Cisco SRE Service Module Configuration and Installation Guide
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Cisco SRE Service Module Configuration and Installation Guide
About the Cisco Service Modules
Recommended Practices for Cisco Service Modules
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Cisco Internal Service Module: Cisco ISM-SRE
Cisco Service Module: Cisco SM-SRE
Cisco ISM-SRE and SM-SRE Network Interfaces
Cisco SM-SRE External Service Module Interface
Configuring the Cisco SRE Module Interface
Configuring the SRE Interface on the Router
Shutting Down and Starting Up the Cisco SRE Module
Installing and Uninstalling a Cisco Application on the Cisco SRE
Installing a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module
Installing a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module: Example
Uninstalling a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module
Uninstalling a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module: Example
Configuring the MGF Interface on the Module
Cisco IOS Software Command Reference
service-module sm install abort
Cisco SRE Service Module Configuration and Installation Guide
First Published: March 22, 2010
Last Updated: August 30, 2011Cisco Services Ready Engine (Cisco SRE) service modules (SMs) installed in one of the SM slots in the Cisco 2900 Series or Cisco 3900 Series Integrated Services Router Generation 2 (Cisco ISR G2) enables the router to host Cisco, third-party, and custom applications.
Contents
•
About the Cisco Service Modules
•
Configuring the Cisco SRE Module Interface
•
Installing and Uninstalling a Cisco Application on the Cisco SRE
•
Configuring the MGF Interface on the Module (Optional)
•
Cisco IOS Software Command Reference
About the Cisco Service Modules
Cisco Internal Service Module-Services Ready Engine (Cisco ISM-SRE) and Cisco Service Module-Services Ready Engine (Cisco SM-SRE) hosted by the Cisco ISR G2 have their own processors, storage, network interfaces, and memory that operate independently of the host router resources. This configuration helps to ensure maximum concurrent routing and application performance. A service-ready deployment model enables branch-office applications to be provisioned remotely on the modules at any time. The Cisco ISM-SRE and Cisco SM-SRE also support Cisco Software Licensing (CSL) and Pay-as-you-Grow (PAY-GO) features.
Factory Installed Cisco SRE
Customers can buy a service-ready Cisco 2911, Cisco 2921, Cisco 2951, Cisco 3925, or Cisco 3945 Series ISR G2 in which the module slots are already filled with Cisco ISM-SRE or SM-SRE modules. These modules may or may not have software already installed on them. Cisco SRE software supports this hardware-software decoupling, or PAY-GO model, by permitting you to provision and pay for software services separately from the hardware and after the services are deployed.
The Cisco SRE bootloader allows for greater flexibility and eliminates the requirement for a separate bootloader for each new application software to be installed. Cisco SRE supports installing and uninstalling Cisco-authorized software, such as Cisco Unity Express, Cisco Application eXtension Platform (Cisco AXP), and Cisco IP Video Surveillance using Cisco IOS software commands and prevents unauthorized software and applications from running on Cisco SRE modules.
Installing the Cisco SRE Hardware
If the Cisco SRE is not preinstalled in the host router at the factory, you must first install the Cisco SRE hardware in your host Cisco 2911, Cisco 2921, Cisco 2951, or Cisco 3900 Series ISR G2. To install the module, see the "Cisco Internal Service Module: Cisco ISM-SRE" section or the "Cisco Service Module: Cisco SM-SRE" section, depending on whether your Cisco SRE is a Cisco ISM-SRE or an SM-SRE.
After installing the Cisco SRE hardware, use Cisco IOS commands to configure the Cisco SRE as an SM interface of the host router. To configure the Cisco SRE as an interface to the Cisco ISR G2, see the "Configuring the Cisco SRE Module Interface" section.
Installing the Cisco-Authorized Application
To install Cisco-authorized software applications on Cisco SRE modules, see the "Installing a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module" section.
Cisco SRE also supports a common uninstall process across all supported software. To uninstall Cisco-authorized software applications on a Cisco SRE module, see the "Uninstalling a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module" section.
Table 1 lists those Cisco-authorized applications that are compatible with the Cisco SRE.
Table 1 Cisco-Authorized Applications Compatible with Cisco SRE Module
Cisco AXP
Cisco Unified SRSV-CUE1 release 8.0.2 and later versions
Cisco Unity Express
Cisco UMG2 release 8.0.2 and later versions
Cisco Video Management and Storage System
WAAS3
1 Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Voicemail-Cisco Unity Express
2 Cisco Unified Messaging Gateway
3 WAAS = Wide Area Application Services.
If you are already familiar with the parameters to be configured, you can manually enter the values to be used without having to run the installer for user interaction. For example, instead of being prompted with the language options for Cisco Unity Express, you can enter the appropriate variable string and the installer verifies the values against the valid language options and does not prompt you for that option during the interactive portion of the installation process.
See your application's command-line interface (CLI) administrator guide for details on how to configure application parameters using the CLI.
Some configuration options may be set using Cisco Configuration Professional web-based applications. See www.cisco.com/go/ciscocp for more details about downloading and using Cisco Configuration Professional.
To upgrade Cisco SRE software to the later version, see the application's installation and upgrade guide.
After the application software is installed, the SMs have their own startup and run-time configurations that are independent of the Cisco IOS configuration on the host router. The SMs do not have an external console port. Instead, you launch and configure each module through the host router by means of a configuration session on the module. After the session, you can return to the router's CLI and clear the session.
The host router and the SM (the module is also referred to as an appliance or blade or, with installed software, a service module)—provide a router-integrated application platform for accelerating data-intensive applications.
Typically, such applications involve the following services:
•
Application-oriented networking
•
Contact centers and interactive voice-response applications
•
Content caching and delivery
•
Data and video storage
•
Voice mail and auto-attendant applications
To configure and manage the Cisco ISM-SRE and SM-SRE modules, you should understand the following topics:
•
Recommended Practices for Cisco Service Modules
•
Cisco Internal Service Module: Cisco ISM-SRE
•
Cisco Service Module: Cisco SM-SRE
•
Cisco ISM-SRE and SM-SRE Network Interfaces
Prerequisites
Router
•
Plan software installations, upgrades, or downgrades for times when you can take all applications that run on the host router out of service or offline.
•
Ensure that you have the appropriate Cisco 2911, Cisco 2921, Cisco 2951, or Cisco 3900 Series ISR G2s to serve as the host router. The Cisco ISM-SRE and SM-SRE are supported on the following routers:
–
Cisco 2911, Cisco 2921, Cisco 2951, and Cisco 3900 Series ISR G2s
•
Ensure that the host router is running Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M or a later software release. To see which release your router is currently running, examine the output from the show version command. Also, see your platform documentation for the required Cisco IOS software release.
NoteWhen minimum release requirements are met, you can change images on either the router or the SRE modules without affecting performance.
•
Software, including its release version, must be compatible with Cisco ISM-SRE or SM-SRE. For more information on compatibility, see your software application documentation.
•
Ensure that you have an FTP or HTTP server to which an installation file (in ZIP format) can be downloaded from Cisco.com and unzipped prior to installation being performed from the router.
•
There must be a 100-kpbs or faster effective link between the router and the FTP server.
Restrictions
•
Cisco router and Cisco SRE module on which software is to be installed or uninstalled must be compatible with Cisco SRE, such as a Cisco ISM-SRE or SM-SRE installed in a Cisco 2911, Cisco 2921, Cisco 2951, or Cisco 3900 Series ISR G2.
•
In releases earlier than Cisco IOS Release 15.1(4)M, you cannot use the Cisco router to install or uninstall software on two or more Cisco SRE modules in the same router, at the same time. You must wait until the install or uninstall completes before issuing a command to initiate a second process on the same module. This restriction does not apply to Cisco IOS Release 15.1(4)M and later releases.
•
While installing or uninstalling software, you cannot use the reset or shutdown commands in Cisco IOS software to reset or shut down the Cisco SRE module.
•
The following hard disk drive (HDD) spare assemblies are not exchangeable:
–
SM-HDDA-SATA500GB for the SM-SRE-700-K9 and SM-SRE-900-K9
–
SM-HDDB-SATA500GB for SM-SRE-710-K9 and SM-SRE-910-K9
Recommended Practices for Cisco Service Modules
This section describes recommended practices for safe and effective installation of the hardware described in this document, and includes the following sections:
•
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electrostatic discharge can damage equipment and impair electrical circuitry. Electrostatic discharge occurs when electronic printed circuit cards, such as those used in Cisco service modules and network modules, are improperly handled and can result in complete or intermittent equipment failure. Always observe the following electrostatic discharge damage (ESD) prevention procedures when installing, removing, and replacing Cisco service modules, Cisco network modules, Cisco interface cards, Cisco expansion modules, or other electronic printed circuit cards:
•
We recommend use of shielded cable on the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) port for maximum ESD protection.
•
Make sure that the router chassis is electrically connected to earth ground.
•
Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap, and make sure that it makes good contact with your skin.
•
Connect the wrist strap clip to an unpainted portion of the chassis frame to channel unwanted ESD voltages to ground.
CautionThe wrist strap and clip must be used correctly to ensure proper ESD protection. Periodically confirm that the resistance value of the ESD-preventive wrist strap is between 1 and 10 megohms (Mohm).
•
If no wrist strap is available, ground yourself by touching the metal part of the router chassis.
Cisco Internal Service Module: Cisco ISM-SRE
•
Install the Cisco ISM-SRE in the internal service module (ISM) slot of the Cisco 1900 Series, 2900 Series, or Cisco 3900 Series ISR G2 router. See the following for installation details:
–
Cisco 1900 Series Hardware Installation Guide
–
Cisco 2900 Series and 3900 Series Hardware Installation Guide
–
Cisco Network Modules and Interface Cards Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
•
All Cisco ISM-SRE models ship from the factory with the hardware preinstalled as listed in Table 2.
Table 2 Cisco ISM-SRE Hardware
ISM-SRE-300-K9
1.066 GHz
4 GB
512 MB
Cisco Service Module: Cisco SM-SRE
•
Install the Cisco SM-SRE in one of the SM slots in the Cisco 2911, Cisco 2921, Cisco 2951, or Cisco 3900 Series router. See Installing Cisco Network Modules and Service Modules in Cisco Access Routers and Cisco Network Modules and Interface Cards Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information.
•
All Cisco SM-SRE models ship from the factory with the hardware preinstalled as listed in Table 3. Note: Modules SM-SRE-900-K9 and SM-SRE-910-K9 have 2 x 500 GB hard drives giving a total of 1 TB with RAID 1 architecture. (RAID = Redundant Array of Independent Disks.)
•
Make a note of the SM's location in the host router:
–
slot—Number of the router slot in which the SM is installed. After you install the module, you can get this information from the router's show running-config command output.
–
port—Port number of the module interface. This value is always 0.
You need this information for the "Configuring the SRE Interface on the Router" section and the "Opening and Closing a Session" section.
Cisco ISM-SRE and SM-SRE Network Interfaces
The SM communicates with the host router through two internal Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interfaces (see Figure 1). One GE interface connects to the router Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) backplane and is configured and managed using the Cisco IOS CLI; the other GE interface connects to the multi-gigabit fabric (MGF) which is configured using the Cisco IOS CLI and managed by the Cisco-authorized application installed on the module. This section covers the following topics:
•
Cisco SM-SRE External Service Module Interface
Figure 1 Router and Cisco ISM-SRE and SM-SRE Interfaces
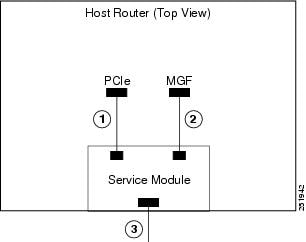
Service-Module Interface
The service-module interface is used to access the SM console for configuration. Visible only to the Cisco IOS software on the host router, the service-module interface is an internal Gigabit Ethernet interface between the router and the Cisco ISM-SRE or the SM-SRE. The service-module interface connects to the router's PCIe backplane, and all configuration and management of the service-module interface is performed using the Cisco IOS CLI.
MGF Interface
NoteThe MGF interface is not supported by Cisco WAAS.
The MGF interface enables the Cisco ISM-SRE or the SM-SRE to communicate with one or more SMs installed in the host router. This interface is an internal Gigabit Ethernet interface using a High-Speed Intrachassis Module Interconnect (HIMI) connection to the router's MGF, providing a logical connection between SMs. Configuration of the MGF interface is performed from the Cisco IOS CLI. The Cisco-authorized application running on the Cisco ISM-SRE or the SM-SRE manages the connections. For more information on configuring the MGF, see the Multi-Gigabit Fabric on the Router chapter of the Cisco 3900 Series, 2900 Series, and 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Software Configuration Guide.
Cisco SM-SRE External Service Module Interface
The external service-module interface can be used to monitor LAN traffic. You can also select the external interface as the management interface for the SM. The external interface cannot be used for downloading applications.
Visible only to the SM software on the Cisco SM-SRE, the external service-module interface is the Gigabit Ethernet interface connector on the Cisco SM-SRE faceplate. The external interface supports data requests and data transfers from outside sources, and it provides direct connectivity to the LAN through an RJ-45 connector.
Configuring the Cisco SRE Module Interface
This section describes how to configure basic network parameters for the SM using the Cisco IOS CLI.
This section contains the following tasks:
•
Configuring the SRE Interface on the Router
•
Opening and Closing a Session
•
Shutting Down and Starting Up the Cisco SRE Module
NoteIf you lose power or connection during any of the following procedures, the system usually detects the interruption and tries to recover. If it fails to recover, reinstall the system using the boothelper.
Configuring the SRE Interface on the Router
Your first configuration task is to set up the internal interface between the Cisco ISM-SRE or SM-SRE module and the host router, which then enables you to access the SM to install and configure Cisco applications.
To configure the Cisco ISM-SRE or SM-SRE interface to the host router, complete the following steps.
SUMMARY STEPS
From the Host-Router CLI
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface ism 0/0
or
interface sm slot/04.
ip address router-side-ip-address subnet-mask
or
ip unnumbered type number5.
service-module ip address module-side-ip-address subnet-mask
6.
service-module ip default-gateway gateway-ip-address
7.
no shutdown
8.
end
9.
ip route prefix mask ip-address
10.
copy running-config startup-config
11.
show running-config
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
enable
password
Example:Router> enable
Router> password
Router#
Enters privileged EXEC mode on the host router. Enter your password if prompted.
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:Router# configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode on the host router.
Step 3
interface ism 0/0
or
interface sm slot/0
Example:Router(config)# interface ism 0/0
or
Router(config)# interface sm 1/0
Enters interface configuration mode for the slot and port where the ISM resides.
or
Enters interface configuration mode for the slot and port where the SM resides.
Step 4
ip address router-side-ip-address subnet-mask
or
ip unnumbered type number
Example:Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
or
Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered gigabitethernet 1/0
Specifies the IP address for the router side of the interface.
•
router-side-ip-address subnet-mask—IP address and subnet mask for the router.
or
Enables IP processing on an interface without assigning an explicit IP address to the interface.
•
type—Type of interface on which the router has an assigned IP address.
•
number—Number of the interface on which the router has an assigned IP address.
Note
The unnumbered interface cannot be another unnumbered interface.
Step 5
service-module ip address module-side-ip-address subnet-mask
Example:Router(config-if)# service-module ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
Specifies the IP address for the module side of the interface.
•
module-side-ip-address—IP address for the module.
•
subnet-mask—Subnet mask to append to the IP address; must be in the same subnet as the host router
Step 6
service-module ip default-gateway gateway-ip-address
Example:Router(config-if)# service-module ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
Specifies the IP address of the default gateway for the module.
•
gateway-ip-address—IP address for the default router.
Note
If you configured the ip unnumbered command on the SM interface in Step 4, set the IP address of the default gateway to the IP address of the unnumbered interface.
Step 7
no shutdown
Example:Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Restarts a disabled interface.
Step 8
end
Example:Router(config-if)# end
Returns to global configuration mode on the host router.
Step 9
ip route prefix mask ip-address
Example:Router# ip route 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 sm1/0
Establishes static routes.
Note
When the ip unnumbered command is configured on the SM interface in Step 4, you must use the ip route command to add a static route to the SM.
Step 10
copy running-config startup-config
Example:Router# copy running-config startup-config
Saves the router's new running configuration as the startup configuration.
Step 11
show running-config
Example:Router# show running-config
Displays the router's running configuration, so that you can verify address configurations.
Examples
The following example shows the configuration of the internal interface between the Cisco ISM-SRE and the router:
interface ISM0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
service-module ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
service-module default-gateway 192.168.1.1
hold-queue 60 out
The following example shows the configuration of the internal interface between the Cisco SM-SRE and the router:
interface SM1/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
service-module ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
service-module ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
hold-queue 60 out
The following example shows the configuration of the internal interface between the Cisco SM-SRE and the router where the ip unnumbered command is configured on the interface and a static route to the SM is created:
Interface G0/0ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0hold-queue 60 outinterface SM1/0ip unnumbered g0/0service-module ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0service-module default-gateway 192.168.1.1hold-queue 60 outip route 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.255 sm1/0Opening and Closing a Session
You can now open and close a session on the Cisco ISM-SRE or SM-SRE.

Note
•
Before you install your application software, opening a session brings up the bootloader. At the bootloader prompt, the module status will be "is trying to recover from error." After you install the software, opening a session brings up the application.
•
You can conduct only one session at a time.
To first check the running status and then open or close a session with the SRE module, complete the following steps:
SUMMARY STEPS
From the Host-Router CLI
1.
enable
2.
service-module ism 0/0 status
or
service-module sm slot/0 status3.
service-module ism 0/0 session
or
service-module sm slot/0 sessionFrom the Service-Module Interface
4.
Perform configuration or other procedures.
5.
Control-Shift-6 x
From the Host-Router CLI
6.
service-module ism 0/0 session clear
or
service-module sm slot/0 session clearDETAILED STEPS
Step 1
enable
password
Example:Router> enable
Router> password
Router#
Enters privileged EXEC mode on the host router. Enter your password if prompted.
Step 2
service-module ism 0/0 status
or
service-module sm slot/0 status
Example:Router# service-module ism 0/0 status
or
Router# service-module sm 1/0 status
Displays the status of the Cisco ISM-SRE module,
or
displays the status of the Cisco SM-SRE module, so that you can ensure that the module is running (that is, in steady state).
Note
If the module is not running, start it with one of the startup commands listed in the "Shutting Down and Starting Up the Cisco SRE Module" section.
Step 3
service-module ism 0/0 session
or
service-module sm slot/0 session
Example:Router# service-module ism 0/0 session
Trying 10.10.10.1, 2065 ... Open
or
Router# service-module sm 1/0 session
Trying 10.10.10.1, 2065 ... Open
Begins a session on the Cisco ISM-SRE module,
or
begins a session on the Cisco SM-SRE module.
Perform one of the following:
•
To interrupt the auto-boot sequence and access the bootloader, quickly type ***.
•
To start a configuration session, press Enter.
Step 4
Example (Bootloader):
ServicesEngine boot-loader> config
Example (Configuration):
SE-Module> configure terminal
SE-Module(config)>
.
.
.
SE-Module(config)>exit
SE-Module> write
Enters bootloader or configuration commands on the module as needed. Use bootloader commands for debugging and troubleshooting purposes only.
•
Bootloader command choices include boot, config, exit, help, ping, reboot, show, and verify.
•
Enter configuration commands. Exit global configuration mode with the exit command. Save your new configuration with the write command. Notice that you do not use the enable command and the prompt does not change from >.
Step 5
Press Control-Shift-6 x.
Closes the service-module session and returns to the host router CLI.
Note
The service-module session stays up until you clear it in the next step. While it remains up, you can return to it from the router CLI by pressing Enter.
Step 6
service-module ism 0/0 session clear
or
service-module sm slot/0 session clear
Example:Router# service-module ism 0/0 session clear
or
Router# service-module sm 1/0 session clear
Clears the service-module session for the Cisco ISM-SRE module,
or
Clears the service-module session for the Cisco SM-SRE module. When prompted to confirm this command, press Enter.
Shutting Down and Starting Up the Cisco SRE Module
To shut down or start up the SM, select from the common router commands listed in Table 4.

Note
The tables in these sections list only the most common router commands.
•
To view a complete list of available interface commands, type ? at the prompt
(Example:Router(config-if)#?).•
To view a complete list of command keyword options, type ? at the end of the command
(Examples:Router#service-module ism ? or Router# service-module sm ?).

Note
•
Some shutdown commands can potentially disrupt service. If the command output for such a command displays a confirmation prompt, confirm by pressing Enter or cancel by typing n and pressing Enter. You can prevent the prompt from displaying by using the no-confirm keyword.
•
Some commands shut the module or application down and then immediately restart it.
Table 4 Common Shutdown and Startup Commands
service-module ism 0/0 reload
or
service-module sm slot/0 reload
Shuts down the SM operating system gracefully and then restarts it from the bootloader.
service-module ism 0/0 reset
or
service-module sm slot/0 reset
Resets the hardware on a module. Use this command only to recover from shutdown or a failed state.
CautionUsing this command does not provide an orderly software shutdown and may impact file operations that are in progress.
service-module ism 0/0 session
or
service-module sm slot/0 session
Accesses the specified service engine and begins an SM configuration session.
service-module ism 0/0 shutdown
or
service-module sm slot/0 shutdown
Shuts down the SM operating system gracefully. Use when removing or replacing a hot-swappable module during OIR.1 After shutting down the operating system using these commands, use the service-module ism reset or service-module sm reset command to restart it.
service-module ism 0/0 status
or
service-module sm slot/0 status
Displays configuration and status information for the SM hardware and software.
shutdown
Shuts down the entire system (both the host router and the SM) gracefully.
1 OIR = online insertion and removal.
Installing and Uninstalling a Cisco Application on the Cisco SRE
This section contains the following topics:
•
Installing a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module (required)
•
Uninstalling a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module (required)
Prerequisites
•
Follow the instructions in your application-specific documentation for obtaining and preparing your application files for installation. After downloading your application's installation file(s) onto an FTP or HTTP server, make sure that all the installation files are in the same directory.
•
Configure the SRE module interface as described in the "Configuring the Cisco SRE Module Interface" section.
Installing a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module
To use Cisco SRE to install, reinstall, or update Cisco-authorized software, complete the following steps. See the installation and upgrade documentation for the specific application to be installed for more details.
NoteTo stop the install while the files are being downloaded and before the actual installation begins, use the service-module ism install abort or service-module sm install abort command. For more information, see Cisco IOS Interface and Component Command Reference.
Once the installation begins, do not enter commands on the module until the "Installation successful..." message appears.To install a Cisco-authorized software application on the SRE module, complete the following steps.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
service-module ism slot/port install url url [script filename] [argument "string"] [force]
or
service-module sm slot/port install url url [script filename] [argument "string"] [force]3.
service-module ism slot/port status
or
service-module sm slot/port status4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Installing a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module: Example
The following example is a snapshot of an installation of Cisco Unity Express version 8.0.1 on a Cisco ISM-SRE. Commands entered and significant output appear in bold text.
c2911# service-module ism 0/0 install url ftp://test:test@10.50.10.25/cue-vm-k9.sme.8.0.1.pkgDelete the installed Cisco Unity Express and proceed with new installation? [no]: yLoading 8.0.1/cue-vm-k9.sme.8.0.1.pkg.install.sre ![OK - 22272/4096 bytes]...Application-specific messages...c2911# Install successful on ISM0/0
Uninstalling a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module
To use Cisco SRE to uninstall Cisco-authorized software and to uninstall a Cisco-authorized software application on the SRE module, perform the following steps:
NoteThis procedure completely erases the disk or compact flash on the services engine and removes the application keys. It does not remove application licenses.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
service-module ism slot/port uninstall [force]
or
service-module sm slot/port uninstall [force]
3.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Uninstalling a Cisco-Authorized Application on a Cisco SRE Module: Example
The following example is a snapshot of the process of uninstalling Cisco Unity Express version 8.0.1 on a Cisco ISM-SRE. Commands entered and significant output appear in bold text:
Router# service-module ism 0/0 uninstallDelete the installed Cisco Unity Express permanently? [no]: yesRouter#Service module in slot 0 shutting down in 105 seconds...Service module in slot 0 shutting down in 90 seconds...Service module in slot 0 shutting down in 75 seconds...Service module in slot 0 shutting down in 60 seconds...Service module in slot 0 shutting down in 45 seconds...Service module in slot 0 shutting down in 30 seconds...Service module in slot 0 shutting down in 15 seconds...Uninstall successful on ISM0/0
Configuring the MGF Interface on the Module
NoteThe MGF interface is not supported by Cisco WAAS.
Cisco 3900 series and Cisco 2900 series Generation 2 ISRs use MGF for the modules and interface cards to inter-communicate on the router. MGF configuration is optional. Legacy modules that support Cisco HIMI also support MGF to inter-communicate on the router. Next generation module drivers integrate with the MGF to perform port configurations, configure packet flow, and control traffic buffering.
This procedure applies to Cisco SREs running software releases earlier than Cisco IOS Release 15.1(3)T. The commands used to configure the MGF interface in this procedure are not available in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(3)T and later software releases.
SUMMARY STEPS
From the Host-Router CLI
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface ism 0/1
or
interface sm slot/14.
service-module ip address module-side-ip-address subnet-mask
5.
end
6.
copy running-config startup-config
7.
show running-config
DETAILED STEPS
Examples
The following example shows the configuration of the interface between the Cisco ISM-SRE and the MGF:
interface ISM0/1
service-module ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
The following example shows the configuration of the interface between the Cisco SM-SRE and the MGF:
interface SM1/1
service-module ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
Cisco IOS Software Command Reference
The following commands are new or have been modified.
•
service-module sm install abort
For information about commands in this guide, see the Cisco IOS Interface and Hardware Component Command Reference at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/interface/command/reference/ir_book.html.
For information about all Cisco IOS commands, use the Command Lookup Tool at http://tools.cisco.com/Support/CLILookup or the Cisco IOS Master Command List, All Releases, at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html.
service-module sm install abort
To abort the installation of a specific application module that is SRE-enabled, use the service-module sm install abort command in privileged EXEC mode.
service-module sm slot/port install abort [force]
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to abort the installation of an SRE-enabled application module if any failure occurs. You will not be prompted to confirm the action. After entering this command, you have to wait for the final abort message to appear on the console before proceeding with a new installation.
Examples
The following example aborts the installation of an SRE-enabled application module:
WAE# service-module sm 1/0 install abort
service-module sm install
To use Cisco SRE to install an application on a service module (Cisco SM-SRE), use the service-module sm install command in privileged EXEC mode.
service-module sm slot/port install url url [script filename] [argument "string"] [force]
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command uses a common module-dependent bootloader on Cisco SRE to install a Linux-based application, such as Cisco Unity Express or Cisco AXP, on a service module (Cisco SM-SRE).
The slash mark (/) is required between the slot argument and the port argument.
You can only issue one instance of this command at a time on a router. You cannot use this command to install an application on two or more services engine modules in the same router at a time.
The Tcl script to be run must reside in the same FTP or HTTP server and directory as the application packages to be installed. If a credential is required, the user name and password must be imbedded in the url as shown in the following example:
Router# service-module sm 1/0 install url ftp://username:passwd@server.com/axp-k9.sme.1.6.1.pkgIf two or more of the optional keyword/argument combinations are used with this command, they must be issued in the order presented in the command syntax. For example, you cannot use the force keyword before the script or argument keywords nor the argument keyword before the script keyword when you issue this command.
Use the script filename keyword/argument combination with this command to specify that the Cisco IOS software use some Tcl script other than the default installer during the installation.
Use the argument "string" keyword/argument combination with this command to manually provide variables during installation process and bypass the user interaction feature of the installer. The variable must include the left and right quotation marks ("").
Use the force keyword with this command to install an application without prompting for user input. If you use this keyword and if the application requires you to provide certain variables during the installation, you should also use the argument "string" keyword/argument combination to manually provide the required variables because the force keyword will direct the installer to bypass all user interaction during the installation.
To stop the install while the Tcl script is being downloaded, use the service-module sm install abort command. This command cannot be used once the actual installation begins.
Examples
The following example shows how to use this command to run a "help.sre" Tcl script rather than the default installation Tcl script:
Router# service-module sm 1/0 install url ftp://server.com/cue script help.sreRouter#The following example shows how to direct the installer to use the specified language variable for US English instead of prompting you with language options for Cisco Unity Express:
Router# service-module sm 1/0 install url ftp://server.com/cue argument "lang=en_us"Router#The following example shows the messages displayed on the module console during a successful installation using Cisco SRE:
Feb 6 19:09:22.526 EDT: %SM_INSTALL-6-INST_PROG: Service-Module-SM 1/0 PROGRESSING: Validating package signature ...1 .Feb 6 19:09:23.058 EDT: %SM_INSTALL-6-INST_PROG: Service-Module-SM 1/0 PROGRESSING: Parsing package manifest files ...1 .Feb 6 19:09:44.742 EDT: %SM_INSTALL-6-INST_PROG: Service-Module-SM 1/0 PROGRESSING: Starting payload download1 .Feb 6 19:09:52.022 EDT: %SM_INSTALL-6-INST_PROG: Service-Module-SM 1/0 PROGRESSING: Performing Hot install ...1 .Install successful on Service-Module-SM 1/0 Feb 6 19:10:28.826 EDT: %SM_INSTALL-6-INST_SUCC: Service-Module-SM 1/0 SUCCESS: install-completed .
Related Commands
service-module sm log clear
To clear all entries in the Cisco SRE operations log, use the service-module sm log clear command in privileged EXEC mode.
service-module sm slot/port log clear
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Defaults
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The Cisco SRE operations log records the last 25 operations and the results of each operation for a maximum of 50 messages. The operations are stored in time order. Use this command to clear all entries from the log.
Examples
The following example clears all entries from the Cisco SRE operations log:
Router# service-module sm 1/0 log clear
service-module sm log show
To display the last 25 operations executed on the Cisco SRE and the results of each operation, use the service-module sm log show command in privileged EXEC mode.
service-module sm slot/port log show
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Defaults
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The Cisco SRE operations log records the last 25 operations and the results of each operation for a maximum of 50 messages. The operations are stored in time order.
Examples
The following example shows that the last operation performed on the Cisco SRE was a successful package installation.
Router# service-module sm 1/0 log show"Total number of logs = 21 Jun 15 2011 19:50:53.910:Install initiated for SM1/0: pkg_name: cue-vm-k9.SPA.sme.8.6.1.pkg, script: , arg: , force: 02 Jun 15 2011 19:57:17.712:Install successful on SM1/0. Please wait for module to reset before next operation."service-module sm uninstall
To use Cisco SRE to uninstall an application on a service module (Cisco SM-SRE), use the service-module sm uninstall command in privileged EXEC mode.
service-module sm slot/port uninstall [force]
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command completely erases the disk or compact flash of the SRE-enabled services engine module and removes the application keys. It does not remove application licenses.
The slash mark (/) is required between the slot argument and the port argument.
You can only issue one instance of this command at a time on a router. You cannot use this command to uninstall an application on two or more services engine modules in a router at a time.
Use the force keyword with this command to uninstall an application without first prompting for confirmation.
Examples
The following example shows how to use this command to uninstall an application without first prompting for confirmation:
Router# service-module sm uninstall 1/0 forceRouter#Related Commands
service-module sm install
Uses Cisco SRE to install an SRE-supported application on an SRE-enabled services engine module.
service-module sm status
To display configuration information related to the hardware and software on an SM-SRE service module, use the service-module sm status command in privileged EXEC mode.
service-module sm slot/port status [detailed]
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to:
•
Display the SM-SRE's software release version
•
Check the SM-SRE status (steady or down)
•
Display hardware information for the SM-SRE, including CPU, memory, and interface information
Examples
The following example displays information for an SM-SRE:
Router# service-module sm 1/0 statusService Module is Cisco SM1/0Service Module supports session via TTY line 67Service Module is in Steady stateService Module heartbeat-reset is enabledGetting status from the Service Module, please wait..Cisco Unity Express 8.6.1.2CUE Running on SMModule resource information:CPU Frequency: 1862 MHzMemory Size: 4016 MBDisk 0 Size: 500107 MBDisk 1 Size: 1887 MBNo install/uninstall in progressThe following example displays detailed information for an SM-SRE:
# service-module SM 1/0 status detailedService Module is Cisco SM1/0Service Module supports session via TTY line 67Service Module is in Steady stateService Module heartbeat-reset is enabledGetting status from the Service Module, please wait..Cisco Unity Express 8.6.1.2CUE Running on SMModule resource information:CPU Frequency: 1862 MHzMemory Size: 4016 MBDisk 0 Size: 500107 MBDisk 1 Size: 1887 MBNo install/uninstall in progressNo localstoreRelated Commands
Module Command Reference
The following commands are new or have been modified.
•
show software install history
show log name
To display a log file on the module, use the show log name command in privileged EXEC mode.
show log name filename
Syntax Description
Defaults
None
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to display specified log file on the module.
Examples
The following example shows the output options for the show log name command:
se-172-25-223-77# show log name install.log | ?begin Begin with the line that matchesexclude Exclude lines that matchinclude Include lines that matchpage Paginate output (--More--)Related Commands
show software install history
To display a history of installed and upgraded applications from the module, use the show software install history command in privileged EXEC mode.
show software install history [paged]
Syntax Description
Defaults
None
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to display a history of installed and upgraded applications on the module.
Examples
The following example shows the prepositioned applications on the module:
se-172-25-223-77# show software install historyAdditional References
The following sections provide references related to the Cisco SM-SRE.
Related Documents
Cisco applications supported on the Cisco SRE
•
Cisco Application eXtension Platform
•
Cisco Video Management and Storage System
Cisco IOS commands
•
Cisco IOS Interface and Hardware Component Command Reference
Service module installation
•
Installing Cisco Network Modules and Service Modules in Cisco Access Routers
•
Cisco High-Speed Intrachassis Module Interconnect (HIMI) Configuration Guide
•
Cisco Network Modules and Interface Cards Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
Technical Assistance
Glossary
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)

 Feedback
Feedback