- Index
- Preface
- Product Overview
- Command-Line Interfaces
- Configuring the Switch for the First Time
- Administering the Switch
- Configuring Interfaces
- Checking Port Status and Connectivity
- Configuring Supervisor Engine Redundancy Using RPR and SSO
- Configuring NSF with SSO Supervisor Engine Redundancy
- Environmental Monitoring and Power Management
- Configuring Power over Ethernet
- Configuring Switches with Cisco Network Assistant
- Configuring VLANs, VTP, and VMPS
- Configuring Layer 2 Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring SmartPort Macros
- Configuring STP and MST
- Configuring Optional STP Features
- Configuring EtherChannel
- Configuring IGMP Snooping and Filtering
- Configuring 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
- Configuring CDP
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring Unidirectional Ethernet
- Configuring Layer 3 Interfaces
- Configuring Cisco Express Forwarding
- Configuring IP Multicast
- Configuring NetFlow
- Configuring Policy-Based Routing
- Configuring VRF-lite
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring Voice Interfaces
- Configuring 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring RMON
- Configuring Control Plane Policing
- Configuring DHCP Snooping and IP Source Guard
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring Network Security with ACLs
- Configuring Private VLANs
- Configuring Port Unicast and Multicast Flood Blocking
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- Configuring Dynamic VLAN Membership
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring SNMP
- Performing Diagnostics on the Catalyst 4500 Series Switch
- Configuring MIB Support
- Configuring WCCPv2 Services
- Acronyms
- Understanding and Configuring Multiple Spanning Trees
- Command List
- Overview of Port Security
- Port Security on Access Ports
- Configuring Port Security on Access Ports
- Examples
- Example 1: Setting Maximum Number of Secure Addresses
- Example 2: Setting a Violation Mode
- Example 3: Setting the Aging Timer
- Example 4: Setting the Aging Timer Type
- Example 5: Configuring a Secure MAC Address
- Example 6: Configuring Sticky Port Security
- Example 7: Setting a Rate Limit for Bad Packets
- Example 8: Clearing Dynamic Secure MAC Addresses
- Examples
- Example 1: Displaying Security Settings for the Entire Switch
- Example 2: Displaying Security Settings for an Interface
- Example 3: Displaying all Secure Addresses for the Entire Switch
- Example 4: Displaying a Maximum Number of MAC Addresses on an Interface
- Example 5: Displaying Security Settings on an Interface for a VLAN Range
- Example 6: Displaying Secured MAC Addresses and Aging Information on an Interface
- Example 7: Displaying Secured MAC Addresses for a VLAN Range on an Interface
Configuring Port Security
This chapter describes how to configure port security on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It provides an overview of port security on the Catalyst 4500 series switch and details the configuration on various types of ports such as access, voice, trunk and private VLAN.

Note ![]() For complete syntax and usage information for the switch commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Command Reference and related publications at this location:
For complete syntax and usage information for the switch commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Command Reference and related publications at this location:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps4324/index.html
If the command is not found in the Cisco Catalyst 4500 Command Reference, you can locate it in the larger Cisco IOS library. Refer to the Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Cisco IOS Command Reference and related publications at this location:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6350/index.html
This chapter consists of these sections:
•![]() Port Security on Access Ports
Port Security on Access Ports
•![]() Port Security on a Private VLAN Port
Port Security on a Private VLAN Port
•![]() Displaying Port Security Settings
Displaying Port Security Settings
•![]() Configuring Port Security with Other Features/Environments
Configuring Port Security with Other Features/Environments
•![]() Port Security Guidelines and Restrictions
Port Security Guidelines and Restrictions
•![]() Troubleshooting Port Security
Troubleshooting Port Security
Command List
This table lists the commands most commonly used with Port Security.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
errdisable recovery cause psecure-violation |
Brings a secure port out of error-disabled state |
|
errdisable recovery interval |
Customizes the time to recover from a specified error disable cause |
|
port-security mac-address |
Configures all secure MAC addresses on each VLAN |
|
port-security maximum |
Configures a maximum number of MAC addresses on an interface |
|
private-vlan association add |
Creates an association between a secondary VLAN and a primary VLAN |
Example of Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port |
private-vlan isolated |
Designates the VLAN as a private VLAN |
Configuring Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port |
private-vlan primary |
Specifies the VLAN as the primary private VLAN |
Configuring Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port |
switchport mode private-vlan host |
Specifies that ports with valid private VLAN trunk association become active host private VLAN trunk ports |
Configuring Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port |
switchport private-vlan host-association |
Defines a host association on an isolated host port |
Configuring Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port |
switchport private-vlan mapping |
Defines a private VLAN for the promiscuous ports |
Configuring Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port |
switchport port-security |
Enables port security |
|
switchport port-security aging static |
Configures static aging of MAC addresse. |
|
switchport port-security aging time |
Specifies an aging time for a port |
|
switchport port-security limit rate invalid-source-mac |
Sets the rate limit for bad packets |
|
switchport port-security mac-address |
Configures a secure MAC address for an interface |
|
switchport port-security mac-address <mac_address> sticky |
Specifies the sticky MAC address for an interface |
|
switchport port-security mac-address sticky |
Enables sticky Port Security |
|
no switchport port-security mac-address sticky |
Converts a sticky secure MAC address to a dynamic MAC secure address |
|
switchport port-security maximum |
Sets the maximum number of secure MAC addresses for an interface |
|
switchport port-security violation |
Sets the violation mode |
|
no switchport port-security violation |
Sets the violation mode |
|
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q |
Sets the encapsulation mode to dot1q |
Example 1: Configuring a Maximum Limit of Secure MAC Addresses for all VLANs |
Overview of Port Security
Port security enables you to restrict the number of MAC addresses (termed secure MAC addresses) on a port, allowing you to prevent access by unauthorized MAC addresses. It also allows you to configure a maximum number of secure MAC addresses on a given port (and optionally for a VLAN for trunk ports). When a secure port exceeds the maximum, a security violation is triggered, and a violation action is performed based on the violation action mode configured on the port.
If you configure the maximum number of secure MAC addresses as 1 on the port, the device attached to the secure port is assured sole access to the port.
If a secure MAC address is secured on a port, that MAC address is not allowed to enter on any other port off that VLAN. If it does, the packet is dropped unnoticed in the hardware. Other than through the interface or port counters, you do not receive a log message reflecting this fact. Be aware that this condition does not trigger a violation. Dropping these packets in the hardware is more efficient and can be done without putting additional load on the CPU.
Port Security has the following characteristics:
•![]() It allows you to age out secure MAC addresses. Two types of aging are supported: inactivity and absolute.
It allows you to age out secure MAC addresses. Two types of aging are supported: inactivity and absolute.
•![]() It supports a sticky feature whereby the secure MAC addresses on a port are retained through switch reboots and link flaps.
It supports a sticky feature whereby the secure MAC addresses on a port are retained through switch reboots and link flaps.
•![]() It can be configured on various types of ports such as access, voice, trunk and private VLAN ports.
It can be configured on various types of ports such as access, voice, trunk and private VLAN ports.
This overview contains the following topics:
•![]() Maximum Number of Secure MAC Addresses
Maximum Number of Secure MAC Addresses
Secure MAC Addresses
Port Security supports the following types of secure MAC addresses:
•![]() Dynamic or Learned—Dynamic secure MAC addresses are learned when packets are received from the host on the secure port. You might want to use this type if the user's MAC address is not fixed (laptop).
Dynamic or Learned—Dynamic secure MAC addresses are learned when packets are received from the host on the secure port. You might want to use this type if the user's MAC address is not fixed (laptop).
•![]() Static or Configured—Static secure MAC addresses are configured by the user through CLI or SNMP. You might want to use this type if your MAC address remains fixed (PC).
Static or Configured—Static secure MAC addresses are configured by the user through CLI or SNMP. You might want to use this type if your MAC address remains fixed (PC).
•![]() Sticky—Sticky addresses are learned like dynamic secure MAC addresses, but persist through switch reboots and link flaps like static secure MAC addresses. You might want to use this type if a large number of fixed MAC addresses exist and you do not want to configure MAC addresses manually (100 PCs secured on their own ports).
Sticky—Sticky addresses are learned like dynamic secure MAC addresses, but persist through switch reboots and link flaps like static secure MAC addresses. You might want to use this type if a large number of fixed MAC addresses exist and you do not want to configure MAC addresses manually (100 PCs secured on their own ports).
If a port has reached its maximum number of secure MAC addresses and you try to configure a static secure MAC address, your configuration is rejected and an error message displays. If a port has reached its maximum number of secure MAC addresses and a new dynamic secure MAC address is added, a violation action is triggered.
You can clear dynamic secure MAC addresses with the clear port-security command. You can clear sticky and static secure MAC addresses one at a time with the no form of the
switchport port-security mac-address command.
Maximum Number of Secure MAC Addresses
A secure port has a default of one MAC address. You can change the default to any value between 1 and 3,000. The upper limit of 3,000 guarantees one MAC address per port and an additional 3,000 across all ports in the system.
After you have set the maximum number of secure MAC addresses on a port, you can include the secure addresses in an address table in one of the following ways:
•![]() You can configure the secure MAC addresses with the switchport port-security mac-address mac_address interface configuration command.
You can configure the secure MAC addresses with the switchport port-security mac-address mac_address interface configuration command.
•![]() You can configure all secure MAC addresses on a range of VLANs with the port-security mac-address VLAN range configuration command for trunk ports.
You can configure all secure MAC addresses on a range of VLANs with the port-security mac-address VLAN range configuration command for trunk ports.
•![]() You can allow the port to dynamically configure secure MAC addresses with the MAC addresses of connected devices.
You can allow the port to dynamically configure secure MAC addresses with the MAC addresses of connected devices.
•![]() You can configure some of the addresses and allow the rest to be dynamically configured.
You can configure some of the addresses and allow the rest to be dynamically configured.

Note ![]() If a port's link goes down, all dynamically secured addresses on that port are no longer secure.
If a port's link goes down, all dynamically secured addresses on that port are no longer secure.
•![]() You can configure MAC addresses to be sticky. These can be dynamically learned or manually configured, stored in the address table, and added to the running configuration. After these addresses are saved in the configuration file, the interface does not need to dynamically relearn them when the switch restarts. Although you can manually configure sticky secure addresses, this action is not recommended.
You can configure MAC addresses to be sticky. These can be dynamically learned or manually configured, stored in the address table, and added to the running configuration. After these addresses are saved in the configuration file, the interface does not need to dynamically relearn them when the switch restarts. Although you can manually configure sticky secure addresses, this action is not recommended.

Note ![]() On a trunk port, a maximum number of secure MAC addresses can be configured on both the port and port VLAN. The port's maximum value can be greater than or equal to the port VLAN maximum(s) but not less than the port VLAN maximum(s). The port VLAN maximum enforces the maximum allowed on a given port on a given VLAN. If the maximum is exceeded on a given VLAN but the port's maximum is not exceeded, the port still shuts down. The entire port is shut down even if one of the VLANs on the port has actually caused the violation.
On a trunk port, a maximum number of secure MAC addresses can be configured on both the port and port VLAN. The port's maximum value can be greater than or equal to the port VLAN maximum(s) but not less than the port VLAN maximum(s). The port VLAN maximum enforces the maximum allowed on a given port on a given VLAN. If the maximum is exceeded on a given VLAN but the port's maximum is not exceeded, the port still shuts down. The entire port is shut down even if one of the VLANs on the port has actually caused the violation.
Aging Secure MAC Addresses
You might want to age secure MAC addresses when the switch may be receiving more than 3,000 MAC addresses ingress.

Note ![]() Aging of sticky addresses is not supported.
Aging of sticky addresses is not supported.
By default, port security does not age out the secure MAC addresses. After learned, the MAC addresses remain on the port until either the switch reboots or the link goes down (unless the sticky feature is enabled). However, port security does allow you to configure aging based on the absolute or inactivity mode and aging interval (in minutes, from 1 to n).
•![]() Absolute mode: ages between n and n+1
Absolute mode: ages between n and n+1
•![]() Inactivity mode: ages between n+1 and n+2
Inactivity mode: ages between n+1 and n+2
Use this feature to remove and add PCs on a secure port without manually deleting the existing secure MAC addresses, while still limiting the number of secure addresses on a port.
Unless static aging is explicitly configured with the switchport port-security aging static command, static addresses are not aged even if aging is configured on the port.

Note ![]() The aging increment is one minute.
The aging increment is one minute.
Sticky Addresses on a Port
By enabling sticky port security, you can configure an interface to convert the dynamic MAC addresses to sticky secure MAC addresses and to add them to the running configuration. You might want to do this if you do not expect the user to move to another port, and you want to avoid statically configuring a MAC address on every port.

Note ![]() If you use a different chassis, you might need another MAC address.
If you use a different chassis, you might need another MAC address.
To enable sticky port security, enter the switchport port-security mac-address sticky command. When you enter this command, the interface converts all the dynamic secure MAC addresses, including those that were dynamically learned before sticky learning was enabled, to sticky secure MAC addresses.
The sticky secure MAC addresses do not automatically become part of the configuration file, which is the startup configuration used each time the switch restarts. If you save the running config file to the configuration file, the interface does not need to relearn these addresses when the switch restarts. If you do not save the configuration, they are lost.
If sticky port security is disabled, the sticky secure MAC addresses are converted to dynamic secure addresses and are removed from the running configuration.
After the maximum number of secure MAC addresses is configured, they are stored in an address table. To ensure that an attached device has sole access of the port, configure the MAC address of the attached device and set the maximum number of addresses to one, which is the default.
A security violation occurs if the maximum number of secure MAC addresses to a port has been added to the address table and a workstation whose MAC address is not in the address table attempts to access the interface.
Violation Actions
A security violation is triggered when the number of secure MAC addresses on the port exceeds the maximum number of secure MAC addresses allowed on the port.

Note ![]() A secure violation is not triggered if the host secured on one port shows up on another port. The Catalyst 4500 series switch drops such packets on the new port silently in the hardware and does not overload the CPU.
A secure violation is not triggered if the host secured on one port shows up on another port. The Catalyst 4500 series switch drops such packets on the new port silently in the hardware and does not overload the CPU.
You can configure the interface for one of following violation modes, which are based on the response to the violation:
•![]() Restrict—A port security violation restricts data (that is, packets are dropped in software), causes the SecurityViolation counter to increment, and causes an SNMP Notification to be generated. You might want to configure this mode in order to provide uninterrupted service/access on a secure port.
Restrict—A port security violation restricts data (that is, packets are dropped in software), causes the SecurityViolation counter to increment, and causes an SNMP Notification to be generated. You might want to configure this mode in order to provide uninterrupted service/access on a secure port.
The rate at which SNMP traps are generated can be controlled by the
snmp-server enable traps port-security trap-rate command. The default value ("0") causes an SNMP trap to be generated for every security violation.
•![]() Shutdown—A port security violation causes the interface to shut down immediately. You might want to configure this mode in a highly secure environment, where you do not want unsecured MAC addresses to be denied in software and service interruption is not an issue.
Shutdown—A port security violation causes the interface to shut down immediately. You might want to configure this mode in a highly secure environment, where you do not want unsecured MAC addresses to be denied in software and service interruption is not an issue.
When a secure port is in the error-disabled state, you can bring it out of this state automatically by configuring the errdisable recovery cause psecure-violation global configuration command or you can manually reenable it by entering the shutdown and no shut down interface configuration commands. This is the default mode.
You can also customize the time to recover from the specified error disable cause (default is 300 seconds) by entering the errdisable recovery interval interval command.
Invalid Packet Handling
You might want to rate limit invalid source MAC address packets on a secure port if you anticipate that a device will send invalid packets (such as traffic generator, sniffer, and bad NICs). Port security considers packets with all zero MAC addresses, as well as multicast or broadcast source MAC address, as invalid packets. You can chose to rate limit these packets, and if the rate is exceeded, trigger a violation action for the port.
Port Security on Access Ports
These sections describe how to configure port security:
•![]() Configuring Port Security on Access Ports
Configuring Port Security on Access Ports
Configuring Port Security on Access Ports
To restrict traffic through a port by limiting and identifying MAC addresses of the stations allowed to the port, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
Switch(config)# interface interface_id
|
Enters interface configuration mode and specifies the physical interface to configure. |
Step 2 |
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access |
Sets the interface mode. Note |
Step 3 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security
|
Enables port security on the interface. To return the interface to the default condition as nonsecure port, use the no switchport port-security command. |
Step 4 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security maximum value |
(Optional) Sets the maximum number of secure MAC addresses for the interface. The range is 1 to 3072; the default is 1. To return the interface to the default number of secure MAC addresses, use the no |
Step 5 |
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
[aging {static | time aging_time | type {absolute
| inactivity}]
|
Sets the aging time and aging type for all secure addresses on a port. Use this feature to remove and add PCs on a secure port without manually deleting the existing secure MAC addresses while still limiting the number of secure addresses on a port. The static keyword enables aging for statically configured secure addresses on this port. The time aging_time keyword specifies the aging time for this port. Valid range for aging_time is from 0 to 1440 minutes. If the time is equal to 0, aging is disabled for this port. The type keyword sets the aging type as absolute or inactive. • • To disable port security aging for all secure addresses on a port, use the |
Step 6 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security
violation {restrict | shutdown}
|
(Optional) Sets the violation mode, the action to be taken when a security violation is detected, as one of these: • • Note To return the violation mode to the default condition (shutdown mode), use the |
Step 7 |
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security limit
rate invalid-source-mac packets_per_sec
|
Sets the rate limit for bad packets. Default is 10 pps. |
Step 8 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security mac-address mac_address |
(Optional) Enters a secure MAC address for the interface. You can use this command to configure a secure MAC addresses. If you configure fewer secure MAC addresses than the maximum, the remaining MAC addresses are dynamically learned. To delete a MAC address from the address table, use the no switchport port-security mac-address mac_address command. Note |
Step 9 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security
mac-address sticky
|
(Optional) Enable sticky learning on the interface. To disable sticky learning on an interface, use the |
Step 10 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security mac-address mac_address sticky [vlan [voice | access]] |
Specifies the sticky mac-address for the interface. When you specify the vlan keyword, the mac-address becomes sticky in the specified VLAN. To delete a sticky secure MAC addresses from the address table, use the Note |
Step 11 |
Switch(config-if)# end |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Step 12 |
Switch# show port-security address
interface interface_id
Switch# show port-security address |
Verifies your entries. |

Note ![]() To clear dynamically learned port security MAC addresses in the CAM table, use the
To clear dynamically learned port security MAC addresses in the CAM table, use the
clear port-security dynamic command. The address keyword enables you to clear a secure MAC addresses. The interface keyword enables you to clear all secure addresses on an interface. The VLAN keyword allows you to clear port security MACs on a per-VLAN per-port basis.
Examples
The following examples are provided:
•![]() Example 1: Setting Maximum Number of Secure Addresses
Example 1: Setting Maximum Number of Secure Addresses
•![]() Example 2: Setting a Violation Mode
Example 2: Setting a Violation Mode
•![]() Example 3: Setting the Aging Timer
Example 3: Setting the Aging Timer
•![]() Example 4: Setting the Aging Timer Type
Example 4: Setting the Aging Timer Type
•![]() Example 5: Configuring a Secure MAC Address
Example 5: Configuring a Secure MAC Address
•![]() Example 6: Configuring Sticky Port Security
Example 6: Configuring Sticky Port Security
•![]() Example 7: Setting a Rate Limit for Bad Packets
Example 7: Setting a Rate Limit for Bad Packets
•![]() Example 8: Clearing Dynamic Secure MAC Addresses
Example 8: Clearing Dynamic Secure MAC Addresses
Example 1: Setting Maximum Number of Secure Addresses
This example shows how to enable port security on the Fast Ethernet interface 3/12 and how to set the maximum number of secure addresses to 5. The violation mode is the default, and no secure MAC addresses are configured.
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 3/12
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 5
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch# show port-security interface fastethernet 3/12
Port Security : Enabled
Port Status : Secure-up
Violation Mode : Shutdown
Aging Time : 0 mins
Aging Type : Absolute
SecureStatic Address Aging : Enabled
Maximum MAC Addresses : 5
Total MAC Addresses : 0
Configured MAC Addresses : 0
Sticky MAC Addresses : 0
Last Source Address:Vlan : 0000.0000.0000:0
Security Violation Count : 0
Example 2: Setting a Violation Mode
This example shows how to set the violation mode on the Fast Ethernet interface 3/12 to restrict.
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 3/12
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security violation restrict
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
SNMP traps can be enabled with a rate-limit to detect port-security violations due to restrict mode. The following example shows how to enable traps for port-security with a rate of 5 traps per second:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# snmp-server enable traps port-security trap-rate 5
Switch(config)# end
Switch#
Example 3: Setting the Aging Timer
This example shows how to set the aging time to 2 hours (120 minutes) for the secure addresses on the Fast Ethernet interface 5/1:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 5/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security aging time 120
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
This example shows how to set the aging time to 2 minutes:
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security aging time 2
You can verify the previous commands with the show port-security interface command.
Example 4: Setting the Aging Timer Type
This example shows how to set the aging timer type to Inactivity for the secure addresses on the Fast Ethernet interface 3/5:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 3/5
Switch(config-if)# switch port-security aging type inactivity
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch# show port-security interface fastethernet 3/5
Port Security : Enabled
Port Status : Secure-up
Violation Mode : Shutdown
Aging Time : 0 mins
Aging Type : Inactivity
SecureStatic Address Aging : Disabled
Maximum MAC Addresses : 1
Total MAC Addresses : 0
Configured MAC Addresses : 0
Sticky MAC Addresses : 0
Last Source Address:Vlan : 0000.0000.0000:0
Security Violation Count : 0
Example 5: Configuring a Secure MAC Address
This example shows how to configure a secure MAC address on Fast Ethernet interface 5/1 and to verify the configuration:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 5/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 10
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address 0000.0000.0003 (Static secure MAC)
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#show port address
Secure Mac Address Table
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports Remaining Age
(mins)
---- ----------- ---- ----- -------------
1 0000.0000.0003 SecureConfigured Fa5/1 -
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) : 2
Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) : 3072
Example 6: Configuring Sticky Port Security
This example shows how to configure a sticky MAC address on Fast Ethernet interface 5/1 and to verify the configuration:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fa5/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 5
Switch(config-if)# end

Note ![]() Sending traffic to the ports causes the system to configure the port with sticky secure addresses.
Sending traffic to the ports causes the system to configure the port with sticky secure addresses.
Switch# show port-security address
Secure Mac Address Table
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports Remaining Age
(mins)
---- ----------- ---- ----- -------------
1 0000.0000.0001 SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
1 0000.0000.0002 SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
1 0000.0000.0003 SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) : 2
Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) : 3072
Switch# show running-config interface fastEthernet 5/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 344 bytes
!
interface FastEthernet5/1
switchport mode access
switchport port-security
switchport port-security maximum 5
switchport port-security mac-address sticky
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0001
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0002
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0003
end
Switch#
Example 7: Setting a Rate Limit for Bad Packets
The following example shows how to configure rate limit for invalid source packets on Fast Ethernet interface 5/1:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 5/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security limit rate invalid-source-mac 100
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
The following example shows how to configure rate limit for invalid source packets on Fast Ethernet interface 5/1:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 5/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security limit rate invalid-source-mac none
Switch(config-if)# end
Switch#
Example 8: Clearing Dynamic Secure MAC Addresses
The following example shows how to clear a dynamic secure MAC address:
Switch# clear port-security dynamic address 0000.0001.0001
The following example shows how to clear all dynamic secure MAC addresses on Fast Ethernet interface 2/1:
Switch# clear port-security dynamic interface fa2/1
The following example shows how to clear all dynamic secure MAC addresses in the system:
Switch# clear port-security dynamic
Port Security on a Private VLAN Port
You can configure port security on a private VLAN port to take advantage of private VLAN functionality as well as to limit the number of MAC addresses.

Note ![]() This section follows the same configuration model that was presented for access ports.
This section follows the same configuration model that was presented for access ports.
These sections describe how to configure trunk port security on host and promiscuous ports:
•![]() Configuring Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port
Configuring Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port
•![]() Example of Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port
Example of Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port
•![]() Configuring Port Security on a Private VLAN Promiscous Port
Configuring Port Security on a Private VLAN Promiscous Port
•![]() Example of Port Security on a Private VLAN Promiscous Port
Example of Port Security on a Private VLAN Promiscous Port
Configuring Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port
Figure 31-1 illustrates a typical topology for port security implemented on private VLAN host ports. In this topology, the PC connected through port a on the switch can communicate only with the router connected through the promiscuous port on the switch. The PC connected through port a cannot communicate with the PC connected through port b.
Figure 31-1 Port Security on Isolated Private VLAN Host Ports
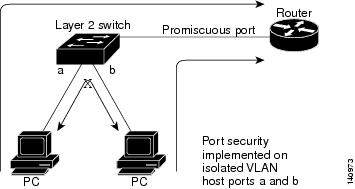

Note ![]() Dynamic addresses secured on an isolated private VLAN host port on private VLANs are secured on the secondary VLANs, and not primary VLANs.
Dynamic addresses secured on an isolated private VLAN host port on private VLANs are secured on the secondary VLANs, and not primary VLANs.
To configure port security on an isolated private VLAN host port, perform this task:
Example of Port Security on an Isolated Private VLAN Host Port
The following example shows how to configure port security on an isolated private VLAN host port, Fast Ethernet interface 3/12:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# vlan 6
Switch(config-vlan)# private-vlan isolated
Switch(config-vlan)# exit
Switch(config)# vlan 3
Switch(config-vlan)# private-vlan primary
Switch(config-vlan)# private-vlan association add 6
Switch(config-vlan)# exit
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 3/12
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode private-vlan host
Switch(config-if)# switchport private-vlan association host 3 6
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# end
Configuring Port Security on a Private VLAN Promiscous Port
To configure port security on a private VLAN promiscuous port, perform this task:
Example of Port Security on a Private VLAN Promiscous Port
The following example shows how to configure port security on a private VLAN promiscuous port, Fast Ethernet interface 3/12:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# vlan 6
Switch(config-vlan)# private-vlan isolated
Switch(config-vlan)# exit
Switch(config)# vlan 3
Switch(config-vlan)# private-vlan primary
Switch(config-vlan)# private-vlan association add 6
Switch(config-vlan)# exit
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 3/12
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode private-vlan promiscuous
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode private-vlan mapping 3 6
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# end
Port Security on Trunk Ports
You might want to configure port security on trunk ports in metro aggregation to limit the number of MAC addresses per VLAN. Trunk port security extends port security to trunk ports. It restricts the allowed MAC addresses or the maximum number of MAC addresses to individual VLANs on a trunk port. Trunk port security enables service providers to block the access from a station with a different MAC address than the ones specified for that VLAN on that trunk port. Trunk port security is also supported on private VLAN trunk ports.
These sections describe how to configure trunk port security:
•![]() Configuring Trunk Port Security
Configuring Trunk Port Security
•![]() Examples of Trunk Port Security
Examples of Trunk Port Security
•![]() Trunk Port Security Guidelines and Restrictions
Trunk Port Security Guidelines and Restrictions
Configuring Trunk Port Security
Trunk port security is used when a Catalyst 4500 series switch has a dot1q or isl trunk attached to a neighborhood Layer 2 switch. This may be used, for example, in metro aggregation networks (Figure 31-2).
Figure 31-2 Trunk Port Security
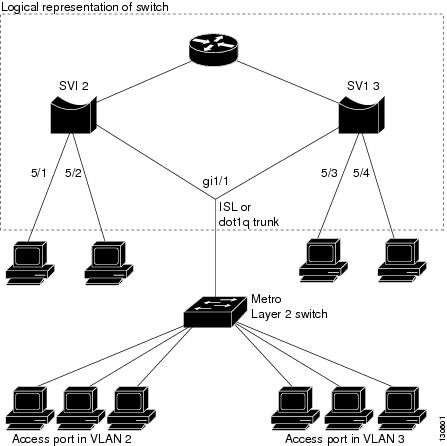
You can configure various port security related parameters on a per-port per-VLAN basis.

Note ![]() The steps involved in configuring port security parameters is similar to those for access ports. In addition to those steps, the following per-port per-VLAN configuration steps are supported for trunk ports.
The steps involved in configuring port security parameters is similar to those for access ports. In addition to those steps, the following per-port per-VLAN configuration steps are supported for trunk ports.
To configure port security related parameters on a per-VLAN per-port basis, perform this task:
Examples of Trunk Port Security
The following examples are provided:
•![]() Example 1: Configuring a Maximum Limit of Secure MAC Addresses for all VLANs
Example 1: Configuring a Maximum Limit of Secure MAC Addresses for all VLANs
•![]() Example 2: Configuring a Maximum Limit of Secure MAC Addresses for Specific VLANs
Example 2: Configuring a Maximum Limit of Secure MAC Addresses for Specific VLANs
•![]() Example 3: Configuring Secure MAC Addresses in a VLAN Range
Example 3: Configuring Secure MAC Addresses in a VLAN Range
Example 1: Configuring a Maximum Limit of Secure MAC Addresses for all VLANs
This example shows how to configure a secure MAC-address and a maximum limit of secure MAC addresses on Gigabit Ethernet interface 1/1 for all VLANs:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface g1/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
Switch(config-if)# sw mode trunk
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 3
Switch# show port-security in gi1/1 vlan
Default maximum: 3
VLAN Maximum Current
1 3 0
2 3 0
3 3 0
4 3 0
5 3 0
6 3 0
Switch#
Switch# show running interface gi1/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 161 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/1
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport mode trunk
switchport port-security
switchport port-security maximum 3 vlan
end
Example 2: Configuring a Maximum Limit of Secure MAC Addresses for Specific VLANs
This example shows how to configure a secure MAC-address on interface g1/1 in a specific VLAN or range of VLANs:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface g1/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
Switch(config-if)# sw mode trunk
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# vlan-range 2-6
Switch(config-if-vlan-range)# port-security maximum 3
Switch(config-if)# exit
Switch# show port-security interface g1/1 vlan
Default maximum: not set, using 3072
VLAN Maximum Current
2 3 0
3 3 0
4 3 0
5 3 0
6 3 0
Switch#
Example 3: Configuring Secure MAC Addresses in a VLAN Range
This example shows how to configure a secure MAC-address in a VLAN on interface g1/1:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface g1/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
Switch(config-if)# sw mode trunk
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
Switch(config-if)# vlan-range 2-6
Switch(config-if-vlan-range)# port-security mac-address 1.1.1
Switch(config-if-vlan-range)# port-security mac-address sticky 1.1.2
Switch(config-if-vlan-range)# port-security mac-address sticky 1.1.3
Switch(config-if-vlan-range)# exit
Switch# show port-security interface g1/1 address vlan 2-4
Secure Mac Address Table
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports Remaining Age
(mins)
---- ----------- ---- ----- -------------
2 0001.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
2 0001.0001.0002 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
2 0001.0001.0003 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
3 0001.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
3 0001.0001.0002 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
3 0001.0001.0003 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
4 0001.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
4 0001.0001.0002 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
4 0001.0001.0003 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses: 9
Switch#
Trunk Port Security Guidelines and Restrictions
Follow these guidelines when configuring port security related parameters on a per-port per-VLAN basis:
•![]() A secure MAC-address cannot be configured on a VLAN that is not allowed on a regular trunk port.
A secure MAC-address cannot be configured on a VLAN that is not allowed on a regular trunk port.
•![]() The configuration on the primary VLAN on the private VLAN trunk is not allowed. The CLI is rejected and an error message is displayed.
The configuration on the primary VLAN on the private VLAN trunk is not allowed. The CLI is rejected and an error message is displayed.
•![]() If a specific VLAN on a port is not configured with a maximum value (directly or indirectly), the maximum configured for the port is used for that VLAN. In this situation, the maximum number of addresses that can be secured on this VLAN is limited to the maximum value configured on the port.
If a specific VLAN on a port is not configured with a maximum value (directly or indirectly), the maximum configured for the port is used for that VLAN. In this situation, the maximum number of addresses that can be secured on this VLAN is limited to the maximum value configured on the port.
Each VLAN can be configured with a maximum count that is greater than the value configured on the port. Also, the sum of the maximum configured values for all the VLANs can exceed the maximum configured for the port. In either of these situations, the number of MAC addresses secured on each VLAN is limited to the lesser of the VLAN configuration maximum and the port configuration maximum. Also, the number of addresses secured on the port across all VLANs cannot exceed a maximum that is configured on the port.
•![]() For private VLAN trunk ports, the VLAN on which the configuration is being performed must be in either the allowed VLAN list of the private VLAN trunk or the secondary VLAN list in the association pairs. (The CLI is rejected if this condition is not met.) The allowed VLAN list on a private VLAN trunk is intended to hold the VLAN-IDs of all the regular VLANs that are allowed on the private VLAN trunk.
For private VLAN trunk ports, the VLAN on which the configuration is being performed must be in either the allowed VLAN list of the private VLAN trunk or the secondary VLAN list in the association pairs. (The CLI is rejected if this condition is not met.) The allowed VLAN list on a private VLAN trunk is intended to hold the VLAN-IDs of all the regular VLANs that are allowed on the private VLAN trunk.
•![]() Removal of an association pair from a PVLAN trunk causes all static and sticky addresses associated with the secondary VLAN of the pair to be removed from the running configuration. Dynamic addresses associated with the secondary VLAN are deleted from the system.
Removal of an association pair from a PVLAN trunk causes all static and sticky addresses associated with the secondary VLAN of the pair to be removed from the running configuration. Dynamic addresses associated with the secondary VLAN are deleted from the system.
Similarly, when a VLAN is removed from the list of allowed PVLAN trunks, the addresses associated with that VLAN are removed.

Note ![]() For a regular or private VLAN trunk port, if the VLAN is removed from the allowed VLAN list, all the addresses associated with that VLAN are removed.
For a regular or private VLAN trunk port, if the VLAN is removed from the allowed VLAN list, all the addresses associated with that VLAN are removed.
Port Mode Changes
Generally, when a port mode changes, all dynamic addresses associated with that port are removed. All static or sticky addresses and other port security parameters configured on the native VLAN are moved to the native VLAN of the port in the new mode. All the addresses on the non-native VLANs are removed.
The native VLAN refers to the following VLAN on the specified port type:
For example, when the mode changes from access to private VLAN trunk, all the static or sticky addresses configured on the access VLAN of the access port are moved to the private VLAN native VLAN of the private VLAN trunk port. All other addresses are removed.
Similarly, when the mode changes from private VLAN trunk to access mode, all the static or sticky addresses configured on the private VLAN native VLAN are moved to the access VLAN of the access port. All other addresses are removed.
When a port is changed from trunk to private VLAN trunk, addresses associated with a VLAN on the trunk are retained if that VLAN is present in the allowed list of private VLAN trunk or the secondary VLAN of an association on the private VLAN trunk. If the VLAN is not present in either of them, the address is removed from the running configuration.
When a port is changed from private VLAN trunk to trunk, a static or sticky address is retained if the VLAN associated with the address is present in the allowed VLAN list of the trunk. If the VLAN is not present in the allowed list, the address is removed from running configuration.
Port Security on Voice Ports
You might want to configure port security in an IP Telephony environment when a port is configured with a data VLAN for a PC and a voice VLAN for a Cisco IP Phone.
These sections describe how to configure port security on voice ports:
•![]() Configuring Port Security on Voice Ports
Configuring Port Security on Voice Ports
•![]() Examples of Voice Port Security
Examples of Voice Port Security
•![]() Voice Port Security Guidelines and Restrictions
Voice Port Security Guidelines and Restrictions
Configuring Port Security on Voice Ports
To configure port security on a voice port, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
Switch(config)# interface interface_id
|
Enters interface configuration mode and specifies the physical interface to configure. |
Step 2 |
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access |
Sets the interface mode. Note |
Step 3 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security
|
Enables port security on the interface. To return the interface to the default condition as nonsecure port, use the no switchport port-security command. |
Step 4 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security
violation {restrict | shutdown}
|
(Optional) Sets the violation mode, the action to be taken when a security violation is detected, as one of these: • • Note To return the violation mode to the default condition (shutdown mode), use the |
Step 5 |
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security limit
rate invalid-source-mac packets_per_sec
|
Sets the rate limit for bad packets. Default is 10 pps. |
Step 6 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security mac-address mac_address [vlan {voice | access}] |
(Optional) Specifies a secure MAC address for the interface. When you specify the vlan keyword, addresses are configured in the specified VLAN. • • You can use this command to configure secure MAC addresses. If you configure fewer secure MAC addresses than the maximum, the remaining MAC addresses are dynamically learned. To delete a MAC address from the address table, use the no switchport port-security mac-address mac_address command. Note |
Step 7 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security
mac-address sticky
|
(Optional) Enable sticky learning on the interface. To disable sticky learning on an interface, use the |
Step 8 |
Switch(config-if)# [no] switchport port-security mac-address mac_address sticky [vlan {voice | access}] |
Specifies the sticky mac-address for the interface. When you specify the vlan keyword, the mac-address becomes sticky in the specified VLAN. • • To delete a sticky secure MAC addresses from the address table, use the Note |
Step 9 |
Switch(config-if)# end |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Step 10 |
Switch# show port-security address
interface interface_id
Switch# show port-security address |
Verifies your entries. |

Note ![]() To clear dynamically learned port security MAC addresses in the CAM table, use the
To clear dynamically learned port security MAC addresses in the CAM table, use the
clear port-security dynamic command. The address keyword enables you to clear a secure MAC addresses. The interface keyword enables you to clear all secure addresses on an interface. The VLAN keyword allows you to clear port security MACs on a per-VLAN per-port basis.
Examples of Voice Port Security
The following examples are provided:
•![]() Example 1: Configuring Maximum MAC Addresses for Voice and Data VLANs
Example 1: Configuring Maximum MAC Addresses for Voice and Data VLANs
•![]() Example 2: Configuring Sticky MAC Addresses for Voice and Data VLANs
Example 2: Configuring Sticky MAC Addresses for Voice and Data VLANs
Example 1: Configuring Maximum MAC Addresses for Voice and Data VLANs
This example shows how to designate a maximum of one MAC address for a voice VLAN (for a Cisco IP Phone, let's say) and one MAC address for the data VLAN (for a PC, let's say) on Fast Ethernet interface 5/1 and to verify the configuration:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fa5/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 1 vlan voice
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 1 vlan access
Switch(config-if)# end

Note ![]() Sending traffic to the ports causes the system to configure the port with sticky secure addresses.
Sending traffic to the ports causes the system to configure the port with sticky secure addresses.
Switch# show port-security address
Secure Mac Address Table
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports Remaining Age
(mins)
---- ----------- ---- ----- -------------
1 0000.0000.0001 SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
3 0000.0000.0004 SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) : 1
Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) : 3072
Switch# show running-config interface fastEthernet 5/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 344 bytes
!
interface FastEthernet5/1
switchport mode access
switchport voice vlan 3
switchport port-security
switchport port-security maximum 1 vlan voice
switchport port-security maximum 1 vlan access
switchport port-security mac-address sticky
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0001
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0004 vlan voice
end
Switch#
Example 2: Configuring Sticky MAC Addresses for Voice and Data VLANs
This example shows how to configure sticky MAC addresses for voice and data VLANs on Fast Ethernet interface 5/1 and to verify the configuration:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# interface fa5/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.obob vlan voice
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0005 vlan access
Switch(config-if)# end

Note ![]() Sending traffic to the ports causes the system to configure the port with sticky secure addresses.
Sending traffic to the ports causes the system to configure the port with sticky secure addresses.
Switch# show port-security address
Secure Mac Address Table
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports Remaining Age
(mins)
---- ----------- ---- ----- -------------
1 0000.0000.0001 SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
1 0000.0000.0002 SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
1 0000.0000.0003 SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
3 0000.0000.0004 SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
1 0000.0000.0005 SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
3 0000.0000.0b0b SecureSticky Fa5/1 -
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) : 5
Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) : 3072
Switch# show running-config interface fastEthernet 5/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 344 bytes
!
interface FastEthernet5/1
switchport mode access
switchport voice vlan 3
switchport port-security
switchport port-security maximum 5 vlan voice
switchport port-security mac-address sticky
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0001
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0002
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0003
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0004 vlan voice
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0005
switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.0000.0b0b vlan voice
end
Switch#
Voice Port Security Guidelines and Restrictions
Port security as implemented on voice ports behaves the same as port security on access ports:
•![]() You can configure sticky port security on voice ports. If sticky port security is enabled on a voice port, addresses secured on data and voice VLANs are secured as sticky addresses.
You can configure sticky port security on voice ports. If sticky port security is enabled on a voice port, addresses secured on data and voice VLANs are secured as sticky addresses.
•![]() You can configure maximum secure addresses per VLAN. You can set a maximum for either the data VLAN or the voice VLAN. You can also set a maximum per-port, just as with access ports.
You can configure maximum secure addresses per VLAN. You can set a maximum for either the data VLAN or the voice VLAN. You can also set a maximum per-port, just as with access ports.
•![]() You can configure port security MAC addresses on a per-VLAN basis on either the data or voice VLANs.
You can configure port security MAC addresses on a per-VLAN basis on either the data or voice VLANs.
•![]() Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SG, you required three MAC addresses as the maximum parameter to support an IP Phone and a PC. With Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SG and later releases, the maximum parameter must be configured to two, one for the phone and one for the PC.
Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SG, you required three MAC addresses as the maximum parameter to support an IP Phone and a PC. With Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SG and later releases, the maximum parameter must be configured to two, one for the phone and one for the PC.
Displaying Port Security Settings
Use the show port-security command to display port-security settings for an interface or for the switch.
To display traffic control information, perform one or more of these tasks:
Examples
The following examples are provided:
•![]() Example 1: Displaying Security Settings for the Entire Switch
Example 1: Displaying Security Settings for the Entire Switch
•![]() Example 2: Displaying Security Settings for an Interface
Example 2: Displaying Security Settings for an Interface
•![]() Example 3: Displaying all Secure Addresses for the Entire Switch
Example 3: Displaying all Secure Addresses for the Entire Switch
•![]() Example 4: Displaying a Maximum Number of MAC Addresses on an Interface
Example 4: Displaying a Maximum Number of MAC Addresses on an Interface
•![]() Example 5: Displaying Security Settings on an Interface for a VLAN Range
Example 5: Displaying Security Settings on an Interface for a VLAN Range
•![]() Example 6: Displaying Secured MAC Addresses and Aging Information on an Interface
Example 6: Displaying Secured MAC Addresses and Aging Information on an Interface
•![]() Example 7: Displaying Secured MAC Addresses for a VLAN Range on an Interface
Example 7: Displaying Secured MAC Addresses for a VLAN Range on an Interface
Example 1: Displaying Security Settings for the Entire Switch
This example shows how to display port security settings for the entire switch:
Switch# show port-security
Secure Port MaxSecureAddr CurrentAddr SecurityViolation Security Action
(Count) (Count) (Count)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Fa3/1 2 2 0 Restrict
Fa3/2 2 2 0 Restrict
Fa3/3 2 2 0 Shutdown
Fa3/4 2 2 0 Shutdown
Fa3/5 2 2 0 Shutdown
Fa3/6 2 2 0 Shutdown
Fa3/7 2 2 0 Shutdown
Fa3/8 2 2 0 Shutdown
Fa3/10 1 0 0 Shutdown
Fa3/11 1 0 0 Shutdown
Fa3/12 1 0 0 Restrict
Fa3/13 1 0 0 Shutdown
Fa3/14 1 0 0 Shutdown
Fa3/15 1 0 0 Shutdown
Fa3/16 1 0 0 Shutdown
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) :8
Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) :3072
Global SNMP trap control for port-security :20 (traps per second)
Example 2: Displaying Security Settings for an Interface
This example shows how to display port security settings for Fast Ethernet interface 5/1:
Switch# show port-security interface fastethernet 5/1
Port Security : Enabled
Port Status : Secure-up
Violation Mode : Shutdown
Aging Time : 0 mins
Aging Type : Absolute
SecureStatic Address Aging : Disabled
Maximum MAC Addresses : 1
Total MAC Addresses : 1
Configured MAC Addresses : 0
Sticky MAC Addresses : 1
Last Source Address:Vlan : 0000.0001.001a:1
Security Violation Count : 0
Example 3: Displaying all Secure Addresses for the Entire Switch
This example shows how to display all secure MAC addresses configured on all switch interfaces:
Switch# show port-security address
Secure Mac Address Table
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports Remaining Age
(mins)
---- ----------- ---- ----- -------------
1 0000.0001.0000 SecureConfigured Fa3/1 15 (I)
1 0000.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Fa3/1 14 (I)
1 0000.0001.0100 SecureConfigured Fa3/2 -
1 0000.0001.0101 SecureConfigured Fa3/2 -
1 0000.0001.0200 SecureConfigured Fa3/3 -
1 0000.0001.0201 SecureConfigured Fa3/3 -
1 0000.0001.0300 SecureConfigured Fa3/4 -
1 0000.0001.0301 SecureConfigured Fa3/4 -
1 0000.0001.1000 SecureDynamic Fa3/5 -
1 0000.0001.1001 SecureDynamic Fa3/5 -
1 0000.0001.1100 SecureDynamic Fa3/6 -
1 0000.0001.1101 SecureDynamic Fa3/6 -
1 0000.0001.1200 SecureSticky Fa3/7 -
1 0000.0001.1201 SecureSticky Fa3/7 -
1 0000.0001.1300 SecureSticky Fa3/8 -
1 0000.0001.1301 SecureSticky Fa3/8 -
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) :8
Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) :3072
Example 4: Displaying a Maximum Number of MAC Addresses on an Interface
This example shows how to display the maximum allowed number of secure MAC addresses and the current number of secure MAC addressees on Gigabit Ethernet interface 1/1:
Switch# show port-security interface g1/1 vlan
Default maximum: 22
VLAN Maximum Current
2 22 3
3 22 3
4 22 3
5 22 1
6 22 2
Example 5: Displaying Security Settings on an Interface for a VLAN Range
This example shows how to display the port security settings on Gigabit Ethernet interface 1/1 for VLANs 2 and 3:
Switch# show port-security interface g1/1 vlan 2-3
Default maximum: 22
VLAN Maximum Current
2 22 3
3 22 3
Example 6: Displaying Secured MAC Addresses and Aging Information on an Interface
This example shows how to display all secure MAC addresses configured on Gigabit Ethernet
interface 1/1 with aging information for each address.
Switch# show port-security interface g1/1 address
Secure Mac Address Table
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports Remaining Age(mins)
---- ----------- ---- ----- -------------
2 0001.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
2 0001.0001.0002 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
2 0001.0001.0003 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
3 0001.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
3 0001.0001.0002 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
3 0001.0001.0003 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
4 0001.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
4 0001.0001.0002 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
4 0001.0001.0003 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
5 0001.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
6 0001.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
6 0001.0001.0002 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses: 12
Example 7: Displaying Secured MAC Addresses for a VLAN Range on an Interface
This example shows how to display all secure MAC addresses configured on VLANs 2 and 3 on
Gigabit Ethernet interface 1/1 with aging information for each address:
Switch# show port-security interface g1/1 address vlan 2-3
Secure Mac Address Table
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports Remaining Age(mins)
---- ----------- ---- ----- -------------
2 0001.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
2 0001.0001.0002 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
2 0001.0001.0003 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
3 0001.0001.0001 SecureConfigured Gi1/1 -
3 0001.0001.0002 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
3 0001.0001.0003 SecureSticky Gi1/1 -
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses: 12
Switch#
Configuring Port Security with Other Features/Environments
The following topics are discussed:
•![]() Configuring Port Security in a Wireless Environment
Configuring Port Security in a Wireless Environment
DHCP and IP Source Guard
You might want to configure port security with DHCP and IP Source Guard to prevent IP spoofing by unsecured MAC addresses. IP Source Guard supports two levels of IP traffic filtering:
•![]() Source IP address filtering
Source IP address filtering
•![]() Source IP and MAC address filtering
Source IP and MAC address filtering
When used in source IP and MAC address filtering, IP Source Guard uses private ACLs to filter traffic based on the source IP address, and uses port security to filter traffic based on the source MAC address. So, port security must be enabled on the access port in this mode.
When both features are enabled, the following limitations apply:
•![]() The DHCP packet is not subject to port security dynamic learning.
The DHCP packet is not subject to port security dynamic learning.
•![]() If multiple IP clients are connected to a single access port, port security cannot enforce exact binding of source IP and MAC address for each client.
If multiple IP clients are connected to a single access port, port security cannot enforce exact binding of source IP and MAC address for each client.
Let's say that clients reside on an access port with the following IP/MAC address:
–![]() client1: MAC1 <---> IP1
client1: MAC1 <---> IP1
–![]() client2: MAC2 <---> IP2
client2: MAC2 <---> IP2
Then, any combination of the source MAC and IP address traffic is allowed:
–![]() MAC1 <---> IP1, valid
MAC1 <---> IP1, valid
–![]() MAC2 <---> IP2, valid
MAC2 <---> IP2, valid
–![]() MAC1 <---> IP2, invalid
MAC1 <---> IP2, invalid
–![]() MAC2 <---> IP1, invalid
MAC2 <---> IP1, invalid
IP traffic with the correct source IP and MAC address binding will be permitted and port security will dynamically learn its MAC address. IP traffic with source addresses that are not in the binding will be treated as invalid packets and dropped by port security. To prevent a denial of service attack, you must configure port security rate limiting for the invalid source MAC address.
802.1X Authentication
You might want to configure port security with 802.1X authentication to prevent MAC spoofing. 802.1X is not supported on regular or private VLAN trunks. On access ports and PVLAN host or promiscuous ports, both port security and 802.1X can be configured simultaneously. When both are configured, hosts must be 802.1X authenticated before port security can secure the MAC address of the host. Both 802.1X and port security must approve of the host or a security violation will be triggered. The type of security violation will depend on which feature rejects the port: if the host is allowed by 802.1X (for example, because the port is in multi-host mode) but is disallowed by port security, the port-security violation action will be triggered. If the host is allowed by port security but rejected by 802.1X (for example, because the host is non-authorized on a single-host mode port) then the 802.1X security violation action will be triggered.

Note ![]() 802.1X, port-security and VVID can all be configured on the same port.
802.1X, port-security and VVID can all be configured on the same port.
For more information on the interaction between 802.1X and Port Security, see
"Using 802.1X with Port Security" on page 13.
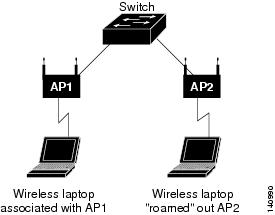
Configuring Port Security in a Wireless Environment
If access points are connected to a secure port, do not configure a static MAC address for your users. A MAC address might move from one access point to another and might cause security violations if both the access points are connected on the same switch.
Figure 31-3 illustrates a typical topology of port security in a wireless environment.
Figure 31-3 Port Security in a Wireless Environment
Port Security Guidelines and Restrictions
Follow these guidelines when configuring port security:
•![]() You cannot enable port security on dynamic access ports.
You cannot enable port security on dynamic access ports.
•![]() You cannot enable port security on EtherChannels.
You cannot enable port security on EtherChannels.
•![]() A secure port cannot be a destination port for the Switch Port Analyzer (SPAN).
A secure port cannot be a destination port for the Switch Port Analyzer (SPAN).
•![]() A secure port cannot belong to an EtherChannel port-channel interface.
A secure port cannot belong to an EtherChannel port-channel interface.
•![]() A secure port and a static MAC address configuration for an interface are mutually exclusive.
A secure port and a static MAC address configuration for an interface are mutually exclusive.
•![]() When you enter a maximum secure address value for an interface, and the new value is greater than the previous value, the new value overwrites the previously configured value. If the new value is less than the previous value and the number of configured secure addresses on the interface exceeds the new value, the command is rejected.
When you enter a maximum secure address value for an interface, and the new value is greater than the previous value, the new value overwrites the previously configured value. If the new value is less than the previous value and the number of configured secure addresses on the interface exceeds the new value, the command is rejected.
•![]() While configuring trunk port security on a trunk port, you do not need to account for the protocol packets (like CDP and BPDU) because they are not learned and secured.
While configuring trunk port security on a trunk port, you do not need to account for the protocol packets (like CDP and BPDU) because they are not learned and secured.
•![]() You cannot enable port security aging on sticky secure MAC addresses.
You cannot enable port security aging on sticky secure MAC addresses.
•![]() To restrict MAC spoofing using port security, you must enable 802.1X authentication.
To restrict MAC spoofing using port security, you must enable 802.1X authentication.
•![]() You cannot configure port security on dynamic ports. You must change the mode to access before you enable port security.
You cannot configure port security on dynamic ports. You must change the mode to access before you enable port security.
Troubleshooting Port Security
The following topics are discussed:
•![]() Verifying that an Address is Secure
Verifying that an Address is Secure
Verifying that an Address is Secure
Secure addresses appear as static entries in the output of show mac-address-table static command. If the secure VLAN associated with that MAC address is a regular or primary VLAN, the address associated with that VLAN appears in the output of the show port-security address command. If the VLAN associated with that MAC address is a secondary VLAN, the address appears in the primary VLAN in the output of the command.
After the static MAC address is configured on an interface with port-security or sticky port-security enabled, ensure that the MAC address appears in the output of the show mac-address-table static command. If it does not appear, it is likely that the configuration is incomplete.
In the following example, the private VLAN host port fa6/2 is configured with host association (2,3) and secure address 1.2.3. VLAN 2 is configured as primary and VLAN 3 as secondary:
Switch# show running-config interface fa6/2
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 193 bytes
!
interface FastEthernet6/2
switchport private-vlan host-association 2 3
switchport mode private-vlan host
switchport port-security
switchport port-security mac-address 0001.0002.0003
end
Switch# show vlan private-vlan
Primary Secondary Type Ports
------- --------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------
2 primary
3 isolated
Switch# show port-security address
Secure Mac Address Table
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports Remaining Age
(mins)
---- ----------- ---- ----- -------------
3 0001.0002.0003 SecureConfigured Fa6/2 -
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) : 0
Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) : 3072
Switch# show mac-address-table static
Multicast Entries
vlan mac address type ports
-------+---------------+-------+--------------------------------------------
1 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1,Fa6/15
2 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1
3 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1
4 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1
5 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1
6 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1
Switch#
Although the address 1.2.3 displays as a secure address in the output of the show port-security address command, it is not secure until it shows up in the output of show mac-address-table static command. This is because the association between VLAN 2 and VLAN 3 is incomplete. These VLAN s are configured as primary and secondary respectively, but no VLAN association exists. Establishing this association will make the address secure.
The following example shows how to establish a VLAN association:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# vlan 2
Switch(config-vlan)# private-vlan association 3
Switch(config-vlan)# end
Switch# show mac-address-table static
Unicast Entries
vlan mac address type protocols port
-------+---------------+--------+---------------------+--------------------
2 0001.0002.0003 static FastEthernet6/2
Multicast Entries
vlan mac address type ports
-------+---------------+-------+--------------------------------------------
1 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1,Fa6/15
2 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1
4 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1
5 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1
6 ffff.ffff.ffff system Fa6/1
Switch#
When configured on voice VLAN ports, sticky port security is applicable only to the access VLAN, not to the voice VLAN. Addresses are secured on voice VLANs as dynamic entries only; voice VLANs do not support static or sticky secure addresses.
Common System Error Messages
The following topics describe the most common error messages categories associated with implementing port security:
Port Security Violation
Each interface has a default or configured number of MAC addresses that you can secure when port security is enabled. You should determine the number of MAC addresses that can be secured per port and configure the interface with that number of addresses. With proper configuration and under anticipated operating conditions, port security continues to work normally.
Virus infections, hostile workstations, or accidentally reconfiguring hosts, can cause end hosts to send out packets with more than the expected number of MAC addresses. This causes a port security violation. Under such conditions, the system logs the following error message and sends a trap if SNMP traps for port security are enabled.
*Jul 26 10:23:54.267: %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: psecure-violation error detected on Gi2 /3, putting Gi2/3 in err-disable state *Jul 26 10:23:54.271: %PORT_SECURITY-2-PSECURE_VIOLATION: Security violation occurred, caused by MAC address 0001.0600.0101 on port GigabitEthernet2/3
Based on the violation mode, either the port can be error-disabled (shutdown mode), or the packets from the unsecure addresses can be dropped in the software (restrict mode).
To ensure that the CPU is not loaded when such an event occurs, you should set the violation mode to shutdown. You can configure errdisable recovery and timeout to ensure an automatic recovery from the error-disable state.
Configuration Management
You can configure a secure trunk port with static or sticky secure addresses. If you change the set of allowed VLANs on the trunk port, configured static or sticky secure addresses located on certain VLANs are erased by the software. Under such conditions, the following error message is logged, identifying the VLANs where the VLAN-based maximum (see Example 1: Setting Maximum Number of Secure Addresses) and static or sticky secure addresses are erased by the software:
01:52:47: %PORT_SECURITY-6-VLAN_REMOVED: VLAN 2 is no longer allowed on port Fa7/2. Its port security configuration has been removed.
You can convert a port configured with port security and static or sticky secure addresses to a router port or hotswap it out of the system. If this happens, the configuration on the port is ineffective in the system; that is, the addresses that are secured on the port can be secured on other ports.
To ensure that the configuration is restored when the port is either converted back to a Layer 2 switchport or hotswapped into the system, the software retains the configuration. When such a port is made available, the software ensures that the configured static or sticky secure addresses are not secured on other ports. If the software observes such an address on the port that is inserted, it erases the address.
Under these conditions, the following error message is logged:
*Jul 26 10:35:05.311: %PORT_SECURITY-6-ADDR_REMOVED: Address <1:0001.0600.0100> exists on port Gi2/4. It has been removed from port Gi2/3.
*Jul 26 10:35:35.591: %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: psecure-violation error detected on Gi2 /3, putting Gi2/3 in err-disable state *Jul 26 10:35:35.595: %PORT_SECURITY-2-PSECURE_VIOLATION: Security violation occurred, caused by MAC address 0001.0600.0100 on port GigabitEthernet2/3.
kenl
debug Command
Issuing the debug port-security command displays messages associated with the execution of port security. The output is useful for engineers and TAC in debugging port security-related issues.

Note ![]() The output might not remain the same across releases.
The output might not remain the same across releases.
Here is an example of how to enable debugging port-security:
Switch# debug port-security
All Port Security debugging is on
 Feedback
Feedback