Cisco uBR10012 - Cisco IOS Release 12.2 BC
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco uBR10012 Universal Broadband Router for Cisco IOS Release 12.2 BC
Cisco uBR10012 Universal Broadband Router
Cisco uBR10012 Router Cable Interface
Determining Your Software Release
Upgrading to a New Software Release
Limitations on Upstream Modulation Parameters for PacketCable VoIP Calls
Access Lists on the Cisco uBR10012 Router
Avoiding the Dropping of SNMP Traps
BPI+ Multicast is Not Supported on Bundled Subinterfaces
Cable Device, Host, and Modem Commands Not Supported
Cable Modems Becoming Stuck in the TFTP Transfer State
Changes to the cable source-verify Command
Changes to the cable tftp-enforce Command
Configuring the CMTS Cable Interface When Configuring a CM for Routing Mode
Configuring the Routing Protocol Causes a Reset of the Cable Modems
Deleting Internal Access Lists Can Cause System Malfunction
Deprecated and Removed Cable MIB Objects
EIGRP, IS-IS, and OSPF Not Supported on Cable Interfaces
FastEthernet Interface Automatically Negotiates
Limitation on Vendor-Specific Information in the DOCSIS Configuration File
Minimum Revision for the Cisco uBR-LCP Line Card Processor
Redundant PRE Modules Are Not Supported Before Release 12.2(4)XF
Removing IGMP Static Groups on Cable Interfaces
Reformatting Flash Cards Required in Release 12.2(11)BC3a and Later
Show Interface Counters are Separate for Master and Slave Interfaces
Synchronization of the System Clocks
Unsupported Counter for Policy Maps
Upgrading When Using Shared Secret Passwords
Using cable helper-address and ip helper-address Commands
Using the show cable modem Command After an HCCP Switchover
Use of the FastEthernet Port on the PRE Module
Web Cache Communication Protocol Is Not Supported
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2i
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2i
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2h
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2h
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2g
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2g
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2f
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2f
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2e
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2e
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2d
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2d
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2c
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2c
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2b
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2b
Show Controllers Cable Extensions
Source Verify Lease-Query Throttling
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2a
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2a
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2
Command-Line Interface (CLI) Enhancements
Command Enhancements for the Cisco uBR10012 Router
Extended Upstream Frequency Ranges
N+1 Support for Load Balancing
SNMP Support for Virtual Interfaces
DOCSIS Configuration File Changes for Type-Length-Value (TLV)
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1g
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1g
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1f
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1f
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1e
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1e
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1d
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1d
Source Verify Lease-Query Throttling
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1c
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1c
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1b
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1b
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1a
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1a
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1
Command-Line Interface Enhancements
Load Balancing for the Cisco CMTS
N+1 Operations for the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S Cable Interface Line Card
Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) Awareness
PacketCable Support for the Cisco uBR10012 Router
PacketCable Debug Enhancements
Support for Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter Version 3.0
Virtual Interfaces on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S Card
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3d
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3d
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3c
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3c
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3b
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3b
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3a
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3a
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3
Support for the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S Cable Interface Line Card
OC-48 DPT Support for the uBR10012
New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3
Cisco uBR10012 Route Processor Redundancy Plus and DOCSIS SSO
VLAN support for the Cisco uBR10012
PBR support for the Cisco uBR10012
Shared Spectrum Support on the uBR10012
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC2a
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC2a
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC2
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC2
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1b
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1b
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1a
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1a
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1
New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1
cable source-verify leasetimer Command
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(8)BC2a
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(8)BC2a
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(8)BC2
New Software Features in Release 12.2(8)BC2
Adding Load Information and a Timestamp to Show Commands
Display Modem Capabilities with the show cable modem mac Command
Support for the cable modem vendor Command
Support for the cable tftp-enforce Command
Support for a Secondary Shared Secret
N+1 Redundancy Support on Cable Interface Line Cards
Enhancement to the show hccp brief Command
Enhancement to the cable filter group Command
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(8)BC1
Support for LCP2 Cable Interface Line Cards
Support for 128 MB Flash Cards
New Software Features in Release 12.2(8)BC1
EXEC Commands in Configuration Mode
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(4)BC1b
New Software Features in Release 12.2(4)BC1b
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(4)BC1a
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(4)BC1a
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(4)BC1
Cisco uBR10-SRP-OC12SML DPT WAN Card
New Software Feature in Release 12.2(4)BC1
Support for the cable power Command
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(4)XF1
New Software Features in Release 12.2(4)XF1
N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(4)XF
Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16C Cable Interface Line Card
Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16E Cable Interface Line Card
PRE1 Performance Routing Engine
DC PEM with Alarm Status Connector
New Software Feature in Release 12.2(4)XF
Route Processor Redundancy Support
Support for the cable monitor Command
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(2)XF1
No New Software Feature in Release 12.2(2)XF1
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(2)XF
No New Software Feature in Release 12.2(2)XF
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(1)XF1
New Software Feature in Release 12.2(1)XF1
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(1)XF
New Software Feature in Release 12.2(1)XF
Cisco uBR-MC5X20S Cable Interface Line Card
Route Processor Redundancy Plus (RPR+)
Console Port Usage After a PRE1 Module Switchover
Flap Detection on WAN Interfaces During Switchover
Link States Reinitialized After Switchover
MIB Variables Reinitialized After Switchover
SNMP Not Supported During Switchover
Telnet Sessions Disconnected During Switchover
Encrypted Multicast Not Supported
Gigabit Ethernet Performance Limitations on Small Packets
Downstream Rate-limiting Cannot Be Disabled
Channel-width and Minislot Size
N+1 Redundancy Limitations and Restrictions
PacketCable and N+1 Interoperation
Encrypted Multicast Not Supported
N+1 Redundancy and Cable Modem Compatibility
N+1 Redundancy and Configuring Static Multicast Groups
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2i
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2i
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2h
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2h
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2g
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2g
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2f
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2f
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2e
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2e
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2d
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2d
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2c
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2c
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2b
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2b
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2a
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2a
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1g
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1g
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1f
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1f
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1e
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1e
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1d
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1d
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1c
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1c
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1b
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1b
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1a
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1a
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3d
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3d
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3b
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3b
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3a
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3a
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC2a
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC2a
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC2
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC2
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1b
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1b
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1a
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1a
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC2a
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC2a
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC2
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC2
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC1
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC1
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(4)BC1b
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(4)BC1b
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3ca
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3ca
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(4)XF1
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(4)XF1
Cisco IOS Software Documentation Set
Release 12.2 Documentation Set
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Release Notes for Cisco uBR10012 Universal Broadband Router for Cisco IOS Release 12.2 BC
November 2, 2005
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i
OL-2772-21
These release notes for the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router document the cable-specific, early deployment 12.2 BC train, describing the enhancements and caveats provided in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i. This release includes features in previous Cisco IOS 12.2BC Releases. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i is a child of Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.
The 12.2 BC train is an interim release train that provides DOCSIS 1.1 two-way support, along with support for selected new features. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i provides a migration path from the earlier 12.2 XF releases.
These release notes are updated with each release in the train. For a list of the software caveats that apply to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i, see the "Caveats" section and Caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T. Use these release notes in conjunction with the cross-platform Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T located on Cisco.com and the Documentation CD-ROM.

Note
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i does not include support for telco-return images.

Note
You can find the most current Cisco IOS documentation on Cisco.com. This set of electronic documents may contain updates and modifications made after this document was initially published.
Cisco recommends that you view the field notices for this release to see if your software or hardware platforms are affected. If you have an account on Cisco.com, you can find field notices at http://www.cisco.com/warp/customer/770/index.shtml. If you do not have a Cisco.com login account, you can find field notices at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/770/index.shtml.
Contents
These release notes describe the following topics:
•
MIBs
•
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Inheritance Information
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i is an early deployment release that is a child of Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T. All features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T and specifically all features and caveats in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T6 are in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i.
Table 1 References for the Cross-Platform Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T
•
Determining the Software Version
•
Upgrading to a New Software Release
To view information about the topics in the left-hand column, click Cross-Platform System Requirements at: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122relnt/xprn122t/122treqs.htm
•
New and Changed Information (Feature Descriptions)
•
MIBs
•
Important Notes
To view information about the topics in the left-hand column.
For Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T, go to:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122relnt/xprn122t/122tnewf.htm
Scroll down and click New Hardware and Software Features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T, or MIBs, or Important Notes.
•
Related Documentation
•
Obtaining Documentation
•
Obtaining Technical Assistance
To view information about the topics in the left-hand column, go to:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122relnt/xprn122t/122tdocs.htm
Introduction
For information on new features and the Cisco IOS documentation set supported by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i, see the "New and Changed Information" section and the "Related Documentation" section.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i supports the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router, which provides a high-capacity, high-throughput cable modem termination system (CMTS), optimized for aggregating traffic at the edge of the cable network. Designed for cable operators and service providers, the platform connects residential subscribers via cable modems, digital set-top boxes, or IP telephony cable modems for high-speed data, broadband entertainment, and IP telephony solutions.
The Cisco uBR10012 router uses the industry-proven Parallel eXpress Forwarding (PXF) technology, derived from the Cisco ESR10000 edge services router, to provide consistent, high-performance throughput, even as software features are added and additional services are deployed.
In addition, it supports a variety of broadband access technologies, including Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS), gigabit ethernet, and optical. With support for multiple standards, operators can choose the appropriate services and devices to optimize their capital investment with a single CMTS platform. With access to current and future software enhancements, the Cisco uBR10012 also ensures investment protection as standards and customer needs continue to evolve.
Cable companies and Internet service providers (ISPs) can allocate radio frequency (RF) channel capacity for Internet access or high priority services using a hybrid fiber/coax (HFC) or an all-coax cable plant. Cisco currently provides three router-based DOCSIS CMTS solutions that offer a wider feature set and better manageability than bridge-based systems.
Cisco uBR10012 Universal Broadband Router
The Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router brings the powerful performance and proven reliability of the industry-leading, DOCSIS-qualified Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband router product line to the next level of performance, capacity, and throughput. The Cisco uBR10012 platform provides a complete, easy-to-use, integrated router and cable modem termination system (CMTS) package, with feature-rich software and unparalleled customer service and support. With access to current and future software enhancements, the Cisco uBR10012 routers ensure investment protection as standards evolve.
The Cisco uBR10012 router supports up to eight cable interface line cards for connection to subscriber cable modems (CMs) and set-top boxes (STBs). Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i supports the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S-D cable interface line card, Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S Spectrum Management Card, Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16C, Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16E, and Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC28C cable interface line cards.

Note
The LCP versions of the above cable interface line cards have reached end-of-life and are no longer sold, but these cards are still supported by the Cisco uBR10012 router.
For connection to the Internet and other networks, the Cisco uBR10012 router supports up to four network uplink line cards, each of which can support connections as fast as 1Gb/s (Gigabit Ethernet). Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i supports OC-12 POS, Gigabit Ethernet connectivity, the Cisco OC-12 DPT line card, and the Cisco OC-48 DPT/POS interface module.

Note
For detailed descriptions of the Cisco uBR10012 router chassis and components, see the hardware documents listed in the "Related Documentation" section.
Cisco uBR10012 Router Cable Interface
The cable interface in the Cisco uBR10012 router serves as the RF cable TV interface, supporting downstream and upstream signals. The downstream is output as an IF signal suitable for use with an external upconverter. Your cable plant, combined with your planned and installed subscriber base, service offering, and external network connections, determines what combination of Cisco uBR10012 cable interfaces, network uplink line cards, and other components that you should use.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i supports the following cable interface line cards, which can be installed in the Cisco uBR10012 chassis in any combination:
•
Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S-D cable interface line card, designed for the Cisco uBR10012 router to provide the highest port density, contains five downstream ports and twenty upstream ports, with DOCSIS MAC management and spectrum management capabilities.
•
Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S Spectrum Management Card with advanced spectrum management features with one downstream and six upstreams.
•
Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16C cable interface line card, based on the existing Cisco uBR-MC16C line card, with one downstream and six upstreams.
•
Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16E cable interface line card, based on the existing Cisco uBR-MC16E line card, with one downstream and six upstreams.
•
Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC28C cable interface line card, based on the existing Cisco uBR-MC28C line card, with two downstreams and eight upstreams divided into two domains. This provides the ability to support a large volume of cable modem subscribers using only one chassis.

Note
Unless otherwise indicated, all references to the LCP2 versions of the cable interface line cards also apply to the LCP versions of these cards, which have reached end-of-life and are no longer being sold.
All cable interface line cards, except for the Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16E, support the Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS). DOCSIS supports the 6 MHz North American channel plans using the ITU J.83 Annex B RF standard. The downstream uses a 6 MHz channel width in the 85 to 860 MHz frequency range, and the upstream supports the 5 to 42 MHz frequency range.
The Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16E cable interface line card supports the European Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications (EuroDOCSIS). EuroDOCSIS supports the 8 MHz Phase Alternating Line (PAL) and Systeme Electronique Couleur Avec Memoire (SECAM) channel plans using the ITU J.112 Annex A RF standard. The downstream uses an 8 MHz channel width in the 85 to 860 MHz frequency range, and the upstream supports multiple channel widths in the 5 to 65 MHz frequency range.
Early Deployment Releases
These release notes describe Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i for the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router. Release 12.2 XF is an early deployment (ED) release based on Release 12.2 T, which serves as the train's starting point. Early deployment releases contain fixes to software caveats as well as support for new Cisco hardware and software features. Feature support is cumulative from release to release, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2 lists any features supported by the Cisco uBR10012 router in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i. For complete feature information, see the Cisco uBR10012 Universal Broadband Router Hardware Installation Guide, the Field Replaceable Units (FRUs) documents, and the Cisco uBR10012 Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide.
1 Only major features are listed.
2 MIB = Management Information Base
System Requirements
This section describes the system requirements for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i and includes the following sections:
•
Determining Your Software Release
•
Upgrading to a New Software Release
Memory Recommendations
Table 3 displays the memory recommendations of the Cisco IOS feature sets for the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i. Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband routers are available with a 48-MB or 120-MB Type II PCMCIA Flash memory card or 128 MB Flash Disk card.
Table 3 Memory Recommendations for the Cisco uBR10012 Routers, Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i Feature Sets
Flash
Memory
DRAM
Memory
FromDOCSIS BPI IP Plus
ubr10k-k8p6-mz1
40 MB Flash
128 MB DRAM
RAM
1 The Cisco IOS 12.2(11)BC3 image cannot be loaded from a 128 MB Flask Disk. This image is not available in the Cisco IOS 12.2(11)BC2a rebuild release.

Note
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 only, the ubr10k-k8p6-mz software image could not be loaded from a 128 MB Flash Disk card. See caveat CSCea65301 in Bug Toolkit for more information. This caveat was fixed, and this limitation removed, in Cisco ISO 12.2(11)BC3a and later Release 12.2 BC releases.
Supported Hardware
For detailed descriptions of the new hardware features, see the "New and Changed Information" section. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i supports the following hardware on Cisco uBR10012 routers:

Note
The Cisco uBR10012 router is compatible with Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter 2.0 and Cisco Cable Manager 2.0.
Determining Your Software Release
To determine the version of Cisco IOS software running on the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router, log in to the router and enter the show version EXEC command:
Router> show versionCisco Internetwork Operating System SoftwareIOS (tm) 12.2 BC Software (uBR10k-k8p6-mz), Version 12.2(15)BC2i, RELEASE SOFTWAREUpgrading to a New Software Release
For general information about upgrading to a new software release, see Cisco IOS Upgrade Ordering Instructions located at: http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/cc/pd/iosw/prodlit/957_pp.htm.
Feature Set Tables
The Cisco IOS software is packaged in feature sets consisting of software images—depending on the platform. Each feature set contains a specific set of Cisco IOS features.
Table 5 lists the features and feature sets supported by the Cisco uBR10012 routers in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i and uses the following conventions:
•
Yes—The feature is supported in the software image.
•
No—The feature is not supported in the software image.

Note
This table might not be cumulative or list all the features in each image. You can find the most current Cisco IOS documentation on Cisco.com. These electronic documents may contain updates and modifications made after the hard-copy documents were printed. For a list of the 12.1 T-train features in this platform, refer to Feature Navigator. For more information about Feature Navigator, see the "Cisco Feature Navigator" section.
The asterisk (*) in Table 5 indicates that the feature set and its image are not available in the Cisco IOS 12.2(11)BC2a rebuild release. The feature set and image are available in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i.
Table 5 Feature List by Feature Sets for Cisco uBR10012 Universal Broadband Routers
Yes
DOCSIS 1.0 and 1.1 Support
Yes
DHCP1 Server
Yes
DRP2 Server Agent
Yes
IP Enhanced IGRP3 Route Authentication
Yes
IP Fragmentation Support
Yes
IP Multicast Echo Support
Yes
Multicast Routing (MFIB) Support
Yes
Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) Awareness—BGP, OSPF, and Integrated IS-IS
Yes
Policy-Based Routing Support
Yes
Unicast Routing (FIB) Support
Yes
BPI4 and BPI+ MIB
Yes
Cable Intercept (CALEA) Support
Yes
Cable Intercept (CALEA) Support for PacketCable Operations
No
Cable Interface Dual Hardware Queue Support
Yes
Cable Interface Flow Control Support
Yes
Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter Version 3.0 Support
Yes
Cisco Call History MIB Command Line Interface
Yes
Cisco IOS Internationalization
Yes
DOCSIS Ethernet MIB Objects Support (RFC 2665)
Yes
DOCSIS OSSI5 Objects Support (RFC 2233)
Yes
DOCSIS 1.1 N+1 Redundancy Support on Cable Interface Line Cards
Yes
Dynamic Ranging Support
Yes
Entity MIB, Phase 1
Yes
Gigabit Ethernet Line Card Support
Yes
Interface Bundling
Yes
Interface Command Enhancements
Yes
Internal Modem Configuration File Editor
Yes
LinkUp/Down Traps Support (RFC 2233)
Yes
Load Balancing for the Cisco CMTS
Yes
MIB Enhancements
Yes
N+1 Operations for the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S Cable Interface Line Card
Yes
OC-12 POS Line Card
Yes
PacketCable Support for the Cisco uBR10012 Router
Yes
RF Interface MIB
Yes
Route Processor Redundancy Plus (RPR+) and DSSO6
Yes
SNMP Cable Modem Remote Query
Yes
Yes
Subscriber MIB Packet Filtering
Yes
Virtual Interfaces on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S Card
Yes
Bidirectional PIM9
Yes
Stub IP Multicast Routing
Yes
252 Operator Configurable QoS Service Profiles for DOCSIS 1.0
Yes
Admission Control for Load Balancing
Yes
Admission Control (Including Weighting Functions per QoS Profile)
Yes
DHCP/PPoE Packet Divert Support
Yes
DOCSIS 1.0 Configuration File Editor (IOS CLI-based)
Yes
DOCSIS 1.0+10 QoS Enhancements
Yes
Downstream DOCSIS 1.1 Classification Support
Yes
Downstream DOCSIS 1.1 Queuing Support
Yes
Downstream QoS Handling
Yes
Downstream Traffic Shaping
Yes
Dynamic Map-Advance
Yes
Dynamic Upstream Modulation
Yes
Guaranteed Upstream Minimum Throughput per Modem for DOCSIS 1.0
Yes
Improved Upstream QoS
Yes
JIB Upstream Header Support
Yes
JIB Downstream Header Support
Yes
Modular QoS CLI Support (for non-cable interfaces)
Class-Based Weighted Fair Queuing (CB-WFQ)
Low Latency Queuing (LLC)
Shaping
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Multiple SID Support for DOCSIS 1.0+
Yes
Multiple SID Support for DOCSIS 1.1
Yes
Multiple SID Support (static only)
Yes
QoS Configuration
Yes
QoS Policy Propagation via Border Gateway Protocol (QPPB)
Yes
QoS Profile Enforcement
Yes
QoS Profile Management via SNMP, IOS CLI, or Dynamic
Yes
RTP11 Header Compression
Yes
Shared Spectrum Support
Yes
Subscriber Traffic Management
Yes
Time of Day (ToD) Server
Yes
ToS Bit Restamping and ToS-based QoS for DOCSIS 1.0
Yes
ToS Overwrite Support
Yes
Upstream Address Verification
Yes
Upstream Traffic Shaping
Yes
Automated Double Authentication
Yes
BPI and BPI+ Encryption
Yes
Cable source-verify
Yes
Cable source-verify DHCP, Including lease-query
Yes
Cisco IOS Firewall Enhancements
Yes
Dynamic Mobile Hosts
Yes
Dynamic Shared Secret
Yes
HTTP12 Security
Yes
IP Security Access List Support
Yes
Named Method Lists for AAA13 Authorization & Accounting
Yes
Per-User Configuration
Yes
Secure Shell (SSH)
Yes
SNMP Access Lists, Including Logging Features
Yes
TACACS+
Yes
TFTP-enforce
Yes
MPLS Disposition Support
MPLS Imposition on Cable Subinterfaces Support
Yes
MPLS VPN Support for Subinterfaces and Interface Bundles
Yes
PAD14 Subaddressing
Yes
1 DHCP = Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
2 DRP = Director Response Protocol
3 IGRP = Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
4 BPI = Baseline Privacy Interface
5 OSSI = Operations Support System Interface
6 DSSO = DOCSIS Stateful Switchover
7 SNMPv2 = Simple Network Management Protocol version 2
8 SNMPv3 = Simple Network Management Protocol version 3
9 PIM = Protocol Independent Multicast
10 The DOCSIS 1.0+ QoS Enhancements is a set of Cisco's Quality of Service extensions to DOCSIS 1.0 to enable basic VoIP service over the DOCSIS link before DOCSIS 1.1 becomes available. The main enhancements include support for dynamic creation and teardown of flows during voice calls, support for one new unsolicited grant service (UGS) slot scheduling mechanism for voice slots, and per IP-precedence rate shaping on the downstream.
11 RTP = Real-Time Transport Protocol
12 HTTP = Hypertext Transfer Protocol
13 AAA =authentication, authorization, and accounting
14 PAD = packet assembler/disassembler
Important Notes
The following sections contain important notes about Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i that apply to the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router.
Limitations on Upstream Modulation Parameters for PacketCable VoIP Calls
When PacketCable support is enabled on the Cisco CMTS to provide Voice over IP (VoIP) support, the following combinations of upstream modulation parameters should not be used, because the channel width is too small to allow the upstream MAC scheduler to provide sufficient grants for reliable VoIP communications.
The following Table lists unsupported Upstream Parameter Combinations for VoIP Calls:
We recommend configuring upstreams that are being used for PacketCable operations and VoIP calls for a channel width that is larger than 400 KHz. (These channel widths and upstream parameter combinations can still be used, however, for best-effort data communications.)
Access Lists on the Cisco uBR10012 Router
The Parallel eXpress Forwarding (PXF) processors on the Cisco uBR10012 router provide the increased performance of Turbo Access Control Lists (Turbo ACL) by default by automatically compiling all access lists when access lists are configured.
You do not need to use the access-list compiled command to enable the Turbo ACL feature. You can display these access lists by using the show access-lists command without the compiled option.

