Cisco ISG Design and Deployment Guide: ATM Aggregation Using Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(28)SB5
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Cisco ISG Design and Deployment Guide:
ATM AggregationInformation About ISG and ATM Aggregation
ISG with ATM Aggregation Platform Support
ISG with ATM Aggregation High-Level Network Topology
Routing Protocols and Traffic Delivery
ISG Service Bundles for ATM Deployment Models
Basic Internet Access Service Bundle
Triple Play Plus Service Bundle
Model 1: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG with Multiservice Service Bundle over PPPoE
Model 2: Cisco 10000 Router as ISG with Multiservice Service Bundle
over PPPoEModel 3: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG with Triple Play Plus
Service Bundle over IP and PPPoEModel 4: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG LNS with Multiservice
Service BundleBasic Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow
Prerequisites for Configuration
Basic Configuration Requirements
Configuring the ISG in Network Model 1
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
Configuring PPPoE and the Connections to the CPE and PE
Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
Configuring Inbound and Outbound Access Lists
Configuring ISG Control Policies for Network Model 1
Configuring the Global Prepaid Services Configuration
Configuring the BOD1MTIME Service
Configuring the BOD2MTIME Service
Configuring Profiles for Network Model 1
Configuring the Time-Based ISG Subscriber Services
Configuring User Profiles for Time-Based Customers
Configuring the CPE Bridge in Network Model 1
Configuring the PE in Network Model 1
Model 2 Configuration: Cisco 10000 Router as ISG with Multiservice Service Bundle over PPPoE
Configuring the ISG in Network Model 2
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
Configuring PPPoE and the Connections to the CPE and PE
Configuring ISG Control Policies for Network Model 2
Configuring Control Class Maps
Configuring a Virtual Template Interface and Assigning Control Policy
Configuring Profiles for Network Model 2
Configuring PPPoE User Profiles
Creating the PBHK Service Profile
Configuring the BOD Service Profiles
Configuring the CPE Bridge in Network Model 2
Configuring the PE in Network Model 2
Configuring the ISG in Network Model 3
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
Configuring PPPoE and the Connections to the CPE and PE
Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
Configuring Inbound and Outbound Access Lists
Configuring QoS for Triple Play Plus
Configuring Triple Play Plus Access Lists
Configuring Profiles for Network Model 3
Configuring the CPE Bridge in Network Model 3
Configuring the PE in Network Model 3
Model 4 Configuration: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG LNS with Service Bundle
Configuring the ISG as LNS in Network Model 4
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
Configuring PPPoE and the Connection to the LAC
Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
Configuring Inbound and Outbound Access Lists
Configuring the ISG as LAC in Network Model 4
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
Configuring the Connection to the ISG LNS and PPPoE
Configuring User Profiles for ISP-1
Configuring the Connection to the LAC
Configuring L2TP Forwarding from the LAC to the ISG LNS
Configuring User Profiles for ISP-2
Configuring the Connection to the ISG LNS
Configuring the Connection to the Cisco SESM
Configuring the Subscriber's Default PPP Profile
Configuring Service Profiles for Network Model 4
ISG Subscriber Services Configuration
AAA Server Service Configuration for ISP-2
Configuring the CPE in Network Model 4
Configuring the Ethernet Interface and DHCP
Configuring the Outbound Interface
Configuring the Dialer Interface and NAT
Configuring the PE in Network Model 4
ISG Configuration Information Verification
Basic ISG Operation Verification
Subscriber Service Verification
Verification of Default BOD256K Service
show Command Output for BOD1MTIME Service
show Command Output for History of Service Changes
Cisco ISG Design and Deployment Guide:
ATM Aggregation
First Published: March 22, 2006Last Updated: January 21, 2009This document uses model networks tested in a Cisco lab to describe how to deploy a service provider broadband-based network using Cisco 7200, 7300, or 10000 routers as a Cisco Intelligent Service Gateway (ISG) and ATM as the aggregation technology. The Cisco ISG software provides a feature set that assists the service provider with provisioning and maintaining broadband networks that have many types of edge devices and many subscribers and services. The Cisco ISG software combines real-time session and flow control with programmable, dynamic policy control to deliver flexible and scalable subscriber session management capabilities. The role of the Cisco ISG software is to execute policies that identify and authenticate subscribers, and to provide access to the services that the subscriber is entitled to access. The role of the Cisco ISG router is deployment at network access control points so subscribers can access services through the software.
ISG Software Feature Sets
Cisco IOS software is packaged in feature sets that are supported on specific platforms. The Cisco ISG software is supported on Cisco 7200, 7300, and 10000 series routers. To get updated information regarding platform support and ISG feature sets, access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, you must have an account on Cisco.com. Qualified users can establish an account on Cisco.com by following the directions at http://www.cisco.com/register. If you have an account but have forgotten or lost your account information, send a blank e-mail to cco-locksmith@cisco.com. An automatic check will verify that your e-mail address is registered with Cisco.com. If the check is successful, account details with a new random password will be e-mailed to you.
Contents
•
Information About ISG and ATM Aggregation
•
Prerequisites for Configuration
•
Model 2 Configuration: Cisco 10000 Router as ISG with Multiservice Service Bundle over PPPoE
•
Model 4 Configuration: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG LNS with Service Bundle
Information About ISG and ATM Aggregation
This section contains the following topics:
•
ISG with ATM Aggregation Platform Support
•
ISG with ATM Aggregation High-Level Network Topology
•
Routing Protocols and Traffic Delivery
•
ISG Service Bundles for ATM Deployment Models
ATM Aggregation
The emerging generation of broadband network software and hardware has been designed to help Internet service providers (ISPs) control, manage, and bill subscribers for bandwidth and quality of service (QoS). For more advanced deployments, ISPs have requested dynamic bandwidth and dynamic QoS capabilities based on service types and time with selection via a prearranged service agreement. The Cisco ISG software provides dynamic policies with permissions, services, QoS, and so on, that define the requisite control to enable revenue-generating services.
The result of configuring an ISG is a collection of powerful and dynamic policies that can be applied to the subscriber session. The new policies are a superset of the Service Selection Gateway (SSG) concept of a service. With the ISG software, new subscriber rules allow you to build policies based on conditional events by triggering service actions. Services can be implemented within virtual routing contexts.
The dynamic policy enforcement inherent in the ISG software allows consistent, tailored, and secure user services to be deployed in the network, triggered by a service or by a user—concepts referred to in the ISG software as push and pull.
The ISG has the ability to initiate and manage sessions consistently, regardless of the access protocol type, network service, or session traffic policies configured. The ISG software provides seamless integration with existing Cisco IOS IP services such as Domain Name System (DNS), QoS, access control lists (also access lists or ACLs), Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), virtual private network (VPN) routing and forwarding (VRF) instances, and Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS).
The ISG software also provides enhanced accounting of services for both use and application, and for services such as prepaid, compared to previous service provider feature sets. You will also find distributed conditional debugging that has been enhanced to provide the ability to monitor and debug sessions and services based on identity.
ISG with ATM Aggregation Platform Support
Cisco's broadband aggregation portfolio offers comprehensive solutions for broadband service deployment that provides innovative technologies for simplified operations, revenue-generating network services, comprehensive management, and proven high availability. The aggregation of traffic received from an ATM-based digital subscriber line (DSL) network element is supported in the ISG software by the following Cisco hardware:
•
The Cisco 7200 series router with the NPE-G1 network processing engine card, and the stackable, operationally efficient Cisco 7300 series router are compact and mid-ranged, designed for incremental expansion of the service provider network, and targeted for deployment at the network edge. Both routers have a long list of features especially suited for broadband aggregation and the network service provider, and are capable of supporting 8,000 sessions with extended memory configurations.
•
The Cisco 10000 series router with the PRE2 performance routing engine card provides carrier-class delivery of over 32,000 simultaneous subscriber sessions.
ISG with ATM Aggregation High-Level Network Topology
Figure 1 shows a typical network topology for the models that will be used in this document.
Figure 1 High-Level ATM Network Topology

Note that some of the models described in this document deploy the ISG as an L2TP network server (LNS), which serves as a connection between the Subscriber Edge Services Manager (SESM) and the first ISG in the network.
The following elements play key roles in the network topology shown in Figure 1:
•
CPE—The customer premises equipment (CPE) router is a small router such as the Cisco 800 series router that is used either as a bridge or to initiate PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) connections from the customer PC to the Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol (L2TP) access concentrator (LAC).
•
Local loop—DSL services provide dedicated, point-to-point, public network access over twisted-pair copper wire on the local loop which occurs in the last mile between the service provider's central office and a customer site such as a house or office building. DSL technology uses existing twisted-pair telephone lines to transport high-bandwidth data to service subscribers. DSL delivers high-bandwidth data rates to dispersed locations with relatively small changes to the existing telco infrastructure.
•
DSLAM—The Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) aggregates multiple incoming DSL connections into a single ATM line. It is maintained at a point of presence (POP) separate from the ISP's central network.

Note
The configuration of the DSLAM will not be discussed in this document.
•
ISG—A Cisco router such as the Cisco 7200, 7300, and 10000 series is configured as an ISG to control subscriber access at the edge of an IP/MPLS network.
•
ISG as LAC—In the L2TP deployments in this document, the ISG also serves as a LAC. It is maintained by the ISP as part of its central network. It receives incoming sessions from the DSLAM and forwards them to the appropriate retail ISP by establishing an L2TP tunnel with the LNS. The LAC contacts the ISP's authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) server to determine the forwarding information based on the subscriber's domain name.
•
ISG as LNS—An LNS is used only in L2TP deployments. The LNS terminates the L2TP tunnel from the LAC and the PPPoE session from the subscriber. It is maintained by the ISP on its central network. The ISG LNS authenticates the user by contacting the AAA server for ISP, and assigns the user a VRF. The ISG LNS also communicates with the AAA server when the user requests additional services.
•
ISG as BRAS—A Broadband Remote Access Server (BRAS) is a high-density ISG router that supports thousands of simultaneous active sessions for the widest variety of broadband architectures. BRAS platform enhancements are enabling service providers to generate additional per-subscriber revenue while lowering operating and capital expenditures.
•
PE—The provider edge (PE) router maintains VRF information. It is the final endpoint on the ISP's network that terminates the user session. The ISP uses VRF to segment customers easily without having to specify different subnets for different classes of customers.
•
DHCP server—A DHCP server can be used to dynamically assign reusable IP addresses to devices in the network. Using a DHCP server can simplify device configuration and network management by centralizing network addressing. In the deployments described in this document, a Cisco CNS Network Registrar (CNR) server is used as the DHCP server.

Note
Configuring the Cisco CNR is beyond the scope of this document. For information on configuring the Cisco CNR, see the Cisco CNS Network Registrar documentation at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/netmgtsw/ps1982/index.html
•
Policy server —A policy server is the network element that provides the service control that allows for the management and modification of services in real time. The Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager (SESM) is a policy server that provides service selection and connection management in broadband and mobile wireless networks. The Cisco SESM provides a web portal to enable users to access services. ISPs can customize the web portal to their needs. (The Installation and Configuration Guide for the Cisco SESM is at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/net_mgmt/subscriber_edge_services_manager/3.2/administration/guide/captive_portal/cportal.html
•
Billing server—The billing server maintains user account information, including the amount of credit remaining for prepaid services. When users initiate services, the ISG contacts the billing server to determine if the user has credit available.
•
AAA server—In IP and PPPoE deployments, the network utilizes a single AAA server. The AAA server maintains user authentication information and information about services available to users. When the ISG receives a user's username and password, it forwards it to the AAA server for authentication. When a user activates a service, the ISG contacts the AAA server, which replies with information on the service to the ISG.
The deployments using PPPoE over L2TP described in this document simulate two ISPs working together, but each with their own AAA server. ISP-1 offers wholesale service to other ISPs. ISP-2 contracts with ISP-1 to receive wholesale service, which it then offers to retail customers.
•
The AAA server for ISP-1 (known as AAA-1 in the deployment model) maintains forwarding information for the retail ISPs. When queried by the ISG LAC, it sends forwarding information based on the user's domain name.
•
The AAA server for ISP-2 (known as AAA-2 in the deployment model) maintains user authentication information as well as information on the services available to users. When the LNS receives a user's username and password, it forwards them to AAA-2 for authentication. When a user activates a service, the LNS contacts AAA-2. AAA-2 then replies with information on the service to the LNS.
Instead of using single AAA servers, ISPs can maintain multiple AAA servers to be used for separate domains or for round-robin load balancing.
Routing Protocols and Traffic Delivery
This section summarizes the routing protocols used in the ISG ATM network, in the following sections:
•
QoS
•
DHCP
Routing Protocols
When designing the network, you have three basic choices for how to deliver traffic from the ISG at the wholesale ISP to the retail ISP:
•
IP routed—Traffic is IP-routed from the ISG to the retail ISP.
•
PPP terminated—The DSLAM delivers traffic to the ISG using PPPoE. The ISG terminates the PPPoE and then IP routes traffic to the retail ISP.
•
L2TP tunneled—The DSLAM delivers traffic to the ISG using PPPoE. The ISG then establishes an L2TP tunnel with an LNS at the retail ISP. The LNS terminates the PPPoE, and IP is used to route the traffic in the retail ISP's network. Using an L2TP tunnel offers the advantage that it can support both ATM and Gigabit Ethernet as the aggregation technology.
Traffic Delivery
The network deployed in the ATM-to-ISG LNS aggregation model uses the L2TP tunneled method. In all models, the DSLAM delivers traffic to the first ISG using an ATM permanent virtual circuit (PVC).
The model networks in this document use the following access technologies:
•
IP sessions
•
PPPoE sessions
•
PPPoE over L2TP sessions
DSL deployments described in this document are based on routed ATM (per RFC 2684) and ATM Routed Bridge Encapsulation (RBE).
QoS
Cisco IOS QoS software supports three types of service models: best-effort services, IntServ, and DiffServ. QoS capabilities vary depending on the platform and session types.
On Cisco 7200 and 7300 series routers:
•
Policing is available on IP and PPP sessions.
•
Shaping is available on PPP sessions.
On the Cisco 10000 router:
•
IP sessions are not supported.
•
Policing is supported on PPP sessions.
•
Shaping is supported at the virtual local area network (VLAN) or ATM PVC level, but not at the session level.
Hierarchical QoS is possible; for example, policing at the session level followed by a policer at the flow level.
It is worth noting that if best-effort user network interfaces (UNIs) reside in the same network as differentiated QoS networks, it is required that even best-effort UNIs re-mark all their traffic to the proper classification.
DHCP
As described in RFC 2131, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, DHCP provides configuration parameters to Internet hosts. DHCP consists of two components: a protocol for delivering host-specific configuration parameters from a DHCP server to a host, and a mechanism for allocating network addresses to hosts. DHCP is built on a client/server model, where designated DHCP server hosts allocate network addresses and deliver configuration parameters to dynamically configured hosts. By default, Cisco routers running Cisco IOS software include DHCP server and relay agent software.
DHCP supports three mechanisms for IP address allocation:
•
Automatic allocation—DHCP assigns a permanent IP address to a client.
•
Dynamic allocation—DHCP assigns an IP address to a client for a limited period of time (or until the client explicitly relinquishes the address).
•
Manual allocation—The network administrator assigns an IP address to a client, and DHCP is used simply to convey the assigned address to the client.
Automatic DHCP address allocation is typically based on an IP address, whether it be the gateway IP or the incoming interface IP address. In some networks, it is necessary to use additional information to further determine which IP addresses to allocate. Using the relay agent information option (option 82) permits the Cisco IOS relay agent to include additional information about itself when forwarding client-originated DHCP packets to a DHCP server.
IP Sessions
An IP session includes all the traffic that is associated with a single subscriber IP address. If the IP address is not unique to the system, other distinguishing characteristics such as VRF or a MAC address form part of the identity of the session. An ISG can be configured to create IP sessions upon receipt of DHCP messages (packets) and unknown IP source addresses. IP sessions may be hosted for a connected subscriber device (one routing hop from the ISG) or one that is many hops from the gateway.
The following events may be used to signal the start of an IP session:
•
DHCPDISCOVER message.
If the following conditions are met, receipt of a DHCPDISCOVER message will trigger the creation of an IP session:
–
The ISG serves as a DHCP relay or server for new IP address assignments.
–
Subscribers are configured for DHCP.
–
The DHCPDISCOVER message is the first DHCP request received from the subscriber.
•
Unrecognized source IP address.
In the absence of a DHCPDISCOVER message, a new IP session is triggered by the appearance of an IP packet with an unrecognized source IP address.
Because there is no inherent control protocol for IP sessions, the following events can be used to terminate a session:
•
DHCPRELEASE message from the host or subscriber, or a lease expiry packet.
•
Idle timeout.
•
Session timeout.
•
Account logoff.
ISG Service Bundles for ATM Deployment Models
Because of the large number of ISG software services available, we have developed a list of services that are representative of what the general market is using. We have grouped the features into service bundles. The following service bundles are deployed in the network models used in this document:
•
Basic Internet Access Service Bundle
•
Triple Play Plus Service Bundle
Basic Internet Access Service Bundle
The Basic Internet Access service bundle consists of traditional Layer 3 VPN access. Subscribers establish Layer 2 access connections over a Layer 3 VPN technology—in this case, an MPLS VPN. The bandwidth for all users is capped at a static 128 kbps upstream and 256 kbps downstream.

Note
The specific bandwidths described in this document are used only as examples. ISPs are free to configure any bandwidth levels that their service requires.
Multiservice Service Bundle
The Multiservice service bundle consists of the following features:
Layer 3 VPN Access
The default service for subscribers in the Multiservice service bundle is Layer 3 VPN access. All ISPs that deploy ISG software services begin with Layer 3 VPN access. In the ATM-to-ISG LNS aggregation network, access is accomplished using basic DSL connectivity. Subscribers establish Layer 2 access connections over a Layer 3 VPN technology, in this case, using a MPLS VPN. Subscriber bandwidth for basic Layer 3 VPN access is capped at 128 kbps upstream and 256 kbps downstream.
Bandwidth on Demand
Bandwidth on demand enables subscribers to temporarily increase their upstream and downstream bandwidths for either a set duration of time or a set volume of bandwidth. Subscribers first establish basic connectivity with a default cap on bandwidth, and then access a website maintained by the Cisco SESM where subscribers trigger a request for bandwidth on demand. The ISP authorizes the subscriber for the service and bills the subscriber's account. Bandwidth on demand can be either prepaid or post paid. The service remains active until either the subscriber deactivates the service or the subscriber terminates the session.
Prepaid Services
For prepaid services, subscribers pay into their accounts before the service is initiated. When a subscriber activates the service, the billing server charges the subscriber's account either for the time that the service is active or for the amount of bandwidth the subscriber uses. The service remains active until either the subscriber's account is depleted or the subscriber deactivates the service or terminates the session. As an example, for the model 1 scenario in this document, prepaid service will be enabled to pay for bandwidth on demand.
Triple Play Plus Service Bundle
The term triple play refers to delivery of three foundation services for broadband networks:
•
Basic broadband (Internet) connectivity
•
Voice over IP (VoIP)
•
Broadcast video for video on demand
The Triple Play Plus service bundle includes gaming and advanced QoS features
When subscribers initiate a session, they are granted basic broadband connectivity. If subscribers wish to activate one of the advanced services (VoIP, video on demand, and gaming), they go the web portal maintained by Cisco SESM and select the service. The advanced services are granted a higher level of QoS than other services to ensure that subscribers can maintain the necessary level of bandwidth for the activity they select.

Note
In the deployments described in this document, the advanced services are deployed only for IP sessions; however, the ISG software supports these services on both IP and PPPoE.
The ATM Deployment Models
The following tested networks are presented in this document as models for you to use to deploy your ISG and ATM-based network:
•
Model 1: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG with Multiservice Service Bundle over PPPoE
•
Model 2: Cisco 10000 Router as ISG with Multiservice Service Bundle over PPPoE
•
Model 3: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG with Triple Play Plus Service Bundle over IP and PPPoE
•
Model 4: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG LNS with Multiservice Service Bundle
Model 1: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG with Multiservice Service Bundle over PPPoE
In this deployment, the service provider wants to expand its traditional, static DSL service by deploying the Multiservice service bundle, which consists of bandwidth on demand and prepaid services. When customers activate these services, the network allocates additional bandwidth to them, based on either time or volume of bandwidth. The management of the available minutes will be done via a billing server external to the ISG.
Deployment model 1 offers the following two methods for subscriber authentication:
•
Subscribers can be authenticated based on their username on the local AAA server.
•
Subscribers can be automatically connected to a service domain based on the domain downloaded from an initial local AAA lookup.
Subscriber authentication takes place within the domain of the ISP by a remote AAA server lookup. The following advanced ISG software services are then available to the user:
•
BOD1MVOLUME: 1 Mbps
•
BOD1MTIME: 1 Mbps
•
BOD2MVOLUME: 2 Mbps
For volume-based service, subscribers are billed according to the amount of bandwidth they use. For time-based service, subscribers are billed according to the length of time the service is active.

Note
The specific bandwidths described in this document are used only as examples. ISPs are free to configure any bandwidth levels that their service requires.
In this deployment, subscribers will not be able to switch from a time-based prepaid service to a volume-based prepaid service or vice versa. Rather, ISPs can offer both time-based and volume-based services, and individual subscribers can access one or the other, but not both. Typically, ISPs will only deploy either time-based or volume-based services for subscribers, but not both simultaneously.
The following sections describe the deployment model that configures a Cisco 7200 router as an ISG with the multiservice service bundle over PPPoE:
Model 1 Network Topology
Figure 2 shows the topology of network model 1.
Figure 2 Model 1 Network Topology

Model 1 Device List
Table 1 lists the devices used in the model 1 test network. Note that a Cisco 7206 or 7301 router can be used as the ISG.
Model 1 Protocol Flow
Figure 3 shows how traffic is routed across the network.
Figure 3 Model 1 Protocol Flow

Model 1 Traffic Flow
Figure 4 shows the protocols that are active at each device in the network.
Figure 4 Model 1 Traffic Flow

Model 1 QoS Strategy
Figure 5 shows all the interfaces in the network where QoS could potentially be configured. Here "Up" refers to the upstream interface between the two devices, and "Dw" refers to the downstream interface. The interfaces shown are the points where QoS is configured for this deployment.
Figure 5 Model 1 QoS Interfaces

Table 2 describes the QoS strategy that is deployed on each of the interfaces shown in Figure 5.
Model 1 Call Flows
The following call flows describe the operation of the network:
•
Basic Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for PPPoE Sessions
Basic Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for PPPoE Sessions
Figure 6 shows the call flow process of establishing basic Layer 3 VPN access. Each user session begins with this process before initiating advanced ISG software services.
Figure 6 Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for PPPoE Sessions
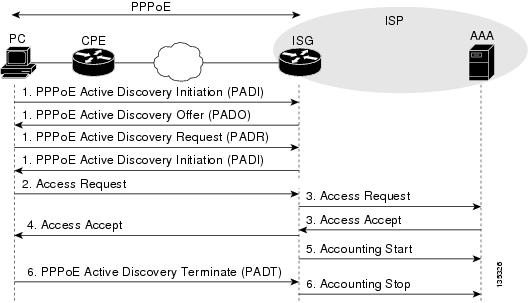
Following is an explanation of the sequence of events in Figure 6:
1.
The subscriber initiates a PPPoE connection from the PC to the ISG by way of the CPE.
2.
The client initiates the session by sending an Access Request message to the ISG.
3.
The ISG sends the subscriber information to the AAA server. The AAA server authenticates the user and sends the ISG the appropriate service profile to the ISG.
4.
After the user has been successfully authenticated, the ISG sends an Access Accept message to the client.
5.
The ISG sends an Accounting Start message to the AAA server.
6.
When the subscriber ends the session, the client sends a PPPoE Terminate message to the ISG, and the ISG terminates the session and sends an Accounting Stop message to the AAA server.
Prepaid Services Call Flow
Figure 7 shows the call flow process of establishing prepaid services. In this configuration, a subscriber initiates a service that will be named BOD1MTIME in the configuration.
Figure 7 Prepaid Services Call Flow for PPPoE Sessions

Following is an explanation of the sequence of events in Figure 7:
1.
The subscribers selects the BOD1MTIME service on the Cisco SESM web interface dashboard.
2.
The Cisco SESM sends an Access Request message to the ISG for the subscriber's information.
3.
The ISG replies to the Cisco SESM with an Access Accept message containing the subscriber's information.
4.
The Cisco SESM sends an Access Request message to the ISG requesting information about the BOD1MTIME service.
5.
The ISG sends an Access Request message to the AAA server requesting information about the BOD1MTIME service.
6.
The AAA server replies to the ISG with an Access Accept message containing the traffic class, BOD1MTIME profile, and the prepaid configuration.
7.
The ISG sends an Access Accept message to the AAA server containing the details of the BOD1MTIME service.
8.
The ISG sends an Access Request message to the billing server, notifying it that the subscriber has initiated the BOD1MTIME service.
9.
The billing server replies with an Access Accept message that authorizes the subscriber for a set quota of time.
10.
The ISG sends an Accounting Request to the billing server with the subscriber's username and an event time stamp.
11.
After the subscriber quota is depleted, the ISG sends a Reauthorization request to renew the quota.
12.
The billing server reauthorizes the subscriber and sends a renewed quota to the ISG.
Steps 12 and 13 are repeated until either the subscriber terminates the BOD1MTIME service or the subscriber runs out of quota on the billing server.
Model 2: Cisco 10000 Router as ISG with Multiservice Service Bundle
over PPPoEThis deployment scenario is similar to the Multiservice service bundle over PPPoE deployment for model 1, but with the following differences:
•
The ISG configuration is performed on a Cisco 10000 router.
•
The prepaid service is not configured for bandwidth on demand; instead, these services are paid for using postpaid via per-service accounting.
•
Model 2 uses Layer 2 ATM shaping for downstream traffic and the addition of upstream policing.
The following sections describe the deployment model that configures a Cisco 10000 router as an ISG with the multiservice service bundle over PPPoE:
Model 2 Network Topology
Figure 8 shows the network topology of this deployment.
Figure 8 Model 2 Network Topology

Model 2 Device List
Table 3 lists the devices used in the model 2 test network.
Model 2 Call Flow
Figure 9 shows the authenticated domain call flow used in this model.
Figure 9 Authenticated Domain Call Flow

Following is an explanation of the sequence of events in Figure 9:
1.
The call flow begins with the PPPoE Discovery phase as defined in RFC 2516. The session is initiated when an Access Request message from the client device is received. The Cisco BRAS is configured for auto-domain operation, and the Access Request message is not transparently forwarded to the local AAA server.
2.
The BRAS performs a service profile download for the selected auto-domain name using the globally configured service password. When the service profile is received, it is determined that the auto-domain service is a proxy service and that authentication should take place with the remote ISP AAA server. Authentication details are contained in the proxy service profile.
3.
The BRAS forwards the Access Request message originally received from the client device to the remote ISP AAA server. If authentication is successful, an Access Accept message is returned to BRAS, which may contain either an explicitly configured IP address or a locally valid IP pool name.
4.
Once the auto-domain service has been successfully activated, the BRAS sends an Access Accept message to the client device. If a service domain IP address has already been assigned to the session in the Access-Accept message from the remote ISP AAA server, this IP address is returned to the client device in attribute 8 of the Access Accept message.
5.
ISG software accounting starts after the Authentication Success is sent to the client. It is also possible that a Start Accounting message can be sent from the Client; however, this would be used to validate that the customer is actually active (up), and if the customer claims not to be, you can pull down the session. The Accounting Start Request message is sent by the client, and is transparently proxied to the AAA server.
6.
When the session is complete, the Client sends a PPPoE Terminate message that causes the BRAS to terminate the session.
Model 3: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG with Triple Play Plus
Service Bundle over IP and PPPoEIn network model 3, an ISP offers the Triple Play Plus service bundle, which consists of advanced services designed for gaming subscribers. The services include voice over IP (VoIP), broadcast video, and as prioritized traffic to the ISP's own gaming servers.
This deployment supports Transparent Autologin (TAL) based on the subscriber's MAC address, which requires that subscriber MAC addresses be configured manually. If MAC address-based authentication fails, subscribers are redirected to the web portal maintained by the Cisco SESM, where they can manually log in.
The following sections describe the deployment model that configures a Cisco 7200 ISG with the Triple Play Plus service bundle over IP and PPPoE:
Model 3 Network Topology
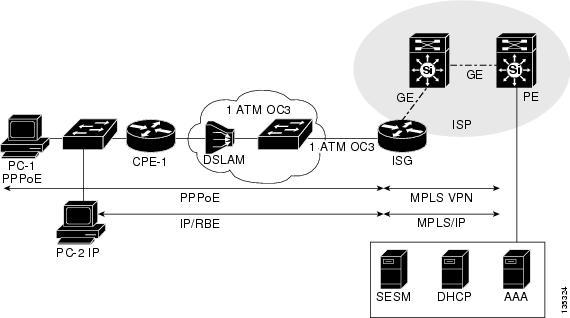
Figure 10 shows the topology of network model 3.
Figure 10 Model 3 Network Topology
Model 3 Device List
Table 4 lists the devices used in the model 3 test network. Note that either a Cisco 7206 or 7301 router can be used as the ISG.
Model 3 Protocol Flow
Figure 11 shows how traffic is routed across the network.
Figure 11 Model 3 Protocol Flow

Figure 12 shows the protocols that are active at each device in the network.
Figure 12 Model 3 Protocol Stack

Model 3 QoS Strategy
Figure 13 shows all of the interfaces in the network where QoS could potentially be configured. Here, "Up" refers to the upstream interface between the two devices, and "Dw" refers to the downstream interface. The interfaces shown are the points where QoS is configured for this deployment.
Figure 13 Model 3 QoS Interfaces

Table 5 describes the QoS strategy that is deployed on each of the interfaces shown in Figure 13.
Model 3 Call Flows
The following call flows describe the operation of the model 3 test network:
•
Basic Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for PPPoE Sessions
•
Basic Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for IP Sessions
Basic Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for PPPoE Sessions
For PPPoE sessions, the process of establishing basic Layer 3 VPN access is the same as the process for Model 1. For details of that process, see the "Basic Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for PPPoE Sessions" section.
Basic Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for IP Sessions
For IP sessions, the ISG architecture supports several methods of authenticating the user, which lead to multiple call flows. The authentication method used depends on whether or not the ISP configures the TAL feature. TAL enables the ISG to authenticate subscribers on the basis of either source IP address or MAC address.
When TAL is not enabled, subscribers are authenticated manually. When subscribers initiate a session, the ISG sends them to the Cisco SESM (using the Layer 4 Redirect feature). Subscribers then enter their usernames and passwords.
Figure 14 shows the call flow process of establishing basic Layer 3 VPN access for IP sessions with non-TAL authentication.
Figure 14 Non-TAL Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for IP Sessions

Following is an explanation of the sequence of events in Figure 14:
1.
The client sends a DHCPDISCOVER message to the ISG. The ISG then relays this message by sending a DHCPDISCOVER notify message to the DHCP server. The ISG creates the IP session upon receiving the DHCPDISCOVER message from the PC client.
2.
The DHCP server sends a DHCPOFFER message to the client.
3.
The client sends a DHCPREQUEST message to the DHCP server.
4.
The DHCP server assigns the client an IP address and sends it in a DHCPACK message to the client. The DHCP server sends an IP address update message to the ISG to notify it of the IP address allocation.
5.
The subscriber's port is now allowed to connect only over HTTP to an IP address for the Cisco SESM. Other HTTP requests are sent to the Cisco SESM by the Layer 4 Redirect feature. The subscriber then enters username and password information.
6.
The Cisco SESM sends the username and password to the ISG in an Access Request message.
7.
The ISG sends an Access Request message to the AAA server.
8.
The AAA server authenticates the subscriber and sends an Access Accept message to the ISG.
9.
The ISG sends an Access Accept message to the Cisco SESM, authorizing it to begin service for the subscriber.
10.
When the subscriber terminates the session, the client sends a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCP server.
11.
The DHCP server responds with a DHCPACK message.
12.
The ISG sends a Terminate Session message to the DHCP server, and the DHCP server confirms that the session is ended by sending a Session Stop message to the ISG.
Figure 15 shows the call flow process of establishing basic Layer 3 VPN access for IP sessions with TAL authentication.
Figure 15 TAL-Based Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for IP Sessions

Following is an explanation of the sequence of events in Figure 15:
1.
The client sends a DHCPDISCOVER message to the ISG.
2.
The ISG sends an Authorization Request to the AAA server.
3.
The AAA server performs TAL authentication based on either the clients' IP address or MAC address and sends an Authorization Reply message to the ISG.
4.
If the client is successfully authenticated, the ISG sends an Access Accept message to the Cisco SESM. If the client fails TAL authentication, the subscriber will be sent to the Cisco SESM by Layer 4 redirect to manually log in.
5.
The ISG relays the DHCPDISCOVER Notify message to the DHCP server. The ISG then creates an IP session.
6.
The DHCP server sends a DHCPOFFER message to the client.
7.
The client sends a DHCPREQUEST message to the DHCP server.
8.
The DHCP server assigns the client an IP address and sends it in a DHCPACK message to the client. The DHCP server sends an IP address update message to the ISG to notify it of the IP address allocation.
9.
When the subscriber terminates the session, the client sends a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCP server.
10.
The DHCP server responds with a DHCPACK message.
11.
The ISG sends a Terminate Session message to the DHCP server, and the DHCP server confirms that the session is ended by sending a Session Stop message to the ISG.
Model 4: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG LNS with Multiservice
Service BundleThe motivation for deploying this network is an ISP's desire to broaden the flexibility of its DSL deployments beyond traditional, static DSL service. Basic Layer 3 VPN access is established first. The following advanced ISG software services are then deployed:
•
Bandwidth on demand—Enables subscribers to temporarily increase their upstream and downstream bandwidths. This increased bandwidth can be charged to the subscriber's account on either a duration or a volume basis.
•
Prepaid services—Enables subscribers to purchase short-term DSL access, using either time or volume limits.

Note
In this deployment, subscribers will not be able to switch from a time-based prepaid service to a volume-based prepaid service or vice versa. Subscribers will have access to both time-based and volume-based services. This scenario is presented to describe the full range of ISG software services available. Typically, ISPs will only deploy either time-based or volume-based services for subscribers, but not both simultaneously.
The following sections describe the deployment model that configures a Cisco 7200 as ISG LNS with the Multiservice service bundle:
•
Basic Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow
Model 4 Network Topology
Figure 16 shows the topology of network model 4.
Figure 16 Model 4 Network Topology

Model 4 Device List
Table 6 describes devices used in the model 4 test network. Note that both a Cisco 7206 and 7301 can be used as an ISG LAC and LNS.
Table 6 Model 4 Device List
CPE
Cisco 837
LAC
Cisco 7206 or Cisco 7301
ISG LNS
Cisco 7206 or Cisco 7301
PE
Cisco 6509
Model 4 Protocol Flow
PPP is tunneled from the LAC to the ISG LNS. At the ISG LNS, the PPP session is terminated, and the encapsulated IP session is routed on through the ISP's network. The identity of the customer is uniquely maintained only by the PPP session. Figure 17 shows how the PPP session is routed across the network.
Figure 17 Model 4 Protocol Flow

Figure 18 shows the protocols that are active at each device in the network.
Figure 18 Model 4 Protocol Stack

Model 4 QoS Strategy
Figure 19 shows all of the interfaces in the network where QoS could potentially be configured, where "Up" refers to the upstream interface between the two devices, and "Dw" refers to the downstream interface. The interfaces shown are the points where QoS is configured for this deployment.
Figure 19 Model 4 QoS Interfaces
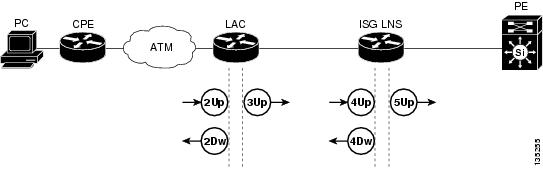
Table 7 describes the QoS strategy that is deployed on each of the interfaces shown in Figure 19.
Table 7 Model 4 QoS Strategy
2Up
LAC
CPE
LAC
Virtual circuit (VC) shaping parameters are defined by a domain profile on AAA-1 using the DBS feature.
2Dw
LAC
LAC
CPE
VC shaping parameters are defined by a domain profile on AAA-1 using the DBS feature.
3Up
LAC
LAC
ISG LNS
All traffic is reclassified as best effort DSCP is set to 0.
4Up
ISG LNS
LAC
ISG LNS
Multiple bandwidth-on-demand services are defined on AAA-2 using the QU attribute.1
4Dw
ISG LNS
ISG LNS
LAC
Multiple bandwidth-on-demand services are defined on AAA-2 using the QD attribute.
5Up
ISG LNS
ISG LNS
PE
Upstream traffic is marked as the default service, and the MPLS Experimental bit 0 by the service policy governing the outbound Gigabit Ethernet interface.
1 Attributes are listed in the Cisco SSG-to-ISG DSL Broadband Migration Guide.
Basic Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow
Figure 20 shows the call flow process of establishing basic Layer 3 VPN access. Each subscriber session begins with this process before initiating advanced ISG software services.
Figure 20 Layer 3 VPN Access Call Flow for the Cisco ISG LNS

Following is an explanation of the sequence of events in Figure 20:
1.
The subscriber initiates a PPPoE connection from the PC to the LAC by way of the CPE.
2.
The PC and the LAC establish a PPP connection.
3.
The LAC contacts the AAA-1 server to retrieve domain authentication information for L2TP.
4.
The LAC establishes an L2TP tunnel with the ISG LNS. This step is necessary only if an L2TP tunnel does not already exist.
5.
The LAC forwards the subscriber PPP session and associated information to the ISG LNS.
6.
The ISG LNS contacts the AAA-2 server to authenticate the subscriber. Once the subscriber is authenticated, the ISG LNS clones a virtual-access interface from the virtual template.
7.
The ISG LNS sends a Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) response to the subscriber. The IP Control Protocol (IPCP) negotiation is performed, and the route to the ISG LNS is installed. The PPP session now runs between the subscriber and the ISG LNS, while the ISG forwards the PPP traffic over the L2TP tunnel.
8.
The ISG LNS sends an Accounting Start message to the AAA-2 server.
9.
The subscriber and the ISG LNS use IPCP to negotiate the link details, including the IP address. IPCP is responsible for configuring, enabling, and disabling the IP protocol modules on both ends of the PPP link. IPCP uses the same packet exchange mechanism as the link control protocol (LCP). IPCP packets may not be exchanged until PPP has reached the Network-Layer Protocol phase.
Prepaid Service Call Flow
Figure 21 shows the call flow process that occurs when a subscriber initiates prepaid services.
Figure 21 Prepaid Services Call Flow for the Cisco ISG LNS

Following is an explanation of the sequence of events in Figure 21:
1.
The subscriber selects the BOD1MTIME service on the Cisco SESM web page dashboard.
2.
The Cisco SESM sends an Access Request message to the ISG LNS for the subscriber's information.
3.
The ISG LNS replies to the Cisco SESM with an Access Accept message containing the subscriber's information.
4.
The Cisco SESM sends an Access Request message to the ISG LNS requesting information on the BOD1MTIME service.
5.
The ISG LNS sends an Access Request message to the AAA-2 server requesting information on the BOD1MTIME service.
6.
The AAA-2 server replies to the ISG LNS with an Access Accept message containing the traffic class, the BOD1MTIME profile, and the prepaid configuration.
7.
The ISG LNS sends an Access Accept message to the AAA-2 server containing the details of the BOD1MTIME service.
8.
The ISG LNS sends an Access Request message to the billing server, notifying it that the subscriber has initiated the BOD1MTIME service.
9.
The billing server replies with an Access Accept message that authorizes the subscriber for a set quota of time.
10.
The ISG LNS sends an accounting request to the billing server with the subscriber's username and an event time stamp.
11.
When the subscriber quota is depleted, the ISG LNS sends a reauthorization request to renew the quota.
12.
The billing server reauthorizes the subscriber and sends a renewed quota to the ISG LNS.
Steps 8 through 12 are repeated until either the subscriber terminates the BOD1MTIME service or the subscriber runs out of quota on the billing server.
Prerequisites for Configuration
Before you use the configuration information in this document, you must be familiar with the following topics:
•
Basic Configuration Requirements
Basic Configuration Requirements
Before the networks described in this document are deployed, the following baseline network operations must be configured:
•
For models 1 and 2, basic PPPoE connection between PC clients and the ISG must be established.
•
For model 3, basic IP ATM RBE connectivity must be established between the PC and the ISG.
•
For model 4, L2TP must be configured between the ISG LAC and the LNS. The subscriber must also be able to establish a PPPoE connection over the L2TP tunnel to the LNS.
Network administrators should also be familiar with the topics listed in the "Additional References" section.
Configuration Passwords
As you read through the configurations in this document, you will come across several types of passwords that will be required, such as for the Cisco IOS, for the Cisco Access Registrar (CAR) and AAA RADIUS server, for the billing server, and so on. The configurations in this document use the word "cisco" frequently as a password. You will need to provide unique passwords for each of these areas in your network, and determine some secure method for identifying which passwords are associated with a particular service.
Vendor-Specific Attributes
The configurations in this document use RADIUS vendor-specific attributes. These attributes are described in the following Cisco documentation:
•
RADIUS Attribute-Value Pairs and Dictionary Management
•
RADIUS Vendor-Proprietary Attributes
•
"RADIUS Service and User Profile Attributes " in the Cisco SSG-to-ISG DSL Broadband Migration Guide
Table 8 summarizes the numeric definitions for some more commonly used RADIUS subattributes.

Note
The Command-Code string must be converted to hexadecimal in ISGs running Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(28)SB or earlier software. Also note that the attribute identifier is always 26, and the Cisco vendor identifier is always 9.
Model 1 Configuration: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG with Multiservice Service Bundle over PPPoE
Deployment model 1 was designed for the service provider that wants to expand traditional, static DSL service by deploying bandwidth on demand and prepaid services, which are part of the Multiservice service bundle. When customers activate these services, the network allocates additional bandwidth to them, based on either time or volume of bandwidth. The management of the available minutes is done via a billing server external to the ISG.
This network involves a single service provider. The DSLAM delivers traffic to the ISG using PPPoE. The ISG terminates PPPoE and routes the IP traffic through the ISP network. Subscriber identities are maintained through PPPoE authentication, and the uniqueness of the DSL line is maintained by a dedicated Layer 2 path to the ISG over an ATM PVC that is cross-connected to the subscriber at the DSLAM.
It is best if services are applied at the ISG. It is possible—but more difficult—to apply services at the DSLAM; however, the services at the DSLAM are not part of the PPP link.
The user's PC initiates a PPPoE session to the ISG across the ATM network. The CPE in this model is configured as a bridge. The ISG then forwards the subscriber session to the PE over an MPLS VPN. The PPPoE user profile pulled from the AAA server contains the VRF name, session-timeout value, idle-timeout, and default services assigned to this subscriber.
Figure 22 shows the basic devices that are configured for this model.
Figure 22 Basic Device Topology for Network Model 1

The following tasks are performed to deploy network model 1:
•
Configuring the ISG in Network Model 1
•
Configuring ISG Control Policies for Network Model 1
•
Configuring Profiles for Network Model 1
•
Configuring the CPE Bridge in Network Model 1
•
Configuring the PE in Network Model 1
Configuring the ISG in Network Model 1
The following configuration tasks are performed on the LNS:
•
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
•
Configuring PPPoE and the Connections to the CPE and PE
•
Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
•
Configuring Inbound and Outbound Access Lists
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
In this configuration, connections to the CAR AAA server, the Cisco SESM, and two billing servers are configured. Vendor-specific attribute (VSA) accounting and authentication are enabled, and the loopback interface 0 is used for AAA communications.
aaa new-model!! Configures the AAA server group for the CAR AAA server.aaa group server radius CAR_SERVERserver 10.100.2.36 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813!! Configures the AAA server group for the BILLING_SERVER billing server.aaa group server radius BILLING_SERVERserver 10.100.12.89 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646! Configures AAA for the CAR AAA server.aaa authentication login default noneaaa authentication ppp default group CAR_SERVER! Configures authentication for prepaid customers on the BILLING_SERVER billing server.aaa authentication ppp PREPAID_AUTHEN_LIST group BILLING_SERVERaaa authorization network default group CAR_SERVER! Configures authorization for prepaid customers on the BILLING_SERVER billing server.aaa authorization network PREPAID_AUTHOR_LIST group BILLING_SERVERaaa authorization subscriber-service default local group radiusaaa accounting network default start-stop group CAR_SERVER! Configures accounting for prepaid customers on the BILLING_SERVER billing server.aaa accounting network PREPAID_ACCNT_LIST start-stop group BILLING_SERVER! Configures the connection to the Cisco SESMaaa server radius sesmclient 10.100.4.38key ciscoport 1812message-authenticator ignore!! Loopback 0 is used for communicating with AAA, the billing servers, and SESM.interface Loopback0ip address 10.200.1.53 255.255.255.255! Instructs the router to use loopback 0 to communicate with the AAA RADIUS servers.ip radius source-interface Loopback0!! These RADIUS attributes are required for prepaid services.radius-server attribute 44 include-in-access-reqradius-server attribute 8 include-in-access-reqradius-server attribute 55 access-request includeradius-server attribute 25 access-request include! The CAR AAA server.radius-server host 10.100.1.35 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key cisco! The BILLING_SERVER billing server.radius-server host 10.100.12.89 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 key ciscoradius-server retransmit 5radius-server timeout 15radius-server vsa send accountingradius-server vsa send authenticationConfiguring PPPoE and the Connections to the CPE and PE
The ISG is configured to receive PPPoE sessions from the PC client by way of the DSLAM. A PPP local pool and MPLS VRF tables are created for incoming subscribers.
no ip dhcp use vrf connected!! Globally enables MPLS VRFs for incoming subscribers.ip vrf VPN10005rd 100:5route-target export 100:5route-target import 100:5!!ip cef!!! The BBA group method is used to configure PPPoE.bba-group pppoe BBA_LM_ATM5virtual-template 8sessions per-vc limit 1!! This virtual circuit (VC) class is applied to the ATM PVC.vc-class atm VC_LM_ATM8! Associates the VC class with the above bba-group.protocol pppoe group BBA_LM_ATM8! Enables dynamic bandwidth selection.dbs enable maximumencapsulation aal5snap!! Gigabit Ethernet interface 0/3 points to the PE.interface GigabitEthernet0/3ip address 10.40.1.53 255.255.255.0! The PBHK feature is enabled on this interface.ip portbundle outsideload-interval 30duplex fullspeed 1000media-type gbicnegotiation autompls mtu 1522mpls ipservice-policy output QOS_OUT_MPLS_UPLINKip rsvp bandwidth 100000!! ATM interface 1/0.105 points to the CPE.interface ATM1/0.105 point-to-pointdescription Deployment Model 3atm pppatm passiveno atm enable-ilmi-trappvc 105/45! The VC class is associated with the PVC.class-vc VC_LM_ATM8! This can be changed to restrict PPPoE sessions on the PVC.pppoe max-sessions 1!! PPPoE subscribers use this virtual template.interface Virtual-Template8description LM ATM8 PTA Subscriberno ip addressno peer default ip addressno keepaliveppp timeout authentication 100ppp timeout aaaload-interval 30ppp mtu adaptiveppp authentication chapservice-policy control RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8!! IP Pool that is assigned to PPPoE subscribers.ip local pool cpe3_pool-53-VPN10005 192.168.3.210 192.168.3.250! Loopback interface for PPPoE userinterface Loopback5ip vrf forwarding VPN10005ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.255Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
Basic ISG subscriber services are configured, including Layer 4 redirect to the Cisco SESM and the Port-Bundle Host Key (PBHK) feature. When the PBHK feature is enabled, TCP packets from subscribers are mapped to a local IP address for the ISG gateway and a range of ports. This mapping allows the portal to identify the ISG gateway from which the session originated.
! Configures the connection to the Cisco SESM for Layer 4 Redirect functionality.redirect server-group SESM_SERVER_GROUPserver ip 10.100.4.38 port 8080! Enables port bundle host key (PBHK) access to the Cisco SESM. Each loopback interface! can support up to 4031 bundles. If additional capacity is required, configure additional! loopback interfaces.ip portbundlematch access-list 135! The Loopback 0 interface is used to communicate with the Cisco SESM.source Loopback0!!! This command is enabled by default. It sets the number of rules that are displayed! in the show subscriber session detail command.subscriber policy recording rules limit 64Configuring Inbound and Outbound Access Lists
Basic access lists are configured to govern subscribers' Internet access, and an access list is created for the PBHK feature.

Note
To prevent revealing actual network addresses, the following configurations use IP addresses made up of letters instead of numbers.
! This access list is referenced in the AAA service profiles. It governs incoming! Internet traffic. The Internet access lists should prevent subscribers from accessing! the Cisco SESM and other management devices to help prevent denial-of-service attacks.!ip access-list extended INTERNET_IN_ACLdeny ip any 2XZ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XJ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XH.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XK.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XL.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XM.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XN.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XP.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XQ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XR.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any 10.200.0.0 0.0.255.255permit ip any any!! This access list is called out in the AAA subscriber profile. It governs outgoing! Internet traffic. The Internet access lists should prevent subscribers from accessing! the Cisco SESM and other management devices to help prevent denial-of-service attacks.!ip access-list extended INTERNET_OUT_ACLdeny ip 2XZ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip 10.200.0.0 0.0.255.255 anydeny ip XJ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XH.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XK.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XL.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XM.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XN.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XP.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XQ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XR.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anypermit ip any any!! The following access lists are used in the ip portbundle command configuration above.! They only permit traffic to the Cisco SESM.access-list 135 permit ip any host 10.100.4.38access-list 135 deny ip any any! The following access lists are used for L4REDIRECT SERVICESip access-list extended L4REDIRECT_IN_ACLpermit ip any anyip access-list extended L4REDIRECT_OUT_ACLpermit ip 10.100.0.0 0.0.255.255 anydeny ip any anyConfiguring ISG Control Policies for Network Model 1
The following configuration tasks are performed on the ISG to enable the time-based prepaid advanced ISG subscriber services (although volume-based prepaid services could also have been configured):
•
Configuring the Global Prepaid Services Configuration
•
Configuring the BOD1MTIME Service
•
Configuring the BOD2MTIME Service
Configuring the Global Prepaid Services Configuration
The global attributes of the prepaid services are configured for each of the two billing servers.
! This is the global configuration for the PREPAID_CONFIG prepaid billing server.subscriber feature prepaid PREPAID_CONFIGthreshold time 20 seconds! Specifies the size of the threshold the ISG requests from the billing server. The! threshold is an increment of the user's quota. When the threshold (in this case 1000! bytes) is exhausted, the ISG requests another 1000 bytes from the subscriber's account.! This continues until the subscriber terminates the session or the subscriber's account! is depleted.threshold volume 1000 bytesinterim-interval 3 minutes! References the authorization list in the above AAA configuration.method-list author PREPAID_AUTHOR_LIST! References the accounting list in the above AAA configuration.method-list accounting PREPAID_ACCNT_LIST! This is the prepaid password that is configured on the billing servers.password cisco
Note
If you configure only default values for a prepaid service, the configuration will not appear in show running-config command output, but the configuration will be active.
! This is the global configuration for the default prepaid service.subscriber feature prepaid defaultthreshold time 20 seconds! The quota size for this service is set at 200 bytes.threshold volume 200 bytesinterim-interval 3 minutesmethod-list author defaultmethod-list accounting defaultpassword cisco!! This command is enabled by default. It sets the number of rules that are displayed in! the show subscriber session detail command.subscriber policy recording rules limit 64subscriber authorization enable! Creates the policy map that is used for time based service.policy-map type control RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8! When a session is initiated, PBHK is applied and the subscriber is redirected to the! Cisco SESM to select a service.class type control always event session-start1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICE2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE!! The quota-depleted event is triggered when either a prepaid threshold is not configured,! or if the quota is depleted before the billing server replenishes the quota.class type control always event quota-depleted! Specifies that traffic won't be dropped when the quota is depleted.1 set-param drop-traffic FALSE!! The credit-exhausted event is triggered when the subscriber's account is empty.class type control always event credit-exhausted! Redirects subscriber's whose accounts are depleted to the Cisco SESM.1 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE!
Note
The specific bandwidths described in this document are used only as examples. ISPs are free to configure any bandwidth levels that their service requires.
Configuring the BOD1MTIME Service
For each of the additional services to be configured, a control class map is configured to define matching conditions used by the policy map to trigger events that start and stop the service.
! This control class map defines the BOD1MTIME_CLASS service.class-map type control match-all BOD1MTIME_CLASSmatch service-name BOD1MTIME!! When subscribers start the service, the other services are unapplied.policy-map control RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8class type control BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service-start1 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD1MTIME_CLASS3 service-policy type service identifier service-name! When subscribers stop the service, it is unapplied, and Layer 4 redirect is applied to! redirect the subscriber to the Cisco SESM.class type control BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service-stop1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-name2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEConfiguring the BOD2MTIME Service
The same method used for BOD1MTIME is used to configure the BOD2MTIME service.
class-map type control match-all BOD2MTIME_CLASSmatch service-name BOD2MTIME!
policy-map type control RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8class type control BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service-start1 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD1MTIME3 service-policy type service identifier service-name!class type control BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service-stop1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-name2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEConfiguring Profiles for Network Model 1
The following configuration tasks are performed on the AAA server:
•
Configuring the Time-Based ISG Subscriber Services
•
Configuring User Profiles for Time-Based Customers
Configuring the Time-Based ISG Subscriber Services
The following profile specifies the details of the BOD1MTIME service. For all of the ISG software services, a priority level must be configured in order for the Layer 4 Redirect feature to work properly. When the subscriber's credit is exhausted, the Layer 4 Redirect feature (BOD1MTIME in this configuration) is added to the subscriber's existing service, but it will not be applied if the priority levels are not configured.
[ BOD1MTIME/Attributes ]! All of the user-selectable services are given the priority level 10.Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name INTERNET_IN_ACL priority 10"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name INTERNET_OUT_ACL priority 10"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-AVPair = subscriber:accounting-list=PREPAID_ACCNT_LISTCisco-AVPair = prepaid-config=PREPAID_CONFIGCisco-AVPair = atm:peak-cell-rate=1024Cisco-AVPair = atm:sustainable-cell-rate=1024! The I attribute tells the Cisco SESM that the name of this service is! BOD1MTIME.Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IBOD1MTIME! The R attribute is required in service profiles for compatibility with SSG,! to define subscriber services that will be displayed in the SESM web page.Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0The following profile specifies the details of the BOD2MTIME service:
[ BOD2MTIME/Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name INTERNET_IN_ACL priority 10"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name INTERNET_OUT_ACL priority 10"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-AVPair = subscriber:accounting-list=PREPAID_ACCNT_LISTCisco-AVPair = prepaid-config=PREPAID_CONFIGCisco-AVPair = atm:peak-cell-rate=2048Cisco-AVPair = atm:sustainable-cell-rate=2048Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IBOD2MTIMECisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0Configuring Layer 4 Redirect
This attribute enables the Layer 4 Redirect feature.
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SERVICES/L4REDIRECT_SERVICE/Attributes ]! The Layer 4 Redirect feature is given the priority level 5, which is a higher priority! than the user-selectable features. This ensures that subscribers are redirected when! their accounts are exhausted.Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:l4redirect=redirect to group SESM_SERVER_GROUP"Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IL4REDIRECT_SERVICEConfiguring PBHK
This profile enables the PBHK feature on the AAA server, which enables access to the SESM by way of the PBHK feature.
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SERVICES/PBHK_SERVICE/Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = ip:portbundle=enable! The I attribute tells the Cisco SESM that the name of this service is! PBHK_SERVICE. Nonsubscriber services such as PBHK are defined only on the ISG itself! and not displayed in the SESM service selection web page, and so are defined in a! service profile without the R attribute.Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IPBHK_SERVICEConfiguring User Profiles for Time-Based Customers
The following profile configures a user profile for time-based customers:
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/ie2-C7206-ATM/C72_DM2_3640/Attributes ]Cisco-AVpair = ip:vrf-id=VPN10005Cisco-AVpair = "ip:ip-unnumbered=loopback 5"Cisco-AVpair = ip:addr-pool=cpe3_pool-53-VPN10005! The N attribute at the beginning of the two Account-Info scripts specifies that these! are services that customers can activate. Time-based subscribers are authorized to! access the BOD1MTIME and BOD2MTTIME services.Cisco-SSG-Account-Info = NBOD1MTIMECisco-SSG-Account-Info = NBOD2MTIMEidle-timeout = 1800session-timeout = 18000Configuring the CPE Bridge in Network Model 1
The following bridge configuration establishes basic connectivity across the network and enables the user to establish basic Layer 3 VPN access:
no aaa new-modelip subnet-zerono ip domain lookup!!ip audit notify logip audit po max-events 100no ftp-server write-enable!interface Ethernet0no ip addressbridge-group 1hold-queue 100 out!interface ATM0no ip addressno atm ilmi-keepalivedsl operating-mode auto!interface ATM0.5 multipointpvc 5/45encapsulation aal5snap!bridge-group 1!interface FastEthernet1no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet2no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet3no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet4no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!ip classless!ip http serverno ip http secure-server!bridge 1 protocol ieeeConfiguring the PE in Network Model 1
The following basic configuration is required for all of the deployment models. The PE is configured to assign subscribers to a VRF, and then to allow users to access the Cisco SESM.
! Configures the VRF to which subscribers are assigned.ip vrf VPN10005rd 100:5route-target export 100:5route-target import 100:5!!router bgp 100no synchronizationbgp router-id 10.200.1.45bgp log-neighbor-changesredistribute connectedredistribute staticneighbor 10.200.1.41 remote-as 100neighbor 10.200.1.41 update-source Loopback0no auto-summary!!! Allows VRF routes into the BGP routing table.address-family ipv4 vrf VPN10005redistribute connectedredistribute staticno auto-summaryno synchronizationnetwork 10.44.103.0 mask 255.255.255.0aggregate-address 10.44.103.0 255.255.255.0 summary-onlyexit-address-family!!! Redistributes a route for subscribers in VRF VPN10005 from the global routing table into! the VRF routing domain. This route is used for subscribers to access the Cisco SESM.! This command is only necessary when the PBHK feature is enabled.ip route vrf VPN10005 10.100.3.34 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet3/14 10.100.3.34Model 2 Configuration: Cisco 10000 Router as ISG with Multiservice Service Bundle over PPPoE
Deployment model 2 provides DSL subscribers with bandwidth on demand defined in the multiservice service bundle over PPPoE. In this scenario, the ISP wants to provide a means for the customer to request temporary bandwidth increase. A customer with 512 kbps of network bandwidth downstream, for example, can request a temporary bandwidth increase of up to 2 Mbps. Figure 23 shows the basic devices that are configured for this deployment.
Figure 23 Basic Device Topology for Network Model 2

The following tasks are performed to deploy network model 2:
•
Configuring the ISG in Network Model 2
•
Configuring ISG Control Policies for Network Model 2
•
Configuring Profiles for Network Model 2
•
Configuring the CPE Bridge in Network Model 2
•
Configuring the PE in Network Model 2
Configuring the ISG in Network Model 2
The following tasks are performed to configure the ISG:
•
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
•
Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
•
Configuring PPPoE and the Connections to the CPE and PE
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
Following is a basic AAA configuration, including connection to the RADIUS server:
aaa new-model!!! Configures the connection to the AAA server and identifies it as CAR_SERVERaaa group server radius CAR_SERVERserver 10.100.1.35 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813!aaa group server radius CAR_SERVER_C10Kserver 10.100.100.179 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813!aaa authentication login default noneaaa authentication login IP_AUTHEN_LIST group CAR_SERVER_C10Kaaa authentication ppp default group CAR_SERVER_C10Kaaa authentication ppp PPP_USER_LIST group CAR_SERVER_C10Kaaa authorization network default group CAR_SERVER_C10Kaaa authorization subscriber-service default local group CAR_SERVER_C10Kaaa accounting update periodic 1aaa accounting network default start-stop group CAR_SERVER_C10Kaaa accounting network CAR_ACCNT_LIST start-stop group CAR_SERVER_C10K!aaa server radius sesmclient 10.100.3.34client 10.100.100.178key ciscoport 1812message-authenticator ignoreConfiguring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
The following configurations enable PBHK access to the Cisco SESM. Each loopback interface can support up to 4032 bundles. If additional capacity is required, configure additional loopback interfaces.
ip portbundlesource Loopback0match access-list 198! The Loopback 0 interface is used to communicate with the Cisco SESM.interface Loopback0ip address 10.200.1.54 255.255.255.255! Assigns the port bundle to the uplink interfaceinterface GigabitEthernet8/0/0ip portbundle outside! Configures the access lists for PBHKaccess-list 198 permit ip any host 10.100.3.34access-list 198 deny ip any any! Configures the access lists for BOD servicesaccess-list extended INTERNET_IN_ACLpermit ip any anyip access-list extended INTERNET_OUT_ACLpermit ip any anyConfiguring PPPoE and the Connections to the CPE and PE
The following configuration shows how the broadband bba-group method is used to configure PPPoE. The virtual circuit class is applied to the ATM PVC.

Note
To prevent revealing actual network addresses, the following configurations use IP addresses made up of letters instead of numbers.
bba-group pppoe BBA_LM_ATM1virtual-template 1!!vc-class atm VC_LM_ATM1! Associates the VC class with the above bba-group.protocol pppoe group BBA_LM_ATM1vbr-nrt 256 128 50! Enables dynamic bandwidth selection.dbs enable maximumencapsulation aal5snapweight 10interface ATM1/0/0no ip addressatm over-subscription-factor 50atm pvp 110 10000 cdvt 1400!interface ATM1/0/0.53 point-to-pointpvc 110/53class-vc VC_LM_ATM1! Defines PPPoE IP address poolip local pool C10K_POOL X.2.0.1 X.2.0.254! Defines loopback address for PPPoE subscribersinterface Loopback53ip vrf forwarding 10kvpn1ip address 10.53.53.1 255.255.255.0Configuring ISG Control Policies for Network Model 2
The following sections provide configurations of control and policy class maps:
•
Configuring Control Class Maps
•
Configuring a Virtual Template Interface and Assigning Control Policy
Configuring Control Class Maps
Before configuring services, first define each service by creating a control class map. Then configure instructions on how to start and stop the service as class controls. The following configuration shows control class maps for each of the services defined for deployment model 2:
class-map type control match-all BOD1M_CLASS_LM1match service-name BOD1M_LM1!class-map type control match-all BOD2M_CLASS_LM1match service-name BOD2M_LM1!class-map type control match-all DEFAULT_CLASS_LM1match service-name DEFAULT_BW_512!Configuring a Control Policy
The following configuration shows the control policies that are configured for model 2:
policy-map type control RULE_LM_ATM1class type control BOD1M_CLASS_LM1 event service-start1 service-policy type service unapply name BOD2M_LM12 service-policy type service unapply name DEFAULT_BW_5123 service-policy type service identifier service-name!class type control BOD2M_CLASS_LM1 event service-start1 service-policy type service unapply name BOD1M_LM12 service-policy type service unapply name DEFAULT_BW_5123 service-policy type service identifier service-name!class type control DEFAULT_CLASS_LM1 event service-start1 service-policy type service unapply name BOD1M_LM12 service-policy type service unapply name BOD2M_LM13 service-policy type service identifier service-name!class type control BOD1M_CLASS_LM1 event service-stop1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-name2 service-policy type service name DEFAULT_BW_512!class type control BOD2M_CLASS_LM1 event service-stop1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-name2 service-policy type service name DEFAULT_BW_512!class type control always event session-start1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICE2 collect identifier unauthenticated-domain3 authorize aaa password lab identifier unauthenticated-domainConfiguring a Virtual Template Interface and Assigning Control Policy
The following configuration shows how the ISG control policy map RULE_LM_ATM1 is used to instruct PPP to authenticate on the basis of domain name:
interface Virtual-Template1no ip addressno peer default ip addressno keepalive! PPP CHAP authentication is used on the virtual template.ppp authentication chapppp ipcp address uniqueservice-policy type control RULE_LM_ATM1Configuring Profiles for Network Model 2
The following sections provide configurations of domain, user, and service profiles created on a AAA server for deployment model 2:
•
Configuring PPPoE User Profiles
•
Creating the PBHK Service Profile
•
Configuring the BOD Service Profiles
Configuring a Domain Profile
The following policies will capture the unauthenticated domain name and authenticate users on the basis of the domain name. The domain profile points to a AAA method list to perform full username authentication.
Name = 10kvpn1Attributes/Cisco-AVpair = "subscriber:policy-directive=authenticate aaa list PPP_USER_LIST" CheckItems/Configuring PPPoE User Profiles
The following attributes are used to create the PPPoE RADIUS user profile:
Name = ftc101_user1@10kvpn1Attributes/Cisco-AVpair = "ip:ip-unnumbered=loopback 53"Cisco-AVpair = ip:addr-pool=C10K_POOLCisco-AVpair = ip:vrf-id=10kvpn1Cisco-SSG-Account-Info = ADEFAULT_BW_512Cisco-SSG-Account-Info = NDEFAULT_BW_512Cisco-SSG-Account-Info = NBOD1M_LM1Cisco-SSG-Account-Info = NBOD2M_LM1idle-timeout = 1800session-timeout = 180000Creating the PBHK Service Profile
The following attributes create the PBHK service profile in the CAR/AAA server:
Name = PBHK_SERVICEAttributes/Cisco-AVPair = ip:portbundle=enableCisco-SSG-Service-Info = IPBHK_SERVICEConfiguring the BOD Service Profiles
The following attributes create the profile that provides the temporary bandwidth increase for subscribers:
Name = SESM-SERVICESDescription =BOD1M_LM1/Name = BOD1M_LM1Attributes/Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name INTERNET_IN_ACL priority 10"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name INTERNET_OUT_ACL priority 10"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-AVPair = subscriber:accounting-list=CAR_ACCNT_LISTCisco-AVPair = atm:peak-cell-rate=1024Cisco-AVPair = atm:sustainable-cell-rate=1024Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IBOD1M_LM1Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = QU;512000;256000Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0CheckItems/BOD2M_LM1/Attributes/Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name INTERNET_IN_ACL priority 10"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name INTERNET_OUT_ACL priority 10"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-AVPair = subscriber:accounting-list=CAR_ACCNT_LISTCisco-AVPair = atm:peak-cell-rate=2048Cisco-AVPair = atm:sustainable-cell-rate=2048Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IBOD2M_LM1Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = QU;1024000;512000Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0CheckItems/DEFAULT_BW_512/Name = DEFAULT_BW_512Attributes/Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name INTERNET_IN_ACL priority 10"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name INTERNET_OUT_ACL priority 10"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-AVPair = subscriber:accounting-list=CAR_ACCNT_LISTCisco-AVPair = atm:peak-cell-rate=512Cisco-AVPair = atm:sustainable-cell-rate=512Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IDEFAULT_BW_512Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = QU;512000;256000Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0CheckItems/Configuring the CPE Bridge in Network Model 2
Following is the configuration of the CPE bridge:
no aaa new-modelip subnet-zerono ip domain lookup!!ip audit notify logip audit po max-events 100no ftp-server write-enable!interface Ethernet0no ip addressbridge-group 1hold-queue 100 out!interface ATM0no ip addressno atm ilmi-keepalivedsl operating-mode auto!interface ATM0.10 multipointpvc 10/53encapsulation aal5snap!bridge-group 1!interface FastEthernet1no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet2no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet3no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet4no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!ip classless!ip http serverno ip http secure-server!bridge 1 protocol ieee!Configuring the PE in Network Model 2
The PE is configured to assign subscribers to a VRF and to allow subscribers to access the Cisco SESM.
ip vrf 10kvpn1rd 200:1route-target export 200:1route-target import 200:1router bgp 100no synchronizationbgp router-id 10.200.1.45bgp log-neighbor-changesneighbor 10.200.1.41 remote-as 100neighbor 10.200.1.41 update-sourceLoopback0no auto-summary!! Enables BGP VPNv4 neighbors.address-family vpnv4neighbor 10.200.1.41 activateneighbor 10.200.1.41 send-community bothexit-address-family!! Allows VRF routes into the BGP routing table.address-family ipv4 vrf 10kvpn1redistribute connectedno auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-family!Model 3 Configuration: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG with Triple Play Plus Service Bundle over IP and PPPoE
Deployment model 3 involves a single ISP. In this deployment, two peering IP interfaces are configured between the CPE and the ISG: one for IP connections and one for PPPoE connections. This configuration allows all subscribers to use PPPoE for data traffic, regardless of whether they are subscribing to the basic service or to the triple-play package. This dual-purpose approach eases support and conversion issues and allows the ISP to gradually convert to a full IP routed scheme.
Figure 24 shows the basic devices that are configured for this deployment.
Figure 24 Basic Device Topology for Network Model 3

The following tasks are performed to deploy network model 3:
•
Configuring the ISG in Network Model 3
•
Configuring Profiles for Network Model 3
•
Configuring the CPE Bridge in Network Model 3
•
Configuring the PE in Network Model 3
Configuring the ISG in Network Model 3
The following baseline configuration tasks are performed on the ISG:
•
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
•
Configuring PPPoE and the Connections to the CPE and PE
•
Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
•
Configuring Inbound and Outbound Access Lists
•
Configuring QoS for Triple Play Plus
•
Configuring Triple Play Plus Access Lists
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
In this AAA configuration, connections to the CAR AAA server, the Cisco SESM, and two billing servers are configured. VSA accounting and authentication are enabled, and the loopback interface 0 is used for AAA communications.
aaa new-model!! Configures the AAA server group for the CAR AAA server.aaa group server radius CAR_SERVERserver 10.100.2.36 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813!! Configures AAA for the CAR AAA server.aaa authentication login default noneaaa authentication login IP_AUTHEN_LIST group CAR_SERVERaaa authentication ppp default group CAR_SERVER! Configures the connection to the Cisco SESMaaa server radius sesmclient 10.100.4.38key ciscoport 1812message-authenticator ignore!! Loopback 0 is used for communicating with AAA, the billing servers, and SESM.interface Loopback0ip address 10.200.1.53 255.255.255.255! Instructs the router to use loopback 0 to communicate with the AAA RADIUS servers.ip radius source-interface Loopback0!! The CAR AAA server.radius-server host 10.100.1.35 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key ciscoradius-server retransmit 5radius-server timeout 15radius-server vsa send accountingradius-server vsa send authenticationConfiguring PPPoE and the Connections to the CPE and PE
The ISG is configured to receive PPPoE sessions from the CPE by way of the DSLAM, and MPLS VRF tables are created for incoming subscribers.
no ip dhcp use vrf connected!! Globally enables MPLS VRFs for incoming subscribers.ip vrf VPN10003rd 100:3route-target export 100:3route-target import 100:3!ip cef!!! The BBA group method is used to configure PPPoE.bba-group pppoe BBA_LM_ATM2virtual-template 2!! This virtual circuit (VC) class is applied to the ATM PVC.vc-class atm VC_LM_ATM2! Associates the VC class with the above bba-group.protocol pppoe group BBA_LM_ATM2! Enables dynamic bandwidth selection.dbs enable maximumencapsulation aal5snapservice-policy control RULE_PTA_LM_ATM2!! Gigabit Ethernet interface 0/3 points to the PE.interface GigabitEthernet0/3ip address 10.40.1.53 255.255.255.0! The PBHK feature is enabled on this interface.ip portbundle outsideload-interval 30duplex fullspeed 1000media-type gbicnegotiation autompls mtu 1522mpls ipservice-policy output QOS_OUT_MPLS_UPLINKip rsvp bandwidth 100000!! ATM interface 1/0.103 points to the CPE.interface ATM1/0.103 point-to-pointip unnumbered Loopback3ip verify unicast reverse-pathip helper-address 10.100.1.37no ip redirectsno ip unreachablesno ip proxy-arpip subscriberinitiator dhcpatm route-bridged ipno atm enable-ilmi-trapntp disablepvc 103/43! The VC class is associated with the PVC.class-vc VC_LM_ATM2service-policy input QOS_IN_LM_ATM2service-policy output QOS_OUT_LM_ATM2service-policy control RULE_IP_LM_ATM2!! PPPoE subscribers use this virtual template.interface Virtual-Template2description LM ATM2 PTA Subscriberno ip addressno peer default ip addressno keepaliveppp authentication chapppp timeout authentication 100ppp timeout aaa!! The PPPoE pool that is assigned to subscribers.ip local pool cpe3_pool-53 192.168.3.2 192.168.3.100Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
The baseline ISG software services, Layer 4 redirect, ISG software authentication methods, and PBHK are configured. When the PBHK feature is enabled, TCP packets from subscribers are mapped to a local IP address for the ISG gateway and a range of ports. This mapping allows the portal to identify the ISG gateway from which the session originated.
! Configures the connection to the Cisco SESM for Layer 4 Redirect functionality.redirect server-group SESM_SERVER_GROUPserver ip 10.100.3.34 port 8080!! This policy map governs authentication.policy-map control RULE_IP_LM_ATM2! Unauthenticated traffic is dropped after the timer expires.class control IP_UNAUTH_COND event timed-policy-expiry1 service disconnect!class control always event session-start! PBHK must be applied before authorization, because if subscribers are authorized first,! ISG software will skip the remaining steps and PBHK won't be applied.1 service-policy service name PBHK_SERVICE! Authorizes subscribers based on their MAC address. If authorization is successful, the! remaining steps are skipped.2 authorize aaa password lab identifier mac-address! If authorization fails, subscribers are redirected to the Cisco SESM.3 service-policy service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE! When users are redirected, the IP_UNAUTH_TIMER gives them 5 minutes to manually! authenticate at the Cisco SESM before the session is dropped.4 set-timer IP_UNAUTH_TIMER 5!class control always event account-logon! Authorization is performed based on the IP_AUTHEN_LIST.1 authenticate aaa list IP_AUTHEN_LIST! If authorization fails, users are redirected to the Cisco SESM.2 service-policy service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE!!policy-map control RULE_PTA_LM_ATM2class control always event session-start1 service-policy service name PBHK_SERVICE!!! Enables port bundle host key (PBHK) access to the Cisco SESM. Each loopback interface! can support up to 4031 bundles. If additional capacity is required, configure additional! loopback interfaces.ip portbundlematch access-list 135! The Loopback 0 interface is used to communicate with the Cisco SESM.source Loopback0!! This class map specifies that a timer is initiated for unauthenticated sessions. If the! subscriber does not authenticate before the timer expires, the session is dropped.class-map control match-all IP_UNAUTH_CONDmatch timer IP_UNAUTH_TIMERmatch authen-status unauthenticatedConfiguring Inbound and Outbound Access Lists
Basic access lists are configured to govern subscribers' Internet access, and an access list is created for the PBHK feature.

Note
To prevent revealing actual network addresses, the following configurations use IP addresses made up of letters instead of numbers.
! This access list is referenced in the AAA subscriber profile. It governs incoming! Internet traffic. The Internet access lists should prevent subscribers from accessing! the Cisco SESM and other management devices to help prevent denial-of-service attacks.!ip access-list extended Internet-in-acldeny ip any 2XZ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XJ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XH.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XK.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XL.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XM.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XN.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XP.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XQ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XR.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any 10.200.0.0 0.0.255.255permit ip any any!! The following access list is called out in the AAA subscriber profile. It! governs outgoing Internet traffic. The Internet access lists should prevent! subscribers from accessing the Cisco SESM and other management devices to! help prevent denial-of-service attacks.!ip access-list extended Internet-out-acldeny ip 2XZ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip 10.200.0.0 0.0.255.255 anydeny ip XJ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XH.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XK.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XL.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XM.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XN.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XP.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XQ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XR.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anypermit ip any any!! This access list is used in the ip portbundle configuration above.access-list 135 permit ip any host 10.100.4.38access-list 135 deny ip any anyConfiguring QoS for Triple Play Plus
The Triple Play Plus service bundle is configured by specifying different levels of QoS for each of the user-selectable services. Three DSCP levels are configured: gaming, call control, and voice. The video-on-demand service uses the same DSCP as the voice service. Policy maps are then used to apply this QoS configuration to the inbound and outbound interfaces.
! These class maps specify the various DSCP levels.class-map match-any QOS_GROUP_CALL_CONTROLmatch qos-group 2class-map match-any GAMINGmatch ip dscp af21class-map match-any QOS_GROUP_GAMINGmatch qos-group 3class-map match-any CALL_CONTROLmatch ip dscp cs3class-map match-any QOS_GROUP_VOICEmatch qos-group 1class-map match-any VOICEmatch ip dscp ef!!! This policy map governs QoS for the outbound interface to the CPE.policy-map QOS_OUT_LM_ATM2class VOICEpriority 128class CALL_CONTROLbandwidth percent 5class GAMINGbandwidth percent 20! This policy map governs QoS for the outbound interface to the PE.policy-map QOS_OUT_MPLS_UPLINKclass QOS_GROUP_VOICEset mpls experimental topmost 5class QOS_GROUP_CALL_CONTROLset mpls experimental topmost 3class QOS_GROUP_GAMINGset mpls experimental topmost 2class class-defaultset mpls experimental topmost 0! This policy map governs QoS for the inbound interface from the CPE.policy-map QOS_IN_LM_ATM2class VOICE! Caps bandwidth for VoIP and VoD traffic at 128 kbps.police cir 128000exceed-action dropset qos-group 1class CALL_CONTROL! Caps bandwidth for call control traffic at 12.5 kbps.police cir 12500exceed-action dropset qos-group 2class GAMING! Caps bandwidth for gaming traffic at 75 kbps.police cir 75000exceed-action dropset qos-group 3! This policy map governs QoS for the default service.policy-map QOS_IN_LM_ATM2_256Kclass class-default! Caps bandwidth for basic connectivity traffic at 256 kbps.police cir 256000exceed-action dropset qos-group 1service-policy QOS_IN_LM_ATM2Configuring Triple Play Plus Access Lists
The following access lists govern the access of subscribers who have activated the various services:
! The gaming access lists allow gaming subscribers to access only the gaming server.ip access-list extended GAMING_IN_ACLpermit ip any 10.47.0.0 0.0.255.255deny ip any anyip access-list extended GAMING_OUT_ACLpermit ip 10.47.0.0 0.0.255.255 anydeny ip any any! The opengarden access lists govern the access of users who have not activated an! advanced service.ip access-list extended OPENGARDEN_IN_ACLpermit ip any 10.100.0.0 0.0.255.255permit ip any 10.48.0.0 0.0.255.255permit ip any 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255ip access-list extended OPENGARDEN_OUT_ACLpermit ip 10.100.0.0 0.0.255.255 anypermit ip 10.48.0.0 0.0.255.255 anypermit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 anyip access-list extended SESM-in-aclpermit ip any host 10.100.3.34deny ip any anyip access-list extended SESM-out-aclpermit ip host 10.100.3.34 anydeny ip any any! The VoD access lists allow VoD subscribers to access only the VoD server.ip access-list extended VOD_IN_ACLpermit ip any 10.46.0.0 0.0.255.255deny ip any anyip access-list extended VOD_OUT_ACLpermit ip 10.46.0.0 0.0.255.255 anydeny ip any any! The VoIP access lists allow VoIP subscribers to access only the VoD server.ip access-list extended VOIP_IN_ACLpermit ip any 10.45.0.0 0.0.255.255deny ip any anyip access-list extended VOIP_OUT_ACLpermit ip 10.45.0.0 0.0.255.255 anydeny ip any anyConfiguring Profiles for Network Model 3
The following configuration tasks are performed on the AAA server:
Configuring Layer 4 Redirect
This attribute enables the Layer 4 Redirect feature.
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SERVICES/L4REDIRECT_SERVICE/Attributes ]! The Layer 4 Redirect feature is given the priority level 5, which is a higher priority! than the user-selectable features. This ensures that subscribers are redirected when! their accounts are exhausted.Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:l4redirect=redirect to group SESM_SERVER_GROUP"Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IL4REDIRECT_SERVICEConfiguring PBHK
This profile enables the PBHK feature on the AAA server, which enables access to the SESM by way of the PBHK feature.
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SERVICES/PBHK_SERVICE/Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = ip:portbundle=enable! The I attribute tells the Cisco SESM that the name of this service is named! "PBHK_SERVICE". Nonsubscriber services such as PBHK are defined only on the ISG itself! and not displayed in the SESM service selection web page, and so are defined in a! service profile without the R attribute.Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IPBHK_SERVICEConfiguring Service Profiles
The following service profile enables the GAMING_SERVICE service:
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SERVICES/GAMING_SERVICE/Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name GAMING_IN_ACL"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name GAMING_OUT_ACL"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"! The "I" in the attribute tells the Cisco SESM that the name of this service is! "IGAMING_SERVICE".Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IGAMING_SERVICE! The R attribute is required in service profiles for compatibility with SSG,! to define subscriber services that will be displayed in the SESM web page.Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0The following service profile enables the OPENGARDEN_SERVICE service. The term Open garden is from an SSG feature that provides default service and basic Internet access.
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SERVICES/OPENGARDEN_SERVICE/Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name OPENGARDEN_IN_ACL"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name OPENGARDEN_OUT_ACL"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IOPENGARDEN_SERVICEThe following service profile enables the VOIP_SERVICE service:
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SERVICES/VOIP_SERVICE/Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name VOIP_IN_ACL"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name VOIP_OUT_ACL"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IVOIP_SERVICECisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0The following service profile enables the VOD_SERVICE service:
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SERVICES/VOD_SERVICE/Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name VOD_IN_ACL"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name VOD_OUT_ACL"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IVOD_SERVICECisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0The following service profile enables the INTERNET_SERVICE service. Subscribers select this service to return to the default service, basic Internet access.
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SERVICES/INTERNET_SERVICE/Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = ip:inacl=Internet-in-aclCisco-AVPair = ip:outacl=Internet-out-aclCisco-SSG-Service-Info = IINTERNET_SERVICECisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0Configuring User Profiles
The following user profile is for IP sessions that use MAC address-based TAL:
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/ie2-C7206-ATM/0000.1001.1014/Attributes ]Cisco-SSG-Account-Info = AOPENGARDEN_SERVICECisco-SSG-Account-Info = AVOIP_SERVICECisco-SSG-Account-Info = AVOD_SERVICECisco-SSG-Account-Info = AGAMING_SERVICEThe following user profile is for PPPoE users:
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/ie2-C7206-ATM/C72_DM3_1188/Attributes ]Cisco-AVpair = ip:vrf-id=VPN_C72_DM3_2038Cisco-AVpair = "ip:ip-unnumbered=loopback 2001"Cisco-AVpair = ip:addr-pool=C72_DM3_2001Cisco-SSG-Account-Info = AINTERNET_SERVICEConfiguring the CPE Bridge in Network Model 3
The following configuration establishes basic connectivity across the network and enables the user to establish basic Layer 3 VPN access:
no aaa new-modelip subnet-zerono ip domain lookup!!ip audit notify logip audit po max-events 100no ftp-server write-enable!interface Ethernet0no ip addressbridge-group 1hold-queue 100 out!interface ATM0no ip addressno atm ilmi-keepalivedsl operating-mode auto!interface ATM0.5 multipointpvc 5/43encapsulation aal5snap!bridge-group 1!interface FastEthernet1no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet2no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet3no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet4no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!ip classless!ip http serverno ip http secure-server!bridge 1 protocol ieeeConfiguring the PE in Network Model 3
The following basic configuration is required for all deployment models. The PE is configured to assign subscribers to a VRF and to allow users to access the Cisco SESM.
! Configures the VRF to which subscribers are assigned.ip vrf VPN10003rd 100:3route-target export 100:3route-target import 100:3!!router bgp 100no synchronizationbgp router-id 10.200.1.45bgp log-neighbor-changesredistribute connectedredistribute staticneighbor 10.200.1.41 remote-as 100neighbor 10.200.1.41 update-source Loopback0no auto-summary!!! Allows VRF routes into the BGP routing table.address-family ipv4 vrf VPN10003redistribute connectedredistribute staticno auto-summaryno synchronizationnetwork 10.44.103.0 mask 255.255.255.0aggregate-address 10.44.103.0 255.255.255.0 summary-onlyexit-address-family!!! Redistributes a route for subscribers in VRF VPN10003 from the global routing table into! the VRF routing domain. This route is used for subscribers to access the Cisco SESM.! This command is only necessary when the PBHK feature is enabled.ip route vrf VPN10003 10.100.3.34 255.255.255.255 GigabitEthernet3/14 10.100.3.34Model 4 Configuration: Cisco 7200 and 7300 Routers as ISG LNS with Service Bundle
Network model 4 uses the Cisco 7206 or 7301 routers as ISGs, ATM as the aggregation technology, and L2TP tunnels to securely deliver traffic across the Internet.
The model 4 network involves two ISPs:
•
ISP-1 offers wholesale service to other ISPs.
•
ISP-2 contracts with ISP-1 to receive wholesale service, which it then offers to retail customers.
For this scenario, the subscriber's PC connects to the CPE, which initiates a PPPoE session to the LAC (maintained by ISP-1) across either an ATM or a DSL network. The LAC then establishes an L2TP tunnel with the ISG LNS (maintained by ISP-2) and forwards the PPPoE session to the LNS. The LNS assigns the subscriber a VRF and assigns the subscriber the default service, which is a capped bandwidth of 256 kbps. The following advanced ISG software services are then available to the subscriber:
•
BOD1MVOLUME—1 Mbps downstream, 256 kbps upstream
•
BOD2MVOLUME—2 Mpbs downstream, 512 kbps upstream
For volume-based service, subscribers are billed according to the amount of bandwidth they use.
Figure 25 shows the basic devices that are configured for this deployment.
Figure 25 Basic Device Topology for Network Model 4

The following tasks are performed to deploy model 4. The configurations establish basic connectivity across the network and enables the subscriber to establish basic Layer 3 VPN access.
•
Configuring the ISG as LNS in Network Model 4
•
Configuring the ISG as LAC in Network Model 4
•
Configuring User Profiles for ISP-1
•
Configuring User Profiles for ISP-2
•
Configuring Service Profiles for Network Model 4
•
Configuring the CPE in Network Model 4
•
Configuring the PE in Network Model 4
Configuring the ISG as LNS in Network Model 4
The following baseline configuration tasks are performed on the ISG LNS:
•
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
•
Configuring PPPoE and the Connection to the LAC
•
Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
•
Configuring Inbound and Outbound Access Lists
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
In the following AAA configuration, connections to the AAA server, the Cisco SESM, and two billing servers are configured. VSA accounting and authentication are enabled, and the loopback interface 0 is used for AAA communications.
aaa new-model!! Configures the AAA server group for the CAR AAA server.aaa group server radius CAR_SERVERserver 10.100.2.36 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813!! Configures the AAA server group for the BILLING_SERVER billing server.aaa group server radius BILLING_SERVERserver 10.100.6.88 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646!! Configures AAA for the CAR AAA server.aaa authentication login default noneaaa authentication login IP_AUTHEN_LIST group CAR_SERVERaaa authentication ppp default group CAR_SERVER! The following commands configure authentication, authorization, and accounting for the! CAR AAA server and the two billing servers.aaa authentication ppp PREPAID_AUTHEN_LIST group BILLING_SERVERaaa authorization network default group CAR_SERVERaaa authorization network PREPAID_AUTHOR_LIST group BILLING_SERVERaaa authorization subscriber-service default local group radiusaaa accounting network default start-stop group CAR_SERVERaaa accounting network PREPAID_ACCNT_LIST start-stop group BILLING_SERVER! Configures the connection to the Cisco SESMaaa server radius sesmclient 10.100.4.38key ciscoport 1812message-authenticator ignore!! Loopback 0 is used for communicating with AAA, the billing servers, and SESM.interface Loopback0ip address 10.200.1.55 255.255.255.255ip router isis Remote_ISP! Instructs the router to use loopback 0 to communicate with the AAA RADIUS servers.ip radius source-interface Loopback0!! These RADIUS attributes are required for prepaid services.radius-server attribute 44 include-in-access-reqradius-server attribute 8 include-in-access-reqradius-server attribute 55 include-in-acct-reqradius-server attribute 55 access-request includeradius-server attribute 25 access-request include! The CAR AAA server.radius-server host 10.100.2.36 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key Cisco! The BILLING_SERVER billing server.radius-server host 10.100.6.88 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 key CiscoConfiguring PPPoE and the Connection to the LAC
In the following configuration, a virtual private dialup network (VPDN) is configured to receive L2TP tunnels from the LAC over which the PPPoE sessions are sent. A DHCP pool and MPLS VRF tables are created for incoming subscribers.

Note
To prevent revealing actual network addresses, the following configurations use IP addresses made up of letters instead of numbers.
no ip dhcp use vrf connected!! Globally enables MPLS VRFs for incoming subscribers.ip vrf VPN11006rd 200:6route-target export 200:6route-target import 200:6!!ip cef!vpdn enablevpdn ip udp ignore checksum!! VPDN group 1 terminates PPPoE clients that come in from the LAC over L2TP tunnels.vpdn-group 1accept-dialinprotocol l2tpvirtual-template 5terminate-from hostname sp_laclocal name sp_lnsl2tp tunnel password 0 lab!!interface Loopback1ip vrf forwarding VPN11006ip address 100.6.6.6 255.255.255.255!! Gigabit Ethernet interface 0/3 points to the ISG LNS.interface GigabitEthernet0/3ip address XL.22.1.55 255.255.255.0! The PBHK feature is enabled on this interface.ip portbundle outsideip flow ingressip router isis Remote_ISPload-interval 30duplex fullspeed 1000media-type gbicnegotiation autompls mtu 1522mpls label protocol ldpmpls ipno keepalive!! PPPoE subscribers terminated from L2TP tunnels use this virtual template.interface Virtual-Template5no ip addressload-interval 30no peer default ip addressno keepaliveppp mtu adaptiveppp authentication chap! Applies this policy map to PPPoE subscribers.service-policy type control RULE_PPP_VOLUME_LM_ATM5!! The DHCP pool that is assigned to subscribers.ip local pool cpe6_pool-53 192.168.6.2 192.168.6.254!Configuring Baseline ISG Subscriber Services
Basic ISG subscriber services are configured, including Layer 4 redirect to the Cisco SESM and the PBHK feature. When the PBHK feature is enabled, TCP packets from subscribers are mapped to a local IP address for the ISG gateway and a range of ports. This mapping allows the portal to identify the ISG gateway from which the session originated. Also, the default service, BOD256K_CLASS is configured, limiting subscribers' bandwidth to 256 kbps.
! Configures the connection to the Cisco SESM for Layer 4 Redirect functionality.redirect server-group SESM-Serverserver ip 10.100.4.38 port 8080!!! Creates the class map BOD256K_CLASS, which is the default service applied to all! subscribers.class-map type control match-any BOD256K_CLASSmatch service-name BOD256K!class type control BOD256K_CLASS event service-start1 service-policy type service identifier service-name!! Applies PBHK to all subscribers so they can access the Cisco SESM.class type control always event session-start1 service local2 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICE!! If both the quota from the billing server and idle time equal zero, the connection is! dropped.class type control always event quota-depleted1 set-param drop-traffic FALSE!! If the quota from the billing server equals zero, but the idle time is greater than! zero, Layer 4 redirect is activated.class type control always event credit-exhausted1 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE!! Enables port bundle host key (PBHK) access to the Cisco SESM.ip portbundlematch access-list 110! The Loopback 0 interface is used to communicate with the Cisco SESM.source Loopback0Configuring Inbound and Outbound Access Lists
Basic access lists are configured to govern subscribers' Internet access, and an access list is created for the PBHK feature.

Note
To prevent revealing actual network addresses, the following configurations use IP addresses made up of letters instead of numbers.
! This access list is referenced in the AAA subscriber profile. It governs incoming! Internet traffic.ip access-list extended Internet-in-acldeny ip any 2XZ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XJ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XH.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XK.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XL.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XM.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XN.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XP.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any XQ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255deny ip any 10.200.0.0 0.0.255.255permit ip any any! This access list is called out in the AAA subscriber profile. It governs outgoing! Internet traffic.ip access-list extended Internet-out-acldeny ip 2XZ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip 10.200.0.0 0.0.255.255 anydeny ip XJ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XH.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XK.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XL.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XM.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XN.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XP.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anydeny ip XQ.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 anypermit ip any any!access-list 101 permit ip any any! This access list is used in the ip portbundle configuration above.access-list 110 permit ip any anyaccess-list 111 deny tcp any host 10.100.4.38 eq wwwaccess-list 111 deny tcp any host 10.100.4.38 eq 8080access-list 111 permit tcp any any eq wwwConfiguring the ISG as LAC in Network Model 4
The following baseline configuration tasks are performed on the LAC:
•
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
•
Configuring the Connection to the ISG LNS and PPPoE
Configuring AAA and the Connection to the RADIUS Server
A basic AAA configuration is entered, and the connection to the RADIUS server is configured, including VSA accounting and authentication.
aaa new-model!aaa authentication login default none! setup RADIUS server for authenticationaaa authentication ppp default group radius localaaa authorization network default group radius localaaa accounting network default start-stop group radius!!aaa session-id common!interface Loopback0ip address 10.200.1.49 255.255.255.255!! Use Loopback 0 to communicate with radius serverip radius source-interface Loopback0!!radius-server host 10.100.1.35 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key Ciscoradius-server vsa send accountingradius-server vsa send authenticationConfiguring the Connection to the ISG LNS and PPPoE
The connection to the ISG LNS is configured. The LAC uses VPDN to initiate L2TP tunnels to the ISG LNS, which are used to carry the subscriber PPPoE sessions. An ISG software control policy map is used to instruct L2TP to authenticate on the basis of the domain name, and a BBA group is used to configure PPPoE.
no ip dhcp use vrf connected!subscriber policy recording rules limit 64subscriber access pppoe pre-authorize nas-port-id defaultsubscriber authorization enable! Enables VPDN globally, which is used for PPPoE.vpdn enablevpdn ip udp ignore checksumvpdn search-order domain!no mpls traffic-eng auto-bw timers frequency 0call rsvp-sync!!!! This control policy map instructs L2TP to authenticate based on domain name.policy-map type control RULE_L2TP_LM_ATM5class type control always event session-start1 collect identifier unauthenticated-domain2 authorize identifier unauthenticated-domain!!! The BBA group method is used to configure PPPoE (alternatively, the vpdn-group! method could be used).bba-group pppoe BBA_LM_ATM5virtual-template 5sessions auto cleanup!! This virtual circuit (VC) class is applied to the ATM PVC.vc-class atm VC_LM_ATM5! Associates the VC class with the above bba-group.protocol pppoe group BBA_LM_ATM5! Enables dynamic bandwidth selection.dbs enable maximumencapsulation aal5snap! Applies the L2TP rule above to the VC class.service-policy type control RULE_L2TP_LM_ATM5!! Interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/3 points to the LNS.interface GigabitEthernet0/3ip address 172.31.1.49 255.255.255.0! The port bundle host key (PBHK) feature is enabled on the interface.ip portbundle outsideip flow ingressload-interval 30duplex fullspeed 1000media-type gbicnegotiation auto!!interface ATM2/0.101 point-to-pointip flow ingressno atm enable-ilmi-trappvc 106/46! The VC class is associated with the PVC.class-vc VC_LM_ATM5! This can be changed to restrict PPPoE sessions on the PVC.pppoe max-sessions 1!!! The PPP CHAP configuration is entered on the virtual template.interface Virtual-Template5no ip addressno peer default ip addressno keepaliveppp authentication chapppp timeout aaaConfiguring User Profiles for ISP-1
The following baseline configuration tasks are performed on the AAA server for ISP-1:
•
Configuring the Connection to the LAC
•
Configuring L2TP Forwarding from the LAC to the ISG LNS
Configuring the Connection to the LAC
This profile allows the LAC router access to the AAA CAR server. The IP address 10.200.1.49 is the address of the loopback interface on the LAC.
--> cd ie2-c7206-ge[ //localhost/Radius/Clients/ie2-C7206-GE ]Name = ie2-C7206-GEDescription =IPAddress = 10.200.1.49SharedSecret = ciscoType = NASVendor =IncomingScript~ =OutgoingScript~ =EnablePOD = FALSEConfiguring L2TP Forwarding from the LAC to the ISG LNS
This profile and the corresponding attributes instruct the LAC to establish an L2TP tunnel to the ISG LNS, based on the "@isp.com" portion of the username. The IP address 10.200.1.55 is the address of the loopback interface on the ISG LNS.
--> cd isp.com[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SESMServices/isp.com ]Name = isp.comDescription =Password = <encrypted>Enabled = TRUEGroup~ =BaseProfile~ =AuthenticationScript~ =AuthorizationScript~ =UserDefined1 =AllowNullPassword = FALSEAttributes/CheckItems/--> ls attributes/[ Attributes ]Cisco-AVpair = vpdn:tunnel-id=sp_lacCisco-AVpair = vpdn:l2tp-tunnel-password=labCisco-AVpair = vpdn:tunnel-type=l2tpCisco-AVpair = vpdn:ip-addresses=10.200.1.55Cisco-AVpair = atm:peak-cell-rate=3000Cisco-AVpair = atm:sustainable-cell-rate=3000idle-timeout = 86400Configuring User Profiles for ISP-2
The following baseline configuration tasks are performed on the AAA server for ISP-2:
•
Configuring the Connection to the ISG LNS
•
Configuring the Connection to the Cisco SESM
•
Configuring the Subscriber's Default PPP Profile
Configuring the Connection to the ISG LNS
This profile allows the ISG LNS to have access to the AAA CAR server.
--> cd ie2-c7206-lns[ //localhost/Radius/Clients/ie2-C7206-LNS ]Name = ie2-C7206-LNSDescription =IPAddress = 10.200.1.55SharedSecret = ciscoType = NASVendor =IncomingScript~ =OutgoingScript~ =EnablePOD = FALSEConfiguring the Connection to the Cisco SESM
This profile connects the AAA CAR server to the Cisco SESM.
--> cd ie2-sesm-1b[ //localhost/Radius/Clients/ie2-SESM-1b ]Name = ie2-SESM-1bDescription =IPAddress = 10.100.4.38SharedSecret = ciscoType = NASVendor =IncomingScript~ =OutgoingScript~ =EnablePOD = FALSEConfiguring User Profiles
This profile and the following attributes specify the ISG subscriber services that are allowed:
--> cd cpe6_1@isp.com[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SESMSubscribers/cpe6_1@isp.com ]! Specifies the username that the CPE uses.Name = cpe6_1@isp.comDescription =! This password must match the one configured on the CPE.Password = <encrypted>Enabled = TRUEGroup~ =! Specifies the name of the PPP profile.BaseProfile~ = Default-PPP-UsersAuthenticationScript~ =AuthorizationScript~ =UserDefined1 =AllowNullPassword = FALSEAttributes/CheckItems/--> ls attributes/[ Attributes ]! Assigns subscribers to vrf VPN11006.Cisco-AVpair = "lcp:interface-config=ip vrf forwarding VPN11006"Cisco-AVpair = "lcp:interface-config=ip unnumbered loopback 1"! Assigns an address to this DHCP pool on the LNS.Cisco-AVpair = ip:addr-pool=cpe6_pool-53! The A in front of BOD256K designates autologin, which means that the default service! is BOD256k.Cisco-SSG-Account-Info = ABOD256KCisco-SSG-Account-Info = NBOD256K! Specifies the other services that the subscriber is allowed to access.Cisco-SSG-Account-Info = NBOD1MVOLUMECisco-SSG-Account-Info = NBOD2MVOLUME! Specifies the total session timeout value (optional).Session-Timeout = 86400This profile and the following attributes configure the default service, BOD256K:
--> cd bod256k[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SESMServices/BOD256K ]! This service is not a prepaid service because there is no "prepaid-config" line.Name = BOD256K[ Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name Internet-in-acl"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name Internet-out-acl"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IBOD256KCisco-SSG-Service-Info = QU;128000;8000;8000;D;256000;16000;16000Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0Configuring Layer 4 Redirect
This attribute enables the Layer 4 Redirect feature.
[ Attributes ]! Instructs Layer 4 redirect to send traffic to ACL 111 on the ISG LNS.Cisco-AVPair = "ip:l4redirect=redirect list 111 to group SESM-Server duration 30 frequency 180"Configuring PBHK
This profile and the following attribute enable access to the SESM using the PBHK feature:
--> cd pbhk_service[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SESMServices/PBHK_SERVICE ]Name = PBHK_SERVICE[ Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = ip:portbundle=enableConfiguring the Subscriber's Default PPP Profile
This profile and the following attributes configure the PPP profile that is used in the subscriber's base profile:
--> cd default-ppP-users/[ //localhost/Radius/Profiles/default-PPP-users ]Name = default-PPP-usersDescription =Attributes/--> ls attributes/[ Attributes ]Ascend-Idle-Limit = 1800Framed-MTU = 1500Framed-Protocol = PPPFramed-Routing = None! Configures the length of the idle timeout on PPP sessions, after which the session is! dropped.Idle-timeout = 180Service-Type = FramedConfiguring Service Profiles for Network Model 4
The following tasks are performed to enable the advanced ISG subscriber services:
•
ISG Subscriber Services Configuration
•
AAA Server Service Configuration for ISP-2
ISG Subscriber Services Configuration
The following configuration tasks are performed on the ISG LNS to enable the advanced ISG subscriber services:
•
Configuring the Global Prepaid Services Configuration
•
Configuring Control Class Maps for Model 4
•
Configuring Control Policy for Model 4
Configuring the Global Prepaid Services Configuration
The global attributes of the prepaid services are configured for each of the two billing servers.
! This is the global configuration for the PREPAID_CONFIG prepaid billing server.subscriber feature prepaid PREPAID_CONFIGthreshold time 10 secondsthreshold volume 1000 bytesinterim-interval 3 minutes! References the authorization list in the above AAA configuration.method-list author PREPAID_AUTHOR_LIST! References the accounting list in the above AAA configuration.method-list accounting PREPAID_ACCNT_LIST! This is the prepaid password that is configured on the billing servers.password prepaidcisco!subscriber policy recording rules limit 64Configuring Control Class Maps for Model 4
Following are configurations for the control class maps:
class-map type control match-any BOD256K_CLASSmatch service-name BOD256K!class-map type control match-all BOD2MVOLUME_CLASSmatch service-name BOD2MVOLUME!class-map type control match-all BOD1MVOLUME_CLASSmatch service-name BOD1MVOLUME!Configuring Control Policy for Model 4
Following are configurations for the control policies:
policy-map type control RULE_PPP_VOLUME_LM_ATM5class type control BOD256K_CLASS event service-start1 service-policy type service unapply name BOD1MVOLUME2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD2MVOLUME3 service-policy type service identifier service-name!class type control BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event service-start1 service-policy type service unapply name BOD256K2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD2MVOLUME_LM53 service-policy type service identifier service-name!class type control BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event service-start1 service-policy type service unapply name BOD256K2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD1MVOLUME_LM53 service-policy type service identifier service-name!class type control BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event service-stop1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-name2 service-policy type service name BOD256K!class type control BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event service-stop1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-name2 service-policy type service name BOD256K!class type control always event session-start1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICE2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE!class type control always event quota-depleted1 set-param drop-traffic FALSE!class type control always event credit-exhausted1 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE!AAA Server Service Configuration for ISP-2
The following configuration tasks are performed on the AAA server for ISP-2 to enable the advanced ISG subscriber services:
•
Configuring the BOD1MVOLUME Service
•
Configuring the BOD2MVOLUME Service
•
Configuring Layer 4 Redirect upon Depletion of Quotas Run
Configuring the BOD1MVOLUME Service
The following profile and attributes configure the BOD1MVOLUME service:
--> cd bod1mvolUME/[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SESMServices/BOD1MVOLUME ]Name = BOD1MVOLUME[ Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name Internet-in-acl"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name Internet-out-acl"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-AVPair = prepaid-config=PREPAID_CONFIGCisco-SSG-Service-Info = IBOD1MVOLUMECisco-SSG-Service-Info = QU;256000;16000;16000;D;1000000;64000;64000Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0Configuring the BOD2MVOLUME Service
The following profile and attributes configure the BOD2MVOLUME service:
Name = BOD2MVOLUME[ Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name Internet-in-acl"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name Internet-out-acl"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-AVPair = prepaid-config=PREPAID_CONFIGCisco-SSG-Service-Info = IBOD2MVOLUMECisco-SSG-Service-Info = QU;512000;32000;32000;D;2000000;128000;128000Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0Configuring Layer 4 Redirect upon Depletion of Quotas Run
The following profile enables Layer 4 redirect when the subscriber's quota or funds from the billing server are exhausted:
[ //localhost/Radius/UserLists/SESMServices/L4REDIRECT_SERVICE ]Name = L4REDIRECT_SERVICE[ Attributes ]Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=in default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:traffic-class=out default drop"Cisco-AVPair = "ip:l4redirect=redirect to group SESM_SERVER_GROUP"Cisco-SSG-Service-Info = IL4REDIRECT_SERVICEConfiguring the CPE in Network Model 4
The following baseline configuration tasks are performed on the CPE:
•
Configuring the Ethernet Interface and DHCP
•
Configuring the Outbound Interface
•
Configuring the Dialer Interface and NAT
Configuring the Ethernet Interface and DHCP
In the following configuration, interface Ethernet 0 is configured to connect to the subscriber PC, and DHCP is enabled for incoming sessions:
interface Ethernet0ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0ip nat insideload-interval 30no cdp enablehold-queue 100 out!ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.10.1!! DHCP configuration for interface Ethernet 0 subscribersip dhcp pool CLIENTimport allnetwork 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0default-router 10.10.10.1lease 0 2Configuring the Outbound Interface
In the following configuration, ATM interface 0.6 is configured as a PVC. This is the outbound interface from the CPE to the DSLAM.
interface ATM0.6 point-to-point! This is the PVC which is going to the ATM DSLAMpvc 6/46encapsulation aal5snap! This associates the PVC with dialer 1pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1Configuring the Dialer Interface and NAT
In the following configuration, dialer interface 1 is configured to receive incoming connections from the subscriber. CHAP is used for the CPE's username and password, and Network Address Translation (NAT) is enabled for outbound traffic.
interface Dialer1ip address negotiatedip nat outside! using PPPencapsulation pppip route-cache flowdialer pool 1no cdp enable!The username and password are set for CHAPppp chap hostname cpe6_1@isp.comppp chap password 7 060A0E23!! Enables subscribers on the inside of E0 to access outside using NATip nat inside source list 1 interface Dialer1 overload!ip classless! set the default gateway out the dialer 1 interfaceip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Dialer1!! allow E0 subscribers to be NAT translatedaccess-list 1 permit 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255! refers to ACL 1dialer-list 1 protocol ip permitno cdp runConfiguring the PE in Network Model 4
The PE is configured to assign subscribers to a VRF and to allow subscribers to access the Cisco SESM.
! The VRF that subscribers are assigned to.ip vrf VPN11006rd 200:6route-target export 200:6route-target import 200:6!!router bgp 200no synchronizationbgp router-id 10.200.1.43bgp log-neighbor-changesnetwork 10.100.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0network 10.200.1.43 mask 255.255.255.255network 10.31.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0network 10.83.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0network 10.85.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0network 10.86.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0network 10.87.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0network 10.88.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0neighbor 10.200.1.47 remote-as 200neighbor 10.200.1.47 ebgp-multihop 10neighbor 10.200.1.47 update-source Loopback0no auto-summary!! Enables BGP VPNv4 neighborsaddress-family vpnv4neighbor 10.200.1.47 activateneighbor 10.200.1.47 send-community extendedexit-address-family!!! Allows VRF routes into the BGP routing table.address-family ipv4 vrf VPN11006redistribute connectedredistribute staticno auto-summaryno synchronizationexit-address-family!!! Creates an IP route for subscribers in VRF VPN11006 to access the Cisco SESM.ip route vrf VPN11006 10.100.4.38 255.255.255.255 Vlan6 10.100.4.38Configuration Verification
The following sections describe how to verify configurations for the model deployments:
•
ISG Configuration Information Verification
•
Basic ISG Operation Verification
•
Subscriber Service Verification
The commands described in these sections can be used on Cisco 7200, 7300, and 10000 series routers.
ISG Configuration Information Verification
Use the show subscriber policy condition command to show the number of times each policy has been executed.
ie2-C7206-ATM# show subscriber policy condition
Class-map Action Exec Hit Miss Comp--------- ------ ---- --- ---- ----match-any TAL_STATIC_DM3 match identifier source-ip-addr36131 036131 0match-any TAL_STATIC_DM3 match identifier source-ip-addr3613128932 719928932match-all IP_UNAUTH_COND match identifier timer IP_UNAUT1662416624 0 0match-all IP_UNAUTH_COND match identifier authen-status 1662454261119811198match-any TAL_STATIC_DM4 match identifier source-ip-addr23502 023502 0match-any TAL_STATIC_DM4 match identifier source-ip-addr2350222902 60022902match-all BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS_L match identifier service-name B 0 0 0 0match-all BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS_L match identifier service-name B 0 0 0 0match-all BOD2MTIME_CLASS_DM2 match identifier service-name B 1 0 1 1match-all BOD1MTIME_CLASS_DM2 match identifier service-name B4632546325 0 0Key:"Exec" - The number of times this line was executed"Hit" - The number of times this line evaluated to TRUE"Miss" - The number of times this line evaluated to FALSE"Comp" - The number of times this line completed the execution of itscondition without a need to continue on to the endUse the clear subscriber policy conditions command to clear the statistics of subscriber policy changes.
ie2-C7206-ATM# clear subscriber policy conditionsie2-C7206-ATM#ie2-C7206-ATM# show subscriber policy conditionsClass-map Action Exec Hit Miss Comp--------- ------ ---- --- ---- ----match-any TAL_STATIC_DM3 match identifier source-ip-addr 0 0 0 0match-any TAL_STATIC_DM3 match identifier source-ip-addr 0 0 0 0match-all IP_UNAUTH_COND match identifier timer IP_UNAUT 0 0 0 0match-all IP_UNAUTH_COND match identifier authen-status 0 0 0 0match-any TAL_STATIC_DM4 match identifier source-ip-addr 0 0 0 0match-any TAL_STATIC_DM4 match identifier source-ip-addr 0 0 0 02match-all BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS_L match identifier service-name B 0 0 0 0match-all BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS_L match identifier service-name B 0 0 0 0match-all BOD2MTIME_CLASS_DM2 match identifier service-name B 1 0 1 1match-all BOD1MTIME_CLASS_DM2 match identifier service-name B 0 0 0 0Key:"Exec" - The number of times this line was executed"Hit" - The number of times this line evaluated to TRUE"Miss" - The number of times this line evaluated to FALSE"Comp" - The number of times this line completed the execution of itscondition without a need to continue on to the endUse the show subscriber service command to list details of all of the services configured on the ISG.
ie2-C7206-ATM# show subscriber service
Service "PBHK_SERVICE":Version 1:SVM ID : 47000002Locked by : SVM-Feature-Info [196]Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : PM-Service [3626]Locked by : PM-Info [3626]Locked by : FM-Bind [3430]Profile : 21E3C738Profile name: PBHK_SERVICE, 3628 referencesportbundle "enable"ssg-service-info "IPBHK_SERVICE"Feature : Portbundle HostkeyFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredService "GAMING_SERVICE":Version 1:SVM ID : 5E000003Child ID : FB000007Locked by : SVM-Feature-Info [4]Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : PM-Service [722]Locked by : PM-Info [722]Locked by : FM-Bind [718]Locked by : TC-Child [1]Locked by : Accounting-Feature [718]Profile : 21E3AE18Profile name: GAMING_SERVICE, 1440 referencesidletime 1800 (0x708)traffic-class "in access-group name GAMING_IN_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name GAMING_OUT_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "out default drop"accounting-list "CAR_ACCNT_LIST"ssg-service-info "IGAMING_SERVICE"ssg-service-info "R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0"Feature : TCFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 28 bytes:: 000000 00 00 FB 00 00 07 00 00 ........: 000008 00 0A 01 00 00 00 21 D2 ......!.: 000010 F4 F8 00 00 00 0A 01 00 ........: 000018 00 00 64 BD ..d.
Note
Portbundle Hostkey and Traffic class cannot be configured under the same policy group.
Version 1:SVM ID : FB000007Parent ID : 5E000003Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : FM-Bind [719]Locked by : TC-Parent [1]Feature : Idle TimeoutFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 8 bytes:: 000000 00 00 00 1B 77 40 01 01 ....w@..Feature : AccountingFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 24 bytes:: 000000 00 00 5E 00 00 03 64 BE ..^...d.: 000008 03 B0 00 00 00 0F 00 00 ........: 000010 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........Service "VOD_SERVICE":Version 1:SVM ID : AB000004Child ID : 41000008Locked by : SVM-Feature-Info [4]Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : PM-Service [720]Locked by : PM-Info [720]Locked by : FM-Bind [716]Locked by : TC-Child [1]Locked by : Accounting-Feature [716]Profile : 21E3AD58Profile name: VOD_SERVICE, 1442 referencesidletime 1800 (0x708)traffic-class "in access-group name VOD_IN_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name VOD_OUT_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "out default drop"accounting-list "CAR_ACCNT_LIST"ssg-service-info "IVOD_SERVICE"ssg-service-info "R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0"Feature : TCFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 28 bytes:: 000000 00 00 41 00 00 08 00 00 ..a.....: 000008 00 0A 01 00 00 00 53 18 ......s.: 000010 C0 28 00 00 00 0A 01 00 .(......: 000018 00 00 53 19 ..s.Version 1:SVM ID : 41000008Parent ID : AB000004Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : FM-Bind [716]Locked by : TC-Parent [1]Feature : Idle TimeoutFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 8 bytes:: 000000 00 00 00 1B 77 40 01 01 ....w@..Feature : AccountingFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 24 bytes:: 000000 00 00 AB 00 00 04 52 30 ......r0: 000008 4C B8 00 00 00 0F 00 00 l.......: 000010 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........Service "VOIP_SERVICE":Version 1:SVM ID : 39000005Child ID : E2000009Locked by : SVM-Feature-Info [4]Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : PM-Service [719]Locked by : PM-Info [719]Locked by : FM-Bind [715]Locked by : TC-Child [1]Locked by : Accounting-Feature [716]Profile : 21E3AD38Profile name: VOIP_SERVICE, 1440 referencesidletime 1800 (0x708)traffic-class "in access-group name VOIP_IN_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name VOIP_OUT_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "out default drop"accounting-list "CAR_ACCNT_LIST"ssg-service-info "IVOIP_SERVICE"ssg-service-info "R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0"Feature : TCFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 28 bytes:: 000000 00 00 E2 00 00 09 00 00 ........: 000008 00 0A 01 00 00 00 23 2C ......#,: 000010 33 B0 00 00 00 0A 01 00 3.......: 000018 00 00 52 0C ..r.Version 1:SVM ID : E2000009Parent ID : 39000005Locked by : SVM-Feature-Info [3]Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : FM-Bind [716]Locked by : SM-SIP-Apply [3]Locked by : TC-Parent [1]Feature : Idle TimeoutFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 8 bytes:: 000000 00 00 00 1B 77 40 01 01 ....w@..Feature : AccountingFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 24 bytes:: 000000 00 00 39 00 00 05 51 12 ..9...q.: 000008 60 F0 00 00 00 0F 00 00 `.......: 000010 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........Service "OPENGARDEN_SERVICE":Version 1:SVM ID : 77000006Child ID : E300000ALocked by : SVM-Feature-Info [5]Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : PM-Service [722]Locked by : PM-Info [722]Locked by : FM-Bind [717]Locked by : TC-Child [1]Profile : 21E3AD18Profile name: OPENGARDEN_SERVICE, 1446 referencestraffic-class "in access-group name OPENGARDEN_IN_ACL"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name OPENGARDEN_OUT_ACL"traffic-class "out default drop"ssg-service-info "IOPENGARDEN_SERVICE"Feature : TCFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 28 bytes:: 000000 00 00 E3 00 00 0A 00 00 ........: 000008 00 00 01 00 00 00 51 0F ......q.: 000010 28 C0 00 00 00 00 01 00 (.......: 000018 00 00 51 12 ..q.Version 1:SVM ID : E300000AParent ID : 77000006Locked by : SVM-Feature-Info [3]Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : FM-Bind [717]Locked by : SM-SIP-Apply [3]Locked by : TC-Parent [1]Service "L4REDIRECT_SERVICE":Version 1:SVM ID : AC000030Child ID : 6D000031Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : PM-Service [267]Locked by : PM-Info [2707]Locked by : FM-Bind [268]Locked by : TC-Child [1]Profile : 242C1A08Profile name: L4REDIRECT_SERVICE, 5149 referencestraffic-class "in access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"traffic-class "out default drop"l4redirect "redirect to group SESM_SERVER_GROUP"ssg-service-info "IL4REDIRECT_SERVICE"Feature : TCFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 28 bytes:: 000000 00 00 6D 00 00 31 00 00 ..m..1..: 000008 00 05 01 00 00 00 53 B8 ......s.: 000010 CF C0 00 00 00 05 01 00 ........: 000018 00 00 24 19 ..$.Version 1:SVM ID : 6D000031Parent ID : AC000030Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : FM-Bind [267]Locked by : TC-Parent [1]Feature : L4 RedirectFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 20 bytes:: 000000 00 00 64 72 B7 F8 64 72 ..dr..dr: 000008 B7 F8 00 00 00 01 00 00 ........: 000010 00 00 00 00 ....Service "BOD1MTIME_DM2":Version 1:SVM ID : 19000053Child ID : 13000054Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : PM-Service [2440]Locked by : PM-Info [2440]Locked by : FM-Bind [2440]Locked by : TC-Child [1]Locked by : Accounting-Feature [2440]Profile : 242C1A48Profile name: BOD1MTIME_DM2, 4882 referencestraffic-class "in access-group name INTERNET_IN_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name INTERNET_OUT_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "out default drop"accounting-list "PREPAID_ACCNT_LIST"peak-cell-rate 1024 (0x400)sustainable-cell-rat 1024 (0x400)ssg-service-info "IBOD1MTIME_DM2"ssg-service-info "R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0"Feature : TCFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 28 bytes:: 000000 00 00 13 00 00 54 00 00 .....t..: 000008 00 0A 01 00 00 00 56 B7 ......v.: 000010 49 80 00 00 00 0A 01 00 i.......: 000018 00 00 24 62 ..$bSIP : Info 23E85AB8 access: PPPoE info: PPPoEVersion 1:SVM ID : 13000054Parent ID : 19000053Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : FM-Bind [2440]Locked by : TC-Parent [1]Feature : AccountingFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 24 bytes:: 000000 00 00 19 00 00 53 24 70 .....s$p: 000008 61 68 00 00 00 0F 00 00 ah......: 000010 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........Service "INTERNET_SERVICE":Version 1:SVM ID : EE000055Locked by : SVM-Printer [1]Locked by : PM-Service [200]Locked by : PM-Info [200]Locked by : FM-Bind [200]Profile : 21E3AC78Profile name: INTERNET_SERVICE, 402 referencesinacl "INTERNET_IN_ACL"outacl "INTERNET_OUT_ACL"ssg-service-info "IINTERNET_SERVICE"ssg-service-info "R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0"Feature : Per-User ACLFeature IDB type : Sub-if or not requiredFeature Data : 52 bytes:: 000000 00 00 26 0C 07 A6 00 00 ..&.....: 000008 00 00 00 00 00 00 F6 01 ........: 000010 07 B3 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........: 000018 00 00 00 00 00 01 00 00 ........: 000020 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........: 000028 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........: 000030 00 00 00 00 ....Use the show subscriber policy rule command to show all rules that are configured on the ISG and the number of times they have been executed.
ie2-C7206-ATM# show subscriber policy rule
Rule: internal-rule-acct-logonClass-map: always event account-logonAction: 1 authenticate aaa list defaultExecuted0Rule: RULE_L2TP_LM_ATM7Class-map: always event session-startAction: 1 collect identifier unauthenticated-domainExecuted0Action: 2 authorize identifier unauthenticated-domainExecuted0Rule: RULE_L2TP_LM_ATM3Class-map: always event session-startAction: 1 collect identifier unauthenticated-domainExecuted0Action: 2 authorize identifier unauthenticated-domainExecuted0Rule: RULE_IP_LM_ATM2Class-map: IP_UNAUTH_COND event timed-policy-expiryAction: 1 service disconnectExecuted5388Class-map: TAL_STATIC_DM3 event session-startAction: 1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICEExecuted29007Action: 2 authorize identifier source-ip-addressExecuted28662Action: 3 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted5588Action: 4 set-timer IP_UNAUTH_TIMER 5Executed5588Class-map: always event session-startAction: 1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICEExecuted7199Action: 2 authorize identifier mac-addressExecuted6004Action: 3 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted5999Action: 4 set-timer IP_UNAUTH_TIMER 5Executed5999Class-map: always event account-logonAction: 1 authenticate aaa list IP_AUTHEN_LISTExecuted0Action: 2 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Rule: RULE_PTA_LM_ATM2Class-map: always event session-startAction: 1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICEExecuted0Rule: RULE_IP_LM_ATM7Class-map: TAL_STATIC_DM4 event session-startAction: 1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICEExecuted22957Action: 2 authorize identifier source-ip-addressExecuted22902Action: 3 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted37Action: 4 set-timer IP_UNAUTH_TIMER 5Executed37Class-map: IP_UNAUTH_COND event timed-policy-expiryAction: 1 service disconnectExecuted38Class-map: always event session-startAction: 1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICEExecuted600Action: 2 authorize identifier mac-addressExecuted200Action: 3 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted1Action: 4 set-timer IP_UNAUTH_TIMER 5Executed1Class-map: always event account-logonAction: 1 authenticate aaa list IP_AUTHEN_LISTExecuted0Action: 2 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Rule: RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8Class-map: BOD1MTIME_CLASS_DM2 event service-startAction: 1 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted47256Action: 2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD2MTIME_DM2Executed47256Action: 3 service-policy type service identifier service-nameExecuted47256Class-map: BOD2MTIME_CLASS_DM2 event service-startAction: 1 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Action: 2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD1MTIME_DM2Executed0Action: 3 service-policy type service identifier service-nameExecuted0Class-map: BOD2MTIME_CLASS_DM2 event service-stopAction: 1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-nameExecuted0Action: 2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Class-map: BOD1MTIME_CLASS_DM2 event service-stopAction: 1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-nameExecuted1Action: 2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted1Class-map: always event session-startAction: 1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICEExecuted49636Action: 2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted48636Class-map: always event quota-depletedAction: 1 set-param drop-traffic FALSEExecuted0Class-map: always event credit-exhaustedAction: 1 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Class-map: always event internal-event-cre-t-expAction: 1 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Rule: RULE_PTA_VOLUME_LM_ATM8Class-map: BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS_DM2 event service-startAction: 1 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Action: 2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD2MVOLUME_DM2Executed0Action: 3 service-policy type service identifier service-nameExecuted0Class-map: BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS_DM2 event service-startAction: 1 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Action: 2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD1MVOLUME_DM2Executed0Action: 3 service-policy type service identifier service-nameExecuted0Class-map: BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS_DM2 event service-stopAction: 1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-nameExecuted0Action: 2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Class-map: BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS_DM2 event service-stopAction: 1 service-policy type service unapply identifier service-nameExecuted0Action: 2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Class-map: always event session-startAction: 1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICEExecuted0Action: 2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Class-map: always event quota-depletedAction: 1 set-param drop-traffic FALSEExecuted0Class-map: always event credit-exhaustedAction: 1 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Class-map: always event internal-event-cre-t-expAction: 1 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEExecuted0Key:"Exec" - The number of times this rule action line was executedBasic ISG Operation Verification
Use the show subscriber statistics command to show a summary of the number of active sessions and a brief history of session activity.
ie2-C7206-ATM# show subscriber statistics
Current Subscriber Statistics:Number of sessions currently up: 3227Number of sessions currently pending: 193Number of sessions currently authenticated: 3101Number of sessions currently unauthenticated: 0Highest number of sessions ever up at one time: 3760Mean up-time duration of sessions: 00:05:12Total number of sessions up so far: 105408Mean call rate per minute: 484, per hour: 35200Number of sessions failed to come up: 3401Access type based session count:PPPoE sessions = 2640Traffic-Class sessions = 4594IP sessions = 780Use the show subscriber session command to show basic information for all active subscribers.
ie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber sessionl
Current Subscriber Information: Total sessions 3370Uniq ID Interface State Service Identifier Up-time! This is the VID for the subscriber4910 Vi2.2122 authen Local Term C72_DM2_3021 00:03:41! This is the VID for the subscriber's traffic classes1748 Traffic-Cl unauthen Ltm Internal 00:04:2710709 Traffic-Cl unauthen Ltm Internal 00:04:236514 Vi2.78 authen Local Term C72_DM2_1078 00:04:555650 Traffic-Cl unauthen Ltm Internal C72_DM2_1446 00:04:463771 Traffic-Cl unauthen Ltm Internal 00:01:012601 Vi2.1558 authen Local Term C72_DM2_2097 00:04:123508 Traffic-Cl unauthen Ltm Internal 00:01:169767 Traffic-Cl unauthen Ltm Internal C72_DM2_1390 00:04:48Use the show ip route vrf command to show routing table information for the VPN11006 VRF. In the following output, there is one active subscriber session.

Note
To prevent revealing actual network addresses, the following configurations use IP addresses made up of letters instead of numbers.
ie2-C7206-LNS# show ip route vrf VPN11006
Routing Table: VPN11006Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGPD - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter areaN1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGPi - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static routeo - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static routeGateway of last resort is not setXR.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnetsB XR.1.206.0 [200/0] via 10.200.1.43, 4d19h1XT.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnetsC 1XT.6.6.6 is directly connected, Loopback1192.168.6.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets! This shows that the subscriber is connected and part of vrf VPN11006C 192.168.6.2 is directly connected, Virtual-Access32XW.6.6.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnetsB 2XW.6.6.6 [200/0] via 10.200.1.56, 4d19h10.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnetsB 10.100.4.38 [200/0] via 10.200.1.43, 4d19hSubscriber Service Verification
Use the show subscriber session username command to show detailed information for the subscriber with the username c72_DM2_1078.
The following output shows a subscriber with the BOD1MTIME_DM2 service:
ie2-C7206-ATM# show subscriber session username C72_DM2_1078
Unique Session ID: 6514Identifier: C72_DM2_1078SIP subscriber access type(s): PPPoE/PPPCurrent SIP options: Req Fwding/Req FwdedSession Up-time: 00:06:17, Last Changed: 00:06:17AAA unique ID: 102346Interface: Virtual-Access2.78Policy information:Context 25559F94: Handle 310104C8Authentication status: authenActive services associated with session:! Indicates the services that the subscriber is using.name "BOD1MTIME_DM2"name "PBHK_SERVICE", applied outwith active sessionRules, actions and conditions executed:subscriber rule-map RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8condition always event session-start1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICE2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEsubscriber rule-map RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS_DM2 event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-all BOD1MTIME_CLASS_DM2match identifier service-name BOD1MTIME_DM2 [TRUE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS_DM2 event service-start1 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD2MTIME_DM23 service-policy type service identifier service-nameSession inbound features:Feature: PPP Idle TimeoutTimeout value is 1800Idle time is 00:06:25Feature: Layer 4 RedirectRule table is emptyTraffic classes:Traffic class session ID: 3947ACL Name: INTERNET_IN_ACL, Packets = 0, Bytes = 0Default traffic is droppedUnmatched Packets (dropped) = 0, Re-classified packets (redirected) = 0! Portbound Hostkey information for the subscriber.Feature: Portbundle HostkeyPortbundle IP = 10.200.1.53 Bundle Number = 1229Session outbound features:Feature: PPP Idle TimeoutTimeout value is 1800Idle time is 00:06:25Traffic classes:Traffic class session ID: 3947! Identifies the ACL that restricts inbound traffic. The ACL is configured on the ISG,! and it is applied to the subscriber based on the subscriber profile on the AAA server.ACL Name: INTERNET_OUT_ACL, Packets = 0, Bytes = 0Default traffic is droppedUnmatched Packets (dropped) = 0, Re-classified packets (redirected) = 0Non-datapath features:Feature: Session TimeoutTimeout value is 18000 seconds! Indicates the amount of time remaining before the session times out.Time remaining is 04:53:33Feature: IP ConfigPeer IP Address: 0.0.0.0 (F/F)Address Pool: C72_DM2_8003 (F)Unnumbered Intf: Lo8001Configuration sources associated with this session:! Indicates how long the BOD1MTIME_DM2 service has been active.Service: BOD1MTIME_DM2, Active Time = 00:06:26AAA Service ID = 1441613880Service: PBHK_SERVICE, Active Time = 00:06:27Interface: Virtual-Template8, Active Time = 00:06:27Use the show subscriber session username C72_DM2_1078 detail to show additional details about the subscriber's session.
ie2-C7206-ATM# show subscriber session username C72_DM2_1078 detail
Unique Session ID: 6514Identifier: C72_DM2_1078SIP subscriber access type(s): PPPoE/PPPCurrent SIP options: Req Fwding/Req FwdedSession Up-time: 00:06:32, Last Changed: 00:06:32AAA unique ID: 102346Interface: Virtual-Access2.78Policy information:Context 25559F94: Handle 310104C8Authentication status: authenDownloaded User profile, excluding services:service-type 2 [Framed]Framed-Protocol 1 [PPP]routing FalseFramed-MTU 1500 (0x5DC)timeout 18000 (0x4650)idletime 1800 (0x708)! The A attribute configures auto-login, which indicates that BOD1MTIME_DM2 is the default! service.ssg-account-info "ABOD1MTIME_DM2"! The N indicates that the subscriber is allowed access the BOD2MTIME_DM2 service based! on the subscriber's AAA profile.ssg-account-info "NBOD2MTIME_DM2"idletime 1800 (0x708)vrf-id "VPN_C72_DM2_1003"ip-unnumbered "loopback 8001"addr-pool "C72_DM2_8003"Downloaded User profile, including services:portbundle "enable"service-type 2 [Framed]Framed-Protocol 1 [PPP]routing FalseFramed-MTU 1500 (0x5DC)timeout 18000 (0x4650)idletime 1800 (0x708)ssg-account-info "ABOD1MTIME_DM2"ssg-account-info "NBOD2MTIME_DM2"idletime 1800 (0x708)vrf-id "VPN_C72_DM2_1003"ip-unnumbered "loopback 8001"addr-pool "C72_DM2_8003"traffic-class "in access-group name INTERNET_IN_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name INTERNET_OUT_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "out default drop"accounting-list "PREPAID_ACCNT_LIST"peak-cell-rate 1024 (0x400)sustainable-cell-rat 1024 (0x400)ssg-service-info "IBOD1MTIME_DM2"ssg-service-info "R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0"Config history for session (recent to oldest):Access-type: Web-service-logon Client: SMPolicy event: Process Config (Service)Profile name: BOD1MTIME_DM2, 4882 referencestraffic-class "in access-group name INTERNET_IN_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name INTERNET_OUT_ACL priority 10"traffic-class "out default drop"accounting-list "PREPAID_ACCNT_LIST"peak-cell-rate 1024 (0x400)sustainable-cell-rat 1024 (0x400)ssg-service-info "IBOD1MTIME_DM2"ssg-service-info "R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0"Access-type: Max Client: SM! Describers the Layer 4 Redirect service, which is not currently applied.Policy event: Process Config (Unapplied) (Service)Profile name: L4REDIRECT_SERVICE, 5082 referencestraffic-class "in access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"traffic-class "out default drop"l4redirect "redirect to group SESM_SERVER_GROUP"ssg-service-info "IL4REDIRECT_SERVICE"Access-type: PPP Client: SMPolicy event: Process ConfigProfile name: apply-config-only, 28 referencesservice-type 2 [Framed]Framed-Protocol 1 [PPP]routing FalseFramed-MTU 1500 (0x5DC)timeout 18000 (0x4650)idletime 1800 (0x708)ssg-account-info "ABOD1MTIME_DM2"ssg-account-info "NBOD2MTIME_DM2"idletime 1800 (0x708)vrf-id "VPN_C72_DM2_1003"ip-unnumbered "loopback 8001"addr-pool "C72_DM2_8003"Access-type: PPPoE Client: SMPolicy event: Service Selection Request (Service)Profile name: L4REDIRECT_SERVICE, 5082 referencestraffic-class "in access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name IP_REDIRECT_ACL priority 5"traffic-class "out default drop"l4redirect "redirect to group SESM_SERVER_GROUP"ssg-service-info "IL4REDIRECT_SERVICE"Access-type: PPPoE Client: SMPolicy event: Service Selection Request (Service)Profile name: PBHK_SERVICE, 3379 referencesportbundle "enable"ssg-service-info "IPBHK_SERVICE"Active services associated with session:name "BOD1MTIME_DM2"name "PBHK_SERVICE", applied outwith active sessionRules, actions and conditions executed:subscriber rule-map RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8condition always event session-start1 service-policy type service name PBHK_SERVICE2 service-policy type service name L4REDIRECT_SERVICEsubscriber rule-map RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS_DM2 event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-all BOD1MTIME_CLASS_DM2! Services that are active are identified as "TRUE."match identifier service-name BOD1MTIME_DM2 [TRUE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PTA_TIME_LM_ATM8condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS_DM2 event service-start1 service-policy type service unapply name L4REDIRECT_SERVICE2 service-policy type service unapply name BOD2MTIME_DM23 service-policy type service identifier service-nameSession inbound features:Feature: PPP Idle TimeoutTimeout value is 1800Idle time is 00:06:35Feature: Layer 4 RedirectRule table is emptyTraffic classes:Traffic class session ID: 3947! Identifies the ACL that restricts inbound traffic. The ACL is configured on the ISG LNS,! and it is applied to the subscriber based on the subscriber profile on the AAA server.ACL Name: INTERNET-IN-ACL, Packets = 0, Bytes = 0Default traffic is droppedUnmatched Packets (dropped) = 0, Re-classified packets (redirected) = 0Feature: Portbundle Hostkey! Identifies the PBHK IP address and the bundle number. This information can be used to! troubleshoot PBHK with the show ip portbundle command.Portbundle IP = 10.200.1.53 Bundle Number = 1229Session outbound features:Feature: PPP Idle TimeoutTimeout value is 1800Idle time is 00:06:35Traffic classes:Traffic class session ID: 3947ACL Name: INTERNET_OUT_ACL, Packets = 0, Bytes = 0Default traffic is droppedUnmatched Packets (dropped) = 0, Re-classified packets (redirected) = 0Non-datapath features:Feature: Session TimeoutTimeout value is 18000 secondsTime remaining is 04:53:23Feature: IP ConfigPeer IP Address: 0.0.0.0 (F/F)Address Pool: C72_DM2_8003 (F)Unnumbered Intf: Lo8001Configuration sources associated with this session:Service: BOD1MTIME_DM2, Active Time = 00:06:35AAA Service ID = 1441613880Service: PBHK_SERVICE, Active Time = 00:06:36Interface: Virtual-Template8, Active Time = 00:06:36
Basic LNS Verification
Use the show subscriber session command to show basic information for all active subscribers. In the following output, there is one active subscriber session:
ie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber session
Current Subscriber Information: Total sessions 1Uniq ID Interface State Service Identifier Up-time! This is the VID for the subscriber520 Vi3 authen Local Term cpe6_1@isp.com 00:12:03! This is the VID for the subscriber's traffic class521 Traffic-Cl unauthen Ltm Internal 00:12:03Use the show ip route vrf VPN11006 command to show routing table information for the VRF.

Note
To prevent revealing actual network addresses, the following configurations use IP addresses made up of letters instead of numbers.
In the following output, there is one active subscriber session:
ie2-C7206-LNS# show ip route vrf VPN11006
Routing Table: VPN11006Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGPD - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter areaN1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGPi - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static routeo - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static routeGateway of last resort is not setXR.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnetsB XR.1.206.0 [200/0] via 10.200.1.43, 4d19h1XT.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnetsC 1XT.6.6.6 is directly connected, Loopback1192.168.6.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets! This shows that the subscriber is connected and part of vrf VPN11006C 192.168.6.2 is directly connected, Virtual-Access32XW.6.6.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnetsB 2XW.6.6.6 [200/0] via 10.200.1.56, 4d19h10.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnetsB 10.100.4.38 [200/0] via 10.200.1.43, 4d19hie2-C7206-LNS#Verification of Default BOD256K Service
Use the show subscriber session uid 520 command to show detailed information for the subscriber with UID 520.
The following output is for a subscriber with the default BOD256K service:
ie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber session uid 520
Unique Session ID: 520Identifier: cpe6_1@isp.comSIP subscriber access type(s): VPDN/PPPCurrent SIP options: Req Fwding/Req FwdedSession Up-time: 00:12:10, Last Changed: 00:12:10AAA unique ID: 472Interface: Virtual-Access3Policy information:Context 212C1F2C: Handle 41000819Authentication status: authenUser profile, excluding services:service-type 2 [Framed]Framed-Protocol 1 [PPP]routing FalseFramed-MTU 1500 (0x5DC)timeout 86400 (0x15180)idletime 180 (0xB4)! The A attribute configures auto-login, which indicates that BOD256K! is the default service.ssg-account-info "ABOD256K"! The N indicates that the subscriber is allowed access to these services based on the! user's AAA profile.ssg-account-info "NBOD256K"ssg-account-info "NBOD1MTIME"ssg-account-info "NBOD2MTIME"ssg-account-info "NBOD1MVOLUME"ssg-account-info "NBOD2MVOLUME"idletime 1800 (0x708)interface-config "ip"interface-config "ip"addr-pool "cpe6_pool-53"! Indicates the current active services.Active services associated with session:name "BOD256K"! PBHK was applied when the session was started, as configured in the policy-map.name "PBHK_SERVICE", applied outwith active session! Because BOD256K is not a prepaid service, prepaid is not active.Prepaid context: not presentRules, actions and conditions executed:subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition always event session-start1 service-policy type service service PBHK_SERVICEsubscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD1MTIME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD1MTIME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD2MTIME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD2MTIME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD256K_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD256K_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD256K [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD1MVOLUME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD1MVOLUME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD2MVOLUME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD2MVOLUME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD1MTIME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD1MTIME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD2MTIME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD2MTIME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD256K_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD256K_CLASS! Services that are active are identified as "TRUE."match identifier service-name BOD256K [TRUE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD256K_CLASS event service-start1 service-policy service unapply service BOD1MTIME2 service-policy service unapply service BOD2MTIME3 service-policy service unapply service BOD1MVOLUME4 service-policy service unapply service BOD2MVOLUME5 service-policy service identifier service-nameSession inbound features:Traffic classes:Traffic class session ID: 521! Identifies the ACL that restricts inbound traffic. The ACL is configured on the ISG LNS,! and it is applied to the subscriber based on the subscriber profile on the AAA server.ACL Name: Internet-in-acl, Packets = 4, Bytes = 368Default traffic is droppedUnmatched Packets (dropped) = 0, Re-classified packets (redirected) = 0Feature: Portbundle Hostkey! Identifies the PBHK IP address and the bundle number. This information can be used to! troubleshoot PBHK with the show ip portbundle command.Portbundle IP = 10.200.1.55 Bundle Number = 761Session outbound features:Feature: PPP Idle TimeoutTimeout value is 1800! The current elapsed idle time.Idle time is 00:12:11Traffic classes:Traffic class session ID: 521ACL Name: Internet-out-acl, Packets = 0, Bytes = 0Default traffic is droppedUnmatched Packets (dropped) = 0, Re-classified packets (redirected) = 0Non-datapath features:Feature: Interface-ConfigFeature: Session TimeoutTimeout value is 86400 secondsTime remaining is 23:47:48Feature: IP ConfigAddress Pool: cpe6_pool-53Unnumbered Intf: [None]Configuration sources associated with this session:Service: BOD256K, Active Time = 00:12:11Service: PBHK_SERVICE, Active Time = 00:12:11Interface: Virtual-Template5, Active Time = 00:12:11Use the show subscriber session command with a session identifier to show detailed information for the subscriber with UID 521. The following output is for a subscriber with the default BOD256K service:
ie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber session uid 521
Unique Session ID: 521Identifier:SIP subscriber access type(s): Traffic-ClassCurrent SIP options: NoneSession Up-time: 00:12:14, Last Changed: 00:12:14AAA unique ID: 0Policy information:Context 212C1B18: Handle 5A00081CAuthentication status: unauthenPrepaid context: not presentSession inbound features:Feature: Policing! Identifies the upstream policing rates for the BOD256K service. These rates are defined! on the AAA server in the BOD256K service profile.Upstream Params:Average rate = 128000, Normal burst = 8000, Excess burst = 8000Config level = ServiceSession outbound features:Feature: Policing! Identifies the downstream policing rates for the BOD256K service. These rates are! defined on the AAA server in the BOD256K service profile.Dnstream Params:Average rate = 256000, Normal burst = 16000, Excess burst = 16000Config level = ServiceConfiguration sources associated with this session:Service: BOD256K, Active Time = 00:12:14show Command Output for BOD1MTIME Service
The following examples provide reports for subscribers who have activated the BOD1MTIME service:
ie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber session
Current Subscriber Information: Total sessions 1Uniq ID Interface State Service Identifier Up-time520 Vi3 authen Local Term cpe6_1@isp.com 00:14:17522 Traffic-Cl unauthen Ltm Internal cpe6_1@isp.com 00:00:11ie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber session uid 520Unique Session ID: 520Identifier: cpe6_1@isp.comSIP subscriber access type(s): VPDN/PPPCurrent SIP options: Req Fwding/Req FwdedSession Up-time: 00:14:29, Last Changed: 00:00:23AAA unique ID: 472Interface: Virtual-Access3Policy information:Context 212C1F2C: Handle 41000819Authentication status: authenUser profile, excluding services:service-type 2 [Framed]Framed-Protocol 1 [PPP]routing FalseFramed-MTU 1500 (0x5DC)timeout 86400 (0x15180)idletime 180 (0xB4)ssg-account-info "ABOD256K"ssg-account-info "NBOD256K"ssg-account-info "NBOD1MTIME"ssg-account-info "NBOD2MTIME"ssg-account-info "NBOD1MVOLUME"ssg-account-info "NBOD2MVOLUME"idletime 1800 (0x708)interface-config "ip"interface-config "ip"addr-pool "cpe6_pool-53"Active services associated with session:! Indicates that the BOD1MTIME service is active.name "BOD1MTIME"name "PBHK_SERVICE", applied outwith active sessionPrepaid context: not presentRules, actions and conditions executed:subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition always event session-start1 service-policy service service PBHK_SERVICEsubscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD1MTIME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD1MTIME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD2MTIME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD2MTIME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD256K_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD256K_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD256K [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD1MVOLUME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD1MVOLUME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD2MVOLUME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD2MVOLUME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD1MTIME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD1MTIME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD2MTIME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD2MTIME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD256K_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD256K_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD256K [TRUE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD256K_CLASS event service-start1 service-policy service unapply service BOD1MTIME2 service-policy service unapply service BOD2MTIME3 service-policy service unapply service BOD1MVOLUME4 service-policy service unapply service BOD2MVOLUME5 service-policy service identifier service-namesubscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD1MTIME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD1MTIME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD2MTIME_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD2MTIME [FALSE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD256K_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD256K_CLASSmatch identifier service-name BOD256K [TRUE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD256K_CLASS event service-start1 service-policy service unapply service BOD1MTIME2 service-policy service unapply service BOD2MTIME3 service-policy service unapply service BOD1MVOLUME4 service-policy service unapply service BOD2MVOLUME5 service-policy service identifier service-namesubscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service-startsubscriber condition-map match-any BOD1MTIME_CLASS! Indicates that the BOD1MTIME service is active.match identifier service-name BOD1MTIME [TRUE]subscriber rule-map RULE_PPP_ATM5condition BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service-start1 service-policy service unapply service BOD256K2 service-policy service unapply service BoD2MTIME3 service-policy service unapply service BOD1MVOLUME4 service-policy service unapply service BOD2MVOLUME5 service-policy service identifier service-nameSession inbound features:Traffic classes:Traffic class session ID: 522ACL Name: Internet-in-acl, Packets = 17, Bytes = 1157Default traffic is droppedUnmatched Packets (dropped) = 0, Re-classified packets (redirected) = 0Feature: Portbundle HostkeyPortbundle IP = 10.200.1.55 Bundle Number = 761Session outbound features:Feature: PPP Idle TimeoutTimeout value is 1800Idle time is 00:00:24Traffic classes:Traffic class session ID: 522ACL Name: Internet-out-acl, Packets = 26, Bytes = 28894Default traffic is droppedUnmatched Packets (dropped) = 0, Re-classified packets (redirected) = 0Non-datapath features:Feature: Interface-ConfigFeature: Session TimeoutTimeout value is 86400 secondsTime remaining is 23:45:28Feature: IP ConfigAddress Pool: cpe6_pool-53Unnumbered Intf: [None]Configuration sources associated with this session:Service: BOD1MTIME, Active Time = 00:00:25Service: PBHK_SERVICE, Active Time = 00:14:31Interface: Virtual-Template5, Active Time = 00:14:31ie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber session uid 522
Unique Session ID: 522Identifier: cpe6_1@isp.comSIP subscriber access type(s): Traffic-ClassCurrent SIP options: NoneSession Up-time: 00:00:27, Last Changed: 00:00:21AAA unique ID: 0Policy information:Context 212C1C74: Handle 40000821Authentication status: unauthen! Indicates that prepaid is now active to PREPAID_CONFIG.Prepaid context: PREPAID_CONFIGthreshold time 10 secondsthreshold volume 1000 bytesmethod-list author PREPAID_AUTHOR_LISTmethod-list accounting PREPAID_ACCNT_LISTpassword prepaidciscoInterim 3State PREPAID_FEATURE_RUNNINGFlow idle ? NOAcct start sent ? YESSession inbound features:Feature: PolicingUpstream Params:! Identifies the upstream policing rates for the BOD1MTIME service.Average rate = 256000, Normal burst = 16000, Excess burst = 16000Config level = ServiceFeature: Prepaid Volume MonitorThreshold:4294967295 - Quota:4294967295Usage(since last update):0 - Total:0Current states: StartSession outbound features:Feature: PolicingDnstream Params:! Identifies the downstream policing rates for the BOD1MTIME service.Average rate = 1000000, Normal burst = 64000, Excess burst = 64000Config level = ServiceFeature: Prepaid Volume MonitorThreshold:4294967295 - Quota:4294967295Usage(since last update):0 - Total:0Current states: StartNon-datapath features:! Shows the time statistics for the prepaid services.Feature: Time MonitorThreshold: 90 (seconds) - Quota: 100 (seconds)Session time: 21 (seconds)Configuration sources associated with this session:Service: BOD1MTIME, Active Time = 00:00:27show Command Output for History of Service Changes
Use the show subscriber policy conditions command as shown in the following examples to show the history of subscriber service changes:
ie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber policy conditions
Class-map Action Exec Hit Miss Comp--------- ------ ---- --- ---- ----match-any BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS match identifier service-name B 256 7 249 7match-any BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS match identifier service-name B 257 9 248 9match-any BOD2MTIME_CLASS match identifier service-name B 534 4 530 4match-any BOD256K_CLASS match identifier service-name B 505 259 246 259match-any BOD1MTIME_CLASS match identifier service-name B 548 37 511 37Key:"Exec" - The number of times this line was executed"Hit" - The number of times this line evaluated to TRUE"Miss" - The number of times this line evaluated to FALSE"Comp" - The number of times this line completed the execution of itscondition without a need to continue on to the endie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber policy profile
Current policy profile DB contents are:Profile name: PBHK_SERVICE, 4 referencesportbundle "enable"Profile name: apply-config-only, 3 referencesservice-type 2 [Framed]Framed-Protocol 1 [PPP]routing FalseFramed-MTU 1500 (0x5DC)timeout 86400 (0x15180)idletime 180 (0xB4)ssg-account-info "ABOD256K"ssg-account-info "NBOD256K"ssg-account-info "NBOD1MTIME"ssg-account-info "NBOD2MTIME"ssg-account-info "NBOD1MVOLUME"ssg-account-info "NBOD2MVOLUME"idletime 1800 (0x708)interface-config "ip"interface-config "ip"addr-pool "cpe6_pool-53"Profile name: BOD256K, 4 referencestraffic-class "in access-group name Internet-in-acl"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name Internet-out-acl"traffic-class "out default drop"ssg-service-info "IBOD256K"ssg-service-info "QU;128000;8000;8000;D;256000;16000;16000"ssg-service-info "R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0"policy-handle 1509951516 (0x5A00081C)Profile name: BOD1MTIME, 5 referencestraffic-class "in access-group name Internet-in-acl"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name Internet-out-acl"traffic-class "out default drop"ssg-service-info "IBOD1MTIME"ssg-service-info "QU;256000;16000;16000;D;1000000;64000;64000"ssg-service-info "R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0"policy-handle 1073743905 (0x40000821)Profile name: BOD1MTIME, 3 referencestraffic-class "in access-group name Internet-in-acl"traffic-class "in default drop"traffic-class "out access-group name Internet-out-acl"traffic-class "out default drop"ssg-service-info "IBOD1MTIME"ssg-service-info "QU;256000;16000;16000;D;1000000;64000;64000"ssg-service-info "R10.43.1.0;255.255.255.0"policy-handle 889194527 (0x3500081F)----------------------------------------------------------Entries in Profile dB subscribers for exact match----------------------------------------------------------No entries found in Profile dBie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber policy rules
Rule Class-map Action Exec---- --------- ------ ----internal-rule always event account-logon 1 authenticate aaa list default 0RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service 1 service-policy service unapply 21RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service 2 service-policy service unapply 21RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service 3 service-policy service unapply 21RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service 4 service-policy service unapply 21RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service 5 service-policy service identif 21RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service 1 service-policy service unapply 3RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service 2 service-policy service unapply 3RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service 3 service-policy service unapply 3RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service 4 service-policy service unapply 3RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service 5 service-policy service identif 3RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD256K_CLASS event service-s 1 service-policy service unapply 259RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD256K_CLASS event service-s 2 service-policy service unapply 259RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD256K_CLASS event service-s 3 service-policy service unapply 259RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD256K_CLASS event service-s 4 service-policy service unapply 259RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD256K_CLASS event service-s 5 service-policy service identif 259RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 1 service-policy service unapply 5RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 2 service-policy service unapply 5RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 3 service-policy service unapply 5RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 4 service-policy service unapply 5RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 5 service-policy service identif 5RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 1 service-policy service unapply 4RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 2 service-policy service unapply 4RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 3 service-policy service unapply 4RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 4 service-policy service unapply 4RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 5 service-policy service identif 4RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service 1 service-policy service unapply 1RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MTIME_CLASS event service 2 service-policy service service 1RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service 1 service-policy service unapply 16RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MTIME_CLASS event service 2 service-policy service service 16RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 1 service-policy service unapply 3RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 2 service-policy service service 3RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 1 service-policy service unapply 4RULE_PPP_ATM5 BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS event servi 2 service-policy service service 4RULE_PPP_ATM5 always event session-start 1 service-policy service service 233RULE_PPP_ATM5 always event quota-depleted 1 set-param drop-traffic FALSE 0RULE_PPP_ATM5 always event credit-exhausted 1 service-policy service service 0RULE_PPP_ATM5 always event internal-event-c 1 service-policy service unapply 0Key:"Exec" - The number of times this rule action line was executedClearing Statistics
Use the clear subscriber policy conditions command to clear the statistics of subscriber policy changes.
ie2-C7206-LNS# clear subscriber policy conditionsie2-C7206-LNS#ie2-C7206-LNS# show subscriber policy conditionsClass-map Action Exec Hit Miss Comp--------- ------ ---- --- ---- ----match-any BOD2MVOLUME_CLASS match identifier service-name B 0 0 0 0match-any BOD1MVOLUME_CLASS match identifier service-name B 0 0 0 0match-any BOD2MTIME_CLASS match identifier service-name B 0 0 0 0match-any BOD256K_CLASS match identifier service-name B 0 0 0 0match-any BOD1MTIME_CLASS match identifier service-name B 0 0 0 0Key:"Exec" - The number of times this line was executed"Hit" - The number of times this line evaluated to TRUE"Miss" - The number of times this line evaluated to FALSE"Comp" - The number of times this line completed the execution of itscondition without a need to continue on to the endAdditional References
The following sections provide references related to configuring the ISG in an ATM-based broadband network:
Related Documents
Broadband and DSL configuration
Cisco IOS Broadband and DSL Configuration Guide, Release 12.4
CAR configuration procedure
Cisco CNS Access Registrar Installation and Configuration Guide, 3.5
CNR configuration procedure
ISG software configuration
L2TP VPDN for dialin and dialout configuration
Cisco IOS VPDN Configuration Guide, Release 12.4
QoS configuration
Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide, Release 12.4
RADIUS attributes
RADIUS Attribute-Value Pairs and Dictionary Management
RADIUS Vendor-Proprietary Attributes
"RADIUS Service and User Profile Attributes" in the Cisco SSG-to-ISG DSL Broadband Migration Guide
Virtual template interface configuration
"Configuring Virtual Template Interfaces" in the Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Configuration Guide, Release 12.4
Standards
RFCs
Technical Assistance
Glossary
AAA—Authentication, authorization, and accounting
AAL5/SNAP—ATM adaptation Layer 5/Subnetwork Access Protocol
ACL—Access control list or access list
ATU-R—ADSL Transmission Unit—remote
BRAS—Broadband Remote Access Server
CAR—Cisco Access Registrar
CHAP—Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
CNR—CNS Network Registrar
CPE—customer premises equipment
DBS—Dynamic Bandwidth Selection
DHCP—Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DNS—Domain Name System
DSCP—Differentiated Services Code Point
DSL—Digital subscriber line
DSLAM—Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer
IPCP—IP Control Protocol
ISG—Intelligent Service Gateway
ISP—Internet service provider
L2TP—Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol
LAC—L2TP access concentrator
LCP—Link control protocol28
LNS—L2TP network server
MAC—Media Access Control
MPLS—Multiprotocol Label Switching
NAT—Network Address Translation
OC—optical carrier
PBHK—Port-Bundle Host Key
PE—provider edge
PPPoE—PPP over Ethernet
PVC—permanent virtual circuit
QoS—quality of service
RBE—Routed Bridge Encapsulation
SESM—Subscriber Edge Services Manager
SSG—Service Selection Gateway
TAL—Transparent Autologin
UNI—user network interface
VoIP—Voice over IP
VPDN—virtual private dialup network
VPN—Virtual Private Network
VRF—VPN routing and forwarding instances
VSA—vendor-specific attribute

Note
See Internetworking Terms and Acronyms for terms not included in this glossary.

Copyright © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback