Integrating Cisco Unity Express with Cisco CallManager Express 3.0 and Later
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Integrating Cisco CallManager Express and Cisco Unity Express
Prerequisites for Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
Restrictions for Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
Information About Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
How to Integrate Cisco with Cisco Unity Express
Configuring Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express for Calls Between IP Phones on the Same Router
Configuring Interfaces and a Static Route
Verifying Interfaces and Static Routes
Configuring Dial Peers for Cisco CME Phones to Call Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail
Configuring Cisco CME V3.2 and Higher for WAN H.323 Calls to Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail
Configuring Cisco CME Versions 3.0 and 3.1 for WAN H.323 Calls to Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail
Number of Loopback Ephone-dns Needed
Loopback Ephone-dn Interaction
Configuration Examples for Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
Single Router Configuration: Example
WAN H.323 Configuration for Cisco CME Versions 3.2 and Higher: Example
WAN H.323 Configuration for Cisco CME Versions 3.0 and 3.1: Example
Integrating Cisco CallManager Express and Cisco Unity Express
This document describes how to configure Cisco CallManager Express (CME) versions 3.0 and higher with Cisco Unity Express to work together to provide voice mail. In this document are configuration instructions for allowing voice mail between IP phones on the same router and from different sites over WAN H.323.
This document contains integration configuration instructions only. Information about configuring Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express is located in the system administrator guides in the Cisco CME index at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/ip_ph/ip_ks/index.htm and in the Cisco Unity Express index at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/unityexp/index.htm.
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Cisco CME is Cisco IOS software based. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.

Note
Cisco Unity Express is not Cisco IOS software based. For support and download information regarding Cisco Unity Express, go to the Software Center website at http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/sw-voice.shtml.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
•
Restrictions for Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
•
Information About Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
•
How to Integrate Cisco with Cisco Unity Express
•
Configuration Examples for Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
Prerequisites for Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
•
You must run versions of Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express that are compatible. For compatibility information, see Table 1, where "yes" indicates versions of Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express that are compatible.
•
Cisco Unity Express must be installed on each Cisco CME host router. Cisco Unity Express cannot provide voice-mail services across Cisco CME routers. For Cisco Unity Express installation instructions, refer to the system administrator guides in the Cisco Unity Express index.
•
You must be able to place calls between phones on the same router using H.323. For more information about configuration, go to the Cisco CallManager Express index and click the desired Cisco CME version and System Administrator Guide.
•
Cisco Unity Express must be installed and configured. For more information, go to the Cisco Unity Express index and click the desired Cisco Unity Express version and System Administrator Guide.
•
Cisco Unity Express and Cisco CME's user interfaces must be enabled. The Cisco Unity Express interface is enabled during installation when an administrator name and password are created. The Cisco CME interface can be enabled anytime after Cisco CME installation. For instructions on how to enable the Cisco CME interface, go to the Cisco CallManager Express index and click the desired Cisco CME version > System Administrator Guide > Setting Up the Cisco CME GUI > Setting Up GUI Access for the System Administrator. Perform the steps in the "Setting up the HTTP Server" and "Setting Up GUI Access for the System Administrator" sections.
The following example configuration enables the Cisco CME interface:
ip http serverip http path flash:telephony-serviceweb admin system name test password testdn-webedittime-webedit
Note
Cisco CME interface files must be installed in the router's flash memory.
Restrictions for Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
•
Ephone-dns used for loopback cannot be dual-line ephone-dns.
•
Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express do not support central call processing.
•
Cisco Unity Express cannot provide voice-mail services across Cisco CME routers. Cisco Unity Express can provide voice mail services only for phones on its host Cisco CME router.
•
Cisco CME 3.2 released in Cisco IOS Software 12.3(8)T and 12.3(11)T and running on Cisco 1760 with T1 modules should not use the Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express GUIs. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios123/123relnt/xprn123t/123tnewf.htm#wp1799702.
Information About Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
To configure Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express for WAN H.323 calls, you should understand the following:
Features
Cisco Unity Express voice mail on Cisco CME routers provides the following features:
•
Call forward to personal greeting—When an incoming call is routed to an unanswered or busy extension, the call is forwarded to the voice mail of the subscriber. The caller then hears the personal greeting of the subscriber and can leave a message.
•
Easy message access—A subscriber can retrieve messages without entering a user ID. Cisco Unity Express identifies a subscriber by the extension from which the call originated. A password may be required.
•
Identified subscriber messaging—Using the extension from which the call originated, Cisco Unity Express automatically identifies the sending subscriber who leaves a message during a forwarded internal call.
•
Message waiting indication—When a message is waiting for a subscriber, Cisco Unity Express notifies the Cisco CME system to activate the message-waiting indicator (MWI) on the subscriber extension.
•
Cisco Unity Express support of up to eight voice ports.
Configuration
Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express voice mail can be configured for one site with a single router or for multiple sites with one router per site and WAN H.323 links between sites. Voice-mail features are available for IP phones using the same router and for remote WAN H.323 calls. Each router supports voice mail for its IP phones only, so each Cisco CME router must have Cisco Unity Express configured. As shown in Figure 1, Cisco Unity Express supports local and WAN H.323 calls. If a call is busy or is not answered, the call is sent to voice mail on the called number's router.
Figure 1 Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail Support for Local and WAN H.323 Calls

It is not necessary to make fundamental changes to your existing Cisco CME configuration. The required voice-mail configuration elements include the following:
•
For voice mail between IP phones on the same router:
–
The Cisco Unity Express module must communicate with the host Cisco CME router.
–
If an internal call is busy or unanswered, the ephone-dn must forward it to a voice-mail pilot or access number.
–
Message-waiting indicator (MWI) ephone-dns must be defined.
•
For voice mail between phones on different gateways (H.323):
–
The above criteria for voice mail between IP phones on the same router must be met.
–
Each router must be configured so WAN H.323 calls will route through loopback ephone-dns directly.
Administration
Voice-mail system administration tasks may be performed by using the Cisco Unity Express interface. After voice mail has been configured, Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express interfaces will share the same information about phones, extensions, and system parameters. Integration configuration will not change the interfaces' usage.
Loopback Ephone-dns

Note
Loopback ephone-dns are required for integrating Cisco Unity Express with Cisco CME versions 3.0 and 3.1. They are not necessary for Cisco CME V3.2 and higher.
Cisco Unity Express uses Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) signals only. When calls on the same router are forwarded to Cisco Unity Express, the calls' dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) tones are automatically presented to Cisco Unity Express as SIP notify messages. For WAN H.323 calls, SIP conversion must take place using loopback ephone-dns, which are ephone-dns configured with the loopback-dn command. For more information about loopback ephone-dns, see the "Configuring Cisco CME Versions 3.0 and 3.1 for WAN H.323 Calls to Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail" section.
How to Integrate Cisco with Cisco Unity Express
Integrating Cisco CME for Cisco Unity Express for WAN H.323 calls involves the following tasks:
•
Configuring Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express for Calls Between IP Phones on the Same Router
•
Configuring Cisco CME V3.2 and Higher for WAN H.323 Calls to Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail
•
Configuring Cisco CME Versions 3.0 and 3.1 for WAN H.323 Calls to Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail
Configuring Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express for Calls Between IP Phones on the Same Router

Note
If your voice mail is working between local phones on your routers, skip this section and go to the "Configuring Cisco CME Versions 3.0 and 3.1 for WAN H.323 Calls to Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail" section.
Configuration is performed using the Cisco CME command-line interface (CLI) and the Cisco Unity Express CLI. You can start with a new Cisco CME configuration or modify an existing one. Integration configuration does not require changes to your existing configuration structure. It involves the add-on configuration described in this section.
Configuring Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express for voice mail on a single router involves enabling communication between the Cisco Unity Express module and the host Cisco CME router, enabling call forwarding from the ephone-dns to a voice-mail pilot number, and enabling message-waiting indicators (MWIs).
To enable communication between the Cisco Unity Express module and the host Cisco CME router, perform the following tasks:
•
Configuring Interfaces and a Static Route
•
Configuring Dial Peers for Cisco CME Phones to Call Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail
To enable call forwarding from ephone-dns to a voice-mail pilot number and to enable MWIs, perform the following tasks:
•
Configuring Voice-Mail Access
Configuring Interfaces and a Static Route
For communication to take place between Cisco Unity Express and Cisco CME, several interfaces must be created. The first is an interface to the router hosting Cisco CME. See the interface fastethernet0/1 command in Figure 2. The second is an interface that links together the Cisco Unity Express and Cisco CME ports and IP addresses. See the interface service-engine0/0 command in Figure 2.

Note
The Cisco Unity Express and Cisco CME must use IP addresses with the same subnet address.
In addition, a static route to the Cisco Unity Express NM or AIM has to be created because Cisco CME cannot build a route dynamically.
Figure 2 Communication Between the Cisco CME Router and Cisco Unity Express
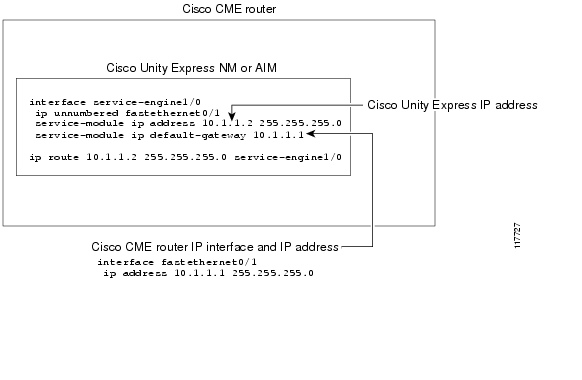
Prerequisites
The following information is required for activating the software:
•
Slot and unit numbers of the Cisco Unity Express module on the Cisco IOS router hosting Cisco Unity Express.
•
IP address and subnet mask of the Cisco IOS router hosting Cisco Unity Express or the unnumbered interface type and number.
•
IP address of the Cisco Unity Express module. This IP address must be on the same subnet as the Cisco IOS router hosting Cisco Unity Express.
•
IP address of the default gateway of the Cisco Unity Express router. This IP address must be the same IP address as the Cisco IOS router hosting Cisco Unity Express.

Note
Use the Cisco Unity Express CLI for configuring the service-engine interface command.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
interface fastethernetslot/interface_subinterface
2.
ip address ip-address mask
3.
exit
4.
interface service-engineslot/interface_subinterface
5.
ip unnumbered fastethernetslot/interface_subinterface
6.
service-module ip address ce-side-ip-addr subnet-mask
7.
service module ip default-gateway gw-ip-addr
8.
exit
9.
ip route ip-address mask service-engineslot/interface_subinterface
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying Interfaces and Static Routes
To verify that interfaces and static routes are configured correctly, perform the following steps:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
show interface service-engine slot/interface_subinterface
2.
service-module service-engine slot/interface_subinterface status
3.
show running interface interface-type slot/interface_subinterface
4.
show ip route ip-address
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
show interface service-engine slot/interface_subinterface
Use this command to make sure that the service-engine interface is in an Up/Up state as shown below. No IP traffic will pass through unless the interface is in this state.
Router# show interface service-engine 1/0Service-Engine1/0 is up, line protocol is upHardware is I82559FE, address is 0008.e35f.6e80 (bia 0008.e35f.6e80)Step 2
service-module service-engine slot/interface_subinterface status
Use this command to make sure that the service-module status is steady state. Cisco IOS software uses Router Blade Control Protocol (RBCP) for IP address communication, and RBCP messages for IP addresses take effect only when the module is in a steady state. If the module is not in a steady state, then, depending on what state the module is in, either wait for Cisco Unity Express to reach a steady state or reload or reset the module.
Router# service-module service-engine 1/0 statusService Module is Cisco Service-Engine1/0Service Module supports session via TTY line 33Service Module is in Steady stateGetting status from the Service Module, please wait..cisco service engine 1.0Step 3
show running interface interface-type slot/interface_subinterface
Use this command to make sure that the IP addresses have been configured for the service-engine interface and Cisco Unity Express. Also, check the IP default gateway for Cisco Unity Express. Use the following show commands to check the IP addresses assigned to Cisco Unity Express. In the example, the IP address for Cisco Unity Express is 10.10.10.2, and the default gateway is 10.10.10.1. Note that the IP address of the service-engine interface is same as that of the Fast Ethernet 0/0 interface.
Router# show running interface service-engine 1/0Building configuration...Current configuration :211 bytesinterface Service-Engine1/0ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0service-module ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0service-module ip default-gateway 10.10.10.1endRouter# show running interface FastEthernet0/0Building configuration...Current configuration :211 bytesinterface FastEthernet0/0ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0duplex autospeed autoendStep 4
show ip route ip-address
If you are using an IP unnumbered scheme of addresses, use the show ip route command to make sure that the host route (/32 mask) has been configured for the IP address assigned to Cisco Unity Express; for example:
Router# show ip route 10.10.10.2Routing entry for 10.10.10.2/32Known via "static", distance 1, metric 0 (connected)Routing Descriptor Blocks:* directly connected, via Service-Engine1/0Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
Troubleshooting Tips
If you can ping Cisco Unity Express from the router itself, but not from outside, check the default gateway for Cisco Unity Express. It should be the IP address of the Cisco CME interface. If this is the case, you can also ping the router hosting Cisco Unity Express.
Configuring Dial Peers for Cisco CME Phones to Call Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail
A dedicated dial peer is required for facilitating communication between Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express. The destination-pattern command under dial peer 1 assigns a set of phone numbers dedicated to applications such as Cisco Unity Express. If no other applications are going to be used, you could set the destination pattern to one number only, such as 2000. Note that the voice-mail pilot number must be within the dial peer's destination-pattern range (see the "Configuring Voice-Mail Access" section), and the ephone-dns must be configured for call forwarding to the voice-mail number (see the "Configuring Voice-Mail Access" section), which triggers the use of the dial peer.
The Cisco Unity Express dial peer must use Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for call sessions and for translating dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) tones into SIP notify messages. A codec must be designated, and voice activity detection (VAD) must be switched off.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
dial-peer voice tag voip
2.
destination-pattern [+] string [T]
3.
session protocol sipv2
4.
session target ipv4:destination-pattern
5.
dtmf-relay sip-notify
6.
no vad
7.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting Tips
Make sure that the voice-mail number has an appropriate SIP dial peer pointing to the correct destination. In the example commands shown in the "Detailed Steps" section above, dial-peer 1's destination pattern of 2... will allow for a voice-mail pilot number between 2000 and 2999. If you are running the auto-attendant and the greeting management system (GMS), they could each use one of dial-peer 1's extension numbers. If they do not use one of these numbers, they must use a new dial peer or separate dial peers, depending on their pilot numbers.
Configuring Voice-Mail Access
Cisco CME configuration must include the creation of a voice-mail pilot number that is within the range of the destination pattern for the dial peer that you just created (see the "Configuring Dial Peers for Cisco CME Phones to Call Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail" section). The voice-mail pilot number is the telephone number that is speed-dialed when the Messages button on a Cisco IP phone is pressed or when a busy or unanswered call is forwarded to voice mail. One voice-mail pilot extension number is configured for voice messaging for all Cisco IP phones connected to the router. In addition, ephone-dns must be configured to forward unanswered or busy calls to the voice-mail number.
SUMMARY STEPS

Note
The commands in the Summary Steps and Detailed Steps sections do not provide all of the ephone-dn configuration elements. For information about how ephone-dns must be configured for IP telephony, go to the Cisco CallManager Express index and click the desired Cisco CME version and then System Administrator Guide > Setting Up Phones > Setting Up Initial Extensions and Phones. You can use the automated, partially automated, or manual procedures described there.
1.
telephony-service
2.
voicemail phone-number
3.
exit
4.
ephone-dn dn-tag
5.
call-forward busy directory-number
6.
call-forward noan directory-number timeout seconds
7.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring MWIs
The MWI mechanism turns on the light indicator on Cisco IP phones and other devices, such as the Cisco ATA-186, to inform the user that a voice-mail message is waiting. The MWI mechanism is initiated after someone leaves a voice-mail message and is turned off after the user listens to voice mail. The internal MWI mechanism of the CME router is explained in Figure 3.

Note
For extensions associated with analog telephone adaptors (ATAs), the message-waiting indication (MWI) is a lit function button on the ATA and a stutter dial tone on the connected analog phone.
Figure 3 MWI Mechanism on a Cisco CME Router Hosting Cisco Unity Express

In the network topology in Figure 3, the following events take place:
1.
The Cisco IP phone with the extension 1001 receives a call, and the call is not answered.
2.
The Cisco IP phone with the extension 1001 forwards the call to voice mail.
3.
The greeting for extension 1001 plays, and a voice-mail message is left.
4.
Cisco Unity Express places an MWI notification call to the MWI processing ephone-dn 8000 and appends 1001 as the calling party ID for the notification call. The number 80001001 is dialed.
5.
Ephone-dn 8000 accepts the MWI notification call and switches on the message-waiting light for extension 1001.
6.
When the phone user at extension 1001 listens to all of the voice mail, Cisco Unity Express places an MWI notification call to ephone-dn 8001 and appends 1001 as the calling party ID. The number 80011001 is dialed.
For these events to occur, the mwi on and mwi off commands are required. MWI status notification calls are processed by dummy ephone-dns, which are ephone-dns that are not used for phone calls. One MWI processing ephone-dn must be allocated to activate MWIs, and another must be allocated to deactivate MWIs.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
ephone-dn dn-tag
2.
number number
3.
mwi {on | off}
4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying MWIs
To verify that MWIs are configured properly, perform the following steps:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
Test MWI.
2.
show telephony-service ephone-dn
3.
show ccn application
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Test MWI.
To test that the MWI ephone-dns are working correctly, dial 8000 plus the extension of a phone near you. The MWI should light on that phone. Next, dial 8001 plus the same phone's extension number. The MWI light should turn off.
Step 2
show telephony-service ephone-dn
Use this Cisco IOS command to make sure that the MWI on and off numbers are followed by trailing dots (.) and that the number of dots is equivalent to the extension length of the system. For example, if the extension length is four digits, the MWI on and off ephone-dns have to use the format "8000...." and "8001....".
Router# show telephony-service ephone-dnephone-dn 30number 8000....mwi onephone-dn 31number 8001....mwi offStep 3
show ccn application
If the MWI on and off ephone-dns' number formats are shown as correct for the show telephony-service ephone-dn output, but MWI still does not work, use Cisco Unity Express's show ccn application command to ensure that the MWI on and off numbers are the same as those configured in Cisco CME.
Router# show ccn applicationName: ciscomwiapplicationDescription: ciscomwiapplicationScript: setmwi.aefID number: 0Enabled: yesMaximum number of sessions: 4strMWI_OFF_DN: 8001strMWI_ON_DN: 8000CallControlGroupID: 0If they do not match, run Cisco Unity Express's interface and go to Administration > Synchronize Information > Synchronize. Then run the show ccn application command again to verify that Cisco CME's and Cisco Unity Express's MWI on and off numbers match.
Troubleshooting Tips
If the MWI ephone-dn numbers match for Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express, and MWI still does not work, do the following:
•
Check the SIP gateway address for Cisco Unity Express and run Cisco Unity Express's show ccn subsystem SIP command. The SIP gateway address should be the same address as the Cisco CME router's. MWI will not work if the Cisco CME router address and the IP address of the SIP subsystem are different. Typically, a default gateway address is used.
•
From Cisco Unity Express, make sure that ciscomwiapplication is enabled. MWI will not work if the application is disabled.
If MWI does not work for a particular ephone-dn, make sure that the ephone-dn has a valid mailbox on the system. The DN must be associated with a user, and the user must have a mailbox on the Cisco Unity Express system. If the DN does have a mailbox, run the Cisco Unity Express mwi refresh telephonenumber command.
Also check that the mailbox has a new voice-mail message over four seconds in length, which is the minimum required for message activation.
Configuring Cisco CME V3.2 and Higher for WAN H.323 Calls to Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail

Note
This section describes how to configure Cisco CME to receive WAN H.323 calls from a WAN interface. You can start with a new Cisco CME configuration or modify an existing one. Integration configuration does not require changes to your existing configuration structure. It requires adding the configuration described in this section.
For Cisco Unity Express, WAN H.323 calls must be converted to SIP. To enable H.323-to-SIP conversion you must use the allow-connections command. A dial peer and translation rule are required too. In addition to the dial peer created in the "Configuring Dial Peers for Cisco CME Phones to Call Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail" section for the voice-mail extension number, a dial peer is required for incoming calls to your voice mail's E.164 number (for example, 4085552000). A translation rule must be created to convert the E.164 call to the voice-mail pilot number (for example, 2000) so the call can be sent to voice mail.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
voice service voip
2.
allow-connections h323 to sip
3.
exit
4.
dial-peer voice tag voip
5.
destination-pattern [+] string [T]
6.
translate-outgoing called name-tag
7.
session protocol sipv2
8.
session target ipv4:destination-pattern
9.
dtmf-relay sip-notify
10.
codec codec
11.
no vad
12.
exit
13.
voip-incoming translation-rule called tag-number
14.
translation-rule tag-number
15.
rule tag-name input-matched-pattern substituted-pattern
16.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Cisco CME Versions 3.0 and 3.1 for WAN H.323 Calls to Cisco Unity Express Voice Mail

Note
This section describes how to configure Cisco CME to receive WAN H.323 calls from a WAN interface. You can start with a new Cisco CME configuration or modify an existing one. Integration configuration does not require changes to your existing configuration structure. It requires adding the configuration described in this section.
For Cisco Unity Express, WAN H.323 calls are forwarded differently from calls from within routers. Instead of being matched to an ephone-dn, WAN H.323 calls must first go to loopback ephone-dns before ringing an extension, so they can be translated into SIP and forwarded to voice mail if the extension is busy or does not answer.
Loopback ephone-dns consist of two ephone-dns. The first loopback ephone-dn terminates the WAN H.323 call and translates it to SIP to allow communication with Cisco Unity Express. The called number is converted from the translation rule number (9408....) to an E.164 number (408....) and forwarded to the second loopback ephone-dn. The second loopback ephone-dn transfers the E.164 number (408....). The dialplan-pattern command truncates the number (4081...) to an extension number (1001, for example, if the called number were 4085551001), and the call is sent to the correct ephone-dn. If the called extension is busy or unanswered, the call is forwarded to voice mail (2000).
translation-rule 1rule 1 ^408 9408ephone-dn 20number 9408555....loopback-dn 21 forward 10no huntstopephone-dn 21number AAloopback-dn 20telephony-servicedialplan-pattern 1 4085551... extension-length 4 extension pattern 1...ephone-dn 1number 1001telephony-servicevoicemail 2000WAN H.323 calls are sent to loopback ephone-dns using translation rules. Translation rules are used to translate the called number of a WAN H.323 call to a number that triggers the use of loopback ephone-dns. In the following example, the voip-incoming translation-rule and translation-rule commands convert all called numbers starting with 408 to 9408:
voip-incoming translation-rule called 1translation-rule 1rule ^408 9408The translation rule sends calls to loopback ephone-dns with matching numbers (for example, 9408555....). Here is an example of a pair of loopback ephone-dns:
ephone-dn 20number 9408555....loopback-dn 21 forward 10preference 2no huntstopephone-dn 21number AAloopback-dn 20no huntstopAll calls starting with 408 are converted to 9408 by translation rule 1, so calls can be picked up by loopback ephone-dns with the number 9408555.... command and translated back to 408555.... with the loopback-dn 21 forward 10 command.

Note
Other Cisco IOS commands can be used for configuring loopback ephone-dns. For more information, go to the Cisco CallManager Express index and click the desired Cisco CME version and then System Administrator Guide > Loopback Call Routing.
Number of Loopback Ephone-dns Needed
Multiple loopback ephone-dns are needed to handle anticipated WAN H.323 call volume that will be forwarded to Cisco Unity Express. WAN H.323 calls are picked up by the highest-preference loopback ephone-dn available. As seen in Figure 4, if there are four loopback ephone-dns and the first two are in use, the call will go to the available loopback ephone-dn with the highest preference. In the case of Figure 4, ephone-dn 24 is used. Note that a loopback ephone-dn with no specified preference defaults to the highest preference of zero (0).
When deciding on the number of loopback ephone-dn pairs for your configuration, consider the number of calls that will be forwarded to voice mail on each gateway. If all loopback ephone-dn pairs are in use, WAN H.323 calls cannot go through. To keep this from happening, configure enough loopback ephone-dn pairs to accommodate peak traffic.
The number of allowable loopback ephone-dn pairs per Cisco CME system is equal to the maximum number of ephone-dns minus the ephone-dns in use. To find the ephone-dn maximums for your Cisco CME systems, refer to CLI help for the ephone-dn command.
Figure 4 Loopback Ephone-dn Pickup Preference for New WAN H.323 Calls

Loopback Ephone-dn Interaction
The first loopback ephone-dn does the following:
•
Accepts the called number.
•
Terminates the call.
•
Translates the call to SIP.
•
Forwards the call to the second loopback ephone-dn.
The forward number keyword and argument in the loopback-dn command forwards a designated number of the called number's last digits to the second loopback ephone-dn. See Figure 5.
Figure 5 Translation Rule and First Loopback Ephone-dns

As shown in Figure 6, the second loopback ephone-dn forwards the last ten digits of the SIP call. The dialplan pattern command converts the E.164 or ten-digit number to an extension number and sends the call to the appropriate ephone-dn. If the call is unanswered or busy, the call is forwarded to voice mail.
Figure 6 Second Loopback-dn and Dial-Plan Pattern
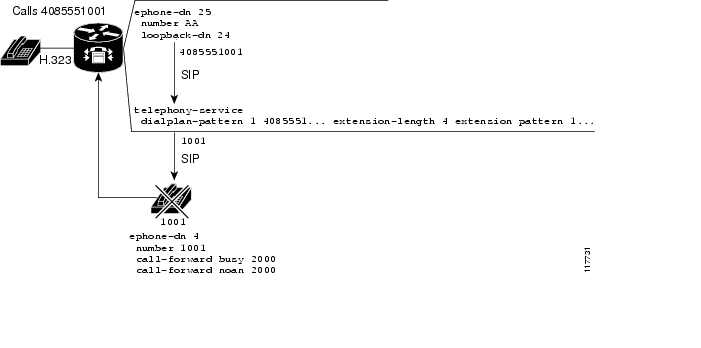
To forward an unanswered or busy call to Cisco Unity Express voice mail, a second dial-plan pattern is required. When Cisco Unity Express is used as the voice-mail system for Cisco CME and a Cisco Unity Express pilot number matches the extension pattern used in a dialplan-pattern command in telephony-service mode, the Cisco Unity Express pilot number is automatically expanded to the matching full E.164 number format when the call is forwarded to Cisco Unity Express. You must create a dial peer for this expanded number in addition to the dial peer for the extension number. Because Cisco Unity Express does not support E.164 format for its pilot numbers, you must create a translation rule under the expanded-number dial peer that converts the expanded number back to its extension equivalent. The Cisco Unity Express pilot number is translated back to its extension equivalent, which is then passed through to Cisco Unity Express.
In the following example, the Cisco Unity Express pilot number is 2000. Dial-plan pattern 2 expands that number to 4085552000 when calls are forwarded from extensions. Calls to the Cisco Unity Express pilot number are picked up by dial peer 2, which sends the call to the session target (Cisco Unity Express) and uses translation rule 2 to convert the number back to a four-digit extension (2000), which is passed through to Cisco Unity Express.
voip-incoming translation-rule called 1translation-rule 1rule ^408 9408translation-rule 2rule 1 4085552 2dial-peer voice 1 voipdescription "SIP Dial Peer to Cisco Unity Express using four-digit number"destination-pattern 2...session protocol sipv2session target ipv4:10.10.10.2dtmf-relay sip-notifycodec g711ulawno vaddial-peer voice 2 voipdescription "SIP dial peer to Cisco Unity Express with E.164 translated to four-digit number"destination-pattern 4085552...translate-outgoing called 2session protocol sipv2session target ipv4:10.10.10.2dtmf-relay sip-notifycodec g711ulawno vadtelephony-servicemax-ephones 5max-dn 96ip source-address 10.1.1.100 port 2000create cnf-files version-stamp Jan 01 2002 00:00:00dialplan-pattern 1 4085551... extension-length 4 extension-pattern 1...dialplan-pattern 2 4085552... extension-length 4 extension-pattern 2...voicemail 2000Prerequisites
•
Regardless of whether you have a Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express configuration or not, you must start voice-mail configuration with the basic configuration elements described in the "Prerequisites for Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express" section. Your configuration can include additional Cisco CME configuration features.
•
Cisco Unity Express must be configured on all of the host Cisco CME routers. For more information, see the "How to Integrate Cisco with Cisco Unity Express" section.
Restrictions
Ephone-dns used for loopback cannot be dual-line ephone-dns.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
voip-incoming translation-rule called tag-number
2.
translation-rule tag-number
3.
rule name-tag input-matched-pattern substituted-pattern
4.
rule name-tag input-matched-pattern substituted-pattern
5.
exit
6.
ephone-dn first-dn-tag
7.
number number
8.
loopback-dn second-dn-tag forward number-of-digits
9.
preference preference-order
10.
no huntstop
11.
exit
12.
ephone-dn second-dn-tag
13.
number dummy-number
14.
loopback-dn first-dn-tag
15.
exit
16.
telephony-service
17.
dialplan-pattern dial-plan-tag pattern extension-length length extension-pattern pattern
18.
dialplan-pattern dial-plan-tag pattern extension-length length extension-pattern pattern
19.
exit
20.
dial-peer voice tag voip
21.
destination-pattern [+] string [T]
22.
session protocol sipv2
23.
session target ipv4:destination-pattern
24.
dtmf-relay sip-notify
25.
codec codec
26.
no vad
27.
exit
28.
Repeat the commands from Step 20 through Step 26.
29.
translate-outgoing called name-tag
30.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Integrating Cisco CME with Cisco Unity Express
This section provides the following configuration examples:
•
Single Router Configuration: Example
•
WAN H.323 Configuration for Cisco CME Versions 3.2 and Higher: Example
•
WAN H.323 Configuration for Cisco CME Versions 3.0 and 3.1: Example
Single Router Configuration: Example
The following example is for a single router running Cisco CME and Cisco Unity Express. The voice-mail number is 2000. The destination-pattern command under dial peer 1 assigns a set of phone numbers dedicated to applications such as Cisco Unity Express. If no other applications are going to be used, you could set the destination pattern to 2000 only.
The Cisco CME router interface is FastEthernet 0/0, and the IP address is 10.3.6.33. The Cisco Unity express IP address is 10.3.6.33. The service-engine interface is used to link the two IP addresses and the FastEthernet 0/0 and Service-Engine 0/0 ports.
Ephone-dn 1 through ephone-dn 9 forward busy and unanswered calls to voice-mail extension 2000. The MWI is switched on and off, respectively, by ephone-dn 30 and ephone-dn 31.
ip dhcp pool phone1host 10.40.0.11 255.255.0.0client-identifier 0100.0a41.2b7d.e9option 150 ip 10.40.0.1default-router 10.40.0.1ip dhcp pool phone2host 10.40.0.12 255.255.0.0client-identifier 0100.09b7.f755.f5option 150 ip 10.40.0.1default-router 10.40.0.1ip dhcp pool phone3host 10.40.0.13 255.255.0.0client-identifier 0100.0c30.de5e.a8option 150 ip 10.40.0.1default-router 10.40.0.1!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 10.3.6.33 255.255.0.0duplex autospeed autointerface Service-Engine0/0ip unnumbered FastEthernet0/0service-module ip address 10.3.6.133 255.255.0.0service-module ip default-gateway 10.3.6.33hold-queue 60 outinterface FastEthernet0/1ip address 10.40.0.1 255.255.0.0duplex autospeed autoip classlessip route 10.3.6.133 255.255.255.255 Service-Engine0/0ip http serverip http path flash:dial-peer voice 1 voipdestination-pattern 2...session protocol sipv2session target ipv4:10.3.6.133dtmf-relay sip-notifycodec g711ulawno vadtelephony-serviceload 7960-7940 P00303010102max-ephones 24max-dn 48ip source-address 10.40.0.1 port 2000system message Welcome to CUEcreate cnf-files version-stamp 7960 Jan 12 2004 16:00:52voicemail 2000max-conferences 8web admin system name test password testdn-webedittime-webeditephone-dn 1number 1001description user1name user1call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 2number 1002description user2name user2call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 3number 1003description user3name user3call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 4number 1004description user4name user4call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 5number 1005description user5name user5call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 6number 1006description user6name user6call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 7number 1007call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 8number 1008call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 30number 8000....mwi onephone-dn 31number 8001....mwi offephone 1username "user1" password nullmac-address 000A.412B.7DE9type 7910button 1:1ephone 2username "user2" password nullmac-address 0009.B7F7.55F5type 7960button 1:2 2:3 3:4 4:5 5:8ephone 3username "user3" password nullmac-address 000C.30DE.5EA8button 1:6 2:7WAN H.323 Configuration for Cisco CME Versions 3.2 and Higher: Example
The following configuration example shows how to integrate a Cisco CME hosting Cisco Unity Express with WAN H.323 networks. For this configuration, a dial peer is created for the voice-mail pilot number (2000). Note that this dial peer is also necessary for a single-router configuration. The second dial peer is for incoming E.164 calls (4085552000) to voice mail. It enables callers from the PSTN to check voice mail and is optional. Translation rule 1 converts the E.164 voice-mail number to the voice-mail pilot number (2000), so the call can be sent to voice mail. Finally, H.323 calls are translated to SIP with the allow-connections command.
voice service voipallow-connections h323 to sipdial-peer voice 1 voipdescription "SIP Dial Peer to Cisco Unity Express using four-digit number"destination-pattern 2...session protocol sipv2session target ipv4:10.3.2.153dtmf-relay sip-notifycodec g711ulawno vaddial-peer voice 2 voipdescription "SIP dial peer to Cisco Unity Express with E.164 translated to four-digit number"destination-pattern 4085552...translate-outgoing called 1session protocol sipv2session target ipv4:10.3.2.153dtmf-relay sip-notifycodec g711ulawno vadvoip-incoming translation-rule called 1translation-rule 1rule 1 4085552 2WAN H.323 Configuration for Cisco CME Versions 3.0 and 3.1: Example
The following configuration example shows how to integrate a Cisco CME hosting Cisco Unity Express with WAN H.323 networks. This configuration uses Cisco CME loopback ephone-dns to send WAN H.323 calls to Cisco Unity Express.
The voice-mail pilot number is 2000. The destination-pattern command under dial peer 1 assigns a set of phone numbers dedicated to applications such as Cisco Unity Express. If no other applications are going to be used, you could set the destination pattern to 2000 only.
The configuration includes three ephone-dns (ephone-dn 1 through ephone-dn 3) and three pairs of loopback ephone-dns (ephone-dns 20/21, ephone-dns 22/23, and ephone-dns 24/25).
All incoming calls starting with 408555 are transferred to loopback ephone-dns using translation rule 1, which prepends a 9 to the called numbers. The prepended number is picked up by a pair of available loopback ephone-dns with the highest preference. The loopback ephone-dns translate the WAN H.323 call to SIP and remove the prepended 9. Dial-plan pattern 1 converts the 10-digit E.164 number to an extension number, and the call reaches its intended destination, where it is answered, unanswered, or encounters a busy signal.
The call-forward command in ephone-dn configuration mode and dial-plan pattern 2 are required for facilitating the transfer of unanswered or busy calls to Cisco Unity Express voice mail. When calls are forwarded to voice mail, the dialplan-pattern command automatically expands the voice-mail pilot number to its matching E.164 format. Dial-peer 2 allows for the acceptance and transference of the E.164 number. Because Cisco Unity Express does not support E.164 pilot numbers, translation rule 2 converts the expanded number back to its extension equivalent.
ip dhcp pool Phone1host 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255client-identifier 0100.09b7.f754.49option 150 ip 10.1.1.100default-router 10.1.1.100ip dhcp pool Phone2host 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255client-identifier 0100.0f34.87ee.75default-router 10.1.1.100option 150 ip 10.1.1.100ip dhcp pool Phone3host 10.1.1.3 255.255.255.255client-identifier 0100.0943.6645.9ddefault-router 10.1.1.100option 150 ip 10.1.1.100ip host host1 10.1.1.6ip host host2 10.1.1.2no ftp-server write-enablevoip-incoming translation-rule called 1translation-rule 1rule 1 ^408 9408translation-rule 2rule 1 4085552 2interface GigabitEthernet0/0ip address 10.3.2.53 255.255.0.0duplex autospeed autointerface GigabitEthernet0/1ip address 10.1.1.100 255.255.255.255duplex autospeed autointerface Service-Engine1/0ip unnumbered GigabitEthernet0/0service-module ip address 10.3.2.153 255.255.0.0service-module ip default-gateway 10.3.2.53ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.3.0.1ip route 10.3.2.153 255.255.255.255 Service-Engine1/0ip http serverip http path flash:control-planedial-peer voice 1 voipdescription "SIP Dial Peer to Cisco Unity Express using four-digit number"destination-pattern 2...session protocol sipv2session target ipv4:10.3.2.153dtmf-relay sip-notifycodec g711ulawno vaddial-peer voice 2 voipdescription "SIP dial peer to Cisco Unity Express with E.164 translated to four-digit number"destination-pattern 4085552...translate-outgoing called 2session protocol sipv2session target ipv4:10.3.2.153dtmf-relay sip-notifycodec g711ulawno vadtelephony-servicemax-ephones 5max-dn 96ip source-address 10.1.1.100 port 2000create cnf-files version-stamp Jan 01 2002 00:00:00dialplan-pattern 1 4085551... extension-length 4 extension-pattern 1...dialplan-pattern 2 4085552... extension-length 4 extension-pattern 2...voicemail 2000max-conferences 8web admin system name sysadmin password sysadminephone-dn 1number 1001name user1call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 2number 1002name user2call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 3number 1003name user3call-forward busy 2000call-forward noan 2000 timeout 10ephone-dn 10number 8000....mwi onephone-dn 11number 8001....mwi offephone-dn 20number 9408555....loopback-dn 21 forward 10no huntstopephone-dn 21number AAloopback-dn 20ephone-dn 22number 9408555....loopback-dn 23 forward 10preference 1no huntstopephone-dn 23number AAloopback-dn 22ephone-dn 24number 9408555....loopback-dn 25 forward 10preference 2no huntstopephone-dn 25number AAloopback-dn 24ephone 1username "user1" password nullmac-address 0009.B7F7.5449button 1:1ephone 2username "usar2" password nullmac-address 000F.3487.EE75button 1:2ephone 3username "user3" password nullmac-address 0009.4366.459Dbutton 1:3Additional References
The following sections provide references related to configuring Cisco CallManager Express and Cisco Unity Express for WAN H.323 calls.
Related Documents
Cisco Unity Express 1.0 and higher system administration
Cisco CME System 3.0 and higher system administration
Cisco CME System 3.0 and higher command reference
Cisco IOS voice commands
Cisco IOS Voice Command Reference, Release 12.3T
Cisco IOS commands
Cisco IOS Commands Master List, Release 12.3
Standards
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature.
—
MIBs
RFCs
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature.
—

Copyright © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback