Cable Modem High-Speed WAN Interface Cards
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Cable Modem High-Speed WAN Interface Cards
Cisco Cable Modem HWIC (HWIC-CABLE-D-2)
Cisco Cable Modem HWIC (HWIC-CABLE-E/J-2)
Platform Support for Cisco Cable Modem HWICs
Connecting the Cisco Cable Modem HWIC
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
Cable Modem High-Speed WAN Interface Cards
Revised: 6/7/07, OL-12855-01Overview
This document describes Cisco cable modem high-speed WAN interface cards (HWICs) and how to connect Cisco cable modem HWICs to the network and contains the following sections:
•
Platform Support for Cisco Cable Modem HWICs
•
Connecting the Cisco Cable Modem HWIC
•
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
For an overview of Cisco interface cards used for Cisco access routers see the Cisco Interface Cards for Cisco Access Routers document.
Cisco Cable Modem HWICs
This section describes the features of the Cisco cable modem HWICs and contains the following sections:
•
Cisco Cable Modem HWIC (HWIC-CABLE-D-2)
•
Cisco Cable Modem HWIC (HWIC-CABLE-E/J-2)
•
LEDs
The Cisco cable modem HWICs allow the router to communicate over a cable high-speed data (HSD) network for office-to-Internet connectivity or for branch-to-branch connectivity. Supported on a wide range of platforms, the Cisco cable modem HWIC is suitable for deployments ranging from small office/home office (SOHO) to small and medium business (SMB) to enterprise branch offices. When the Cisco cable modem HWIC is combined with the powerful Cisco IOS software and Cisco access routers, an unparalleled range of services becomes possible, all within a single, easily manageable platform. This combination allows a provider or business to minimize operational expenses while maximizing the potential return on invested capital.
The Cisco cable modem HWICs are designed to be fully compliant with DOCSIS 2.0 standards in the United States, Europe, and Japan. Cisco cable modem HWICs provide secure, high-speed connections over cable modem hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) cable network.

Note
To see the DOCSIS 2.0 U.S. requirements and specifications, see the ComLabs website at
http://www.cablemodem.com/specifications/specifications20.html
To see Euro DOCSIS 2.0 requirements, see the tComLabs website at
http://www.excentis.com
The following modules are available:
•
1-port DOCSIS 2.0 Cable Modem HWIC (HWIC-CABLE-D-2)
•
1-port Euro/J-DOCSIS 2.0 Cable Modem HWIC (HWIC-CABLE-E/J-2)

Note
Online insertion and removal (OIR) is not supported on the Cisco cable modem HWICs.

Note
Up to four Cisco cable modem HWICs can be inserted in the chassis, depending on the availability of chassis slots.
Cisco Cable Modem HWIC (HWIC-CABLE-D-2)
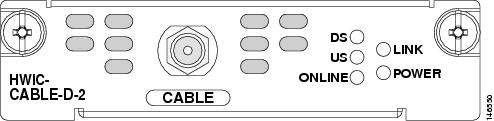
Figure 135 shows the faceplate of the Cisco cable modem HWIC, United States version (HWIC-CABLE-D-2).
Figure 135 Cisco Cable Modem HWIC (HWIC-CABLE-D-2) Faceplate
Cisco Cable Modem HWIC (HWIC-CABLE-E/J-2)
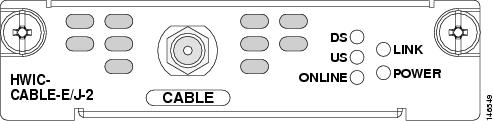
Figure 136 shows the faceplate of the Cisco cable modem HWIC, European and Japanese version (HWIC-CABLE-E/J-2).
Figure 136 Cisco Cable Modem HWIC (HWIC-CABLE-E/J-2) Faceplate
Port Numbering
Table 43 shows the different interface port types on the Cisco routers. For information about port numbering on interface cards in specific routers, see the Cisco Interface Cards Installation Guide.

Note
For specific information regarding port numbering for the routers that support Cisco cable modem HWICs, see the hardware installation documentation for your router at http://www.cisco.com/.
Table 43 Port Numbering on the Cisco Routers
1841, 2800, and 3800 ISRs
x/y/z
IAD2431, 3725, 3745
x/y
815 ISR
x

Note
The slot number for all WIC interfaces on Cisco ISRs is always 0. (The W0 and W1 slot designations are for physical slot identification only.) Interfaces in the WICs are numbered from right to left, starting with 0/0 for each interface type, regardless of which physical slot the WICs are installed in.

Note
The slot for WICs on the Cisco 2430 IADs is numbered slot 0. WIC interfaces are numbered by interface with this slot number and an interface number, starting with 0 and continuing from right to left.
LEDs
The Cisco cable modem HWIC LEDs show green, orange, and off states for system and port status. Table 44 describes the Cisco cable modem HWIC LEDs and their meanings when the Cisco cable modem HWIC is going through the registration process.
For more information about DOCSIS 2.0 compliant LED functionality, see the CableLabs website at http://www.cablelabs.com
Accessibility
These HWICs can be configured using the Cisco command-line interface (CLI). The CLI conforms to Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act because it is text based and because it relies on a keyboard for navigation. All functions of the router can be configured and monitored through the CLI.
For a complete list of guidelines and Cisco products adherence to accessibility, see Cisco Accessibility Products at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/web/about/responsibility/accessibility/products
Platform Support for Cisco Cable Modem HWICs
The Cisco Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) cable modem HWICs are supported in the following Cisco routers: Cisco IAD2431 Integrated Access Devices; Cisco 3725, and Cisco 3745 routers; and Cisco 1800 (modular), Cisco 2800, and Cisco 3800 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs).

Note
The Cisco 815 ISR for Broadband Cable does not support WIC or HWIC modules, however, the underlying cable modem technology is identical to that of the cable modem HWIC.
Table 45 shows the Cisco router platforms that support the Cisco cable modem HWICs.
Table 45 Cisco Router Support for WICs and HWICs
8151
Note
The performance of the 815 matches the performance of the WIC mode. The cable modem in the 815 is a fixed configuration and is not field replaceable.
Yes
No
1800
No
Yes
IAD24311
Yes
No
2800 series
No
Yes
3700 series1
Yes
No
3800 series
No
Yes
1 When the cable modem HWIC is placed in these routers, the HWIC operates only in WAN interface card (WIC) mode, providing total throughput on the cable modem HWIC of 16 MB (8 MB upstream and 8 MB downstream).

Note
For specific information about WIC/HWIC support for the routers that support the Cisco cable modem HWICs, see the hardware installation documentation for your router at www.cisco.com.
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Connecting the Cisco Cable Modem HWIC
To connect the Cisco cable modem HWIC to the router, follow these steps:
Step 1
Verify that the router is powered off.
Step 2
Insert the Cisco cable modem HWIC in the HWIC slot of the Cisco router.

Note
For specific information regarding WIC/HWIC support for the routers that support Cisco cable modem HWICs, see the hardware installation documentation for your router at www.cisco.com.
Step 3
Locate the RF coaxial cable coming from the coaxial cable CATV wall outlet.
Step 4
Install a cable splitter/directional coupler, if needed, to separate signals for TV and computer usage. If necessary, also install a high-pass filter to prevent interference between the TV and computer signals.
Step 5
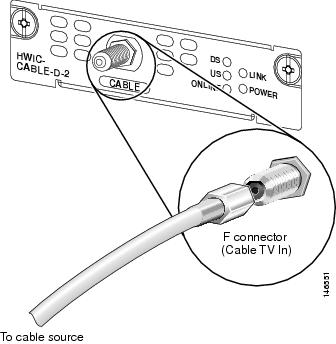
Connect the RF coaxial cable to the Cisco cable modem HWIC F-connector. Hand-tighten the connector, making sure that it is finger tight; then give it a 1/6-turn with a wrench. See Figure 137
Figure 137 Connecting the CATV Coaxial Cable to the Cisco Cable Modem HWIC
Step 6
Power on the router.
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
For information on obtaining documentation, obtaining support, providing documentation feedback, security guidelines, and also recommended aliases and general Cisco documents, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html

Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback