp-proxy-client dhcp-server 10.100.0.5 10.100.0.6 dhcp-gateway-address 10.27.3.1 exit ! gprs maximum-pdp-context-allowed 45000 gprs qos map canonical-qos gprs gtp path-echo-interval 0 gprs dfp max-weight 32
GGSN2 Configuration Statements
service gprs ggsn ! hostname GGSN2 ! ip dfp agent gprs port 1111 password Password1 0 inservice ! ip domain-name gprs.com ! interface FastEthernet1/0 description TO SLB ip address 10.1.1.202 255.255.255.0 ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache duplex half interface Virtual-Template1 description GTP VIRTUAL TEMPLATE ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 encapsulation gtp gprs access-point-list gprs1 ! ip route 10.111.111.111 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet1/0 ! gprs access-point-list gprs1 access-point 1 access-point-name gprs.company.com access-mode non-transparent ip-address-pool dhcp-proxy-client dhcp-server 10.100.0.5 10.100.0.6 dhcp-gateway-address 10.27.3.1 exit ! gprs maximum-pdp-context-allowed 45000 gprs qos map canonical-qos gprs gtp path-echo-interval 0 gprs dfp max-weight 32
GGSN3 Configuration Statements
service gprs ggsn ! hostname GGSN3 ! ip dfp agent gprs port 1111 password Password1 0 inservice ! ip domain-name gprs.com ! interface FastEthernet1/0 description TO SLB ip address 10.1.1.203 255.255.255.0 ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache duplex half ! interface Virtual-Template1 description GTP VIRTUAL TEMPLATE ip address 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.0 encapsulation gtp gprs access-point-list gprs1 ! ip route 10.111.111.111 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet1/0 ! gprs access-point-list gprs1 access-point 1 access-point-name gprs.company.com access-mode non-transparent ip-address-pool dhcp-proxy-client dhcp-server 10.100.0.5 10.100.0.6 dhcp-gateway-address 10.27.3.1 exit ! gprs maximum-pdp-context-allowed 45000 gprs qos map canonical-qos gprs gtp path-echo-interval 0 gprs dfp max-weight 32
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing NAT and GTP Cause Code Inspection
The following example uses the same basic configuration as in the "Example: How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing and NAT" section, including the network shown in the figure above, but with the GTP cause code inspection enabled. In this configuration:
- The GSN idle timer is set to 20 seconds.
- The GTP request idle timer is set to 15 seconds.
- The virtual server accepts PDP context creates only from International Mobile Subscriber IDs (IMSIs) with carrier code mcc 222 mnc 22.
Following are the configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above, with the addition of NAT and GTP cause code inspection support:
For more detailed GGSN configuration examples, refer to the Cisco IOS Mobile Wireless Configuration Guide .
IOS SLB Configuration Statements
hostname GTP_SLB ! ip domain-name gprs.com ! ip slb timers gtp gsn 20 ! ip slb serverfarm GPRS nat server real 192.168.1.1 weight 1 faildetect numconns 1 numclients 1 inservice ! real 192.168.2.2 weight 1 faildetect numconns 1 numclients 1 inservice ! real 192.168.3.3 weight 1 faildetect numconns 1 numclients 1 inservice ! ip slb vserver FOR_GPRS virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 0 service gtp-inspect idle gtp request 15 client gtp carrier-code mcc 222 mnc 22 serverfarm GPRS inservice ! ip slb dfp password Password1 0 agent 10.1.1.201 1111 30 0 10 agent 10.1.1.202 1111 30 0 10 agent 10.1.1.203 1111 30 0 10 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 description TO SERVERFARM GPRS ip address 10.1.1.100 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects duplex half ! interface FastEthernet3/0 description TO SGSN ip address 10.2.1.100 255.255.255.0 no ip mroute-cache duplex half ! ip route 10.111.111.111 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet1/0 ip route 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.1.1.201 ip route 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.1.1.202 ip route 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.255 10.1.1.203
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GPRS Load Balancing Maps
The following sample configuration enables IOS SLB to support multiple server farms behind a GPRS load balancing virtual server, using access point names (APNs) to select server farms. Server farm farm6 is configured without an associated map, and therefore acts as a default server farm. If IOS SLB cannot match any of the other server farm maps, and a default server farm is configured, IOS SLB sends the GPRS request to the default serverfarm.
ip slb map 1 gtp apn cisco* ip slb map 4 gtp apn abc.microsoft.com apn xyz.intel.com ip slb map 5 gtp apn yahoo.com ! ip slb serverfarm farm1 real 10.0.0.1 inservice real 10.0.0.2 inservice ip slb serverfarm farm2 real 10.0.0.3 inservice real 10.0.0.4 inservice ip slb serverfarm farm3 real 10.0.0.5 inservice real 10.0.0.6 inservice ip slb serverfarm farm4 real 10.0.0.7 inservice real 10.0.0.8 inservice ip slb serverfarm farm5 real 10.0.0.9 inservice real 10.0.0.10 inservice ip slb serverfarm farm6 real 10.0.0.11 inservice ! ip slb map 1 gtp apn cisco* ip slb map 4 gtp apn abc.microsoft.com apn xyz.intel.com ip slb map 5 gtp apn yahoo.com ! ip slb vserver GGSN_SERVER virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 0 service gtp serverfarm farm1 backup farm2 map 1 priority 3 serverfarm farm4 map 4 priority 1 serverfarm farm5 map 5 priority 4 serverfarm farm6 inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Dual-Stack Addresses for GTP Load Balancing
The following sample configuration enables IOS SLB to support dual-stack addresses for GTP load balancing.
ip slb serverfarm SF1 real 172.16.88.5 weight 1 inservice ! ip slb serverfarm SF2 real 172.16.88.6 weight 1 inservice ! ip slb serverfarm SF3 real 172.16.88.7 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2388:BB03:3329:8612 weight 1 inservice ! ip slb serverfarm SF4 real 172.16.88.8 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2388:BB03:3423:8912 weight 1 inservice ! ip slb vserver VS2 virtual 4.3.2.1 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2341:AA03:2323:8912 udp 0 service gtp serverfarm sf1 backup sf2 ipv6-primary sf3 ipv6-backup sf4 idle gtp request 90 idle gtp imsi 10000000 sticky gtp imsi group 1 gtp notification cac 3 inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with VPN Server Load Balancing
The figure below shows a typical VPN server load-balancing configuration. In this configuration:
- VPN flows are balanced between real servers 20.20.20.10 and 20.20.20.20.
- Clients connect to 10.10.1.1, the IOS SLB virtual server address.
- There is a sticky connection between the ESP virtual server and the UDP virtual server.
- The cryptographic key exchange occurs through IKE (ISAKMP; port 500).
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
ip slb serverfarm VPN nat server real 20.20.20.10 inservice real 20.20.20.20 inservice failaction purge ! ip slb vserver ESP virtual 10.10.1.1 ESP serverfarm VPN sticky 3600 group 69 inservice ! ip slb vserver UDP virtual 10.10.1.1 UDP isakmp serverfarm VPN sticky 3600 group 69 inservice
Examples How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for a GPRS Network
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for a Simple IP CDMA2000 Network
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for a Mobile IP CDMA2000 Network
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for Multiple Service Gateway Farms
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing Firewall Load Balancing "Sandwich"
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing Maps
- Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing Accelerated Data Plane Forwarding
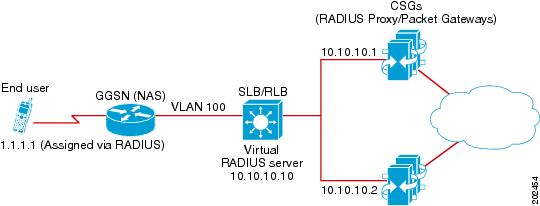
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for a GPRS Network
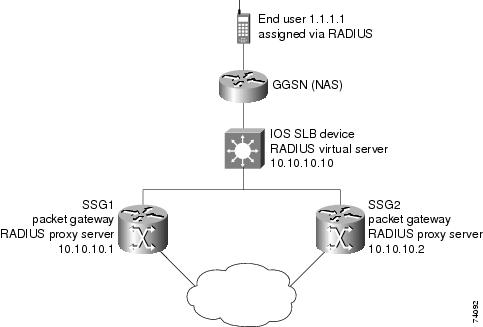
The figure below shows a typical IOS SLB RADIUS load-balancing configuration for a GPRS network. In this configuration:
- RADIUS requests are load-balanced between SSG RADIUS proxy servers 10.10.10.1 and 10.10.10.2.
- End-user data packets are routed to the IOS SLB device.
- End-user data packets from the 1.1.1.0 subnet are directed by IOS SLB to SSG1.
- End-user data packets from the 1.1.2.0 subnet are directed by IOS SLB to SSG2.
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
ip slb route 1.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 framed-ip ! ip slb serverfarm SSGFARM nat server real 10.10.10.1 inservice real 10.10.10.2 inservice ! ip slb vserver RADIUS_ACCT virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 1813 service radius serverfarm SSGFARM idle radius request 20 idle radius framed-ip 7200 sticky radius framed-ip group 1 inservice ! ip slb vserver RADIUS_AUTH virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 1812 service radius serverfarm SSGFARM idle radius request 20 idle radius framed-ip 7200 sticky radius framed-ip group 1 inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for a Simple IP CDMA2000 Network
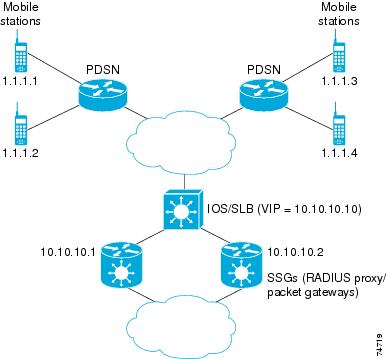
The figure below shows a typical IOS SLB RADIUS load-balancing configuration for a CDMA2000 network with simple IP service. In this configuration:
- The RADIUS virtual server IP address for the PDSNs is 10.10.10.10.
- RADIUS requests are load-balanced between SSG RADIUS proxy servers 10.10.10.1 and 10.10.10.2.
- End-user data packets are routed to the IOS SLB device.
- End-user data packets from the 1.1.0.0 network are routed to the SSGs.
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
ip slb route 1.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 framed-ip
!
ip slb serverfarm SSGFARM
nat server
real 10.10.10.1
inservice
real 10.10.10.2
inservice
!
ip slb vserver RADIUS_SIP
virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 0 service radius
serverfarm SSGFARM
idle radius framed-ip 3600
sticky radius username
sticky radius framed-ip
inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for a Mobile IP CDMA2000 Network
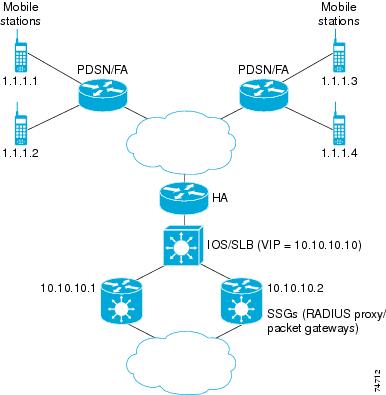
The figure below shows a typical IOS SLB RADIUS load-balancing configuration for a CDMA2000 network with Mobile IP service. In this configuration:
- The RADIUS virtual server IP address for the PDSNs and the HA is 10.10.10.10.
- RADIUS requests are load-balanced between SSG RADIUS proxy servers 10.10.10.1 and 10.10.10.2.
- End-user data packets are routed to the IOS SLB device.
- End-user data packets from the 1.1.0.0 network are routed to the SSGs.
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
ip slb route 1.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 framed-ip
!
ip slb serverfarm SSGFARM
nat server
real 10.10.10.1
inservice
real 10.10.10.2
inservice
!
ip slb vserver RADIUS_SIP
virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 0 service radius
serverfarm SSGFARM
idle radius framed-ip 3600
sticky radius username
sticky radius framed-ip
inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing for Multiple Service Gateway Farms
The following sample configuration enables IOS SLB to balance packet flows for a set of subscribers among multiple service gateway server farms (in this sample, a server farm of SSGs and a server farm of CSGs):
ip slb route 1.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 framed-ip ! ip slb serverfarm SSGFARM nat server real 10.10.10.1 inservice real 10.10.10.2 inservice ! ip slb serverfarm CSGFARM nat server real 20.20.20.1 inservice real 20.20.20.2 inservice ! ip slb vserver SSG_AUTH virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 1812 service radius serverfarm SSGFARM idle radius request 20 idle radius framed-ip 7200 sticky radius framed-ip group 1 access Vlan20 route framed-ip inservice ! ip slb vserver SSG_ACCT virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 1813 service radius serverfarm SSGFARM idle radius request 20 idle radius framed-ip 7200 sticky radius framed-ip group 1 access Vlan20 route framed-ip inservice ! ip slb vserver CSG_ACCT virtual 20.20.20.20 udp 1813 service radius serverfarm CSGFARM idle radius request 25 idle radius framed-ip 0 sticky radius framed-ip access Vlan30 route framed-ip inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing Firewall Load Balancing "Sandwich"
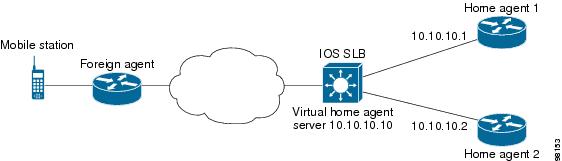
The figure below shows a RADIUS load balancing/firewall load balancing "sandwich" on one IOS SLB device. In this sample configuration:
- The RADIUS load balancing virtual IP address is 5.5.5.5.
- The subscriber framed-IP network is 1.0.0.0/255.0.0.0.
- VL105, VL106, VL107, and VL108 are VLANs.
- RADIUS requests arriving on VLAN VL105 are balanced to 10.10.106.42 and 10.10.106.43.
- User traffic is stickied based on framed-IP address assignments in the 1.0.0.0 subnet.
- Firewall load balancing on the other side (10.10.107.42/43) ensures that return path traffic to the subscriber is delivered to the correct gateway.
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
ip vrf client rd 0:1 ! ip slb probe P742 ping address 10.10.107.42 interval 120 ! ip slb probe P743 ping address 10.10.107.43 interval 120 ! ip slb route 1.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 framed-ip ip slb route framed-ip deny ! ip slb firewallfarm SERVER access inbound Vlan108 access outbound Vlan107 inservice real 10.10.107.42 probe P742 inservice real 10.10.107.43 probe P743 inservice protocol tcp sticky 180 destination protocol datagram sticky 180 destination predictor hash address port ! ip slb serverfarm SF1 nat server access Vlan106 ! real 10.10.106.42 inservice real 10.10.106.43 inservice ! ip slb vserver VS1 virtual 5.5.5.5 udp 0 service radius serverfarm SF1 sticky radius framed-ip access Vlan105 route framed-ip access Vlan105 inservice ! mls flow ip interface-full ! !************************************************* !* Switchports, port channels and trunks * !* added to vlans 105-108 (left out for brevity) * !************************************************* ! interface Vlan105 ip vrf forwarding client ip address 10.10.105.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Vlan106 ip vrf forwarding client ip address 10.10.106.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Vlan107 ip address 10.10.107.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Vlan108 ip address 10.10.108.2 255.255.255.0 ! ip route 10.10.105.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.107.42 ip route vrf client 10.10.108.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.106.42
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing Maps
The following sample configuration enables IOS SLB to support multiple server farms behind a RADIUS load balancing virtual server, using RADIUS calling station IDs and usernames to select server farms. Server farm farm3 is configured without an associated map, and therefore acts as a default server farm. If IOS SLB cannot match any of the other server farm maps, and a default server farm is configured, IOS SLB sends the RADIUS request to the default serverfarm.
ip slb serverfarm CSGFARM predictor route-map rlb-pbr ip slb serverfarm AAAFARM nat server real 10.10.10.1 inservice real 10.10.10.2 inservice ip slb vserver RADIUS_ACCT virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 1813 service radius serverfarm CSGFARM radius inject acct 1 key 0 cisco inservice ip slb vserver RADIUS_AUTH virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 1812 service radius serverfarm AAAFARM radius inject auth 1 calling-station-id radius inject auth timer 45 radius inject auth vsa cisco inservice ! interface vlan 100 ip policy route-map rlb-pbr ! access-list 1 permit 0.0.0.1 255.255.255.254 access-list 2 permit 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.254 ! route-map rlb-pbr permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 10.10.10.1 ! route-map rlb-pbr permit 20 match ip address 2 set ip next-hop 10.10.10.2
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with RADIUS Load Balancing Accelerated Data Plane Forwarding
The following IOS SLB configuration has the following characteristics:
- There is a virtual RADIUS server with IP address 10.10.10.10 that manages Network Access Server (NAS) devices.
- There are two packet gateways with IP addresses 10.10.10.1 and 10.10.10.2.
- RADIUS traffic destined for the virtual RADIUS server is distributed between the packet gateways, based on mapped framed-IP addresses, according to route map rlb-pbr.
- Server farm CSGFARM is configured with real IP addresses that match the possible results for route map rlb-pbr.
- End user traffic arriving on VLAN 100 is routed to the correct Cisco Content Services Gateway (CSG) based on access control lists (ACLs):
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
ip slb serverfarm CSGFARM predictor route-map rlb-pbr ip slb serverfarm AAAFARM nat server real 10.10.10.1 inservice real 10.10.10.2 inservice ! ip slb vserver RADIUS_ACCT virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 1813 service radius serverfarm CSGFARM radius inject acct 1 key 0 cisco inservice ! ip slb vserver RADIUS_AUTH virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 1812 service radius serverfarm AAAFARM radius inject auth 1 calling-station-id radius inject auth timer 45 radius inject auth vsa cisco inservice ! interface vlan 100 ip policy route-map rlb-pbr ! access-list 1 permit 0.0.0.1 255.255.255.254 access-list 2 permit 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.254 ! route-map rlb-pbr permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip next-hop 10.10.10.1 ! route-map rlb-pbr permit 20 match ip address 2 set ip next-hop 10.10.10.2
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Home Agent Director
The following sample configuration enables IOS SLB to balance Mobile IP RRQs among multiple home agents.
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
ip slb serverfarm HA_FARM nat server real 10.10.10.1 inservice real 10.10.10.2 inservice ip slb vserver VIRTUAL_HA virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 434 service ipmobile serverfarm HA_FARM inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Sticky Connections
The following sample configuration assigns all HTTP connections from a subnet to the same real server in server farm PUBLIC:
ip slb vserver http serverfarm PUBLIC sticky 30 group 1 netmask 255.255.255.248 virtual 20.20.20.20 tcp 80 inservice
The following sample configuration adds HTTPS connections to the above configuration, using the same sticky information but with a different virtual server:
ip slb vserver https serverfarm PUBLIC sticky 30 group 1 netmask 255.255.255.248 virtual 20.20.20.20 tcp 443 inservice
Now, all HTTP and HTTPS connections from the subnet are assigned to the same real server. For example, if a user connects to HTTP, then a second user connects to HTTPS, both connections are assigned to the same real server.
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with GTP IMSI Sticky Database
The following sample configuration shows how to enable the IOS SLB GTP IMSI sticky database:
ip slb serverfarm GGSN_FARM failaction gtp purge real 10.20.10.1 weight 1 faildetect numconns 255 numclients 8 inservice ! real 10.20.10.2 weight 1 faildetect numconns 255 numclients 8 inservice ! real 10.20.10.3 weight 1 faildetect numconns 255 numclients 8 inservice ! ip slb vserver GGSN_SERVER1 virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 3386 service gtp serverfarm GGSN_FARM backup GGSN_FARM idle gtp request 90 idle gtp imsi 10000000 sticky gtp imsi group 1 gtp notification cac 3 inservice ! ip slb vserver GGSN_SERVER2 virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 2123 service gtp serverfarm GGSN_FARM backup GGSN_FARM idle gtp request 90 idle gtp imsi 10000000 sticky gtp imsi group 1 gtp notification cac 3 inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with ASN Sticky Database
The following sample configuration shows how to enable the IOS SLB ASN sticky database:
ip slb entries sticky 15000 800000 ip slb serverfarm ASNLB_FARM failaction asn purge ! real 10.20.10.1 weight 1 faildetect numconns 255 numclients 8 inservice ! real 10.20.10.2 weight 1 faildetect numconns 255 numclients 8 inservice ! real 10.20.10.3 weight 1 faildetect numconns 255 numclients 8 inservice ! ip slb vserver ASNLB_SERVER virtual 10.10.10.10 udp 0 service asn serverfarm ASNLB_FARM idle asn request 90 idle asn msid 100000 sticky asn msid group 1 gw port 63082 replicate casa 100.100.100.102 100.100.100.101 1024 password hello inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with Transparent Web Cache Load Balancing
In the following sample configuration, virtual server WEBCACHE examines all web flows passing through the load-balancing device and dispatches them to server farm WEBCACHE-FARM. The client exclude statement ignores flows originating from subnet 80.80.7.0, enabling the real servers 80.80.7.188 and 80.80.7.189 to communicate with the Internet as needed.
ip slb serverfarm WEBCACHE-FARM real 80.80.7.188 inservice real 80.80.7.189 inservice ip slb vserver WEBCACHE virtual 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 tcp www serverfarm WEBCACHE-FARM client 80.80.7.0 255.255.255.0 exclude inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB with KAL-AP Agent
In the following sample configuration, the client is configured to send a Domain Name System (DNS) query abcd.comto the GSS. The Global Site Selector (GSS) in the DUBLIN site receives the requests from the client. The GSS answers the DNS query with the virtual IP address of either CHICAGO (10.0.0.100) or NEWYORK (10.0.0.200), based on the load reported by those virtual servers.
Following are the IOS SLB configuration statements for the configuration shown in the figure above:
GSS
shared-keepalive kalap 192.168.1.1 capp-secure enable key kap shared-keepalive kalap 192.168.2.1 capp-secure enable key kap ! answer vip 10.0.0.100 name CHICAGO activate keepalive type kalap tag 192.168.1.1 chicao.com answer vip 10.0.0.200 name NEWYORK activate keepalive type kalap tag 192.168.2.1 newyork.com ! answer-group ABCD owner System type vip answer-add 10.0.0.100 name CHICAGO weight 1 order 0 load-threshold 254 activate answer-add 10.0.0.200 name NEWYORK weight 1 order 0 load-threshold 254 activate dns rule ABCDGPRS owner System source-address-list Anywhere domain-list abcd.com query a clause 1 vip-group method least-loaded ttl 20 count 1 sticky disable
Site-1 IOS SLB - CHICAGO
ip slb capp udp peer port 6000 secret 0 kap ! ip slb serverfarm SF kal-ap domain chicago.com farm-weight 200 real 10.10.10.1 inservice real 10.10.10.2 inservice ! ip slb vserver chicago virtual 10.0.0.100 udp 0 serverfarm SF inservice ! ip slb dfp agent 10.10.10.1 5000 30 0 10 agent 10.10.10.2 5000 30 0 10 ! int vlan100 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Site-2 IOS SLB - NEWYORK
ip slb capp udp peer port 6000 peer 192.1.1.1 secret 0 test peer 10.100.100.100 port 1234 ! ip slb serverfarm SF kal-ap domain newyork.com farm-weight 6200 real 10.20.20.1 inservice real 10.20.20.2 inservice real 10.20.20.3 inservice real 10.20.20.4 inservice ! ip slb vserver chicago virtual 10.0.0.200 udp 0 serverfarm SF inservice ! ip slb dfp agent 10.10.10.1 5000 30 0 10 agent 10.10.10.2 5000 30 0 10 ! int vlan200 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
Example How to Configure Combined IOS SLB
ip slb serverfarm SF1 nat server real 172.16.88.5 weight 1 inservice ip slb serverfarm SF3 nat server real 172.16.88.7 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2388:BB03:3329:8612 weight 1 inservice ip slb vserver VS1 virtual 4.3.2.1 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2341:AA03:2323:8912 udp 500 serverfarm sf1 ipv6-primary sf3 idle 5 sticky 5 group 1 inservice ip slb vserver VS2 virtual 4.3.2.1 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2341:AA03:2323:8912 udp 4500 serverfarm sf1 ipv6-primary sf3 idle 5 sticky 5 group 1 inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB IPv6 Configuration
ip vrf iWSG rd 200:1 ! ip slb probe PING ping ! ip slb serverfarm SF-IPv6 probe PING nat server access Vlan6 ! real 172.16.88.7 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2388:BB03:3329:8612 weight 1 inservice ! real 172.16.88.8 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2388:BB03:3423:8912 weight 1 inservice ! ip slb vserver VS-IPv6 virtual 4.3.2.1 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2341:AA03:2323:8912 udp 500 serverfarm ipv6-primary SF-IPv6 idle 5 sticky 5 group 1 access Vlan5 inservice standby HSRP-WSG ! ip slb vserver VS2-IPv6 virtual 4.3.2.1 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2341:AA03:2323:8912 udp 4500 serverfarm ipv6-primary SF-IPv6 idle 5 sticky 5 group 1 access Vlan5 inservice standby HSRP-WSG ! ip slb dfp agent 172.16.88.7 1111 60 10 agent 172.16.88.8 1111 60 10 ! interface Vlan5 description Client_facing_interface ip vrf forwarding iWSG ip address 5.5.5.33 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 5:5:5::33/60 standby 2 ip 5.5.5.44 standby 2 priority 101 standby 2 preempt standby 2 name HSRP-WSG interface Vlan6 description Server_facing_interface ip vrf forwarding iWSG ip address 172.16.88.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 55:55:55::33/60
Example How to Configure Combined IOS SLB
ip slb serverfarm SF1 nat server real 172.16.88.5 weight 1 inservice ip slb serverfarm SF3 nat server real 172.16.88.7 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2388:BB03:3329:8612 weight 1 inservice ip slb vserver VS1 virtual 4.3.2.1 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2341:AA03:2323:8912 udp 500 serverfarm sf1 ipv6-primary sf3 idle 5 sticky 5 group 1 inservice ip slb vserver VS2 virtual 4.3.2.1 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2341:AA03:2323:8912 udp 4500 serverfarm sf1 ipv6-primary sf3 idle 5 sticky 5 group 1 inservice
Example How to Configure IOS SLB IPv6 Configuration
ip vrf iWSG rd 200:1 ! ip slb probe PING ping ! ip slb serverfarm SF-IPv6 probe PING nat server access Vlan6 ! real 172.16.88.7 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2388:BB03:3329:8612 weight 1 inservice ! real 172.16.88.8 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2388:BB03:3423:8912 weight 1 inservice ! ip slb vserver VS-IPv6 virtual 4.3.2.1 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2341:AA03:2323:8912 udp 500 serverfarm ipv6-primary SF-IPv6 idle 5 sticky 5 group 1 access Vlan5 inservice standby HSRP-WSG ! ip slb vserver VS2-IPv6 virtual 4.3.2.1 ipv6 2342:2342:2343:FF04:2341:AA03:2323:8912 udp 4500 serverfarm ipv6-primary SF-IPv6 idle 5 sticky 5 group 1 access Vlan5 inservice standby HSRP-WSG ! ip slb dfp agent 172.16.88.7 1111 60 10 agent 172.16.88.8 1111 60 10 ! interface Vlan5 description Client_facing_interface ip vrf forwarding iWSG ip address 5.5.5.33 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 5:5:5::33/60 standby 2 ip 5.5.5.44 standby 2 priority 101 standby 2 preempt standby 2 name HSRP-WSG interface Vlan6 description Server_facing_interface ip vrf forwarding iWSG ip address 172.16.88.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 55:55:55::33/60

 Feedback
Feedback