Note
The Cisco uBR10012 router does not compile simple access lists that have a small number of rules, because it is more efficient to process these lists in the standard manner than to compile them. The State column in the show access-lists compiled command identifies these access lists as "Non TA Operational."
For complete information about access lists, see the "Traffic Filtering and Firewall" volume in the Cisco IOS Release 12.1 Security Configuration Guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios121/121cgcr/secur_c/scprt3/index.htm
Acterna DCMTA v1.1 Tool
The Acterna DCMTA v1.1 tool is no longer available from Acterna, starting with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1.
The Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter 3.0 (CBT) replaces the DCMTA tool. For more information, see the Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter documentation, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/trblshtr/cbt30/index.htmAvoiding the Dropping of SNMP Traps
When the snmp-server enable traps command is given without any options, it enables all traps, which can generate a significant number of traps at key events, such as system power-up. If the SNMP queue is not large enough to handle all of the traps, new traps will be dropped without notification until the existing traps are sent and slots become available in the queue.
You can do two things to avoid dropping traps in this situation:
•
Increase the SNMP trap queue size. The default queue size is 10, which is insufficient to handle all traps. Use the snmp-server queue-length length global configuration command to increase the queue size. The length parameter can range from 10 to 1000. Increase the queue size until traps are no longer dropped.
•
Disable unneeded SNMP traps. For example, if you do not need SYSLOG traps (which are sent for every message displayed on the console), disable those traps as follows:
router(config)# snmp-server enable trapsrouter(config)# no snmp-server enable traps syslogBPI+ Multicast is Not Supported on Bundled Subinterfaces
BPI-encrypted multicasts are not supported on the Cisco uBR10012 router on cable subinterfaces that are also configured as part of a bundle. BPI-encrypted multicasts are supported on bundled cable interfaces or on cable subinterfaces, but not on bundled cable subinterfaces.
Cable Device, Host, and Modem Commands Not Supported
The Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router does not support the following commands:
•
cable device access-group
•
cable host access-group
•
cable modem access-group
Cable Modems Becoming Stuck in the TFTP Transfer State
Cable modems can become stuck in the TFTP transfer state under the following conditions. This state is indicated as "init(o)" by the show cable modem command.
•
The Dynamic Shared Secret feature is enabled on the cable interface, using the cable dynamic-secret command.
•
The cable modems on that cable interface are downloading a DOCSIS configuration file that is greater than 4 Kbytes in size.
•
A large number of cable modems are registering at the same time. Some or all of those cable modems could also be downloading the DOCSIS configuration file using multiple TFTP transfers that use multiple TFTP ports on the Cisco CMTS router.
This situation can cause the TFTP server to run out of available ports, resulting in the cable modems failing the TFTP download stage. To prevent this situation from happening, temporarily disable the Dynamic Shared Secret feature on the cable interface or reduce the size of the DOCSIS configuration file.
Changes to the cable source-verify Command
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and later releases, the cable source-verify dhcp command extends IP address verification to CPE devices that had been online using a valid IP address but then were reconfigured by the user with an unused static IP address. With Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and later, CPE devices are not allowed online when they are using static IP addresses that have not been allocated by the DHCP server. If you are using the cable source-verify command with the dhcp option, the CPE device must use an IP address that has been assigned by the DHCP server.

CautionIn current Cisco IOS Release 12.2 BC software images, the Cisco CMTS can crash with a "bus error exception" when the cable source-verify command is configured on a cable interface, and the routing configuration of that interface is being changed while traffic is passing through the interface. To avoid this problem, temporarily disable this feature (using no cable source-verify) on the interface before you configure the routing parameters. Then after you have finished the routing configuration, reenable the feature using the cable source-verify command. Alternatively, you can also change the routing parameters when the interface is not passing traffic (such as when the interface is shut down).
Changes to the cable tftp-enforce Command
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and later releases, when the cable tftp-enforce command is configured on the cable interface, the Cisco uBR10012 router can occasionally allow a cable modem to temporarily come online before the system has received confirmation that the cable modem has downloaded the proper DOCSIS configuration file. This situation can occur when the cable interface line card receives a registration request (REG-REQ) message from a cable modem before the PRE1 module has notified the line card whether the modem did download the proper file from the TFTP server.
In previous Cisco IOS releases, these cable modems were not allowed to come online (or marked as TFTP violators) even if they had successfully downloaded the appropriate DOCSIS configuration file. In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and later releases, however, the Cisco uBR10012 router allows these cable modems to temporarily come online until the PRE1 module has finished determining the modem's TFTP status. If the system determines that the modem did not download the appropriate DOCSIS configuration file, it is then taken offline (or marked as a TFTP violator).

Note
In the above situation, cable modems that do not download a DOCSIS configuration file are marked as "offline" instead of "reject(c)" by the show cable modem command. The console still displays the %UBR10000-4-REGISTRATION_BEFORE_TFTP error message, however, to allow you to identify these cable modems as TFTP violators.
Configuring the CMTS Cable Interface When Configuring a CM for Routing Mode
If you have configured a Cisco cable modem for routing mode and are also using the cable-modem dhcp-proxy nat command on the cable modem, you must configure the corresponding cable interface on the Cisco uBR10012 router with the cable dhcp-giaddr policy command. Otherwise, the cable interface could flap and the CM could go offline unpredictably.
Configuring the Routing Protocol Causes a Reset of the Cable Modems
Be aware that when configuring a routing protocol, the Cisco IOS software must reset the interfaces to enable the change. This normally does not significantly affect operations on the interface, except that when this is done on a cable interface, it causes all cable modems on that particular downstream to reinitialize, potentially interfering with data transmission on that downstream. Therefore you should use routing global configuration commands, such as router rip, on a cable interface only when a minimum of subscribers would be affected.
CPE IP Addressing
If the IP address of a DHCP CPE is changed to a currently unused static IP address, the new IP address is not allowed into the CMTS router's host table and the CMTS router's Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table. Consequently, traffic destined to the static IP address is dropped by the Cisco CMTS router.
Deleting Internal Access Lists Can Cause System Malfunction
The Cisco uBR10012 router uses internal access lists for various functions. These internal access lists do not appear in the running configuration but are displayed in the show access-list output for debugging purposes. The internal access lists are prefixed with 'CMTS_PKT_FILTER_GROUP'.
If these access lists are removed using the Global Configuration CLI, the router can malfunction, including resulting in a system failure.
The following is an example of how an ACL is deleted in Global Configuration mode:
conf tno ip access-list extended CMTS_PKT_FILTER_GROUP_255endThis issue is documented in CSCin54155 in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1. The workaround is to not delete or disable these internal access-lists.
Deprecated and Removed Cable MIB Objects
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and later releases, the DOCS-IF-EXT-MIB has been deprecated and removed. The objects in this MIB have been replaced by new objects in the DOCS-IF-MIB and the proposed DOCS-RFI-MIB, so as to conform to the requirements given in the DOCSIS 2.0 Operations Support System Interface Specification (SP-OSSIv2.0-I04-030730). In particular, the following objects are replaced as indicated:
•
docsIfDocsisCapability (replaced by docsIfDocsisBaseCapability)
•
docsIfDocsisOperMode (replaced by docsIfDocsisBaseCapability)
•
docsIfCmtsCmStatusDocsisMode (replaced by docsIfCmtsCmStatusDocsisRegMode)
Also, the following objects have been removed from traps and notifications in DOCS-CABLE-DEVICE-TRAP-MIB because they duplicate existing objects:
•
docsIfDocsisCapability
•
docsIfDocsisOperMode
DOCSIS 1.0 BPI Support
To conform with a recent change in the DOCSIS 1.0 Baseline Privacy Interface (BPI) Specification, Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC1 and later releases require that the Baseline Privacy Configuration Settings Option (Type 17) must be included in the DOCSIS configuration file for all DOCSIS 1.0 cable modems attempting to register for BPI encryption. If the type 17 option is not included, an "Unauthorized SAID" warning will appear in the CMTS console, and the cable modem will not be allowed to come online.
Previous Cisco IOS Releases allowed DOCSIS 1.0 cable modems to register for BPI encryption and to come online, even if the DOCSIS configuration file did not include the type 17 option. The change to the DOCSIS BPI specification, however, made the type 17 option mandatory for BPI operation.
For more information about this requirement, see the TAC technical note on Cisco.com at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/109/bpi_changes_23895.html.
EIGRP, IS-IS, and OSPF Not Supported on Cable Interfaces
The Cisco uBR10012 router supports advanced routing protocols such as Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS), and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) only on the WAN interfaces, not on the cable interfaces. On cable interfaces, use a routing protocol that is supported by the cable modems, such as RIPv2.
FastEthernet Interface Automatically Negotiates
The FastEthernet interface on the PRE1 module (interface F0/0/0) ignores the link speed and duplex settings but instead always automatically negotiates the correct speed and duplex settings with the device at the other end of the connection.
Limitation on Vendor-Specific Information in the DOCSIS Configuration File
DOCSIS requires that when the cable modem sends its Registration Request (REG-REQ) message to the CMTS, it must include the configuration information found in the DOCSIS configuration file. This configuration information must include all vendor-specific information fields (VSIF). Because MAC-layer management messages, such as REG-REQ, have a maximum data size of 1522 bytes, this limits the amount of VSIF information that can be included in the DOCSIS configuration file.
In particular, the maximum packet size imposes a limit on the number of Cisco IOS CLI commands you can include as VSIF fields in the DOCSIS configuration file. The exact number of commands that will fit depends on the other configuration information included in the file, as well as the length of each command.
If the REG-REQ message is larger than 1522 bytes, the cable modem will likely report errors similar to the following errors that appears on Cisco uBR900 series cable access routers:
%LINK-4-TOOBIG: Interface cable-modem0, Output packet size of 1545 bytes too big%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface cable-modem0, changed state to downIn addition, the CMTS will also report that the cable modem timed out during the registration process. If this occurs, you can try the following steps:
•
Reduce the length of the commands by using the abbreviated form of the command. For example, you can specify the int c0 instead of the full command interface cable-modem 0.
•
SNMP MIB objects are not included in the Registration Request message, so wherever possible, replace the CLI commands with the corresponding SNMP MIB object statements in the DOCSIS configuration file.
•
If a large number of CLI commands must be given, use VSIF option 128 to download a Cisco IOS configuration file to the cable modem.
For complete details on what is included in the REG-REQ message, see Chapter 6 of the current DOCSIS 1.1 specification (SP-RFIv1.1-I07-010829 or later).
Minimum Revision for the Cisco uBR-LCP Line Card Processor
The Cisco uBR-LCP line processor card must be at revision 4.4 or greater and be using the boothelper image from Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XF1 or later to support the Cisco uBR-MC16C and Cisco uBR-MC16E cable interface line cards.
PRE PXF Resets Unexpectedly
The Performance Routing Engine (PRE) Parallel eXpress Forwarding (PXF) processors can reset unexpectedly while generating the following ICMP response packets — ICMP Echo Reply, ICMP network unreachable, and ICMP TTL expired when any of the following features are configured:
•
input Packet Intercept
•
input ACL with logging
•
input ACL with more than 255 entries
•
input Packet Filter Group with more than 255 packet filters
•
input QoS config on the backhaul interfaces with more than 255 entries
Use one of the following possible workarounds:
•
Do not configure the above mentioned features, or
•
Take the following steps to minimize ICMP response packet generation by PXF processors:
–
Add a default route to a valid next-hop to avoid generation of ICMP network unreachable packets by the PXF.
–
Drop ICMP echo requests to the primary address of the CMTS interfaces to avoid generation of ICMP echo response by the PXF.
Note that pings to the secondary addresses are not handled by the PXF.

Note
There is no user configurable command to avoid generation of ICMP TTL expired.
This issue is documented in caveat CSCea75288 in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3a and resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3b.
PRE Module Not Supported
The Cisco uBR10012 router supports only the PRE1 module in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC1, and later releases including Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3. If you attempt to boot the Cisco uBR10012 router with one of these software releases and a PRE module, the router will print the following error message and fall through to the ROM monitor:
%%Error: PRE not supported with this image rommon>To correct this error, replace the PRE modules in the router with PRE1 modules. To continue using the original PRE modules, you must reload the router with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1 or an earlier 12.2 BC release.
Redundant PRE Modules Are Not Supported Before Release 12.2(4)XF
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF introduced support for the Route Processor Redundancy (RPR) feature for the Performance Routing Engine (PRE) cards. This allows two PRE modules to be installed in a Cisco uBR10012 chassis for redundant operation.
Earlier releases of software for the Cisco uBR10012 router do not support RPR. In these earlier releases, two PRE modules can be installed in a Cisco uBR10012 chassis, but Cisco does not guarantee that upon a failure of the primary PRE module, the redundant PRE module can automatically bring up all DOCSIS cable interface line cards.
For more information about the RPR feature, see the Route Processor Redundancy (RPR) on the Cisco uBR10012 Universal Broadband Router feature module, available on Cisco.com and the Customer Documentation CD-ROM.
Removing IGMP Static Groups on Cable Interfaces
When you use the no ip igmp static-group command to remove an IGMP static group on a master cable subinterface, the mroute entries still exist for all of the slave interfaces.
To complete the removal, you must also use the following commands to remove the IGMP configuration on the slave cable interfaces:
clear ip mroute <multicast address>clear ip igmp group <master or subinterface>For more information on the commands, refer to the Cisco IOS Command Reference, Release 12.2 T at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122tcr/crftindx.htm
Reformatting Flash Cards Required in Release 12.2(11)BC3a and Later
Flash Disk cards that were formatted using Cisco IOS software releases 12.2(4)BC1 through 12.2(8)BC2 should be reformatted using Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3a or later. Flash Disk cards formatted with these earlier software releases could have intermittent timing problems that
could prevent files from being read on the disks and thus prevent a PRE1 module from booting using the software on the disk.
Show Interface Counters are Separate for Master and Slave Interfaces
The Cisco uBR10012 router uses a distributed architecture that does not include the slave interface input packet counters when you use the show interface command to display information for a master cable interface. This is different than normal behavior for most Cisco interfaces, where the input packet counters on the master interface include the input packet counts for all associated slave interfaces. On the Cisco uBR10012 router, you must use the show interface command on both the master and slave cable interfaces to get a total count of the input packets.
SNR Algorithm Updated
Since Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1, the algorithm for calculating the SNR estimate in the show controllers cable upstream command was refined for a more accurate value. The new SNR estimate uses the algorithm as recommended by the chip manufacturer, and depending on plant characteristics, the new SNR value could be up to 6 dB lower than the values shown in earlier software releases.

Note
This value is only an estimate—for the most accurate value, use specialized test equipment like a spectrum analyzer.
Synchronization of the System Clocks
Ensure that the system clocks on the CMTS and on the time-of-day (ToD) servers are synchronized. If this does not occur, the clocks on the CMs will not match the clocks on the CMTS, which could interfere with Baseline Privacy Interface Plus (BPI+) operations. In particular, this could prevent the proper verification of the digital certificates on the CM.
Unsupported Counter for Policy Maps
The "Packets marked" counter that is displayed by the show policy-map interface command is not supported on the Cisco uBR10012 router and always shows 0. However, the first "packets" counter for each Class-map is also the "Packets marked" value, so use the "packets" counter for both values.
For example, the following output shows that the "Packets marked" counter is 0, but the "packets" value is 1000, which means the "Packets marked" counter is also 1000 packets.
Router# show policy-map interface GigabitEthernet 4/0/0GigabitEthernet4/0/0Service-policy input:setClass-map:matchany (match-any)1000 packets, 1024000 bytes5 minute offered rate 0 bps, drop rate 0 bpsMatch:anyQoS Setqos-group 3Packets marked 0Upgrading When Using Shared Secret Passwords
Cisco IOS Release 12.2 BC changed the encryption algorithm used for the shared-secret command. If you are upgrading from Cisco IOS Release 12.1 EC or Cisco IOS Release 12.0 SC, you cannot cut and paste the "shared-secret" configuration lines that include an encrypted password. Instead, you must re-enter the original shared secret passwords at the CLI prompt.
For example, if the actual shared secret password is "cm-sharedsecret-password," you would enter the cable shared-secret cm-sharedsecret-password command at the CLI prompt. If you have enabled password encryption, the configuration file will then show only the newly encrypted password.
The following example shows a typical configuration session:
Router# config tRouter(config)# service password-encryptionRouter(config)# int c6/0Router(config-if)# cable shared-secret cm-sharedsecret-passwordRouter(config-if)# exitRouter(config)# exitRouter# show running-config | include sharedcable shared-secret 7 0458064B1C294D5C0C1D161211190910673B253B20222D0103Router#
Note
This change only affects the encryption of the passwords that are stored in the configuration file. It does not affect the actual encryption that is used between the CMTS and CMs, so you do not need to change the shared secret in the DOCSIS configuration files for the CMs.
Using cable helper-address and ip helper-address Commands
On the Cisco CMTS, the Cisco IOS software provides two commands to forward User Datagram Protocol (UDP) broadcasts, such as DHCP/BOOTP packets, that are received on an interface—the ip helper-address and cable helper-address commands.
Use the ip helper-address command on all non-cable interfaces, and use the cable helper-address command for cable interfaces.
The cable helper-address command is optimized for cable interfaces and DOCSIS networks and should be used on cable interfaces instead of the ip helper-address command.
For more information on the ip helper-address command, refer to the Cisco IOS Command Reference, Release 12.2 T index page at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122tcr/crftindx.htm
For more information on the cable helper-address command, refer to the "Cable Modem Termination System Commands" chapter of the Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/bbccmref/bbcmts.htm
Using the show cable modem Command After an HCCP Switchover
If you are using HCCP 1+1 or N+1 Redundancy, the new primary processor after a switchover automatically creates a new database of the online cable modems. This means that the show cable modem ip-address and show cable modem ip-address cnr commands might not show a particular cable modem until the CMTS receives IP traffic from that cable modem.
You can force IP traffic by using the ping ip-address command, and then the show cable modem ip-address and show cable modem ip-address cnr commands will show the cable modem. You can also display any particular cable modem by using the show cable modem | include ip-address command.
Use of the FastEthernet Port on the PRE Module
The FastEthernet interface on the PRE module is intended for network management access and should not be used for WAN connectivity purposes. For WAN connections, use the appropriate network uplink cards, which take full advantage of the system's high-performance PXF processing subsystem.
Web Cache Communication Protocol Is Not Supported
The Cisco uBR10012 router does not support the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) feature set in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i.
Field Notices and Bulletins
•
Field Notices—Cisco recommends that you view the field notices for this release to see if your software or hardware platforms are affected. If you have an account on Cisco.com, you can find field notices at http://www.cisco.com/warp/customer/770/index.shtml. If you do not have a Cisco.com login account, you can find field notices at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/770/index.shtml.
•
Product Bulletins—If you have an account on Cisco.com, you can find product bulletins at http://www.cisco.com/warp/customer/cc/general/bulletin/index.shtml. If you do not have a Cisco.com login account, you can find product bulletins at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/cc/general/bulletin/iosw/index.shtml.
•
What's New for IOS — What's New for IOS lists recently posted Cisco IOS software releases and software releases that have been removed from Cisco.com. If you have an account on Cisco.com, you can access What's New for IOS at http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/sw-ios.shtml or by logging in and selecting Software Center: Cisco IOS Software: What's New for IOS.
New and Changed Information
The following sections list the new hardware and software features supported by the Cisco uBR10012 router for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i. These sections also show the features inherited since Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XF1.
For more information about these features, refer to the documents listed in the "Related Documentation" section.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2i
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2i
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2h
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2h.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2h
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2h.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2g
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2g.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2g
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2g.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2f
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2f.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2f
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2f.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2e
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2e.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2e
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2e.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2d
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2d.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2d
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2d.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2c
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2c.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2c
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2c.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2b
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2b.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2b
The following software features are new in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2b.
Cable Arp Filter Enhancement
The ip-requests-filtered option was added to the show cable arp-filter command to display the specific Service IDs (SIDs) that are generating or forwarding a minimum number of ARP packets.
Show Controllers Cable Extensions
The Show Controllers Cables Extensions feature has been supported for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2b.
In this feature, the mem-stats, memory, proc-cpu, and tech-support keywords execute the related command on the processor that runs on are added to obtain the relevant information from the onboard processor on Broadband Processing Engine (BPE) cable interface line cards, such as the Cisco uBR-MC16U/X, Cisco uBR-MC28U/X, and Cisco uBR-MC5X20S/U cards. This allows the user to obtain information that is specific for that particular cable interface card, as opposed to having to run these commands on the entire router.
Source Verify Lease-Query Throttling
When the cable source-verify dhcp and no cable arp commands are configured on a cable interface, problems can occur when viruses, denial of service (DoS) attacks, and theft-of-service attacks begin scanning a range of IP addresses, in an attempt to find unused addresses. When the Cisco CMTS router is verifying unknown IP addresses, this type of scanning generates a large volume of DHCP lease queries, which can result in a number of problems, such as dropped packets and high CPU utilization of both the Cisco CMTS router and DHCP server.
To prevent these problems, you can enable filtering of these requests on upstream interfaces, downstream interfaces, or both. When this feature is enabled, the Cisco CMTS allows only a certain number of DHCP LEASEQUERY requests for each service ID (SID) on an interface within the configured interval time period. If a SID generates more lease queries than the maximum, the router drops the excess number of requests until the next interval period begins.
For more information on this feature, see the document "Filtering Cable DHCP Lease Queries", at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/cblsrcvy.htm

Note
The Source Verify Lease-Query Throttling feature is only available in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1d and Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2b.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2a
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2a.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2a
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2a.
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2
The following hardware feature is new in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1.
Cisco uBR10-MC5X20U
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20U cable interface line card is one of the new Broadband Processing Engine (BPE) series of cable interfaces that are available for the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router. The BPE cards provide increased performance and advanced Radio Frequency (RF) management, as well as innovative, integrated tools for sophisticated content, traffic and network management.
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20U contains five downstream ports and twenty upstream ports. Each downstream port includes an onboard integrated upconverter that generates an RF signal suitable for connection to a combiner and transmission on the coaxial cable network, without the need for any external upconverters.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 and later releases, the downstream ports support 64-QAM and 256-QAM, and the upstream ports support QPSK, 8-QAM, 16-QAM, 32-QAM, and 64-QAM modulation, depending on the upstream's mode of operation. The upstream ports are initially configured to form five DOCSIS MAC domains, with each downstream port having four upstream ports. However, in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 and later releases, you can use the Virtual Interface feature to configure upstream ports as desired.
Depending on the configuration, the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20U line card supports either DOCSIS or Euro-DOCSIS operation:
•
DOCSIS cable networks are based on the ITU J.83 Annex B physical layer standard and Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS, Annex B) specification, which use 6 MHz National Television Systems Committee (NTSC) channel plans. In this mode, the downstream uses a 6 MHz channel width in the 85 to 860 MHz frequency range, and the upstream supports multiple channel widths in the 5 to 42 MHz frequency range.
•
EuroDOCSIS cable networks are based on the ITU J.112 Annex A physical layer standard and European DOCSIS (EuroDOCSIS, Annex A) specification, which use 8 MHz Phase Alternating Line (PAL) and Systeme Electronique Couleur Avec Memoire (SECAM) channel plans. In this mode, the downstream uses an 8 MHz channel width in the 85 to 860 MHz frequency range, and the upstream supports multiple channel widths in the 5 to 65 MHz frequency range.
When operating in either the DOCSIS or EuroDOCSIS mode of operation, the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20U card supports the following types of networks:
•
TDMA-only mode, which supports only DOCSIS 1.0 and DOCSIS 1.1 cable modems.
•
A-TDMA-only mode, which supports DOCSIS 2.0 cable modems.
•
Mixed TDMA/A-TDMA mode, which supports both DOCSIS 1.0/DOCSIS 1.1 and DOCSIS 2.0 cable modems on the same upstream.

Note
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20U card also supports the extended frequency ranges that are used in Japanese Annex B networks: 70 to 860 MHz (downstream) and 5 to 55 Mhz (upstream).
For information on installing the Cisco uBR-MC5X20U card, see the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S/U Cable Interface Line Card, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/ubr10k/ubr10012/frus/ubrmc520.htmFor information on configuring the Cisco uBR-MC5X20U card, see the Configuring the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20U-D Cable Interface Line Card, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/mc5x20u.htm
Note
The load-interval interface configuration command is not supported on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S/U cable interface line cards, even though the CLI accepts the command for these interfaces.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC2
The following software features are new in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2.
Advanced TDMA Support
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 supports the A-TDMA Service feature, which provides support for DOCSIS 2.0 Advanced Time Division Multiple Access (A-TDMA) upstream modulation profiles on the Cisco uBR-MC16U/X, Cisco uBR-MC28U/X, and Cisco uBR-MC5X20S/U Broadband Processing Engine (BPE) cable interface line cards. This feature supplements the existing support for DOCSIS 1.0 and DOCSIS 1.1 Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) modulation profiles.
For more information on the A-TDMA service feature, see the Configuring A-TDMA Modulation Profiles document, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/atdmafm.htmCable ARP Filter
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 adds support for the cable arp filter command, which enables service providers to filter ARP request and reply packets, to prevent a large volume of such packets from interfering with the other traffic on the cable network. For more information, see the Cable ARP Filtering document, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/cblarpfl.htmCommand-Line Interface (CLI) Enhancements
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 has enhanced or updated the following commands:
•
cable dhcp-giaddr—Supports a new option, strict, that uses the GIADDR IP address as the source IP address in the forwarded DHCP OFFER packet, when using the policy option. By default, the Cisco CMTS changes the source IP address in the DHCPOFFER packet to match that of the primary address on the cable interface. Use the strict option to prevent this behavior, which could interfere with any access lists applied to the CM when the CM is using a different subnet from the cable interface's primary address space.

CautionYou cannot use the strict option with the internal DHCP server that is onboard the Cisco CMTS router, because the strict option requires the use of DHCP relay operation, which is not performed by DHCP termination points such as the internal DHCP server.
•
cable downstream frequency—Changed to allow the center frequency to be set only in 250 KHz increments. Previously, this command allowed the center frequency to be specified in 125 KHz increments, but this had to be changed to support all of the operational modes of the Broadband Processing Engine (BPE) cards that include integrated onboard upconverters (such as the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S/U).
•
cable modem qos profile—Supports a new option, no-persistence, which specifies that the quality-of-service (QoS) profile for a cable modem should not remain in force when the modem reboots. Instead, when a cable modem reboots, it uses the QoS profile specified in its DOCSIS configuration file. The default is without this option, so that the QoS profile remains in force for cable modems across reboots.
•
cable primary-sflow-qos11 keep—Specifies whether the Cisco CMTS should preserve the DOCSIS 1.1 service flow traffic counters after a DOCSIS 1.1-provisioned CM goes offline and then comes back online. This allows service providers to track the total usage of CMs over a period of time, regardless of the number of times the CMs go offline and reboot.
•
cable service flow qi-rate-limit {all | none | standard | threshold n}—Configures the Cisco CMTS for how it should grant bandwidth requests for extra bandwidth (packets that have the Queue Indicator (QI) bit set) for Unsolicited Grant Service (UGS) service flows.
•
cable spectrum-group, cable upstream spectrum-group, show cable spectrum-group—The maximum number of spectrum groups has been increased from 32 to 40.
•
cable upstream fragment-force—Specifies the size of DOCSIS 1.1 frames that should be fragmented, as well as the number of fragments that should be created when fragmenting. By default, the Cisco CMTS fragments DOCSIS frames that are 2,000 bytes or larger in size, and it fragments these frames into three equally-sized fragments.

Note
On the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S/U cable interface line cards, do not use a fragment size greater than 2,000 bytes. On all other cable interface line cards, do not use a fragment size greater than 3,500 bytes, unless otherwise instructed by a Cisco TAC engineer.
•
clear cable hop—Clears the forward error corrections (FEC) hop counters on one or all cable interfaces.
•
debug hccp sync cable cpe-management—Displays debugging for SYNC messages that concern CPE-related parameters, such as MAX CPE, MAX CPE IP, and max learnable addresses.
•
dir filesystem: and show filesystem:—These commands display a new field that shows the time zone for the file's date and time. The time zone field shows the number of hours the timezone is offset from the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) timezone. For example:
Router# dir disk0:Directory of disk0:/1 -rw- 5666024 Jan 24 1981 07:20:02 -05:00 ubr7200-kboot-mz.122BC2 -rw- 19445128 Jan 30 2004 10:24:40 -05:00 ubr7200-ik9s-mz.12215BC13 -rw- 19680432 Feb 4 2004 09:17:44 -05:00 ubr7200-ik9s-mz.12215BC24 -rw- 1289 Sep 4 2003 18:53:30 -04:00 startup.cfg5 -rw- 241940 Jan 27 2004 18:07:06 -05:00 system-log47906816 bytes total (2883584 bytes free)Router#•
show cable modem verbose—This command now also shows the total time that a particular cable modem has been online.
•
show hccp detail—This command now shows separate lists of the critical and non-critical CLI commands that are being synchronized for each Working and Protect interface and subinterface.
For more information on these command changes, see the Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/bbccmref/index.htmCommand Enhancements for the Cisco uBR10012 Router
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 added or enhanced the following commands on the Cisco uBR10012 router:
•
cable per-cpe-acl—Defines an access list (ACL) to be applied on a Cisco uBR10012 router to customer premises equipment (CPE) devices that are currently unknown, providing a way to control the network access of unknown CPE devices. The Cisco uBR10012 router applies the specified ACL to any CPE device that is not in its host tables, or that does not have another ACL applied to its IP or MAC addresses.
•
debug cr10k-rp ha-error and debug cr10k-rp ha-recovery—New commands to aid in troubleshooting N+1 HCCP redundancy operation.
•
All show hardware pxf commands have been renamed as show pxf.
•
switchover pxf restart—Specifies the maximum number of times that a PXF processor can crash during a specified time period before the router switches over to the redundant PRE-1 module. If the PXF processors crash this number of times, the router assumes a hardware problem and initiates a switchover to the redundant PRE-1 module.
For more information on these commands, see the Commands for the Cisco uBR10012 Router document, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/bbccmref/bbub10k.htmDOCS-IF-MIB Update
The DOCS-IF-MIB (released as RFC 2670) has been updated to conform to the version 5 of the DOCSIS 2.0 RF MIB Specification (draft-ietf-ipcdn-docs-rfmibv2-05.txt).
Extended Upstream Frequency Ranges
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 adds support for the extended upstream frequency range that is used in cable networks in Japan and other areas. This feature also clarifies the configuration of DOCSIS and EuroDOCSIS networks, so that the router shows only those upstream and downstream frequencies that are valid for each mode of operation.
A new CLI command, cable freq-range, was also added to support this feature on the Cisco uBR-MC16U/X and Cisco uBR-MC28U/X cards. For more information, see the Support for Extended Upstream Frequency Ranges, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/mclcjfm.htmN+1 Support for Load Balancing
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 supports configuring a cable interface for both load balancing and N+1 HCCP redundancy.
PacketCable Enhancements
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 supports PacketCable operations on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S/U cable interface line cards on the Cisco uBR10012 router, and on the Cisco uBR-MC16U/X and Cisco uBR-MC28U/X cards on the Cisco uBR7246VXR router.
In addition, cable interfaces can be configured for both PacketCable operations and for N+1 HCCP redundancy. The debug packetcable hccp and show packetcable event commands have been added as part of this support.
SNMP Support for Virtual Interfaces
The Virtual Interfaces feature allows a physical upstream connector to be associated as a logical upstream interface for use with any downstream. Previously, an upstream was hard-coded for use with a particular downstream, but the Virtual Interfaces feature allows each physical upstream connector on the card to be mapped as a logical upstream interface for use with any of the other downstreams.
The Virtual Interfaces feature was initially supported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 for the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S cable interface line card. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 added support for Virtual Interfaces on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20U cable interface line card, and also introduced SNMP support for Virtual Interfaces.
Changes to ENTITY-MIB
To enable SNMP support for Virtual Interfaces, Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 changed how the entPhysicalTable in the ENTITY-MIB displays the information for cable interface line cards. Previously, the cable interface line card was the parent to one or more MAC domains, and each MAC domain then was the parent to one downstream and one or more upstreams.
Because an upstream can now be associated with any MAC domain and downstream in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2, the ENTITY-MIB no longer associates upstreams and downstreams with specific MAC domains, but instead shows all of them as being children of the line card. The entityPhysicalParentRelPos also now numbers the upstreams in sequential order, followed by the downstreams, so that on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S cards, the upstreams are numbered from 0 to 19, and the downstreams from 20 to 24.
Figure 1 shows the difference in how the entPhysicalTable in the ENTITY-MIB organized a Cisco uBR-MC5X20S cable interface line card in previous releases and in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2. For consistency, all cable interface line cards use this approach, even if they do not support the Virtual Interfaces feature.
Figure 1 ENTITY-MIB Changes for Virtual Interface Support on Cable Interface Line Cards
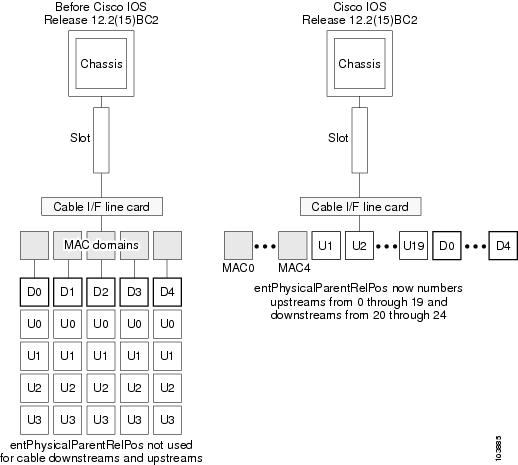
Operation of the ENTITY-MIB with Virtual Interfaces
The following are the key points in how the ENTITY-MIB shows the physical relationship of objects when the Virtual Interfaces feature is configured:
•
The entPhysicalTable shows information only about the physical card and its connectors. This table's configuration is fixed when the router boots or when a new card is installed in the chassis, and this configuration is not updated to show any logical mappings.
The entPhysicalTable index numbers for the card and its ports never change unless the card is physically removed and another type of card is installed in its slot. For example, if the entPhysicalName.50 object returns a value of "Cable6/1-US0" after the router boots, it always returns this value, no matter how the card and its upstream ports are configured.
For example, the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S and Cisco uBR-MC5X20U cards contain 20 upstreams, which the entPhysicalTable numbers from 0 to 19, regardless of how the upstreams are mapped using Virtual Interfaces. Similarly, the entPhysicalParentRelPos objects number the 20 upstreams as children 0 through 19, and the 5 downstreams as children 20 through 24. This numbering never changes, regardless of the Virtual Interfaces configuration.
•
The mapping between the physical upstream connectors and the logical upstream interfaces is shown in the entityAliasMappingTable. Each entry in this table contains the ifDescr index (as defined in the ifTable in the IF-MIB) that maps to the physical connector that is being used for that interface. The Virtual Interfaces feature automatically updates the entityAliasMappingTable to show the mapping between the physical upstream connectors and the logical interfaces, whenever the cable upstream connector is used.
For example, when a Cisco uBR-MC5X20S card is installed in slot 8/1 in a Cisco uBR10012 router, the ENTITY-MIB would typically list the upstreams similar to the following (the exact index numbers would depend on the number and type of other cards that are installed in the chassis):
!entPhysicalDescr.81 = LBT4522 PHYentPhysicalDescr.82 = LBT4522 PHY...entPhysicalDescr.99 = LBT4522 PHYentPhysicalDescr.100 = LBT4522 PHY!entPhysicalVendorType.81 = cevPortRfUsentPhysicalVendorType.82 = cevPortRfUs...entPhysicalVendorType.99 = cevPortRfUsentPhysicalVendorType.100 = cevPortRfUs!entPhysicalName.81 = Cable8/1-US0entPhysicalName.82 = Cable8/1-US1...entPhysicalName.99 = Cable8/1-US18entPhysicalName.100 = Cable8/1-US19
Note
The index numbers shown in entPhysicalTable never change during normal operation of the router. For example, using the above sample output, index 81 in the entPhysicalTable always points to the first upstream on the card in slot 8/1 (Cable8/1-US0). This index numbering is guaranteed to remain the same until you either reboot the router or until you change the router's physical configuration by adding or removing hardware components.
The default configuration for the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S automatically maps each physical connector to its default logical interface (physical connector 0 maps to C8/1/0U0, connector 1 maps to C8/1/0U1, and so on, until physical connector 19 maps to C8/1/4U3). Using the above example, the entAliasMappingIdentifierTable defaults to a configuration similar to the following:
entAliasMappingIdentifier.81.0 = ifIndex.28 (ifDescr.28 = Cable8/1/0-upstream0)entAliasMappingIdentifier.82.0 = ifIndex.29 (ifDescr.29 = Cable8/1/0-upstream1)entAliasMappingIdentifier.83.0 = ifIndex.30 (ifDescr.30 = Cable8/1/0-upstream2)entAliasMappingIdentifier.84.0 = ifIndex.31 (ifDescr.31 = Cable8/1/0-upstream3)entAliasMappingIdentifier.85.0 = ifIndex.33 (ifDescr.33 = Cable8/1/1-upstream0)entAliasMappingIdentifier.86.0 = ifIndex.34 (ifDescr.34 = Cable8/1/1-upstream1)entAliasMappingIdentifier.87.0 = ifIndex.35 (ifDescr.35 = Cable8/1/1-upstream2)entAliasMappingIdentifier.88.0 = ifIndex.36 (ifDescr.36 = Cable8/1/1-upstream3)entAliasMappingIdentifier.89.0 = ifIndex.38 (ifDescr.38 = Cable8/1/2-upstream0)entAliasMappingIdentifier.90.0 = ifIndex.39 (ifDescr.39 = Cable8/1/2-upstream1)entAliasMappingIdentifier.91.0 = ifIndex.40 (ifDescr.40 = Cable8/1/2-upstream2)entAliasMappingIdentifier.92.0 = ifIndex.41 (ifDescr.41 = Cable8/1/2-upstream3)entAliasMappingIdentifier.93.0 = ifIndex.43 (ifDescr.43 = Cable8/1/3-upstream0)entAliasMappingIdentifier.94.0 = ifIndex.44 (ifDescr.44 = Cable8/1/3-upstream1)entAliasMappingIdentifier.95.0 = ifIndex.45 (ifDescr.45 = Cable8/1/3-upstream2)entAliasMappingIdentifier.96.0 = ifIndex.46 (ifDescr.46 = Cable8/1/3-upstream3)entAliasMappingIdentifier.97.0 = ifIndex.48 (ifDescr.48 = Cable8/1/4-upstream0)entAliasMappingIdentifier.98.0 = ifIndex.49 (ifDescr.49 = Cable8/1/4-upstream1)entAliasMappingIdentifier.99.0 = ifIndex.50 (ifDescr.50 = Cable8/1/4-upstream2)entAliasMappingIdentifier.100.0 = ifIndex.51 (ifDescr.51 = Cable8/1/4-upstream3)The entAliasMappingIdentifierTable mapping, however, can change whenever the cable upstream connector command is used to enable the Virtual Interfaces feature. For example, upstream 2 on C8/1/4 is normally mapped to physical upstream connector 18 (entPhysicalTable index 99), but it can be mapped to physical upstream connector 0 (entPhysicalTable index 81) with the following commands:
Router(config)# interface cable 8/1/4Router(config-if)# cable upstream 2 connector 0Router(config-if)#In the default configuration, the ENTITY-MIB shows the following for these two upstreams:
entPhysicalName.81 = Cable8/1-US0entPhysicalName.99 = Cable8/1-US18entAliasMappingIdentifier.81 = ifIndex.28 (ifDescr.28 = Cable8/1/0-upstream0)entAliasMappingIdentifier.99 = ifIndex.50 (ifDescr.50 = Cable8/1/4-upstream2)After the cable upstream connector command is used, the ENTITY-MIB is updated as follows. (Note that only the entAliasMappingIdentifier objects have changed.)
entPhysicalName.81 = Cable8/1-US0entPhysicalName.99 = Cable8/1-US18entAliasMappingIdentifier.81 = ifIndex.50 (ifDescr.50 = Cable8/1/4-upstream2)entAliasMappingIdentifier.99 =
Note
The above example shows that physical connector upstream 0 is now mapped to the logical interface upstream 2 on Cable 8/1/4, and that physical connector upstream 18 is no longer in use. Its entAliasMappingIdentifier will return NULL until the cable upstream connector command maps another logical upstream to this particular physical connector.
DOCSIS Configuration File Changes for Type-Length-Value (TLV)

Note
A Type-Length-Value (TLV) is a tuple within a DOCSIS or PacketCable configuration file.
•
Vendor-Specific Information Field to Authorize Dynamic Service Requests
•
IGMP Blanket Forwarding in the TLV Field for Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Vendor-Specific Information Field to Authorize Dynamic Service Requests
DOCSIS 1.1 cable modems can request additional bandwidth via the DOCSIS 1.1 dynamic services mechanism, by sending dynamic service add (DSA) and dynamic service change (DSC) messages (known collectively as DSX messages).
By default, the CMTS grants these requests because a DOCSIS-compliant cable modem does not request services that would violate their provisioned service flows. However, a cable modem that is using software that is not DOCSIS-compliant, or that is using software that has been hacked to include unauthorized changes that violate the DOCSIS specifications, could use dynamic services requests to obtain bandwidth that the user is not authorized to use. Users could also use dynamic services requests as part of a denial-of-service attack on the cable network.
To prevent this, Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 supports including an optional vendor-specific information field (VSIF) in the DOCSIS configuration file to enable or disable DSX requests by the cable modem. This is illustrated below with the Type-Length-Value (TLV) of 43:
•
TLV = 43 (VSIF)
•
SubTLV 12, Length = 1
•
Value = 0, denies all DSX requests
•
Value = 1, allows all DSX requests
For example, the following string of decimal digits in the DOCSIS configuration file enables DSX requests for a cable modem:
43-08-08-03-00-00-12-12-01-01This string translates to the following TLV values:
TLV = 43Length = 08SubTLV = 08Length = 03Value = 00-00-12SubTLV = 12Length = 1Value = 1 (change to 0 to disable DSX requests)Additional information about the TLV value on the Cisco CMTS is available in these documents:
•
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Administrator's Guide Release 2.7
•
Cisco CMTS Configuration FAQ, TAC Document 12180
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk804/technologies_q_and_a_item09186a00800a4ae5.shtml
•
DHCP and the DOCSIS Configuration File for Cable Modems , TAC Document 10961
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk168/technologies_tech_note09186a0080180f11.shtml
DSX Values in the TLV Field
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 supports a new TLV value for DSX/DSA. Dynamic Service Exchange is a DOCSIS 1.1 QoS signaling mechanism providing Dynamic Service Add, Change and Delete functions (reference PacketCable specification PKT-TR-MM-ARCH-V01-030627).
•
The new TLV value of 12 supports DSX/DSA enable and disable functions
•
By default, all DSX requests are allowed.
Additional information about the TLV value on the Cisco CMTS is available in these documents:
•
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Administrator's Guide Release 2.7
•
Cisco CMTS Configuration FAQ, TAC Document 12180
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk804/technologies_q_and_a_item09186a00800a4ae5.shtml
•
DHCP and the DOCSIS Configuration File for Cable Modems , TAC Document 10961
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk168/technologies_tech_note09186a0080180f11.shtml
IGMP Blanket Forwarding in the TLV Field for Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 introduces a new TLV value for IGMP forwarding, in support of the Routing Information Protocol (RIP):
•
The new TLV value of 135 enables the cable modem to support blanket IGMP forwarding requests, per RIP.
•
By default, blanket IGMP forwarding is disabled.
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC introduces support for Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMPv3) Source Specific Multicast (SSM). This enhancement provides support for virtual interface bundling on the Cisco CMTS. IGMP is used by IPv4 systems to report their IP multicast group memberships to any neighboring multicast routers. Additional information about IGMP is available in the following documents:
•
Multicast Support for IGMPv3 SSM and Virtual Interface Bundling
Additional information about Routing Information Protocol is available in the following document:
•
Configuring Routing Information Protocol
Additional information about the TLV value on the Cisco CMTS is available in these documents:
•
Cisco Broadband Access Center for Cable Administrator's Guide Release 2.7
•
Cisco CMTS Configuration FAQ, TAC Document 12180
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk804/technologies_q_and_a_item09186a00800a4ae5.shtml
•
DHCP and the DOCSIS Configuration File for Cable Modems , TAC Document 10961
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk168/technologies_tech_note09186a0080180f11.shtml
show cable modem verbose
The show cable modem verbose command has also been enhanced to show whether DSX messages are supported for a particular cable modem. For example, the following excerpt from the command shows the display when a cable modem is allowed to make DSX requests:
Router# show cable modem 0010.7bb3.fcd1 verboseMAC Address : 00C0.7bb3.fcd1IP Address : 10.20.113.2Prim Sid : 1QoS Profile Index : 6Interface : C5/0/U5sysDescr : Vendor ABC DOCSIS 2.0 Cable Modem...Active Classifiers : 0 (Max = NO LIMIT)DSA/DSX messages : permit allDynamic Secret : A3D1028F36EBD54FDCC2F74719664D3FRouter#If DSX requests are not allowed, the DSA/DSX messages line shows "reject all."

Tip
We recommend also using the cable dynamic-secret and cable tftp-enforce commands to ensure that users cannot substitute their own DOCSIS configuration file in place of the original file provided by the service provider.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1g
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1g.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1g
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1g.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1f
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1f.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1f
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1f.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1e
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1e.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1e
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1e.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1d
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1d.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1d
The following software features are new in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1d.
Source Verify Lease-Query Throttling
When the cable source-verify dhcp and no cable arp commands are configured on a cable interface, problems can occur when viruses, denial of service (DoS) attacks, and theft-of-service attacks begin scanning a range of IP addresses, in an attempt to find unused addresses. When the Cisco CMTS router is verifying unknown IP addresses, this type of scanning generates a large volume of DHCP lease queries, which can result in a number of problems, such as dropped packets and high CPU utilization of both the Cisco CMTS router and DHCP server.
To prevent these problems, you can enable filtering of these requests on upstream interfaces, downstream interfaces, or both. When this feature is enabled, the Cisco CMTS allows only a certain number of DHCP LEASEQUERY requests for each service ID (SID) on an interface within the configured interval time period. If a SID generates more lease queries than the maximum, the router drops the excess number of requests until the next interval period begins.
For more information on this feature, see the document "Filtering Cable DHCP Lease Queries", at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/cblsrcvy.htm

Note
The Source Verify Lease-Query Throttling feature is only available in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1d and Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2b.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1c
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1c.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1c
The following software feature is new in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1c.
Cable ARP Filter
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2 adds support for the cable arp filter command, which enables service providers to filter ARP request and reply packets, to prevent a large volume of such packets from interfering with the other traffic on the cable network. For more information, see the Cable ARP Filtering document, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/cblarpfl.htmNo New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1b
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1b.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1b
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1b
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1a
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1a.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1a
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1a
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(15)BC1
The following software features are new in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1.
Command-Line Interface Enhancements
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 supports the following additions and enhancements to the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI):
•
The cable slfog global configuration command has been added to support a log of deleted service flow entries that is maintained in the DOCSIS-QOS SNMP MIB, which is required by the DOCSIS 2.0 specifications. This command enables service flow logging and configures the number and duration of entries in the log.
•
The clear cable modem flap-list command was added to reset a particular cable modem's flap list counters to zero.
•
The output for the show cable modem verbose command includes the value of the sysDescr SNMP attribute, as reported by the cable modem. This field shows a value only when the cable modem remote-query command has been enabled.
For a complete description of these commands and the changes, see the Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/bbccmref/index.htmDynamic Shared Secret
The Dynamic Shared Secret feature provides service providers a way of providing higher levels of security for their Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) cable networks, by using randomized, single-use shared secrets to verify the DOCSIS configuration files that are downloaded to each cable modem. The Dynamic Shared Secret feature is enabled using the cable dynamic-secret interface configuration command.
The Dynamic Shared Secret feature automatically creates a unique DOCSIS shared secret on a per-modem basis, creating a one-time use DOCSIS configuration file that is valid only for the current session. This ensures that a DOCSIS configuration file that has been downloaded for one cable modem can never be used by any other modem, nor can the same modem reuse this configuration file at a later time.
This patent-pending feature is designed to guarantee that all registered modems are using only the quality of service (QoS) parameters that have been specified by the DOCSIS provisioning system for that particular modem at the time of its registration.
For information on the Dynamic Shared Secret feature, see the Configuring a Dynamic Shared Secret for the Cisco CMTS document, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/ubrdmic.htm
Note
The Dynamic Shared Secret feature does not affect the use of the original shared secret or secondary shared secrets that are configured using the cable shared-secondary-secret and cable shared-secret commands. If these shared secrets are configured, the Cisco CMTS continues to use them to validate the original DOCSIS configuration file that is downloaded from the TFTP server. If the DOCSIS configuration file fails to pass the original or secondary shared secret verification checks, the cable modem is not allowed to register, and the Dynamic Shared Secret feature is not invoked for that particular cable modem.

Tips
Verify that a cable modem is able to register with the Cisco CMTS before enabling the Dynamic Shared Secret feature.
Load Balancing for the Cisco CMTS
The Load Balancing on the Cisco CMTS feature allows service providers to optimally use both downstream and upstream bandwidth, enabling the deployment of new, high-speed services such as voice and video services. This feature also can help reduce network congestion due to the uneven distribution of cable modems across the cable network and due to different usage patterns of individual customers.
By default, the Cisco CMTS platforms use a form of load balancing that attempts to equally distribute the cable modems to different upstreams when the cable modems register. You can refine this form of load balancing by imposing a limit on the number of cable modems that can register on any particular upstream, using the cable upstream admission-control command.
However, this default form of load balancing affects the cable modems only when they initially register with the Cisco CMTS. It does not dynamically rebalance the cable modems at later times, such as when they might change upstream channels in response to RF noise problems, or when bandwidth conditions change rapidly because of real-time traffic such as Voice over IP (VoIP) and video services. It also does not affect how the cable modems are distributed among downstream channels.
For more information about the Load Balancing feature, see the Configuring Load Balancing on the Cisco CMTS document, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/cmtslbg.htmN+1 Operations for the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S Cable Interface Line Card
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 supports N+1 HCCP redundancy when using the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S cable interface line card on the Cisco uBR10012 router. For information on configuring and using N+1 redundancy, see the N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS chapter in the Cisco CMTS Feature Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/cab_rout/cmtsfg/ufgnpls1.htmNonstop Forwarding (NSF) Awareness
The Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) Awareness feature, introduced in Cisco IOS release 12.2(15)T and inherited by Cisco IOS release 12.2(15)BC1, allows customer premises equipment (CPE) routers that are NSF-aware to assist NSF-capable routers perform nonstop forwarding of packets.
The NSF Awareness feature is supported on three IP routing protocols—Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), and Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS).
BGP NSF Awareness
BGP NSF Awareness assists NSF-capable neighbors to continue forwarding packets during a Stateful Switchover (SSO) operation. The BGP NFS Awareness feature allows an NSF-aware router that is running BGP to forward packets along routes that are already known for a router that is performing an SSO operation.
If you use BGP, you need to enable NSF Awareness using the bgp graceful-restart command in global configuration mode. This procedure enables smooth switchover operations on the Cisco uBR10012 CMTS.
For information on the BGP NSF Awareness feature for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T, refer to the BGP Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) Awareness feature module at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122t/122t15/ftbgpnsf.htm
For configuration information, refer to the "Configuring BGP" section in the Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/fipr_c/ipcprt2/1cfbgp.htm
OSPF NSF Awareness
The local router's awareness of NSF allows the integrity and accuracy of the RIB and link state database occurring on the neighboring NSF-capable router to be maintained during the switchover process.
For information on the OSPF NSF Awareness feature for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T, refer to the OSPF Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) Awareness feature module at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122t/122t15/ftosnsfa.htm
For configuration information, refer to the "Configuring OSPF" section in the Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/fipr_c/ipcprt2/1cfospf.htm
Integrated IS-IS NSF Awareness
The local router's awareness of NSF allows the integrity and accuracy of the RIB and link state database occurring on the neighboring NSF-capable router to be maintained during the switchover process.
For information on the Integrated IS-IS NSF Awareness feature for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T, refer to the Integrated IS-IS Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) Awareness feature module at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122t/122t15/isnsfawa.htm
For configuration information, refer to the "Configuring Integrated IS-IS" section in the Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/fipr_c/ipcprt2/1cfisis.htm
PacketCable Support for the Cisco uBR10012 Router
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 supports PacketCable operations for the Cisco uBR10012 router, in addition to the existing support for the Cisco uBR7246VXR router. For information on configuring and using PacketCable, see the PacketCable for the Cisco CMTS chapter in the Cisco CMTS Feature Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/cab_rout/cmtsfg/ufg_pkcb.htmPacketCable Debug Enhancements
The following debug commands have been added or enhanced to support PacketCable operations:
•
debug packetcable ipc
•
debug packetcable cops
•
debug packetcable gate events process
•
debug packetcable subscriber
In addition, most of the other debug packetcable commands have been modified so that they display output only when the appropriate debug packetcable subscriber command has been given. For a complete description of these commands and the changes, see the Cisco CMTS Debugging Commands chapter in the Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/bbccmref/bbcmtsde.htmSubscriber Traffic Management
The Subscriber Traffic Management feature allows service providers to identify and control subscribers who exceed the maximum bandwidth allowed under their registered quality of service (QoS) profiles. This feature supplements current techniques such as Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR) and access control lists (ACLs) to ensure a minority of users do not consume a majority of the cable network's bandwidth.
Current subscriber controls, such as NBAR and ACLs, examine all packets coming into the CMTS. These techniques can curb a large volume of problem traffic, but they are not as effective in dealing with the latest generation of peer-to-peer file-sharing applications that can swamp a network's available bandwidth. The Subscriber Traffic Management feature allows service providers to focus on a minority of potential problem users, without impacting network performance or other users who are abiding by their service agreements.
In addition, when a cable modem goes offline and remains offline for 24 hours, the Cisco CMTS deletes its service flow IDs from its internal databases, and also deletes the modem's traffic counters. This can allow some users to exceed their bandwidth limits, go offline, and come back online with new counters.
The Subscriber Traffic Management feature helps to thwart these types of theft-of-service attacks by implementing a penalty period for cable modems that violate their service level agreements (SLA). Even if the cable modem goes offline, its counters are still reset, but the CMTS continues to enforce the penalty period.
For more information about the Subscriber Traffic Management feature, see the Subscriber Traffic Management for the Cisco CMTS document, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/ubsubmon.htmSupport for Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter Version 3.0
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 supports version 3.0 of the Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter, which includes graphic-based spectrum analysis for supported platforms and cable interface line cards. For more information, see the Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter documentation, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/trblshtr/cbt30/index.htmVirtual Interfaces on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S Card
The Virtual Interfaces feature provides additional flexibility and efficiency in the allocation and usage of the upstreams on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S card for the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router. By default, four upstreams are assigned to each downstream, but this feature allows providers to associate any combination of upstreams (up to 8) to each downstream.
The onboard processors on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S card provides the processing power necessary to allow configurable MAC domains, so that the upstreams are no longer fixed by their physical location, but can be assigned to any of the five downstreams on the card, depending on the particular requirements of each MAC domain.
For more information about the Virtual Interfaces feature, see the Configuring Virtual Interfaces on the the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S Card document, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122newft/122limit/122bc/122bc_15/mc5x2vif.htmNo New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3d
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3d.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3d
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3d.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3c
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3c.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3c
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3c.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3b
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3b.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3b
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3b.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3a
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3a.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3a
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3a.
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 supports the following new hardware feature for the Cisco uBR10012 router.
Support for the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S Cable Interface Line Card
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card, is designed for the Cisco uBR10012 router to provide the highest port density available in Cisco cable interface line cards. The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card is a 20 by 16 inch card, that transmits and receives RF signals between the subscriber and the headend over a hybrid fiber/coax (HFC) system.
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card supports downstream and upstream traffic over a Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS)-based cable modem network. The card supports all DOCSIS 1.1-specified Annex B radio frequency (RF) data rates, channel widths, and modulation schemes and has DOCSIS MAC management and spectrum management capabilities.
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card supports 6-MHz National Television Systems Committee (NTSC) channel operation, using standard (STD), Harmonic Related Carrier (HRC), or Incremental Related Carrier (IRC) frequency plans conforming to EIA-S542. The card supports downstream channels in the 88 to 860 MHz range, and upstream channels in the 5 to 42 MHz range.
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card contains five downstream ports and twenty upstream ports. The downstream ports support 64-QAM and 256-QAM, and the upstream ports support QPSK and 16-QAM modulation.
Each downstream port includes an onboard integrated upconverter that generates an RF signal suitable for connection to a combiner and transmission on the coaxial cable network, without the need for any external upconverters. This can save both the money and rack space required by an external upconverter, as well as reduce the complexity of the equipment at the headend site.
Upstream data from the subscriber, comes through the upstream ports (US0-US19) on the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20 cable interface line card. The line card processes and configures the data and sends it across the backplane to the WAN card and out to the Internet.
Downstream data to the subscriber, comes from the Internet through the WAN card, and across the backplane to the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20 cable interface line card. The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S card processes and configures the data and sends it out through the appropriate downstream port (DS0 - DS4) to be combined with the rest of the downstream signals in the headend. Each downstream port includes an inboard integrated upconverter.
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S-D cable interface line card is available with space-saving dense (D) connectors.
Table 7 shows the supported DOCSIS modulation schemes.
Table 7 Supported DOCSIS Modulation Schemes
Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S-D
QAM-64, QAM-256
QPSK, QAM-16
Restrictions
•
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 and the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card require the use of the Cisco PRE1 module in the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router. If you are using redundant processors, both processors must be Cisco PRE1 modules.
•
The following software features are not supported for the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3:
–
Cable Monitor
–
HCCP 1+1 and N+1 redundant configurations (this feature is supported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and later releases)
–
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)
•
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card includes onboard spectrum analyzer hardware. However, card support for advanced spectrum management features on the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card will commence with future Cisco IOS releases. Future advanced spectrum management support will include all features currently available with the Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S cable interface line card.
•
The configuration of the downstream and upstream ports is fixed into five domains. (This restriction is removed when using the Virtual Interfaces feature in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and later releases.)
•
The load-interval interface configuration command is not supported on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20S/U cable interface line cards, even though the CLI accepts the command for these interfaces.

Note
For information on additional limitations and restrictions for the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card, see Cisco uBR-MC5X20S Cable Interface Line Card in the Limitations and Restrictions section of this release note.

Note
For information on installing and cabling the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S-D cable interface line card, refer to the FRU document, Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S Cable Interface Line Card. For information on configuring the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S-D cable interface line card, refer to the New Features document, Configuring the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S Cable Interface Line Card.
OC-48 DPT Support for the uBR10012
The Cisco uBR10012 OC-48 Dynamic Packet Transport (DPT)/POS interface module is a dual mode module, providing interface support for Packet over SONET (POS) or Spatial Reuse Protocol (SRP).
The Cisco uBR10012 OC-48 DPT/POS interface module supports SONET Section Data Communications Channel (SDCC) in either POS or SRP modes.
•
POS technology is ideally suited for Internet and/or IP networks, because it provides superior bandwidth utilization efficiency over other transport methods. POS can support a single connection or redundant connections to provide a robust, high-speed, high-throughput transport for IP traffic.
•
SRP is the media-independent Media Access Control (MAC)-layer protocol that enables DPT functionality in ring configurations. The SRP MAC protocol provides the base functionality for addressing, packet stripping, bandwidth control, and control message propagation on the packet ring.
The Cisco uBR10012 OC-48 DPT/POS interface module has a pair of OC-48c, fiber-optic standard connector (SC) duplex ports that provide an SC connection for either the single-mode short-reach or single-mode long-reach version.

Note
When using the show interface pos or show interface srp commands to display information about an interface, be aware that the byte counters used for these commands are 32-bit counters, which have a maximum size of approximately 4.3 billion. The result is the byte counters could wrap back to 0 if the Cisco uBR10012 OC-48 DPT/SRP interface module is passing large amounts of traffic.
For additional information on the Cisco uBR10012 OC-48 DPT/POS interface module, refer to the following documentation:
•
Configuring the Cisco uBR10012 OC-48 DPT/POS Interface Module at:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/ubr10k/ubr10012/ub10ksw/ub1048p1.htm•
Quick Start Guide for installing the Cisco OC-48 DPT/POS interface module at the following Cisco uBR10012 Quick Start Guide Index:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/ubr10k/ubr10012/qsg/index.htm•
Field Replaceable Unit (FRU) document for the Cisco OC-48 DPT/POS interface module at the following Cisco uBR10012 FRU Index:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/ubr10k/ubr10012/frus/index.htmNew Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC3
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 supports the following new software features for the Cisco uBR10012 router.
Cisco uBR10012 Route Processor Redundancy Plus and DOCSIS SSO
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 introduces support for Route Processor Redundancy Plus (RPR+) and DOCSIS Stateful Switchover (DSSO) on the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router.
RPR+ in combination with DSSO enhances the high-availability and redundancy offered by the earlier Route Processor Redundancy (RPR) feature on the Cisco uBR10012 router.
In standard RPR, the standby route processor (RP) suspended its initialization midway through the startup process. To complete the initialization during a switchover, all line cards were reset and the switch fabric was reinitialized.
RPR+ is a substantial improvement over RPR in that RPR+ provides a faster switchover by fully initializing and fully configuring the standby RP. The configuration data on the standby RP is fully synchronized with the active RP. With RPR+, the communication with line cards is reinitialized, but the line cards are not reset.
When two RPs are installed in a Cisco uBR10012 router chassis, one RP acts as the active RP, and the other acts as the standby or backup RP. If the active RP fails, or is removed from the system, the standby RP detects the failure and initiates a switchover. During a switchover, the standby RP assumes control of the router, connects with the network interfaces, and activates the local network management interface and system console.
Using the RPR+ feature, the standby RP is fully initialized and configured. This allows RPR+ to dramatically shorten the switchover time if the active RP fails, or if a manual switchover is performed. Because both the startup config and running config are continually synchronized from the active to the standby RP, line cards are not reset during a switchover. The interfaces remain up during this transfer, so neighboring routers do not detect a link flap (that is, the link does not go down and back up).
Using DSSO while running RPR+ increases service uptime by instantaneously switching over between dual route processors should one processor fail. Switchover takes place without resetting or reloading line cards or affecting related subsystems or processes. The advantage of DSSO (with RPR+) is that a switchover between the primary and standby RP will not require the cable interfaces to be reset, nor will the modems reregister or go offline. Furthermore, the cable modems retain their service IDs (SIDs) through the switchover.

Note
Depending on the network configuration and on the configuration of the Ethernet and FastEthernet interfaces, the network could take between 3 to 25 seconds after an RPR+ switchover before all end-to-end connections are fully restored. During that time it is possible that some packets might be dropped.
Each RP contains all the resources required to operate the router, such as bootflash memory, Flash disks, Ethernet ports, and console port. In the default operation, the Standby RP also synchronizes the major systems files, such as the Cisco IOS startup configuration file, so that during a switchover, the Standby RP can duplicate the Active RP's configuration. This process also resets the cable and network uplink interfaces.

Note
Encrypted multicast broadcast is not supported during a PRE1 switchover.

Note
For information on RPR+ restrictions, see Route Processor Redundancy Plus (RPR+) in the Limitations and Restrictions section of this release note.
For more information on the RPR+ feature, refer to the feature module Route Processor Redundancy Plus on the Cisco uBR10012 Universal Broadband Router at the following Cisco uBR10012 Router Software Features index:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/ubr10k/ubr10012/ub10ksw/index.htm
VLAN support for the Cisco uBR10012
Cisco IOS IEEE 802.1Q provides support for IEEE 802.1Q encapsulation for Virtual LANs (VLANs). VLANs can be implemented with Cisco IOS platforms in environments where the IEEE 802.1Q encapsulation standard is required. With the introduction of the Cisco IOS IEEE 802.1Q Support feature, Cisco IOS supported 802.1Q VLAN encapsulation, in addition to the currently supported ISL and IEEE 802.10 SDE encapsulations.
Release 12.2(15)BC2i adds 802.1Q VLAN support for the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router. Service providers can use 802.1Q VLANs on gigabit Ethernet interfaces to provide isolation between different content providers' traffic. 802.1Q VLANs may be mapped to MPLS VPN, maintaining traffic separation across an MPLS infrastructure.
For more information, refer to the IEEE 802.1.Q Configuration guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/mar_3200/mar_conf/m511m80.htm
Refer also to the Cisco IOS IEEE 802.1Q Support guide for command reference information at the following URL:
PBR support for the Cisco uBR10012
Policy-Based Routing (PBR) provides a tool for expressing and implementing the forwarding or routing of data packets, on the basis of the policies that are defined by network administrators. PBR allows policy override on routing protocol decisions by selectively applying policies based on access list and/or packet size.
Network administrators can also use PBR to selectively change the IP ToS, IP precedence, and IP QoS Group fields for matching incoming packets on an interface.
The Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router supports a maximum of 255 PBR policies and 32 route maps within each policy. The following subset of policy-based routing commands is supported in this release of Cisco IOS software:
•
ip policy route-map map-tag
•
route-map map-tag [permit | deny] [sequence-number]
•
match ip address {ACL-number | ACL-name} [ACL-number | ACL-name ...]
•
match length min max
•
set [default] interface type number [type number ...]
•
set ip [default] next-hop ip-address [ip-address ...]
•
set ip precedence value
•
set ip qos-group value
•
set ip tos value
•
show route-map [map-tag]
For more information on PBR, refer to the "Configuring Policy-Based Routing" chapter in the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/fqos_c/fqcprt1/qcfpbr.htm
Shared Spectrum Support on the uBR10012
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 adds support for the cable spectrum-group shared command for the Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S cable interface line card. The cable spectrum-group shared command in global configuration mode allows the upstream ports in a spectrum group to share the same upstream frequencies. The default upstream port frequency is the same for all ports in the spectrum group.
Because this command forces upstream ports to use the same spectrum, do not use this command for overlapping carriers. This command also does not enable any sort of load balancing on the shared upstreams.
For syntax and important usage information, refer to the "Cisco CMTS Commands" chapter of the Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/bbccmref/bbcmts.htm
clear cable modem Commands
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 adds support for two new clear cable modem commands:
•
clear cable modem delete
This command removes one or more CMs from the internal address and routing tables.
•
clear cable modem offline
This command removes offline CMs from the internal address and routing tables for a cable interface.
For syntax and usage information on the commands, refer to the "Cisco CMTS Commands" chapter of the Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/bbccmref/bbcmts.htm
debug cable Commands
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 adds support for the following new debug commands:
•
debug cable arp
This command enables debugging of the Address Resolution Protocol when it is used on the cable interface.
•
debug cable dhcp
This command enables debugging of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) when it is used on the cable interface.
•
debug cable encap
This command enables debugging of encapsulated Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) packets on the cable interface.
For syntax and usage information on the debug commands, refer to the "Cisco CMTS Debugging Commands" chapter of the Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/bbccmref/bbcmtsde.htm
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC2a
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2a.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC2a
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2a.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC2
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC2
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1b
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1b.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1b
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1b.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1a
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1a.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1a
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1a.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(11)BC1
cable source-verify leasetimer Command
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1 introduces the cable source-verify leasetimer <n> command.
The leasetimer option allows you to configure how often the timer checks the lease times, so as to specify the maximum amount of time a customer premises equipment (CPE) device can use an IP address that was previously assigned by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server but whose lease time has since expired. The time period can range from 1 minute to 240 minutes (4 hours), with a grace period of 2 minutes to allow a PC enough time to make a DHCP request to renew the IP address.
To turn off the timer, so that the CMTS no longer checks the lease times, issue the cable source-verify command without the dhcp option, or turn off the feature entirely with the no cable source-verify command. The leasetimer option takes effect only when the dhcp option is also used on an interface or subinterface.
The leasetimer option adds another level of verification by activating a timer that periodically examines the lease times for the IP addresses for known CPE devices. If the CMTS discovers that the DHCP lease for a CPE device has expired, it removes that IP address from its database, preventing the CPE device from communicating until it makes another DHCP request. This prevents users from treating DHCP-assigned addresses as static addresses, as well as from using IP addresses that were previously assigned to other devices.

Note
The leasetimer option for the cable source-verify command cannot be configured on subinterfaces. Instead, configure the command on the master interface, and the leasetimer will apply to all subinterfaces as well.
The following example shows how to enable the leasetimer feature so that every two hours, the CMTS checks the IP addresses in the CPE database for that particular interface for expired lease times:
router# configure terminalrouter#(config) interface c1/0router(config-if)# cable source-verify dhcprouter(config-if)# cable source-verify leasetimer 120For more information on the command, refer to the "Cisco Cable Modem Termination System Commands" chapter in the Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/bbccmref/bbcmts.htm
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(8)BC2a
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2a.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(8)BC2a
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2a.
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(8)BC2
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2 supports the following new hardware feature for the Cisco uBR10012 router.
Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S Spectrum Management Card with Advanced Spectrum Management Features for the Cisco uBR10012 Router
The Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S cable interface line card has a DOCSIS-based cable interface that supports one downstream and six upstreams. It incorporates a daughter board with hardware-based spectrum management features that provide the following features:
•
Integrates a DOCSIS cable interface line card with an onboard spectrum analyzer that continuously analyzes the upstream spectrum quality in the DOCSIS frequency range of 5 to 42 MHz
•
Includes hardware-assisted frequency hopping, providing for more intelligent and faster frequency selection than software-only solutions
•
Reduces the response time to ingress noise that could cause modems to drop offline
•
Eliminates guided frequency hopping by initiating frequency hops to known clean channels
•
Improves frequency agility to help eliminate dropped packets and thereby maintain full upstream data rates
•
Supports frequency agility in dense-mode combining environments across a shared spectrum
•
Restricts frequency hopping to a set of discrete frequencies or to a range of frequencies, as desired
•
Allows frequency hop conditions to be customized for specific plant environments and requirements
•
Optionally schedules frequency hops to take advantage of known usage patterns or plant conditions
•
Optionally dynamically reduces channel width to allow cable modems to remain online, even in noisy upstream conditions
•
The Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S line card can be installed in existing deployments of the Cisco uBR10012 router.
•
As is the case with the other cable interface line cards, the Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S line card supports Online Insertion and Removal (OIR), allowing for hotswappable upgrades and maintenance
The Advanced Spectrum Management Features for the Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S cable interface line card, available in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2, are a software-only upgrade that provides the following additional features:
•
Supports proactive channel management to avoid the impacts of ingress and keep subscribers online and connected.
•
Offers flexible configuration choices, allowing users to determine the priority of the actions to be taken when ingress noise on the upstream exceeds the allowable thresholds. The configurable actions are frequency hopping, switching the modulation profile, and reducing the channel width.
•
Performs CNR calculations using DSP algorithms in real-time on a per-interface and per-modem basis.
•
Intelligently determines when to modify the frequency, channel width, or modulation scheme based on CNR calculations in the active channel. Previously, frequency and channel width changes occurred when the number of missed station maintenance polls exceeded a user-defined threshold.
•
Enhances the Dynamic Upstream Modulation feature for the Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S line card. This feature supports dynamic modulation using two upstream profiles. The primary profile (typically using 16 QAM modulation) remains in effect at low noise conditions, but if upstream conditions worsen, the cable modems switch to the secondary profile (typically using QPSK modulation) to avoid going offline. When the noise conditions improve, the modems are moved back to the primary profile.
When using a Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S line card on a Cisco uBR7200 series router running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2, the spectrum management hardware uses the real-time CNR readings from the DSPs on the MC16S daughter card instead of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) values from the Broadcom 3137 chip to determine the signal quality of the upstream channel. The CNR value is a more accurate description of noise conditions on the upstream.
•
Provides an SNMP interface to so that a network management workstation or other graphical tool can obtain spectrum information for either a particular cable modem or for an entire upstream. The frequency resolution can be as fine as 12 KHz.

Note
The CISCO-CABLE-SPECTRUM MIB has been enhanced to provide this support.
•
Supports Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter 3.0 (CBT), starting with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1. CBT replaces the DCMTA tool from Acterna. CBT includes graphic-based spectrum analysis for supported platforms and cable interface line cards. For more information, see the Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter documentation, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/trblshtr/cbt30/index.htm•
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2, supported management tools include the DOCSIS Cable Modem Test Analyzer (DCMTA) from Acterna. The DCMTA software provides spectrum analyzer capability for an individual upstream port or an individual cable modem. Spectrum data is extracted from the Cisco uBR-MC16S cable interface line card using SNMP, allowing for live troubleshooting of an upstream port or individual cable modem. The DCMTA software supports simultaneous client access to a single or multiple CMTS, upstreams, or cable modems.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and later, the Acterna DCMTA tool is no longer available from Acterna.

Note
To contact Acterna about the DCMTA software, call 1-800-Acterna or visit http://www.acterna.com.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(8)BC2
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2 supports the following new software features for the Cisco uBR10012 router.
Adding Load Information and a Timestamp to Show Commands
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2 adds a new command, exec prompt timestamp, that adds load information and a timestamp to all show commands. This can be useful for troubleshooting and system analysis.
The new command has the following syntax in line configuration mode:
Router(config-line)# [no] exec prompt timestampThe command has the following syntax in User EXEC mode, so that users who do not know the enable password can also timestamp their show commands:
Router> terminal [no] exec prompt timestampThe following example shows how to enable and disable the timestamp for the console connection:
Router# config tRouter(config)# line console 0Router(config-line)# exec prompt timestampRouter(config-line)# no exec prompt timestampThe following example shows how to enable and disable the timestamp for the first five telnet connections:
Router(config)# line vty 0 4Router(config-line)# exec prompt timestampRouter(config-line)# no exec prompt timestampThe following example shows how to enable and disable the timestamp when logged into User EXEC mode:
Router> terminal exec prompt timestampRouter> terminal no exec prompt timestampDisplay Modem Capabilities with the show cable modem mac Command
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2 and later 12.2 BC releases, the mac option displays both the maximum DOCSIS Version of the CM as well as the currently provisioned DOCSIS version. This allows you to see both the capabilities of the CM as well as its current provisioning.
Router# show cable modem macMAC Address MAC Prim Ver Prov Frag Concat PHS Priv DS USState Sid Saids Sids0010.64ff.e4ad online 1 DOC1.1 DOC1.0 yes yes yes BPI+ 0 40010.f025.1bd9 init(rc) 2 DOC1.0 DOC1.0 no no no BPI 0 00010.9659.4447 online(pt) 3 DOC1.0 DOC1.0 no yes no BPI 0 00010.9659.4461 online(pt) 4 DOC1.0 DOC1.0 no yes no BPI 0 00010.64ff.e459 online 5 DOC1.0 DOC1.0 no yes no BPI 0 00020.4089.7ed6 online 6 DOC1.0 DOC1.0 no no no BPI 0 00090.9607.3831 online(pt) 7 DOC1.0 DOC1.0 no no no BPI 0 00090.9607.3830 online(pt) 1 DOC1.0 DOC1.0 no no no BPI 0 00050.7366.12fb init(i) 2 DOC1.0 DOC1.0 no no no BPI 0 00010.fdfa.0a35 online(pt) 3 DOC1.1 DOC1.1 yes yes yes BPI+ 0 4Support for the cable modem vendor Command
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2 adds support for associating the name of a vendor with its Organizational Unique Identifier (OUI), so that the vendor name can appear in the displays of the show cable modem vendor command. The software comes with a default database that contains approximately 300 OUIs associated with approximately 60 vendor names, and you can use the cable modem vendor command in global configuration mode to create new associations or overwrite existing associations.
The syntax of the cable modem vendor command is:
[no] cable modem vendor OUI [vendor-name]
where OUI is the first 3 octets (3 bytes, 6 hexadecimal digits) of the CM MAC address and typically indicates the vendor for the CM. Each octet should be separated by a period or colon (for example: 00:01:02 or 00.01.02). The vendor-name is the arbitrary string identifying the vendor for this OUI.
If you specify an OUI with the cable modem vendor command that already exists in the OUI database, the previous value is overwritten with the new value. You can use the default prefix to restore the original value for an OUI in the default database.
Use the no cable modem vendor command to remove the association between an OUI and a vendor name. The show cable modem vendor command then displays only the OUI as the vendor name.

Tip
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is the official issuer of OUI values. The IEEE OUI web site is at http://standards.ieee.org/regauth/oui/index.shtml.
The following shows several examples of the cable modem vendor command using Cisco OUIs:
Router(config)# cable modem vendor 00:01:42 CiscoRouter(config)# cable modem vendor 00:01:43 CiscoRouter(config)# cable modem vendor 00:01:63 CiscoRouter(config)# cable modem vendor 00:01:64 CiscoRouter(config)# cable modem vendor 00:0A:41 CiscoRouter(config)# cable modem vendor 00:0A:42 CiscoThe following example shows sample output for the vendor option on the Cisco uBR10012 router:
Router# show cable modem vendorVendor MAC Address I/F MAC Prim RxPwr Timing Num BPIState Sid (db) Offset CPE EnbThomson 0010.9507.01db C5/1/0/U5 online 1 0.00 938 1 NEricsson 0080.37b8.e99b C5/1/0/U5 online 2 -0.25 1268 0 NCisco 0002.fdfa.12ef C6/1/0/U0 online 13 0.00 1920 1 NCisco 0002.fdfa.137d C6/1/0/U0 online 16 -0.50 1920 1 NCisco 0003.e38f.e9ab C6/1/0/U0 online 3 -0.25 1926 1 NCisco 0001.9659.519f C6/1/1/U2 online 26 0.25 1930 1 NMotorola 0020.4005.3f06 C7/0/0/U0 online 2 0.00 1901 1 NMotorola 0020.4006.b010 C7/0/0/U5 online 3 0.25 1901 1 NCisco 0050.7302.3d83 C7/0/0/U0 online 18 -0.25 1543 1 NCisco 00b0.6478.ae8d C7/0/0/U5 online 44 0.50 1920 21 NCisco 00d0.bad3.c0cd C7/0/0/U5 online 19 0.00 1543 1 NCisco 00d0.bad3.c0cf C7/0/0/U0 online 13 0.00 1546 1 NCisco 00d0.bad3.c0d5 C7/0/0/U0 online 12 -0.50 1546 1 NRouter#Support for the cable tftp-enforce Command
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2 adds support for the new cable tftp-enforce cable interface configuration command, which requires all cable modems on a cable interface to attempt a TFTP request for the DOCSIS configuration file through the cable interface with the Cisco CMTS router before being allowed to register and come online. This can help prevent the following situations from occurring:
•
Users who attempt theft-of-service by reconfiguring their local networks to allow the downloading of an unauthorized DOCSIS configuration file from a local TFTP server. Typically, some users do this to obtain services that they have not paid for, such as higher guaranteed bandwidths or a higher priority Quality of Service (QoS) profile.
•
Some brands or models of cable modems might be running older software releases that cache the DOCSIS configuration file and use the cached version instead of downloading the actual file from a TFTP server during the registration process. Although this can marginally speed up the registration process, it also violates the DOCSIS requirements and could create a situation in which the cable modem is not using the proper DOCSIS configuration file. A user might then be mistakenly accused of theft-of-service, when in reality the problem is the non-DOCSIS-compliant cable modem.
The cable tftp-enforce command identifies these situations and can block these cable modems from registering and coming online. This command also has an option that allows these cable modems to come online, but it also identifies the cable modems so that the network administrators can investigate the situation further before taking any action.
Command Syntax
The new command has the following syntax:
cable tftp-enforce [mark-only]no cable tftp-enforce [mark-only]When the command is used without the mark-only option, cable modems that do not download a TFTP file are blocked from registering and coming online. The mark-only option allows the cable modems to come online, but it also prints a warning message and marks the cable modems in the show cable modem command.

Tips
Cisco recommends that you initially configure cable interfaces with the mark-only option, so that potential problems are identified without initially interfering with users' ability to come online. After you identify and resolve these initial problems, reconfigure the cable interfaces without the mark-only option to block problem cable modems that attempt to come online without downloading a valid DOCSIS configuration file.
The default behavior is not to require the TFTP download through the cable interface with the Cisco CMTS router. Each cable interface must be configured with this command to require the TFTP download.
Enforcing TFTP Downloads and Blocking Non-Compliant Cable Modems
The following example shows how to enforce TFTP downloads for all of the cable modems on cable interface 3/0. These cable modems must attempt a TFTP download of the DOCSIS configuration file through their cable interface with the Cisco CMTS router. If they do not, they are not allowed to register or come online.
Router# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface cable 3/0Router(config-if)# cable tftp-enforceRouter(config-if)# exitRouter(config)#When the cable tftp-enforce command is configured, the following message is displayed on the console when a cable modem attempts to register without first attempting a TFTP download through the cable interface with the Cisco CMTS router:
06:53:57: %UBR7200-4-REGISTRATION_BEFORE_TFTP: Registration request unexpected:Cable Modem did not attempt TFTP. Registration Rejected. CM Mac Addr <00ff.ff66.12fb>When a cable modem is rejected for not attempting a TFTP download, it is marked as having a Message Integrity Check (MIC) failure—reject(m)—in the show cable modems command.
Router# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface cable 3/0Router(config-if)# cable tftp-enforceRouter(config-if)# exitRouter(config)#Router# show cable modemsInterface Prim Online Timing Rec QoS CPE IP address MAC addressSid State Offset PowerCable3/0/U1 1 online(pt) 2734 0.50 5 0 10.1.1.38 00ff.fffa.0a35Cable3/0/U0 2 online(pt) 2729 0.25 5 0 10.1.1.50 00ff.ff07.382fCable3/0/U0 3 init(i) 2732 0.25 2 0 10.1.1.48 00ff.ff03.307dCable3/0/U1 4 online(pt) 2737 0.75 5 0 10.1.1.34 00ff.ff59.4477Cable3/0/U1 5 reject(m) 2215 0.25 2 0 10.1.1.47 00ff.ff66.12fbRouter#
Note
DOCSIS-compliant cable modems that are rejected with a MIC failure go into the offline state for a short period of time and then retry the registration process.
The debug cable registration command can be used to display additional information:
Router# debug cable interface c3/0 verboseRouter# debug cable registrationCMTS registration debugging is onJun 6 23:27:15.859: Registration request from 00ff.ff66.12fb, SID 7 on Cable3/0/U1Jun 6 23:27:15.859: Found a network access control parameter: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found a class of service block: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found Baseline Privacy config: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found Max CPE: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found CM MIC: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found CMTS MIC: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found modem ip: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found modem capabilities: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Finished parsing REG RequestJun 6 23:27:15.859: Cable Modem sent Registration Request without attemptingrequired TFTP22:33:21 %UBR7200-4-REGISTRATION_BEFORE_TFTP: Registration request unexpected:Cable Modem did not attempt TFTP. Registration Rejected. CM Mac Addr <00ff.ff66.12fb>Registration failed for Cable Modem 00ff.ff66.12fb on interface Cable3/0/U0:CoS/Sflow/Cfr/PHS failed in REG-REQJun 6 23:27:15.859: REG-RSP Status : failure (2)Jun 6 23:27:15.859: Registration Response:Jun 6 23:27:15.859: 0x0000: C2 00 00 1B 00 00 00 50 73 4E B4 19 00 05 00 E0Jun 6 23:27:15.859: 0x0010: 56 AC 00 09 00 00 03 01 07 00 00 02 02Jun 6 23:27:15.859: Registration Response TransmittedIdentifying Non-Compliant Cable Modems But Allowing Them to Come Online
The mark-only option of the cable tftp-enforce command allows CMs that do not attempt a TFTP download through the cable interface to come online, but the Cisco CMTS router displays a warning message on the console and marks the cable modem in the show cable modem command with a pound sign (#). This option allows network providers to identify potential problems and to investigate them before taking any corrective action.
When the mark-only option is configured, the following message is displayed on the console when a cable modem attempts to register without first attempting a TFTP download through the cable interface with the Cisco CMTS router:
06:53:57: %UBR7200-4-REGISTRATION_BEFORE_TFTP: Registration request unexpected:Cable Modem did not attempt TFTP. Modem marked with #. CM Mac Addr <00ff.ff66.12fb>In addition, the cable modem is marked with a pound sign (#) in the show cable modems command:
Router# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface cable 3/0Router(config-if)# cable tftp-enforce mark-onlyRouter(config-if)# exitRouter(config)#Router# show cable modemsInterface Prim Online Timing Rec QoS CPE IP address MAC addressSid State Offset PowerCable3/0/U1 1 online(pt) 2734 0.50 5 0 10.1.1.38 00ff.fffa.0a35Cable3/0/U0 2 online(pt) 2729 0.25 5 0 10.1.1.50 00ff.ff07.382fCable3/0/U0 3 init(i) 2732 0.25 2 0 10.1.1.48 00ff.ff03.307dCable3/0/U1 4 online(pt) 2737 0.75 5 0 10.1.1.34 00ff.ff59.4477Cable3/0/U1 5 #online 2213 0.25 6 0 10.1.1.47 00ff.ff66.12fbRouter#The debug cable registration command can be used to display additional information:
Jun 6 23:27:15.859: Registration request from 00ff.ff66.12fb, SID 7 on Cable3/0/U1Jun 6 23:27:15.859: Found a network access control parameter: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found a class of service block: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found Baseline Privacy config: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found Max CPE: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found CM MIC: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found CMTS MIC: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found modem ip: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Found modem capabilities: OkJun 6 23:27:15.859: Finished parsing REG RequestJun 6 23:27:15.859: Cable Modem sent Registration Request without attemptingrequired TFTP23:27:15: %UBR7200-4-REGISTRATION_BEFORE_TFTP: Registration request unexpected:Cable Modem did not attempt TFTP. Modem marked with #. CM Mac Addr <00ff.ff66.12fb>Jun 6 23:27:15.859: Sec sids obtained for all requested classes of serviceJun 6 23:27:15.859: Performing connection admission control (CAC) for each SidJun 6 23:27:15.859: CAC Status for ClassID:1 is CAC_SUCCESSJun 6 23:27:15.859: Registration Status: ok (0)Jun 6 23:27:15.859: Registration Response TransmittedSupport for a Secondary Shared Secret
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2 adds support for one or more secondary shared-secret keys that cable modems can use to successfully process the DOCSIS configuration file and register with the Cisco CMTS. Secondary shared secrets can be defined with the cable shared-secondary secret command, which has the following syntax:
cable shared-secondary secret index index-num [0 | 7] authentication-key
no cable shared-secondary secret index index-num
where index-num specifies the order in which the Cisco CMTS will use the secondary shared-secrets to verify the cable modem during the registration process. The valid range is 1 to 16. The authentication-key is the secondary shared secret string, where 0 indicates it is unencrypted and 7 indicates it is encrypted.

Note
To store the authentication-key in encrypted form in the configuration file, also use the service password-encryption command.
The cable modem must use the proper shared secret encryption string to successfully decrypt and process the configuration file, and then register with the Cisco CMTS. If the cable modem does not have the proper encryption string, it will be unable to calculate the proper MIC value, and the show cable modem command will show reject(m) for the modem to indicate a MIC authentication failure.
The cable shared-secondary-secret command allows a cable operator to specify up to 16 alternate DOCSIS shared secrets. If a cable modem has a MIC authentication failure during registration, the CMTS then checks the MIC values using the alternate shared secrets. If a match is found, the cable modem is allowed online. If none of the alternate MIC values match the value returned by the CM, the CMTS refuses to allow the cable modem to come online and instead logs a MIC authentication failure.
The use of secondary shared secrets allow the MSO to gradually phase in changes to the shared secret key. If a shared secret has been compromised, or if the MSO decides to regularly change the shared secret, the MSO can use the cable shared-secret command to immediately change the primary shared secret. The previous key can then be made a secondary shared secret, using the cable shared-secondary-secret command, so that CMs can continue to register until the MSO can change all of the DOCSIS configuration files to use the new shared secret.
To use the secondary shared-secret feature, you must do the following:
•
You must specify a shared secret with the cable shared-secret command. The cable shared-secondary-secret command has no effect if you have not specified a primary shared secret.

Note
At any particular time, the majority of cable modems should use the primary shared secret to avoid excessive registration times.
•
Create DOCSIS configuration files that use the shared-secret encryption string to create the MD5 MIC value. This can be done using the Cisco DOCSIS Configurator tool by entering the shared-secret string in the CMTS Authentication field in the Miscellaneous parameters.

Note
The shared-secret string itself is not saved in the DOCSIS configuration file, so you must re-enter the string in the CMTS Authentication field whenever you create or edit a DOCSIS configuration file using the Cisco DOCSIS Configurator tool.
•
Use the cable shared-secondary-secret command to configure the cable interfaces with one or more matching shared-secret strings. The string configured on an interface must match the string used to create the DOCSIS configuration files downloaded to the CMs on that interface, or the CMs will not be able to register. You can use different shared secrets for each interface, if you are also using a different set of configuration files for each interface.
•
To encrypt the shared-secret strings in the CMTS configuration, you must include the service password-encryption global configuration command in the router's configuration.

Note
You cannot use the secondary shared secret feature with the files created by the internal DOCSIS configuration file editor (cable config-file command) because the internal DOCSIS configuration file editor automatically obtains the correct shared secret from the interface when the modems register.
The following example shows how to specify multiple secondary shared-secret string using encrypted keys:
Router# config tRouter(config)# service password-encryptionRouter(config)# int c6/0Router(config-if)# cable shared-secret n01jk_1aRouter(config-if)# cable shared-secondary-secret index 1 cabl3-x21bRouter(config-if)# cable shared-secondary-secret index 2 dasc9_ruld55ist5q3zRouter(config-if)# cable shared-secondary-secret index 3 j35u556_x_0Router(config-if)# exitRouter(config)# exitRouter# show running-config | include sharedcable shared-secret 7 1407513181A0F13253920cable shared-secondary-secret 7 14031A021F0D39263D3832263104080407cable shared-secondary-secret 7 071B29455D000A0B18060615142B38373F3C2726111202431259545D6cable shared-secondary-secret 7 0501555A34191B5F261D28420A555DRouter#
Note
In this example, the shared-secret strings are initially entered as clear text, but because the service password-encryption command has been used, the strings are encrypted in the configuration file.
See the "Cisco Cable Modem Termination System Commands" chapter in the Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide for more information about the cable shared-secondary secret command at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/bbccmref/bbcmts.htm
N+1 Redundancy Support on Cable Interface Line Cards
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2, the Cisco uBR10012 now supports N+1 Redundancy on the Cisco uBR-MC16S, Cisco uBR-MC16C, and Cisco uBR-MC16E cable interface line cards on DOCSIS 1.1 networks.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1b introduced DOCSIS 1.1 N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco uBR10012. This feature extended the previous HCCP 1+1 cable interface redundancy feature, where one cable interface is designated the working interface, and a second cable interface is the protect interface. The protect interface comes online only when the working interface fails. The N+1 Redundancy feature allowed a single cable interface to act as the protect interface for up to 7 cable interfaces in the Cisco uBR10012 router, thereby significantly reducing the cost of providing redundant operation. The cable interface connections are made through the Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2, the Cisco uBR-MC16S card can be used as the protect cable interface or working cable interface, with either another Cisco uBR-MC16S card or a Cisco uBR-MC16C card. Table 8 shows how a switchover in each of these configurations affects the intelligent spectrum management features of the Cisco uBR-MC16S card.

Note
Encrypted multicast broadcast is not supported across a line card switchover.

Note
For complete information about the N+1 Redundancy feature, see the "N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS" chapter in the Cisco CMTS Feature Guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/cab_rout/cmtsfg/ufgnpls1.htm
Enhancement to the show hccp brief Command
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2 and later 12.2 BC releases, the brief option now shows the amount of time left before the next resynchronization and the time left before a restore:
Router# show hccp briefInterface Config Grp Mbr Status WaitToResync WaitToRestoreCa5/0/0 Protect 1 3 standby 00:01:50.892Ca7/0/0 Working 1 3 active 00:00:50.892 00:01:50.892Router#Enhancement to the cable filter group Command
The status option was added to the cable filter group command to allow filter groups to be activated and deactivated without removing the filter group's configuration.
For example, the following command would deactivate a filter without changing its configuration:
Router(config)# cable filter group 1 index 1 status inactiveThe following command would reactivate this filter:
Router(config)# cable filter group 1 index 1 status active
Note
Filter groups are active by default when created.
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(8)BC1
Support for LCP2 Cable Interface Line Cards
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC1 adds support for the LCP2, the Enhanced Line Card Processor. The LCP2 cable interface line card is compatible with the previous LCP cable interface line card and can be used in place of the Line Card Processor (LCP) for any currently supported cable interface line card.
Table 9 LCP and LCP2 Cable Interface Line Cards Comparison
LCP
263 MHz
75 MHz
LCP2
400 MHz
100 MHz
The order numbers for the LCP2 and cable interface line card combinations are:
•
UBR10-LCP2, UBR10-LCP2= Line Card Processor 2 card.
•
UBR10-LCP2-MC16E, UBR10-LCP2-MC16E= Cisco uBR-MC16E and LCP2 card combination.
•
UBR10-LCP2-MC16C, UBR10-LCP2-MC16C= Cisco uBR-MC16C and LCP2 card combination.
•
UBR10-LCP2-MC28C, UBR10-LCP2-MC28C= Cisco uBR-MC28C and LCP2 card combination.
•
UBR10-LCP2-MC28-B, UBR10-LCP2-MC28-B= Cisco uBR-MC28C-BNC and LCP2 card combination.
Support for 128 MB Flash Cards
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC1 adds support for the 128 MB Flash Disk card (product order number ESR-PRE-MEM-FD128=).
New Software Features in Release 12.2(8)BC1
The following new software features are supported by the Cisco uBR10012 routers in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC1.
EXEC Commands in Configuration Mode
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC1, you can now issue EXEC-level Cisco IOS commands (such as show, clear, and debug commands) from within global configuration mode or other configuration modes by issuing the do command followed by the EXEC command. For example, you can display the run-time configuration file from within global configuration mode by issuing the following command:
Router(config)# do show running-config
Note
You cannot use the do command to execute the configure terminal EXEC command because issuing the configure terminal command changes the mode to configuration mode.
Secure Shell Support
Secure Shell (SSH) allows network administrators to securely log in to the Cisco uBR10012 router, using authentication and encryption at the application layer and providing a secure connection even when logging in over insecure networks such as the Internet. Secure Shell allows an administrator to securely monitor and configure a router without having to be logged into the router's local console port or directly connected to the Ethernet port on the router's I/O controller.
To configure SSH on the Cisco uBR10012 router, use the following command in global configuration mode:
uBR10k(config)# crypto key generate rsa general-keysWhen you are asked the size of the key seed, enter a value of at least 1024.
To verify whether SSH is configured on the Cisco uBR10012 router, use the following command in Privileged EXEC mode:
uBR10k# show ip sshSSH Enabled - version 1.5Authentication timeout: 120 secs; Authentication retries: 3To verify whether the Cisco uBR10012 router has an SSH connection, use the following command in Privileged EXEC mode:
uBR10k# show sshConnection Version Encryption State Username1 1.5 DES Session started adminNo New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(4)BC1b
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1b.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(4)BC1b
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1b includes support for the following new software features.
DOCSIS 1.1 N+1 Redundancy
The DOCSIS 1.1 N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS feature extends the existing HCCP 1+1 cable interface redundancy feature, where one cable interface is designated the working interface, and a second cable interface is the protect interface. The protect interface comes online only when the working interface fails. The N+1 Redundancy feature allows a single cable interface to act as the protect interface for up to 7 cable interfaces in the Cisco uBR10012 router, thereby significantly reducing the cost of providing redundant operation. The cable interface connections are made through the Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1b supports N+1 Redundancy on the Cisco uBR10012 router only.

Note
The N+1 Redundancy feature, used in conjunction with the Cisco uBR-RFSW RF switch, can now be used in DOCSIS 1.1 networks.

Note
For complete information about the N+1 Redundancy feature, see the "N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS" chapter in the Cisco CMTS Feature Guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/cab_rout/cmtsfg/ufgnpls1.htm
SNMP Cable Modem Remote Query
The remote query feature allows the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) to use Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) requests to periodically poll online CMs to gather the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), upstream power value, transmit timing offset, micro reflection value, and modem state. To enable the remote query feature, use the cable modem remote-query command. To display the collected statistics, use the show cable modem remote-query command, or display the attributes in the CISCO-DOCS-REMOTE-QUERY-MIB MIB. You can also generate SNMP traps to inform the SNMP manager when remote query polling has completed by using the snmp-server enable cable cm-remote-query command.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(4)BC1a
There are no new hardware features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1a.
No New Software Features in Release 12.2(4)BC1a
There are no new software features in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1a.
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(4)BC1
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1 supports the following for new hardware features.
Cisco uBR10-SRP-OC12SML DPT WAN Card
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1 supports the Cisco uBR10-SRP-OC12SML DPT WAN card on the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router. In this configuration, a DPT/OC12 Port Adapter is fitted into a processor board that has an NPE400 CPU complex using a R7000A processor. The Cisco IOS image for the DPT/OC12 WAN card runs on this processor. The WAN card processor is responsible for performing all SRP MAC processing and the drivers for the DPT/OC12 Port Adapter.
The DPT/OC12 functionality can be summarized as follows:
•
Provides 2-fiber OC-12c dual ring connection (supports two 2-fiber rings) on the Cisco uBR10012. Capable of sending and receiving data and control on one or both rings simultaneously.
•
Implements the Spatial Reuse Protocol (SRP ver 1) MAC to obtain fair shared access to the OC-12x rings.
•
Provides ring wrap upon adjacent fiber or node failure.
•
Supports single-mode intermediate-reach and long-reach capability for FCS. The software design does not exclude support for multimode capabilities.
•
Provides interoperability with other routers supporting DPT OC12, including Cisco ubr7200, Cisco 7200 series, Cisco 7500 series, and GSR routers.
•
Supports SONET DCC channel.
•
Supports online insertion and removal (OIR) of the entire Port Adapter assembly.
•
Supports interface with the PRE for packet forwarding (PRE does the routing and switching).
•
Uses the backplane ethernet for exchange of CLI, SNMP, and general management messages with the PRE.
•
Uses three front panel LEDs to indicate the state of the card (Power, Status and Maintenance LED).

Note
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1 does not support the CISCO-SRP-MIB.my MIB for the Cisco uBR10-SRP-OC12SML DPT WAN card.
New Software Feature in Release 12.2(4)BC1
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1 includes support for the following new software features.
Support for the cable power Command
The cable power command provides a way to use the command-line interface (CLI) to manually power a cable interface line card on or off in the Cisco uBR10012 router. This command is typically not used during normal operations, but it can be used for lab, diagnostic, and troubleshooting purposes.
Using this command to first power off and then power on a card is functionally equivalent to performing an online insertion and removal (OIR) of the card. You can also use the LC Power off Status Reg and Line Card Presence Status Reg fields in the show controllers clock-reference command to determine whether a cable interface line card is actually present in the chassis and whether it has been powered on or off.

Note
For full documentation on this command, and for important notes and limitations on its use, see the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System Commands chapter in the Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide.
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(4)XF1
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF1 supports the following for new hardware features.
Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch
The Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch provides the physical cabling support for the N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS feature, which allows a single cable interface to act as the protect interface for up to 7 cable interfaces in the Cisco uBR10012 router, thereby significantly reducing the cost of providing redundant operation. The cable interface connections are made through the Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch, which provides the connections required for both upstream and downstream port redundancy.

Note
For complete information about the Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch, see the documents in the Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch documentation directory on Cisco.com.
New Software Features in Release 12.2(4)XF1
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF1 includes support for the following new software features.
N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS
The N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS feature extends the existing HCCP 1+1 cable interface redundancy feature, where one cable interface is designated the working interface, and a second cable interface is the protect interface. The protect interface comes online only when the working interface fails.
The N+1 Redundancy feature allows a single cable interface to act as the protect interface for up to 7 cable interfaces in the Cisco uBR10012 router, thereby significantly reducing the cost of providing redundant operation. The cable interface connections are made through the Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch.

Note
For complete information about the N+1 Redundancy feature, see the N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS chapter in the Cisco CMTS Feature Guide.
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(4)XF
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF includes support for the following new hardware features.
Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16C Cable Interface Line Card
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF adds support for the Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16C cable interface line card, which is a combination of the Cisco uBR-LCP and Cisco uBR-MC16C line cards. The Cisco uBR-LCP card adapts the Cisco uBR-MC16C to the electrical requirements and form factor of the Cisco uBR10012 chassis.
The Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16C line card provides one downstream and six upstreams that support the DOCSIS (Annex B) 6 MHz North American channel plans using the ITU J.83 Annex B RF standard. The downstream uses a 6 MHz channel width in the 85 to 860 MHz frequency range, and the upstream supports the 5 to 42 MHz frequency range.
The Cisco uBR10012 chassis supports a maximum of eight Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16C line cards. The Cisco uBR10012 chassis also supports the Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16C card along with any combination of the other supported cable interface line cards, up to a maximum of eight cards.

Note
The Cisco uBR-LCP line processor card must be at revision 4.4 or greater and be using the boothelper image from Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XF1 or later to support the Cisco uBR-MC16C cable interface line card.
Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16E Cable Interface Line Card
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF adds support for the Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16E cable interface line card, which is a combination of the Cisco uBR-LCP and Cisco uBR-MC16E line cards. The Cisco uBR-LCP card adapts the Cisco uBR-MC16E to the electrical requirements and form factor of the Cisco uBR10012 chassis.
The Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16E cable interface line card provides one downstream and six upstreams that support the EuroDOCSIS (Annex A) standard. EuroDOCSIS supports the 8 MHz Phase Alternating Line (PAL) and Systeme Electronique Couleur Avec Memoire (SECAM) channel plans using the ITU J.112 Annex A RF standard. The downstream uses an 8 MHz channel width in the 85 to 860 MHz frequency range, and the upstream supports multiple channel widths in the 5 to 65 MHz frequency range.
The Cisco uBR10012 chassis supports a maximum of eight Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16E line cards. The Cisco uBR10012 chassis also supports the Cisco uBR-LCP-MC16E card along with any combination of the other supported cable interface line cards, up to a maximum of eight cards.

Note
The Cisco uBR-LCP line processor card must be at revision 4.4 or greater and be using the boothelper image from Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XF1 or later to support the Cisco uBR-MC16E cable interface line card.
PRE1 Performance Routing Engine
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF adds support for the PRE1 Performance Routing Engine processor card on the Cisco uBR10012 router. The PRE1 module enhances the existing PRE module functionality by adding support for Error Checking and Correction (ECC) for all onboard memory, replacing the simpler parity error algorithm.
Where parity error detection can only detect errors, the ECC feature helps protect against processor downtime by correcting errors as well as detecting them. The PRE1 module can automatically correct single-bit errors as small as 1 bit per nibble, protecting the PRE1 module from memory corruption due to transient memory problems.
The ECC feature is also more sensitive and precise in detecting errors. The PRE1 module can detect an error in only 1 bit out of each 64-bit block. It can also detect errors in two, three, or four bits in each 64-bit block.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF automatically enables the ECC feature on PRE1 modules. Two CLI commands are also enhanced to provide information about ECC operation:
•
show hardware pxf xcm—Adds a display for the ECC counters for each PRE1 module. For the older PRE modules, this command shows the message "ECC is not supported for this revision."
•
clear pxf xcm counters—Adds support for clearing the ECC counters.
The show version command also indicates whether a PRE or PRE1 module is the active processor module.

Note
The order number for the PRE1 module is UBR10-PRE1. The order number for a spare PRE1 module is UBR10-PRE1=.
DC PEM with Alarm Status Connector
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF supports the new model of the DC Power Entry Module (PEM), which is identical in form and function to the original DC PEM, except that the new model includes an RJ-45 connector on the front panel to connect to the power supply monitoring connector on the optional 2400-watt AC-input power shelf.

Note
If you are not using the optional 2400-watt AC-input power shelf, both models of DC PEM are functionally identical.
New Software Feature in Release 12.2(4)XF
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF include supports for the following new software features.
Route Processor Redundancy Support
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF introduces support for Route Processor Redundancy (RPR) on the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router. The RPR feature enables the Cisco uBR10012 to use two PRE or PRE1 modules in a redundant configuration, so that if the primary PRE or PRE1 module fails or becomes inactive, the system automatically performs a failover, where the secondary PRE or PRE1 module takes over and assumes full responsibility for systems operations.
The RPR feature does not require a full reboot of the system to perform a failover. When the system is originally initialized, the secondary PRE or PRE1 module performs an abbreviated initialization routine—the module performs all self-checks and loads the Cisco IOS software, but instead of performing normal systems operations it begins monitoring the primary PRE module. If the secondary PRE or PRE1 module detects a failure in the primary module, it can quickly assume the primary responsibility for systems operations.
Support for the cable monitor Command
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF supports the cable monitor command, which allows an external LAN packet analyzer or other server to monitor inbound and outbound data packets for specific types of traffic sent between the Cisco CMTS and the cable modems on a cable interface. This feature enables the CMTS administrator to analyze traffic problems with customer data exchanges. For complete information on configuring and using this feature, see the Cable Monitor for the Cisco CMTS chapter in the Cisco CMTS Feature Guide, available on Cisco.com and the Customer Documentation CD-ROM.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(2)XF1
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XF1 does not include support for any new hardware features.
No New Software Feature in Release 12.2(2)XF1
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XF1 does not include support for any new software features.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(2)XF
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XF does not include support for any new hardware features.
No New Software Feature in Release 12.2(2)XF
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XF does not include support for any new software features.
No New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(1)XF1
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(1)XF1 does not include support for any new hardware features.
New Software Feature in Release 12.2(1)XF1
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(1)XF1 adds software support for DOCSIS Baseline Privacy Interface (BPI) encryption and authentication.
New Hardware Features in Release 12.2(1)XF
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(1)XF introduces the Cisco uBR10012 router chassis and the FRU components described in Cisco uBR10000 Series Universal Broadband Router Hardware Installation Guide and the Field Replaceable Units (FRUs) documents.
New Software Feature in Release 12.2(1)XF
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(1)XF introduces software support for the Cisco uBR10012 router, as described in the Cisco uBR10000 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide.
Limitations and Restrictions
The following limitations and restrictions apply to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i.
Load-balancing and N+1
When N+1 switchover occurs, load-balancing configurations do not carry over from Working to Protect interface(s). Therefore upstreams and downstreams do not balance cable modems on the Protect interface(s).
Cisco uBR-MC5X20S Cable Interface Line Card
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 has the following limitations and restrictions:
•
When you change the symbol rate on the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card, and then immediately use the show controller cable upstream command, you can see the notation, "US phy SNR_estimate - Unknown" for a brief period of time. Wait a minute and reissue the command to get an accurate signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) value.
•
Occasionally, after the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card is installed, when you issue the show proc cpu command, you see a CPU utilization value of 100% even when the card is not processing any traffic. This is due to a temporary timing readjustment and you can ignore the value. Reissue the command after a few minutes to get an accurate CPU utilization value.
•
When fragmentation is not used and concatenation is enabled, which can result in packet sizes larger than 2KB, the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card can drop packets. This is by design and you can avoid the problem by enabling fragmentation. Or if you disable fragmentation, then limit the maximum concatenation burst parameter to 2KB.
•
The show interface cable sid counter verbose command always displays a value of 0 for concatenated packets, even when concatenation is enabled for cable modems on a Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface.
•
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 and the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card require the use of the Cisco PRE1 module in the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router. If you are using redundant processors, both processors must be Cisco PRE1 modules.
•
The following software features are not supported for the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i:
–
Cable Monitor
–
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)

Note
HCCP 1+1 and N+1 redundant configurations are not supported in releases prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1.
•
The Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card includes onboard spectrum analyzer hardware. However, card support for advanced spectrum management features on the Cisco uBR10-MC5X20S cable interface line card will commence with future Cisco IOS releases. Future advanced spectrum management support will include all features currently available with the Cisco uBR-LCP2-MC16S cable interface line card.

Note
Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and the introduction of virtual interfaces, the configuration of the downstream and upstream ports was fixed into five domains.
Route Processor Redundancy Plus (RPR+)
The RPR+ feature introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 has the following limitations and restrictions:
Console Port Usage After a PRE1 Module Switchover
When a primary PRE1 module fails, and the secondary PRE1 module becomes the primary PRE1 module, you must use the console port on the new primary PRE1 module to give Cisco IOS CLI commands and display statistics for the system. If you have connected your PC or terminal to the console port on a primary PRE1 module and a switchover occurs, you will no longer be able to access the console, and the display will read "Secondary console disabled."
To access the console, move the PC or terminal's serial cable to the console port on the other PRE1 module, which is now acting as the primary PRE1 module.
External Management Stations
External management stations lose connectivity with the cable modem termination system (CMTS) during PRE1 switchover. Stations must reestablish connectivity after the switchover between PRE1 modules is complete.
Flap Detection on WAN Interfaces During Switchover
Neighboring routers detect flapping on WAN interfaces during a switchover. The neighboring routers reconverge after the switchover is complete.

Note
Cable interfaces do not flap during a switchover. Service may be temporarily suspended for approximately 30 seconds during a switchover and reinitialization, but service to cable interfaces does not stop.
Link States Reinitialized After Switchover
The synchronization of link states is not maintained between the Active Route Processor (RP) and Standby RP. Link states are re-initialized after switchover
MIB Variables Reinitialized After Switchover
All MIB variables are re-initialized following a switchover.
SNMP Not Supported During Switchover
SNMP persistence is not supported through a PRE1 switchover.
Telnet Sessions Disconnected During Switchover
A switchover automatically disconnects any Telnet sessions on the primary (failed) PRE1 module.
Encrypted Multicast Not Supported
Encrypted multicast broadcast is not supported during a PRE1 switchover.
Gigabit Ethernet Performance Limitations on Small Packets
On the Cisco uBR10012 router, processing small packets (64 bytes or fewer) limits a Gigabit Ethernet interface to approximately 80% of full line rate performance. Full performance is attained when the Gigabit Ethernet interface is processing packets that are 80 bytes or larger.
Downstream Rate-limiting Cannot Be Disabled
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2, you can no longer disable downstream rate-limiting on the Cisco uBR10012 router by using the no cable downstream rate-limit command. You can use the cable downstream rate-limit command to change the rate-limiting on the downstream ports, but you cannot disable downstream rate-limiting entirely.
Channel-width and Minislot Size
Cable modems can go offline if you manually change the channel-width on an upstream without also changing the minislot size to the corresponding value. This restriction applies more to DOCSIS 1.0 and older cable modems. See the following examples for the correct channel-width and minislot pairings:
cable upstream 0 channel-width 3200000cable upstream 0 minislot 4cable upstream 0 channel-width 1600000cable upstream 0 minislot 8cable upstream 0 channel-width 800000cable upstream 0 minislot 16cable upstream 0 channel-width 400000cable upstream 0 minislot 32cable upstream 0 channel-width 200000cable upstream 0 minislot 64Frame Relay Not Supported
•
Frame Relay is not currently supported on any interfaces on the Cisco uBR10012 router.
•
Although commands for Frame Relay support appear as part of the CLI on the Cisco uBR10012 router, Frame Relay operations are not supported on the network uplink WAN interface line cards.
N+1 Redundancy Limitations and Restrictions
PacketCable and N+1 Interoperation
PacketCable operations can be configured together with HCCP N+1 redundancy, but the PacketCable states are not synchronized between the Working and Protect interfaces. If a switchover occurs, existing voice calls continue. However when the user hangs up, PacketCable event messages are not generated because the Protect interface is not aware of the previous call states.
New voice calls can be made and proceed in the normal fashion.
Encrypted Multicast Not Supported
DOCSIS 1.1 N+1 Redundancy does not support encrypted multicast broadcasts across a line card switchover.
N+1 Redundancy and Cable Modem Compatibility
For a cable modem to be compatible with N+1 Redundancy support on the Cisco uBR10012, the cable modem must be DOCSIS 1.0 certified, so that it is able to tolerate disconnections from the coaxial cable network for five to fifteen seconds, without the cable modem going offline and reinitializing.
N+1 Redundancy and Configuring Static Multicast Groups
N+1 Redundancy on the uBR10012 is not supported when you are also configuring static multicast groups with the ip igmp static-group commands. If the static multicast groups are configured along with N+1 Redundancy, the PRE module may hang after a switchover. This limitation is described in caveat CSCdy11181.
MIBs
Current MIBs
To obtain lists of supported MIBs by platform and Cisco IOS release, and to download MIB modules, go to the Cisco MIB web site on Cisco.com at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
Supported MIBs
The Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router supports the following categories of MIBs:
•
SNMP standard MIBs—These MIBs are required by any agent supporting SNMPv1 or SNMPv2 network management.
•
Cisco's platform and network-layer enterprise MIBs—Common across most of Cisco's router platforms. If your network management applications are already configured to support other Cisco routers, such as the 2600 series router, no further configuration is needed unless the version of Cisco IOS software being used has updated these MIBs.
•
Cable-specific MIBs—Provide information about the cable interfaces and related information on the Cisco uBR10012 router. They include both DOCSIS-specific MIBs and Cisco-specific enterprise MIBs. If your network management applications have not already been configured for the Cisco uBR10012 routers, these MIBs must be loaded.
•
Deprecated MIBs—Supported in earlier releases of Cisco IOS software but have been replaced by more standardized, scalable MIBs. Network Management applications and scripts should convert to the replacement MIBs as soon as possible.
•
CISCO-ENTITY-VENDORTYPE-OID-MIB
The cable-specific MIBs are described in the following section. For information on the SNMP standard MIBs and Cisco's platform and network-layer enterprise MIBs, see Cisco's MIB web site at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
Cable-Specific MIBs
Table 10 shows the cable-specific MIBs that are supported on the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router. The table also provides a brief description of each MIB's contents and the Cisco IOS Software Release in which the MIB was initially functional—earlier releases might have had unsupported prototype versions of the MIB; later releases might have added new attributes and functionality. Because of interdependencies, the MIBs must be loaded in the order given in the table.

Note
The names given in Table 10 are the filenames for the MIBs as they exist on Cisco's FTP site (ftp://ftp.cisco.com/pub/mibs/ or http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml). Most MIBs are available in both SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 versions; the SNMPv1 versions have V1SMI as part of their filenames.

Note
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i does not support the CISCO-SRP-MIB.my MIB for the Cisco uBR10-SRP-OC12SML DPT WAN card.
Table 10 Cable-Specific MIBs Supported on Cisco uBR10012 Routers
SNMPv2-SMI.my
SNMPv2-SMI-V1SMI.my
This module specifies the Structure of Management Information (SMI) for SNMPv2, as defined in RFC1902.
12.2(1)XF1
SNMPv2-TC.my
SNMPv2-TC-V1SMI.my
This module defines the textual conventions as specified in RFC1903.
12.2(1)XF1
SNMPv2-MIB.my
SNMPv2-MIB-V1SMI.my
The management protocol, SNMPv2, provides for the exchange of messages that convey management information between the agents and the management stations, as defined in RFC1907.
12.2(1)XF1
CISCO-SMI.my
CISCO-SMI-V1SMI.my
This module specifies the SMI for Cisco's enterprise MIBs.
12.2(1)XF1
CISCO-TC.my
CISCO-TC-V1SMI.my
This module defines the textual conventions used in Cisco's enterprise MIBs.
12.2(1)XF1
IF-MIB.my
IF-MIB-V1SMI.my
This module describes generic objects for the Layer 3 network interface sublayers. This MIB is an updated version of MIB-II's if table and incorporates the extensions defined in RFC2233.
12.2(1)XF1
DOCS-IF-MIB.my
DOCS-IF-MIB-V1SMI.my
This module describes the DOCSIS-compliant Radio Frequency (RF) interfaces in CMs and the CMTS. This MIB has been released as an RFC2670.
12.2(1)XF1
DOCS-BPI-MIB.my
DOCS-BPI-MIB-V1SMI.my
This module describes the attributes for the DOCSIS 1.0-specified Baseline Privacy Interface (BPI) on cable modems and the CMTS.
12.2(1)XF1
DOCS-BPI-PLUS-MIB.my1
DOCS-BPI-PLUS-MIB-V1SMI.my
This module describes the attributes for the DOCSIS 1.1-specified Baseline Privacy Interface Plus (BPI+) on CMs and the CMTS. This is revision 05 of the MIB.
Note
In DOCSIS 1.1 operation, this MIB replaces the DOCSIS 1.0 version, DOCS-BPI-MIB.
12.2(1)XF1
CISCO-DOCS-EXT-MIB.my
CISCO-DOCS-EXT-MIB-V1SMI.my
This module extends the DOCSIS standard RFI MIB (DOCS-IF-MIB) with Cisco-specific extensions, such as QoS attributes and connection status and other information regarding the cable modems and CPE devices supported by the CMTS.
12.2(1)XF1
CISCO-CABLE-SPECTRUM-MIB.my
CISCO-CABLE-SPECTRUM-MIB-V1SMI.my
This module describes the spectrum management and flap list attributes.
Note
The Cisco uBR10012 router supports only the flap list attributes in this MIB.
12.2(2)XF1
DOCS-QOS-MIB.my1
DOCS-QOS-MIB-V1SMI.my
This module describes the quality of service (QoS) attributes. This is revision 04 of the MIB.
12.2(2)XF1
IGMP-MIB (RFC2933)1
This module describes the IGMP protocol attributes, as defined in RFC2933.
12.2(2)XF1
DOCS-IF-EXT-MIB.my1
This is the extension of module of the RFC2670 (DOCS-IF-MIB).
12.2(2)XF1
1 These MIBs are in draft form. They have not yet been finalized by the DOCSIS committee and are subject to change with future releases.
Deprecated MIBs
Old Cisco MIBs will be replaced in a future release. Currently, OLD-CISCO-* MIBs are being converted into more scalable MIBs without affecting existing Cisco IOS products or network management system (NMS) applications. You can update from deprecated MIBs to the replacement MIBs as shown in Table 11.

Note
Some of the MIBs listed in Table 11 represent feature sets that are not supported on Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband routers.

Note
Cisco Management Information Base (MIB) User Quick Reference is no longer published. If you have an account with Cisco.com, you can find the current list of MIBs supported by Cisco. To reach the Cisco Network Management Toolkit, go to Cisco.com, press Login, and then go to Software Center: Network Mgmt Products: Cisco Network Management Toolkit: Cisco MIB.
Caveats
Caveats describe unexpected behavior in Cisco IOS software releases. Severity 1 caveats are the most serious caveats; severity 2 caveats are less serious. Severity 3 caveats are moderate caveats, and only selected severity 3 caveats are included in the caveats document.
All caveats in Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T and specifically in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T6 are also in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i.
For information on caveats in Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T, see Caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T. This document lists severity 1 and severity 2 caveats and only selected severity 3 caveats, and is located on Cisco.com and the Documentation CD-ROM.
Caveat numbers and brief descriptions for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i and earlier releases are listed in this section.

Note
If you have an account on Cisco.com, you can use the Bug Toolkit to find select caveats of any severity. To reach the Bug Toolkit, log in to Cisco.com and click Technical Support: Tools & Utilities: Software BUG TOOLKIT (under Configuration Tools). Another option is to enter the following URL in your web browser or go to
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Bugtool/launch_bugtool.pl
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2i
This section documents possible unexpected behavior by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i and describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
There are no known open caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2i
The caveats listed in Table 13 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2i. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Table 12 Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2i
CSCei61732
Cisco IOS may permit arbitrary code execution after exploitation of a heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability. Cisco has included additional integrity checks in its software, as further described below, that are intended to reduce the likelihood of arbitrary code execution.
Cisco has made free software available that includes the additional integrity checks for affected customers.
This advisory is posted at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20051102-timers.shtml.
CSCei76358
Through normal software maintenance processes, Cisco is removing deprecated functionality. These changes have no impact on system operation or feature availability.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2h
This section documents possible unexpected behavior by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2h and describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
There are no known open caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2h.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2h
The caveats listed in Table 13 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2h. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Table 13 Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2h
CSCef68324
Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) software is vulnerable to a Denial of Service (DoS) and potentially an arbitrary code execution attack from a specifically crafted IPv6 packet. The packet must be sent from a local network segment. Only devices that have been explicitly configured to process IPv6 traffic are affected. Upon successful exploitation, the device may reload or be open to further exploitation.
Cisco has made free software available to address this vulnerability for all affected customers.
More details can be found in the security advisory that is posted at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20050729-ipv6.shtml.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2g
This section documents possible unexpected behavior by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2g and describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
There are no known open caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2g.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2g
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2g. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2f
This section documents possible unexpected behavior by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2f and describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
There are no known open caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2f.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2f
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2f. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Table 15 Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2f
CSCed78149
TCP connections may be vulnerable to spoofed ICMP packets. A spoofed ICMP packet may cause the TCP connection to use a very low segment size for 10 minutes at a time.
This issue is observed when TCP connections are configured for PMTU discovery. Note that PMTU discovery is disabled by default on a router.
Workaround: Disable PMTU discovery.
CSCed85422
Upconverter of UBR10-MC5X20S-D works with different rf-power value being configured on running-configuration.
After booting up without saving changes for rf-power value.
Workaround: Re-configure appropriate rf-power value.
CSCed89010
The hccp reverttime command does not work correctly. Although configured, it reverts back just after suspend timer (WaitToRestore) comes to zero with following messages:
SYS-3-TIMERNEG: Cannot start timer (0x65720F10) with negative offset (-362867296).-Process= "HCCP_CTRL", ipl= 0, pid= 156-Traceback= 60540674 6053DD5C 6033F0CC 60340E34 60342B90 60343BA8This issue occurs when setting up a large number like "65535" as "hccp reverttime".
Workaround: Using a revert timer value less than or equal to 35791 minutes. Or, using no hccp revertive command.
CSCee24856
A 520 line card may unexpectedly reload because of a bad JIB header packet, which causes the code to index to an invalid IDB. The unexpected reload is then caused by a reference to the IDB.
Workaround: Add JIB header checking code to the JIB is receive routine for the low priority queue.
CSCee44374
If the CLC unexpectedly reloads shortly after being booted, an "uninitialized timer" message like the following:
%SYS-3-MGDTIMER: Uninitialized timer, timer stop in hccp code shows up.There are no known workarounds.
CSCee67450
A Cisco device running IOS and enabled for the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is vulnerable to a Denial of Service (DoS) attack from a malformed BGP packet.
Only devices with the command bgp log-neighbor-changes configured are vulnerable. The BGP protocol is not enabled by default, and must be configured in order to accept traffic from an explicitly defined peer. Unless the malicious traffic appears to be sourced from a configured, trusted peer, it would be difficult to inject a malformed packet.
Cisco has made free software available to address this problem.
This issue is tracked by CERT/CC VU#689326.
This advisory will be posted at
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20050126-bgp.shtml
CSCef23733
Redundant PRE may continuously reload on bootup. This condition can occur if a PRE switch over occurred since loading the previous version of software and during the previous load of software on the currently active/previously redundant PRE some linecards were in the process of booting. If this condition persists a reload of both PRE's is necessary.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCef23937
N+1 switchover events will NOT work properly in a setup which does NOT have RF switch between the Working and Protect LC.
Workaround: Have a dummy config line in the HCCP config for RF switch, even if there is no RF switch physically present.
CSCef44225
A document that describes how the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) could be used to perform a number of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks against the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) has been made publicly available. This document has been published through the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Draft process, and is entitled "ICMP Attacks Against TCP" (draft-gont-tcpm-icmp-attacks-03.txt).
These attacks, which only affect sessions terminating or originating on a device itself, can be of three types:
1. Attacks that use ICMP "hard" error messages
2. Attacks that use ICMP "fragmentation needed and Don't Fragment (DF) bit set" messages, also known as Path Maximum Transmission Unit Discovery (PMTUD) attacks
3. Attacks that use ICMP "source quench" messagesSuccessful attacks may cause connection resets or reduction of throughput in existing connections, depending on the attack type.
Multiple Cisco products are affected by the attacks described in this Internet draft.
Cisco has made free software available to address these vulnerabilities. In some cases there are workarounds available to mitigate the effects of the vulnerability.
This advisory is posted at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20050412-icmp.shtml.
The disclosure of these vulnerabilities is being coordinated by the National Infrastructure Security Coordination Centre (NISCC), based in the United Kingdom. NISCC is working with multiple vendors whose products are potentially affected. Its posting can be found at: http://www.niscc.gov.uk/niscc/docs/re-20050412-00303.pdf?lang=en.
CSCef44699
A document that describes how the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) could be used to perform a number of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks against the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) has been made publicly available. This document has been published through the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Draft process, and is entitled "ICMP Attacks Against TCP" (draft-gont-tcpm-icmp-attacks-03.txt).
These attacks, which only affect sessions terminating or originating on a device itself, can be of three types:
1. Attacks that use ICMP "hard" error messages
2. Attacks that use ICMP "fragmentation needed and Don't Fragment (DF) bit set" messages, also known as Path Maximum Transmission Unit Discovery (PMTUD) attacks
3. Attacks that use ICMP "source quench" messagesSuccessful attacks may cause connection resets or reduction of throughput in existing connections, depending on the attack type.
Multiple Cisco products are affected by the attacks described in this Internet draft.
Cisco has made free software available to address these vulnerabilities. In some cases there are workarounds available to mitigate the effects of the vulnerability.
This advisory is posted at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20050412-icmp.shtml.
The disclosure of these vulnerabilities is being coordinated by the National Infrastructure Security Coordination Centre (NISCC), based in the United Kingdom. NISCC is working with multiple vendors whose products are potentially affected. Its posting can be found at: http://www.niscc.gov.uk/niscc/docs/re-20050412-00303.pdf?lang=en.
CSCef60659
A document that describes how the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) could be used to perform a number of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks against the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) has been made publicly available. This document has been published through the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Draft process, and is entitled "ICMP Attacks Against TCP" (draft-gont-tcpm-icmp-attacks-03.txt).
These attacks, which only affect sessions terminating or originating on a device itself, can be of three types:
1. Attacks that use ICMP "hard" error messages
2. Attacks that use ICMP "fragmentation needed and Don't Fragment (DF) bit set" messages, also known as Path Maximum Transmission Unit Discovery (PMTUD) attacks
3. Attacks that use ICMP "source quench" messagesSuccessful attacks may cause connection resets or reduction of throughput in existing connections, depending on the attack type.
Multiple Cisco products are affected by the attacks described in this Internet draft.
Cisco has made free software available to address these vulnerabilities. In some cases there are workarounds available to mitigate the effects of the vulnerability.
This advisory is posted at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20050412-icmp.shtml.
The disclosure of these vulnerabilities is being coordinated by the National Infrastructure Security Coordination Centre (NISCC), based in the United Kingdom. NISCC is working with multiple vendors whose products are potentially affected. Its posting can be found at: http://www.niscc.gov.uk/niscc/docs/re-20050412-00303.pdf?lang=en.
CSCef75363
After a N+1 switch over, the ARP entry for CPE devices may not be automatically created until subscriber traffic forces an ARP refresh. This may add a small delay to traffic recovery during the ARP request/response exchange.
Workaround. CPE traffic will recover without any user intervention.
CSCef79820
The mac-scheduler is not cleared properly with non packetcable call. As a result, the mac-scheduler is full little by little after every a call and can not make a call due to DSA_MULTIPLE_ERRORS.
This issue occurs when the docsis-mode is tdma-atdma (mix) mode in Cisco IOS software version 12.2(15)BC2a later.
Workaround: Use "cable upstream x shutdown" and "no cable upstream x shutdown"
CSCef87118
In version 12.2(15)BC2c, the DHCPD Receive process may hold memory when DMIC is used.
When DMIC is used, about 368 bytes of memory is lost on the CMTS for each config file used for the modem. This loss would keep growing till the system runs out of memory.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCef89820
The Line card unexpectedly reloads during N+1 switchover.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCeg07988
When using the SNMP set command to change a modulation profile through the docsIfCmtsModulationEntry the CMTS will accept the change on the MIBs but will not apply it.
If SNMP get is done on it, it will show the update Val, it also updating the modulation profile in the CMTS CLI but the modems will not apply it to the modems.
The CMTS does not send the Update UCD to the CM. When they are forcing the UCD update by CLI using the Command: cable modulation-profile X the CMTS accepts it and sends the new UCD to CM.
This issue was observed on 12.2(15)BC2b on a uBR10012 router with a PRE1 and a mc520 card.
Workaround: Use the CLI to change the modulation profiles.
CSCeg12481
DHCP Proxy feature configured on the Cable Modem is not supported by CMTS.
The CMTS is dropping the DHCPOFFER from the DHCP server if the ip address assigned to a CPE does not belong to any directly connected interface.
This problem is being triggered by CSCee84392.
This message is the one that could be seen if DHCP debug is enabled:
Oct 23 02:51:28.252 GMT: DHCPGLEAN hwidb/idb Cable6/1/0/NULL not found for MAC 0007.0e06.560c Ipaddr10.1.1.220 Giaddr 10.1.1.1 DHCP type 2 droppedThere are no known workarounds.
CSCeg14041
A Cisco uBR100012 router with PRE1-RP processor running 12.2(15)BC2d may unexpectedly reload due to bus error after an interface flapping. The sequence and error message would be seen as follows:
UTC2: %UBR10000-6-CMMOVED: Cable modem <MAC_address> has been moved from interface Cable8/1/0 to interface Cable8/1/3.Unexpected exception, CPU signal 10, PC = 0x6013AFA8-Traceback= 6013AFA8 6021D5D4 601F8B9C 602BB304 602BB848 602E67AC 602E6CE4 602E6D70 602E7AE4The unexpected reload is due to memory corruption.
Workaround: Do not issue CLI "clear cable flap-list all"
CSCeg23455
The PXF queue allocation fails due to insufficient queue resources, although there are only small number of queues on the interface. Further investigation found that the problem was caused by stale secondary (dynamic) service flows on the RP.
The source of this problem in unclear, but it is likely to have been induced by PRE switchover event.
Workaround: Clear the cable modems to which the stale service flow belongs.
CSCeg30130
In CSCee32618, the user got a traceback following a "No current_if_info" message. The DDTS was unreproducible but I added some additional print outs in case this happened again.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCeg36445
A Cisco Universal Broadband Router may reload unexpectedly as a result of its memory getting corrupted. This will cause a switch-over to the Standby PRE.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCeg42335
A Cisco uBR10012(Pre1) Broadband Router may experience a packet latency/loss issue on cable interfaces when "cable source-verify [dhcp]" is configured.
This issue is observed on a Cisco uBR10012(Pre1) Broadband Router that run Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC02 when the cable interfaces have "cable source-verify [dhcp]" configured. The issue may occur also in other releases.
Workaround: Turn off source verify, reload the box then shutdown all the cable interfaces (or all the cable bundle master interfaces) and then bring them up one by one. Micro reload pxf and Pxf switchover.
CSCeg44108
A Cisco uBR-10000 family router may trigger a PXF processor unexpected reload.
A large access-list must be applied on a Cable interface. The unexpected reload often happens shortly after cable modems are coming online and requesting their ip address using DHCP, or when broadcast traffic is sent to the Cable interface, or if the access-list is modified.
The router will log the following messages:
%PXF-2-FAULT: T1 SW Exception: CPU[t1r2c1] 0x00000680 at 0x0C8D LR 0x090A%PXF-2-FAULT: T1 Exception summary: CPU[t1r2c1] Stat=0x00000003 HW=0x00000000 LB=0x00000000 SW=0x00000680The PXF processor will resume operating, but may unexpectedly reload again in a cycle until the condition has been cleared.
The unexpected reload is observed only when a split ACL is in use. Splits in ACLs can be observed with "show pxf cpu access-list security".
Workaround: Use a smaller ACL if possible. When modifying the access-list, detach it from the Cable interface beforehand and re-attach it when done.
CSCeg55961
For the entPhysicalName need to display the type of PRE as well along with the interface name. So, basically it needs to specify whether the interface belongs to the active PRE or the standby PRE.
Currently the output displays the following:
entPhysicalName.29 = FastEthernet0/0/0It needs to be changed to:
entPhysicalName.29 = PRE_X:FastEthernet0/0/0Whereas "X" may be A or B. At any given time, either "A" or "B" would be Active or standby.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCeg56960
The following occurs on the linecard when a PRE switchover happens:
SLOT 5/0: Dec 15 15:13:26.445 UTC: %REQGRP-3-SYSCALL: System call for command 2 (slot5/0) : Nonblocking request failed (Cause: internal error)-Traceback= 60460610 604776C8 6047C89C 6047C910 6044A778 6044A87C 602C16D8This issue occurs if all ipc traffic is not properly cleared.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCeg71922
One or more linecards cards resets every 49 days. The exact interval is 7 weeks, 0 days, 17 hours, 2 minutes, 47 seconds (based on the rollover of a 32-bit 1 millisecond timer).
A crashinfo file is left on the linecard with CPU Hog messages from the "CMTS Mac Timer" process, followed by a watchdog reset.
It is a matter of probability as to whether or not the bug will be seen. If there is only 1 call up at the rollover time with a service flow with an activity timer, it has a 1 in 50 chance of crashing. The probability goes up with more calls in place.
This issue occurs under the following conditions:
–
Linecard must have been up for 49 days
–
Service flows must have a non-zero activity timer
–
Packetcable configurations are more vulnerable than pure data configurations because voice service flows typically use activity timers.
This issue has been observed on uBR10012 MC5X20 linecards, but any cable configuration, including the uBR7246VXR router, that uses service flow activity timers is vulnerable.
Workaround: There is no perfect known workaround. However, the following are possibilities:
–
Set the service flow activity timer to zero a few hours before the clock will rollover. Reenable the activity timer after the rollover.
–
Check the uptime of the cards in the system, schedule a card reload prior to the rollover.
–
If N+1 is configured: switch a cards to the redundant card, reload the working card and then revert. Repeat for all cards approaching the 49 day rollover point. Note that the up time of a linecard can be seen with the show diag command.
CSCin80987
In a HA enabled CMTS if, a "clear cable modem" CLI is invoked and the CMTS any time later performs a PRE switchover and qos profile reference counts on the standby PRE will be completely wrong.
This causes the qos profile deletion/addition behavior to be completely wrong after the switchover for all times to come.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCin84603
Executing the no debug all command or the undebug all command can result in the following error message, along with a traceback:
%SCHED-7-WATCH: Attempt to enqueue uninitialized watched queue (address 0).This issue occurs only when an SRP/OC-12 line card is installed in the CMTS.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCin87306
The linecard unexpectedly reloads or shows traceback with alignment errors at time of PRE switchover.
This issue occurs when redundant PREs are on a uBR10012. This issue does not apply to uBR7246 and is specific to the 12.2(15)BC2 release train.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCsa59600
A document that describes how the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) could be used to perform a number of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks against the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) has been made publicly available. This document has been published through the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Draft process, and is entitled "ICMP Attacks Against TCP" (draft-gont-tcpm-icmp-attacks-03.txt).
These attacks, which only affect sessions terminating or originating on a device itself, can be of three types:
1. Attacks that use ICMP "hard" error messages
2. Attacks that use ICMP "fragmentation needed and Don't Fragment (DF) bit set" messages, also known as Path Maximum Transmission Unit Discovery (PMTUD) attacks
3. Attacks that use ICMP "source quench" messagesSuccessful attacks may cause connection resets or reduction of throughput in existing connections, depending on the attack type.
Multiple Cisco products are affected by the attacks described in this Internet draft.
Cisco has made free software available to address these vulnerabilities. In some cases there are workarounds available to mitigate the effects of the vulnerability.
This advisory is posted at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20050412-icmp.shtml.
The disclosure of these vulnerabilities is being coordinated by the National Infrastructure Security Coordination Centre (NISCC), based in the United Kingdom. NISCC is working with multiple vendors whose products are potentially affected. Its posting can be found at: http://www.niscc.gov.uk/niscc/docs/re-20050412-00303.pdf?lang=en.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2e
This section documents possible unexpected behavior by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2e and describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
There are no known open caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2e.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2e
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2e. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2d
This section documents possible unexpected behavior by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2d and describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
There are no known open caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2d.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2d
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2d. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2c
All the caveats listed in Table 37 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2c. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2c
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2c. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2b
All the caveats listed in Table 37 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2b. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2b
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2b. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2a
All the caveats listed in Table 37 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2a. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2a
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2a. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2
All the caveats listed in Table 37 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC2
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1g
This section documents possible unexpected behavior by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1g and describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
There are no known open caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1g.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1g
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1g. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1f
This section documents possible unexpected behavior by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1f and describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
There are no known open caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1f.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1f
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1f. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1e
This section documents possible unexpected behavior by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1e and describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
There are no known open caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1e.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1e
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1e. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1d
All the caveats listed in Table 37 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1d. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1d
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1d. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1c
All the caveats listed in Table 37 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1c. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1c
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1c. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Table 32 Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1c
CSCdz85628
Unable to get the MIB value "cdrqCmtsCmStatusTable" from another SNMP agent.
Workaround: Display the remote-query info from the command line using show cable modem remote-query command on CMTS.
CSCec65787
show proc mem sorted may crash the router with a large number of modems.
Workaround: Use show proc mem.
CSCec76205
A PRE switch-over to the Standby PRE fails with 34,000 modems on the uBR10012 router. The process takes 5 minutes and line cards reset and modems do not come online.
Successful switch-overs have been performed with 10K-15K modems at other sites. It's unknown what the modem limit is.
Workaround: Reset the Line-cards manually to bring modems back online.
CSCec83212
During modem registration the Active PRE will consume all IO memory when the modem count reaches 27K-29K.
This problem is specific to 12.2(15)BC1a.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCec87802
High cpu utilization mostly due to CEF Scanner.
This issue is observed on a uBR10012 router series that is running IOS 12.2(15)BC1.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCed02703
Background statistics collection called from the CEF process is consuming high CPU levels on the RP when the CMTS is in steady state.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCed03064
SNMP ENGINE process CPU usage is triggered by external MIB objects query. As long as there are one or many network management system querying the CMTS for some MIB objects, the SNMP ENGINE process will consume some CPU usage as SNMP ENGINE process is normal priority process.
Querying ifTable could cause high CPU spike. For example, getting the whole ifTable with get next command could cause high CPU spike above 30% in 35K CMs system with total CPU load around 75%.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCed09930
A Cisco Universal Broadband Router may reload unexpectedly as a result of its memory getting corrupted.
This issue occurs only when using the CMTS remote query feature.
Workaround: Disable the remote query by no cable modem remote-query.
CSCed16691
PXF internal packet memory for a certain linecard may get stuck after a uBR10012 router boots up. This will cause all packets coming into that linecard to get dropped. When RP detects that PXF IPM is stuck by default it will print a PXF_DMA-3-FBB_LINE_CARD error message
If packet drops are observed one can recover by executing the microcode reload pxf command.
Automatic PXF reload can be configured using the exception pxf ipm command in the global configuration.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCed17260
In VPN environment, when there are CMs/CPEs getting the same ip address in different subinterfaces, a newly added source-verify entry with the same ip address may overwrite the previous CMs/CPEs source-verify entries. This does not cause any connectivity problem, however, will cause performance and scalability issues.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCed17487
If we have around 44K modems on a uBR10012 router, it may take up to 9 minutes for the PRE failover to complete.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCed21438
The CMTS rewrites the IP source of the DHCP OFFER to the pc client and changes it to the PRIMARY subnet on the Cable interface which breaks ACL's that are installed in the CM DOCSIS config file.
This is when running "cable dhcp-giaddr policy" where the relay-agent is smart enough to decide how to populate the giaddr with the correct subnet depending whether the BROADCAST is coming from a PC or cable modem. The CMTS is following the rule according to RFC 1542 with regards to the giaddr, yet the spec does NOT specify clear cut rules for the source IP address of the packet. Cisco implementation rewrites the IP Source to the cable modem subnet during the OFFER. This is not wrong but under certain conditions where security filters reside in the DOCSIS config file get broken.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCed27956
A vulnerability in the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) specification (RFC793) has been discovered by an external researcher. The successful exploitation enables an adversary to reset any established TCP connection in a much shorter time than was previously discussed publicly. Depending on the application, the connection may get automatically re-established. In other cases, a user will have to repeat the action (for example, open a new Telnet or SSH session). Depending upon the attacked protocol, a successful attack may have additional consequences beyond terminated connection which must be considered. This attack vector is only applicable to the sessions which are terminating on a device (such as a router, switch, or computer) and not to the sessions that are only passing through the device (for example, transit traffic that is being routed by a router). In addition, this attack vector does not directly compromise data integrity or confidentiality.
All Cisco products which contain TCP stack are susceptible to this vulnerability.
This advisory is available at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20040420-tcp-ios.shtml, and it describes this vulnerability as it applies to Cisco products that run Cisco IOS® software.
A companion advisory that describes this vulnerability for products that do not run Cisco IOS software is available at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20040420-tcp-nonios.shtml.
CSCed31927
During a PRE switch-over, a IPC trace-back may be noticed with a high number of modems.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCed38527
A vulnerability in the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) specification (RFC793) has been discovered by an external researcher. The successful exploitation enables an adversary to reset any established TCP connection in a much shorter time than was previously discussed publicly. Depending on the application, the connection may get automatically re-established. In other cases, a user will have to repeat the action (for example, open a new Telnet or SSH session). Depending upon the attacked protocol, a successful attack may have additional consequences beyond terminated connection which must be considered. This attack vector is only applicable to the sessions which are terminating on a device (such as a router, switch, or computer) and not to the sessions that are only passing through the device (for example, transit traffic that is being routed by a router). In addition, this attack vector does not directly compromise data integrity or confidentiality.
All Cisco products which contain TCP stack are susceptible to this vulnerability.
This advisory is available at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20040420-tcp-ios.shtml, and it describes this vulnerability as it applies to Cisco products that run Cisco IOS® software.
A companion advisory that describes this vulnerability for products that do not run Cisco IOS software is available at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20040420-tcp-nonios.shtml.
CSCed45663
In a specific circumstance a cmts will crash due to a bus error when the cable arp filter request-send command is configured. Specifically, BPI or BPI+ must be enabled and there must be IP traffic to a destination with no arp entry from a BPI modem for the crash to occur. This IP traffic will force an arp request to be sent. The filter logic will crash when determining if the arp request should be sent or filtered.
This crash will not occur if BPI is not configured on the chassis.
Workaround: If BPI is configured, disable the cable arp filter request-send command. The cable arp filter reply-accept can still be used regardless of the BPI configuration.
CSCed55652
When CIR flows are being used in a uBR10012 router, certain race conditions that can occur while configuring queues may result in lowered performance for flows on affected downstreams.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCed60220
A memory leak occurs in the *Dead* process on the PRE.
Workaround: Disable AAA Exec Accounting and Network accounting.
CSCed68829
Some modems might not be queried from SNMP cdxCmCpeTable and linecard CLI "show cable device access-group".
Workaround: shut/no shut the cable interface.
CSCed72979
Cable Line Cards may become unresponsive under certain conditions. If this happens, the card will go offline, but it will not reboot itself. It has to be reset manually using the hw-module reset command.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCed76837
If there are lots of CM/CPE in the linecard, the SNMP query MIB tables related the CM/CPE info will possibly have SNMP-3-CPUHOG message and trackback. Also the CM/CPE may have connection problem (drop offline or lose VPN).
The MIB tables are listed below. They are all invoke the same API to get the sorted table which the entry is searched.
CISCO-DOCS-EXT-MIB:cdxCmCpeTable,DOCS-IF-MIB:docsIfCmtsMacToCmTableDOCS-QOS-MIB:docsQosCmtsMacToSrvFlowTableCISCO-DOCS-REMOTE-QUERY-MIB:cdrqCmtsCmStatusTableAfter fix:
–
All the SNMP query for above tables will get info from RP/NPE only. So LC will not be affected.
–
The SNMP query Get EXACT will have real time response.
–
SNMP Get NEXT for above MIB tables is too expensive in a big system since it needs to go through whole CM/CPE in order to know which CM/CPE is the next entry of the query. Users are recommended to use SNMP GET EXACT to retrieve the info for a specific device.
In order to prevent CPU spiking for GET NEXT for above MIB tables, In the CMTS which number of devices (CM/CPE) is greater than 1000, the SNMP query GET NEXT will not get any entries returned. GetBulk has also the same problem as GetNext since internally, it searches for the next entry.
There are no known workarounds.
CSCee07031
Wrong cdxCmCpeCmStatusIndex value which does not matched the docsIfCmtsCmStatusIndex. MIB object affected by this problem: cdxCmCpeCmStatusIndex and docsIfCmtsCmPtr
There are no known workarounds.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1b
All the caveats listed in Table 37 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1b. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1b
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1b. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1a
All the caveats listed in Table 37 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1a. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1a
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1a. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1
All the caveats listed in Table 37 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1
The caveats listed in Table 38 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Table 38 Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(15)BC1
CSCdu53656
A Cisco device running IOS and enabled for the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is vulnerable to a Denial of Service (DOS) attack from a malformed BGP packet. The BGP protocol is not enabled by default, and must be configured in order to accept traffic from an explicitly defined peer. Unless the malicious traffic appears to be sourced from a configured, trusted peer, it would be difficult to inject a malformed packet. BGP MD5 is a valid workaround for this problem.
Cisco has made free software available to address this problem. For more details, please refer to this advisory, available at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20040616-bgp.shtml.
CSCdz23695
CPE database not updated with static IP address of new CPE until ARP
CSCdz46435
Traceback at frame_relay_extract_addr after igmp_get_mac_or_ip_srcad
CSCdz51438
Sch_p2:LC crashes after shut/no-shut us & clear cab modem all reset
CSCdz64816
<clear cable modem> syntax change
CSCdz68844
uBR10k:Blank system messages in logs and on syslog server
CSCdz71127
corrupted packet can cause input queue wedge - reg to CSCdx02283
CSCdz76022
uBR10k:sh int cable modem outputs incorrectly method.
CSCdz79703
SSO should failover if CEF gets disabled
CSCea02355
rare ip packets may cause input queue wedge
CSCea05168
UBR10k does not update mcast counters correctly while process switch
CSCea12543
MC520:power-level CLI does not work for 3.2MHz below -4 dbmv
CSCea22226
show cable hop runs Corr/Uncorr FEC counters together
CSCea25341
N+1/10k:Cannot show CNR per modem after switch-over
CSCea28131
A Cisco device running IOS and enabled for the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is vulnerable to a Denial of Service (DOS) attack from a malformed BGP packet. The BGP protocol is not enabled by default, and must be configured in order to accept traffic from an explicitly defined peer. Unless the malicious traffic appears to be sourced from a configured, trusted peer, it would be difficult to inject a malformed packet. BGP MD5 is a valid workaround for this problem.
Cisco has made free software available to address this problem. For more details, please refer to this advisory, available at http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20040616-bgp.shtml.
CSCea33742
MC520:modem fail to come online on unspecified upstream port
CSCea40614
Unable to disable parser error while coping start-up config to run
CSCea41322
CPUHOG error or bug error during switch over.
CSCea45202
DOCSIS:UCC is broken in DOCSIS1.1 mode
CSCea46180
UBR10K:mcast packets drop when join grp is defined in cable interface
CSCea46256
LC-HA:PXF incorrectly initialized for sub-interfaces
CSCea50802
Do not divert packets to PRE when modem online(d)
CSCea53519
PRE-HA: cable src-verify command not synced to secn pre after n+1 swi
CSCea54735
LC-HA: ip access-group <n> out CLI not synched across to Protect
CSCea57059
Add separate CLI to display different queue types
CSCea57487
LC-HA:IP address not synced to Standby PRE after N+1 switchover
CSCea61183
MC520S:Upstream down when spectrum group configured on upstream
CSCea63996
LC-HA: Protect interfaces may not go to Standby mode
CSCea65629
PRE-HA: Running config is executed twice on the Standby PRE
CSCea65880
UBR10K-6-CM_INCONSISTENCY msg and modem does not come up
CSCea69629
LC-HA: Line card crash after shut/no shut.
CSCea76756
ubr10k hang when source-verify dhcp and relay info opt configured
CSCea77176
Some MC520 cards not recognized with latest Flo_t image
CSCea77196
High CPU Utilization when unreachable packets come in SRP interface
CSCea82308
hide atp command due to being obsolete and causing traceback
CSCea83499
P2P app occasional small pkts dropped with MC520S in Downstream
CSCea83586
Downstream Sid Counters Increment Even If The Modems Are Offline
CSCea84297
cable qos profile [x] tos-overwrite AND OR requires CM re-register
CSCea87906
Spurious memory access made at 0x608E78D8 reading 0x0
CSCea90050
N+1/MC520S:US stuck on switchover - US PHY locks up
CSCea91498
Disable ATDMA CLIs
CSCeb00422
LC-HA:CPU Hog during switch-over with a large # of sub-interfaces
CSCeb00560
PRE crash at cmts_remove_bundle_entry & cmts_dhcp_glean
CSCeb00788
<clear cab modem delete> need to block IPC for layer 3
CSCeb03134
PRE-HA: configs not reflected on the standby PRE after lc switch
CSCeb05516
Line card may not recover after a crashing
CSCeb05570
PRE-HA - CPU Hog error at process = CR10K Request dispatcher
CSCeb11980
SUBMON: Make penalty qos profile enforcement persistence toggelable
CSCeb13104
IPC errors after overnight test - IPC message header cache is empty
CSCeb13563
5x20:CMTS crash observed after show cr10k cablex/x/x que cir
CSCeb16059
URB10K/VI: Snmpwalk - infinite loop at ifStackTable with VI
CSCeb18023
Traceback observed while applying service-policy to FastEthernet i/f
CSCeb22150
PXF drops pkts int ToRP q - buffer depletion under high load
CSCeb23929
PRE-HA: Shared/non-shared spectrum takes modems offline on RP
CSCeb24403
MC520:Illegal map after a UCD causes TI phy to lock up
CSCeb34775
%ALIGN-3-SPURIOUS traceback at pktcbl_cops_notify during bulk call
CSCeb38825
LC-HA: After switchover, Col2 MRI-Classif Table incorrect
CSCeb41300
10K:US overlap in shared mode, modems not online when changed CW
CSCeb44456
UBR10K - cable tftp-enforce mark-only flag wrongly CM
CSCeb45392
Add protection for a NULL pointer in cmts_bind_cm_to_upstream
CSCeb45601
PRE-HA: Pre switchover causes Protect cards to non-functional state
CSCeb50730
Mcast packets not all forwarded on MC520S
CSCeb51215
Crash from access to freed sh_mdb in c10k_mdfs_rp_update_stats
CSCeb51881
UBR10K:SNMP CPUHOG messages when line card is in down state
CSCeb52496
LC-HA:US overlap in spectrum management shared environment
CSCeb53299
LC-HA: Put in debug and workaround for CSCea63958 (MRI ASSERT crash)
CSCeb55392
LC-HA:PRE crash during LC switch-over; spectrum management related
CSCeb58199
LC-HA: Line card crash during switch over, with spectrum management
CSCeb58771
fair_enqueue called from process without int protection
CSCeb59552
Modems stay online and pingable with upstream freq Unassigned
CSCeb59760
10k/16S:Upstreams are still down after no shut
CSCeb59860
Should display NA for not support cli PHS counter.
CSCeb60153
LC-HA:PRE crash during switch-over when PRE CPU is above 90%
CSCeb64070
Potential crash in tbb_send_IPC_message after malloc failure
CSCeb68955
Fix for CSCea60819 (PRE crash on N+1 sw...) lost due to sync damage
CSCeb71752
PRE crash in sch_rp_setup_cable_queue()
CSCeb73026
LC-HA:HCCP_ASSERT message after switch-over.
CSCeb75194
LC-HA: Fast Fault Detection fails permanently after 1st trigger
CSCeb77720
When DMIC is enabled modems stuck at init(o) for >1600 byte conf fil
CSCeb78345
Initial maintenance slots not created under some circumstances
CSCeb85608
DS Mcast Pkt CRC error when mcast echo is enabled
CSCec00765
10k/16S:Upstream hops to the same frequency
CSCec00865
10k/16S:ACK39 after CMTS runs for 5 days
CSCec01544
GigE bouncing after access-list applied and removed
CSCin26768
LC-HA: Traffic matches wrong cfr on switchover followed by DSC
CSCin29305
PRE-HA: Traceback and MCASTECHO: Fail to obtain vcci for hwidb:
CSCin29836
UBR10K:ccsFlapLastClearTime reads 00 00s after clear cable flap all
CSCin37048
PRE-HA: Packets are not forwarding through secondary Dn SF after swit
CSCin37063
ip helper-address not removed when cable bundle <non-existent-bundle
CSCin37549
Traceback and Spurious memory access made at cmts_propagate_ip_confi
CSCin44163
Ambiguous command: for cli cable upstream 0 minislot-size 1
CSCin45098
Incoming PHS pkts after UCC are counted as InputErrors by CMTS
CSCin48353
cable shared-secret functionality is not working with ubr10000 image
CSCin48383
QoS profile in use can be made not-in-service
CSCin49248
PRE-HA: Standby crash by removing HCCP configs, then PRE switch-over
CSCin49445
MC520U:UBR crashed when docsQosServiceFlowStatsTable was queried
CSCin49468
LC-HA:CPE connectivity failed under N+1 switch over with source-veri
CSCin49570
Spurious memory access observed at cable_exec_command after qos enfo
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3d
There are no open caveats specific to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3d that require documentation in the release notes.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3d
The caveat listed in Table 39 is resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3d. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Table 39 Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
CSCeb78345
Initial maintenance slots not created under some circumstances
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
Except for the caveats listed as closed and resolved in Table 40, Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3c contains the same open caveats as Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3b, which are listed in Table 41.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
The caveats listed in Table 40 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3c. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Table 40 Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
CSCdz71127
corrupted packet can cause input queue wedge - reg to CSCdx02283
Cisco routers and switches running Cisco IOS software and configured to process Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) packets are vulnerable to a Denial of Service (DoS) attack. A rare sequence of crafted IPv4 packets sent directly to the device may cause the input interface to stop processing traffic once the input queue is full. No authentication is required to process the inbound packet. Processing of IPv4 packets is enabled by default. Devices running only IP version 6 (IPv6) are not affected. A workaround is available.
Cisco has made software available, free of charge, to correct the problem.
This advisory is available at:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20030717-blocked.shtml
CSCea02355
rare ip packets may cause input queue wedge
Cisco routers and switches running Cisco IOS software and configured to process Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) packets are vulnerable to a Denial of Service (DoS) attack. A rare sequence of crafted IPv4 packets sent directly to the device may cause the input interface to stop processing traffic once the input queue is full. No authentication is required to process the inbound packet. Processing of IPv4 packets is enabled by default. Devices running only IP version 6 (IPv6) are not affected. A workaround is available.
Cisco has made software available, free of charge, to correct the problem.
This advisory is available at:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/707/cisco-sa-20030717-blocked.shtml
CSCeb09043
CMTS stops generating Initial Maintenance opportunities
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3b
All the caveats listed in Table 41 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3b. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3b
The caveat listed in Table 42 is resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3b. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3a
All the caveats listed in Table 43 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3a. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats. All caveats still open in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3 are also in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3a.
Table 43 Open Caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3a
CSCea75288
Repeated PXF crash with due to ICMP unreachable
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3a
The caveats listed in Table 44 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3a. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3
All the caveats listed in Table 45 are open and reported in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3
The caveats listed in Table 46 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC2a
There are no open caveats specific to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2a that require documentation in the release notes. All open caveats in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2 are also in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2a.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC2a
The caveat listed in Table 47 is resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2a. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Table 47 Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC2a
CSCea04804
wrong ubr10k-p6-mz image failed CLC image loading
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC2
All the caveats listed in Table 48 are open in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC2
The caveats listed in Table 49 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC2. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1b
There are no open caveats specific to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1b that require documentation in the release notes.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1b
The caveat listed in Table 50 is resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1b. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Table 50 Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1b
CSCdz16916
Static hosts behind CM w/ multiple IP on one MAC loose connectivity
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1a
All the caveats listed in Table 51 are open in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1a. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1a
All the caveats listed in Table 52 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1a. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1
All the caveats listed in Table 53 are open in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC1
All the caveats listed in Table 54 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC1. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC2a
There are no open caveats specific to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2a that require documentation in the release notes.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC2a
All the caveats listed in Table 55 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2a. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC2
All the caveats listed in Table 56 are open in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC2
All the caveats listed in Table 57 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC2. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC1
All the caveats listed in Table 58 are open in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC1. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(8)BC1
All the caveats listed in Table 59 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)BC1. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(4)BC1b
All the caveats listed in Table 60 are open in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1b. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(4)BC1b
All the caveats listed in Table 61 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1b. This table describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3ca
All the caveats listed in Table 62 are open in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3ca. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3ca
All the caveats listed in Table 63 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3ca. This section describes only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
All the caveats listed in Table 64 are open in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)BC3c. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Table 64 Open Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
CSCdv89704
Fantail and PRE are not sync
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(11)BC3c
All the caveats listed in Table 65 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Open Caveats for Release 12.2(4)XF1
All the caveats listed in Table 66 are open in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF1. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Closed and Resolved Caveats for Release 12.2(4)XF1
All the caveats listed in Table 67 are resolved in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)XF1. This table lists only severity 1 and 2 caveats and select severity 3 caveats.
Related Documentation
The following sections describe the documentation available for the Cisco uBR10012. These documents consist of hardware and software installation guides, Cisco IOS configuration guides and command references, system error messages, and other documents.
Documentation is available as printed manuals or electronic documents. Use these release notes with these documents:
•
Cisco IOS Software Documentation Set
Release-Specific Documents
The following documents are specific to Cisco IOS Release 12.2 and are located on Cisco.com and the Documentation CD-ROM:
•
Cross-Platform Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 12.2
On Cisco.com at:
Technical Documents: Cisco IOS Software: Cisco IOS Release 12.2: Release Notes: Cross-Platform Release Notes
On the Documentation CD-ROM at:
Cisco Product Documentation: Cisco IOS Software Configuration: Cisco IOS Release 12.2: Release Notes: Cross-Platform Release Notes
•
Product bulletins, field notices, and other release-specific documents on Cisco.com at:
Technical Documents
•
Caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2
As a supplement to the caveats listed in "Caveats" in these release notes, see Caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2, which contains caveats applicable to all platforms for all maintenance releases of Cisco IOS Release 12.2.
On Cisco.com at:
Technical Documents: Cisco IOS Software: Cisco IOS Release 12.2: Release Notes: Caveats
On the Documentation CD-ROM at:
Cisco Product Documentation: Cisco IOS Software Configuration: Cisco IOS Release 12.2: Caveats

Note
If you have an account on Cisco.com, you can also use the Bug Toolkit to find select caveats of any severity. To reach the Bug Toolkit, log in to Cisco.com and click Service & Support: Software Center: Cisco IOS Software: BUG TOOLKIT. Another option is to go to http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Bugtool/launch_bugtool.pl.
Platform-Specific Documents
The following related documents are available on Cisco.com and the Documentation CD-ROM:
•
Cisco uBR10012 Series Hardware Installation Guide
•
Cisco uBR10012 Series Software Configuration Guide
•
Field Replaceable Units (FRUs)
•
Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide
The following documents describe the Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch:
•
Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch Installation and Configuration Guide
•
Cisco uBR-FRSW RF Switch Cabling Instructions
•
Cisco uBR-RFSW RF Switch Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information

Note
Some of the above documentation will not be available on Cisco.com until the official release of the Cisco uBR10012 router and its public software release.
On Cisco.com, beginning under the Service & Support heading:
Technical Documents: Broadband/Cable Solutions: Cisco uBR10000 Series Universal Broadband Routers

Note
The Broadband Command Consolidation is available on Cisco.com through the following path:
Technical Documents: Broadband/Cable Solutions
On the Documentation CD-ROM:
Cisco Product Documentation: Broadband/Cable Solutions: Cisco uBR10000 Series Universal Broadband Routers

Note
The Broadband Command Consolidation is available on the Documentation CD-ROM through the following path: Cisco Product Documentation: Broadband/Cable Solutions

Tip
Information about features of the Cisco uBR10012 universal broadband router, as well as software release notes, are available on Cisco.com at:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/ubr10k/index.htm.
Feature Modules
Feature modules describe new software enhancements, committed as features, supported by Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1, and are updates to the Cisco IOS documentation set. A feature module consists of a brief overview of the feature, benefits, and configuration tasks, and a command reference. As updates, the feature modules are available online only. Feature module information is incorporated in the next printing of the Cisco IOS documentation set.
On Cisco.com at:
Technical Documents: Cisco IOS Software: Cisco IOS Release 12.2: New Feature Documentation
On the Documentation CD-ROM at:
Cisco Product Documentation: Cisco IOS Software Configuration: Cisco IOS Release 12.2: New Feature Documentation
Cisco Feature Navigator
Cisco IOS software is packaged in feature sets that are supported on specific platforms. To get updated information regarding platform support for this feature, access Cisco Feature Navigator. Cisco Feature Navigator dynamically updates the list of supported platforms as new platform support is added for the feature.
Cisco Feature Navigator is a web-based tool that enables you to quickly determine which Cisco IOS software images support a specific set of features and which features are supported in a specific Cisco IOS image. You can search by feature or release. Under the release section, you can compare releases side by side to display both the features unique to each software release and the features in common.
To access Cisco Feature Navigator, you must have an account on Cisco.com. If you have forgotten or lost your account information, send a blank e-mail to cco-locksmith@cisco.com. An automatic check will verify that your e-mail address is registered with Cisco.com. If the check is successful, account details with a new random password will be e-mailed to you. Qualified users can establish an account on Cisco.com by following the directions found at this URL:
Cisco Feature Navigator is updated regularly when major Cisco IOS software releases and technology releases occur. For the most current information, go to the Cisco Feature Navigator home page at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/FeatureNav/FN.pl
Cisco IOS Software Documentation Set
The Cisco IOS software documentation set consists of the Cisco IOS configuration guides, Cisco IOS command references, and several other supporting documents. The Cisco IOS software documentation set is shipped with your order in electronic form on the Documentation CD-ROM, unless you specifically ordered the printed versions.
Documentation Modules
Each module in the Cisco IOS documentation set consists of one or more configuration guides and one or more corresponding command references. Chapters in a configuration guide describe protocols, configuration tasks, and Cisco IOS software functionality, and contain comprehensive configuration examples. Chapters in a command reference provide complete command syntax information. Use each configuration guide with its corresponding command reference.
On Cisco.com and the Documentation CD-ROM, two master hot-linked documents provide information for the Cisco IOS software documentation set.
On Cisco.com, beginning under the Service & Support heading:
Technical Documents: Cisco IOS Software Configuration: Cisco IOS Release 12.2: Configuration Guides and Command References
On the Documentation CD-ROM:
Cisco IOS Software Configuration: Cisco IOS Release 12.2: Configuration Guides and Command References
Release 12.2 Documentation Set

Note
You can find the most current Cisco IOS documentation on Cisco.com and the Documentation CD-ROM. These electronic documents may contain updates and modifications made after the paper documents were printed.
On Cisco.com, beginning under the Service & Support heading:
Technical Documents: Cisco IOS Software Configuration: Cisco IOS Release 12.2: Configuration Guides and Command References
On the Documentation CD-ROM:
Cisco Product Documentation: Cisco IOS Software Configuration: Cisco IOS Release 12.2: Configuration Guides and Command References

Note
The Cisco Management Information Base (MIB) User Quick Reference publication is no longer published. For the latest list of MIBs supported by Cisco, see Cisco Network Management Toolkit on Cisco.com. From Cisco.com, click on the following path: Service & Support: Software Center: Network Mgmt Products: Cisco Network Management Toolkit: Cisco MIB.
Obtaining Documentation
The following sections provide sources for obtaining documentation from Cisco Systems.
World Wide Web
You can access the most current Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at this URL:
Translated documentation is available at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Documentation CD-ROM
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM is updated monthly and may be more current than printed documentation. The CD-ROM package is available as a single unit or as an annual subscription.
Ordering Documentation
You can order Cisco documentation in these ways:
•
Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order Cisco product documentation from the Networking Products MarketPlace:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/order/order_root.pl
•
Registered Cisco.com users can order the Documentation CD-ROM through the online Subscription Store:
http://www.cisco.com/go/subscription
•
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by calling Cisco Systems Corporate Headquarters (California, U.S.A.) at 408 526-7208 or, elsewhere in North America, by calling 800 553-NETS (6387).
Documentation Feedback
You can submit comments electronically on Cisco.com. In the Cisco Documentation home page, click the Fax or Email option in the "Leave Feedback" section at the bottom of the page.
You can email your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
You can submit your comments by mail by using the response card behind the front cover of your document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Document Resource Connection
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883We appreciate your comments.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance. Customers and partners can obtain online documentation, troubleshooting tips, and sample configurations from online tools by using the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) Web Site. Cisco.com registered users have complete access to the technical support resources on the Cisco TAC Web Site.
Cisco.com
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that provides immediate, open access to Cisco information, networking solutions, services, programs, and resources at any time, from anywhere in the world.
Cisco.com is a highly integrated Internet application and a powerful, easy-to-use tool that provides a broad range of features and services to help you with these tasks:
•
Streamline business processes and improve productivity
•
Resolve technical issues with online support
•
Download and test software packages
•
Order Cisco learning materials and merchandise
•
Register for online skill assessment, training, and certification programs
If you want to obtain customized information and service, you can self-register on Cisco.com. To access Cisco.com, go to this URL:
Technical Assistance Center
The Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) is available to all customers who need technical assistance with a Cisco product, technology, or solution. Two levels of support are available: the Cisco TAC Web Site and the Cisco TAC Escalation Center.
Cisco TAC inquiries are categorized according to the urgency of the issue:
•
Priority level 4 (P4)—You need information or assistance concerning Cisco product capabilities, product installation, or basic product configuration.
•
Priority level 3 (P3)—Your network performance is degraded. Network functionality is noticeably impaired, but most business operations continue.
•
Priority level 2 (P2)—Your production network is severely degraded, affecting significant aspects of business operations. No workaround is available.
•
Priority level 1 (P1)—Your production network is down, and a critical impact to business operations will occur if service is not restored quickly. No workaround is available.
The Cisco TAC resource that you choose is based on the priority of the problem and the conditions of service contracts, when applicable.
Cisco TAC Web Site
You can use the Cisco TAC Web Site to resolve P3 and P4 issues yourself, saving both cost and time. The site provides around-the-clock access to online tools, knowledge bases, and software. To access the Cisco TAC Web Site, go to this URL:
All customers, partners, and resellers who have a valid Cisco service contract have complete access to the technical support resources on the Cisco TAC Web Site. The Cisco TAC Web Site requires a Cisco.com login ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a login ID or password, go to this URL to register:
http://www.cisco.com/register/
If you are a Cisco.com registered user, and you cannot resolve your technical issues by using the Cisco TAC Web Site, you can open a case online by using the TAC Case Open tool at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen
If you have Internet access, we recommend that you open P3 and P4 cases through the Cisco TAC Web Site.
Cisco TAC Escalation Center
The Cisco TAC Escalation Center addresses priority level 1 or priority level 2 issues. These classifications are assigned when severe network degradation significantly impacts business operations. When you contact the TAC Escalation Center with a P1 or P2 problem, a Cisco TAC engineer automatically opens a case.
To obtain a directory of toll-free Cisco TAC telephone numbers for your country, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
Before calling, please check with your network operations center to determine the level of Cisco support services to which your company is entitled: for example, SMARTnet, SMARTnet Onsite, or Network Supported Accounts (NSA). When you call the center, please have available your service agreement number and your product serial number.

 Feedback
Feedback