- Finding Feature Information
- Contents
- Restrictions for Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
- Information About Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
- How to Configure Real-Time Resolution
Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
After a user specifies a host name (instead of an IP address) for remote IP Security (IPsec) peer, the Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer feature allows the host name to be domain name server (DNS) resolved before the router establishes the IPsec tunnel. Thus, the router can immediately discover whether the IP address of the peer has changed.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the "Feature Information for Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer" section.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Contents
•![]() Restrictions for Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
Restrictions for Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
•![]() Information About Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
Information About Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
•![]() How to Configure Real-Time Resolution
How to Configure Real-Time Resolution
•![]() Configuration Examples for Real-Time Resolution
Configuration Examples for Real-Time Resolution
•![]() Feature Information for Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
Feature Information for Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
Restrictions for Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
Secure DNS Requirement
It is recommended that you use this feature only with secure DNS and when the DNS responses can be authenticated. Otherwise, an attacker can spoof or forge DNS responses and have access to Internet Key Exchange (IKE) authentication data, such as a certificate. If an attacker has a certificate that is trusted by the initiating host, the attacker can successfully establish Phase 1 IKE security association (SA), or the attacker can try to guess the preshared key that is shared between the initiator and the actual responder.
DNS Initiator
DNS names resolution for remote IPsec peers works only if they are used as an initiator. The first packet that is to be encrypted triggers a DNS lookup; after the DNS lookup is complete, subsequent packets triggers IKE.
Information About Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
To configure real-time resolution for your IPsec peer, you should understand the following concept:
•![]() Real-Time Resolution Through Secure DNS
Real-Time Resolution Through Secure DNS
Real-Time Resolution Through Secure DNS
When specifying the host name of a remote IPsec peer through the set peer command, you can also issue the dynamic keyword, which defers DNS resolution of the host name until right before the IPsec tunnel has been established. Deferring resolution enables the Cisco IOS software to detect whether the IP address of the remote IPsec peer has changed. Thus, the software can contact the peer at the new IP address.
If the dynamic keyword is not issued, the host name is resolved immediately after it is specified. So, the Cisco IOS software cannot detect an IP address change and, therefore, attempts to connect to the IP address that it previously resolved.
DNS resolution assures users that their established IPsec tunnel is secure and authenticated.
How to Configure Real-Time Resolution
This section contains the following task:
•![]() Configuring Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Peers
Configuring Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Peers
Configuring Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Peers
Use this task to configure a router to perform real-time DNS resolution with a remote IPsec peer; that is, the host name of peer is resolved through a DNS lookup right before the router establishes a connection (an IPsec tunnel) with the peer.
Prerequisites
Before creating a crypto map, you should perform the following tasks:
•![]() Define Internet Security Association Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) policies.
Define Internet Security Association Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) policies.
•![]() Define IPsec transform sets.
Define IPsec transform sets.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ![]() crypto map map-name seq-num ipsec-isakmp
crypto map map-name seq-num ipsec-isakmp
4. ![]() match address access-list-id
match address access-list-id
5. ![]() set peer {host-name [dynamic] | ip-address}
set peer {host-name [dynamic] | ip-address}
6. ![]() set transform-set transform-set-name1 [transform-set-name2...transform-set-name6]
set transform-set transform-set-name1 [transform-set-name2...transform-set-name6]
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting Tips
To display crypto map configuration information, use the show crypto map command.
What to Do Next
You need to apply a crypto map set to each interface through which IPsec traffic flows. Applying the crypto map set to an interface instructs the router to evaluate all the interface's traffic against the crypto map set and to use the specified policy during connection or security association (SA) negotiation on behalf of traffic to be protected by crypto.
Configuration Examples for Real-Time Resolution
This section provides the following configuration example:
•![]() Configuring Real-Time Resolution for an IPsec Peer: Example
Configuring Real-Time Resolution for an IPsec Peer: Example
Configuring Real-Time Resolution for an IPsec Peer: Example
Figure 1 and the following example illustrate how to create a crypto map that configures the host name of a remote IPsec peer to DNS resolved through a DNS lookup right before the Cisco IOS software attempts to establish a connection with that peer.
Figure 1 Real-Time Resolution Sample Topology
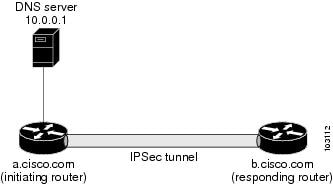
! Configure the initiating router.
hostname a.cisco.com
ip domain name cisco.com
ip name server 10.0.0.1
!
crypto map secure_b 10 ipsec-isakmp
match address 140
set peer b.cisco.com dynamic
set transform-set xset
interface serial1
ip address 30.0.0.1
crypto map secure_b
access-list 140 permit ...
!
! Configure the responding router (the remote IPSec peer).
hostname b.cisco.com
!
crypto map secure_a 10 ipsec-isakmp
match address 150
set peer 30.0.0.1
set transform-set
interface serial0/1
ip address 40.0.0.1
crypto map secure_a
access-list 150 ...
! DNS server configuration
b.cisco.com 40.0.0.1 # the address of serial0/1 of b.cisco.com
Additional References
Related Documents
|
|
|
|---|---|
Crypto maps |
|
ISAKMP policies |
|
IPsec and IKE configuration commands |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
None |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for Real-Time Resolution for IPsec Tunnel Peer
Table 1 lists the release history for this feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.

Note ![]() Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Table 1 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
 Feedback
Feedback