- Index
- Preface
- Overview
- Using the Command-Line Interface
- Getting Started with CMS
- Assigning the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway
- Clustering Switches
- Administering the Switch
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
- Configuring 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring Interface Characteristics
- Configuring Smartports Macros
- Configuring VLANs
- Configuring VTP
- Configuring Private VLANs
- Configuring Voice VLAN
- Configuring STP
- Configuring MSTP
- Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
- Configuring Flex Links
- Configuring DHCP Features and IP Source Guard
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring IGMP Snooping and MVR
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring CDP
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring EtherChannels
- Configuring IP Unicast Routing
- Configuring HSRP
- Configuring IP Multicast Routing
- Configuring MSDP
- Configuring Fallback Bridging
- Troubleshooting
- Supported MIBs
- Working with the Cisco IOS File System, Configuration Files, and Software Images
- Unsupported Commands in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(20)SE
Configuring Voice VLAN
This chapter describes how to configure the voice VLAN feature on the Catalyst 3560 switch. Voice VLAN is referred to as an auxiliary VLAN in some Catalyst 6500 family switch documentation.

Note ![]() For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the command reference for this release.
For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the command reference for this release.
This chapter consists of these sections:
Understanding Voice VLAN
The voice VLAN feature enables access ports to carry IP voice traffic from an IP phone. When the switch is connected to a Cisco 7960 IP Phone, the IP Phone sends voice traffic with Layer 3 IP precedence and Layer 2 class of service (CoS) values, which are both set to 5 by default. Because the sound quality of an IP phone call can deteriorate if the data is unevenly sent, the switch supports quality of service (QoS) based on IEEE 802.1p CoS. QoS uses classification and scheduling to send network traffic from the switch in a predictable manner. For more information on QoS, see "Configuring QoS."
The Cisco 7960 IP Phone is a configurable device, and you can configure it to forward traffic with an 802.1p priority. You can configure the switch to trust or override the traffic priority assigned by an IP Phone.
The Cisco IP Phone contains an integrated three-port 10/100 switch as shown in Figure 15-1. The ports provide dedicated connections to these devices:
•![]() Port 1 connects to the switch or other voice-over-IP (VoIP) device.
Port 1 connects to the switch or other voice-over-IP (VoIP) device.
•![]() Port 2 is an internal 10/100 interface that carries the IP phone traffic.
Port 2 is an internal 10/100 interface that carries the IP phone traffic.
•![]() Port 3 (access port) connects to a PC or other device.
Port 3 (access port) connects to a PC or other device.
Figure 15-1 shows one way to connect a Cisco 7960 IP Phone.
Figure 15-1 Cisco 7960 IP Phone Connected to a Switch
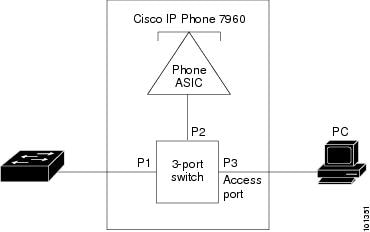
Cisco IP Phone Voice Traffic
You can configure an access port with an attached Cisco IP Phone to use one VLAN for voice traffic and another VLAN for data traffic from a device attached to the phone. You can configure access ports on the switch to send Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) packets that instruct an attached Cisco IP Phone to send voice traffic to the switch in any of these ways:
•![]() In the voice VLAN tagged with a Layer 2 CoS priority value
In the voice VLAN tagged with a Layer 2 CoS priority value
•![]() In the access VLAN tagged with a Layer 2 CoS priority value
In the access VLAN tagged with a Layer 2 CoS priority value
•![]() In the access VLAN, untagged (no Layer 2 CoS priority value)
In the access VLAN, untagged (no Layer 2 CoS priority value)

Note ![]() In all configurations, the voice traffic carries a Layer 3 IP precedence value (the default is 5 for voice traffic and 3 for voice control traffic).
In all configurations, the voice traffic carries a Layer 3 IP precedence value (the default is 5 for voice traffic and 3 for voice control traffic).
Cisco IP Phone Data Traffic
The switch can also process tagged data traffic (traffic in 802.1Q or 802.1p frame types) from the device attached to the access port on the Cisco IP Phone (see Figure 15-1). You can configure Layer 2 access ports on the switch to send CDP packets that instruct the attached Cisco IP Phone to configure the IP phone access port in one of these modes:
•![]() In trusted mode, all traffic received through the access port on the Cisco IP Phone passes through the IP phone unchanged.
In trusted mode, all traffic received through the access port on the Cisco IP Phone passes through the IP phone unchanged.
•![]() In untrusted mode, all traffic in 802.1Q or 802.1p frames received through the access port on the IP phone receive a configured Layer 2 CoS value. The default Layer 2 CoS value is 0. Untrusted mode is the default.
In untrusted mode, all traffic in 802.1Q or 802.1p frames received through the access port on the IP phone receive a configured Layer 2 CoS value. The default Layer 2 CoS value is 0. Untrusted mode is the default.

Note ![]() Untagged traffic from the device attached to the Cisco IP Phone passes through the IP phone unchanged, regardless of the trust state of the access port on the IP phone.
Untagged traffic from the device attached to the Cisco IP Phone passes through the IP phone unchanged, regardless of the trust state of the access port on the IP phone.
Configuring Voice VLAN
This section describes how to configure voice VLAN on access ports. This section contains this configuration information:
•![]() Default Voice VLAN Configuration
Default Voice VLAN Configuration
•![]() Voice VLAN Configuration Guidelines
Voice VLAN Configuration Guidelines
•![]() Configuring a Port Connected to a Cisco 7960 IP Phone
Configuring a Port Connected to a Cisco 7960 IP Phone
Default Voice VLAN Configuration
The voice VLAN feature is disabled by default.
When the voice VLAN feature is enabled, all untagged traffic is sent according to the default CoS priority of the port.
The CoS value is not trusted for 802.1p or 802.1Q tagged traffic.
Voice VLAN Configuration Guidelines
These are the voice VLAN configuration guidelines:
•![]() You should configure voice VLAN on switch access ports; voice VLAN is not supported on trunk ports. You can only configure a voice VLAN on Layer 2 ports.
You should configure voice VLAN on switch access ports; voice VLAN is not supported on trunk ports. You can only configure a voice VLAN on Layer 2 ports.

Note ![]() Voice VLAN is only supported on access ports and not on trunk ports, even though the configuration is allowed.
Voice VLAN is only supported on access ports and not on trunk ports, even though the configuration is allowed.
•![]() Do not configure voice VLAN on private VLAN ports.
Do not configure voice VLAN on private VLAN ports.
•![]() The Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches are capable of automatically providing power to Cisco pre-standard and IEEE 802.3af-compliant powered devices if they are not being powered by an AC power source. For information about PoE interfaces, see the "Configuring Power over Ethernet on an Interface" section.
The Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches are capable of automatically providing power to Cisco pre-standard and IEEE 802.3af-compliant powered devices if they are not being powered by an AC power source. For information about PoE interfaces, see the "Configuring Power over Ethernet on an Interface" section.
•![]() Before you enable voice VLAN, we recommend that you enable QoS on the switch by entering the mls qos global configuration command and configure the port trust state to trust by entering the mls qos trust cos interface configuration command. If you use the auto-QoS feature, these settings are automatically configured. For more information, see "Configuring QoS."
Before you enable voice VLAN, we recommend that you enable QoS on the switch by entering the mls qos global configuration command and configure the port trust state to trust by entering the mls qos trust cos interface configuration command. If you use the auto-QoS feature, these settings are automatically configured. For more information, see "Configuring QoS."
•![]() You must enable CDP on the switch port connected to the Cisco IP Phone to send configuration to the Cisco IP Phone. (CDP is enabled by default globally and on all switch interfaces.)
You must enable CDP on the switch port connected to the Cisco IP Phone to send configuration to the Cisco IP Phone. (CDP is enabled by default globally and on all switch interfaces.)
•![]() The Port Fast feature is automatically enabled when voice VLAN is configured. When you disable voice VLAN, the Port Fast feature is not automatically disabled.
The Port Fast feature is automatically enabled when voice VLAN is configured. When you disable voice VLAN, the Port Fast feature is not automatically disabled.
•![]() If the Cisco IP Phone and a device attached to the Cisco IP Phone are in the same VLAN, they must be in the same IP subnet. These conditions indicate that they are in the same VLAN:
If the Cisco IP Phone and a device attached to the Cisco IP Phone are in the same VLAN, they must be in the same IP subnet. These conditions indicate that they are in the same VLAN:
–![]() They both use 802.1p or untagged frames.
They both use 802.1p or untagged frames.
–![]() The Cisco IP Phone uses 802.1p frames and the device uses untagged frames.
The Cisco IP Phone uses 802.1p frames and the device uses untagged frames.
–![]() The Cisco IP Phone uses untagged frames and the device uses 802.1p frames.
The Cisco IP Phone uses untagged frames and the device uses 802.1p frames.
–![]() The Cisco IP Phone uses 802.1Q frames and the voice VLAN is the same as the access VLAN.
The Cisco IP Phone uses 802.1Q frames and the voice VLAN is the same as the access VLAN.
•![]() The Cisco IP Phone and a device attached to the phone cannot communicate if they are in the same VLAN and subnet but use different frame types because traffic in the same subnet is not routed (routing would eliminate the frame type difference).
The Cisco IP Phone and a device attached to the phone cannot communicate if they are in the same VLAN and subnet but use different frame types because traffic in the same subnet is not routed (routing would eliminate the frame type difference).
•![]() You cannot configure static secure MAC addresses in the voice VLAN.
You cannot configure static secure MAC addresses in the voice VLAN.
•![]() Voice VLAN ports can also be these port types:
Voice VLAN ports can also be these port types:
–![]() Dynamic access port. See the "Configuring Dynamic-Access Ports on VMPS Clients" section for more information.
Dynamic access port. See the "Configuring Dynamic-Access Ports on VMPS Clients" section for more information.
–![]() 802.1x authenticated port. See the "Configuring 802.1x Authentication" section for more information.
802.1x authenticated port. See the "Configuring 802.1x Authentication" section for more information.

Note ![]() If you enable 802.1x on an access port on which a voice VLAN is configured and to which a Cisco IP Phone is connected, the Cisco IP phone loses connectivity to the switch for up to 30 seconds.
If you enable 802.1x on an access port on which a voice VLAN is configured and to which a Cisco IP Phone is connected, the Cisco IP phone loses connectivity to the switch for up to 30 seconds.
–![]() Protected port. See the "Configuring Protected Ports" section for more information.
Protected port. See the "Configuring Protected Ports" section for more information.
–![]() A source or destination port for a SPAN or RSPAN session.
A source or destination port for a SPAN or RSPAN session.
–![]() Secure port. See the "Configuring Port Security" section for more information.
Secure port. See the "Configuring Port Security" section for more information.

Note ![]() When you enable port security on an interface that is also configured with a voice VLAN, you must set the maximum allowed secure addresses on the port to two plus the maximum number of secure addresses allowed on the access VLAN. When the port is connected to a Cisco IP phone, the IP phone requires up to two MAC addresses. The IP phone address is learned on the voice VLAN and might also be learned on the access VLAN. Connecting a PC to the IP phone requires additional MAC addresses.
When you enable port security on an interface that is also configured with a voice VLAN, you must set the maximum allowed secure addresses on the port to two plus the maximum number of secure addresses allowed on the access VLAN. When the port is connected to a Cisco IP phone, the IP phone requires up to two MAC addresses. The IP phone address is learned on the voice VLAN and might also be learned on the access VLAN. Connecting a PC to the IP phone requires additional MAC addresses.
Configuring a Port Connected to a Cisco 7960 IP Phone
Because a Cisco 7960 IP Phone also supports a connection to a PC or other device, a port connecting the switch to a Cisco IP Phone can carry mixed traffic. You can configure a port to decide how the IP phone carries voice traffic and data traffic.
This section includes these topics:
•![]() Configuring IP Phone Voice Traffic
Configuring IP Phone Voice Traffic
•![]() Configuring the Priority of Incoming Data Frames
Configuring the Priority of Incoming Data Frames
Configuring IP Phone Voice Traffic
You can configure a port connected to the Cisco IP Phone to send CDP packets to the phone to configure the way in which the phone sends voice traffic. The phone can carry voice traffic in 802.1Q frames for a specified voice VLAN with a Layer 2 CoS value. It can use 802.1p priority tagging to give voice traffic a higher priority and forward all voice traffic through the native (access) VLAN. The IP phone can also send untagged voice traffic or use its own configuration to send voice traffic in the access VLAN. In all configurations, the voice traffic carries a Layer 3 IP precedence value (the default is 5).
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to configure voice traffic on a port:
This example shows how to configure a port connected to an IP phone to use the CoS value to classify ingress traffic, to use 802.1p priority tagging for voice traffic, and to use and the default native VLAN (VLAN 0) to carry all traffic:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet0/1
Switch(config-if)# mls qos trust cos
Switch(config-if)# switchport voice vlan dot1p
Switch(config-if)# end
To return the port to its default setting, use the no switchport voice vlan interface configuration command.
Configuring the Priority of Incoming Data Frames
You can connect a PC or other data device to a Cisco IP Phone port. To process tagged data traffic (in 802.1Q or 802.1p frames), you can configure the switch to send CDP packets to instruct the IP phone how to send data packets from the device attached to the access port on the Cisco IP Phone. The PC can generate packets with an assigned CoS value. You can configure the Cisco IP Phone to not change (trust) or to override (not trust) the priority of frames arriving on the IP phone port from connected devices.
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to set the priority of data traffic received from the nonvoice port on the Cisco IP Phone:
This example shows how to configure a port connected to an IP phone to not change the priority of frames received from the PC or the attached device:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet0/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport priority extend trust
Switch(config-if)# end
To return the port to its default setting, use the no switchport priority extend interface configuration command.
Displaying Voice VLAN
To display voice VLAN configuration for an interface, use the show interfaces interface-id switchport privileged EXEC command.
 Feedback
Feedback