Cisco Virtual Network Management Center Quick Start Guide, Release 2.0
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center 2.0 Quick Start Guide
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center Documentation
Cisco Virtual Security Gateway Documentation
Cisco Nexus 1000V Series Switch Documentation
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Configuring Chrome for Use with VNMC
Task 2—Configuring VNMC Connectivity with vCenter
Downloading the vCenter Extension File
Registering the vCenter Extension Plug-In in vCenter
Configuring vCenter in VNMC VM Manager
Task 3—Registering an ASA 1000V to VNMC
Task 4—Verifying VSG, VSM, and ASA 1000V Registration in VNMC
Task 6—Configuring a Service Profile in VNMC
Task 7—Configuring a Device Profile in VNMC
Task 8—Configuring a Compute Firewall
Task 9—Assigning a Compute Firewall to a VSG
Task 10—Creating an Edge Security Profile
Task 11—Configuring Access Rules
Task 12—Configuring an Edge Firewall
Task 13—Associating an Edge Firewall with an ASA 1000V Instance
Enabling Policy-Engine Logging in a Monitor Session
Enabling Global Policy-Engine Logging
Troubleshooting VNMC Installation and Configuration
Examining Faults and Configuration Errors for Edge Firewalls
Examining Faults and Configuration Errors for Compute Firewalls
Backing Up VNMC 1.x Data Using the CLI
Upgrading to VNMC 2.0 Using the CLI
Backing Up VNMC 2.0 Using the GUI
Restoring the Previous VNMC Version
Exporting and Importing in VNMC
Exporting VNMC Configuration Data
Importing VNMC Configuration Data
Quick Start Guide
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center 2.0 Quick Start Guide
Revised: July 9, 2013, OL-27555-01
1 Preface
This guide explains how to install Cisco Virtual Network Management Center (VNMC) 2.0.
Related Documentation
The following topics contain information about the documentation available for VNMC and related products:
•
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center Documentation
•
Cisco Virtual Security Gateway Documentation
•
Cisco Nexus 1000V Series Switch Documentation
•
Cisco ASA 1000V Documentation
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center Documentation
The following Cisco Virtual Network Management Center documents are available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps11213/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
•
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center 2.0 Documentation Overview
•
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center 2.0 CLI Configuration Guide
•
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center 2.0 GUI Configuration Guide
•
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center 2.0 Quick Start Guide
•
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center 2.0 Release Notes
•
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center 2.0 XML API Reference Guide
•
Open Source Used in Cisco Virtual Network Management Center, 2.0
Cisco Virtual Security Gateway Documentation
The Cisco Virtual Security Gateway (VSG) for Nexus 1000V Series switch documentation is available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps11208/tsd_products_support_model_home.html
Cisco Nexus 1000V Series Switch Documentation
The Cisco Nexus 1000V Series switch documentation is available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9902/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Cisco ASA 1000V Documentation
The Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) documentation is available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps12233/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as an RSS feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service. Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
2 Installation Prerequisites
The following tables list the requirements for installing and configuring VNMC, and for configuring communications with VSG, ASA 1000V, and Cisco Virtual Supervisor Module (VSM):
•
Table 1: VNMC System Requirements
•
Table 2: Web-Based GUI Client Requirements
•
Table 3: Firewall Ports Requiring Access
•
Table 4: Cisco Nexus 1000V Series Switch Requirements
•
Table 5: Information Required for Installation and Configuration

Note
If you install VNMC with VSG and/or ASA 1000V, memory and disk space requirements are higher than identified in Table 1. For more information, see the Cisco Virtual Security Gateway, Rel. 4.2(1)VSG1(4.1) and Cisco Virtual Network Management Center, Rel. 2.0 Installation and Upgrade Guide.
Table 2 Web-Based GUI Client Requirements
Operating system
Either of the following:
•
Microsoft Windows
•
Apple Mac OS
Browser
Any of the following:
•
Internet Explorer 9.0
•
Mozilla Firefox 11.01
•
Chrome 18.02
Flash Player
Adobe Flash Player plugin (version 11.2)
1 We recommend Mozilla Firefox 11.0 with Adobe Flash Player 11.2.
2 Before you can use Chrome with VNMC 2.0, you must first disable the Adobe Flash Players that are installed by default with Chrome. For more information, see Configuring Chrome for Use with VNMC.
Table 5 Information Required for Installation and Configuration
Name
Location of files
Data store location
Storage location, if more than one location is available
Management port profile name for VM management
Note
The management port profile is the same port profile that is used for VSM. The port profile is configured in VSM and is used for the VNMC management interface.
IP address
Subnet mask
Gateway IP address
Domain name
DNS server
Admin password
Shared secret password for communications between VNMC, VSG, ASA 1000V, and VSM. (See Shared Secret Password Criteria.)
vCenter name
Description
Hostname or IP address
Shared Secret Password Criteria
A shared secret password is a password that is known only to those using a secure communication channel. Passwords are designated as strong if they cannot be easily guessed for unauthorized access. When you set a shared secret password for communications between VNMC, VSG, ASA 1000V, and VSM, adhere to the following criteria for setting valid, strong passwords:
•
Do not include the following items in passwords:
–
These characters: & ' " ` ( ) < > | \ ; $
–
Spaces
•
Make sure your password contains the characteristics of strong passwords as described in Table 6.
Examples of strong passwords are:
•
If2CoM18
•
2004AsdfLkj30
•
Cb1955S21
Configuring Chrome for Use with VNMC
To use Chrome with VNMC 2.0, you must disable the Adobe Flash Players that are installed by default with Chrome.

Note
You must perform this procedure each time your client machine reboots. Chrome automatically enables the Adobe Flash Players when the system on which it is running reboots.
To disable default Adobe Flash Players in Chrome:
Step 1
In the Chrome URL field, enter chrome://plugins.
Step 2
Click Details.
Step 3
Locate the Adobe Flash Player plugins, and disable each one.
Step 4
Download and install Adobe Flash Player version 11.3.300.265.
Step 5
Close and reopen Chrome before logging into VNMC 2.0.
3 Installing VNMC

Note
If you are installing both VNMC and VSG in your environment, refer to the Cisco Virtual Security Gateway, Rel. 4.2(1)VSG1(4.1) and Cisco Virtual Network Management Center, Rel. 2.0 Installation and Upgrade Guide for complete installation instructions.
This procedure describes how to deploy the VNMC OVA, resulting in a VNMC VM.
Before You Begin
•
You must set your keyboard to United States English before installing Cisco VNMC and using the VM console.
•
Verify that the VNMC OVA image is available in the vSphere Client.
•
Make sure that all system requirements are met as specified in Installation Prerequisites.
•
Make sure you have the information identified in Table 5.
•
You must configure NTP on all ESX and ESXi servers that run VNMC, ASA 1000V, VSG, and VSM. For information, see Configuring Network Time Protocol (NTP) on ESX/ESXi 4.1 and ESXi 5.0 hosts using the vSphere Client at http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2012069.
To deploy the VNMC OVA:
Step 1
Use vSphere Client to log into the vCenter Server.
Step 2
Choose the host on which to deploy the VNMC VM.
Step 3
From the File menu, choose Deploy OVF Template.
Step 4
In the Source screen (see Figure 1), choose the VNMC OVA, then click Next.
Step 5
In the OVF Template Details screen, review the details of the VNMC template, then click Next.
Step 6
In the End User License Agreement screen, click Accept, then click Next.
Step 7
In the Name and Location screen, provide the required information, then click Next.
Step 8
In the Deployment Configuration screen, choose VNMC Installer from the Configuration drop-down list, then click Next.
Step 9
In the Datastore screen (see Figure 2), select the data store for the VM, then click Next.
The storage can be local or shared remote, such as NFS or SAN.

Note
If only one storage location is available for an ESX host, this window is not displayed and the VM is assigned to the storage location that is available.
Step 10
In the Disk Format screen, click either Thin provisioned format or Thick provisioned format to store the VM virtual disks, then click Next.
The default is thick provisioned. If you do not want to allocate the storage immediately, use thin provisioned.

Note
You can safely ignore the red text in the window.
Step 11
In the Network Mapping screen, select the management network port profile for the VM, then click Next.
Step 12
In the Properties screen (see Figure 3), provide the required information, and address any errors described in the red text messages below the selection box (if needed, you can enter placeholder information as long as your entry meets the field requirements); then click Next.

Note
You can safely ignore the VNMC Restore fields.
Step 13
In the Ready to Complete screen (see Figure 4), review the deployment settings, then click Finish.

CautionAny discrepancies can cause VM booting issues. Carefully review the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway information.
A progress indicator shows the task progress until VNMC is deployed.
Step 14
After VNMC is successfully deployed, click Close and power on the VNMC VM.
Example Screens Showing OVA Deployment
Figure 1 Source Screen

Figure 2 Datastore Screen
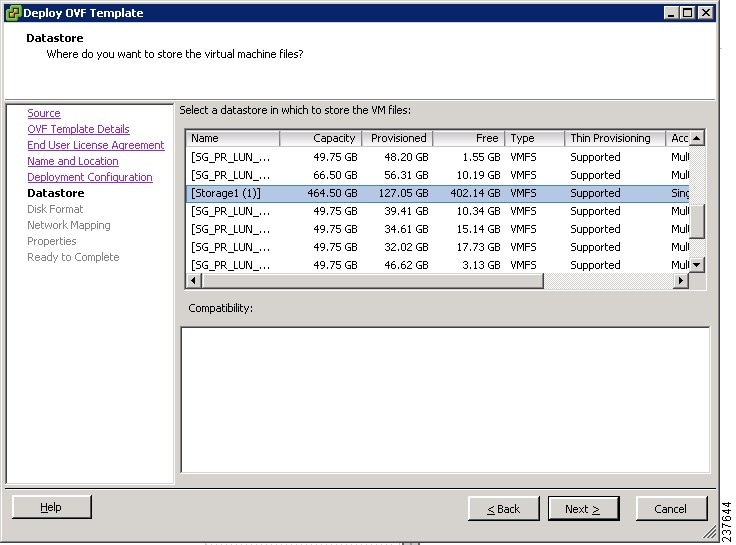
Figure 3 Properties Screen

Figure 4 Ready to Complete Screen

4 Configuring VNMC
Table 7 provides a checklist of the VNMC configuration tasks.
Table 7 Task Checklist for VNMC 2.0 Configuration
Task 4—Verifying VSG, VSM, and ASA 1000V Registration in VNMC
Task 13—Associating an Edge Firewall with an ASA 1000V Instance
Task 1—Configuring NTP
Before you perform any operations in VNMC, configure Network Time Protocol (NTP) on ASA 1000V, VSG, and VSM. If you do not do so, ASA 1000Vs, VSGs, and VSMs will not be able to register with VNMC.
To configure NTP in VNMC, ASA 1000V, VSG, and VSM:
3.
Configuring NTP in ASA 1000V
Configuring NTP in VSM
To configure NTP, enter the following CLI command from the VSM console:
ntp server x.x.x.xwhere x.x.x.x is the NTP server IP address.
Configuring NTP in VSG
To configure NTP, enter the following CLI command from the VSG console:
ntp server x.x.x.xwhere x.x.x.x is the NTP server IP address.

Note
The ntp server command will not be available in the VSG console if you have installed the VNMC policy agent. To configure NTP in VSG, you must uninstall the VNMC policy agent.
Configuring NTP in ASA 1000V
Before you install ASA 1000V in VNMC, be sure to configure NTP on all ESX and ESXi servers that run ASA 1000V. For information, see Configuring Network Time Protocol (NTP) on ESX/ESXi 4.1 and ESXi 5.0 hosts using the vSphere Client.
After installation, ASA 1000V receives the Real Time Clock (RTC) value from the VMware ESX or ESXi host.
Configuring NTP in VNMC
To configure NTP in VNMC:
Step 1
In your browser, enter https://vnmc-ip where vnmc-ip is the VNMC IP address.
Step 2
If you receive a certificate warning, choose to continue to the VNMC login window.
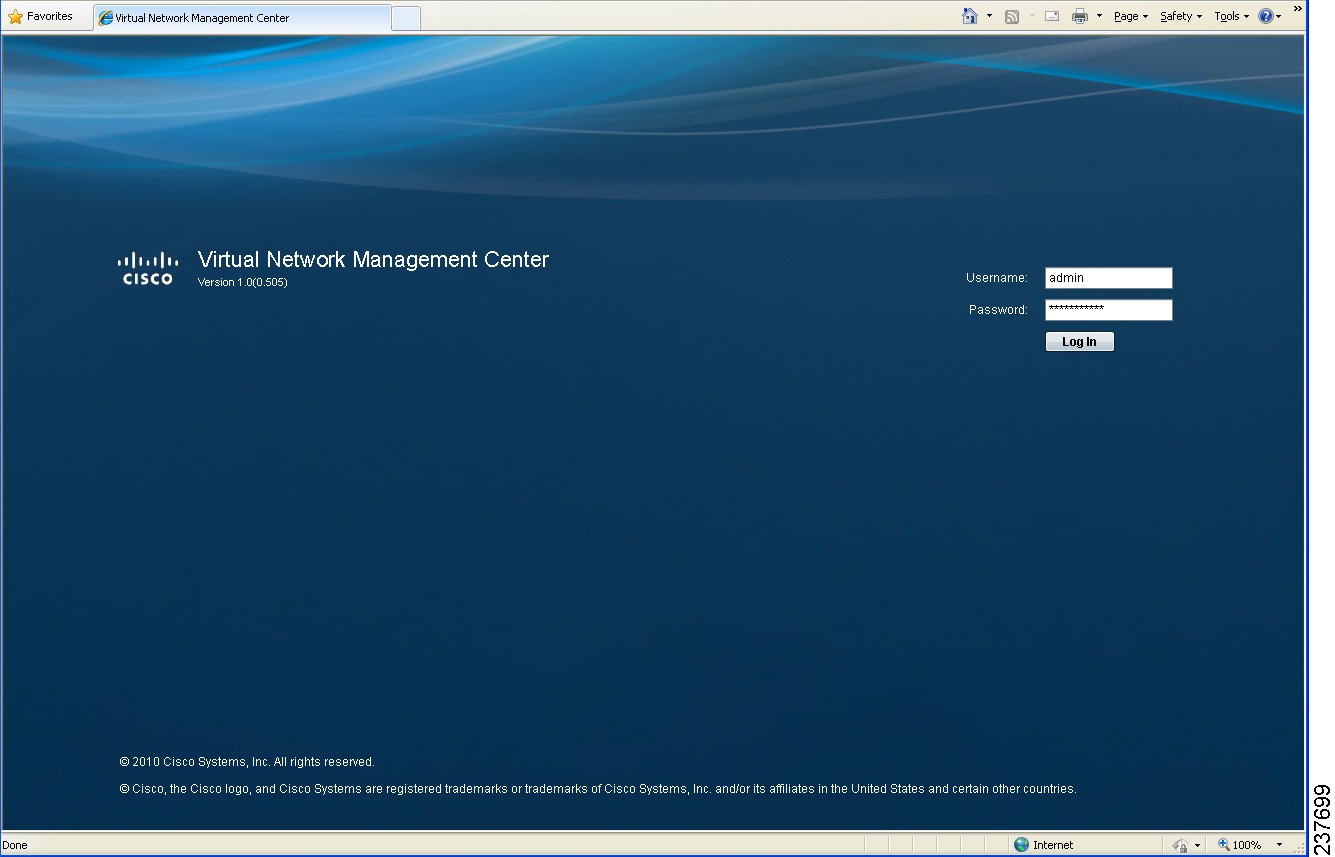
Step 3
In the VNMC login window (see Figure 5), enter the username admin and the admin user password. This is the password that you set when deploying the VNMC OVA (see Step 12 in Installing VNMC).
Step 4
From the VNMC GUI, set the time zone:
a.
Choose Administration > VNMC Profile > root > VNMC Profile > default.
b.
In the General tab, select the time zone.
c.
Click Save.
Step 5
From the VNMC GUI, add an external NTP server as time source:
a.
Choose Administration > VNMC Profile > root > VNMC Profile > default.
b.
In the Policy tab, select Add NTP Server.
c.
Enter the hostname or IP address and click OK.
d.
Click Save.

CautionWe recommend that you do not set the time zone after you add the NTP server.
Example Screen Showing the VNMC Login Window
Figure 5 VNMC Login Window
Task 2—Configuring VNMC Connectivity with vCenter
After you deploy the VNMC OVA, you need to establish connectivity with VMware vCenter by:
1.
Downloading the vCenter Extension File
2.
Registering the vCenter Extension Plug-In in vCenter
3.
Configuring vCenter in VNMC VM Manager
Before You Begin
Make sure you have the information identified in Table 5.
Downloading the vCenter Extension File
The first step in setting up vCenter connectivity is to download the vCenter extension file.
To download the vCenter extension file:
Step 1
In VNMC, choose Administration > VM Managers > VM Managers.
Step 2
In the VM Managers pane (see Figure 6), click Export vCenter Extension.
Step 3
Save the vCenter extension file in a directory that the vSphere Client can access, because you will need to register the vCenter extension plug-in from within your vSphere Client (see Registering the vCenter Extension Plug-In in vCenter).
Example Screen Showing VM Managers Pane
Figure 6 VM Managers Pane

Registering the vCenter Extension Plug-In in vCenter
To register the vCenter extension plug-in in vCenter:
Step 1
From the VMware vSphere client, log into the vCenter Server that you want to manage from within VNMC.
Step 2
In the vSphere client (see Figure 7), choose Plug-ins > Manage Plug-ins.
Step 3
Right-click the window background and choose New Plug-in.

Tip
You might need to scroll down and right-click near the bottom of the window to view the New Plug-in option.
Step 4
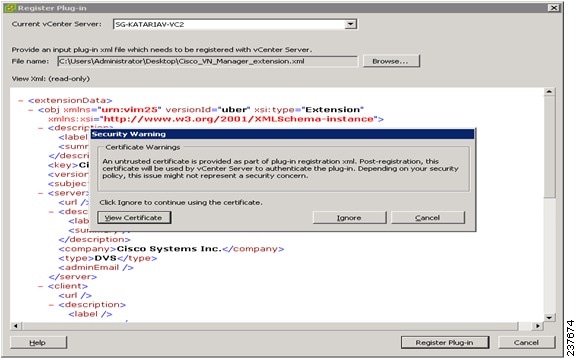
Browse to the VNMC vCenter extension file that you downloaded earlier and click Register Plug-in.
The vCenter Register Plug-in Window (see Figure 8) appears, displaying a security warning.
Step 5
In the security warning message box, click Ignore.
A progress indicator shows the task status.
Step 6
When the success message is displayed, click OK, then click Close.
Example Screens Showing vCenter Extension Plug-In Registration
Figure 7 vSphere Client Directory

Figure 8 vCenter Register Plug-in Window
Configuring vCenter in VNMC VM Manager
To configure vCenter in VNMC VM Manager:
Step 1
In VNMC, choose Administration > VM Managers > VM Managers.
Step 2
In the VM Managers Pane, click Add VM Manager.
Step 3
In the Add VM Manager dialog box, enter the required information for vCenter, then click OK.
A successfully added VM manager is displayed with the following information:
•
Admin State of enable.
•
Operational State of up.
•
VMware vCenter version.
Task 3—Registering an ASA 1000V to VNMC
Before You Begin
•
Before you install ASA 1000V in VNMC, be sure to configure NTP on all ESX and ESXi servers that run ASA 1000V. For more information, see Configuring NTP in ASA 1000V.
•
Deploy ASA 1000V VM using the vSphere Client.
•
Make sure that a network path exists between the ASA 1000V management IP address and the VNMC management IP address.
To register an ASA 1000V to VNMC from within vSphere Client:
Step 1
Choose Home > Inventory > Hosts and Clusters.
Step 2
Navigate to the newly deployed (and powered on) ASA 1000V VM.
Step 3
Click the Console tab to access the ASA 1000V CLI.
Step 4
In the ASA 1000V CLI, configure the VNMC IP address and the shared secret, using:
ciscoasa> enablePassword:ciscoasa# configure terminalciscoasa(config)# vnmc policy-agentciscoasa(config-vnmc-policy-agent)# registration host n.n.n.nciscoasa(config-vnmc-policy-agent)# shared-secret MySharedSecret
Task 4—Verifying VSG, VSM, and ASA 1000V Registration in VNMC
Before You Begin
•
Make sure you have the information identified in Table 5.
•
Do the following:
If you are installing VSM:
a.
Verify that NTP is set up on VSM. For more information, see Task 1—Configuring NTP.
b.
Register VSM to VNMC.
c.
On VSM, verify the VNMC policy agent status.
d.
On VSM, prepare VSG and ASA 1000V port profiles.
If you are registering VSG with VNMC:
a.
Install VSG.
b.
Verify that NTP is set up on VSG. For more information, see Task 1—Configuring NTP.
c.
Register VSG to VNMC.
d.
On VSG, verify the VNMC policy agent status.
If you are registering ASA 1000V with VNMC:
a.
Verify that NTP is set up on all ESX and ESXi servers that run ASA 1000V. For more information, see Task 1—Configuring NTP.
b.
Install ASA 1000V.
c.
Register ASA 1000V to VNMC. For more information, see Task 3—Registering an ASA 1000V to VNMC.
d.
On ASA 1000V, verify the VNMC policy agent status.

Note
For more information on these tasks, see Registering Devices with Cisco VNMC.
To verify if VSG, VSM, and ASA 1000V are registered with VNMC:
Step 1
In VNMC, choose Administration > Service Registry > Clients.
Step 2
Confirm that the table in the Clients window (see Figure 9) contains registered in the Oper State column for the ASA 1000V, VSG, and VSM entries.
Example Screen Showing the Client Window
Figure 9 Clients Window

Task 5—Configuring a Tenant
Tenants are entities (such as businesses, agencies, or institutions) whose data and processes are hosted on VMs in a virtual data center. To provide firewall security for each tenant, you must first configure the tenant in VNMC.
To configure a tenant:
Step 1
Choose Tenant Management > root.
Step 2
In the upper-right corner of the Tenant Management Root pane (see Figure 10), click Create Tenant.
Step 3
In the Create Tenant dialog box, enter a name and brief description for the tenant, then click OK.
The newly created tenant is listed in the navigation pane under root (see Figure 11).
Example Screens Showing Tenant Configuration
Figure 10 Tenant Management Root Pane

Figure 11 VNMC Navigation Pane with Tenant

Task 6—Configuring a Service Profile in VNMC
A profile is a collection of policies. By creating a profile and then applying that profile to one or more objects (such as a data interface for an ASA 1000V or a VSM port profile), you can ensure that those objects have consistent policies.
To configure a compute security profile in VNMC:
Step 1
Choose Policy Management > Service Profiles > root > tenant > Compute Firewall > Compute Security Profiles where tenant is the required tenant.
Step 2
In the General tab, click Add Compute Security Profile.
Step 3
In the Add Compute Security Profile dialog box, enter a name and description for the security profile, then click OK.
Task 7—Configuring a Device Profile in VNMC
To configure a device profile in VNMC:
Step 1
Choose Policy Management > Device Configurations > root > tenant > Device Profiles where tenant is the required tenant.
Step 2
In the General tab, click Add Device Profile.
Step 3
In the New Device Profile dialog box, enter a name and description for the device profile, then click OK.
Task 8—Configuring a Compute Firewall
A compute firewall is a logical virtual entity in VNMC that contains the device profile that you assign to a VSG VM. Any device policies that are in the VNMC device profile are applied to the assigned VSG. After the policy has been applied to the VSG, the compute firewall is in an applied configuration state in VNMC.
To configure a compute firewall:
Step 1
Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Compute Firewalls.
Step 2
In the General tab, click Add Compute Firewall.
Step 3
In the Add Compute Firewall dialog box (see Figure 12), enter the information described in Table 8, then click OK.
The VNMC window is refreshed and displays the newly created compute firewall.
Field Descriptions
Example Screen Showing the Add Compute Firewall Dialog Box
Figure 12 Add Compute Firewall Dialog Box

Task 9—Assigning a Compute Firewall to a VSG
After you configure a compute firewall in VNMC, you can assign it to a VSG so that the device policies in the specified device profile are applied to the VSG.
To assign a compute firewall to a VSG:
Step 1
Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Compute Firewalls > compute-firewall.
Step 2
Right-click the selected compute firewall, and choose Assign VSG.
Step 3
In the Assign VSG dialog box, from the VSG Management IP drop-down list, choose the VSG IP address, then click OK.
As the configuration is applied to the VSG, the Config State status changes from not-applied to applying, and then to applied.
Task 10—Creating an Edge Security Profile
VNMC provides support for virtual edge firewalls, such as an ASA 1000V instance. After you add a virtual edge firewall, you can:
•
Create and configure service policies.
•
Create and configure edge device profile and edge security profiles for the edge firewalls.
•
Create an edge firewall.
•
Apply the required profiles to the edge firewall and an outside edge firewall interface.
To create an edge security profile:
Step 1
Choose Policy Management > Service Profiles > root > tenant > Edge Firewall > Edge Security Profiles.
Step 2
In the General Tab, click Add Edge Security Profile.
Step 3
In the Add Edge Security Profile dialog box that appears, do the following:
a.
In the General tab, enter a name and description for the Edge Security Profile.
b.
In the Ingress tab, choose a policy set from the Ingress Policy Set drop-down list.
c.
In the Egress tab, choose a policy set from the Egress Policy Set drop-down list.

Note
To add an ACL Policy set, click Add ACL Policy Set and follow Task 11—Configuring Access Rules.
Step 4
In the NAT tab, select a NAT policy set from the Policy Set drop-down list. To add a policy set to the list:
a.
Click Add NAT Policy Set.
b.
In the Add NAT Policy Set dialog box that appears, enter the information as described in Table 9.
c.
Click OK.

Note
For information on the VPN and Advanced Tabs, see Cisco Virtual Network Management Center 2.0 GUI Configuration Guide.
Step 5
Click OK.
Field Descriptions
Table 9 Add NAT Policy Set Dialog Box Fields
Name
NAT policy set name.
Description
Brief NAT policy set description.
Admin State
Enable or disable the Admin state.
Policies
1.
Click Add NAT Policy.
2.
In the Add NAT Policy dialog box that appears, enter the information as described in Table 10.
3.
Click OK.
Table 10 Add NAT Policy Dialog Box Fields
Name
NAT policy name.
Description
Brief NAT policy description.
Admin State
Enable or disable the Admin state.
Rule Table
1.
Click Add Rule.
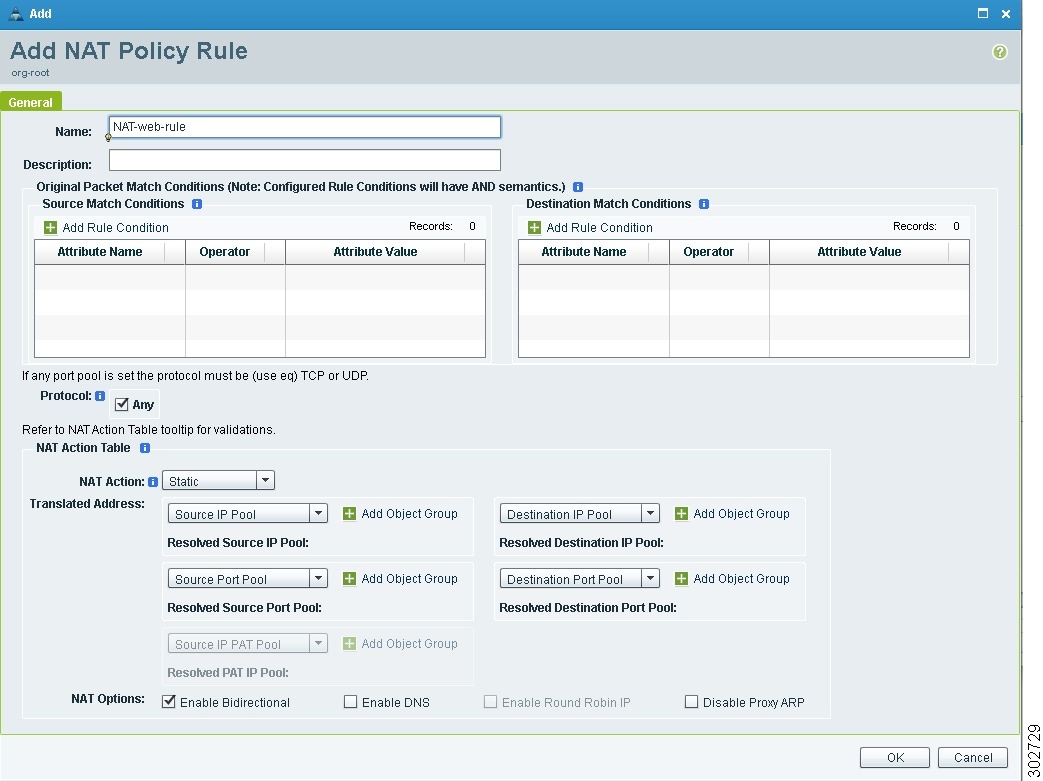
2.
In the Add NAT Policy Rule dialog box (see Figure 13) that appears, enter the information as described in Table 11.
3.
Click OK.
Table 11 Add NAT Policy Rule Dialog Box Fields
Name
NAT policy name.
Description
Brief NAT policy description.
Source Match Conditions
To add a add rule condition to the following:
1.
Click Add Rule Condition.
2.
In the Add Rule Condition dialog box that appears, enter the information as described in Table 12.
3.
Click OK.
Destination Match Conditions
To add a add rule condition to the following:
1.
Click Add Rule Condition.
2.
In the Add Rule Condition dialog box that appears, enter the information as described in Table 12.
3.
Click OK.
Protocol
Protocols to be examined for this policy rule:
•
To examine all protocols, check the Any check box.
•
To examine specific protocols, uncheck the Any check box and specify the required operator and value for this rule.
NAT Action
Choose either a static or a dynamic NAT action.
Source IP Pool
Source Port Pool
Destination IP Pool
Destination Port Pool
Choose the required IP pool or port pool from the drop-down list. To add an object group, do the following:
1.
Click Add Object Group.
2.
In the Add Object Group dialog box that appears, enter the information as described in Table 13.
3.
Click OK.
NAT Options
Choose the required NAT options.
Table 13 Add Object Group Fields
Name
Object group name.
Description
Brief object group description.
Expression
1.
Click Add Object Group Expression.
2.
In the Add Object Group Expression dialog box that appears, enter the information as described in Table 12.
3.
Click OK.
Example Screen Showing the Add NAT Policy Rule Dialog Box
Figure 13 Add NAT Policy Rule Dialog Box
Task 11—Configuring Access Rules
Access rules in VNMC permit or deny traffic based on the following items:
•
Protocol
•
Source IP address or network
•
Destination IP address or network
•
(Optional) Source and destination ports
To configure access rules:
Step 1
Choose Policy Management > Service Policies > root > tenant > Policies > ACL > ACL Policy Sets.
Step 2
In the General tab, click Add ACL Policy Set.
Step 3
In the Add ACL Policy Set Dialog Box (see Figure 14), enter a name and description for the policy set.
Step 4
Select the required ACL Policy, and move it from the Available list to the Assigned list.
Step 5
Add a ACL Policy:
a.
Click Add ACL Policy.
b.
In the Add ACL Policy dialog box, enter a name and description for the policy, then click Add Rule.
c.
In the Add ACL Policy Rule dialog box (see Figure 15), enter the information described in Table 14, then click OK.

Note
For more information about the options available in the Add ACL Policy Rule dialog box, see the online help.
Step 6
Click OK in each of the open dialog boxes.
The VNMC window is refreshed, and the ACL Policy Sets table contains the new policy set.
Field Descriptions
Example Screens Showing Access Rule Configuration
Figure 14 Add ACL Policy Set Dialog Box
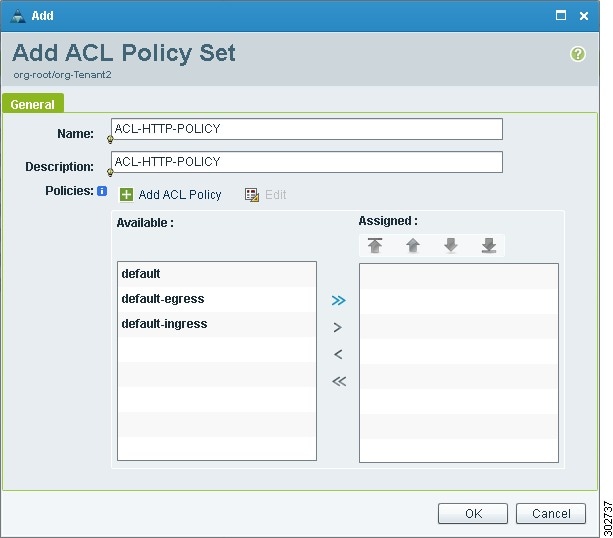
Figure 15 Add ACL Policy Rule Dialog Box

Task 12—Configuring an Edge Firewall
To configure an edge firewall:
Step 1
Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Edge Firewalls.
Step 2
In the General tab, click Add Edge Firewall.
Step 3
In the Add Edge Firewall dialog box (see Figure 16), provide the information described in Table 15.
Step 4
Add one inside and one outside data interface to the edge firewall.
a.
Click Add Data Interface. The Add Data Interface dialog box appears (see Figure 17).
b.
To add one inside data interface, provide the information described in Table 16.
c.
To add one outside data interface, provide the information described in Table 16.
d.
Click OK.
Step 5
Click OK.
Field Descriptions
Example Screen Showing Edge Firewall Configuration
Figure 16 Add Edge Firewall Dialog Box

Figure 17 Add Data Interface Dialog Box
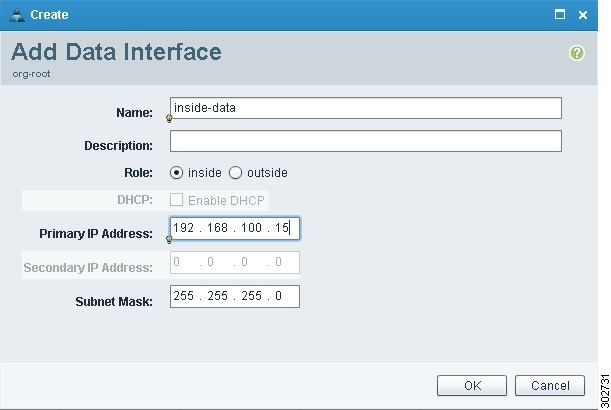
Task 13—Associating an Edge Firewall with an ASA 1000V Instance
To associate an edge firewall with an ASA 1000V instance:
Step 1
Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Edge Firewalls > edge-firewall.
The VNMC GUI displays the newly added edge firewall (see Figure 18) and the following information:
•
Configuration state
•
Association state
•
Pool assignment
•
Faults tab
Step 2
In the General tab, right-click the required edge firewall and choose Assign ASA 1000V.
Step 3
In the Assign ASA 1000V dialog box, choose the required ASA 1000V instance from the ASA 1000V Management IP drop-down list.
Step 4
Click OK.
The VNMC GUI now displays the edge firewall (see Figure 18) and the following additional information:
•
Faults associated with firewall
•
Edge Security Profiles tab (to view associated edge security profiles configured in VSM)
•
ASA 1000V instance information:
–
Service ID
–
Management IP address
–
HA role
–
Association state
–
Reachability
Step 5
To access more ASA 1000V instance properties, task details, faults, or events, click Task in the ASA 1000V Details area.
Example Screen Showing the Newly Added Edge Firewall
Figure 18 Newly Added Edge Firewall with ASA 1000V Information

Task 14—Enabling Logging
If appropriate for your environment, you can configure and enable syslog policies for VSG or ASA 1000V elements by:
•
Enabling Policy-Engine Logging in a Monitor Session
•
Enabling Global Policy-Engine Logging
Configuring and enabling a syslog policy for a VSG or ASA 1000V element ensures that you receive syslog messages for the severities that you specify. For example, depending on the syslog policy, you could receive syslog messages notifying you that a firewall rule has been invoked and that a permit or deny action has been taken.
Logging enables you to monitor traffic, troubleshoot issues, and verify that devices are configured and operating properly.
Enabling Policy-Engine Logging in a Monitor Session
To enable logging level 6 for policy-engine logging in a monitor session:
Step 1
Choose Policy Management > Device Configurations > root > Policies > Syslog.
Step 2
In the Syslog table, select default, then click Edit.
Step 3
In the Syslog Policy dialog box that appears, click the Servers tab.
Step 4
In the Syslog Policy table (see Figure 19), select the primary server type, then click Edit.
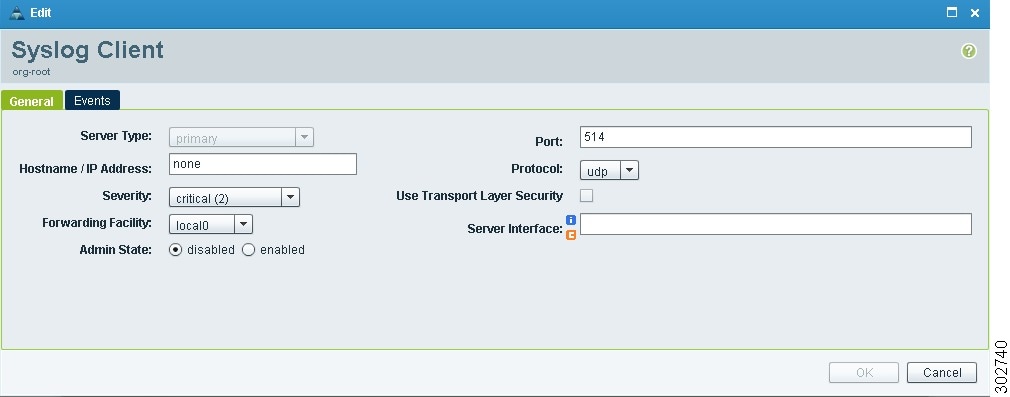
Step 5
In the Syslog Client dialog box (see Figure 20), specify the following information, then click OK:
•
Hostname/IP Address—Enter the syslog server IP address or hostname.
•
Severity—Choose Information(6).
•
Admin State—Choose Enabled.
The Syslog Policy dialog box is refreshed with the updated information.
Step 6
Click OK to save changes and return to the VNMC window.
Example Screens Showing Enabling Policy-Engine Logging
Figure 19 Syslog Policy Dialog Box
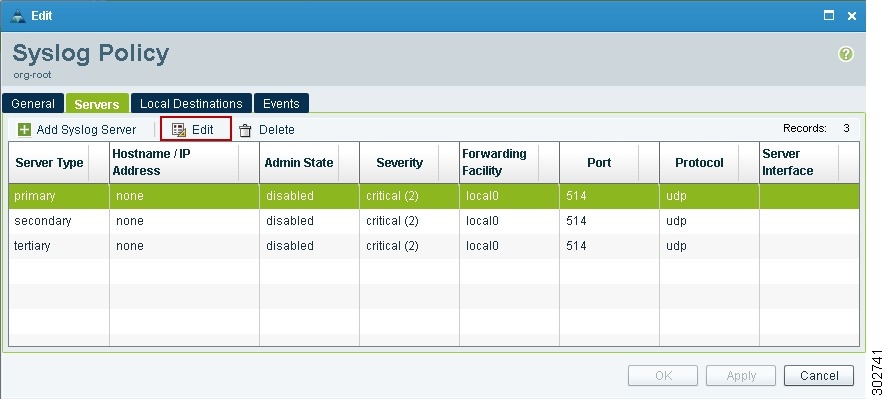
Figure 20 Syslog Client Dialog Box
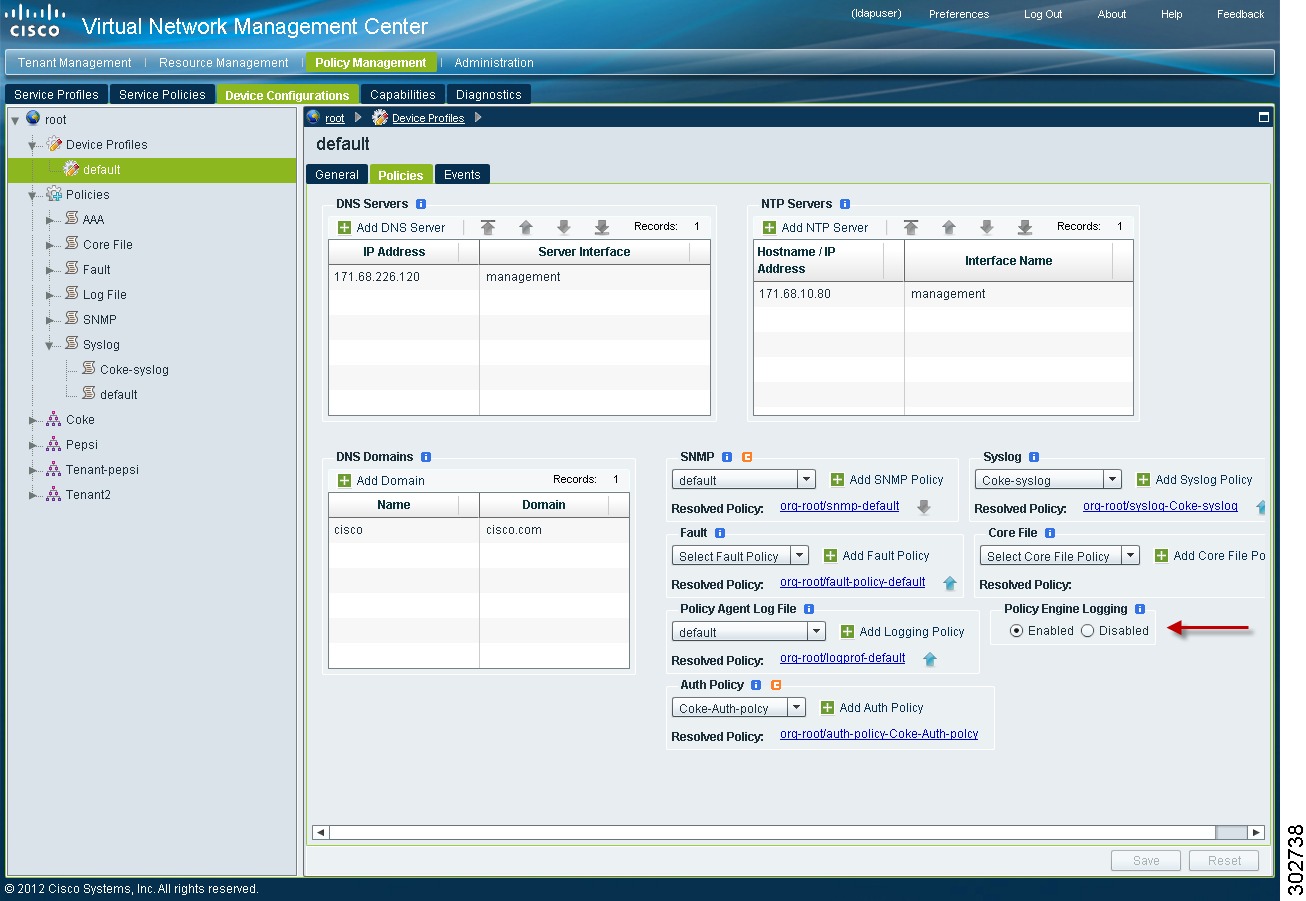
Enabling Global Policy-Engine Logging
To enable global policy-engine logging:
Step 1
Choose Policy Management > Device Configurations > root > Device Profiles > default.
Step 2
In the Device Profiles Pane, click the Policies tab.
Step 3
In the Policy Engine Logging area at the lower-right of the device profiles page (see Figure 21), click Enabled, and then click Save.
Example Screens Showing Global Policy-Engine Logging
Figure 21 Device Profiles Pane
5 Troubleshooting VNMC Installation and Configuration
The VNMC interface provides links to browser windows that enable you to examine policy and configuration errors that prevent the successful application of a policy, or to review the faults and events associated with successfully applied policies and configurations. This same feature enables you to examine the faults associated with a compute firewall or an edge firewall.
Examining Faults and Configuration Errors for Edge Firewalls
Before You Begin
Associate the edge firewall to an ASA 1000V instance.
To examine faults and configuration errors for edge firewalls:
Step 1
Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Edge Firewalls > edge-firewall.
Step 2
In the General tab, in the States area, click View Configuration Faults.
Step 3
In the Fault Table window that appears in a new browser window, click the required tab:
•
Faults—Includes fault severity, affected object, cause, last transition, acknowledgement state, type, and description.
•
Events—Includes identifier, affected object, user, time stamp, cause, and description.
•
Warnings—Includes affected object, scope, and description.
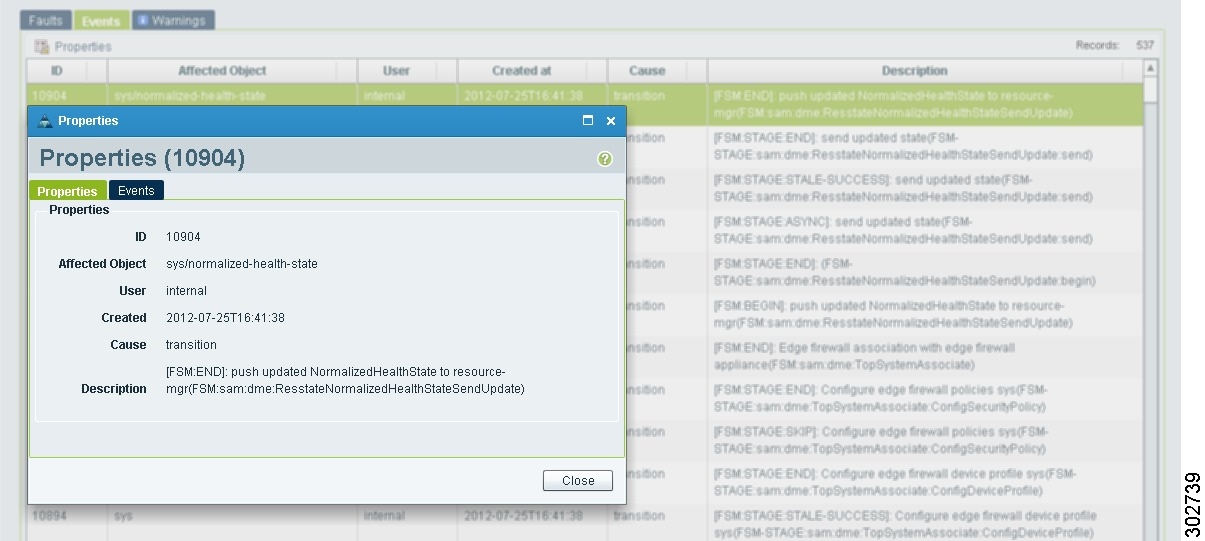
Step 4
To view additional information about an entry, select the entry, then click Properties (see Figure 22).

Tip
You can also double-click an entry to view the properties (fault or event details).
Step 5
To view updated information in the main window, click Refresh Now.
Example of the Fault Table Window Screen
Figure 22 Fault or Event Details
Examining Faults and Configuration Errors for Compute Firewalls
Before You Begin
Associate the compute firewall with a VSG instance.
To examine faults for compute firewalls:
Step 1
Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Compute Firewalls > compute-firewall.
Step 2
In the General tab, in the States area, click View Configuration Faults.
The Fault Table is displayed in a new browser window, and includes the fault severity, affected object, cause, last transition, acknowledgement state, type, and description.
Step 3
To view additional information about an entry, double-click or select the entry, then click Properties.
6 Upgrading VNMC

Note
Use the following upgrade procedure when you upgrade to a newer VNMC version. Backing up from VNMC 1.x and then restoring to VNMC 2.0 is not supported. Exporting from VNMC 1.x and then importing to VNMC 2.0 is also not supported.
To upgrade from VNMC 1.x to VNMC 2.0, complete the following procedures:
1.
Perform a full-state backup of VNMC 1.x by using Secure Copy (SCP) protocol—See Backing Up VNMC 1.x Data Using the CLI.
2.
Upgrade to VNMC 2.0 by using the CLI update bootflash command—See Upgrading to VNMC 2.0 Using the CLI.

Note
After you upgrade from VNMC 1.x to VNMC 2.0, you might see the previous version of VNMC in your browser. To view the upgraded version:
1. Clear the browser cache and browsing history.
2. Close all browser instances.
3. Relaunch the browser.
This note applies to all supported browsers: Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, and Chrome.
Backing Up VNMC 1.x Data Using the CLI
To save a state for recovery purposes, back up your existing VNMC data via SCP.
You can use one of the following methods to back up VNMC data:
•
To use the CLI, continue with this topic.
•
To use the GUI, see Backing Up VNMC 2.0 Using the GUI.
The following procedure uses these settings:
•
Remote file server: 10.2.3.4
•
User name: backupuser
•
Password: worknow
•
Backup file: /tmp/my-backup.etgz on 10.2.3.4
•
XML export file: /tmp/my-XML.tgz on 10.2.3.4
•
VNMC IP address: 10.1.1.10

Note
Be sure to replace these settings with the settings that apply to your environment.
Before You Begin
Temporarily disable the Cisco Security Agent (CSA) on the remote file server.

Note
Do not use TFTP to back up data.
To back up VNMC using the CLI:
Step 1
Using the CLI, log into VNMC as admin:
ssh admin@10.1.1.10Step 2
Enter system mode:
scope systemStep 3
Create a full-state backup file:
create backup scp://user@host/file full-state enabledwhere:
•
user is the user ID.
•
host is the system name.
•
/file is the full path and name of the backup file.
Step 4
When prompted, enter the required password.
Step 5
At the /system/backup* prompt, enter commit-buffer.
Step 6
Log into the SCP server, then make sure that /file exists and that the file size is not zero (0).
Example Backup
vnmc# scope systemvnmc /system # create backup scp://backupuser@10.2.3.4/tmp/my-backup.etgz full-state enabledPassword:vnmc /system/backup* # commit-buffervnmc /system/backup #Upgrading to VNMC 2.0 Using the CLI
After you back up the VNMC 1.x data, you are ready to upgrade to VNMC 2.0.

CautionTo save a state for recovery purposes, perform a backup before beginning the upgrade from VNMC 1.x to VNMC 2.0 (see Backing Up VNMC 1.x Data Using the CLI).

Note
Do not use TFTP to update data.
To upgrade VNMC 2.0 using the CLI:
Step 1
Using the CLI, log into VNMC as admin:
ssh admin@10.1.1.10Step 2
Connect to local-mgmt:
connect local-mgmtStep 3
(Optional) Check the current version of the Cisco VNMC software:
show versionStep 4
Download the 2.0 image from a remote file server:
copy scp://<imageURLtoBinFile> bootflash:/where the VNMC 2.0 image filename is vnmc.2.0.0.XXXX.bin.
Step 5
Upgrade to VNMC 2.0:
update bootflash:/vnmc.2.0.0.XXXX.binStep 6
Restart the server:
service restartStep 7
(Optional) Check whether the VNMC server is operating as desired:
service statusFor the CLI output of this command, see Upgrade CLI Output.
Step 8
(Optional) Verify whether the Cisco VNMC software version is updated:
show versionFor the CLI output of this command, see Upgrade CLI Output.
Step 9
To confirm that VNMC is fully accessible after the upgrade, log in via the GUI.
If your browser displays the previous version of VNMC instead of the upgraded version:
a.
Clear the browser cache and browsing history.
b.
Close all browser instances.
c.
Relaunch the browser.
Examples Showing VNMC Upgrade CLI Outputs
The output of Step 7 (VNMC service status) should look similar to this:SERVICE NAME STATE RETRY(MAX) CORE------------ ----- ---------- ----pmon running N/A N/Acore-svc_cor_dme running 0(4) noservice-reg-svc_reg_dme running 0(4) nocore-svc_cor_secAG running 0(4) noresource-mgr-svc_res_dme running 0(4) nopolicy-mgr-svc_pol_dme running 0(4) nosam_cores_mon.sh running 0(4) novm-mgr-svc_vmm_dme running 0(4) nocore-svc_cor_controllerAG running 0(4) novm-mgr-svc_vmm_vmAG running 0(4) nocore-httpd.sh running 0(4) nocore-svc_cor_sessionmgrAG running 0(4) noThe output of Step 8 (after the upgrade) should look similar to this:
Name Package Version GUI---- ------- ------- ----core Base System 2.0 2.0service-reg Service Registry 2.0 2.0policy-mgr Policy Manager 2.0 2.0resource-mgr Resource Manager 2.0 2.0vm-mgr VM manager 2.0 noneTo restore to the previous VNMC version, see Restoring the Previous VNMC Version.
7 Backing Up and Restoring VNMC

Note
We recommend that you use backup and restore as a disaster recovery mechanism. To migrate configuration data from one VNMC server to another, see Exporting and Importing in VNMC.
VNMC enables you to back up and restore data for the same VNMC version. That is, the following backup and restore operations are supported:
•
Back up VNMC 1.x and restore to VNMC 1.x.
•
Back up VNMC 2.0 and restore to VNMC 2.0.
Backing up one version and restoring to another version (such as backing up VNMC 1.x and restoring to VNMC 2.0) is not supported.

Note
Do not use TFTP for backup and restore operations.
The following topics describe how to back up data and restore data from VNMC 2.0:
•
Backing Up VNMC 2.0 Using the GUI
•
Restoring the Previous VNMC Version
Backing Up VNMC 2.0 Using the GUI
To save a state for recovery purposes, perform a backup via the GUI or CLI, using one of the following methods:
•
To use the CLI, see Backing Up VNMC 1.x Data Using the CLI.
•
To use the GUI, continue with this procedure.
Before You Begin
Temporarily disable the CSA on the remote file server.

Note
Be sure to replace the example settings with the settings that apply to your environment.
To back up VNMC 2.0 using the GUI:
Step 1
Log into the VNMC GUI as admin.
Step 2
Choose Administration > Operations > Backups, then click Create Backup Operation.
Step 3
Provide the following information, then click OK. For more information, see the online help.
•
Admin State—enabled
•
Protocol—scp
•
Hostname / IP Address—10.2.3.4
•
User—backupuser
•
Password—worknow
•
Absolute Path Remote File—/tmp/my-backup.etgz
Step 4
In the navigation pane, expand Backups, choose Backup 10.2.3.4, then choose the Task tab in the System pane.
Step 5
Wait until Previous Status changes to backupSuccess, then log into 10.2.3.4 as backupuser and make sure that /tmp/my-backup.etgz exists and that the file size is not zero (0).
Restoring the Previous VNMC Version
If the upgrade fails, use the CLI to restore the previous version.
Before You Begin
Temporarily disable the CSA on the remote file server.

Note
Be sure to replace the example settings with the settings that apply to your environment.

Note
Do not use TFTP to update data.
To restore to the previous VNMC version:
Step 1
Log into VNMC as admin:
ssh admin@10.1.1.10Step 2
Connect to local-mgmt:
connect local-mgmtStep 3
(Optional) Check the current version of the Cisco VNMC software:
show versionStep 4
Download the 1.x image from a remote file server:
copy scp://imageURLtoBinFile bootflash:/where the VNMC 1.x image filename is vnmc.1.x.0.XXXX.bin.
Step 5
Enter the update command:
update bootflash:/vnmc.1.XXXX.bin forceStep 6
Restore the previous version:
restore scp://backupuser@10.2.3.4/tmp/my-backup.etgzStep 7
Restart the server:
service restartStep 8
(Optional) Check whether the VNMC server is operating as desired:
service statusFor the CLI output of this command, see Restore CLI Output.
Step 9
(Optional) Verify whether the Cisco VNMC software version is restored as desired:
show versionFor the CLI output of this command, see Restore CLI Output.
Step 10
To confirm that VNMC is fully accessible after the upgrade, log in via the GUI.
If your browser displays the previous version of VNMC instead of the upgraded version, clear the browser cache and browsing history.
Example Showing VNMC Restore CLI Outputs
The output of Step 8 (VNMC service status) should look similar to this:
SERVICE NAME STATE RETRY(MAX) CORE------------ ----- ---------- ----pmon running N/A N/Acore-svc_cor_dme running 0(4) noservice-reg-svc_reg_dme running 0(4) nocore-svc_cor_secAG running 0(4) noresource-mgr-svc_res_dme running 0(4) nopolicy-mgr-svc_pol_dme running 0(4) nosam_cores_mon.sh running 0(4) novm-mgr-svc_vmm_dme running 0(4) nocore-svc_cor_controllerAG running 0(4) novm-mgr-svc_vmm_vmAG running 0(4) nocore-httpd.sh running 0(4) nocore-svc_cor_sessionmgrAG running 0(4) noThe output of Step 9 (after the restore) should look similar to this:
Name Package Version GUI----- -------- ------- ---core Base System 1.3 1.3service-reg Service Registry 1.3 1.3policy-mgr Policy Manager 1.3 1.3resource-mgr Resource Manager 1.3 1.3vm-mgr VM manager 1.3 none8 Exporting and Importing in VNMC

Note
Use this procedure to migrate configuration data from one VNMC server to another. To back up and restore VNMC data (as a disaster recovery mechanism), see Backing Up and Restoring VNMC.
VNMC enables you to export and import data for the same VNMC version. That is, the following export and import operations are supported:
•
Export from VNMC 1.x and import into VNMC 1.x.
•
Export from VNMC 2.0 and import into VNMC 2.0.
Exporting from one version and importing into another version (such as exporting from VNMC 1.x and importing into VNMC 2.0) is not supported.

Note
Do not use TFTP data for export and import operations.
Exporting VNMC Configuration Data
Before You Begin
Temporarily disable the CSA on the remote SCP server.

Note
Be sure to replace the example settings with the settings that apply to your environment.
To export configuration data from one VNMC server to another:
Step 1
On the VNMC server from which you would like to export the data, choose Administration > Operations > Backups, then click Create Export Operation.
Step 2
Provide the following information, then click OK:
•
Admin State—enabled
•
Type—Select type. For more information, see the online help.
•
Protocol—scp
•
Hostname / IP Address—10.2.3.4
•
User—backupuser
•
Password—worknow
•
Absolute Path Remote File(.tgz)—/tmp/my-XML.tgz
Step 3
In the navigation pane, expand Backups and choose Export 10.2.3.4. 10.2.3.4 is the remote file server on which the configuration data is created as a .tgz file.
Step 4
Choose the Task tab.
Step 5
Wait until Previous Status changes to exportDataSuccess, and log into 10.2.3.4 as backupuser; then make sure that /tmp/my-XML.tgz exists and that the file size is not zero (0).
Importing VNMC Configuration Data
Before You Begin
Temporarily disable the CSA on the remote SCP server.

Note
Be sure to replace the example settings with the settings that apply to your environment.
To perform the import of the previously exported data:
Step 1
On the VNMC server into which you would like to import the data, choose Administration > Operations > Backups, then click Create Import Operation.
Step 2
Provide the following information, then click OK:
•
Admin State—enabled
•
Protocol—scp
•
Hostname / IP Address—10.2.3.4
•
User—backupuser
•
Password—worknow
•
Absolute Path Remote File(.tgz)— /tmp/my-XML.tgz
Step 3
In the navigation pane, expand Backups and choose Import 10.2.3.4, where 10.2.3.4 is the remote file server to which you exported the file /tmp/my-XML.tgz as described in Exporting VNMC Configuration Data.
Step 4
Click the Task tab and wait until Previous Status changes to importDataSuccess.
The configuration in /tmp/my-XML.tgz will be applied to the VNMC server on which the import operation is performed.

CautionWhen the configuration data is imported into the VNMC server, you may see an error message and get logged out, followed by the display of a new VNMC certificate. This error occurs because the VNMC hostname and/or the VNMC domain name has changed. The VM Manager Extension file will have to be exported again and installed on vCenter. To continue with the import, accept the VNMC certificate and log into VNMC again.
9 Patching VNMC
Use the CLI to apply the patch.
Before You Begin
Temporarily disable the CSA on the remote SCP server.

Note
Be sure to replace the example settings with the settings that apply to your environment.

Note
Do not use TFTP to update data.
To patch VNMC 2.0:
Step 1
Log into the VNMC system to be patched:
ssh admin@10.1.1.10Step 2
Connect to local-mgmt:
connect local-mgmtStep 3
Update the bootflash:
update bootflash: | ftp: | scp: | sftp:For example:
update bootflash:/vnmc.2.0.0.511.binStep 4
Restart the VNMC services:
service restartStep 5
Verify that all services are running:
service statusFor the CLI output of this command, see After Patch CLI Output.
Step 6
To verify that the patch was applied, check the update history:
show update-history
Example of VNMC Service Status After Patch
The output for Step 5 (VNMC service status) should look similar to the following example:
SERVICE NAME STATE RETRY(MAX) CORE------------ ----- ---------- ----pmon running N/A N/Acore-svc_cor_dme running 0(4) noservice-reg-svc_reg_dme running 0(4) nocore-svc_cor_secAG running 0(4) noresource-mgr-svc_res_dme running 0(4) nopolicy-mgr-svc_pol_dme running 0(4) nosam_cores_mon.sh running 0(4) novm-mgr-svc_vmm_dme running 0(4) nocore-svc_cor_controllerAG running 0(4) novm-mgr-svc_vmm_vmAG running 0(4) nocore-httpd.sh running 0(4) nocore-svc_cor_sessionmgrAG running 0(4) no10 Performance and Scalability
Table 17 lists the performance data and scalability data for VNMC 2.0.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2012 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback