Cisco 4G LTE Hardware Installation Guide
Available Languages
Table of Contents
Cisco4G LTE Hardware Installation Guide
Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTE Ports and LEDs
EHWIC-4G-LTE-V, EHWIC-4G-LTE-ST, EHWIC-4G-LTE-VZ Ports and LEDs
Supported Cisco Antennas and Cables
Installing the SIM card on the Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTE
Cisco 4G LTE Hardware Installation Guide
This document provides an overview of the hardware and installation information for Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTEs. Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTEs are single-wide 4G Wireless WAN (WWAN) EHWICs supported on Cisco Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 (ISRs G2).
Contents
Hardware Overview
Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTEs operate over Fourth-Generation Long-Term Evolution (4G LTE) cellular networks and Third-Generation (3G) cellular networks.
Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTEs are single-wide EHWICs supported on Cisco 1900 Series, 2900 Series, and 3900 Series ISRs G2.
The following sections describe the Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTEs:
Cisco 4G WWAN EHWICs
Table 1 describes the Cisco 4G WWAN EHWIC product SKUs.
Table 1 Cisco 4G EHWIC by Mode, Operating Region, and Frequencies
EHWIC-4G-LTE-V, EHWIC-4G-LTE-ST, EHWIC-4G-LTE-VZ Ports and LEDs
Figure 1 shows the front panel view for EHWIC-4G-LTE-V, EHWIC-4G-LTE-ST, and EHWIC-4G-LTE-VZ. Table 2 lists the EHWIC-4G-LTE-V, EHWIC-4G-LTE-ST, and EHWIC-4G-LTE-VZ ports and LED indicators and describes their behavior. The LEDs provide a visual indication of your available services.
Figure 1 Front Panel of the Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTE-V, EHWIC-4G-LTE-ST, and EHWIC-4G-LTE-VZ
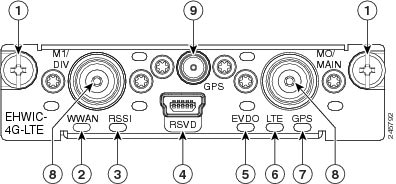
The reserved (RSVD) diagnostic port is not required for normal activation or operation. This port supports modem debug or provisioning. See the “Modem Troubleshooting Using the Diagnostic Port” section in Configuring Cisco 4G LTE Wireless WAN EHWIC for details. |
|
M1/DIV—Diversity antenna connector, female TNC4. M0/MAIN—Main antenna connector, female TNC. GPS—GPS antenna connector, female SMA5. See the “Supported Cisco Antennas and Cables” section for details. |
|
Indicates the EHWIC modem status. Solid green —Indicates the modem is receiving power and is associated and authenticated but not receiving or transmitting data. Fast green blink —Indicates the modem is receiving power and is associated and authenticated. The blink rate is proportional to the transmitted and received data rate. Slow green blink —Indicates the modem is receiving power but is not associated or authenticated and is searching for service. Check the antenna, cable, SIM card, or the user account with your service provider. |
|
Indicates the level of signal strength received by the EHWIC software. Solid green —Indicates a high RSSI (greater than –69 dBm). Medium green blink —Indicates a medium-level RSSI (from –89 dBm to –69 dBm). Slow green blink —Indicates a low-level RSSI (from –99 dBm to –89 dBm). Off —Indicates the RSSI is less than –99 dBm. Check for proper antenna attachment. Adjust antenna placement and orientation. Solid amber —Indicates no service is detected. Relocate the equipment. |
|
Indicates either HSDPA or EVDO is in service. Solid green —Indicates HSDPA is in service. Blinking green —Indicates EVDO service is in use. Off —Indicates that neither HSDPA nor EVDO services are in use. |
|
Indicates whether LTE is in service. |
|
EHWIC-4G-LTE-A, EHWIC-4G-LTE-G, EHWIC-4G-LTE-JP, EHWIC-4G-LTE-BE, EHWIC-4G-LTE-AU, EHWIC-4G-LTE-GB, EHWIC-4G-LTE-CA, and EHWIC-4G-LTE-AT Ports and LEDs
Figure 2 shows the front panel view for EHWIC-4G-LTE-A, EHWIC-4G-LTE-G, EHWIC-4G-LTE-JP, EHWIC-4G-LTE-BE, EHWIC-4G-LTE-AU, EHWIC-4G-LTE-GB. Table 3 lists the EHWIC-4G-LTE-A, EHWIC-4G-LTE-G, EHWIC-4G-LTE-JP, EHWIC-4G-LTE-BE, EHWIC-4G-LTE-AU, EHWIC-4G-LTE-GB, EHWIC-4G-LTE-CA, and EHWIC-4G-LTE-AT ports and LED indicators and describes their behavior.
Figure 2 Front Panel of Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTE-A, EHWIC-4G-LTE-G, EHWIC-4G-LTE-JP, EHWIC-4G-LTE-BE, EHWIC-4G-LTE-AU, EHWIC-4G-LTE-GB, EHWIC-4G-LTE-CA and EHWIC-4G-LTE-AT

The reserved (RSVD) diagnostic port is not required for normal activation or operation. This port supports modem debug or provisioning. See the “Modem Troubleshooting Using the Diagnostic Port” section in Configuring Cisco 4G LTE Wireless WAN EHWIC for details. |
|
M1/DIV—Diversity antenna connector, female TNC6. M0/MAIN—Main antenna connector, female TNC. GPS—GPS antenna connector, female SMA7. See the “Supported Cisco Antennas and Cables” section for details. |
|
Indicates the EHWIC modem status. Solid green —Indicates the modem is receiving power and is associated and authenticated but not receiving or transmitting data. Fast green blink —Indicates the modem is receiving power and is associated and authenticated. The blink rate is proportional to the transmitted and received data rate. Slow green blink —Indicates the modem is receiving power but is not associated or authenticated and is searching for service. Check the antenna, cable, SIM card, or the user account with your service provider. |
|
Indicates the level of signal strength received by the EHWIC software. Solid green —Indicates a high RSSI (greater than –69 dBm). Medium green blink —Indicates a medium-level RSSI (from –89 dBm to –69 dBm). Slow green blink —Indicates a low-level RSSI (from –99 dBm to –89 dBm). Off —Indicates the RSSI is less than –99 dBm. Check for proper antenna attachment. Adjust antenna placement and orientation. Solid amber —Indicates no service is detected. Relocate the equipment. |
|
Indicates HSPA+ is in service. Solid green —Indicates HSPA+ is in service. Off —Indicates that a non-HSPA+ is in service or that there is no service. |
|
Indicates whether LTE is in service. |
|
Indicates whether the GPS is in service. |
Supported Cisco Antennas and Cables
Table 4 lists the Cisco antennas that are supported for use on the Cisco 4G WWAN EHWIC.
Multiband dual 4G LTE antenna. For more information, see Cisco Dual LTE-Single GPS Multi-band Antenna Installation Guide. |
|||
Multiband dipole antenna. For more information, see Cisco 4G/3G Omnidirectional Dipole Antenna (4G-LTE-ANTM-D). |
|||
Multiband omnidirectional ceiling-mount antenna. For more information, see Cisco 4G Indoor Ceiling-Mount Omnidirectional Antenna (4G-ANTM-OM-CM). |
|||
Multiband outdoor omnidirectional stick antenna. For more information, see Cisco Outdoor Omnidirectional Antenna for 2G/3G/4G Cellular (ANT-4G-OMNI-OUT-N). |
|||
1.5 dBi (peak gain with 10-foot cable) or 0.8 dBi (peak gain with 15-foot cable) 3.7 dBi (peak gain with 10-foot cable) or 0.2 dBi (peak gain with 15-foot cable) |
Low-profile outdoor saucer antenna. For more information, see Cisco Integrated 4G Low-Profile Outdoor Saucer Antenna (ANT-4G-SR-OUT-TNC). |
||
This is the default antenna extension base. For more information, see Cisco Single-Port Antenna Stand for Multiband TNC Male-Terminated Portable Antenna (Cisco 4G-AE015-R, Cisco 4G-AE010-R). |
|||
Single-port antenna extension base with 15-foot cable. For more information, see Cisco Single-Port Antenna Stand for Multiband TNC Male-Terminated Portable Antenna (Cisco 4G-AE015-R, Cisco 4G-AE010-R). |
|||
4G lightning arrestor kit for use on Cisco 4G wireless devices. For more information, see Cisco 4G Lightning Arrestor (4G-ACC-OUT-LA). |
|||
4G lightning arrestor kit for use on Cisco 4G wireless devices. For more information, see Lightning Arrestor for the Cisco 1240 Connected Grid Router. |

Note![]() You can use the RG-174/U type cables to adapt the modem external antenna connection to any of the EHWIC cables and antennas.
You can use the RG-174/U type cables to adapt the modem external antenna connection to any of the EHWIC cables and antennas.

Note![]() To comply with FCC requirements for colocation of radio frequency (RF) products, if two or more cellular EHWICs are installed in one chassis, the antennae connected to each card must be located a minimum of 7.9 inches (20 cm) away from the antennae connected to any other card in the system.
To comply with FCC requirements for colocation of radio frequency (RF) products, if two or more cellular EHWICs are installed in one chassis, the antennae connected to each card must be located a minimum of 7.9 inches (20 cm) away from the antennae connected to any other card in the system.
Table 5 lists loss information and operating frequency levels for the ultra-low-loss (ULL) LMR 200 cables and LMR 400 cables available from Cisco for use with Cisco 4G Wireless WAN EHWICs and Cisco 4G Wireless WAN ISR platforms.
|
Plenum Rated?
8
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1.4 dB @ 700 MHz |
|||||
2.3 dB @ 700 MHz |
Figure 3 shows the ULL coaxial cable recommended for Cisco 4G Wireless WAN EHWICs.
Figure 3 Typical Coaxial Cable

TNC Male RA9 |
|||
Figure 4 shows some antenna options for the Cisco 4G Wireless WAN EHWICs.

Installing the SIM card on the Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTE
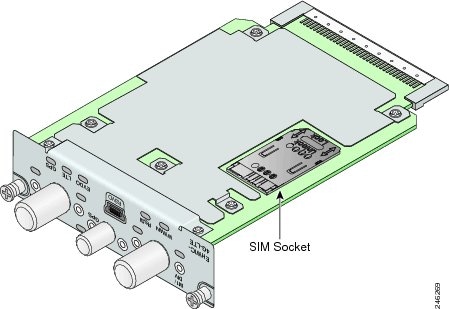
The SIM card socket is located on the bottom side of the EHWIC, as shown in Figure 5. The cover of the SIM card socket contains a slot into which the SIM card is installed.
Figure 5 Location of the SIM Socket on the Bottom Side of the EHWIC
Follow these steps to install the SIM card:
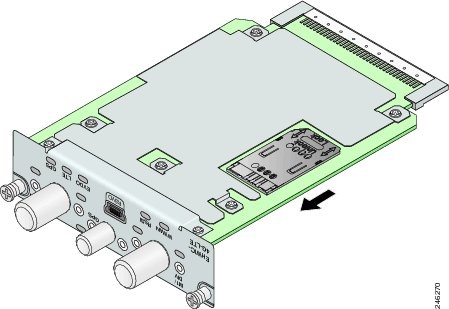
Step 1![]() To unlock the SIM socket cover, slide the cover toward the faceplate in the direction of the unlock arrow, as shown in Figure 6.
To unlock the SIM socket cover, slide the cover toward the faceplate in the direction of the unlock arrow, as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 Unlock the SIM Socket Cover
Step 2![]() Gently lift the cover on its hinges and slide the SIM card into the slot in the cover, as shown in Figure 7.
Gently lift the cover on its hinges and slide the SIM card into the slot in the cover, as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7 Slide SIM card into Slot
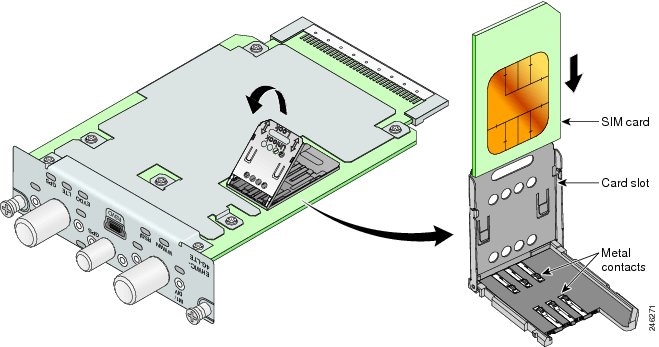
Step 3![]() Gently push down the cover to close, as shown in Figure 8. The SIM card will come in contact with the metal contacts in the socket.
Gently push down the cover to close, as shown in Figure 8. The SIM card will come in contact with the metal contacts in the socket.
Figure 8 Close the SIM Socket Cover

Step 4![]() To lock the cover, slide it away from the faceplate in the direction of the lock arrow, as shown in Figure 9.
To lock the cover, slide it away from the faceplate in the direction of the lock arrow, as shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9 Lock the SIM Socket Cover

Installing Cisco EHWIC-4G-LTE
See Installing Cisco Interface Cards in Cisco Access Routers for instructions on how to install a single-wide interface card in Cisco access routers.
Additional References
Related Documents
Technical Assistance
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2011-2015 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback