- Index
- Preface
- Overview
- Using the Command-Line Interface
- Assigning the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway
- Configuring Cisco IOS CNS Agents
- Clustering Switches
- Administering the Switch
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring Interface Characteristics
- Configuring Smartports Macros
- Configuring VLANs
- Configuring VTP
- Configuring Voice VLAN
- Configuring STP
- Configuring MSTP
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
- Configuring DHCP Features
- Configuring IGMP Snooping and MVR
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring CDP
- Configuring LLDP and LLDP-MED
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLAs Operations
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring IPv6 Host Functions
- Configuring IPv6 MLD Snooping
- Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
- Troubleshooting
- Supported MIBs
- Working with the Cisco IOS File System, Configuration Files, and Software Images
- Recommendations for Upgrading a Catalyst 2950 Switch to a Catalyst 2960 Switch
- Unsupported Commands in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(40)SE
Configuring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links, a pair of interfaces on the Catalyst 2960 switch that provide a mutual backup. It also describes how to configure the MAC address-table move update feature, also referred to as the Flex Links bidirectional fast convergence feature.

Note ![]() For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the command reference for this release.
For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the command reference for this release.
The chapter consists of these sections:
•![]() Understanding Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
Understanding Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
•![]() Configuring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
Configuring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
•![]() Monitoring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
Monitoring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
Understanding Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
This section contains this information:
•![]() VLAN Flex Link Load Balancing and Support
VLAN Flex Link Load Balancing and Support
•![]() MAC Address-Table Move Update
MAC Address-Table Move Update
Flex Links
Flex Links are a pair of a Layer 2 interfaces (switch ports or port channels) where one interface is configured to act as a backup to the other. The feature provides an alternative solution to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). Users can disable STP and still retain basic link redundancy. Flex Links are typically configured in service provider or enterprise networks where customers do not want to run STP on the switch. If the switch is running STP, Flex Links is not necessary because STP already provides link-level redundancy or backup.
You configure Flex Links on one Layer 2 interface (the active link) by assigning another Layer 2 interface as the Flex Link or backup link. When one of the links is up and forwarding traffic, the other link is in standby mode, ready to begin forwarding traffic if the other link shuts down. At any given time, only one of the interfaces is in the linkup state and forwarding traffic. If the primary link shuts down, the standby link starts forwarding traffic. When the active link comes back up, it goes into standby mode and does not forward traffic. STP is disabled on Flex Link interfaces.
In Figure 21-1, ports 1 and 2 on switch A are connected to uplink switches B and C. Because they are configured as Flex Links, only one of the interfaces is forwarding traffic; the other is in standby mode. If port 1 is the active link, it begins forwarding traffic between port 1 and switch B; the link between port 2 (the backup link) and switch C is not forwarding traffic. If port 1 goes down, port 2 comes up and starts forwarding traffic to switch C. When port 1 comes back up, it goes into standby mode and does not forward traffic; port 2 continues forwarding traffic.
You can also choose to configure a preemption mechanism, specifying the preferred port for forwarding traffic. For example, in the example in Figure 21-1, you can configure the Flex Links pair with preemption mode. In the scenario shown, when port 1 comes back up and has more bandwidth than port 2, port 1 begins forwarding traffic after 60 seconds. Port 2 becomes the standby port. You do this by entering the interface configuration switchport backup interface preemption mode bandwidth and switchport backup interface preemption delay commands.
Figure 21-1 Flex Links Configuration Example
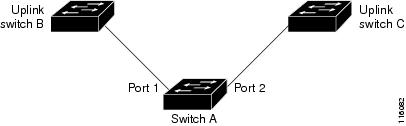
If a primary (forwarding) link goes down, a trap notifies the network management stations. If the standby link goes down, a trap notifies the users.
Flex Links are supported only on Layer 2 ports and port channels, not on VLANs.
VLAN Flex Link Load Balancing and Support
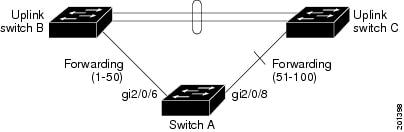
VLAN Flex Link load-balancing allows users to configure a Flex Link pair so that both ports simultaneously forward the traffic for some mutually exclusive VLANs. For example, if Flex Link ports are configured for 1-100 VLANs, the traffic of the first 50 VLANs can be forwarded on one port and the rest on the other port. If one of the ports fail, the other active port forwards all the traffic. When the failed port comes back up, it resumes forwarding traffic in the preferred VLANs. This way, apart from providing the redundancy, this Flex Link pair can be used for load balancing. Also, Flex Link VLAN load-balancing does not impose any restrictions on uplink switches.
Figure 21-2 VLAN Flex Links Load Balancing Configuration Example
MAC Address-Table Move Update
The MAC address-table move update feature allows the switch to provide rapid bidirectional convergence when a primary (forwarding) link goes down and the standby link begins forwarding traffic.
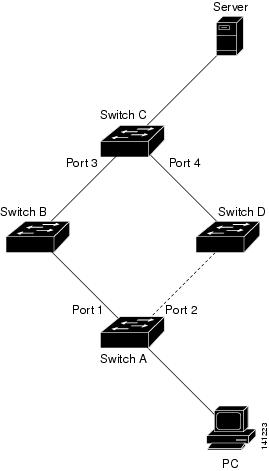
In Figure 21-3, switch A is an access switch, and ports 1 and 2 on switch A are connected to uplink switches B and D through a Flex Link pair. Port 1 is forwarding traffic, and port 2 is in the backup state. Traffic from the PC to the server is forwarded from port 1 to port 3. The MAC address of the PC has been learned on port 3 of switch C. Traffic from the server to the PC is forwarded from port 3 to port 1.
If the MAC address-table move update feature is not configured and port 1 goes down, port 2 starts forwarding traffic. However, for a short time, switch C keeps forwarding traffic from the server to the PC through port 3, and the PC does not get the traffic because port 1 is down. If switch C removes the MAC address of the PC on port 3 and relearns it on port 4, traffic can then be forwarded from the server to the PC through port 2.
If the MAC address-table move update feature is configured and enabled on the switches in Figure 21-3 and port 1 goes down, port 2 starts forwarding traffic from the PC to the server. The switch sends a MAC address-table move update packet from port 2. Switch C gets this packet on port 4 and immediately learns the MAC address of the PC on port 4, which reduces the reconvergence time.
You can configure the access switch, switch A, to send MAC address-table move update messages. You can also configure the uplink switches B, C, and D to get and process the MAC address-table move update messages. When switch C gets a MAC address-table move update message from switch A, switch C learns the MAC address of the PC on port 4. Switch C updates the MAC address table, including the forwarding table entry for the PC.
Switch A does not need to wait for the MAC address-table update. The switch detects a failure on port 1 and immediately starts forwarding server traffic from port 2, the new forwarding port. This change occurs in 100 milliseconds (ms). The PC is directly connected to switch A, and the connection status does not change. Switch A does not need to update the PC entry in the MAC address table.
Figure 21-3 MAC Address-Table Move Update Example
Configuring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
These sections contain this information:
•![]() Configuring VLAN Load Balancing on Flex Links
Configuring VLAN Load Balancing on Flex Links
•![]() Configuring the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
Configuring the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
Default Configuration
The Flex Links are not configured, and there are no backup interfaces defined.
The preemption mode is off.
The preemption delay is 35 seconds.
The MAC address-table move update feature is not configured on the switch.
Configuration Guidelines
Follow these guidelines to configure Flex Links:
•![]() You can configure only one Flex Link backup link for any active link, and it must be a different interface from the active interface.
You can configure only one Flex Link backup link for any active link, and it must be a different interface from the active interface.
•![]() An interface can belong to only one Flex Link pair. An interface can be a backup link for only one active link. An active link cannot belong to another Flex Link pair.
An interface can belong to only one Flex Link pair. An interface can be a backup link for only one active link. An active link cannot belong to another Flex Link pair.
•![]() Neither of the links can be a port that belongs to an EtherChannel. However, you can configure two port channels (EtherChannel logical interfaces) as Flex Links, and you can configure a port channel and a physical interface as Flex Links, with either the port channel or the physical interface as the active link.
Neither of the links can be a port that belongs to an EtherChannel. However, you can configure two port channels (EtherChannel logical interfaces) as Flex Links, and you can configure a port channel and a physical interface as Flex Links, with either the port channel or the physical interface as the active link.
•![]() A backup link does not have to be the same type (Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, or port channel) as the active link. However, you should configure both Flex Links with similar characteristics so that there are no loops or changes in behavior if the standby link begins to forward traffic.
A backup link does not have to be the same type (Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, or port channel) as the active link. However, you should configure both Flex Links with similar characteristics so that there are no loops or changes in behavior if the standby link begins to forward traffic.
•![]() STP is disabled on Flex Link ports. A Flex Link port does not participate in STP, even if the VLANs present on the port are configured for STP. When STP is not enabled, be sure that there are no loops in the configured topology. Once the Flex Link configurations are removed, STP is re-enabled on the ports.
STP is disabled on Flex Link ports. A Flex Link port does not participate in STP, even if the VLANs present on the port are configured for STP. When STP is not enabled, be sure that there are no loops in the configured topology. Once the Flex Link configurations are removed, STP is re-enabled on the ports.
Follow these guidelines to configure VLAN load balancing on the Flex Links feature:
•![]() For Flex Link VLAN load balancing, you must choose the preferred VLANs on the backup interface.
For Flex Link VLAN load balancing, you must choose the preferred VLANs on the backup interface.
•![]() You cannot configure a preemption mechanism and VLAN load balancing for the same Flex Links pair.
You cannot configure a preemption mechanism and VLAN load balancing for the same Flex Links pair.
Follow these guidelines to configure the MAC address-table move update feature:
•![]() You can enable and configure this feature on the access switch to send the MAC address-table move updates.
You can enable and configure this feature on the access switch to send the MAC address-table move updates.
•![]() You can enable and configure this feature on the uplink switches to receive the MAC address-table move updates.
You can enable and configure this feature on the uplink switches to receive the MAC address-table move updates.
Configuring Flex Links
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to configure a pair of Flex Links:
To disable a Flex Link backup interface, use the no switchport backup interface interface-id interface configuration command.
This example shows how to configure an interface with a backup interface and to verify the configuration:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(conf)# interface gigabitethernet0/1
Switch(conf-if)# switchport backup interface gigabitethernet0/2
Switch(conf-if)# end
Switch# show interfaces switchport backup
Switch Backup Interface Pairs:
Active Interface Backup Interface State
------------------------------------------------------------------------
GigabitEthernet0/1 GigabitEthernet0/3 Active Standby/Backup Up
Vlans Preferred on Active Interface: 1-3,5-4094
Vlans Preferred on Backup Interface: 4
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to configure a preemption scheme for a pair of Flex Links:
To remove a preemption scheme, use the no switchport backup interface interface-id preemption mode interface configuration command. To reset the delay time to the default, use the no switchport backup interface interface-id preemption delay interface configuration command.
This example shows how to configure the preemption mode as forced for a backup interface pair and to verify the configuration:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(conf)# interface gigabitethernet0/1
Switch(conf-if)#switchport backup interface gigabitethernet0/2 preemption mode forced
Switch(conf-if)#switchport backup interface gigabitethernet0/2 preemption delay 50
Switch(conf-if)# end
Switch# show interfaces switchport backup detail Active Interface Backup Interface State ------------------------------------------------------------------------ GigabitEthernet0/21 GigabitEthernet0/2 Active Up/Backup Standby
Interface Pair : Gi0/1, Gi0/2
Preemption Mode : forced
Preemption Delay : 50 seconds
Bandwidth : 100000 Kbit (Gi0/1), 100000 Kbit (Gi0/2)
Mac Address Move Update Vlan : auto
Configuring VLAN Load Balancing on Flex Links
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to configure VLAN load balancing on Flex Links:
To disable the VLAN load balancing feature, use the no switchport backup interface interface-id prefer vlan vlan-range interface configuration command.
In the following example, VLANs 1 to 50, 60, and 100 to 120 are configured on the switch:
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/6
Switch(config-if)#switchport backup interface gigabitEthernet 0/8 prefer vlan 60,100-120
When both interfaces are up, Gi0/8 forwards traffic for VLANs 60 and 100 to 120 and Gi0/6 forwards traffic for VLANs 1 to 50.
Switch#show interfaces switchport backup
Switch Backup Interface Pairs:
Active Interface Backup Interface State
------------------------------------------------------------------------
GigabitEthernet0/6 GigabitEthernet0/8 Active Up/Backup Up
Vlans Preferred on Active Interface: 1-50
Vlans Preferred on Backup Interface: 60, 100-120
When a Flex Link interface goes down (LINK_DOWN), VLANs preferred on this interface are moved to the peer interface of the Flex Link pair. In this example, if interface Gi0/6 goes down, Gi0/8 carries all VLANs of the Flex Link pair.
Switch#show interfaces switchport backup
Switch Backup Interface Pairs:
Active Interface Backup Interface State
------------------------------------------------------------------------
GigabitEthernet0/6 GigabitEthernet0/8 Active Down/Backup Up
Vlans Preferred on Active Interface: 1-50
Vlans Preferred on Backup Interface: 60, 100-120
When a Flex Link interface comes up, VLANs preferred on this interface are blocked on the peer interface and moved to the forwarding state on the interface that has just come up. In this example, if interface Gi0/6 comes up, VLANs preferred on this interface are blocked on the peer interface Gi0/8 and forwarded on Gi0/6.
Switch#show interfaces switchport backup
Switch Backup Interface Pairs:
Active Interface Backup Interface State
------------------------------------------------------------------------
GigabitEthernet0/6 GigabitEthernet0/8 Active Up/Backup Up
Vlans Preferred on Active Interface: 1-50
Vlans Preferred on Backup Interface: 60, 100-120
Switch#show interfaces switchport backup detail
Switch Backup Interface Pairs:
Active Interface Backup Interface State
------------------------------------------------------------------------
FastEthernet0/3 FastEthernet0/4 Active Down/Backup Up
Vlans Preferred on Active Interface: 1-2,5-4094
Vlans Preferred on Backup Interface: 3-4
Preemption Mode : off
Bandwidth : 10000 Kbit (Fa0/3), 100000 Kbit (Fa0/4)
Mac Address Move Update Vlan : auto
Configuring the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
This section contains this information:
•![]() Configuring a switch to send MAC address-table move updates
Configuring a switch to send MAC address-table move updates
•![]() Configuring a switch to get MAC address-table move updates
Configuring a switch to get MAC address-table move updates
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to configure an access switch to send MAC address-table move updates:
To disable the MAC address-table move update feature, use the no mac address-table move update transmit interface configuration command. To display the MAC address-table move update information, use the show mac address-table move update privileged EXEC command.
This example shows how to configure an access switch to send MAC address-table move update messages:
Switch(conf)# interface gigabitethernet0/1
Switch(conf-if)# switchport backup interface gigabitethernet0/2 mmu primary vlan 2
Switch(conf-if)# exit
Switch(conf)# mac address-table move update transmit
Switch(conf)# end
This example shows how to verify the configuration:
Switch# show mac-address-table move update
Switch-ID : 010b.4630.1780
Dst mac-address : 0180.c200.0010
Vlans/Macs supported : 1023/8320
Default/Current settings: Rcv Off/On, Xmt Off/On
Max packets per min : Rcv 40, Xmt 60
Rcv packet count : 5
Rcv conforming packet count : 5
Rcv invalid packet count : 0
Rcv packet count this min : 0
Rcv threshold exceed count : 0
Rcv last sequence# this min : 0
Rcv last interface : Po2
Rcv last src-mac-address : 000b.462d.c502
Rcv last switch-ID : 0403.fd6a.8700
Xmt packet count : 0
Xmt packet count this min : 0
Xmt threshold exceed count : 0
Xmt pak buf unavail cnt : 0
Xmt last interface : None
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to configure a switch to get and process MAC address-table move update messages:
To disable the MAC address-table move update feature, use the no mac address-table move update receive configuration command. To display the MAC address-table move update information, use the show mac address-table move update privileged EXEC command.
This example shows how to configure a switch to get and process MAC address-table move update messages:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(conf)# mac address-table move update receive
Switch(conf)# end
Monitoring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
Table 21-1 shows the privileged EXEC commands for monitoring the Flex Links configuration and the MAC address-table move update information.
 Feedback
Feedback