- IPsec Anti-Replay Window: Expanding and Disabling
- Pre-Fragmentation for IPsec VPNs
- Invalid Security Parameter Index Recovery
- IPsec Dead Peer Detection Periodic Message Option
- IPsec NAT Transparency
- DF Bit Override Functionality with IPsec Tunnels
- Crypto Access Check on Clear-Text Packets
- IPsec Security Association Idle Timers
- Low Latency Queueing (LLQ) for IPsec Encryption Engines
IPsec NAT Transparency
The IPsec NAT Transparency feature introduces support for IP Security (IPsec) traffic to travel through Network Address Translation (NAT) or Port Address Translation (PAT) points in the network by addressing many known incompatibilities between NAT and IPsec.
Before the introduction of this feature, a standard IPsec virtual private network (VPN) tunnel would not work if there were one or more NAT or PAT points in the delivery path of the IPsec packet. This feature makes NAT IPsec-aware, thereby, allowing remote access users to build IPsec tunnels to home gateways.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the "Feature Information for IPsec NAT Transparency" section.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Contents
•![]() Restrictions for IPsec NAT Transparency
Restrictions for IPsec NAT Transparency
•![]() Information About IPsec NAT Transparency
Information About IPsec NAT Transparency
•![]() How to Configure NAT and IPsec
How to Configure NAT and IPsec
•![]() Configuration Examples for IPsec and NAT
Configuration Examples for IPsec and NAT
•![]() Feature Information for IPsec NAT Transparency
Feature Information for IPsec NAT Transparency
Restrictions for IPsec NAT Transparency
Although this feature addresses many incompatibilities between NAT and IPsec, the following problems still exist:
Internet Key Exchange (IKE) IP Address and NAT
This incompatibility applies only when IP addresses are used as a search key to find a preshared key. Modification of the IP source or destination addresses by NAT or reverse NAT results in a mismatch between the IP address and the preshared key.
Embedded IP Addresses and NAT
Because the payload is integrity protected, any IP address enclosed within IPsec packets cannot be translated by NAT. Protocols that use embedded IP addresses include FTP, Internet Relay Chat (IRC), Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), H.323, and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP).
Information About IPsec NAT Transparency
To configure the IPsec NAT Transparency feature, you must understand the following concepts:
•![]() Feature Design of IPsec NAT Traversal
Feature Design of IPsec NAT Traversal
Feature Design of IPsec NAT Traversal
The IPsec NAT Transparency feature introduces support for IPsec traffic to travel through NAT or PAT points in the network by encapsulating IPsec packets in a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) wrapper, which allows the packets to travel across NAT devices. The following sections define the details of NAT traversal:
•![]() IKE Phase 1 Negotiation: NAT Detection
IKE Phase 1 Negotiation: NAT Detection
•![]() IKE Phase 2 Negotiation: NAT Traversal Decision
IKE Phase 2 Negotiation: NAT Traversal Decision
•![]() UDP Encapsulation of IPsec Packets for NAT Traversal
UDP Encapsulation of IPsec Packets for NAT Traversal
•![]() UDP Encapsulated Process for Software Engines: Transport Mode and Tunnel Mode ESP Encapsulation
UDP Encapsulated Process for Software Engines: Transport Mode and Tunnel Mode ESP Encapsulation
IKE Phase 1 Negotiation: NAT Detection
During Internet Key Exchange (IKE) phase 1 negotiation, two types of NAT detection occur before IKE Quick Mode begins—NAT support and NAT existence along the network path.
To detect NAT support, you should exchange the vendor identification (ID) string with the remote peer. During Main Mode (MM) 1 and MM 2 of IKE phase 1, the remote peer sends a vendor ID string payload to its peer to indicate that this version supports NAT traversal. Thereafter, NAT existence along the network path can be determined.
Detecting whether NAT exists along the network path allows you to find any NAT device between two peers and the exact location of NAT. A NAT device can translate the private IP address and port to public value (or from public to private). This translation changes the IP address and port if the packet goes through the device. To detect whether a NAT device exists along the network path, the peers should send a payload with hashes of the IP address and port of both the source and destination address from each end. If both ends calculate the hashes and the hashes match, each peer knows that a NAT device does not exist on the network path between them. If the hashes do not match (that is, someone translated the address or port), then each peer needs to perform NAT traversal to get the IPsec packet through the network.
The hashes are sent as a series of NAT discovery (NAT-D) payloads. Each payload contains one hash; if multiple hashes exist, multiple NAT-D payloads are sent. In most environments, there are only two NAT-D payloads—one for the source address and port and one for the destination address and port. The destination NAT-D payload is sent first, followed by the source NAT-D payload, which implies that the receiver should expect to process the local NAT-D payload first and the remote NAT-D payload second. The NAT-D payloads are included in the third and fourth messages in Main Mode and in the second and third messages in Aggressive Mode (AM).
IKE Phase 2 Negotiation: NAT Traversal Decision
While IKE phase 1 detects NAT support and NAT existence along the network path, IKE phase 2 decides whether or not the peers at both ends will use NAT traversal. Quick Mode (QM) security association (SA) payload in QM1 and QM2 is used to for NAT traversal negotiation.
Because the NAT device changes the IP address and port number, incompatibilities between NAT and IPsec can be created. Thus, exchanging the original source address bypasses any incompatibilities.
UDP Encapsulation of IPsec Packets for NAT Traversal
In addition to allowing IPsec packets to traverse across NAT devices, UDP encapsulation also addresses many incompatibility issues between IPsec and NAT and PAT. The resolved issues are as follows:
Incompatibility Between IPsec ESP and PAT—Resolved
If PAT found a legislative IP address and port, it would drop the Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) packet. To prevent this scenario, UDP encapsulation is used to hide the ESP packet behind the UDP header. Thus, PAT treats the ESP packet as a UDP packet, processing the ESP packet as a normal UDP packet.
Incompatibility Between Checksums and NAT—Resolved
In the new UDP header, the checksum value is always assigned to zero. This value prevents an intermediate device from validating the checksum against the packet checksum, thereby, resolving the TCP UDP checksum issue because NAT changes the IP source and destination addresses.
Incompatibility Between Fixed IKE Destination Ports and PAT—Resolved
PAT changes the port address in the new UDP header for translation and leaves the original payload unchanged.
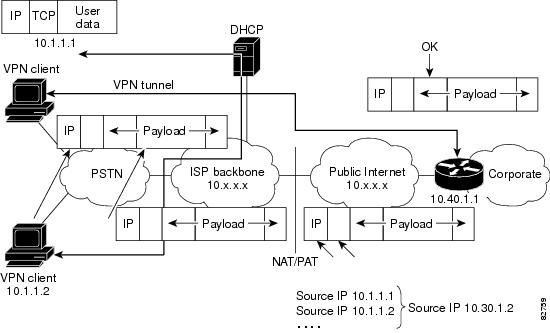
To see how UDP encapsulation helps to send IPSec packets see Figure 1 and Figure 2.
Figure 1 Standard IPsec Tunnel Through a NAT/PAT Point (No UDP Encapsulation)
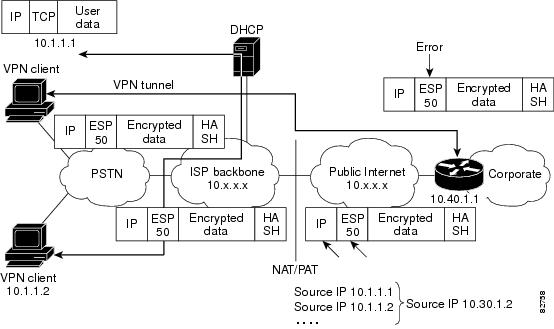
Figure 2 IPsec Packet with UDP Encapsulation
UDP Encapsulated Process for Software Engines: Transport Mode and Tunnel Mode ESP Encapsulation
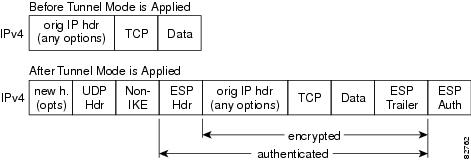
After the IPsec packet is encrypted by a hardware accelerator or a software crypto engine, a UDP header and a non-IKE marker (which is 8 bytes in length) are inserted between the original IP header and ESP header. The total length, protocol, and checksum fields are changed to match this modification. Figure 3 shows an IPsec packet before and after transport mode is applied; Figure 4 shows an IPsec packet before and after tunnel mode is applied.
Figure 3 Transport Mode—IPsec Packet Before and After ESP Encapsulation
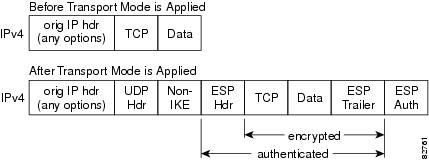
Figure 4 Tunnel Mode—IPsec Packet Before and After ESP Encapsulation
NAT Keepalives
NAT keepalives are enabled to keep the dynamic NAT mapping alive during a connection between two peers. NAT keepalives are UDP packets with an unencrypted payload of 1 byte. Although the current dead peer detection (DPD) implementation is similar to NAT keepalives, there is a slight difference: DPD is used to detect peer status, while NAT keepalives are sent if the IPsec entity did not send or receive the packet at a specified period of time—valid range is between 5 to 3600 seconds.
If NAT keepalives are enabled (through the crypto isamkp nat keepalive command), users should ensure that the idle value is shorter than the NAT mapping expiration time, which is 20 seconds.
How to Configure NAT and IPsec
This section contains the following procedures:
•![]() Configuring NAT Traversal (optional)
Configuring NAT Traversal (optional)
•![]() Disabling NAT Traversal (optional)
Disabling NAT Traversal (optional)
•![]() Configuring NAT Keepalives (optional)
Configuring NAT Keepalives (optional)
•![]() Verifying IPsec Configuration (optional)
Verifying IPsec Configuration (optional)
Configuring NAT Traversal
NAT Traversal is a feature that is auto detected by VPN devices. There are no configuration steps for a router running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T. If both VPN devices are NAT-T capable, NAT Traversal is auto detected and auto negotiated.
Disabling NAT Traversal
You may wish to disable NAT traversal if you already know that your network uses IPsec-awareness NAT (spi-matching scheme). To disable NAT traversal, use the following commands:
SUMMARY STEPS:
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ![]() no crypto ipsec nat-transparency udp-encapsulation
no crypto ipsec nat-transparency udp-encapsulation
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring NAT Keepalives
To configure your router to send NAT keepalives, use the following commands:
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ![]() crypto isakmp nat keepalive seconds
crypto isakmp nat keepalive seconds
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying IPsec Configuration
To verify your configuration, perform the following optional steps:
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() show crypto ipsec sa [map map-name | address | identity] [detail]
show crypto ipsec sa [map map-name | address | identity] [detail]
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for IPsec and NAT
This section provides the following configuration example:
•![]() NAT Keepalives Configuration Example
NAT Keepalives Configuration Example
NAT Keepalives Configuration Example
The following example shows how to enable NAT keepalives to be sent every 20 seconds:
crypto isakmp policy 1
authentication pre-share
crypto isakmp key 1234 address 56.0.0.1
crypto isakmp nat keepalive 20
!
!
crypto ipsec transform-set t2 esp-des esp-sha-hmac
!
crypto map test2 10 ipsec-isakmp
set peer 56.0.0.1
set transform-set t2
match address 101
Additional References
Related Documents
|
|
|
|---|---|
Additional NAT configuration tasks. |
• • • • • |
Additional NAT commands |
|
Additional IPsec configuration tasks |
|
Additional IPsec commands |
|
Information on IKE |
|
Additional information on IKE dead peer detection. |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
None |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
|
|
|
|---|---|
RFC 2402 |
IP Authentication Header |
RFC 2406 |
IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) |
RFC 3947 |
Negotiation of NAT-Traversal in the IKE |
1 Not all supported RFCs are listed. |
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for IPsec NAT Transparency
Table 1 lists the release history for this feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.

Note ![]() Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Glossary
IKE—Internet Key Exchange. Hybrid protocol that implements Oakley key exchange and Skeme key exchange inside the Internet Security Association Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) framework. Although IKE can be used with other protocols, its initial implementation is with IPsec. IKE provides authentication of the IPsec peers, negotiates IPsec keys, and negotiates IPsec security associations (SAs).
IPsec—IP Security. Framework of open standards developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). IPsec provides security for transmission of sensitive information over unprotected networks such as the Internet. IPsec acts at the network layer, protecting and authenticating IP packets between participating IPsec devices ("peers"), such as Cisco routers.
NAT—Network Address Translation. Translates a private IP address used inside the corporation to a public, routable address for use on the outside of the corporation, such as the Internet. NAT is considered a one-to-one mapping of addresses from private to public.
PAT—Port Address Translation. Like NAT, PAT also translated private IP address to public, routable addresses. Unlike NAT, PAT provides a many-to-one mapping of private addresses to a public address; each instance of the public address is associated with a particular port number to provide uniqueness. PAT can be used in environments where the cost of obtaining a range of public addresses is too expensive for an organization.
 Feedback
Feedback