Configuring Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management in a Service Provider Network
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Configuring Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management in a Service Provider Network
Prerequisites for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
Information About Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
Maintenance Intermediate Points
Ethernet CFM and Ethernet OAM Interaction
CFM HA in a Metro Ethernet Network
NSF/SSO Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d
ISSU Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d
How to Set Up Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
Configuring and Enabling the Cross-Check Function
Configuring CFM over Bridge Domains
Configuring Ethernet OAM Interaction with CFM
Configuration Examples for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
Example: Provisioning a Network
Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
Configuring Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management in a Service Provider Network
First Published: June 19, 2006Last Updated: February 5, 2011Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) is an end-to-end per-service-instance Ethernet layer operations, administration, and maintenance (OAM) protocol. It includes proactive connectivity monitoring, fault verification, and fault isolation for large Ethernet metropolitan-area networks (MANs) and WANs.
The advent of Ethernet as a MAN and WAN technology imposes a new set of OAM requirements on Ethernet's traditional operations, which were centered on enterprise networks only. The expansion of Ethernet technology into the domain of service providers, where networks are substantially larger and more complex than enterprise networks and the user base is wider, makes operational management of link uptime crucial. More importantly, the timeliness in isolating and responding to a failure becomes mandatory for normal day-to-day operations, and OAM translates directly to the competitiveness of the service provider.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the "Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network" section.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
•
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
•
Information About Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
•
How to Set Up Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
•
Configuration Examples for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
•
Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
Prerequisites for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
Business Requirements
•
Network topology and network administration have been evaluated.
•
Business and service policies have been established.
•
Partial Route Computation (PRC) codes have been implemented for all supported commands related to configuring High Availability (HA) on a maintenance endpoint (MEP), maintenance intermediate point (MIP), level, service instance ID, cross-check timer, cross-check, and domain.
•
To use Non-Stop Forwarding (NSF) and In Service Software Upgrade (ISSU), Stateful Switchover (SSO) must be configured and working properly.
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
•
In Cisco IOS releases earlier than Release 12.2(33)SRD, CFM and Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) protocol cannot coexist on the same system.
•
CFM cannot function when the following line cards are used on the same system:
–
FI_WS_X6196_RJ45
–
FI_WS_X6196_RJ21
–
FI_WS_X6548_RJ45
–
FI_WS_X6548_RJ21
•
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRD, support for the coexistence of CFM and PVST was introduced; however, for both protocols to function on the same system, each line card must support at least three match registers and at least one line card must be able to support only a 44-bit MAC match. The exception is the Cisco 7600 Series Supervisor Engine 720, which can support CFM/PVST coexistence with only two match registers.
•
CFM loopback messages will not be confined within a maintenance domain according to their maintenance level. The impact of not having CFM loopback messages confined to their maintenance levels occurs at these levels:
–
Architecture—CFM layering is violated for loopback messages.
–
Deployment—A user may potentially misconfigure a network and have loopback messages succeed.
–
Security—A malicious device that recognizes devices' MAC addresses and levels may potentially explore a network topology that should be transparent.
•
Routed interfaces are supported only in Cisco IOS Release 12.4(11)T.
•
CFM is not fully supported on a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) provider edge (PE) device. There is no interaction between CFM and an Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) pseudowire. A CFM packet can be transparently passed like regular data packets only via pseudowire, with the following restrictions:
–
For Policy Feature Card (PFC)-based EoMPLS, which uses a Cisco Catalyst LAN card as the MPLS uplink port, a CFM packet can be transparently passed via an EoMPLS pseudowire like regular data packets. The EoMPLS endpoint interface, however, cannot be a MEP or a MIP, although a CFM MEP or MIP can be supported on regular Layer 2 switchport interfaces.
•
CFM configuration is not supported on an EtherChannel in FastEthernet Channel (FEC) mode.
•
The Ethernet-OAM3.0: CFM Over BD, Untagged feature is supported only on ES20 and ES40 line cards.
•
The HA features NFS/SSO Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d and ISSU Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d are not supported on customer edge (CE) devices.
•
The NFS/SSO Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d feature is not supported for the traceroute and error databases.
•
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRD does not support CFM messages passing through a blocked port.
•
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI1 does not support CFM.
Information About Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
•
Ethernet CFM and Ethernet OAM Interaction
•
NSF/SSO Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d
•
ISSU Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d
Ethernet CFM
Ethernet CFM is an end-to-end per-service-instance Ethernet layer OAM protocol that includes proactive connectivity monitoring, fault verification, and fault isolation. End to end can be PE to PE or CE to CE. A service can be identified as a service provider VLAN (S-VLAN) or an EVC service.
Being an end-to-end technology is the distinction between CFM and other metro-Ethernet OAM protocols. For example, MPLS, ATM, and SONET OAM help in debugging Ethernet wires but are not always end-to-end. 802.3ah OAM is a single-hop and per-physical-wire protocol. It is not end to end or service aware. Ethernet Local Management Interface (E-LMI) is confined between the user-end provider edge (uPE) and CE and relies on CFM for reporting status of the metro-Ethernet network to the CE.
Troubleshooting carrier networks offering Ethernet Layer 2 services is challenging. Customers contract with service providers for end-to-end Ethernet service and service providers may subcontract with operators to provide equipment and networks. Compared to enterprise networks, where Ethernet traditionally has been implemented, these constituent networks belong to distinct organizations or departments, are substantially larger and more complex, and have a wider user base. Ethernet CFM provides a competitive advantage to service providers for which the operational management of link uptime and timeliness in isolating and responding to failures is crucial to daily operations.
Benefits of Ethernet CFM
•
End-to-end service-level OAM technology
•
Reduced operating expense for service provider Ethernet networks
•
Competitive advantage for service providers
•
Supports both distribution and access network environments with the outward facing MEPs enhancement
Customer Service Instance
A customer service instance is an Ethernet virtual connection (EVC), which is identified by an S-VLAN within an Ethernet island, and is identified by a globally unique service ID. A customer service instance can be point-to-point or multipoint-to-multipoint. Figure 1 shows two customer service instances. Service Instance Green is point to point; Service Instance Blue is multipoint to multipoint.
Figure 1

Customer Service Instances
Maintenance Domain
A maintenance domain is a management space for the purpose of managing and administering a network. A domain is owned and operated by a single entity and defined by the set of ports internal to it and at its boundary. Figure 2 illustrates a typical maintenance domain.
Figure 2

Ethernet CFM Maintenance Domain
A unique maintenance level in the range of 0 to 7 is assigned to each domain by a network administrator. Levels and domain names are useful for defining the hierarchical relationship that exists among domains. The hierarchical relationship of domains parallels the structure of customer, service provider, and operator. The larger the domain, the higher the level value. For example, a customer domain would be larger than an operator domain. The customer domain may have a maintenance level of 7 and the operator domain may have a maintenance level of 0. Typically, operators would have the smallest domains and customers the largest domains, with service provider domains between them in size. All levels of the hierarchy must operate together.
Domains should not intersect because intersecting would mean management by more than one entity, which is not allowed. Domains may nest or touch but when two domains nest, the outer domain must have a higher maintenance level than the domain nested within it. Nesting maintenance domains is useful in the business model where a service provider contracts with one or more operators to provide Ethernet service to a customer. Each operator would have its own maintenance domain and the service provider would define its domain—a superset of the operator domains. Furthermore, the customer has its own end-to-end domain which is in turn a superset of the service provider domain. Maintenance levels of various nesting domains should be communicated among the administering organizations. For example, one approach would be to have the service provider assign maintenance levels to operators.
CFM exchanges messages and performs operations on a per-domain basis. For example, running CFM at the operator level does not allow discovery of the network by the higher provider and customer levels.
Network designers decide on domains and configurations. Figure 3 illustrates a hierarchy of operator, service provider, and customer domains and also illustrates touching, intersecting, and nested domains.
Figure 3

Ethernet CFM Maintenance Domain Hierarchy
Maintenance Point
A maintenance point is a demarcation point on an interface (port) that participates in CFM within a maintenance domain. Maintenance points on device ports act as filters that confine CFM frames within the bounds of a domain by dropping frames that do not belong to the correct level. Maintenance points must be explicitly configured on Cisco devices. Two classes of maintenance points exist, MEPs and MIPs.
Maintenance Endpoints
MEPs have the following characteristics:
•
Per maintenance domain (level) and service (S-VLAN or EVC)
•
At the edge of a domain, define the boundary
•
Within the bounds of a maintenance domain, confine CFM messages
•
When configured to do so, proactively transmit CFM continuity check messages (CCMs)
•
At the request of an administrator, transmit traceroute and loopback messages
Inward Facing MEPs
Inward facing means the MEP communicates through the Bridge Relay function and uses the Bridge-Brain MAC address. An inward facing MEP performs the following functions:
•
Sends and receives CFM frames at its level through the relay function, not via the wire connected to the port on which the MEP is configured.
•
Drops all CFM frames at its level (or lower level) that come from the direction of the wire.
•
Processes all CFM frames at its level coming from the direction of the relay function.
•
Drops all CFM frames at a lower level coming from the direction of the relay function.
•
Transparently forwards all CFM frames at its level (or a higher level), independent of whether they come in from the relay function side or the wire side.

Note
For the current Cisco IOS implementation, a MEP of level L (where L is less than 7) requires a MIP of level M > L on the same port; hence, CFM frames at a level higher than the level of the MEP will be catalogued by this MIP.
•
If the port on which the inward MEP is configured is blocked by Spanning-Tree Protocol, the MEP can no longer transmit or receive CFM messages.
Outward Facing MEPs for Routed Ports and Switch Ports
Outward facing means that the MEP communicates through the wire. Outward facing MEPs can be configured on routed ports and switch ports. A MIP configuration at a level higher than the level of the outward facing MEP is not required.
Outward facing MEPs on routed ports use the port MAC address. Outward facing MEPs on port channels use the Bridge-Brain MAC address of the first member link. When port channel members change, the identities of outward facing MEPs do not have to change. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRD supports outward facing MEPs on switch ports and Ethernet flow points (EFPs).
An outward facing MEP performs the following functions:
•
Sends and receives CFM frames at its level via the wire connected to the port where the MEP is configured.
•
Drops all CFM frames at its level (or at a lower level) that come from the direction of the relay function.
•
Processes all CFM frames at its level coming from the direction of the wire.
•
Drops all CFM frames at a lower level coming from the direction of the wire.
•
Transparently forwards all CFM frames at levels higher than the level of the outward facing MEP, independent of whether they come in from the relay function side or the wire side. This function is not applicable to routed ports.
•
If the port on which the outward MEP is configured is blocked by Spanning-Tree Protocol, the MEP can still transmit and receive CFM messages via the wire. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRD does not support CFM messages passing through a blocked port.
Maintenance Intermediate Points
MIPs have the following characteristics:
•
Per maintenance domain (level) and for all S-VLANs enabled or allowed on a port.
•
Internal to a domain, not at the boundary.
•
CFM frames received from MEPs and other MIPs are cataloged and forwarded, using both the wire and the relay function.
•
All CFM frames at a lower level are stopped and dropped, independent of whether they originate from the wire or relay function.
•
All CFM frames at a higher level are forwarded, independent of whether they arrive from the wire or relay function.
•
Passive points respond only when triggered by CFM traceroute and loopback messages.
•
Bridge-Brain MAC addresses are used.
If the port on which a MIP is configured is blocked by Spanning-Tree Protocol, the MIP cannot receive CFM messages or relay them toward the relay function side. The MIP can, however, receive and respond to CFM messages from the wire.
A MIP has only one level associated with it and the command-line interface (CLI) does not allow you to configure a MIP for a domain that does not exist.
Figure 4 illustrates MEPs and MIPs at the operator, service provider, and customer levels.
Figure 4
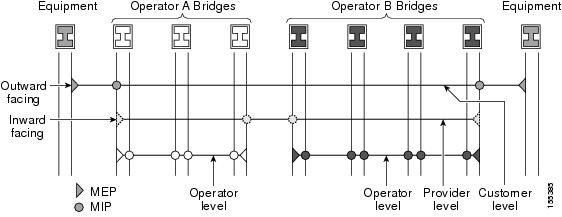
CFM MEPs and MIPs on Customer and Service Provider Equipment, Operator Devices
CFM Messages
CFM uses standard Ethernet frames. CFM frames are distinguishable by EtherType and for multicast messages by MAC address. CFM frames are sourced, terminated, processed, and relayed by bridges. Routers can support only limited CFM functions.
Bridges that cannot interpret CFM messages forward them as normal data frames. All CFM messages are confined to a maintenance domain and to an S-VLAN (PE-VLAN or Provider-VLAN). Three types of messages are supported:
•
Continuity Check
•
Loopback
•
Traceroute
Continuity Check Messages
CFM CCMs are multicast heartbeat messages exchanged periodically among MEPs. They allow MEPs to discover other MEPs within a domain and allow MIPs to discover MEPs. CCMs are confined to a domain and S-VLAN.
CFM CCMs have the following characteristics:
•
Transmitted at a configurable periodic interval by MEPs. The interval can be from 10 seconds to 65535 seconds, the default is 30.
•
Contain a configurable hold-time value to indicate to the receiver the validity of the message. The default is 2.5 times the transmit interval.
•
Catalogued by MIPs at the same maintenance level.
•
Terminated by remote MEPs at the same maintenance level.
•
Unidirectional and do not solicit a response.
•
Carry the status of the port on which the MEP is configured.
Loopback Messages
CFM loopback messages are unicast frames that a MEP transmits, at the request of an administrator, to verify connectivity to a particular maintenance point. A reply to a loopback message indicates whether a destination is reachable but does not allow hop-by-hop discovery of the path. A loopback message is similar in concept to an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo (ping) message.
A CFM loopback message can be generated on demand using the CLI. The source of a loopback message must be a MEP; the destination may be a MEP or a MIP. CFM loopback messages are unicast; replies to loopback messages also are unicast. CFM loopback messages specify the destination MAC address, VLAN, and maintenance domain.
Traceroute Messages
CFM traceroute messages are multicast frames that a MEP transmits, at the request of an administrator, to track the path (hop-by-hop) to a destination MEP. They allow the transmitting node to discover vital connectivity data about the path, and allow the discovery of all MIPs along the path that belong to the same maintenance domain. For each visible MIP, traceroute messages indicate ingress action, relay action, and egress action. Traceroute messages are similar in concept to User Datagram Protocol (UDP) traceroute messages.
Traceroute messages include the destination MAC address, VLAN, and maintenance domain and they have Time To Live (TTL) to limit propagation within the network. They can be generated on demand using the CLI. Traceroute messages are multicast; reply messages are unicast.
Cross-Check Function
The cross-check function is a timer-driven post-provisioning service verification between dynamically discovered MEPs (via CCMs) and expected MEPs (via configuration) for a service. The cross-check function verifies that all endpoints of a multipoint or point-to-point service are operational. The function supports notifications when the service is operational; otherwise it provides alarms and notifications for unexpected endpoints or missing endpoints.
The cross-check function is performed one time. You must initiate the cross-check function from the CLI every time you want a service verification.
SNMP Traps
The support provided by the Cisco IOS software implementation of CFM traps is Cisco proprietary information. MEPs generate two types of Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) traps, continuity check (CC) traps and cross-check traps.
CC Traps
•
MEP up—Sent when a new MEP is discovered, the status of a remote port changes, or connectivity from a previously discovered MEP is restored after interruption.
•
MEP down—Sent when a timeout or last gasp event occurs.
•
Cross-connect—Sent when a service ID does not match the VLAN.
•
Loop—Sent when a MEP receives its own CCMs.
•
Configuration error—Sent when a MEP receives a continuity check with an overlapping MPID.
Cross-Check Traps
•
Service up—Sent when all expected remote MEPs are up in time.
•
MEP missing—Sent when an expected MEP is down.
•
Unknown MEP—Sent when a CCM is received from an unexpected MEP.
Ethernet CFM and Ethernet OAM Interaction
To understand how CFM and OAM interact, you should understand the following concepts:
Ethernet Virtual Circuit
An EVC as defined by the Metro Ethernet Forum is a port-level point-to-point or multipoint-to-multipoint Layer 2 circuit. EVC status can be used by a CE device either to find an alternative path in to the service provider network or in some cases, to fall back to a backup path over Ethernet or over another alternative service such as Frame Relay or ATM.
OAM Manager
The OAM manager is an infrastructure element that streamlines interaction between OAM protocols. The OAM manager requires two interworking OAM protocols, in this case Ethernet CFM and Ethernet OAM. Interaction is unidirectional from the OAM manager to the CFM protocol and the only information exchanged is the user network interface (UNI) port status. Additional port status values available include
•
REMOTE_EE—Remote excessive errors
•
LOCAL_EE—Local excessive errors
•
TEST—Either remote or local loopback
After CFM receives the port status, it communicates that status across the CFM domain.
CFM over Bridge Domains
The Ethernet OAM 3.0—CFM over BD, Untagged feature allows untagged CFM packets to be associated with a MEP. An incoming untagged customer CFM packet has an EtherType of CFM and is mapped to an EVC or bridge domain (BD) based on the encapsulation configured on the EFP. The EFP is configured specifically to recognize these untagged packets.
An EFP is a logical demarcation point of an EVC on an interface and can be associated with a bridge domain. The VLAN ID is used to match and map traffic to the EFP. VLAN IDs have local significance per port similar to ATM/FrameRelay virtual circuits. CFM is supported on a bridge domain associated with an EFP. The association between the bridge domain and the EFP allows CFM to use the encapsulation on the EFP. All EFPs in the same bridge domain form a broadcast domain. The bridge domain ID determines the broadcast domain.
The distinction between a VLAN port and the EFP is the encapsulation. VLAN ports use a default dot1q encapsulation. For EFPs, untagged, single tagged, and double tagged encapsulation exists with dot1q and IEEE dot1ad EtherTypes. Different EFPs belonging to the same bridge domain can use different encapsulations.

Note
The Ethernet OAM 3.0—CFM over BD, Untagged feature is supported only on ES20 and ES40 line cards.
HA Features Supported by CFM
In access and service provider networks using Ethernet technology, HA is a requirement, especially on Ethernet OAM components that manage EVC connectivity. End-to-end connectivity status information is critical and must be maintained on a hot standby route processor (RP).

Note
A hot standby RP has the same software image as the active RP and supports synchronization of line card, protocol, and application state information between RPs for supported features and protocols.
End-to-end connectivity status is maintained on the CE, PE, and access aggregation PE (uPE) network nodes based on information received by protocols such as Ethernet LMI, CFM, and 802.3ah. This status information is used to either stop traffic or switch to backup paths when an EVC is down.
Every transaction involves either accessing or updating data among various databases. If the database is synchronized across active and standby modules, the modules are transparent to clients.
The Cisco IOS infrastructure provides various component application program interfaces (APIs) that help to maintain a hot standby RP. Metro Ethernet HA clients E-LMI, HA/ISSU, CFM HA/ISSU, and 802.3ah HA/ISSU interact with these components, update the database, and trigger necessary events to other components.
Benefits of CFM HA
•
Elimination of network downtime for Cisco IOS software image upgrades, allowing for faster upgrades that result in higher availability than versions earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRD.
•
Elimination of resource scheduling challenges associated with planned outages and late night maintenance windows.
•
Accelerated deployment of new services and applications and facilitation of faster implementation of new features, hardware, and fixes than versions earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRD.
•
Reduced operating costs due to outages while delivering higher service levels than versions earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRD.
•
CFM updates its databases and controls its own HA messaging and versioning, and this control facilitates maintenance.
CFM HA in a Metro Ethernet Network
A standalone CFM implementation does not have explicit HA requirements. When CFM is implemented on a CE or PE with E-LMI, CFM must maintain the EVC state, which requires HA because the EVC state is critical in maintaining end-to-end connectivity. CFM configures the platform with maintenance level, domain, and maintenance point, learns the remote maintenance point information, and maps it to the appropriate EVC. CFM then aggregates data received from all remote ports and updates E-LMI; consequently HA requirements vary for CE and PE.
None of the protocols used in a Metro Ethernet Network (MEN) take action based on an EVC state, but a CE device that uses the E-LMI protocol and receives EVC information will stop sending traffic to the MEN when the EVC is down. When an EVC is down, the CE may also use a backup network, if available.
The CE receives the EVC ID, associated customer VLANs, UNI information, EVC state, and remote UNI ID and state from the MEN. The CE relies on the EVC state to send or stop traffic to the MEN via E-LMI.
The PE has EVC configuration and associated customer VLAN information and derives the EVC state and remote UNI from CFM. This information is sent to the CE using E-LMI.

Note
PEs and CEs running 802.3ah OAM must maintain the port state so peers are not affected by a switchover. This information is also sent to remote nodes in CFM CC messages.
NSF/SSO Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d
The redundancy configurations SSO and NSF are both supported in Ethernet CFM and are automatically enabled. A switchover from an active to a standby RP occurs when the active RP fails, is removed from the networking device, or is manually taken down for maintenance. NSF interoperates with the SSO feature to minimize network downtime following a switchover. The primary function of Cisco NSF is to continue forwarding IP packets following an RP switchover.
For detailed information about SSO, see the "Stateful Switchover" chapter of the Cisco IOS High Availability Configuration Guide. For detailed information about the NSF feature, see the "Cisco Nonstop Forwarding" chapter of the Cisco IOS High Availability Configuration Guide.
ISSU Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d
ISSU allows you to perform a Cisco IOS software upgrade or downgrade without disrupting packet flow. CFM performs a bulk update and a runtime update of the continuity check database to the standby RP, including adding, deleting, or updating a row. This checkpoint data requires ISSU capability to transform messages from one release to another. All the components that perform active RP to standby RP updates using messages require ISSU support.
ISSU is automatically enabled in CFM and lowers the impact that planned maintenance activities have on network availability by allowing software changes while the system is in service. For detailed information about ISSU, see the "Cisco IOS In Service Software Upgrade Process" chapter of the Cisco IOS High Availability Configuration Guide.
How to Set Up Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
•
Configuring Ethernet OAM Interaction with CFM
Designing CFM Domains
Prerequisites
•
Knowledge and understanding of the network topology.
•
Understanding of organizational entities involved in managing the network; for example, operators, service providers, network operations centers (NOCs), and customer service centers.
•
Understanding of the type and scale of services to be offered.
•
Agreement by all organizational entities on the responsibilities, roles, and restrictions for each organizational entity.
•
Determination of the number of maintenance domains in the network.
•
Determination of the nesting and disjoint maintenance domains.
•
Assignment of maintenance levels and names to domains based on agreement between the service provider and operator or operators.
•
Determination of whether the domain should be inward or outward.
SUMMARY STEPS

Note
To have an operator, service provider, or customer domain is optional. A network may have a single domain or multiple domains. The steps listed here show the sequence when all three types of domains will be assigned.
1.
Determine operator level MIPs.
2.
Determine operator level MEPs.
3.
Determine service provider MIPs.
4.
Determine service provider MEPs.
5.
Determine customer MIPs.
6.
Determine customer MEPs.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Determine operator level MIPs.
a.
Starting at lowest operator level domain, assign a MIP at every interface internal to the operator network to be visible to CFM.
b.
Proceed to next higher operator level and assign MIPs.
c.
Verify that every port that has a MIP at a lower level does not have maintenance points at a higher level.
d.
Repeat steps a through d until all operator MIPs are determined.
Step 2
Determine operator level MEPs.
a.
Starting at the lowest operator level domain, assign a MEP at every UNI that is part of a service instance.
b.
Assign a MEP at the network to network interface (NNI) between operators, if there is more than one operator.
c.
Proceed to next higher operator level and assign MEPs.
A port with a MIP at a lower level cannot have maintenance points at a higher level. A port with a MEP at a lower level should have either a MIP or MEP at a higher level.
Step 3
Determine service provider MIPs.
a.
Starting at the lowest service provider level domain, assign service provider MIPs at the NNI between operators (if more than one).
b.
Proceed to next higher service provider level and assign MIPs.
A port with a MIP at a lower level cannot have maintenance points at a higher level. A port with a MEP at a lower level should not have either a MIP or a MEP at a higher level.
Step 4
Determine service provider MEPs.
a.
Starting at the lowest service provider level domain, assign a MEP at every UNI that is part of a service instance.
b.
Proceed to next higher service provider level and assign MEPs.
A port with a MIP at a lower level cannot have maintenance points at a higher level. A port with a MEP at a lower level should have either a MIP or a MEP at a higher level.
Step 5
Determine customer MIPs.
Customer MIPs are allowed only on the UNIs at the uPEs if the service provider allows the customer to run CFM. Otherwise, the service provider can configure Cisco IOS devices to block CFM frames.
a.
Configure a MIP on every uPE, at the UNI port, in the customer maintenance domain.
b.
Ensure the MIPs are at a maintenance level that is at least one higher than the highest level service provider domain.
Step 6
Determine customer MEPs.
Customer MEPs are on customer equipment. Assign an outward facing MEP within an outward domain at the appropriate customer level at the handoff between the service provider and the customer.
Examples
Figure 5 shows an example of a network with a service provider and two operators, A and B. Three domains are to be established to map to each operator and the service provider. In this example, for simplicity we assume that the network uses Ethernet transport end to end. CFM, however, can be used with other transports.
Figure 5 Configuring Domains for Ethernet CFM

What to Do Next
After you have defined the Ethernet CFM domains, configure Ethernet CFM functionality by first provisioning the network and then provisioning service.
Configuring Ethernet CFM
Configuring Ethernet CFM consists of the following tasks:
•
Provisioning the Network (required)
•
Provisioning Service (required)
•
Configuring and Enabling the Cross-Check Function (optional)
•
Configuring CFM over Bridge Domains (optional)
Provisioning the Network
Perform this task to prepare the network for Ethernet CFM.
SUMMARY STEPS
CE-A
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id direction outward
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
exit
6.
ethernet cfm enable
7.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
8.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
9.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
10.
ethernet cfm cc level {any | level-id | level-id-level-id | [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id | [,vlan-id-vlan-id]} [interval seconds] [loss-threshold num-msgs]
11.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc [mep-up] [mep-down] [config] [loop] [cross-connect]
12.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck [mep-unknown | mep-missing | service-up]
13.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
U-PE A
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
5.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
6.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
7.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
8.
exit
9.
ethernet cfm enable
10.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
11.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
12.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
13.
interface type number
14.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
15.
exit
16.
ethernet cfm cc level {any | level-id | level-id-level-id | [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id | [,vlan-id-vlan-id]} [interval seconds] [loss-threshold num-msgs]
17.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc [mep-up] [mep-down] [config] [loop] [cross-connect]
18.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck [mep-unknown | mep-missing | service-up]
19.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
PE-AGG A
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
exit
6.
ethernet cfm enable
7.
interface type number
8.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
9.
interface type number
10.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
11.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
N-PE A
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
6.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
7.
exit
8.
ethernet cfm enable
9.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
10.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
11.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
12.
interface type number
13.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
14.
exit
15.
ethernet cfm cc level {any | level-id | level-id-level-id | [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id | [,vlan-id-vlan-id]} [interval seconds] [loss-threshold num-msgs]
16.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc [mep-up] [mep-down] [config] [loop] [cross-connect]
17.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck [mep-unknown | mep-missing | service-up]
18.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
U-PE B
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
5.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
6.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
7.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
8.
exit
9.
ethernet cfm enable
10.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
11.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
12.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
13.
interface type number
14.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
15.
exit
16.
ethernet cfm cc level {any | level-id | level-id-level-id | [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id | [,vlan-id-vlan-id]} [interval seconds] [loss-threshold num-msgs]
17.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc [mep-up] [mep-down] [config] [loop] [cross-connect]
18.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck [mep-unknown | mep-missing | service-up]
19.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
PE-AGG B
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
exit
6.
ethernet cfm enable
7.
interface type number
8.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
9.
interface type number
10.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
11.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
N-PE B
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm cc level {any | level-id | level-id-level-id | [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id | [,vlan-id-vlan-id]} [interval seconds] [loss-threshold num-msgs]
4.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
5.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
6.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
7.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
8.
exit
9.
ethernet cfm enable
10.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
11.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
12.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
13.
interface type number
14.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
15.
exit
16.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc [mep-up] [mep-down] [config] [loop] [cross-connect]
17.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck [mep-unknown | mep-missing | service-up]
18.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
CE-B
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id [direction outward]
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
exit
6.
ethernet cfm enable
7.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
8.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
9.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
10.
ethernet cfm cc level {any | level-id | level-id-level-id | [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id | [,vlan-id-vlan-id]} [interval seconds] [loss-threshold num-msgs]
11.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc [mep-up] [mep-down] [config] [loop] [cross-connect]
12.
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck [mep-unknown | mep-missing | service-up]
13.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Provisioning Service
Perform this task to set up service for Ethernet CFM. Optionally, when this task is completed, you may configure and enable the cross-check function. To perform this optional task, see the "Configuring and Enabling the Cross-Check Function" section.
SUMMARY STEPS
CE-A
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id [direction outward]
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
6.
exit
7.
ethernet cfm enable
8.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
9.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
10.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
11.
interface type number
12.
ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward | outward domain domain-name] mpid id vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
or
switchport
13.
interface type number.subinterface-number
or
switchport mode trunk
14.
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
or
ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward | outward domain domain-name] mpid id vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
15.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
U-PE A
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
5.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
6.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
7.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
8.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
9.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
10.
exit
11.
ethernet cfm enable
12.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
13.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
14.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
15.
interface type number
16.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
17.
ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward] mpid id vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
18.
ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward] mpid id vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
19.
interface type number
20.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
21.
ethernet cfm cc enable level {any | level-id | ,level-id | level-id-level-id | ,level-id-level-id} vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
22.
ethernet cfm cc enable level {any | level-id | ,level-id | level-id-level-id | ,level-id-level-id} vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
23.
ethernet cfm cc level {any | level-id | level-id-level-id | [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id | [,vlan-id-vlan-id]} [interval seconds] [loss-threshold num-msgs]
24.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
PE-AGG A
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
6.
exit
7.
ethernet cfm enable
8.
interface type number
9.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
10.
interface type number
11.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
12.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
N-PE A
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
6.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
7.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
8.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
9.
exit
10.
ethernet cfm enable
11.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
12.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
13.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
14.
interface type number
15.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
16.
interface type number
17.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
18.
ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward] mpid id vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
19.
exit
20.
ethernet cfm cc enable level {any | level-id | ,level-id | level-id-level-id | ,level-id-level-id} vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
21.
ethernet cfm cc level {any | level-id | level-id-level-id | [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id | [,vlan-id-vlan-id]} [interval seconds] [loss-threshold num-msgs]
22.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
U-PE B
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
5.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
6.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
7.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
8.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
9.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
10.
exit
11.
ethernet cfm enable
12.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
13.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
14.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
15.
interface type number
16.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
17.
ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward] mpid id vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
18.
ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward] mpid id vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
19.
exit
20.
interface type number
21.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
22.
ethernet cfm cc enable level {any | level-id | ,level-id | level-id-level-id | ,level-id-level-id} vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
23.
ethernet cfm cc enable level {any | level-id | ,level-id | level-id-level-id | ,level-id-level-id} vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
24.
ethernet cfm cc level {any | level-id | level-id-level-id | [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id | [,vlan-id-vlan-id]} [interval seconds] [loss-threshold num-msgs]
25.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
PE-AGG B
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
6.
exit
7.
ethernet cfm enable
8.
interface type number
9.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
10.
interface type number
11.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
12.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
N-PE B
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
6.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
7.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
8.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
9.
exit
10.
ethernet cfm enable
11.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
12.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
13.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
14.
interface type number
15.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
16.
interface type number
17.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
18.
ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward] mpid id vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
19.
exit
20.
ethernet cfm cc enable level {any | level-id | ,level-id | level-id-level-id | ,level-id-level-id} vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
21.
ethernet cfm cc level {any | level-id | level-id-level-id | [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id | [,vlan-id-vlan-id]} [interval seconds] [loss-threshold num-msgs]
22.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
CE-B
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id [direction outward]
4.
mep archive-hold-time minutes
5.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
6.
exit
7.
ethernet cfm enable
8.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
9.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
10.
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
11.
interface type number
12.
ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward | outward domain domain-name] mpid id vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
or
switchport
13.
interface type number.subinterface-number
or
switchport mode trunk
14.
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
or
ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward | outward domain domain-name] mpid id vlan {any | vlan-id | ,vlan-id | vlan-id-vlan-id | ,vlan-id-vlan-id}
15.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring and Enabling the Cross-Check Function
Perform this task to configure and enable cross-checking for an inward facing MEP. This task requires you to configure and enable cross-checking on two devices. This task is optional.
Configuring and Enabling Cross-Checking for an Inward Facing MEP
SUMMARY STEPS
U-PE A
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
4.
mep crosscheck mpid id vlan vlan-id [mac mac-address]
5.
end
6.
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay delay
7.
exit
8.
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck {enable | disable} level {level-id | level-id-level-id [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id [,vlan-id-vlan-id]}
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
U-PE B
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id?
4.
mep crosscheck mpid id vlan vlan-id [mac mac-address]
5.
exit
6.
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay delay
7.
exit
8.
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck {enable | disable} level {level-id | level-id-level-id [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id [,vlan-id-vlan-id]}
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring and Enabling Cross-Checking for an Outward Facing MEP
SUMMARY STEPS
CE-A
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id [direction outward]
4.
mep crosscheck mpid id vlan vlan-id [mac mac-address]
5.
exit
6.
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay delay
7.
exit
8.
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck {enable | disable} level {level-id | level-id-level-id [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id [,vlan-id-vlan-id]}
DETAILED STEPS
SUMMARY STEPS
CE-B
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id [direction outward]
4.
mep crosscheck mpid id vlan vlan-id [mac mac-address]
5.
exit
6.
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay delay
7.
exit
8.
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck {enable | disable} level {level-id | level-id-level-id [,level-id-level-id]} vlan {vlan-id | any | vlan-id-vlan-id [,vlan-id-vlan-id]}
DETAILED STEPS
Examples
Configuring Cross-Checking on an Inward Facing MEP
U-PE Aethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4mep crosscheck mpid 402 vlan 100!ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay 60U-PE Bethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4mep crosscheck mpid 401 vlan 100!ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay 60Enabling Cross-Checking on an Inward Facing MEP
U-PE AU-PEA# ethernet cfm mep crosscheck enable level 4 vlan 100U-PE BU-PEB# ethernet cfm mep crosscheck enable level 4 vlan 100Configuring CFM over Bridge Domains
Perform this task to configure Ethernet CFM over bridge domains. This task is optional.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id direction outward
4.
service csi-id evc evc-name
5.
exit
6.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
7.
exit
8.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
9.
service csi-id evc evc-name
10.
mep crosscheck mpid id evc evc-name mac mac-address
11.
exit
12.
ethernet evc evc-name
13.
exit
14.
interface type number
15.
no ip address
16.
service instance id ethernet evc-id
17.
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
18.
bridge-domain bridge-id
19.
cfm mep domain domain-name outward mpid mpid-value
20.
end
21.
configure terminal
22.
interface type number
23.
no ip address
24.
ethernet cfm mip level level-id
25.
service instance id ethernet evc-id
26.
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
27.
bridge-domain bridge-id
28.
cfm mep domain domain-name inward mpid mpid-value
29.
end
30.
configure terminal
31.
ethernet cfm cc enable level level-id evc evc-name
32.
ethernet cfm cc level any evc evc-name interval seconds loss-threshold num-msgs
33.
end
DETAILED STEPS

Note
When configuring CFM over bridge domains where the bridge-domain ID matches the vlan ID service, you must configure the vlan service and the EVC service with the same service name. The bridge-domain is associated with the EVC service. The vlan and the bridge-domain represent the same broadcast domain.
Troubleshooting Tips
To verify and isolate a fault, start at the highest level maintenance domain and do the following:
•
Check the device error status.
•
When a error exists, perform a loopback test to confirm the error.
•
Run a traceroute to the destination to isolate the fault.
•
If the fault is identified, correct the fault.
•
If the fault is not identified, go to the next lower maintenance domain and repeat these four steps at that maintenance domain level.
•
Repeat the first four steps, as needed, to identify and correct the fault.
Configuring Ethernet OAM Interaction with CFM
For Ethernet OAM to function with CFM, you must configure an EVC and the OAM manager and associate the EVC with CFM. Additionally, you must use an inward facing MEP when you want interaction with the OAM manager.
Configuring the OAM Manager

Note
If you configure, change, or remove a UNI service type, EVC, Ethernet service instance, or CE-VLAN configuration, all configurations are checked to ensure that UNI service types are matched with EVC configurations and Ethernet service instances are matched with CE-VLAN configurations. Configurations are rejected if the pairings do not match.
Perform this task to configure the OAM manager on a PE device.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id [direction outward]
4.
service csi-id vlan vlan-id
5.
exit
6.
ethernet evc evc-id
7.
oam protocol {cfm svlan svlan-id domain domain-name | ldp}
8.
exit
9.
Repeat Steps 3 through 8 to define other CFM domains that you want OAM manager to monitor.
10.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling Ethernet OAM
The order in which the global and interface configuration commands are issued determines the configuration. The last command that is issued has precedence.
Perform this task to enable Ethernet OAM on a device or on an interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface type number
4.
ethernet oam [max-rate oampdus | min-rate num-seconds | mode {active | passive} | timeout seconds]
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
•
Example: Provisioning a Network
•
Example: Provisioning Service
Example: Provisioning a Network
This configuration example shows only CFM-related commands. All commands that are required to set up the data path and configure the VLANs on the device are not shown. However, it should be noted that CFM traffic will not flow into or out of the device if the VLANs are not properly configured.
CE-A!ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7 direction outward!!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!!ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3!snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop configsnmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-upU-PE A!ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7!ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4mep archive-hold-time 60!ethernet cfm domain OperatorA level 1mep archive-hold-time 65!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!interface gigabitethernet4/2ethernet cfm mip level 1!ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3!snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop configsnmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-upPE-AGG Aethernet cfm domain OperatorA level 1mep archive-hold-time 65!ethernet cfm enable!interface gigabitethernet3/1ethernet cfm mip level 1!interface gigabitethernet4/1ethernet cfm mip level 1N-PE A!ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4mep archive-hold-time 60!ethernet cfm domain OperatorA level 1mep archive-hold-time 65!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!interface gigabitethernet3/0ethernet cfm mip level 1!ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3!snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop configsnmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-upU-PE B!ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7!ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4mep archive-hold-time 60!ethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2mep archive-hold-time 65!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!interface gigabitethernet2/0ethernet cfm mip level 2!ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3!snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop configsnmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-upPE-AGG Bethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2mep archive-hold-time 65!ethernet cfm enable!interface gigabitethernet1/1ethernet cfm mip level 2!interface gigabitethernet2/1ethernet cfm mip level 2N-PE B!ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3!ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4mep archive-hold-time 60!ethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2mep archive-hold-time 65!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!interface gigabitethernet1/2ethernet cfm mip level 2!snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop configsnmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-upCE-B!ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7 direction outward!!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!!ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3!snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop configsnmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-upExample: Provisioning Service
CE-A!ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7 direction outwardservice Customer1 vlan 100!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!interface gigabitethernet3/2ethernet cfm mep level 7 direction outward domain Customer1 mpid 701 vlan 100!ethernet cfm cc enable level 7 vlan 100ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3U-PE A!ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7!ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4mep archive-hold-time 60service MetroCustomer1 vlan 100!ethernet cfm domain OperatorA level 1mep archive-hold-time 65service MetroCustomer1OpA vlan 100!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!interface gigabitethernet3/2ethernet cfm mip level 7ethernet cfm mep level 4 mpid 401 vlan 100ethernet cfm mep level 1 mpid 101 vlan 100!interface gigabitethernet4/2ethernet cfm mip level 1!ethernet cfm cc enable level 4 vlan 100ethernet cfm cc enable level 1 vlan 100ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3PE-AGG Aethernet cfm domain OperatorA level 1mep archive-hold-time 65service MetroCustomer1OpA vlan 100!ethernet cfm enable!interface gigabitethernet3/1ethernet cfm mip level 1!interface gigabitethernet4/1ethernet cfm mip level 1N-PE A!ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4mep archive-hold-time 60service MetroCustomer1 vlan 100!ethernet cfm domain OperatorA level 1mep archive-hold-time 65service MetroCustomer1OpA vlan 100!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!interface gigabitethernet3/0ethernet cfm mip level 1!interface gigabitethernet4/0ethernet cfm mip level 4ethernet cfm mep level 1 mpid 102 vlan 100!ethernet cfm cc enable level 1 vlan 100ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3U-PE B!ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7!ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4mep archive-hold-time 60service MetroCustomer1 vlan 100!ethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2mep archive-hold-time 65service MetroCustomer1OpB vlan 100!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!interface gigabitethernet1/0ethernet cfm mip level 7ethernet cfm mep level 4 mpid 402 vlan 100ethernet cfm mep level 2 mpid 201 vlan 100!interface gigabitethernet2/0ethernet cfm mip level 2!ethernet cfm cc enable level 4 vlan 100ethernet cfm cc enable level 2 vlan 100ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3PE-AGG Bethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2mep archive-hold-time 65service MetroCustomer1OpB vlan 100!ethernet cfm enable!interface gigabitethernet1/1ethernet cfm mip level 2!interface gigabitethernet2/1ethernet cfm mip level 2N-PE B!ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4mep archive-hold-time 60service MetroCustomer1 vlan 100!ethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2mep archive-hold-time 65service MetroCustomer1OpB vlan 100!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!interface gigabitethernet1/2ethernet cfm mip level 2!interface gigabitethernet2/2ethernet cfm mip level 4ethernet cfm mep level 2 mpid 202 vlan 100!ethernet cfm cc enable level 2 vlan 100ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3CE-B!ethernet cfm domain Customer level 7 direction outwardservice Customer1 vlan 100!ethernet cfm enableethernet cfm traceroute cacheethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60!interface gigabitethernet3/2ethernet cfm mep level 7 direction outward domain Customer1 mpid 702 vlan 100!ethernet cfm cc enable level 7 vlan 100ethernet cfm cc level any vlan any interval 20 loss-threshold 3Additional References
Related Documents
Carrier Ethernet commands: complete command syntax, command mode, command history, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples
Cisco IOS commands: master list of commands with complete command syntax, command mode, command history, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples
Ethernet Local Management Interface on a provider edge device
"Configuring Ethernet Local Management Interface on a Provider Edge Device" module in the Cisco IOS Carrier Ethernet Configuration Guide
IP SLAs for Metro Ethernet
IEEE 802.3ah
IEEE 802.3ah Ethernet in the First Mile
NSF/SSO and MPLS
ISSU feature and functions
Cisco IOS Broadband High Availability In Service Software Upgrade
Performing an ISSU
Cisco IOS In Service Software Upgrade Process and Enhanced Fast Software Upgrade Process
SSO
"Stateful Switchover" chapter of the Cisco IOS High Availability Configuration Guide
Standards
MIBs
CISCO-ETHER-CFM-MIB
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL:
RFCs
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified.
—
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet CFM in a Service Provider Network
Table 1 lists the features in this module and provides links to specific configuration information.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.

Note
Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Table 1 Feature Information for Configuring Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management in a Service Provider Network
CFM Outward Facing MEPs on Switch Ports
12.2(33)SRD Cisco IOS XE 3.1.0SG
The CFM Outward Facing MEPs on Switch Ports feature supports outward facing MEPs on switch ports. It is an enhancement to the Outward Facing MEP feature that supports the network at the distribution and access tiers.
The following sections provide information about this feature:
•
Outward Facing MEPs for Routed Ports and Switch Ports
The following command was introduced or modified: ethernet cfm mep level mpid vlan.
Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management
12.2(33)SRA12.2(33)SRB 12.4(15)T2 12.2(33)SXI Cisco IOS XE 3.1.0SG
Ethernet CFM is an end-to-end per-service-instance Ethernet layer OAM protocol. It includes proactive connectivity monitoring, fault verification, and fault isolation for large Ethernet MANs and WANs.
Ethernet CFM is supported on the Cisco 7600 router in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA and on the Cisco 7200 VXR router in Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T.
The following sections provide information about this feature:
The following commands were introduced or modified: clear ethernet cfm errors, clear ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote, clear ethernet cfm traceroute-cache, debug ethernet cfm all, debug ethernet cfm diagnostic, debug ethernet cfm errors, debug ethernet cfm events, debug ethernet cfm packets, ethernet cfm cc, ethernet cfm cc enable level vlan, ethernet cfm domain level, ethernet cfm enable, ethernet cfm enable (interface), ethernet cfm mep crosscheck, ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay, ethernet cfm mep level mpid vlan, ethernet cfm mip level, ethernet cfm traceroute cache, ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time, ethernet cfm traceroute cache size, mep archive-hold-time, ping ethernet mpid vlan, ping ethernet vlan, service vlan, show ethernet cfm errors, show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local, show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote, show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote crosscheck, show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote detail, show ethernet cfm traceroute-cache, snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc, snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck, traceroute ethernet vlan.
802.3ah and CFM Interworking
12.2(33)SRB 12.2(33)SXI Cisco IOS XE 3.1.0SG
The Ethernet OAM and Ethernet CFM Interworking feature enables Ethernet OAM and CFM to function together in a network.
The following sections provide information about this feature:
•
Ethernet CFM and Ethernet OAM Interaction
Ethernet-OAM3.0: CFM Over BD, Untagged
12.2(33)SRD
Ethernet-OAM3.0 with support for CFM over bridge domains is supported on the Cisco 7600 Series Route Switch Processor 720 and on the Cisco 7600 Series Supervisor Engine 720 in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRD.
The following sections provide information about this feature:
•
Configuring CFM over Bridge Domains
The following commands were introduced or modified: cfm encapsulation, cfm mep domain, debug ethernet cfm all, debug ethernet cfm events, debug ethernet cfm packets, ethernet cfm cc, ethernet cfm cc enable level evc, ethernet cfm mep crosscheck, mep crosscheck mpid evc, mep crosscheck mpid vlan, ping ethernet evc, service evc, show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote crosscheck, show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote detail, traceroute ethernet evc.
ISSU Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d
12.2(33)SRD
ISSU support allows a Cisco IOS software product to perform and upgrade or downgrade without disrupting packet flow.
The following sections provide information about this feature:
•
ISSU Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d
The following command was introduced or modified: debug ethernet cfm ha.
NSF/SSO Support in CFM 802.1ag/1.0d
12.2(33)SRD Cisco IOS XE 3.1.0SG
CFM support for NSF/SSO allows CFM processes that support dual route processors in active/standby mode to continue forwarding packets following a switchover.
The following section provides information about this feature:
Outward Facing MEP
12.4(11)T 12.2(33)SRB 12.2(33)SXI
The Outward Facing MEP feature is an enhancement to Ethernet CFM that supports the distribution and access environments by supporting outward facing MEPs on routed (Layer 3) ports.
Ethernet CFM with support for outward facing MEPs is supported on the Cisco Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) in Cisco IOS Release 12.4(11)T.
The following sections provide information about this feature:
•
Outward Facing MEPs for Routed Ports and Switch Ports
•
Provisioning the Network (CE-A and CE-B)
•
Provisioning Service (CE-A and CE-B)
•
Configuring and Enabling Cross-Checking for an Outward Facing MEP
The following command was introduced or modified: ethernet cfm mep level mpid vlan.
Glossary
CCM—continuity check message. A multicast CFM frame that a MEP transmits periodically to ensure continuity across the maintenance entities to which the transmitting MEP belongs, at the MA level on which the CCM is sent. No reply is sent in response to receiving a CCM.
EVC—Ethernet virtual connection. An association of two or more user-network interfaces.
fault alarm—An out-of-band signal, typically an SNMP notification, that notifies a system administrator of a connectivity failure.
inward-facing MEP—A MEP that resides in a bridge and transmits to and receives CFM messages from the direction of the bridge relay entity.
maintenance domain—The network or part of the network belonging to a single administration for which faults in connectivity are to be managed. The boundary of a maintenance domain is defined by a set of DSAPs, each of which may become a point of connectivity to a service instance.
maintenance domain name—The unique identifier of a domain that CFM is to protect against accidental concatenation of service instances.
MEP—maintenance endpoint. An actively managed CFM entity associated with a specific DSAP of a service instance, which can generate and receive CFM frames and track any responses. It is an endpoint of a single MA, and terminates a separate maintenance entity for each of the other MEPs in the same MA.
MEP CCDB—A database, maintained by every MEP, that maintains received information about other MEPs in the maintenance domain.
MIP—maintenance intermediate point. A CFM entity, associated with a specific pair of ISS SAPs or EISS Service Access Points, which reacts and responds to CFM frames. It is associated with a single maintenance association and is an intermediate point within one or more maintenance entities.
MIP CCDB—A database of information about the MEPs in the maintenance domain. The MIP CCDB can be maintained by a MIP.
MP—maintenance point. Either a MEP or a MIP.
MPID—maintenance endpoint identifier. A small integer, unique over a given MA, that identifies a specific MEP.
OAM—operations, administration, and maintenance. A term used by several standards bodies to describe protocols and procedures for operating, administrating, and maintaining networks. Examples are ATM OAM and IEEE Std. 802.3ah OAM.
operator—Entity that provides a service provider a single network of provider bridges or a single Layer 2 or Layer 3 backbone network. An operator may be identical to or a part of the same organization as the service provider. For purposes of IEEE P802.1ag/D1.0, Draft Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks, the operator and service provider are presumed to be separate organizations.
Terms such as "customer," "service provider," and "operator" reflect common business relationships among organizations and individuals that use equipment implemented in accordance with IEEE P802.1ag/D1.0.
UNI—user-network interface. A common term for the connection point between an operator's bridge and customer equipment. A UNI often includes a C-VLAN-aware bridge component. The term UNI is used broadly in the IEEE P802.1ag/D1.0 standard when the purpose for various features of CFM are explained. UNI has no normative meaning.
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2006-2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback