Voice Interface Cards
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Connecting Voice Interface Cards to the Network
Grounding Requirements for Voice Interface Cards
Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers
Pinout and Cabling Specifications
Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) Interface Cards
Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) Interface Cards
Setting Jumpers on the 2-Port FXO Card
Receive and Transmit (E&M) Interface Cards
Connecting E&M Interface Cards
FXS, FXO, and E&M Interface Card LEDs
Connecting ISDN BRI Interface Cards
Analog Direct Inward Dial (DID) Interface Cards
Connecting an Analog DID Interface Card
Multiflex Trunk Interface Cards
Multiflex Trunk Interface Card LEDs
Connecting a Multiflex Trunk Interface Card
Centralized Automated Message Accounting Trunk Protocol Interface Cards
Connecting the CAMA Interface Card
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
Connecting Voice Interface Cards to the Network
Revised: 11/07/2009, OL-12847-01
This document describes how to connect Cisco voice interface cards to your network. It contains the following sections:
•
Grounding Requirements for Voice Interface Cards
•
Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) Interface Cards
•
Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) Interface Cards
•
Receive and Transmit (E&M) Interface Cards
•
FXS, FXO, and E&M Interface Card LEDs
•
Analog Direct Inward Dial (DID) Interface Cards
•
Multiflex Trunk Interface Cards
•
Centralized Automated Message Accounting Trunk Protocol Interface Cards
•
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
Grounding Requirements for Voice Interface Cards
This section tells where to find instructions on how to properly ground voice interface cards on the following platforms:
•
Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers

Warning
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity.

Warning
To avoid electric shock, do not connect safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits to telephone-network voltage (TNV) circuits. LAN ports contain SELV circuits, and WAN ports contain TNV circuits. Some LAN and WAN ports both use RJ-45 connectors. Use caution when connecting cables.

Warning
To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunication line cord.

Warning
Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first.
Cisco 1700 Series Routers
Grounding on a Cisco 1700 series router is done on the router chassis itself, not on the voice interface cards. For information on chassis grounding on Cisco 1700 series routers, see the hardware installation guide for your router.
Cisco 2600 Series, Cisco 3600 Series, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers
The requirements in this section apply to only the Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 3600 series, and Cisco 3700 series routers.
The cards in this chapter are suitable for exposed plant lead connection. However, the host router chassis must have a permanent protective earth connection before you connect a voice interface card to an exposed plant lead. Make sure that a permanent earth connection is in place before installing the card.
If you find that a router chassis does not have an earth connection and you do not have a grounding kit, take one of the following actions:
•
Order and install a NEBS Level 3/ETSI Compliance Kit.
•
Install an equivalent permanent protective earth connection, using the method described in the installation guide Installing the Grounding Lug on Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Routers.
Cisco ICS 7750
The Cisco ICS 7750 chassis has a grounding lug that needs to be properly connected using a green and yellow 14 American Wire Gauge (AWG) grounding wire. See the "Installing the Cisco ICS 7750" chapter in the Cisco ICS 7750 Installation and Configuration Guide for your software release at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/voiceapp/ps967/prod_installation_guides_list.html
Pinout and Cabling Specifications

Note
See Cisco Modular Access Router Specifications for network-end connectors and pinouts of the cables connecting voice cards. Look under the type of interface card.
Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) Interface Cards
A Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) interface connects directly to a standard telephone, fax machine, or similar device. This interface supplies ringing voltage, dial tone, and so on to the station. The ports are shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 3.

CautionTo comply with the Telcordia GR-1089 NEBS standard for electromagnetic compatibility and safety, connect the 2-port FXS cards (VIC-2FXS and VIC2-2FXS) and 4-port FXS/DID cards (VIC-4FXS/DID) only to intrabuilding or non-exposed wiring or cabling. The intrabuilding cable must be shielded and the shield must be grounded at both ends.

Note
Each port on the 4-port FXS/DID VIC can be configured as either Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) or Direct Inward Dial (DID) when it is used with phones with a Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) load of 1 or less.
If the REN load on any port is greater than 1, all four ports must be configured as either FXS or DID. For information about using analog DID with the 4-port FXS/DID VIC, see the "Analog Direct Inward Dial (DID) Interface Cards" section.

Note
Cisco 2600XM series, Cisco 2691, Cisco 2800 series, Cisco 3600 series, Cisco 3700 series, and Cisco 3800 series routers support DID on the 4-port FXS/DID cards in Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T and later.

Note
The Cisco 1751 router can support three 4-port FXS/DID VICs, up to a maximum of four DID ports. The Cisco 1760 router can support four 4-port FXS/DID VICs, up to a maximum of eight DID ports.

Note
The Cisco ICS 7750 also supports 8 FXS ports on the analog station interface 81 (ASI 81), and 16 FXS ports on the ASI 160. See the "Processor Cards Feature Summary" chapter in the Cisco ICS 7750 System Description document.
Figure 1 2-Port FXS Card Front Panel (VIC-2FXS)
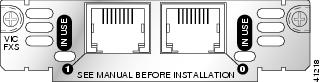
Figure 2 2-Port FXS Card Front Panel (VIC2-2FXS)
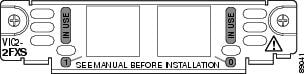
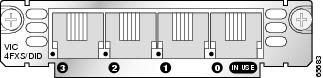
Figure 3 4-Port FXS/DID Card Front Panel (VIC-4FXS/DID)
Connecting FXS Cards
Use a standard straight-through RJ-11 modular telephone cable to connect a VIC-2FXS, VIC-4FXS/DID, or VIC2-2FXS to a telephone or fax machine.

Warning
This equipment contains a ring signal generator (ringer), which is a source of hazardous voltage. Do not touch the RJ-11 (phone) port wires (conductors), the conductors of a cable connected to the RJ-11 port, or the associated circuit-board when the ringer is active. The ringer is activated by an incoming call.

Warning
For connections outside the building where the equipment is installed, the following ports must be connected through an approved network termination unit with integral circuit protection: FXS.

Note
Ports on this interface card are colored gray.
Step 1
Confirm that the router is still turned off.
Step 2
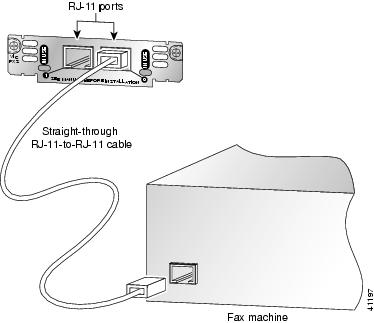
Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-11 cable to an RJ-11 port on the card. (See Figure 4.)
Figure 4 Connecting an FXS Card
Step 3
Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-11 port on the telephone or fax machine.
Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) Interface Cards
A Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) interface connects local calls to a central office or PBX. This is the interface a standard telephone provides. This type of card is illustrated in Figure 5, Figure 6, and Figure 7.
The VIC-2FXO and VIC-2FXO-M1 interface cards are intended for use in North America (United States, Canada, and Mexico).
The VIC-2FXO-EU and VIC-2FXO-M2 interface cards are intended for use in Europe.
The VIC-2FXO-M3 interface card is intended for use in Australia.
The VIC2-2FXO and VIC2-4FXO interface cards are software-configurable for all regions (see Figure 6 and Figure 7).

CautionTo comply with the Telcordia GR-1089 NEBS standard for electromagnetic compatibility and safety, connect the 2-port FXO card (VIC2-2FXO) only to intra-building or non-exposed wiring or cabling. The intrabuilding cable must be shielded and the shield must be grounded at both ends.

Warning
This equipment contains a ring signal generator (ringer), which is a source of hazardous voltage. Do not touch the RJ-11 (phone) port wires (conductors), the conductors of a cable connected to the RJ-11 port, or the associated circuit-board when the ringer is active. The ringer is activated by an incoming call.

Warning
For connections outside the building where the equipment is installed, the following ports must be connected through an approved network termination unit with integral circuit protection.
FXO
Figure 5 2-Port FXO Card Front Panel (VIC-2FXO)
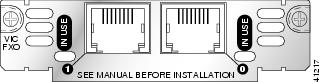
Figure 6 2-Port FXO Card Front Panel (VIC2-2FXO)
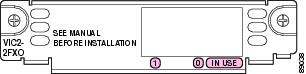
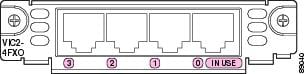
Figure 7 4-Port FXO Card Front Panel (VIC2-4FXO)
Setting Jumpers on the 2-Port FXO Card

Note
This information does not apply to the VIC2-2FXO card.
The FXO voice interface card includes two jumper headers, W3 and W4, to set loop-start or ground-start mode. One jumper configures each FXO port. The default setting is loop-start, which should be satisfactory in most installations. In this setting, jumpers are placed over positions 2 and 3 of headers W3 and W4.
Most modern central office equipment, such as DMS-100 and 5ESS switches, provides calling party control (CPC) and Ring on Seize on loop-start lines. CPC allows quicker disconnection, and Ring on Seize minimizes glare (collision of inbound and outbound calls on the same interface).
If your central office does not provide these features on loop-start, you may want to configure the FXO card for ground-start operation instead by moving the jumpers to positions 1 and 2.
For proper operation, both jumpers on the VIC-2FXO card must be configured identically.

Note
This setting does not apply to VIC-2FXO-EU and VIC-2FXO-M2 interface cards.
Connecting FXO Cards
Use a straight-through RJ-11 cable to connect the FXO voice interface card to the PSTN or PBX through a telephone wall outlet.

Note
Ports on this interface card are colored pink.
Step 1
Confirm that the router is still turned off.
Step 2
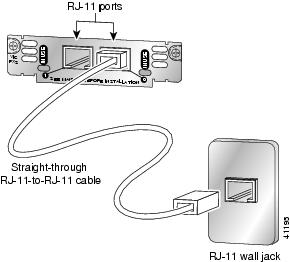
Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-11 cable to an RJ-11 port on the card. (See Figure 8.)
Figure 8 Connecting an FXO Card
Step 3
Connect the other end to an RJ-11 telephone wall outlet.

Note
If you have specified the use of a private line automatic ringdown (PLAR) off-premises extension (OPX) connection mode for an FXO voice port (with loop resistance less than 8000 Ohm), you must ensure that the soft-offhook option is enabled on the port.
This option allows a stepped offhook resistance during seizure which avoids overloading the circuit during offhook in the event that ringing voltage is present on the circuit at the same time as the trunk seizure. The stepped offhook resistance is initially set to 800 Ohms, then adjusts to 50 Ohms when ringing voltage is not present.
To enable soft-offhook command on the port, and to access the connection command with plar opx syntax, see the Cisco Command Lookup Tool.
Receive and Transmit (E&M) Interface Cards
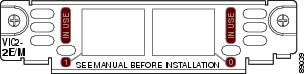
RecEive and transMit (E&M) is a signaling technique for two-wire and four-wire telephone and trunk interfaces. The E&M interface typically connects remote calls from an IP network to a PBX. The cards are illustrated in Figure 9 and Figure 10.

CautionTo comply with the Telcordia GR-1089 NEBS standard for electromagnetic compatibility and safety, connect the 2-port E&M card (VIC2-2E/M) only to intra-building or non-exposed wiring or cabling. The intrabuilding cable must be shielded and the shield must be grounded at both ends.
Figure 9 2-Port E&M Card Front Panel (VIC-2E/M)
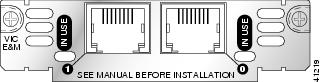
Figure 10 2-Port E&M Card Front Panel (VIC2-2E/M)
Connecting E&M Interface Cards
Use a straight-through RJ-48C cable to connect the E&M card to the PSTN or PBX through a telephone wall outlet.

CautionDo not connect an E&M interface directly to the PSTN.

Note
Ports on the E&M voice interface card are colored brown.
Step 1
Confirm that the router is still turned off.
Step 2
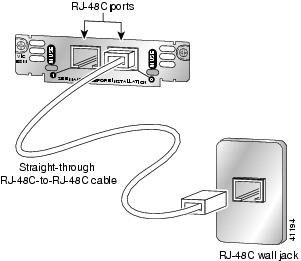
Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-48C-to-RJ-48C cable to an RJ-48C port on the card. (See Figure 11.)
Figure 11 Connecting the 2-Port E&M Card
Step 3
Connect the other end of the cable to an RJ-48C wall outlet.
FXS, FXO, and E&M Interface Card LEDs
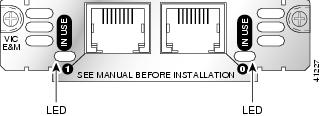
Each voice interface card has IN USE LEDs, one for each port. These LEDs have three states: green when active, off when ready for use, and amber when not ready for use. Figure 12 shows a voice interface card with an E&M interface as an example.
Figure 12 Voice Interface Card LEDs
ISDN BRI Interface Cards
The ISDN BRI S/T voice interface card provides a client-side (TE) ISDN S/T physical interface for connection to an NT1 device terminating an ISDN telephone network. Each port on the interface card can carry two voice calls (one over each ISDN B channel), for a total of four calls per ISDN BRI card.
ISDN BRI NT/TE voice interface cards (VIC-2BRI-NT/TE and VIC2-2BRI-NT/TE) have the same capabilities as the S/T card, but can also be configured to provide a network termination (NT) interface with phantom power.
The Cisco 1751 and Cisco 1760 routers, and the Cisco ICS 7750 platform support both ISDN BRI NT/TE voice interface cards. You can install these cards in any interface card slot in these platforms. These platforms do not support the ISDN BRI S/T voice interface card.
The ISDN BRI NT/TE cards are illustrated in Figure 13 and Figure 14.

CautionTo comply with the Telcordia GR-1089 NEBS standard for electromagnetic compatibility and safety, connect the 2-port ISDN BRI card (VIC2-2BRI-NT/TE) only to intra-building or non-exposed wiring or cabling. The intrabuilding cable must be shielded and the shield must be grounded at both ends.
Figure 13 2-Port ISDN BRI Card Front Panel (VIC-2BRI-NT/TE)
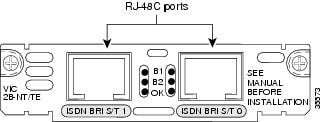
Figure 14 2-Port ISDN BRI Card Front Panel (VIC2-2BRI-NT/TE)
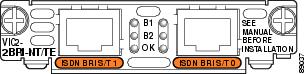
ISDN BRI Card Considerations

Note
Cisco ISDN BRI interface cards support voice ISDN traffic only.

Note
The ISDN BRI restrictions in this section do not apply to the VIC2-2BRI-NT/TE voice interface cards.

Note
The ISDN BRI restrictions in this section do not apply to the Cisco 1751, Cisco 1760, or Cisco ICS 7750 platforms.
To use all four voice channels, you must install the ISDN BRI card in slot 0 of a two-slot voice network module (NM-2V). Slot 1 should remain empty.

Note
If slot 0 is unoccupied, the system treats it as a pair of analog voice ports.
If you install any of the following configurations, the Cisco IOS software disables certain ports, as shown in Table 1:
•
An ISDN BRI voice interface card in a 1-slot voice network module (NM-1V)
•
Two ISDN BRI voice interface cards in a 2-slot voice network module (NM-2V)
•
One ISDN BRI voice interface card and one analog voice interface card (VIC-2FXS, VIC-2FXO, VIC-2FXO-EU, VIC-2FXO-M3, or VIC-2E/M) in a 2-slot voice network module (NM-2V)
Connecting ISDN BRI Interface Cards
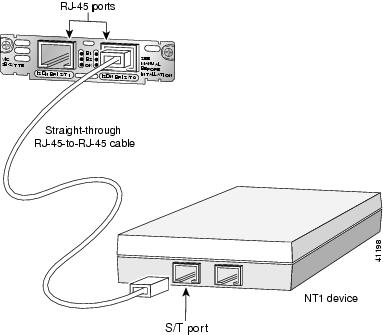
Use a straight-through RJ-45 cable to connect ISDN BRI cards to the ISDN network through a telephone wall outlet or other device.

CautionTo prevent damage to the router, be sure to connect the BRI cable to the BRI connector only, and not to any other RJ-45 connector.
To connect the 2-port ISDN BRI card to the router, follow these steps:
Step 1
Confirm that the router is still turned off.
Step 2
Connect one end of a straight-through RJ-45-to-RJ-45 cable to the RJ-45 port on the card. (See Figure 15.)
Figure 15 Connecting the 2-Port ISDN BRI Card

Note
When the interface is configured as NT and is connecting to a TE device, the cable must have the transmit and receive pins swapped (crossover cable). See Table 2.
Table 2 Interface Pin Numbers and Functions
Pin 3/T+
Pin 3/R+
Pin 3/T+
Pin 4/R+
Pin 4/T+
Pin 4/R+
Pin 5/R-
Pin 5/T-
Pin 5/R-
Pin 6/T-
Pin 6/R-
Pin 6/T-
1 Use a straight-through cable for NT interfaces.
2 Use a crossover cable for TE interfaces.
Step 3
Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 wall outlet or other device.
ISDN BRI Interface Card LEDs
ISDN BRI voice interface cards have three LEDs, as listed in Table 3.
Table 3 ISDN BRI Voice Interface Card LEDs
B1
Call active on B1 channel
B2
Call active on B2 channel
OK
Interface is connected to an ISDN network
Analog Direct Inward Dial (DID) Interface Cards
A Direct Inward Dial (DID) voice interface provides DID service to extensions on a PBX. Figure 16 shows the VIC-2DID card, and Figure 17 shows the VIC-4FXS/DID card.

CautionTo comply with the Telcordia GR-1089 NEBS standard for electromagnetic compatibility and safety, connect the 4-port FXS/DID card (VIC-4FXS/DID) only to intra-building or non-exposed wiring or cabling. The intrabuilding cable must be shielded and the shield must be grounded at both ends.

Note
Each port on the 4-port FXS/DID VIC can be configured as either Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) or Direct Inward Dial (DID) when it is used with phones with a Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) load of 1 or less.
If the REN load on any port is greater than 1, all four ports must be configured as either FXS or DID. For information about using FXS with the 4-port FXS/DID VIC, see the "Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) Interface Cards" section.

Note
Cisco 2600XM series, Cisco 2691, Cisco 2800 series, Cisco 3600 series, Cisco 3700 series, and Cisco 3800 series routers support DID on the 4-port FXS/DID cards in Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T and later.
Figure 16 2-Port Analog DID Voice Interface Card
Figure 17 4-Port Analog FXS/DID Voice Interface Card

Connecting an Analog DID Interface Card
Use a standard straight-through RJ-11 modular telephone cable to connect the VIC-2DID or VIC-4FXS/DID interface card to a PSTN or PBX.
Step 1
Install the grounding lug on the router. See the hardware installation guide for your router for detailed instructions. (Grounding on the Cisco 1700 series routers is done on the router chassis, and does not need a grounding lug.)
Step 2
Confirm that the router is still turned off.
Step 3
Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-11 cable to an RJ-11 port on the card. (See Figure 18.)
Figure 18 Connecting an Analog DID Interface Card
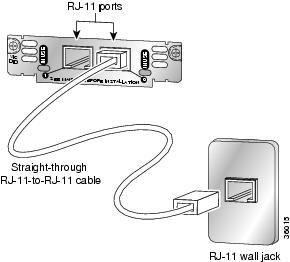

CautionThe VIC-2DID or the VIC-4FXS/DID interface cards may be damaged if connected to a standard PSTN line. Ensure that lines to the PSTN are provisioned for DID.
Step 4
Connect the other end of the cable to a telephone wall outlet or to a PBX.
Multiflex Trunk Interface Cards
Multiflex trunk interface cards support generic 1- or 2-port T1 or E1 trunk interfaces for voice, data, and integrated voice and data applications. These cards provide basic structured and unstructured service for T1 or E1 networks.
They can be used as trunk interfaces for voice and data services, as fractional n x 64-kbps service for WANs (Frame Relay or leased line), or for time-division multiplexing (TDM) drop-and-insert (voice and data integration) services.
Multiflex trunk interface cards provide voice and data access to the PSTN domain through TDM ports, and include an integrated channel service unit/data service unit (CSU/DSU).
Some 2-port multiflex trunk interface cards also support the drop-and-insert process, which adds data to a T1 or E1 data stream, or terminates data from a T1 or E1 data stream to other devices connected to the drop-and-insert equipment.

CautionWhen both ports on a VWIC-2MFT-T1, VWIC-2MFT-E1, VWIC-2MFT-G703, or VWIC-2MFT-E1-DI interface card are configured as clock source line, then they must be set to the same clock source. If they are not set to the same clock source, timing slips can occur. Each port on the VWIC2-2MFT-T1/E1 and VWIC2-2MFT-G703 interface cards can be set to independent clock sources for data applications.

CautionTo comply with the Telcordia GR-1089 NEBS standard for electromagnetic compatibility and safety, connect the VWIC-2MFT-G703 only to intra-building or non-exposed wiring or cabling. The intrabuilding cable must be shielded and the shield must be grounded at both ends.

CautionTo comply with the Telcordia GR-1089 NEBS standard for electromagnetic compatibility and safety, connect the VWIC2-2MFT-T1/E1, VWIC2-1MFT-T1/E1, VWIC2-1MFT-G703, VWIC2-2MFT-G703 ports only to intra-building or nonexposed wiring or cabling. The intrabuilding cable must be shielded and the shield must be grounded at both ends. The intra-building port(s) of the equipment or subassembly must not be metallically connected to interfaces that connect to the OSP or its wiring. These interfaces are designed for use as intra-building interfaces only (Type 2 or Type 4 ports as described in GR-1089-CORE, Issue 4) and require isolation from the exposed OSP cabling. The addition of Primary Protectors is not sufficient protection in order to connect these interfaces metallically to OSP wiring.
This section describes the following multiflex trunk interface cards:
•
1-port T1 multiflex trunk interface card (VWIC-1MFT-T1)
•
2-port T1 multiflex trunk interface card (VWIC-2MFT-T1)
•
1-port E1 multiflex trunk interface card (VWIC-1MFT-E1)
•
2-port E1 multiflex trunk interface card (VWIC-2MFT-E1)
•
1-port E1 multiflex trunk interface card with G.703 support (VWIC-1MFT-G703)
•
2-port E1 multiflex trunk interface card with G.703 support (VWIC-2MFT-G703)
•
2-port T1 multiflex trunk interface card with drop-and-insert capability (VWIC-2MFT-T1-DI)
•
2-port E1 multiflex trunk interface card with drop-and-insert capability (VWIC-2MFT-E1-DI)
•
1-port T1/E1 multiflex trunk interface card (VWIC2-1MFT-T1/E1)
•
2-port T1/E1 multiflex trunk interface card (VWIC2-2MFT-T1/E1)

Note
The VWIC2-1MFT-T1/E1 and VWIC2-2MFT-T1/E1 interface cards are configurable for T1 or E1 service and drop- and insert-capability.
•
1-port E1 multiflex trunk interface card with G.703 support (VWIC2-1MFT-G703)
•
2-port multiflex trunk interface card with G.703 support (VWIC2-2MFT-G703)

Note
The VWIC-1MFT-G703, VWIC2-1MFT-G703, VWIC-2MFT-G703 and VWIC2-2MFT-G703 interface cards allow unstructured E1 traffic that conforms to the ITU-T G.703 standard.
The following multiflex trunk interface cards provide hardware echo cancellation features through an echo canceler expansion module, installed on the main board of the interface card:
•
VWIC2-1MFT-T1/E1
•
VWIC2-2MFT-T1/E1
•
VWIC2-1MFT-G703
•
VWIC2-2MFT-G703
The following expansion modules are available:
•
32-channel echo canceler module for multiflex trunk (EC-MFT-32)
•
64-channel echo canceler module for multiflex trunk (EC-MFT-64)
For information on echo canceler expansion module installation, see the Installing Echo Canceler Expansion Modules on Cisco Interface Cards document.
See Figure 19 for a sample 1-port multiflex trunk interface card, and Figure 20 for a sample 2-port multiflex trunk interface card.
Figure 19 1-Port T1/E1 Multiflex Trunk Interface Card Faceplate (VWIC-1MFT-T1)
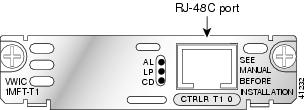
Figure 20 2-Port T1/E1 Multiflex Trunk Interface Card Faceplate (VWIC-2MFT-T1)
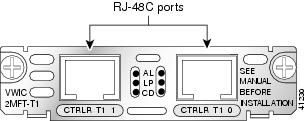
Multiflex Trunk Interface Card LEDs
Multiflex trunk interface cards have three LEDs, which are shown in Figure 19 and Figure 20 and are described in Table 4.
Connecting a Multiflex Trunk Interface Card
For this connection, use the straight-through RJ-48C-to-RJ-48C cable that came with your card.

Note
See Cisco Modular Access Router Specifications for network-end connectors and pinouts of the cables connecting voice cards. Look under the type of interface card.
Confirm that the router is turned off.
Step 5
Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-48C-to-RJ-48C cable to the T1 or E1 port on the card. (See Figure 21.)
Figure 21 Connecting a Multiflex Trunk Interface Card
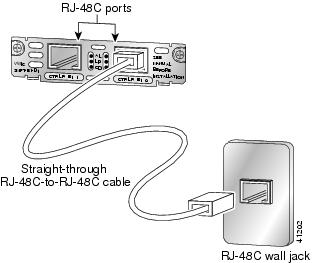
Step 6
Connect the other end to the T1 or E1 wall jack (RJ-48C) at your site.
Step 7
Turn on power to the router.
Step 8
Check that the CD LED comes on, which means that the card's internal DSU/CSU is communicating with the DSU/CSU at the T1 or E1 service provider central office.
Centralized Automated Message Accounting Trunk Protocol Interface Cards
The Centralized Automated Message Accounting (CAMA) trunk protocol interface connects local calls to emergency services. The CAMA card provides the software features required to connect directly to the enhanced 911 (E911) network from the customer premises. It also provides direct connections to a Public Service Answering Point (PSAP) using analog CAMA trunks. The CAMA protocol provides in-band signaling.

Note
For the NM-HD-1V, NM-HD-2V, and NM-HD-2VE voice network modules, and for the Cisco 1751 and 1760 routers, CAMA is supported by the VIC2-2FXO interface card. The VIC-2CAMA card cannot be used with the NM-HD-1V, NM-HD-2V, or NM-HD-2VE voice network modules, or with the Cisco 1751 or Cisco 1760 routers.
CAMA Interface Cards
The 2-port CAMA card is illustrated in Figure 22.
Figure 22 V2-Port CAMA Card Front Panel (VIC-2CAMA)
Connecting the CAMA Interface Card
Use a straight-through RJ-11 cable to connect the VIC-2CAMA voice interface card to the PSTN or PBX through a telephone wall outlet.

Note
Ports on this interface card are colored pink.
Step 1
Confirm that the router is still turned off.
Step 2
Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-11 cable to an RJ-11 port on the card. (See Figure 23.)
Figure 23 Connecting the 2-Port CAMA Card
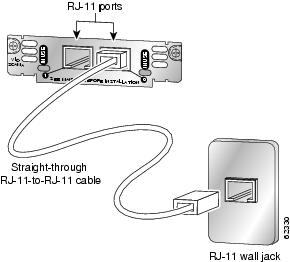
Step 3
Connect the other end of the cable to the telephone wall outlet (RJ-11 port).
Related Documentation
For additional information, see the following documents and resources.
•
Low Density Voice/Fax Network Modules for the Cisco 2600, 3600 and 3700 Series Routers, data sheet
•
Understanding Direct Inward Dial (DID) Voice Interface Cards, tech note
•
Voice Hardware Compatibility Matrix (Cisco 17xx, 26/36/37xx, VG200, Catalyst 4500/4000, Catalyst 6xxx), tech note
•
Cisco 4-Port High-Density FXS/DID Analog Voice Interface Card for the Cisco 1700 Series Modular Access Routers, data sheet
•
Digital J1 Packet Voice Network Module, data sheet
•
FXO, FXS, and E&M Voice Interface Card Support on Cisco 1700 Series Routers
•
Understanding 1-Port and 2-Port E1 Multiflex Trunk Voice/WAN Interface Cards (VWICs), tech note
•
Cisco Digital 1-port and 2-port T1 Multi-Flex Voice WICs, tech note
•
Cisco T1/E1 Multiflex Voice/WAN Interface Cards for the Cisco 1700 Series Modular Access Routers, data sheet
•
Understanding E&M Voice Interface Cards, tech note
•
Analog E&M Voice Signaling Overview, tech note
•
Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E & M Interface Types and Wiring Arrangements, tech note
•
Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E&M Start Dial Supervision Signaling, tech note
•
E&M Cable Pinouts to Connect Cisco 1750/2600/3600 E&M VIC to Nortel PBX Option 11 E&M Trunk, tech note
•
E&M Cable Pinouts Connecting Cisco 1750/2600/3600 E&M VIC to Lucent PBX G3R E&M Trunk, tech note
•
Cisco Network Modules and Interface Cards Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
•
Analog DID for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Routers, Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)T feature module
•
Voice Software Enhancements for the Cisco 1750 and Cisco 1751 Routers, configuration note
•
Configuring and Troubleshooting the VIC-2DID, how-to
•
Analog DID for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Routers, Cisco IOS Release 12.1(5)XM feature module
•
4-Port FXS/DID Voice Interface Card Support on the Cisco 1751 and Cisco 1760 Routers, configuration note
•
Installing and Configuring the 1-Port Digital J1 Voice Interface Cards
•
T1/E1 Multiflex VWIC Enhancements, Cisco IOS Release 12.1(3)T feature module
•
G.703 Configuration for Multiflex Voice/WAN Interface Cards on Cisco 2600 and 3600 Series Routers, Cisco IOS Release 12.1(1)T feature module
•
Configuring 1- and 2-Port T1/E1 Multiflex Voice/WAN Interface Cards on Cisco 2600 and 3600 Series Routers, Cisco IOS Release 12.0(7)T feature module
•
Analog Centralized Automatic Message Accounting E911 Trunk
•
Configuring 2-Port ISDN BRI Voice Interface Cards for the Cisco 1751 and Cisco 1760 Routers, configuration note
•
Cisco IOS ISDN Voice Configuration Guide, Release 12.3
•
"VoIP Configuration" chapter in the Cisco 1751 Router Software Configuration Guide
•
Understanding One Stage and Two Stage Voice Dialing, tech note
•
Structured CES Using Synchronous Clocking and PVCs in a Cisco 3600 Platform, sample configuration
•
Unstructured CES with Synchronous Clocking and PVCs on a 3600 Platform, tech note
•
Using Analog E&M Ports to Interface to Overhead Paging Systems, sample configuration
•
Configuring Connection Trunk for VoIP Gateways, sample configuration
•
"Troubleshooting Analog Voice Interfaces to the IP Network" chapter of the Cisco IOS Voice Troubleshooting and Monitoring Guide
•
Configuring and Troubleshooting the VIC-2DID, how-to
•
Ringing and Idle Voltages on Cisco FXS Interfaces, tech note
•
Analog E&M Troubleshooting Guidelines (Cisco IOS Platforms), tech note
•
Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E&M Start Dial Supervision Signaling, tech note
•
Understanding and Troubleshooting Analog E & M Interface Types and Wiring Arrangements, tech note
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
For information on obtaining documentation, obtaining support, providing documentation feedback, security guidelines, and also recommended aliases and general Cisco documents, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
CCDE, CCENT, CCSI, Cisco Eos, Cisco HealthPresence, Cisco IronPort, the Cisco logo, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco Nurse Connect, Cisco Pulse, Cisco StackPower, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco Unified Computing System, Cisco WebEx, DCE, Flip Channels, Flip for Good, Flip Mino, Flipshare (Design), Flip Ultra, Flip Video, Flip Video (Design), Instant Broadband, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Cisco Capital, Cisco Capital (Design), Cisco:Financed (Stylized), Cisco Store, and Flip Gift Card are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AllTouch, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, Continuum, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Explorer, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GainMaker, GigaDrive, HomeLink, iLYNX, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, Laser Link, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerKEY, PowerPanels, PowerTV, PowerTV (Design), PowerVu, Prisma, ProConnect, ROSA, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0908R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback