- Index
- Preface
- Product Overview
- Command-Line Interfaces
- Smart Port Macros
- Virtual Switching Systems (VSS)
- Enhanced Fast Software Ugrade (eFSU)
- NSF with SSO Supervisor Engine Redundancy
- RPR Supervisor Engine Redundancy
- Interface Configuration
- UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- Power Management and Environmental Monitoring
- EnergyWise
- Online Diagnostics
- Onboard Failure Logging
- Switch Fabric Functionality
- Cisco IP Phone Support
- Power over Ethernet
- Layer 2 LAN Ports
- Flex Links
- EtherChannels
- mLACP for Server Access
- IEEE 802.1ak MVRP and MRP
- VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
- VLANs
- Private VLANs (PVLANs)
- Private Hosts
- IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
- Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
- STP and MST
- Optional STP Features
- Layer 3 Interface Configuration
- Unidirectional Ethernet (UDE) and unidirectional link routing (UDLR)
- Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
- L2VPN Advanced VPLS (A-VPLS)
- IP Unicast Layer 3 Switching
- IPv6 Multicast Layer 3 Switching
- MLD Snooping for IPv6 Multicast Traffic
- IPv4 Multicast Layer 3 Switching
- IGMP Snooping and MVR for IPv4 Multicast Traffic
- Configuring MVR for IPv4 Multicast Traffic
- IPv4 IGMP Filtering and Router Guard
- PIM Snooping
- IPv4 Multicast VPN Support
- PFC QoS
- AutoQoS
- MPLS QoS
- PFC QoS Statistics Data Export
- Network Security
- AutoSecure
- Cisco IOS ACL Support
- Cisco TrustSec (CTS)
- Port ACLs (PACLs) and VLAN ACLs (VACLs)
- Denial of Service Protection
- Control Plane Policing (CoPP)
- DHCP Snooping
- IP Source Guard
- Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Traffic Storm Control
- Unknown Unicast and Multicast Flood Control
- Network Admission Control (NAC)
- IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
- Web-Based Authentication
- Port Security
- NetFlow
- NetFlow Data Export (NDE)
- Call Home
- System Event Archive (SEA)
- Backplane Platform Monitoring
- SPAN, RSPAN, and ERSPAN
- SNMP IfIndex Persistence
- Top-N Reports
- Layer 2 Traceroute Utility
- Mini Protocol Analyzer
- Ethernet Services Line Cards
- Online Diagnostic Tests
- Acronyms
- Understanding the Optional STP Features
- Understanding STP Port Types
- Understanding PortFast
- Understanding Bridge Assurance
- Understanding BPDU Guard
- Understanding PortFast BPDU Filtering
- Understanding UplinkFast
- Understanding BackboneFast
- Understanding EtherChannel Guard
- Understanding Root Guard
- Understanding Loop Guard
- Understanding PVST Simulation
- Configuring the Optional STP Features
- Verifying the Optional STP Features
Configuring Optional STP Features
This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features.

Note ![]() For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master Command List, at this URL:
For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master Command List, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html

Tip ![]() For additional information about Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches (including configuration examples and troubleshooting information), see the documents listed on this page:
For additional information about Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches (including configuration examples and troubleshooting information), see the documents listed on this page:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps708/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Participate in the Technical Documentation Ideas forum
This chapter consists of these sections:
•![]() Understanding the Optional STP Features
Understanding the Optional STP Features
•![]() Configuring the Optional STP Features
Configuring the Optional STP Features
•![]() Verifying the Optional STP Features
Verifying the Optional STP Features

Note ![]() For information on configuring the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), see Chapter 28 "Configuring STP and MST."
For information on configuring the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), see Chapter 28 "Configuring STP and MST."
Understanding the Optional STP Features
The optional features of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) enhance loop prevention, protect against some possible user misconfigurations, and provide better control over the protocol parameters. Although similar functionality may be incorporated into the IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) standard, we recommend using these extensions. With the exception of PVST Simulation, all of these extensions can be used with both Rapid PVST+ and MST. PVST Simulation operates only with MST.
These sections describe the optional features:
•![]() Understanding Bridge Assurance
Understanding Bridge Assurance
•![]() Understanding PortFast BPDU Filtering
Understanding PortFast BPDU Filtering
•![]() Understanding EtherChannel Guard
Understanding EtherChannel Guard
•![]() Understanding PVST Simulation
Understanding PVST Simulation
Understanding STP Port Types
Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI, you can specifically configure a spanning tree port as either an edge port, a network port, or a normal port. The port type determines the behavior of the port with respect to STP extensions.
An edge port, which is connected to a Layer 2 host, can be either an access port or a trunk port.

Note ![]() If you configure a port connected to a Layer 2 switch or bridge as an edge port, you might create a bridging loop.
If you configure a port connected to a Layer 2 switch or bridge as an edge port, you might create a bridging loop.
A network port is connected only to a Layer 2 switch or bridge.

Note ![]() If you mistakenly configure a port that is connected to a Layer 2 host as a spanning tree network port, the port will automatically move into the blocking state.
If you mistakenly configure a port that is connected to a Layer 2 host as a spanning tree network port, the port will automatically move into the blocking state.
The default spanning tree port type is normal, meaning only that its topology is not specified.
In releases earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI, configuring a port with PortFast implies that the port is an edge port; otherwise, the port is considered to be a normal port.
Understanding PortFast
STP PortFast causes a Layer 2 LAN port configured as an access port to enter the forwarding state immediately, bypassing the listening and learning states. You can use PortFast on Layer 2 access ports connected to a single workstation or server to allow those devices to connect to the network immediately, instead of waiting for STP to converge. Interfaces connected to a single workstation or server should not receive bridge protocol data units (BPDUs). When configured for PortFast, a port is still running the spanning tree protocol. A PortFast enabled port can immediately transition to the blocking state if necessary (this could happen on receipt of a superior BPDU). PortFast can be enabled on trunk ports. PortFast can have an operational value that is different from the configured value.

Note ![]() Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI, PortFast options are edge and normal. There is no difference between edge ports and PortFast ports.
Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI, PortFast options are edge and normal. There is no difference between edge ports and PortFast ports.

Understanding Bridge Assurance
With Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI and later releases, you can use Bridge Assurance to protect against certain problems that can cause bridging loops in the network. Specifically, you use Bridge Assurance to protect against a unidirectional link failure or other software failure and a device that continues to forward data traffic when it is no longer running the spanning tree algorithm.

Note ![]() Bridge Assurance is supported only by Rapid PVST+ and MST.
Bridge Assurance is supported only by Rapid PVST+ and MST.
Bridge Assurance is enabled by default and can only be disabled globally. Also, Bridge Assurance is enabled only on spanning tree network ports that are point-to-point links. Finally, both ends of the link must have Bridge Assurance enabled. If the device on one side of the link has Bridge Assurance enabled and the device on the other side either does not support Bridge Assurance or does not have this feature enabled, the connecting port is blocked.
With Bridge Assurance enabled, BPDUs are sent out on all operational network ports, including alternate and backup ports, for each hello time period. If the port does not receive a BPDU for a specified period, the port moves into an inconsistent state (blocking). and is not used in the root port calculation. Once that port receives a BPDU, it resumes the normal spanning tree transitions.
Figure 29-1 shows a normal STP topology, and Figure 29-2 demonstrates a potential network problem when the device fails and you are not running Bridge Assurance.
Figure 29-1 Network with Normal STP Topology
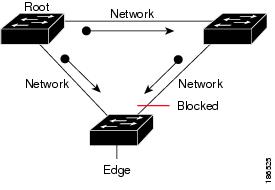
Figure 29-2 Network Problem without Running Bridge Assurance
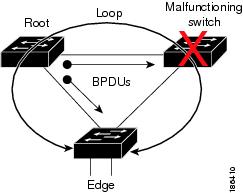
Figure 29-3 shows the network with Bridge Assurance enabled, and the STP topology progressing normally with bidirectional BPDUs issuing from every STP network port. Figure 29-4 shows how the potential network problem shown in Figure 29-2 does not happen when you have Bridge Assurance enabled on your network.
Figure 29-3 Network STP Topology Running Bridge Assurance
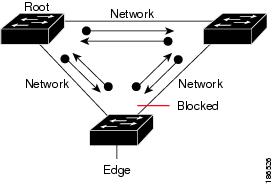
Figure 29-4 Network Problem Averted with Bridge Assurance Enabled

When using Bridge Assurance, follow these guidelines:
•![]() Bridge Assurance runs only on point-to-point spanning tree network ports. You must configure each side of the link for this feature.
Bridge Assurance runs only on point-to-point spanning tree network ports. You must configure each side of the link for this feature.
•![]() We recommend that you enable Bridge Assurance throughout your network.
We recommend that you enable Bridge Assurance throughout your network.
Understanding BPDU Guard
BPDU Guard complements the functionality of PortFast. On PortFast-enabled ports, BPDU Guard provides the protection against Layer 2 loops that STP cannot provide when STP PortFast is enabled.
In a valid configuration, PortFast Layer 2 LAN interfaces (edge ports) do not receive BPDUs. When enabled on a port, BPDU Guard shuts down a port that receives a BPDU. When configured globally, BPDU Guard is only effective on ports in the operational PortFast (edge) state. Reception of a BPDU by a PortFast Layer 2 LAN interface signals an invalid configuration, such as connection of an unauthorized device. BPDU Guard provides a secure response to invalid configurations, because the administrator must manually put the Layer 2 LAN interface back in service. BPDU Guard can be configured at the interface level. When configured at the interface level, BPDU Guard shuts the port down as soon as the port receives a BPDU, regardless of the PortFast configuration.

Note ![]() When enabled globally, BPDU Guard applies to all interfaces that are in an operational PortFast (edge) state.
When enabled globally, BPDU Guard applies to all interfaces that are in an operational PortFast (edge) state.
Understanding PortFast BPDU Filtering
PortFast BPDU filtering allows the administrator to prevent the system from sending or even receiving BPDUs on specified ports.

Note ![]() Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI, PortFast BPDU Filtering is known as PortFast Edge BPDU Filtering.
Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI, PortFast BPDU Filtering is known as PortFast Edge BPDU Filtering.
When configured globally, PortFast BPDU filtering applies to all operational PortFast (edge) ports. Ports in an operational PortFast state are supposed to be connected to hosts, which typically drop BPDUs. If an operational PortFast port receives a BPDU, it immediately loses its operational PortFast status and becomes a normal port. In that case, PortFast BPDU filtering is disabled on this port and STP resumes sending BPDUs on this port.
PortFast BPDU filtering can also be configured on a per-port basis. When PortFast BPDU filtering is explicitly configured on a port, it does not send any BPDUs and drops all BPDUs it receives.

When you enable PortFast BPDU filtering globally and set the port configuration as the default for PortFast BPDU filtering (see the "Enabling PortFast BPDU Filtering" section), then PortFast enables or disables PortFast BPDU filtering.
If the port configuration is not set to default, then the PortFast configuration will not affect PortFast BPDU filtering. Table 29-1 lists all the possible PortFast BPDU filtering combinations. PortFast BPDU filtering allows access ports to move directly to the forwarding state as soon as the end hosts are connected.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Default |
Enable |
Enable |
Enable1 |
Default |
Enable |
Disable |
Disable |
Default |
Disable |
Not applicable |
Disable |
Disable |
Not applicable |
Not applicable |
Disable |
Enable |
Not applicable |
Not applicable |
Enable |
1 The port transmits at least 10 BPDUs. If this port receives any BPDUs, then PortFast and PortFast BPDU filtering are disabled. |
Understanding UplinkFast
UplinkFast provides fast convergence after a direct link failure and achieves load balancing between redundant Layer 2 links using uplink groups. An uplink group is a set of Layer 2 LAN interfaces (per VLAN), only one of which is forwarding at any given time. Specifically, an uplink group consists of the root port (which is forwarding) and a set of blocked ports, except for self-looping ports. The uplink group provides an alternate path in case the currently forwarding link fails.

Note ![]() UplinkFast is most useful in wiring-closet switches. This feature may not be useful for other types of applications.
UplinkFast is most useful in wiring-closet switches. This feature may not be useful for other types of applications.
Figure 29-5 shows an example topology with no link failures. Switch A, the root bridge, is connected directly to Switch B over link L1 and to Switch C over link L2. The Layer 2 LAN interface on Switch C that is connected directly to Switch B is in the blocking state.
Figure 29-5 UplinkFast Example Before Direct Link Failure
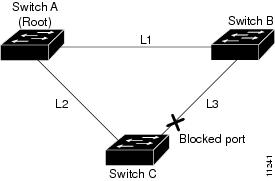
If Switch C detects a link failure on the currently active link L2 on the root port (a direct link failure), UplinkFast unblocks the blocked port on Switch C and transitions it to the forwarding state without going through the listening and learning states, as shown in Figure 29-6. This switchover takes approximately one to five seconds.
Figure 29-6 UplinkFast Example After Direct Link Failure
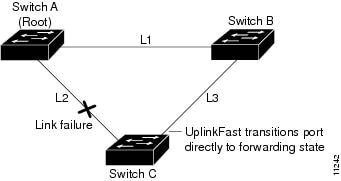
Understanding BackboneFast
BackboneFast is initiated when a root port or blocked port on a network device receives inferior BPDUs from its designated bridge. An inferior BPDU identifies one network device as both the root bridge and the designated bridge. When a network device receives an inferior BPDU, it indicates that a link to which the network device is not directly connected (an indirect link) has failed (that is, the designated bridge has lost its connection to the root bridge). Under normal STP rules, the network device ignores inferior BPDUs for the configured maximum aging time, as specified by the STP max-age command.
The network device tries to determine if it has an alternate path to the root bridge. If the inferior BPDU arrives on a blocked port, the root port and other blocked ports on the network device become alternate paths to the root bridge. (Self-looped ports are not considered alternate paths to the root bridge.) If the inferior BPDU arrives on the root port, all blocked ports become alternate paths to the root bridge. If the inferior BPDU arrives on the root port and there are no blocked ports, the network device assumes that it has lost connectivity to the root bridge, causes the maximum aging time on the root to expire, and becomes the root bridge according to normal STP rules.
If the network device has alternate paths to the root bridge, it uses these alternate paths to transmit a new kind of Protocol Data Unit (PDU) called the Root Link Query PDU. The network device sends the Root Link Query PDU out all alternate paths to the root bridge. If the network device determines that it still has an alternate path to the root, it causes the maximum aging time to expire on the ports on which it received the inferior BPDU. If all the alternate paths to the root bridge indicate that the network device has lost connectivity to the root bridge, the network device causes the maximum aging times on the ports on which it received an inferior BPDU to expire. If one or more alternate paths can still connect to the root bridge, the network device makes all ports on which it received an inferior BPDU its designated ports and moves them out of the blocking state (if they were in the blocking state), through the listening and learning states, and into the forwarding state.
Figure 29-7 shows an example topology with no link failures. Switch A, the root bridge, connects directly to Switch B over link L1 and to Switch C over link L2. The Layer 2 LAN interface on Switch C that connects directly to Switch B is in the blocking state.
Figure 29-7 BackboneFast Example Before Indirect Link Failure

If link L1 fails, Switch C cannot detect this failure because it is not connected directly to link L1. However, because Switch B is directly connected to the root bridge over L1, it detects the failure and elects itself the root and begins sending BPDUs to Switch C indicating itself as the root. When Switch C receives the inferior BPDUs from Switch B, Switch C infers that an indirect failure has occurred. At that point, BackboneFast allows the blocked port on Switch C to move immediately to the listening state without waiting for the maximum aging time for the port to expire. BackboneFast then transitions the Layer 2 LAN interface on Switch C to the forwarding state, providing a path from Switch B to Switch A. This switchover takes approximately 30 seconds, twice the Forward Delay time if the default Forward Delay time of 15 seconds is set. Figure 29-8 shows how BackboneFast reconfigures the topology to account for the failure of link L1.
Figure 29-8 BackboneFast Example After Indirect Link Failure
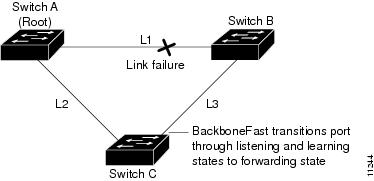
If a new network device is introduced into a shared-medium topology as shown in Figure 29-9, BackboneFast is not activated because the inferior BPDUs did not come from the recognized designated bridge (Switch B). The new network device begins sending inferior BPDUs that indicate that it is the root bridge. However, the other network devices ignore these inferior BPDUs and the new network device learns that Switch B is the designated bridge to Switch A, the root bridge.
Figure 29-9 Adding a Network Device in a Shared-Medium Topology
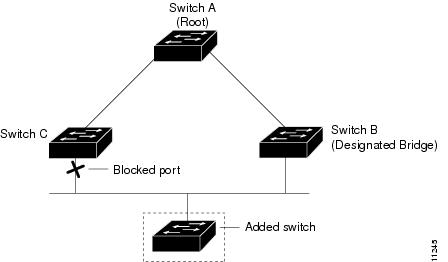
Understanding EtherChannel Guard
EtherChannel guard detects a misconfigured EtherChannel when interfaces on the switch are configured as an EtherChannel while interfaces on the other device are not or when not all the interfaces on the other device are in the same EtherChannel.
In response to misconfiguration detected on the other device, EtherChannel guard puts interfaces on the switch into the errdisabled state.
Understanding Root Guard
The STP root guard feature prevents a port from becoming root port or blocked port. If a port configured for root guard receives a superior BPDU, the port immediately goes to the root-inconsistent (blocked) state.
Understanding Loop Guard
Loop guard helps prevent bridging loops that could occur because of a unidirectional link failure on a point-to-point link. When enabled globally, the loop guard applies to all point-to-point ports on the system. Loop guard detects root ports and blocked ports and ensures that they keep receiving BPDUs from their designated port on the segment. If a loop guard enabled root or blocked port stop a receiving BPDUs from its designated port, it transitions to the loop-inconsistent blocking state, assuming there is a physical link error on this port. The port recovers from this loop-inconsistent state as soon as it receives a BPDU.
You can enable loop guard on a per-port basis. When you enable loop guard, it is automatically applied to all of the active instances or VLANs to which that port belongs. When you disable loop guard, it is disabled for the specified ports. Disabling loop guard moves all loop-inconsistent ports to the listening state.
If you enable loop guard on a channel and the first link becomes unidirectional, loop guard blocks the entire channel until the affected port is removed from the channel. Figure 29-10 shows loop guard in a triangle switch configuration.
Figure 29-10 Triangle Switch Configuration with Loop Guard
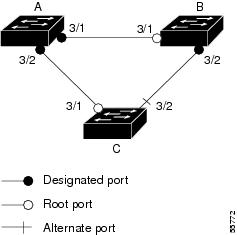
Figure 29-10 illustrates the following configuration:
•![]() Switches A and B are distribution switches.
Switches A and B are distribution switches.
•![]() Switch C is an access switch.
Switch C is an access switch.
•![]() Loop guard is enabled on ports 3/1 and 3/2 on Switches A, B, and C.
Loop guard is enabled on ports 3/1 and 3/2 on Switches A, B, and C.
Enabling loop guard on a root switch has no effect but provides protection when a root switch becomes a nonroot switch.
When using loop guard, follow these guidelines:
•![]() You cannot enable loop guard on PortFast-enabled ports.
You cannot enable loop guard on PortFast-enabled ports.
•![]() You cannot enable loop guard if root guard is enabled.
You cannot enable loop guard if root guard is enabled.
Loop guard interacts with other features as follows:
•![]() Loop guard does not affect the functionality of UplinkFast or BackboneFast.
Loop guard does not affect the functionality of UplinkFast or BackboneFast.
•![]() Enabling loop guard on ports that are not connected to a point-to-point link will not work.
Enabling loop guard on ports that are not connected to a point-to-point link will not work.
•![]() Root guard forces a port to be always designated as the root port. Loop guard is effective only if the port is a root port or an alternate port. You cannot enable loop guard and root guard on a port at the same time.
Root guard forces a port to be always designated as the root port. Loop guard is effective only if the port is a root port or an alternate port. You cannot enable loop guard and root guard on a port at the same time.
•![]() Loop guard uses the ports known to spanning tree. Loop guard can take advantage of logical ports provided by the Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP). However, to form a channel, all the physical ports grouped in the channel must have compatible configurations. PAgP enforces uniform configurations of root guard or loop guard on all the physical ports to form a channel.
Loop guard uses the ports known to spanning tree. Loop guard can take advantage of logical ports provided by the Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP). However, to form a channel, all the physical ports grouped in the channel must have compatible configurations. PAgP enforces uniform configurations of root guard or loop guard on all the physical ports to form a channel.
These caveats apply to loop guard:
–![]() Spanning tree always chooses the first operational port in the channel to send the BPDUs. If that link becomes unidirectional, loop guard blocks the channel, even if other links in the channel are functioning properly.
Spanning tree always chooses the first operational port in the channel to send the BPDUs. If that link becomes unidirectional, loop guard blocks the channel, even if other links in the channel are functioning properly.
–![]() If a set of ports that are already blocked by loop guard are grouped together to form a channel, spanning tree loses all the state information for those ports and the new channel port may obtain the forwarding state with a designated role.
If a set of ports that are already blocked by loop guard are grouped together to form a channel, spanning tree loses all the state information for those ports and the new channel port may obtain the forwarding state with a designated role.
–![]() If a channel is blocked by loop guard and the channel breaks, spanning tree loses all the state information. The individual physical ports may obtain the forwarding state with the designated role, even if one or more of the links that formed the channel are unidirectional.
If a channel is blocked by loop guard and the channel breaks, spanning tree loses all the state information. The individual physical ports may obtain the forwarding state with the designated role, even if one or more of the links that formed the channel are unidirectional.

Note ![]() You can enable UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD) to help isolate the link failure. A loop may occur until UDLD detects the failure, but loop guard will not be able to detect it.
You can enable UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD) to help isolate the link failure. A loop may occur until UDLD detects the failure, but loop guard will not be able to detect it.
•![]() Loop guard has no effect on a disabled spanning tree instance or a VLAN.
Loop guard has no effect on a disabled spanning tree instance or a VLAN.
Understanding PVST Simulation
MST interoperates with Rapid PVST+ with no need for user configuration. The PVST simulation feature enables this seamless interoperability.

Note ![]() PVST simulation is enabled by default when you enable MST. That is, by default, all interfaces on the device interoperate between MST and Rapid PVST+. The ability to disable PVST simulation is introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI.
PVST simulation is enabled by default when you enable MST. That is, by default, all interfaces on the device interoperate between MST and Rapid PVST+. The ability to disable PVST simulation is introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI.
You may want to control the connection between MST and Rapid PVST+ to protect against accidentally connecting an MST-enabled port to a port enabled to run Rapid PVST+. Because Rapid PVST+ is the default STP mode, you may encounter many Rapid PVST+ connections.
Disabling Rapid PVST+ simulation, which can be done per port or globally for the entire device, moves the MST-enabled port to the PVST peer inconsistent (blocking) state once it detects it is connected to a Rapid PVST+-enabled port. This port remains in the inconsistent state until the port stops receiving Shared Spanning Tree Protocol (SSTP) BPDUs, and then the port resumes the normal STP transition process.
The root bridge for all STP instances must all be in either the MST region or the Rapid PVST+ side. If the root bridge for all STP instances are not on one side or the other, the software moves the port into a PVST simulation-inconsistent state.

Note ![]() We recommend that you put the root bridge for all STP instances in the MST region.
We recommend that you put the root bridge for all STP instances in the MST region.
Configuring the Optional STP Features
This section includes the following topics:
•![]() Enabling PortFast BPDU Filtering
Enabling PortFast BPDU Filtering
Enabling PortFast

Enabling PortFast on a Layer 2 Port
To enable PortFast on a Layer 2 port, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
Router(config)# interface {type1 slot/port} | {port-channel port_channel_number} |
Selects a port to configure. |
Step 2 |
Router(config-if)# no spanning-tree portfast |
Configures the port as a normal port. |
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI and later releases: Router(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast edge [trunk] |
Enables edge behavior on a Layer 2 access port connected to a single workstation or server. The trunk keyword enables edge behavior on a trunk port. |
|
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast network |
Configures the port as a network port. Bridge Assurance, if enabled globally, will be enabled on the port. |
|
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast edge disable |
Disables edge behavior on the port. |
|
Earlier releases: Router(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast [trunk] |
Enables PortFast on a Layer 2 access port connected to a single workstation or server. |
|
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast disable |
Disables edge behavior on the port. Port will behave as a normal port. |
|
Step 3 |
Router(config-if)# end |
Exits configuration mode. |
Step 4 |
Router# show running interface {type1 slot/port} | {port-channel port_channel_number} |
Verifies the configuration. |
1 type = fastethernet, gigabitethernet, or tengigabitethernet |
This example shows how to enable and verify PortFast on Fast Ethernet interface 5/8 in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI and later releases:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface fastethernet 5/8
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast edge
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
Router# show running-config interface fastethernet 5/8
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
interface FastEthernet5/8
no ip address
switchport
switchport access vlan 200
switchport mode access
spanning-tree portfast edge
end
Router#
This example shows how to enable and verify PortFast on Fast Ethernet interface 5/8 in releases earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface fastethernet 5/8
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
Router# show running-config interface fastethernet 5/8
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
interface FastEthernet5/8
no ip address
switchport
switchport access vlan 200
switchport mode access
spanning-tree portfast
end
Router#
Configuring the PortFast Default State
To set and verify the default PortFast configuration, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI and later releases: Router(config)# spanning-tree portfast [edge | network | normal] default |
Configures the default state for all switch access ports to be edge, network, or normal. Bridge Assurance will be enabled on all network access ports by default. |
Earlier releases: Router(config)# [no] spanning-tree portfast default |
Configures the default state for all switch access ports to be edge. Use the no prefix to configure the default state to be normal. |
|
Step 2 |
Router(config-if)# end |
Exits configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
Router# show spanning-tree summary totals |
Verifies the global configuration. |
Step 4 |
Router# show spanning-tree interface {type1 slot/port} detail |
Verifies the effect on a specific port. |
1 type = fastethernet, gigabitethernet, or tengigabitethernet |
This example shows how to configure the default switch access port state to be edge in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI and later releases:
Router# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)# spanning-tree portfast edge default
Router(config)# ^Z
This example shows how to configure the default switch access port state to be edge in releases earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI:
Router# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)# spanning-tree portfast default
Router(config)# ^Z
Enabling Bridge Assurance
Release 12.2(33)SXI and later releases support Bridge Assurance. By default, Bridge Assurance is enabled on all network ports on the switch. Disabling Bridge Assurance causes all configured network ports to behave as normal spanning tree ports. To enable or disable Bridge Assurance globally, perform this task:
|
|
|
|---|---|
Router(config)# spanning-tree bridge assurance |
Enables Bridge Assurance on all network ports on the switch. |
This example shows how to enable PortFast Bridge Assurance on all network ports on the switch, and how to configure a network port:
Router(config)# spanning-tree bridge assurance
Router(config)# interface fastethernet 5/8
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast network
Router(config-if)# ^Z
Enabling PortFast BPDU Filtering
These sections describe how to configure PortFast BPDU filtering.
Enabling PortFast BPDU Filtering Globally
To enable PortFast BPDU filtering globally, perform this task:
BPDU filtering is set to default on each edge port. This example shows how to enable PortFast BPDU filtering on the port and verify the configuration in PVST+ mode:
Router(config)# spanning-tree portfast edge bpdufilter default
Router(config)# ^Z
Router# show spanning-tree summary totals
Root bridge for: Bridge VLAN0025
EtherChannel misconfiguration guard is enabled
Extended system ID is enabled
PortFast Edge BPDU Guard Default is disabled
Portfast Edge BPDU Filter Default is enabled
Portfast Default is edge
Bridge Assurance is enabled
Loopguard is disabled
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
Pathcost method used is long
Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
2 vlans 0 0 0 3 3
Router#
Enabling PortFast BPDU Filtering on a Nontrunking Port
To enable or disable PortFast BPDU filtering on a nontrunking port, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
Router(config)# interface {type1 slot/port} |
Selects the interface to configure. |
Step 2 |
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree bpdufilter [enable | disable] |
Enables or disables BPDU filtering on the port. |
Step 3 |
Router(config-if)# end |
Exits configuration mode. |
Step 4 |
Router# show spanning-tree interface {type slot/port} |
Verifies the configuration. |
1 type = fastethernet, gigabitethernet, or tengigabitethernet |
This example shows how to enable PortFast BPDU filtering on a nontrunking port:
Router(config)# interface fastEthernet 4/4
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree bpdufilter enable
Router(config-if)# ^Z
Router# show spanning-tree interface fastEthernet 4/4
Vlan Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Status
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
VLAN0010 Desg FWD 1000 160.196 Edge P2p
Router# show spanning-tree interface fastEthernet 4/4 detail
Port 196 (FastEthernet4/4) of VLAN0010 is forwarding
Port path cost 1000, Port priority 160, Port Identifier 160.196.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 00d0.00b8.140a
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 00d0.00b8.140a
Designated port id is 160.196, designated path cost 0
Timers:message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state:1
The port is in the portfast mode by portfast trunk configuration
Link type is point-to-point by default
Bpdu filter is enabled
BPDU:sent 0, received 0
Router#
Enabling BPDU Guard
These sections describe how to enable BPDU Guard:
•![]() Enabling BPDU Guard on a Port
Enabling BPDU Guard on a Port
Enabling BPDU Guard Globally
To enable BPDU Guard globally, perform this task:
This example shows how to enable BPDU Guard:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# spanning-tree portfast edge bpduguard default
Router(config)# end
Router#
This example shows how to verify the configuration:
Router# show spanning-tree summary totals
Root bridge for: Bridge VLAN0025
EtherChannel misconfiguration guard is enabled
Extended system ID is enabled
PortFast Edge BPDU Guard Default is enabled
Portfast Edge BPDU Filter Default is disabled
Portfast Default is edge
Bridge Assurance is enabled
Loopguard is disabled
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
Pathcost method used is long
Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
2 vlans 0 0 0 3 3
Router#
Enabling BPDU Guard on a Port
To enable BPDU Guard on a port, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
Router(config)# interface {type1 slot/port} | {port-channel port_channel_number} |
Selects a port to configure. |
Step 2 |
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable |
Enables BPDU Guard on the port. |
Step 3 |
Router(config-if)# end |
Exits configuration mode. |
Step 4 |
Router# show spanning-tree Router# show running interface {type1 slot/port} | {port-channel port_channel_number} |
Verifies the configuration. |
1 type = fastethernet, gigabitethernet, or tengigabitethernet |
This example shows how to enable BPDU Guard:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# spanning-tree portfast edge bpduguard default
Router(config)# end
Router#
Enabling UplinkFast
UplinkFast increases the bridge priority to 49152 and adds 3000 to the STP port cost of all Layer 2 LAN ports on the switch, decreasing the probability that the switch will become the root bridge. UplinkFast cannot be enabled on VLANs that have been configured for bridge priority. To enable UplinkFast on a VLAN with bridge priority configured, restore the bridge priority on the VLAN to the default value by entering a no spanning-tree vlan vlan_ID priority command in global configuration mode.

Note ![]() When you enable UplinkFast, it affects all VLANs on the switch. You cannot configure UplinkFast on an individual VLAN.
When you enable UplinkFast, it affects all VLANs on the switch. You cannot configure UplinkFast on an individual VLAN.
To enable UplinkFast, perform this task:
This example shows how to enable UplinkFast:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# spanning-tree uplinkfast
Router(config)# exit
Router#
This example shows how to enable UplinkFast with an update rate of 400 packets per second:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# spanning-tree uplinkfast
Router(config)# spanning-tree uplinkfast max-update-rate 400
Router(config)# exit
Router#
This example shows how to verify that UplinkFast is enabled:
Router# show spanning-tree uplinkfast
UplinkFast is enabled
Router#
Enabling BackboneFast

Note ![]() BackboneFast operates correctly only when enabled on all network devices in the network. BackboneFast is not supported on Token Ring VLANs. This feature is supported for use with third-party network devices.
BackboneFast operates correctly only when enabled on all network devices in the network. BackboneFast is not supported on Token Ring VLANs. This feature is supported for use with third-party network devices.
To enable BackboneFast, perform this task:
This example shows how to enable BackboneFast:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# spanning-tree backbonefast
Router(config)# end
Router#
This example shows how to verify that BackboneFast is enabled:
Router# show spanning-tree backbonefast
BackboneFast is enabled
BackboneFast statistics
-----------------------
Number of transition via backboneFast (all VLANs) : 0
Number of inferior BPDUs received (all VLANs) : 0
Number of RLQ request PDUs received (all VLANs) : 0
Number of RLQ response PDUs received (all VLANs) : 0
Number of RLQ request PDUs sent (all VLANs) : 0
Number of RLQ response PDUs sent (all VLANs) : 0
Router#
Enabling EtherChannel Guard
To enable EtherChannel guard, perform this task:
This example shows how to enable EtherChannel guard:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# spanning-tree etherchannel guard misconfig
Router(config)# end
Router#
This example shows how to verify the configuration:
Router# show spanning-tree summary | include EtherChannel
EtherChannel misconfiguration guard is enabled
To display the interfaces that are in the errdisable state, enter the show interface status err-disable command.
After the misconfiguration has been cleared, interfaces in the errdisable state might automatically recover. To manually return a port to service, enter a shutdown and then a no shutdown command for the interface.
Enabling Root Guard
To enable root guard, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
Router(config)# interface {type1 slot/port} | {port-channel port_channel_number} |
Selects a port to configure. |
Step 2 |
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree guard root |
Enables root guard. |
Step 3 |
Router(config-if)# end |
Exits configuration mode. |
Step 4 |
Router# show spanning-tree Router# show running interface {type1 slot/port} | {port-channel port_channel_number} |
Verifies the configuration. |
1 type = fastethernet, gigabitethernet, or tengigabitethernet |
To display ports that are in the root-inconsistent state, enter the show spanning-tree inconsistentports command.
Enabling Loop Guard
To enable loop guard globally on the switch, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
Router(config)# spanning-tree loopguard default |
Enables loop guard globally on the switch. |
Step 2 |
Router(config)# end |
Exits configuration mode. |
Step 3 |
Router# show spanning-tree interface {type1 slot/port} detail |
Verifies the configuration impact on a port. |
1 type = fastethernet, gigabitethernet, or tengigabitethernet |
This example shows how to enable loop guard globally:
Router# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)# spanning-tree loopguard default
Router(config)# ^Z
Router# show spanning-tree interface fastEthernet 4/4 detail
Port 196 (FastEthernet4/4) of VLAN0010 is forwarding
Port path cost 1000, Port priority 160, Port Identifier 160.196.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 00d0.00b8.140a
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 00d0.00b8.140a
Designated port id is 160.196, designated path cost 0
Timers:message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state:1
The port is in the portfast mode by portfast trunk configuration
Link type is point-to-point by default
Bpdu filter is enabled
Loop guard is enabled by default on the port
BPDU:sent 0, received 0
To enable loop guard on a port, perform this task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
Router(config)# interface {type1 slot/port} | {port-channel port_channel_number} |
Selects a port to configure. |
Step 2 |
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree guard loop |
Configures loop guard. |
Step 3 |
Router(config)# end |
Exits configuration mode. |
Step 4 |
Router# show spanning-tree interface {type slot/port} detail |
Verifies the configuration impact on that port. |
1 type = fastethernet, gigabitethernet, or tengigabitethernet |
This example shows how to enable loop guard:
Router# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)# interface fastEthernet 4/4
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree guard loop
Router(config-if)# ^Z
This example shows how to verify the configuration:
Router# show spanning-tree interface fastEthernet 4/4 detail
Port 196 (FastEthernet4/4) of VLAN0010 is forwarding
Port path cost 1000, Port priority 160, Port Identifier 160.196.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 00d0.00b8.140a
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 00d0.00b8.140a
Designated port id is 160.196, designated path cost 0
Timers:message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state:1
The port is in the portfast mode by portfast trunk configuration
Link type is point-to-point by default
Bpdu filter is enabled
Loop guard is enabled on the port
BPDU:sent 0, received 0
Router#
Configuring PVST Simulation

Note ![]() PVST simulation is enabled by default so that all interfaces on the device interoperate between MST and Rapid PVST+. The ability to disable PVST simulation is introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI.
PVST simulation is enabled by default so that all interfaces on the device interoperate between MST and Rapid PVST+. The ability to disable PVST simulation is introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI.
To prevent an accidental connection to a device that does not run MST as the default STP mode, you can disable PVST simulation. If you disable PVST simulation, the MST-enabled port moves to the blocking state once it detects it is connected to a Rapid PVST+-enabled port. This port remains in the inconsistent state until the port stops receiving BPDUs, and then the port resumes the normal STP transition process.
To enable or disable PVST simulation globally, enter the command using the global keyword, as shown in the following task:
To override the global PVST simulation setting for a port, enter the command in the interface command mode, as shown in the following task:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
Router(config)# interface {type1 slot/port} |
Selects a port to configure. |
Step 2 |
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree mst simulate pvst |
Enables this interface to automatically interoperate with a connected device that is running in Rapid PVST+ mode. |
1 type = fastethernet, gigabitethernet, or tengigabitethernet |
This example shows how to prevent the switch from automatically interoperating with a connecting device that is running Rapid PVST+:
Router(config)# no spanning-tree mst simulate pvst global
This example shows how to prevent a port from automatically interoperating with a connecting device that is running Rapid PVST+:
Router(config)# interface gi3/13
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree mst simulate pvst disable
Verifying the Optional STP Features
This section includes the following topics:
•![]() Using the show spanning-tree Commands
Using the show spanning-tree Commands
•![]() Examples in Release 12.2(33)SXI and Later Releases
Examples in Release 12.2(33)SXI and Later Releases
•![]() Examples in Releases Earlier Than Release 12.2(33)SXI
Examples in Releases Earlier Than Release 12.2(33)SXI
Using the show spanning-tree Commands
You can view spanning tree status and configuration information, both global and port-level, using the show spanning-tree commands described in this section.
To view spanning tree status and configuration information, perform one of the following tasks:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Router# show spanning-tree |
Displays information about the spanning tree, including protocol type and port types. |
|
Router# show spanning-tree summary |
Displays a summary of the spanning tree feature settings and the spanning tree states of the VLANs. |
|
Router# show spanning-tree summary totals |
Displays a summary of the spanning tree feature settings and totals of the VLAN states. |
|
Router# show spanning-tree interface {type1 slot/port} detail |
Displays the spanning tree status details of an interface. |
|
Router# show spanning-tree interface {type1 slot/port} portfast edge |
Displays the spanning tree portfast edge interface operational state for all the instances. In releases earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI, the edge keyword is not used. |
1 type = fastethernet, gigabitethernet, or tengigabitethernet |
Examples in Release 12.2(33)SXI and Later Releases

Note ![]() The output of the show spanning-tree commands in releases earlier than Release 12.2(33)SXI differs from the output in Release 12.2(33)SXI and later releases. The differences are shown in bold in the examples in this section.
The output of the show spanning-tree commands in releases earlier than Release 12.2(33)SXI differs from the output in Release 12.2(33)SXI and later releases. The differences are shown in bold in the examples in this section.
This example displays the spanning-tree status with Bridge Assurance enabled but in the inconsistent state:
Router# show spanning-tree
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Priority 32778
Address 0002.172c.f400
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 0002.172c.f400
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi3/14 Desg BKN*4 128.270 Network, P2p *BA_Inc
Router#
The following inconsistency messages can be appended to the Type field:
•![]() *BA_Inc—Indicates that Bridge Assurance is in the inconsistent state.
*BA_Inc—Indicates that Bridge Assurance is in the inconsistent state.
•![]() *PVST_Peer_Inc—Indicates that the port is in a peer type Inconsistent state.
*PVST_Peer_Inc—Indicates that the port is in a peer type Inconsistent state.
•![]() Dispute—Indicates that a dispute condition is detected.
Dispute—Indicates that a dispute condition is detected.
This example shows the spanning-tree configuration summary:
Router# show spanning-tree summary
Switch is in rapid-pvst mode
Root bridge for: Bridge VLAN0025
EtherChannel misconfiguration guard is enabled
Extended system ID is enabled
PortFast Edge BPDU Guard Default is disabled
Portfast Edge BPDU Filter Default is disabled
Portfast Default is edge
Bridge Assurance is enabled
Loopguard is disabled
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
Pathcost method used is short
PVST Simulation Default is enabled
Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
VLAN0025 0 0 0 1 1
VLAN0030 0 0 0 2 2
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
2 vlans 0 0 0 3 3
Router#
Possible states for the Bridge Assurance field are as follows:
•![]() is enabled
is enabled
•![]() is disabled
is disabled
•![]() is enabled but not active in the PVST mode
is enabled but not active in the PVST mode
This example shows the spanning tree summary when PVST simulation is disabled in any STP mode:
Router# show spanning-tree summary
Switch is in mst mode (IEEE Standard)
Root bridge for: MST0
EtherChannel misconfig guard is enabled
Extended system ID is enabled
Portfast Default is disabled
PortFast BPDU Guard Default is disabled
Portfast BPDU Filter Default is disabled
Loopguard Default is disabled
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
Pathcost method used is long
PVST Simulation Default is disabled
Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
MST0 2 0 0 0 2
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
1 mst 2 0 0 0 2
Possible states for the PVST Simulation Default field are as follows:
•![]() is enabled
is enabled
•![]() is disabled
is disabled
•![]() is enabled but not active in rapid-PVST mode
is enabled but not active in rapid-PVST mode
This example shows the spanning tree summary totals:
Router# show spanning-tree summary totals
Root bridge for: Bridge VLAN0025
EtherChannel misconfiguration guard is enabled
Extended system ID is enabled
PortFast Edge BPDU Guard Default is enabled
Portfast Edge BPDU Filter Default is disabled
Portfast Default is edge
Bridge Assurance is enabled
Loopguard is disabled
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
Pathcost method used is long
Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
2 vlans 0 0 0 3 3
Router#
This example shows the spanning-tree configuration details of an edge port:
Router# show spanning-tree interface gi3/13 detail
Port 269 (GigabitEthernet3/13) of VLAN0002 is forwarding
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.269.
Designated root has priority 32770, address 0002.172c.f400
Designated bridge has priority 32770, address 0002.172c.f400
Designated port id is 128.269, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
Loop guard is enabled by default on the port
The port is in the portfast edge mode by default
BPDU: sent 2183, received 0
This example shows the spanning-tree configuration details of a trunk port:
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast edge trunk
%Warning:portfast should only be enabled on ports connected to a single
host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc... to this
interface when portfast is enabled, can cause temporary bridging loops.
Use with CAUTION
Router(config-if)# ^Z
Router# show spanning-tree interface gi3/13 detail
Port 269 (GigabitEthernet3/13) of VLAN0002 is forwarding
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.269.
Designated root has priority 32770, address 0002.172c.f400
Designated bridge has priority 32770, address 0002.172c.f400
Designated port id is 128.269, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
Loop guard is enabled by default on the port
The port is in the portfast edge trunk mode
BPDU: sent 2183, received 0
Router#
This example shows the spanning-tree configuration details of an edge port when a dispute condition has been detected:
Router# show spanning-tree interface gi3/13 detail
Port 269 (GigabitEthernet3/13) of VLAN0002 is designated blocking (dispute)
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.297.
Designated root has priority 32769, address 0013.5f20.01c0
Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 0013.5f20.01c0
Designated port id is 128.297, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU: sent 132, received 1
Router#
This example shows the spanning tree portfast edge interface operational state for all the instances:
Router# show spanning-tree interface gi3/1 portfast edge
MST0 disabled
MST1 disabled
Examples in Releases Earlier Than Release 12.2(33)SXI

Note ![]() The output of the show spanning-tree commands in releases earlier than Release 12.2(33)SXI differs from the output in Release 12.2(33)SXI and later releases. The differences are shown in bold in the examples in this section.
The output of the show spanning-tree commands in releases earlier than Release 12.2(33)SXI differs from the output in Release 12.2(33)SXI and later releases. The differences are shown in bold in the examples in this section.
This example displays the spanning-tree status:
Router# show spanning-tree
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Priority 32778
Address 0002.172c.f400
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 0002.172c.f400
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi3/14 Desg FWD 4 128.270 Edge, P2p
Router#
This example shows the spanning-tree configuration summary:
Router# show spanning-tree summary
Switch is in rapid-pvst mode
Root bridge for:VLAN0010
EtherChannel misconfiguration guard is enabled
Extended system ID is disabled
Portfast is enabled by default
PortFast BPDU Guard is disabled by default
Portfast BPDU Filter is disabled by default
Loopguard is disabled by default
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
Pathcost method used is long
Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
VLAN0001 0 0 0 1 1
VLAN0010 0 0 0 2 2
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
2 vlans 0 0 0 3 3
Router#
This example shows the spanning-tree configuration summary totals:
Router# show spanning-tree summary totals
Switch is in rapid-pvst mode
Root bridge for:VLAN0010
EtherChannel misconfiguration guard is enabled
Extended system ID is disabled
Portfast is enabled by default
PortFast BPDU Guard is disabled by default
Portfast BPDU Filter is disabled by default
Loopguard is disabled by default
UplinkFast is disabled
BackboneFast is disabled
Pathcost method used is long
Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active
---------------------- -------- --------- -------- ---------- ----------
2 vlans 0 0 0 3 3
Router#
This example shows the spanning-tree configuration details of an edge port:
Router# show spanning-tree interface fastEthernet 4/4 detail
Port 196 (FastEthernet4/4) of VLAN0010 is forwarding
Port path cost 1000, Port priority 160, Port Identifier 160.196.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 00d0.00b8.140a
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 00d0.00b8.140a
Designated port id is 160.196, designated path cost 0
Timers:message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state:1
The port is in the portfast mode by default
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU:sent 10, received 0
This example shows the spanning-tree configuration details of a trunk port:
Router(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast trunk
%Warning:portfast should only be enabled on ports connected to a single
host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc... to this
interface when portfast is enabled, can cause temporary bridging loops.
Use with CAUTION
Router(config-if)# ^Z
Router# show spanning-tree interface fastEthernet 4/4 detail
Port 196 (FastEthernet4/4) of VLAN0010 is forwarding
Port path cost 1000, Port priority 160, Port Identifier 160.196.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 00d0.00b8.140a
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 00d0.00b8.140a
Designated port id is 160.196, designated path cost 0
Timers:message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state:1
The port is in the portfast mode by portfast trunk configuration
Link type is point-to-point by default
BPDU:sent 30, received 0
Router#
This example shows the spanning tree portfast interface operational state for all the instances:
Router# show spanning-tree interface gi3/1 portfast
MST0 disabled
MST1 disabled

Tip ![]() For additional information about Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches (including configuration examples and troubleshooting information), see the documents listed on this page:
For additional information about Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches (including configuration examples and troubleshooting information), see the documents listed on this page:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps708/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Participate in the Technical Documentation Ideas forum
 Feedback
Feedback