Analog Modem WAN Interface Cards
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Analog Modem WAN Interface Cards
WIC-1AM-V2 and WIC-2AM-V2 Features
Understanding Interface Numbering on Analog Modem WICs
Connecting an Analog Modem WIC to a Network
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
Analog Modem WAN Interface Cards
Revised: 6/7/07, OL-12848-01Overview
This document describes Cisco analog modem WICs and how to connect analog modem WICs to a network. It contains the following sections:
•
Understanding Interface Numbering on Analog Modem WICs
•
Connecting an Analog Modem WIC to a Network
•
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
For an overview of Cisco interface cards used for Cisco access routers see the Cisco Interface Cards for Cisco Access Routers document.
Analog Modem WICs
The analog modem WAN interface cards originate or terminate analog telephone transmissions through RJ-11 modular jacks.
There are four analog modem WICs:
•
1-port analog modem WAN interface card (WIC-1AM) (see Figure 102)
•
2-port analog modem WAN interface card (WIC-2AM) (see Figure 103)
•
1-port analog modem WAN interface card, version 2 (WIC-1AM-V2) (see Figure 104)
•
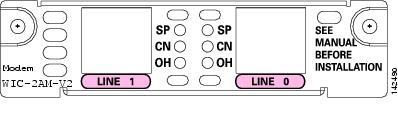
2-port analog modem WAN interface card, version 2 (WIC-2AM-V2) (see Figure 105)
Figure 102 WIC-1AM Front Panel

Figure 103 WIC-2AM Front Panel

Figure 104 WIC-1AM-V2 Front Panel

Figure 105 WIC-2AM-V2 Front Panel
Restrictions
The following warning applies in Australia:

Warning
This equipment will be inoperable when main power fails.
The following warning applies in New Zealand:

Warning
This equipment does not fully meet Telecom's impedance requirements. Performance limitations may occur when used in conjunction with some parts of the network. Telecom will accept no responsibility should difficulties arise in such circumstances.
WIC-1AM and WIC-2AM Features
The WIC-1AM and WIC-2AM interface cards support the following protocols:
•
All standard data rates from 300 bps to 33.6 kbps (V.34bis)
•
V.42bis and MNP 5 data compression
•
V.42, LAPM, and MNP 2 to 4 error correction
•
V.90 up to 56 kbps
•
MNP 10 for high performance under all line conditions
•
MNP 10EC for high performance in analog cellular environments
WIC-1AM-V2 and WIC-2AM-V2 Features
You can upgrade WIC-1AM-V2 and WIC-2AM-V2 WAN interface card modem firmware, if a new image is released. For more information about configuring the WIC-1AM-V2 and WIC-2AM-V2 interface cards, and upgrading the modem firmware, see the Cisco WIC-1AM-V2 and WIC-2AM-V2 Analog Modem WAN Interface Card feature document.
The WIC-1AM-V2 and WIC-2AM-V2 interface cards support the following protocols:
•
All standard data rates from 300 bps to 33.6 kbps (V.34bis)
•
V.42bis and MNP 5 data compression
•
V.42, LAPM, and MNP 2 to 4 error correction
•
V.44 for a higher compression ratio over V.42bis compression technology.
•
V.90 up to 56 kbps
•
V.92 with quick-connect
•
MNP 10 for high performance under all line conditions
•
MNP 10EC for high performance in analog cellular environments
Analog Modem WIC LEDs
The analog modem WIC LEDs are shown in Figure 102 to Figure 105. The functions of the LEDs are described in Table 28.
Table 28 Analog Modem WIC LEDs
SP
Speed indication
•
On = High speed (V.56/V.90)
•
Off = Low speed (V.32/V.32b/V.34)
CN
Connect (carrier detect)
OH
Off-hook status
Understanding Interface Numbering on Analog Modem WICs
Cisco IOS software identifies each modem uniquely by its slot number and port number.
Some Cisco IOS configuration commands identify asynchronous ports by an interface number (or a line number, which is the same as the interface number). The interface number of a port on an 1-port or 2-port analog WAN interface card is related to the slot number where the card is installed and the number of the port in the card.
Slot numbering conventions for Cisco interface cards are explained in the "Interface Card Slots Available on Cisco Access Routers" section on page -8.
Ports in the 1- and 2-port analog modem WAN interface cards are numbered in the same pattern as slot numbers, beginning at 0 at the lower right and continuing from right to left.
The interface number of a port is determined in the following way:
interface-number = (32 x slot-number) + port-number + 1
For example, modem port 1 in slot 1 corresponds to interface number (32 x 1) + 1 + 1 = 34. This is also the line number for the port. Port 1 in slot 1 is always assigned interface number 34, regardless of what is in slot 0. If you move the card from slot 1 to a different slot, however, its interface numbers change.
Table 29 shows the range of interface numbers available for each type of analog modem card in each router slot. (Interface 0 is automatically assigned to the console.)
Table 29 1- and 2-Port Analog Modem WIC Numbering
0
1
1-2
1
33
33-34
2
65
65-66
3
97
97-98
4
129
129-130
5
161
161-162
6
193
193-194
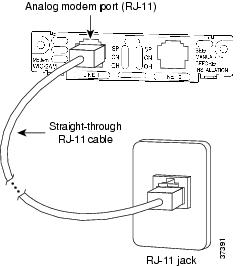
Connecting an Analog Modem WIC to a Network
Use a straight-through RJ-11-to-RJ-11 cable (not included) to connect an analog modem WIC to a network.
Step 1
Turn off and confirm that the router is turned off.

Warning
To comply with the Telcordia GR-1089 NEBS standard for electromagnetic compatibility and safety, connect the WIC-1AM-V2 and WIC-2AM-V2 interface cards only to intra-building or unexposed wiring or cable. The intrabuilding cable must be shielded and the shield must be grounded at both ends. The intra-building port(s) of the equipment or subassembly must not be metallically connected to interfaces that connect to the OSP or its wiring. These interfaces are designed for use as intra-building interfaces only (Type 2 or Type 4 ports as described in GR-1089-CORE, Issue 4) and require isolation from the exposed OSP cabling. The addition of Primary Protectors is not sufficient protection in order to connect these interfaces metallically to OSP wiring.
Step 2
Connect one end of a straight-through RJ-11-to-RJ-11 cable to the pink RJ-11 port labeled LINE on the analog modem WIC.
Step 3
Connect the other end of the cable to a wall telephone outlet, as shown in Figure 106.
Figure 106 Connecting an Analog Modem WIC to a Wall Telephone Outlet
Step 4
Depending on whether you have a 1-port or 2-port analog modem WIC:
•
For 1-port analog modem WICs, you can connect an analog telephone to the RJ-11 port labeled PHONE. This allows the dialout line to be shared between the telephone and the modem.
•
For 2-port analog modem WICs repeat Step 2 and Step 3 to connect the second port to a network.
Step 5
Turn on power to the router.
Related Documentation
Related documentation is available on Cisco.com. For more information, see the "Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines" section.
•
1- and 2-Port V.90 Modem WICs for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Multiservice Platforms, Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)T feature module
•
AT Command Set and Register Summary for V.90 WIC-1AM and WIC-2AM Analog Modem WAN Interface Cards
•
Analog Modem Interface Card Configuration Notes for Cisco 1700 Series Routers
•
Cisco Network Modules and Interface Cards Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
•
Cisco WIC-1AM-V2 and WIC-2AM-V2 Analog Modem WAN Interface Card
•
Modem-Router Connection Guide, tech note
•
Recommended Modemcaps for Internal Digital and Analog Modems on Cisco Access Servers, tech note
•
Understanding Analog Modem WAN Interface Cards (WIC-1AM or WIC-2AM), tech note
•
WAN Interface Card (WIC)/Platform Hardware Compatibility Matrix for 1600, 1700, 2600, 3600, and 3700 Series Routers, tech note
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
For information on obtaining documentation, obtaining support, providing documentation feedback, security guidelines, and also recommended aliases and general Cisco documents, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html

Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback