Label Switched Multicast (LSM) Multicast Label Distribution Protocol (MLDP) based Multicast VPN (MVPN) Support
The Label Switched Multicast (LSM) feature enables service providers to extend the existing IPv4 MPLS backbone network for IPv4 multicast services. By default, MPLS creates an out-label for an in-label for each packet. This feature extends this functionality to create multiple out-labels for a single in-label. The IPv4 Multicast service includes point-to-multipoint (P2MP) and multipoint-to-multipoint (M2M) packet transport. The P2MP packet transport is implemented using Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) P2MP – Traffic Engineering (P2MP-TE) and M2M packet transport is implemented through IPv4 Multicast VPN (MVPN) using multicast Label Distribution Protocol (MLDP). The packet are transported over three types of routers:
- Headend router: Encapsulates the IP packet with one or more labels.
- Midpoint router: Replaces the in-label with an out-label.
- Tailend router: Removes the label from the packet.
LSM is implemented on systems based on EARL 7 or EARL 7.5 versions, which support two modes of multicast replication—ingress and egress. The ingress card performs the replication in case of ingress mode and the multicast traffic throughput is limited to 20 Gb/s. The egress replication mode uses the replication capability of fabric to deliver a copy of a packet to each line card. Distributing the replication process across multiple line cards significantly improves the system throughput. On the Cisco 7600 Series Routers, LSM is implemented in the egress mode.
Note LSM MLDP-based MVPN feature is supported on ES+ and ES20 line cards and these supervisors: RSP720, SUP720, and RSP720-10GE. MLDP is supported on all the egress replication capable line cards.
LSM MLDP-based MVPN feature is supported on ES+ and ES20 line cards and these supervisors: RSP720, SUP720, and RSP720-10GE. MLDP is supported on all the egress replication capable line cards.
For more information on RSVP P2MP-TE, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mpls/configuration/guide/mp_te_p2mp.html
Configuring MLDP MVPN
The MLDP MVPN configuration enables IPv4 multicast packet delivery using MPLS. This configuration uses MPLS labels to construct default and data Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs). The MPLS replication is used as a forwarding mechanism in the core network. For MLDP MVPN configuration to work, ensure that the global MPLS MLDP configuration is enabled.
To configure MVPN extranet support, configure the source multicast VPN Routing and Forwarding (mVRF) on the receiver Provider Edge (PE) router or configure the receiver mVRF on the source PE. MLDP MVPN is supported for both intranet and extranet.
Figure 51-1 shows MLDP based MVPN network.
Figure 51-1 MLDP Based MVPN Network
Packet Flow in MLDP-based MVPN Network
For each packet coming in, MPLS creates multiple out-labels. Packets from the source network are replicated along the path to the receiver network. The CE1 router sends out the native IP multicast traffic. The PE1 router imposes a label on the incoming multicast packet and replicates the labeled packet towards the MPLS core network. When the packet reaches the core router (P), the packet is replicated with the appropriate labels for the MP2MP default MDT or the P2MP data MDT and transported to all the egress PEs. Once the packet reaches the egress PE, the label is removed and the IP multicast packet is replicated onto the VRF interface.
Restrictions and Usage Guidelines
Follow these restrictions and usage guidelines while configuring LSM MLDP based MVPN support:
- MLDP is supported only in the egress replication mode.
- A headend router does not support multiple sub Label Switched Paths (subLSPs) belonging to different tunnels, over the same physical interface.
- NAT with P2MP TE is not supported.
- Process level software forwarding is not supported.
- MLDP-based MVPN is not supported for global IPv4 multicast.
- These are the scale considerations for MLDP based MVPN:
– Maximum number of mVRFs supported is 100.
Maximum number of mVRFs supported is 100.
– Maximum number of multicast routes supported in each MVRF is 100.
Maximum number of multicast routes supported in each MVRF is 100.
- Extranet content group mode should be consistent across all the VRFs. These are the valid content group modes: Supported, Unsupported, and PM-sparse mode.
- Supported content group modes are Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) sparse mode (PIM-SM) and Source Specific Multicast (SSM) traffic.
- Unsupported content group modes are PIM dense mode (PIM-DM) and bidirectional PIM (bidir-PIM) traffic.
- PIM-sparse content group mode is supported if the RP is configured behind the PE router (on CE).
- Only the static multicast route with fallback-lookup option is supported for RPF lookup for extranet.
- MLDP provides only link protection with the FRR TE. Only single hop is supported with MLDP TE, the backup path can have multiple hops.
Configuring Label Switched Multicast on 7600
Deployment of an LSM MLDP-based MVPN involves configuring a default MDT and one or more data MDTs.
A static default MDT is established for each multicast domain. The default MDT defines the path used by PE routers to send multicast data and control messages to other PE routers in the multicast domain. A default MDT is created in the core network using a single MP2MP LSP.
An MLDP based MLDP-based MVPN also supports dynamic creation of the data MDTs for high-bandwidth transmission. For high-rate data sources, a data MDT is created using the P2MP LSPs to off-load the traffic from the default MDT to avoid unnecessary waste of bandwidth to PEs that are not part of the stream. You can configure MLDP MVPN for both the intranet or extranet.
Note Before configuring MLDP based MVPN, ensure that the MPLS is enabled on the core facing interface. For information in MPLS configuration, see the Cisco IOS Multiprotocol Label Switching Configuration Guide. Also, ensure that BGP and any interior gateway protocol (OSPF or ISIS) is enabled on the core router.
Before configuring MLDP based MVPN, ensure that the MPLS is enabled on the core facing interface. For information in MPLS configuration, see the Cisco IOS Multiprotocol Label Switching Configuration Guide. Also, ensure that BGP and any interior gateway protocol (OSPF or ISIS) is enabled on the core router.
Configuring MLDP MVPN (Intranet)
Complete these steps to configure MLDP MVPN for intranet:
- Enabling MPLS MLDP
- Configuring MVPN Routing and Forwarding instance
- Configuring a VRF entry
- Configuring the route distinguisher
- Configuring VPN Id
- Configuring the Route-Target extended community
- Configuring the default MDT
- Configuring Data MDTs (optional)
- Configuring BGP MDT address family
- Configuring BGP vpnv4 address family
- Configuring BGP IPv4 VRF address family
- Configuring PIM SM/SSM mode for the VRFs
Summary Steps
1. enable
enable
2. configure terminal
configure terminal
3. mpls mldp
mpls mldp
4. ip vrf vrf-name
ip vrf vrf-name
5. rd route-distinguisher
rd route-distinguisher
6. vpn id vpn_id
vpn id vpn_id
7. route-target [import | export | both] route-target-ext-community
route-target [import | export | both] route-target-ext-community
8. route-target [import | export | both] route-target-ext-community
route-target [import | export | both] route-target-ext-community
9. mdt default mpls mldp root-node
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
10. mdt data mpls mldp numberofdataMDTs
mdt data mpls mldp numberofdataMDTs
11. mdt data threshold bandwidth
mdt data threshold bandwidth
12. exit
exit
13. ip multicast-routing vrf vrf-name
ip multicast-routing vrf vrf-name
14. end
end
Note See Configuring the MDT Address Family in BGP for Multicast VPN for information on configuring an MDT and vpnv4 address family session on the PE routers to establish MDT peering sessions for MVPN.
See Configuring the MDT Address Family in BGP for Multicast VPN for information on configuring an MDT and vpnv4 address family session on the PE routers to establish MDT peering sessions for MVPN.
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
Step 1 |
enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
- Enter your password when prompted.
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal
Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
mpls mldp
Router(config)# mpls mldp |
Enables MPLS MLDP support.
Note To disable MPLS MLDP use the no mpls mldp command. To disable MPLS MLDP use the no mpls mldp command.
|
Step 4 |
ip vrf vrf-name
Router(config)# ip vrf blue |
Defines the VPN routing instance by assigning a VRF name and enters VRF configuration mode.
- The vrf-name argument is the name assigned to a VRF.
|
Step 5 |
rd route-distinguisher
Router(config-vrf)# rd 10:3 |
Creates routing and forwarding tables. Specify the route-distinguisher argument to add an 8-byte value to an IPv4 prefix to create a VPN IPv4 prefix. You can enter an RD value in either of these formats:
- 16-bit autonomous system number. For example, 101:3.
- 32-bit IP address: your 16-bit number. For example, 192.168.122.15:1.
|
Step 6 |
vpn id vpn-id
Router(config-vrf)# vpn id 10:3 |
Sets or updates a VPN identifier on a VRF. |
Step 7 |
route-target import route-target-ext-community
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:3 |
Creates a route-target extended community for a VRF.
- The import keyword imports the routing information from the target VPN extended community.
- The route-target-ext-community argument adds the route-target extended community attributes to the VRF list of import, export, or both (import and export) route-target extended communities.
|
Step 8 |
route-target export route-target-ext-community
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:3 |
Creates a route-target extended community for a VRF.
- The export keyword exports the routing information from the target VPN extended community.
- The route-target-ext-community argument adds the route-target extended community attributes to the VRF list of import, export, or both (import and export) route-target extended communities.
|
Step 9 |
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2 |
Configures MLDP MDT for a VRF. The root node can be IP address of a loopback or physical interface on any router (source PE, receiver PE or core router) in the provider network. The root node address should be reachable by all the routers in the network. The router from where the signalling occurs functions as the root node. The default MDT must be configured on each PE router to enable the PE routers to receive multicast traffic for this particular MVRF.
Note By default MPLS MLDP is enabled. To disable, use the no mpls mldp command. By default MPLS MLDP is enabled. To disable, use the no mpls mldp command.
Note LSPVIF tunnel is created as a result of mdt default mpls mldp root-node command. LSPVIF tunnel is created as a result of mdt default mpls mldp root-node command.
|
Step 10 |
mdt data mpls mldp numberofdataMDTs
Router(config-vrf)# mdt data mpls mldp 100 |
Configures the MLDP data MDP. |
Step 11 |
mdt data threshold bandwidth
Router(config-vrf)# mdt data threshold 20 |
Configures the threshold value for data MDT.
Note Bandwidth is traffic rate in Kb/s. Bandwidth is traffic rate in Kb/s.
|
Step 12 |
exit
Router(config-vrf)# exit |
Exits the configuration session. |
Step 13 |
ip multicast-routing vrf vrf-name
Router(config)# ip multicast-routing vrf blue |
Enables IPv4 multicast routing for the specified VRF. |
Step 14 |
end
Router(config)# end |
Closes the configuration session. |

Note See Configuring the MDT Address Family in BGP for Multicast VPN for information on configuring an MDT address family session on the PE routers to establish MDT peering sessions for MVPN.
See Configuring the MDT Address Family in BGP for Multicast VPN for information on configuring an MDT address family session on the PE routers to establish MDT peering sessions for MVPN.
Example
This example describes how to configure MLDP MVPN on an intranet:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# mpls mldp
Router(config)# ip vrf blue
Router(config-vrf)# rd 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# vpn id 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2
Router(config-vrf)# mdt data mpls mldp 100
Router(config-vrf)# mdt data threshold 20
Router(config)# ip multicast-routing vrf blue
Verification
Use these commands to verify LSM MLDP based MVPN support intranet configuration:
- To check the MLDP neighbors, use the show mpls mldp neighbor command:
Router# show mpls mldp neighbors
MLDP peer ID : 3.3.3.3:0, uptime 00:41:41 Up,
Path(s) : 3.3.3.3 No LDP Tunnel20
MLDP peer ID : 2.2.2.2:0, uptime 00:17:42 Up,
Path(s) : 3.3.3.3 No LDP Tunnel20
- To check the PIM neighbors, use the show ip pim vrf vrf-name neighbor command:
Router# show ip pim vrf blue neighbor
Mode: B - Bidir Capable, DR - Designated Router, N - Default DR Priority,
P - Proxy Capable, S - State Refresh Capable, G - GenID Capable
Neighbor Interface Uptime/Expires Ver DR
3.3.3.3 Lspvif1 00:06:21/00:01:17 v2 1 / DR S P G
- To check the multicast routes for a given VRF, use show ip mroute vrf vrf_name verbose command:
Router# show ip mroute vrf blue verbose
IP Multicast Routing Table
Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, B - Bidir Group, s - SSM Group, C - Connected,
L - Local, P - Pruned, R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag,
T - SPT-bit set, J - Join SPT, M - MSDP created entry, E - Extranet,
X - Proxy Join Timer Running, A - Candidate for MSDP Advertisement,
U - URD, I - Received Source Specific Host Report,
Z - Multicast Tunnel, z - MDT-data group sender,
Y - Joined MDT-data group, y - Sending to MDT-data group,
V - RD & Vector, v - Vector
Outgoing interface flags: H - Hardware switched, A - Assert winner
Interface state: Interface, Next-Hop or VCD, State/Mode
(40.0.0.2, 232.0.1.4), 00:00:16/00:03:13, flags: sT
Incoming interface: GigabitEthernet3/2/1, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0
Lspvif1, LSM MDT: B0000004 (default), Forward/Sparse, 00:00:16/00:03:13
(*, 224.0.1.40), 00:47:09/00:02:56, RP 0.0.0.0, flags: DPL
Incoming interface: Null, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0
Outgoing interface list: Null
- To check the packet counters, use show ip mroute vrf vrf_name count command:
Router# show ip mroute vrf blue count
2 routes using 1208 bytes of memory
2 groups, 0.50 average sources per group
Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kilobits per second
Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops(OIF-null, rate-limit etc)
Group: 232.0.1.4, Source count: 1, Packets forwarded: 1333, Packets received: 1334
Source: 40.0.0.2/32, Forwarding: 1333/20/46/7, Other: 1334/0/1
Group: 224.0.1.40, Source count: 0, Packets forwarded: 0, Packets received: 0
- To check the MPLS forwarding, use show mpls forwarding-table command:
Router# show mpls forwarding-table
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop
Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface
16 Pop Label IPv4 VRF[V] 0 aggregate/blue
17 Pop Label IPv4 VRF[V] 0 aggregate/red
18 [T] Pop Label 3.3.3.3/32 0 Tu20 point2point
19 [T] 25 2.2.2.2/32 0 Tu20 point2point
20 [T] Pop Label 19.0.0.0/24 0 Tu20 point2point
22 [T] No Label [mdt 55:1111 0][V] \9422 aggregate/red
23 [T] No Label [mdt 55:2222 0][V] \9708 aggregate/blue
[T] Forwarding through a LSP tunnel.
View additional labelling info with the 'detail' option
- To check the contents of a label on SP/DFC, use show mls cef mpls labels mldp_label command:
Router# show mls cef mpls labels op
Codes: + - Push label, - - Pop Label * - Swap Label, E - exp1
Index Local Label Out i/f
Configuring MLDP MVPN for Extranet Services
You can configure MLDP MVPN for extranet services using these methods:
- Source Side Chaining (SSC): Configure the phantom receiver MVRF on the source side router. Multicast routes with fallback loopback should be configured on the source PE.
- Receiver Side chaining (RSC): Configure the phantom source MVRF on the receiver siderouter. Multicast routes with fallback lookup should be configured on the receiver VRF.
See Multicast VPN Extranet Support for more information on MVPN Extranet support on Cisco 7600 series routers. MVPN is supported on PFC3B, PFC3BXL, PFC3C, or PFC3CXL router installations.
Configuring MLDP MVPN for Extranet using SSC
Complete these steps to configure the MLDP MVPN extranet support using SSC:
- Configuring receiver MVRF on the source PE.
- Configuring a loopback address in the receiver VRF on the source PE.
- Configuring fallback multicast route for source address on source PE.
- Configuring fallback multicast route for RP address on the source PE in case of SM mode.
- Configuring static multicast route on recevier PE for loopback IP in the receiver VRF configured on the source PE.
Note This configuration is based on illustration Figure 51-1. Configure multicast routes on the PE1 router.
This configuration is based on illustration Figure 51-1. Configure multicast routes on the PE1 router.
Summary Steps
Configuration on the source PE:
1. enable
enable
2. configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ip vrf vrf-name
ip vrf vrf-name
4. rd route-distinguisher
rd route-distinguisher
5. vpn id vpn_id
vpn id vpn_id
6. route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community
7. route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community
8. mdt default mpls mldp root-node
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
9. end
end
10. interface type instance
interface type instance
11. ip vrf forwarding vrf-name
ip vrf forwarding vrf-name
12. ip address ip-address subnet
ip address ip-address subnet
13. ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] source-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] source-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
14. (For SM Mode) ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] rp-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
(For SM Mode) ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] rp-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
15. end
end
Configuration on the receiver PE:
1. enable
enable
2. configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ip vrf vrf-name
ip vrf vrf-name
4. rd route-distinguisher
rd route-distinguisher
5. vpn id vpn_id
vpn id vpn_id
6. route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community
7. route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community
8. mdt default mpls mldp root-node
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
9. end
end
10. interface type instance
interface type instance
11. ip vrf forwarding vrf-name
ip vrf forwarding vrf-name
12. ip address ip-address subnet
ip address ip-address subnet
13. ip mroute vrf receiver_vrf source_address subnet_mask loopback_ip
ip mroute vrf receiver_vrf source_address subnet_mask loopback_ip
14. end
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration on the source PE:
|
|
|
Step 1 |
enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
- Enter your password when prompted.
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal
Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
ip vrf vrf-name
Router(config)# ip vrf blue |
Defines the VPN routing instance by assigning a VRF name and enters VRF configuration mode.
- The vrf-name argument is the name assigned to a VRF.
|
Step 4 |
rd route-distinguisher
Router(config-if)# rd 10:4 |
Creates routing and forwarding tables. Specify the route-distinguisher argument to add an 8-byte value to an IPv4 prefix to create a VPN IPv4 prefix. You can enter an RD value in either of these formats:
- 16-bit autonomous system number. For example, 101:3.
- 32-bit IP address: your 16-bit number. For example, 192.168.122.15:1.
|
Step 5 |
vpn id vpn-id
Router(config-if)# vpn id 10:4 |
Sets or updates a VPN identifier on a VRF. |
Step 6 |
route-target import route-target-ext-community
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:4 |
Creates a route-target extended community for a VRF.
- The import keyword imports the routing information from the target VPN extended community.
- The route-target-ext-community argument adds the route-target extended community attributes to the VRF list of import, export, or both (import and export) route-target extended communities.
|
Step 7 |
route-target export route-target-ext-community
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:4 |
Creates a route-target extended community for a VRF.
- The export keyword export the routing information to the target VPN extended community.
- The route-target-ext-community argument adds the route-target extended community attributes to the VRF list of import, export, or both (import and export) route-target extended communities.
|
Step 8 |
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2 |
Configures MLDP multicast distribution tree (MDT) for a VRF.
Note LSPVIF tunnel is created as a result of this command. LSPVIF tunnel is created as a result of this command.
|
Step 9 |
end
Router(config-vrf)# end |
Closes the configuration session. |
Step 10 |
interface type instance
Router(config)# interface loopback 3 |
Enters interface configuration mode and names the new loopback interface. |
Step 11 |
ip vrf forwarding vrf-name
Router(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding red |
Associates a VRF instance with an interface or subinterface.
- vrf-name is the name assigned to a VRF.
|
Step 12 |
ip address ip-address subnet-mask
Router(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 |
Specifies the interface IP address and subnet mask.
- ip-address specifies the IP address of the interface.
- subnet-mask specifies the subnet mask of the interface.
|
Step 13 |
ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] source-address mask {fallback-lookup vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
Router(config)# ip mroute vrf red 40.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 fallback-lookup vrf blue |
Configures the RPF lookups originating in a receiver MVRF or in the global routing table to be resolved in a source MVRF or in the global routing table.
- The optional vrf keyword and receiver-vrf-name argument are used to apply a group-based VRF selection policy to RPF lookups originating in the VRF specified for the receiver-vrf-name argument. If the optional vrf keyword and receiver-vrf-name argument are not specified, the group-based VRF selection policy applies to RPF lookups originating in the global table.
|
Step 14 |
ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] rp-address mask {fallback-lookup vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
Router(config-if)# ip mroute vrf red 44.44.44.44 255.255.255.0 fallback-lookup vrf blue |
Configures the RPF lookups originating in a receiver MVRF or in the global routing table for RP (Rendezvous Point) to be resolved in a source MVRF or in the global routing table.
Note This command is required for SM mode only. This command is required for SM mode only.
|
Step 15 |
end
Router(config-vrf)# end |
Closes the configuration session. |
Configuration on receiver PE:
|
|
|
Step 1 |
enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
- Enter your password when prompted.
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal
Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
ip vrf vrf-name
Router(config)# ip vrf blue |
Defines the VPN routing instance by assigning a VRF name and enters VRF configuration mode.
- The vrf-name argument is the name assigned to a VRF.
|
Step 4 |
rd route-distinguisher
Router(config-if)# rd 10:4 |
Creates routing and forwarding tables. Specify the route-distinguisher argument to add an 8-byte value to an IPv4 prefix to create a VPN IPv4 prefix. You can enter an RD value in either of these formats:
- 16-bit autonomous system number: your 32-bit number. For example, 101:3
- 32-bit IP address: your 16-bit number. For example, 192.168.122.15:1
|
Step 5 |
vpn id vpn-id
Router(config-if)# vpn id 10:4 |
Sets or updates a VPN identifier on a VRF. |
Step 6 |
route-target import route-target-ext-community
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:4 |
Creates a route-target extended community for a VRF.
- The import keyword imports the routing information from the target VPN extended community.
- The route-target-ext-community argument adds the route-target extended community attributes to the VRF list of import, export, or both (import and export) route-target extended communities.
|
Step 7 |
route-target export route-target-ext-community
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:4 |
Creates a route-target extended community for a VRF.
- The export keyword exports the routing information to the target VPN extended community.
- The route-target-ext-community argument adds the route-target extended community attributes to the VRF list of import, export, or both (import and export) route-target extended communities.
|
Step 8 |
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2 |
Configures MLDP multicast distribution tree (MDT) for a VRF.
Note LSPVIF tunnel is created as a result of this command. LSPVIF tunnel is created as a result of this command.
|
Step 9 |
end
Router(config-vrf)# end |
Closes the configuration session. |
Step 10 |
interface type instance
Router(config)# interface loopback 3 |
Enters interface configuration mode and names the new loopback interface. |
Step 11 |
ip vrf forwarding vrf-name
Router(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding blue |
Associates a VRF instance with an interface or subinterface.
- vrf-name is the name assigned to a VRF.
|
Step 12 |
ip address ip-address subnet-mask
Router(config-if)# ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 |
Specifies the interface IP address and subnet mask.
- ip-address specifies the IP address of the interface.
- subnet-mask specifies the subnet mask of the interface.
|
Step 13 |
ip mroute vrf receiver_vrf source_address subnet_mask loopback_ip
Router(config-if)# ip mroute vrf red 40.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.1.1 |
Configures the static multicast routes for source addresses in the reciever VRF, where: loopback ip is ip address of the loopback configured in the recevier VRF in the source PE. |
Step 14 |
end
Router(config-vrf)# end |
Closes the configuration session. |
Example
This is sample example for configuring MLDP MVPN for configuring extranet using SSC:
Configuration on the source PE(Configure these steps for both red and blue VRFs)
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip vrf blue
Router(config-if)# rd 10:4
Router(config-if)# vpn id 10:4
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:4
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:4
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2
Router(config)# interface loopback 3
Router(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding red
Router(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
Router(config)# ip mroute vrf red 40.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 fallback-lookup vrf blue
Router(config)# ip mroute vrf red 44.44.44.44 255.255.255.0 fallback-lookup vrf blue
Configuration on the receiver PE
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip vrf blue
Router(config-if)# rd 10:4
Router(config-if)# vpn id 10:4
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:4
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:4
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2
Router(config)# interface loopback 3
Router(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding blue
Router(config-if)# ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 Remove
Router(config-if)# ip mroute vrf red 40.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.1.1
Configuring MLDP MVPN for Extranet Services using RSC
Complete these steps to configuring MLDP MVPN for extranet services using RSC:
- Configuring the source mVRF on the receiver PE router.
- Configuring RPF for MLDP based MVPN extranet support using static multicast routes on the receiver PE.
Note This configuration is based on illustration Figure 51-1. Configure multicast routes on PE2 and PE3 routers.
This configuration is based on illustration Figure 51-1. Configure multicast routes on PE2 and PE3 routers.
Summary Steps
Configuration on Source PE:
1. enable
enable
2. configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ip vrf vrf-name
ip vrf vrf-name
4. rd route-distinguisher
rd route-distinguisher
5. vpn id vpn_id
vpn id vpn_id
6. route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community
7. route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community
8. mdt default mpls mldp root-node
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
9. end
end
Configuration on Receiver PE (Configure these steps for both red and blue VRFs)
1. enable
enable
2. configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ip vrf vrf-name
ip vrf vrf-name
4. rd route-distinguisher
rd route-distinguisher
5. vpn id vpn_id
vpn id vpn_id
6. route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community
7. route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community
8. mdt default mpls mldp root-node
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
9. ip mroute [vrf recevier-vrf-name] source-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
ip mroute [vrf recevier-vrf-name] source-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
10. end
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration on Source PE
|
|
|
Step 1 |
enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
- Enter your password when prompted.
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal
Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
ip vrf vrf-name
Router(config)# ip vrf blue |
Defines the VPN routing instance by assigning a VRF name and enters VRF configuration mode.
- The vrf-name argument is the name assigned to a VRF.
|
Step 4 |
rd route-distinguisher
Router(config-if)# rd 10:3 |
Creates routing and forwarding tables. Specify the route-distinguisher argument to add an 8-byte value to an IPv4 prefix to create a VPN IPv4 prefix. You can enter an RD value in either of these formats:
- 16-bit autonomous system number: your 32-bit number. For example, 101:3
- 32-bit IP address: your 16-bit number. For example, 192.168.122.15:1
|
Step 5 |
vpn id vpn-id
Router(config-if)# vpn id 10:3 |
Sets or updates a VPN identifier on a VRF. |
Step 6 |
route-target import route-target-ext-community
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:3 |
Creates a route-target extended community for a VRF.
- The import keyword imports routing information from the target VPN extended community.
- The route-target-ext-community argument adds the route-target extended community attributes to the VRF list of import, export, or both (import and export) route-target extended communities.
|
Step 7 |
route-target export route-target-ext-community
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:3 |
Creates a route-target extended community for a VRF.
- The export keyword exports the routing information to the target VPN extended community.
- The route-target-ext-community argument adds the route-target extended community attributes to the VRF list of import, export, or both (import and export) route-target extended communities.
|
Step 8 |
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2 |
Configures MLDP multicast distribution tree (MDT) for a VRF.
Note LSPVIF tunnel is created as a result of this command. LSPVIF tunnel is created as a result of this command.
|
Step 9 |
end
Router(config-vrf)# end |
Closes the configuration session. |
Configuration on Receiver PE
|
|
|
Step 1 |
enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
- Enter your password when prompted.
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal
Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
ip vrf vrf-name
Router(config)# ip vrf blue |
Defines the VPN routing instance by assigning a VRF name and enters VRF configuration mode.
- The vrf-name argument is the name assigned to a VRF.
|
Step 4 |
rd route-distinguisher
Router(config-if)# rd 10:3 |
Creates routing and forwarding tables. Specify the route-distinguisher argument to add an 8-byte value to an IPv4 prefix to create a VPN IPv4 prefix. You can enter an RD value in either of these formats:
- 16-bit autonomous system number. For example, 101:3.
- 32-bit IP address: your 16-bit number. For example, 192.168.122.15:1.
|
Step 5 |
vpn id vpn-id
Router(config-if)# vpn id 10:3 |
Sets or updates a VPN identifier on a VRF. |
Step 6 |
route-target import route-target-ext-community
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:3 |
Creates a route-target extended community for a VRF.
- The import keyword imports routing information from the target VPN extended community.
- The route-target-ext-community argument adds the route-target extended community attributes to the VRF list of import, export, or both (import and export) route-target extended communities.
|
Step 7 |
route-target export route-target-ext-community
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:3 |
Creates a route-target extended community for a VRF.
- The export keyword exports the routing information to the target VPN extended community.
- The route-target-ext-community argument adds the route-target extended community attributes to the VRF list of import, export, or both (import and export) route-target extended communities.
|
Step 8 |
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2 |
Configures MLDP multicast distribution tree (MDT) for a VRF.
Note LSPVIF tunnel is created as a result of this command. LSPVIF tunnel is created as a result of this command.
|
Step 9 |
ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] source-address mask {fallback-lookup vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
Router(config)# ip mroute vrf red 40.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 fallback-lookup vrf blue |
Configures RPF lookups originating in a receiver MVRF or in the global routing table to be resolved in a source MVRF or in the global routing table based on group address. Use this command on the receiver PE.
- The optional vrf keyword and receiver-vrf-name argument are used to apply a group-based VRF selection policy to RPF lookups originating in the VRF specified for the receiver-vrf-name argument. If the optional vrf keyword and receiver-vrf-name argument are not specified, the group-based VRF selection policy applies to RPF lookups originating in the global table.
|
Step 10 |
end
Router(config-vrf)# end |
Closes the configuration session. |
Example
This is sample example for configuring MLDP MVPN for configuring extranet using RSC:
Configuration on Source PE:
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)# ip vrf blue1
Router(config-if)# rd 10:3
Router(config-if)# vpn id 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2
mdt default mpls mldp root-node
Router(config)# ip mroute vrf red 40.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 fallback-lookup vrf blue
Configuration on Receiver PE:
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)# ip vrf blue1
Router(config-if)# rd 10:3
Router(config-if)# vpn id 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2
Router(config)# ip mroute vrf red 40.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 fallback-lookup vrf blue
Configuring MLDP TE-FRR Support
TE-FRR provides link protection, however TE-FRR on MLDP provides link protection only for the single hop primary path. Node protection is not supported.These are the highlights:
- Backup tunnel support
- Backup bandwidth protection
For more information on MPLS TE-FRR, see MPLS Point-to-Multipoint Traffic Engineering.
Summary Steps
1. enable
enable
2. configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ip multicast mpls traffic-eng [range {access-list-number | access-list-name}]
ip multicast mpls traffic-eng [range {access-list-number | access-list-name}]
4. mpls mldp path traffic-eng
mpls mldp path traffic-eng
5. end
end
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
Step 1 |
enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
- Enter your password when prompted.
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal
Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
ip multicast mpls traffic-eng [range {access-list-number | access-list-name}]
Router(config)# ip multicast mpls traffic-eng [range {access-list-number | access-list-name}] |
Enables IP multicast traffic on a tail end router enabled with MPLS TE P2MP functionality. |
Step 4 |
mpls mldp path traffic-eng
Router(config)# mpls mldp path traffic-en |
Configures MLDP to use traffic-eng tunnels. |
Step 5 |
end
Router(config)# end |
Closes the configuration session. |
For more information, see MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) - Fast Reroute (FRR) Link and Node Protection.
Configuring MLDP with PIM-based MVPN
MLDP with PIM-based MVPN supports MLDP coexistence with a PIM-based MVPN deployment. Using this feature, you can gradually introduce MLDP in an existing PIM-based MVPN environment, facilitating phased migration towards a complete LSM-based MVPN network infrastructure. If both the MLDP-based MVPN and GRE-based MVPN are configured, MDT selects PIM based MVPN by default. Configure the precedence for MLDP MVPN and PIM based MVPN using the mdt preference option1 option2 command. This example sets MLDP MVPN precedence over PIM based MVPN:
Router(config-vrf)# mdt preference mldp pim
MLDP Support with Load Balancing
MLDP supports load balancing of multicast traffic with Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP) links. For Load balancing to work with MLDP, use the disable mpls mldp forwarding recursive command, which is enabled by default. Also, ensure that the mpls mldp path multipath command is enabled for load balancing to function as expected.
Root Node Redundancy
Configure multiple root nodes in the network using the mdt default mpls mldp ip_address command. The control plane builds a corresponding tree with root at the configured node to enable efficient forwarding. A node in the network selects the nearest root for optimal bandwidth usage. Also, in case a root node is unreachable (due to link failure, or router crash), the node switches to the next available root.
This example describes the root node redundancy configuration:
Router(config)# ip vrf blue1
Router(config-if)# rd 10:3
Router(config-if)# vpn id 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 10:3
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 2.2.2.2
Router(config-vrf)# mdt default mpls mldp 5.5.5.5
Verification
Use these commands to verify LSM MLDP based MVPN support configuration:
- To check the MLDP neighbors, use the show mpls mldp neighbor command:
Router# show mpls mldp neighbors
MLDP peer ID : 3.3.3.3:0, uptime 00:41:41 Up,
Path(s) : 3.3.3.3 No LDP Tunnel20
MLDP peer ID : 2.2.2.2:0, uptime 00:17:42 Up,
Path(s) : 3.3.3.3 No LDP Tunnel20
- To check the PIM neighbors, use the show ip pim vrf vrf_name neighbor command:
Router# show ip pim vrf blue neighbor
Mode: B - Bidir Capable, DR - Designated Router, N - Default DR Priority,
P - Proxy Capable, S - State Refresh Capable, G - GenID Capable
Neighbor Interface Uptime/Expires Ver DR
3.3.3.3 Lspvif1 00:06:21/00:01:17 v2 1 / DR S P G
- To check the multicast routes for a given VRF, use show ip mroute vrf vrf_name verbose command:
Router# show ip mroute vrf blue verbose
IP Multicast Routing Table
Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, B - Bidir Group, s - SSM Group, C - Connected,
L - Local, P - Pruned, R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag,
T - SPT-bit set, J - Join SPT, M - MSDP created entry, E - Extranet,
X - Proxy Join Timer Running, A - Candidate for MSDP Advertisement,
U - URD, I - Received Source Specific Host Report,
Z - Multicast Tunnel, z - MDT-data group sender,
Y - Joined MDT-data group, y - Sending to MDT-data group,
V - RD & Vector, v - Vector
Outgoing interface flags: H - Hardware switched, A - Assert winner
Interface state: Interface, Next-Hop or VCD, State/Mode
(40.0.0.2, 232.0.1.4), 00:00:16/00:03:13, flags: sT
Incoming interface: GigabitEthernet3/2/1, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0
Lspvif1, LSM MDT: B0000004 (default), Forward/Sparse, 00:00:16/00:03:13
(*, 224.0.1.40), 00:47:09/00:02:56, RP 0.0.0.0, flags: DPL
Incoming interface: Null, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0
Outgoing interface list: Null
- To check the packet counters, use show ip mroute vrf vrf_name count command:
Router# show ip mroute vrf blue count
2 routes using 1208 bytes of memory
2 groups, 0.50 average sources per group
Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kilobits per second
Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops(OIF-null, rate-limit etc)
Group: 232.0.1.4, Source count: 1, Packets forwarded: 1333, Packets received: 1334
Source: 40.0.0.2/32, Forwarding: 1333/20/46/7, Other: 1334/0/1
Group: 224.0.1.40, Source count: 0, Packets forwarded: 0, Packets received: 0
- To check the MFIB output and whether hardware switching or software switching is enabled, use show ip mfib vrf vrf_name group_address verbose command:
Router# show ip mfib vrf blue 232.0.1.4 verbose
Entry Flags: C - Directly Connected, S - Signal, IA - Inherit A flag,
ET - Data Rate Exceeds Threshold, K - Keepalive
DDE - Data Driven Event, HW - Hardware Installed
I/O Item Flags: IC - Internal Copy, NP - Not platform switched,
NS - Negate Signalling, SP - Signal Present,
A - Accept, F - Forward, RA - MRIB Accept, RF - MRIB Forward,
Platform per slot HW-Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Byte Count
Platform Entry flags: HF - Hardware Forwarding, NP - Not platform switched,
PF - Partial Hardware Forwarding
Platform Interface flags: HW - Hardware Switched, NP - Not platform switched
Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kbits per second
Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops
I/O Item Counts: FS Pkt Count/PS Pkt Count
(40.0.0.2,232.0.1.4) Flags: K HW
Slot 6: HW Forwarding: 912/41952, Platform Flags: HF
SW Forwarding: 0/0/0/0, Other: 1/0/1
HW Forwarding: 912/20/46/7, Other: 0/0/0
GigabitEthernet3/2/1 Flags: RA A MA
Lspvif1, LSM/B0000004 Flags: RF F NS
- To check the hardware entries on the Switched Processor /Distributed Forwarding Card (SP/DFC), use the show platform software multicast ip cmfib vrf vrf_name group_add verbose command:
Router# show platform software multicast ip cmfib vrf blue 232.0.1.4 verbose
Multicast CEF Entries for VPN#1
(40.0.0.2, 232.0.1.4) IOSVPN:256 (1) PI:1 (1) CR:0 (1) Recirc:0 (1)
Vlan:1033 AdjPtr:442371 FibRpfNf:1 FibRpfDf:1 FibAddr:0x800C0 rwvlans:1033 rwindex:0x7FFA adjmac:000a.f330.2480 rdt:1 E:0 CAP1:0 fmt:Mcast l3rwvld:1 DM:0 mtu:1532 rwtype:L2&L3 met2:0x8002 met3:0x8003
packets:0000000002184 bytes:000000000000139776
V E L0 C:1026 I:0x02014 Starting Offset: 0x8003 V E C:1034 IOSVPN:256 (1) PI:0 (1) CR:1 (1) Recirc:0 (1)
Vlan:1026 AdjPtr:442372 FibRpfNf:0 FibRpfDf:1 FibAddr:0x800C2
rwvlans:1026 rwindex:0x7FFA adjmac:000a.f330.2480 rdt:1 E:0 CAP1:0
fmt:Mcast l3rwvld:1 DM:0 mtu:1532 rwtype:L3 met2:0x0 met3:0x8003
packets:0000000000000 bytes:000000000000000000
Annotation-data: [0x4B417730]
A-vlan: 1033 NS-vlan: 0 RP-rpf-vlan: 0
Met-handle: 0x4510801C New-Met-handle: 0x0
HAL L3-data : [0x46ED8D00]
Flags: 0x4 FIB-index: 0x853 ADJ-index: 0x6C003 NF-addr: 0x0
ML3 entry type: 0x0 [(S,G) shortcut]
Flags: 0xA1000000 Vpn: 256 Rpf: 1033 Rw_index: 0x7FFA
Adj_mtu: 1528 Met2: 0x8002 Met3: 0x8003
---Secondary entry [1]---
HAL L3-data : [0x47206CD0]
Flags: 0x4 FIB-index: 0x854 ADJ-index: 0x6C004 NF-addr: 0x0 ML3 entry type: 0x0 [(S,G) shortcut]
Flags: 0x90000000 Vpn: 256 Rpf: 1026 Rw_index: 0x7FFA
Adj_mtu: 1528 Met2: 0x0 Met3: 0x8003
Sublsp:13, if_number:21, met3_vlan:1034, fib_index:0x800C4, adj_addr:30, l3_id:0x5C107AA0, ml3_entry:0x5C107AC0
HAL L3-data : [0x5C107AA0]
Flags: 0x0 FIB-index: 0x855 ADJ-index: 0x1E NF-addr: 0x0
ML3 entry type: 0xE [MPLS LABEL PUSH shortcut]
Flags: 0x32000000 Vpn: 260 Rpf: 0 Rw_index: 0x0
Adj_mtu: 0 Met2: 0x0 Met3: 0x0 V6-data: NULL
- To check the contents of the LSM adjacency, use show mls cef adjacency entry mpls_label detail command:
Router# show mls cef adjacency entry 30 detail
Index: 30 smac: 000a.f330.2480, dmac: 001b.0de4.2b00
mtu: 65535, vlan: 1031, dindex: 0x2117, l3rw_vld: 1
format: MPLS, flags: 0x8610
label0: 0, exp: 0, ovr: 0
label1: 0, exp: 0, ovr: 0
label2: 20, exp: 0, ovr: 0
packets: 6432, bytes: 411648
- To check the internal VLANs, use show vlan internal usage command:
Router# sh vlan internal usage
---- --------------------
1012 PM vlan process (trunk tagging)
1013 Ls0 Label Replication (0) (0)
1014 Ls1 Label Replication (0) (0)
1015 Control Plane Protection
1021 IPv4 VPN 0 Egress multicast
1022 IP Multicast Partial SC vpn(2)
1023 IPv4 VPN 2 Egress multicast
1024 Multicast VPN 2 QOS Vlan
1025 IP Multicast Partial SC vpn(1)
---- --------------------
1026 IPv4 VPN 1 Egress multicast
1027 Multicast VPN 1 QOS Vlan
1028 IP Multicast Partial SC vpn(0)
1029 Multicast VPN 0 QOS Vlan
1032 GigabitEthernet3/2/2
1033 GigabitEthernet3/2/1
1034 Fa2/1/0 Label Replication (1000000200000000) (1)
1035 Fa2/1/0 Label Replication (1000000200000000) (2)
1036 Gi3/2/2 Label Replication (1600000200000000) (1)
1037 Gi3/2/2 Label Replication (1600000200000000) (2)
- To check the label replication VLANs, use show mpls platform vlan lsm command:
Router# show mpls platform vlan lsm
VLAN Interface Opaque Vrf id MLS VPN hw_id subblock
1013 Lspvif0 0 0 0 258 0x4BC4A190
1014 Lspvif1 0 0 1 259 0x4BC491C0
1034 FastEthernet2/1/0 1000000200000000 1 2 260 0x4BC481F0
1035 FastEthernet2/1/0 1000000200000000 2 3 261 0x4BC481F0
1036 GigabitEthernet3/2/2 1600000200000000 1 4 262 0x4BC47220
1037 GigabitEthernet3/2/2 1600000200000000 2 5 263 0x4BC47220
- To check the labels, use show mpls forwarding-table command:
Router# show mpls forwarding-table
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop
Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface
16 Pop Label IPv4 VRF[V] 0 aggregate/blue
17 Pop Label IPv4 VRF[V] 0 aggregate/red
18 [T] Pop Label 3.3.3.3/32 0 Tu20 point2point
19 [T] 25 2.2.2.2/32 0 Tu20 point2point
20 [T] Pop Label 19.0.0.0/24 0 Tu20 point2point
22 [T] No Label [mdt 55:1111 0][V] \9422 aggregate/red
23 [T] No Label [mdt 55:2222 0][V] \9708 aggregate/blue
[T] Forwarding through a LSP tunnel.
View additional labelling info with the 'detail' option
- To check the contents of a label on SP/DFC, use show mls cef mpls labels mpls_label command:
Router# show mls cef mpls labels 23
Codes: + - Push label, - - Pop Label * - Swap Label, E - exp1
Index Local Label Out i/f
- To check the contents in detail, use show mls cef mpls labels mpls_label detail command:
Router# show mls cef mpls labels 23 detail
Codes: M - mask entry, V - value entry, A - adjacency index, P - FIB Priority
D - FIB Don't short-cut, m - mod-num, E - ELSP?
Format: MPLS - (b | xtag vpn pi cr mcast label1 exp1 eos1 valid2 label2 exp2 eos2)
V(2184): B | 1 0 0 0 0 22 0 1 0 0 0 0 (A:163840,P:0,D:0,m:0 :E:1)
M(2184): F | 1 FFF 0 0 1 FFFFF 0 1 0 0 0 0
- To check the contents of the label ternary content addressable memory (TCAM) adjacency, use show mls cef adj entry adjacency_pointer detail command:
Router# show mls cef adjacency entry 163840 detail
Index: 163840 smac: 000a.f330.2480, dmac: 0100.5e00.000d
mtu: 65535, vlan: 1017, dindex: 0x7FFA, l3rw_vld: 1
format: MPLS, flags: 0x1000008600
label0: 0, exp: 0, ovr: 0
label1: 0, exp: 0, ovr: 0
label2: 0, exp: 0, ovr: 0
Sample Configuration for MLDP MVPN
You can configure MLDP MVPN in these two modes:
- Source Specific Mode (SSM)
- Sparse Mode (SM)
Configuration Example Using SSM mode
These examples are based on the topology shown in Figure 51-1. Consider these scenarios while configuring MLDP MVPN using SSM mode:
- MLDP MVPN Extranet SSC
- MLDP MVPN Extranet RSC
- MLDP MVPN Intranet
MLDP MVPN Extranet SSC
Configuration on PE1 router (Source PE):
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip multicast-routing vrf red3
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip address 101.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 101.3.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet1/22.2
ip address 12.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet8/1
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red3
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 ssm default
ip pim vrf red3 ssm default
ip mroute vrf red3 12.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 fallback-lookup vrf red2
Configuration on P router:
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet2/10
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet2/20
ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
Configuration on PE2 router (Receiver PE):
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red3
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 102.3.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/1.3
ip address 22.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red3
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red3 ssm default
ip mroute vrf red3 12.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 101.3.0.2
Configuraton on PE3 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red3
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
ip address 103.3.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/0.3
ip address 32.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/1
ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red3
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
ip pim vrf red3 ssm default
ip mroute vrf red3 12.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 101.3.0.2
MLDP MVPN Extranet RSC
Configuration on PE1 router (Source PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip address 101.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet1/22.2
ip address 12.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet8/1
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 ssm default
Configuration on P router (Core router)
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet2/10
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet2/20
ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
Configuration ond PE2 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red3
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 102.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 102.3.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/1.3
ip address 22.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red3
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red3 ssm default
ip pim vrf red2 ssm default
ip mroute vrf red3 12.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 fallback-lookup vrf red2
Configuration on PE3 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red3
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
ip address 103.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 103.3.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/0.3
ip address 32.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/1
ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red3
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
ip pim vrf red3 ssm default
ip pim vrf red2 ssm default
ip mroute vrf red3 12.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 fallback-lookup vrf red2
MLDP MVPN Intranet
Configuration ond PE1 router (Source PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip address 101.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet1/22.2
ip address 12.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet8/1
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 ssm default
Configuration on P router (core router)
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet2/10
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet2/20
ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
Configuration on PE2 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 102.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/1.2
ip address 22.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 ssm default
Configuration on PE3 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
ip address 103.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/0.2
ip address 32.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/1
ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 ssm default
Configuration Example Using SM Mode
These examples are based on the topology shown in Figure 51-1. Consider these scenarios while configuring MLDP MVPN using SSM mode:
- MLDP MVPN Extranet SSC
- MLDP MVPN Extranet RSC
- MLDP MVPN Intranet
MLDP MVPN Extranet SSC
Configuration on PE1 router (Source PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip multicast-routing vrf red3
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip address 101.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 101.3.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet1/22.2
ip address 12.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet8/1
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red3
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 rp-address 11.11.11.11
ip pim vrf red3 rp-address 11.11.11.11
ip mroute vrf red3 12.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 fallback-lookup vrf red2
ip mroute vrf red3 11.11.11.11 255.255.0.0 fallback-lookup vrf red2
Configuration on P router
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet2/10
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet2/20
ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
Configuration on PE2 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red3
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 102.3.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/1.3
ip address 22.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red3
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red3 rp-address 11.11.11.11
ip mroute vrf red3 12.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 101.3.0.2
Configuraton on PE3 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red3
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
ip address 103.3.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/0.3
ip address 32.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/1
ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red3
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
ip pim vrf red3 rp-address 11.11.11.11
ip mroute vrf red3 12.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 101.3.0.2
MLDP MVPN Extranet RSC
Configuration on PE1 router (Source PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip address 101.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet1/22.2
ip address 12.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet8/1
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 rp-address 11.11.11.11
Configuration on P router (Core router)
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet2/10
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet2/20
ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
Configuration ond PE2 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red3
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 102.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 102.3.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/1.3
ip address 22.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red3
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 rp-address 11.11.11.11
ip pim vrf red3 rp-address 11.11.11.11
ip mroute vrf red3 12.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 fallback-lookup vrf red2
ip mroute vrf red3 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255 fallback-lookup vrf red2
Configuration on PE3 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red3
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
ip address 103.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 103.3.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/0.3
ip address 32.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/1
ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red3
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 rp-address 11.11.11.11
ip pim vrf red3 rp-address 11.11.11.11
ip mroute vrf red3 12.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 fallback-lookup vrf red2
ip mroute vrf red3 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255 fallback-lookup vrf red2
MLDP MVPN Intranet
Configuration ond PE1 router (Source PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip address 101.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet1/22.2
ip address 12.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet8/1
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 rp-address 11.11.11.11
Configuration ond P router (core router)
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet2/10
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet2/20
ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface TenGigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
Configuration on PE2 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
ip address 102.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/0
ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet4/0/1.2
ip address 22.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 rp-address 11.11.11.11
Configuration on PE3 router (Receiver PE)
mdt default mpls mldp 4.4.4.4
ip multicast-routing vrf red2
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
ip address 103.2.0.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/0.2
ip address 32.2.0.1 255.255.0.0
interface GigabitEthernet3/2/1
ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
address-family ipv4 vrf red2
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
ip pim vrf red2 rp-address 11.11.11.11
Troubleshooting LSM MLDP based MVPN Support
Use these debug commands to troubleshoot the LSM MLDP based MVPN support on C7600 series router:
|
|
|
debug platform software multicast ip cmfib event debug platform software multicast ip cmfib error |
Used for CMFIB issues. |
debug platform software multicast ip hal error debug platform software multicast ip hal event |
Used for MET related issues [SP/DFC]. |
debug mpls platform lsm vm error debug mpls platform lsm vm event |
Used for Label replication vlan related issues [RP/SP/DFC]. |
debug mpls mldp packet debug mpls mldp neighbor debug mpls mldp all |
Used for MLDP debugging [RP]. |
debug ip igmp vrf blue |
Used for IGMP debugs. |
debug ip pim vrf blue hello debug ip pim vrf blue timer debug ip pim vrf blue bsr debug ip pim vrf blue auto-rp |
Used for PIM debugs [RP]. |

![]() LSM MLDP-based MVPN feature is supported on ES+ and ES20 line cards and these supervisors: RSP720, SUP720, and RSP720-10GE. MLDP is supported on all the egress replication capable line cards.
LSM MLDP-based MVPN feature is supported on ES+ and ES20 line cards and these supervisors: RSP720, SUP720, and RSP720-10GE. MLDP is supported on all the egress replication capable line cards.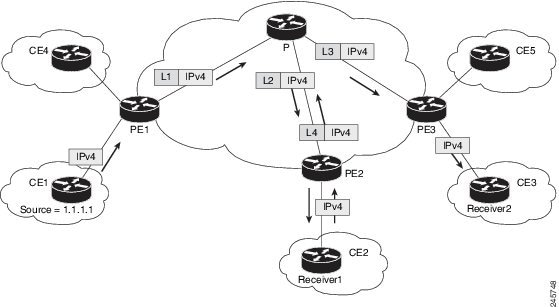
![]() Maximum number of mVRFs supported is 100.
Maximum number of mVRFs supported is 100.![]() Maximum number of multicast routes supported in each MVRF is 100.
Maximum number of multicast routes supported in each MVRF is 100.
![]() Before configuring MLDP based MVPN, ensure that the MPLS is enabled on the core facing interface. For information in MPLS configuration, see the Cisco IOS Multiprotocol Label Switching Configuration Guide. Also, ensure that BGP and any interior gateway protocol (OSPF or ISIS) is enabled on the core router.
Before configuring MLDP based MVPN, ensure that the MPLS is enabled on the core facing interface. For information in MPLS configuration, see the Cisco IOS Multiprotocol Label Switching Configuration Guide. Also, ensure that BGP and any interior gateway protocol (OSPF or ISIS) is enabled on the core router. ![]() route-target [import | export | both] route-target-ext-community
route-target [import | export | both] route-target-ext-community![]() route-target [import | export | both] route-target-ext-community
route-target [import | export | both] route-target-ext-community![]() mdt default mpls mldp root-node
mdt default mpls mldp root-node![]() mdt data mpls mldp numberofdataMDTs
mdt data mpls mldp numberofdataMDTs![]() mdt data threshold bandwidth
mdt data threshold bandwidth![]() ip multicast-routing vrf vrf-name
ip multicast-routing vrf vrf-name
![]() See Configuring the MDT Address Family in BGP for Multicast VPN for information on configuring an MDT and vpnv4 address family session on the PE routers to establish MDT peering sessions for MVPN.
See Configuring the MDT Address Family in BGP for Multicast VPN for information on configuring an MDT and vpnv4 address family session on the PE routers to establish MDT peering sessions for MVPN.
![]() See Configuring the MDT Address Family in BGP for Multicast VPN for information on configuring an MDT address family session on the PE routers to establish MDT peering sessions for MVPN.
See Configuring the MDT Address Family in BGP for Multicast VPN for information on configuring an MDT address family session on the PE routers to establish MDT peering sessions for MVPN.
![]() This configuration is based on illustration Figure 51-1. Configure multicast routes on the PE1 router.
This configuration is based on illustration Figure 51-1. Configure multicast routes on the PE1 router.![]() route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community![]() route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community![]() mdt default mpls mldp root-node
mdt default mpls mldp root-node![]() ip vrf forwarding vrf-name
ip vrf forwarding vrf-name![]() ip address ip-address subnet
ip address ip-address subnet![]() ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] source-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] source-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance] ![]() (For SM Mode) ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] rp-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
(For SM Mode) ip mroute [vrf receiver-vrf-name] rp-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance] ![]() route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community![]() route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community![]() mdt default mpls mldp root-node
mdt default mpls mldp root-node![]() ip vrf forwarding vrf-name
ip vrf forwarding vrf-name![]() ip address ip-address subnet
ip address ip-address subnet![]() ip mroute vrf receiver_vrf source_address subnet_mask loopback_ip
ip mroute vrf receiver_vrf source_address subnet_mask loopback_ip
![]() This configuration is based on illustration Figure 51-1. Configure multicast routes on PE2 and PE3 routers.
This configuration is based on illustration Figure 51-1. Configure multicast routes on PE2 and PE3 routers.![]() route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community![]() route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community![]() mdt default mpls mldp root-node
mdt default mpls mldp root-node![]() route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community![]() route-target import route-target-ext-community
route-target import route-target-ext-community![]() mdt default mpls mldp root-node
mdt default mpls mldp root-node![]() ip mroute [vrf recevier-vrf-name] source-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance]
ip mroute [vrf recevier-vrf-name] source-address mask fallback-lookup {global | vrf source-vrf-name} [distance] ![]() ip multicast mpls traffic-eng [range {access-list-number | access-list-name}]
ip multicast mpls traffic-eng [range {access-list-number | access-list-name}] Feedback
Feedback