PIX/ASA URL Filtering Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document explains how to configure URL filtering on a security appliance.
To filter traffic has these advantages:
-
It can help reduce security risks and prevent inappropriate usage.
-
It can provide greater control over the traffic that passes through the security appliance.
Note: Because URL filtering is CPU-intensive, the use of an external filtering server ensures that the throughput of other traffic is not affected. However, based on the speed of your network and the capacity of your URL filtering server, the time required for the initial connection can be noticeably slower when traffic is filtered with an external filtering server.
Note: Implement filtering from lower security level to higher is not supported. URL filtering only works for outbound traffic, for example, traffic that originates on a high security interface destined for a server on a low security interface.
Prerequisites
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
PIX 500 Series Security Appliance with version 6.2 and later
-
ASA 5500 Series Security Appliance with version 7.x and later
-
Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) 6.0
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
You can filter connection requests that originate from a more secure network to a less secure network. Although you can use access control lists (ACLs) in order to prevent outbound access to specific content servers, it is difficult to manage usage this way because of the size and dynamic nature of the Internet. You can simplify configuration and improve security appliance performance with the use of a separate server that runs one of these Internet filtering products:
-
Websense Enterprise—filters HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. It is supported by PIX firewall version 5.3 and later.
-
Secure Computing SmartFilter, formerly known as N2H2—filters HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and long URL filtering. It is supported by PIX firewall version 6.2 and later.
Compared to the use of access control lists, this reduces the administrative task and improves filtering effectiveness. Also, because URL filtering is handled on a separate platform, the performance of the PIX firewall is much less affected. However, users can notice longer access times to websites or FTP servers when the filtering server is remote from the security appliance.
The PIX firewall checks outbound URL requests with the policy defined on the URL filtering server. The PIX firewall either permits or denies the connection, based on the response from the filtering server.
When filtering is enabled and a request for content is directed through the security appliance, the request is sent to the content server and to the filtering server at the same time. If the filtering server allows the connection, the security appliance forwards the response from the content server to the client that originated the request. If the filtering server denies the connection, the security appliance drops the response and sends a message or return code that indicates that the connection is not successful.
If user authentication is enabled on the security appliance, the security appliance also sends the user name to the filtering server. The filtering server can use user-specific filtering settings or provide enhanced reports with regard to usage.
Configure the ASA/PIX with the CLI
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) in order to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
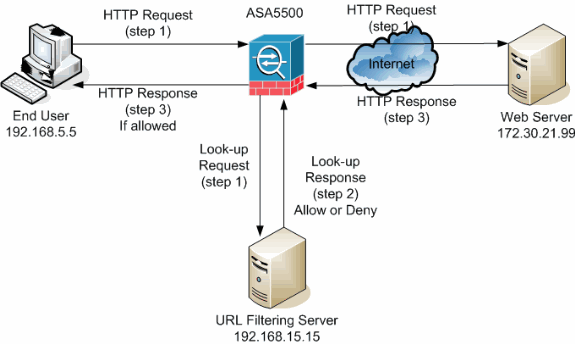
In this example, the URL filtering server is located in a DMZ network. End users located inside the network try to access the web server located outside the network over the Internet.
These steps are completed during the user request for the web server:
-
The end user browses to a page on the web server, and the browser sends an HTTP request.
-
After the security appliance receives this request, it forwards the request to the web server and simultaneously extracts the URL and sends a look-up request to the URL filtering server.
-
After the URL filtering server receives the look-up request, it checks its database in order to determine whether to permit or deny the URL. It returns a permit or deny status with a look-up response to the Cisco IOS® firewall.
-
The security appliance receives this look-up response and performs one of these functions:
-
If the look-up response permits the URL, it sends the HTTP response to the end user.
-
If the look-up response denies the URL, the URL filtering server redirects the user to its own internal web server, which displays a message that describes the category under which the URL is blocked. Thereafter, the connection is reset on both ends.
-
Identify the Filtering Server
You need to identify the address of the filtering server with the url-server command. You must use the appropriate form of this command based on the type of filtering server you use.
Note: For software version 7.x and later, you can identify up to four filtering servers for each context. The security appliance uses the servers in order until a server responds. You can only configure a single type of server, either Websense or N2H2, in your configuration.
Websense
Websense is a third-party filtering software that can filter HTTP requests on the basis of these policies:
-
destination hostname
-
destination IP address
-
keywords
-
user name
The software maintains a URL database of more than 20 million sites organized into more than 60 categories and subcategories.
-
Software version 6.2:
url-server [(if_name)] vendor websense host local_ip [timeout seconds] [protocol {TCP | UDP} version]The url-server command designates the server that runs the N2H2 or Websense URL filtering application. The limit is 16 URL servers. However, you can use only one application at a time, either N2H2 or Websense. Additionally, if you change your configuration on the PIX firewall, it does not update the configuration on the application server. This must be done separately, based on the instructions of the individual vendor.
-
Software version 7.x and later:
pix(config)# url-server (if_name) host local_ip [timeout seconds] [protocol TCP | UDP version 1|4 [connections num_conns] ]
Replace if_name with the name of the security appliance interface that is connected to the filtering server. The default is inside. Replace local_ip with the IP address of the filtering server. Replace seconds with the number of seconds the security appliance must continue to try to connect to the filtering server.
Use the protocol option in order to specify whether you want to use TCP or UDP. With a Websense server, you can also specify the version of TCP you want to use. TCP version 1 is the default. TCP version 4 allows the PIX firewall to send authenticated user names and URL logging information to the Websense server if the PIX firewall has already authenticated the user.
For example, in order to identify a single Websense filtering server, issue this command:
hostname(config)#url-server (DMZ) vendor websense host 192.168.15.15 protocol TCP version 4
Secure Computing SmartFilter
-
PIX version 6.2:
pix(config)#url-server [(if_name)] vendor n2h2 host local_ip[:port number] [timeout <seconds>] [protocol TCP | UDP]
-
Software versions 7.0 and 7.1:
hostname(config)#url-server (if_name) vendor n2h2 host local_ip[:port number] [timeout seconds] [protocol TCP connections number | UDP [connections num_conns]]
-
Software version 7.2 and later:
hostname(config)#url-server (if_name) vendor {secure-computing | n2h2} host <local_ip> [port <number>] [timeout <seconds>] [protocol {TCP [connections <number>]} | UDP]For the vendor {secure-computing | n2h2}, you can use secure-computing as a vendor string. However, n2h2 is acceptable for backward compatibility. When the configuration entries are generated, secure-computing is saved as the vendor string.
Replace if_name with the name of the security appliance interface that is connected to the filtering server. The default is inside. Replace local_ip with the IP address of the filtering server and port <number> with the desired port number.
Note: The default port used by the Secure Computing SmartFilter server to communicate with the security appliance with TCP or UDP is port 4005.
Replace seconds with the number of seconds the security appliance must continue to try to connect to the filtering server. Use the protocol option in order to specify whether you want to use TCP or UDP.
The connections <number> is the number of times to attempt to make a connection between the host and server.
For example, in order to identify a single N2H2 filtering server, issue this command:
hostname(config)#url-server (DMZ) vendor n2h2 host 192.168.15.15 port 4444 timeout 45 protocol tcp connections 10
Or, if you want to use default values, issue this command:
hostname(config)#url-server (DMZ) vendor n2h2 host 192.168.15.15
Configure the Filtering Policy
Note: You must identify and enable the URL filtering server before you enable URL filtering.
Enable URL Filtering
When the filtering server approves an HTTP connection request, the security appliance allows the reply from the web server to reach the client that originated the request. If the filtering server denies the request, the security appliance redirects the user to a block page that indicates that access is denied.
Issue the filter url command in order to configure the policy used to filter URLs:
-
PIX version 6.2:
filter url [http | port[-port] local_ip local_mask foreign_ip foreign_mask] [allow] [proxy-block] [longurl-truncate | longurl-deny] [cgi-truncate]
-
Software version 7.x and later:
filter url [http | port[-port] local_ip local_mask foreign_ip foreign_mask] [allow] [proxy-block] [longurl-truncate | longurl-deny] [cgi-truncate]
Replace port with the port number on which to filter HTTP traffic if a different port than the default port for HTTP (80) is used. In order to identify a range of port numbers, enter the start and end of the range separated by a hyphen.
With filtering enabled, the security appliance stops outbound HTTP traffic until a filtering server permits the connection. If the primary filtering server does not respond, the security appliance directs the filtering request to the secondary filtering server. The allow option causes the security appliance to forward HTTP traffic without filtering when the primary filtering server is unavailable.
Issue the proxy-block command in order to drop all requests to proxy servers.
Note: The remainder of the parameters are used in order to truncate long URLs.
Truncate Long HTTP URLs
The longurl-truncate option causes the security appliance to send only the host name or IP address portion of the URL for evaluation to the filtering server when the URL is longer than the maximum length permitted.
Use the longurl-deny option in order to deny outbound URL traffic if the URL is longer than the maximum permitted.
Use the cgi-truncate option in order to truncate CGI URLs to include only the CGI script location and the script name without any parameters.
This is a general filter configuration example:
hostname(config)#filter url http 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 172.30.21.99 255.255.255.255 allow proxy-block longurl-truncate cgi-truncate
Exempt Traffic from Filtering
If you want to make an exception to the general filtering policy, issue this command:
filter url except local_ip local_mask foreign_ip foreign_mask]
Replace local_ip and local_mask with the IP address and subnet mask of a user or subnetwork that you want to exempt from filtering restrictions.
Replace foreign_ip and foreign_mask with the IP address and subnet mask of a server or subnetwork that you want to exempt from filtering restrictions.
For example, this command causes all HTTP requests to 172.30.21.99, from the inside hosts, to be forwarded to the filtering server except for requests from host 192.168.5.5:
This is a configuration example for an exception:
hostname(config)#filter url except 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.255 172.30.21.99 255.255.255.255
Advanced URL Filtering
This section provides information about advanced filtering parameters, which includes these topics:
-
buffering
-
caching
-
long URL support
Buffer The Web Server Responses
When a user issues a request to connect to a content server, the security appliance sends the request to the content server and to the filtering server at the same time. If the filtering server does not respond before the content server, the server response is dropped. This delays the web server response from the point of view of the web client because the client must reissue the request.
If you enable the HTTP response buffer, replies from web content servers are buffered and the responses are forwarded to the client that makes the request if the filtering server allows the connection. This prevents the delay that can otherwise occur.
In order to buffer responses to HTTP requests, complete these steps:
-
In order to enable buffering of responses for HTTP requests that are pending a response from the filtering server, issue this command:
hostname(config)#url-block block block-buffer-limit
Replace block-buffer-limit with the maximum number of blocks to be buffered.
-
In order to configure the maximum memory available to buffer pending URLs, and to buffer long URLs with Websense, issue this command:
hostname(config)#url-block url-mempool memory-pool-size
Replace memory-pool-size with a value from 2 to 10240 for a maximum memory allocation of 2 KB to 10 MB.
Cache Server Addresses
After a user accesses a site, the filtering server can allow the security appliance to cache the server address for a certain amount of time, as long as every site hosted at the address is in a category that is permitted at all times. Then, when the user accesses the server again, or if another user accesses the server, the security appliance does not need to consult the filtering server again.
Issue the url-cache command if needed to improve throughput:
hostname(config)#url-cache dst | src_dst size
Replace size with a value for the cache size within the range 1 to 128 (KB).
Use the dst keyword in order to cache entries based on the URL destination address. Select this mode if all users share the same URL filtering policy on the Websense server.
Use the src_dst keyword in order to cache entries based on both the source address that initiates the URL request as well as the URL destination address. Select this mode if users do not share the same URL filtering policy on the Websense server.
Enable Filtering of Long URLs
By default, the security appliance considers an HTTP URL to be a long URL if it is greater than 1159 characters. You can increase the maximum length allowed for a single URL with this command:
hostname(config)#url-block url-size long-url-size
Replace long-url-size with the maximum size in KB for each long URL to be buffered.
For example, these commands configure the security appliance for advanced URL filtering:
hostname(config)#url-block block 10 hostname(config)#url-block url-mempool 2 hostname(config)#url-cache dst 100 hostname(config)#url-block url-size 2
Configuration
This configuration includes the commands described in this document:
| ASA 8.0 Configuration |
|---|
ciscoasa#show running-config
: Saved
:
ASA Version 8.0(2)
!
hostname ciscoasa
domain-name Security.lab.com
enable password 2kxsYuz/BehvglCF encrypted
no names
dns-guard
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
speed 100
duplex full
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 172.30.21.222 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
description INSIDE
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 192.168.5.11 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
description LAN/STATE Failover Interface
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/3
description DMZ
nameif DMZ
security-level 50
ip address 192.168.15.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Management0/0
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
boot system disk0:/asa802-k8.bin
ftp mode passive
clock timezone CST -6
clock summer-time CDT recurring
dns server-group DefaultDNS
domain-name Security.lab.com
same-security-traffic permit intra-interface
pager lines 20
logging enable
logging buffer-size 40000
logging asdm-buffer-size 200
logging monitor debugging
logging buffered informational
logging trap warnings
logging asdm informational
logging mail debugging
logging from-address aaa@cisco.com
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu DMZ 1500
no failover
failover lan unit primary
failover lan interface interface GigabitEthernet0/2
failover link interface GigabitEthernet0/2
no monitor-interface outside
icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1
asdm image disk0:/asdm-602.bin
asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
global (outside) 1 interface
nat (inside) 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.30.21.244 1
timeout xlate 3:00:00
timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02
timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00
timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
ldap attribute-map tomtom
dynamic-access-policy-record DfltAccessPolicy
url-server (DMZ) vendor websense host 192.168.15.15 timeout 30 protocol TCP version 1 connections 5
url-cache dst 100
aaa authentication ssh console LOCAL
aaa authentication enable console LOCAL
aaa authentication telnet console LOCAL
filter url except 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.255 172.30.21.99 255.255.255.255
filter url http 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 172.30.21.99 255.255.255.255 allow
proxy-block longurl-truncate cgi-truncate
http server enable
http 172.30.0.0 255.255.0.0 outside
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
telnet 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 inside
telnet timeout 5
ssh 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 inside
ssh timeout 60
console timeout 0
management-access inside
dhcpd address 192.168.5.12-192.168.5.20 inside
dhcpd enable inside
!
threat-detection basic-threat
threat-detection statistics access-list
!
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
!
!
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect ftp
inspect h323 h225
inspect h323 ras
inspect rsh
inspect sqlnet
inspect skinny
inspect sunrpc
inspect xdmcp
inspect sip
inspect netbios
inspect tftp
inspect icmp
!
service-policy global_policy global
url-block url-mempool 2
url-block url-size 2
url-block block 10
username fwadmin password aDRVKThrSs46pTjG encrypted privilege 15
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:db208a243faa71f9b3e92491a6ed2105
: end |
Configure the ASA/PIX with ASDM
This section demonstrates how to configure URL filtering for the security appliance with the Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM).
After you launch ASDM, complete these steps:
-
Choose the Configuration pane.
-
Click Firewall in the list shown in the Configuration pane.
-
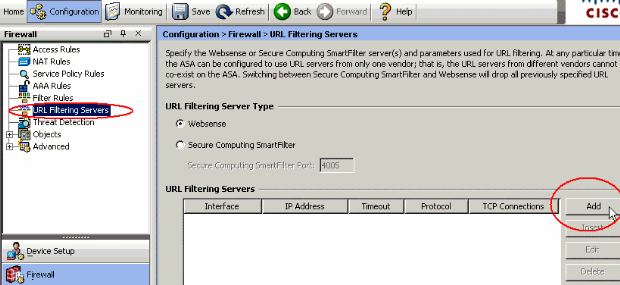
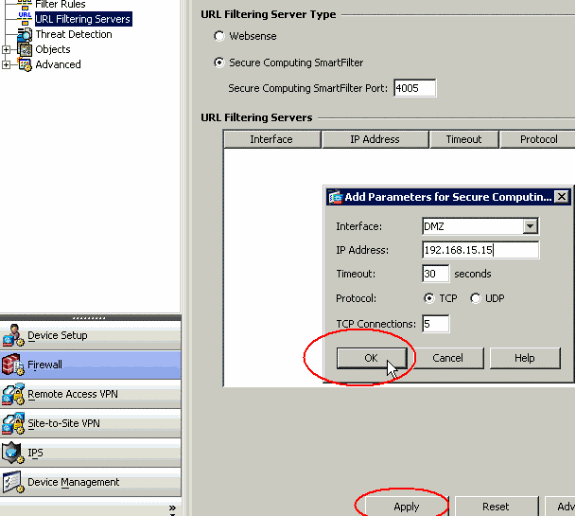
From the Firewall drop-down list, choose URL Filtering Servers. Choose the URL Filtering Server type you want to use, and click Add to configure its parameters.
Note: You must add the filtering server before you can configure filtering for HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP filtering rules.
-
Choose the appropriate parameters in the popup window:
-
Interface—Displays the interface connected to the filtering server
-
IP Address—Displays the IP address of the filtering server
-
Timeout—Displays the number of seconds after which the request to the filtering server times out
-
Protocol—Displays the protocol used to communicate with the filtering server. TCP version 1 is the default. TCP version 4 allows the PIX firewall to send authenticated user names and URL logging information to the Websense server, if the PIX firewall has already authenticated the user
-
TCP Connections—Displays the maximum number of TCP connections allowed to communicate with the URL filtering server
After you enter the parameters, click OK in the popup window and Apply in the main window.
-
-
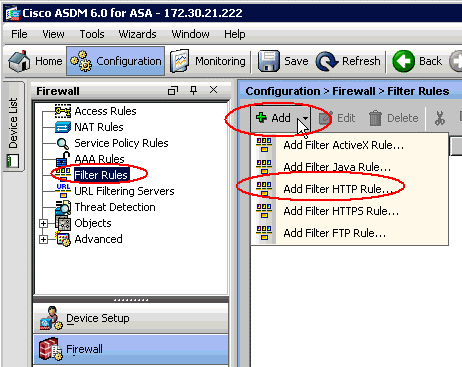
From the Firewall drop-down list, choose Filter Rules. Click the Add button in the main window, and choose the type of rule you want to add. In this example, the Add Filter HTTP Rule is chosen.
-
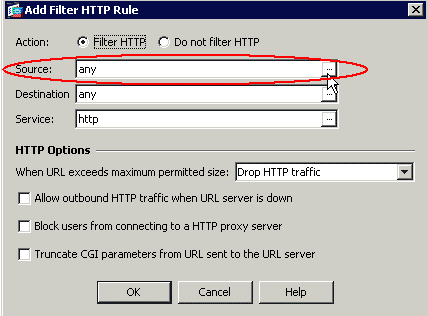
Once the popup window appears, you can click on the browse buttons for Source, Destination and Service options in order to choose the appropriate parameters.
-
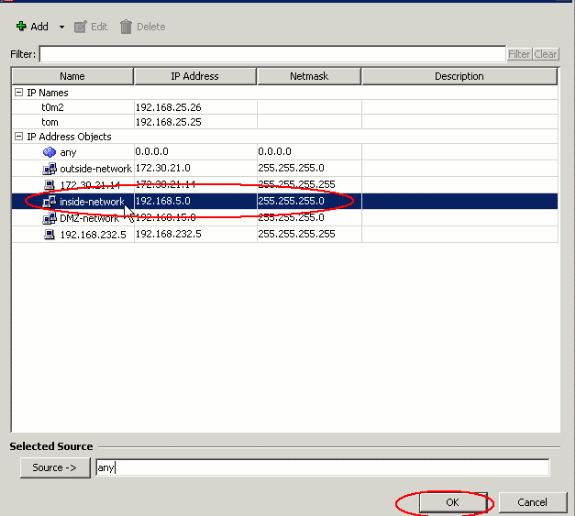
This shows the browse window for the Source option. Make your selection and click OK.
-
After you complete the selection for all parameters, click OK to continue.
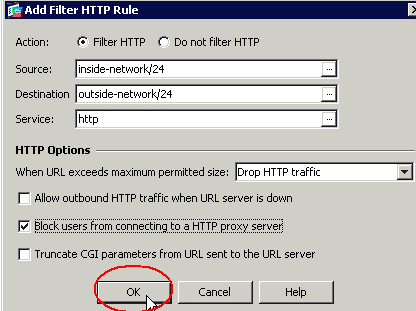
-
Once the appropriate parameters are configured, click Apply in order to submit the changes.
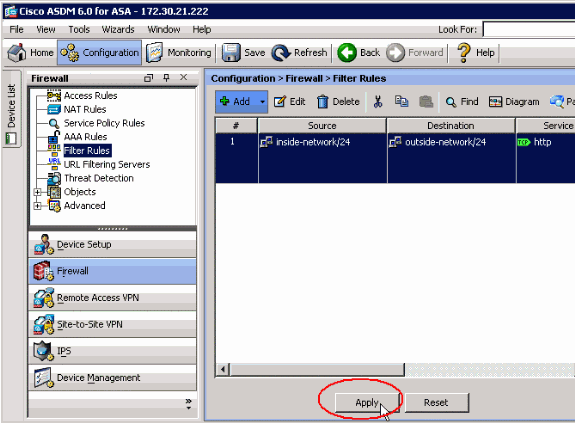
-
For advanced URL filtering options, choose URL Filtering Servers again from the Firewall drop down list, and click the Advanced button in the main window.
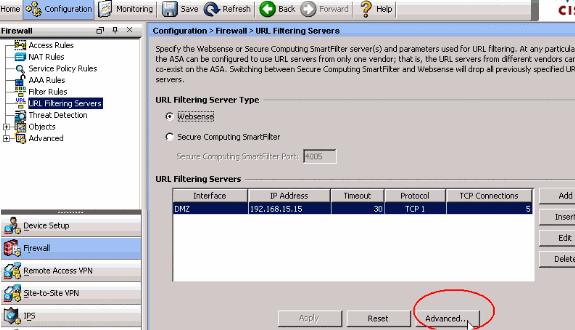
-
Configure the parameters, such as URL cache size, URL buffer size and Long URL support, in the popup window. Click OK in the popup window, and click Apply in the main window in order to continue.
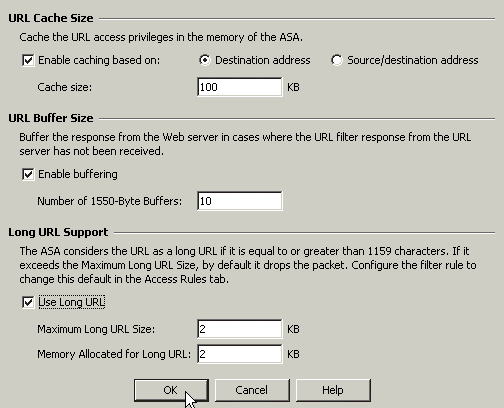
-
Finally, make sure that you save the changes that you make before you terminate the ASDM session.
Verify
Use the commands in this section in order to view URL filtering information. You can use these commands in order to verify your configuration.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT in order to view an analysis of show command output.
-
show url-server—Shows information about the filtering server
For example:
hostname#show url-server url-server (DMZ) vendor n2h2 host 192.168.15.15 port 4444 timeout 45 protocol tcp connections 10
In software version 7.2 and later, issue the show running-config url-server form of this command.
-
show url-server stats—Shows information and statistics about the filtering server
For software version 7.2, issue the show running-config url-server statistics form of this command.
In software version 8.0 and later, issue the show url-server statistics form of this command.
For example:
hostname#show url-server statistics Global Statistics: -------------------- URLs total/allowed/denied 13/3/10 URLs allowed by cache/server 0/3 URLs denied by cache/server 0/10 HTTPSs total/allowed/denied 138/137/1 HTTPSs allowed by cache/server 0/137 HTTPSs denied by cache/server 0/1 FTPs total/allowed/denied 0/0/0 FTPs allowed by cache/server 0/0 FTPs denied by cache/server 0/0 Requests dropped 0 Server timeouts/retries 0/0 Processed rate average 60s/300s 0/0 requests/second Denied rate average 60s/300s 0/0 requests/second Dropped rate average 60s/300s 0/0 requests/second Server Statistics: -------------------- 192.168.15.15 UP Vendor websense Port 15868 Requests total/allowed/denied 151/140/11 Server timeouts/retries 0/0 Responses received 151 Response time average 60s/300s 0/0 URL Packets Sent and Received Stats: ------------------------------------ Message Sent Received STATUS_REQUEST 1609 1601 LOOKUP_REQUEST 1526 1526 LOG_REQUEST 0 NA Errors: ------- RFC noncompliant GET method 0 URL buffer update failure 0
-
show url-block—Shows the configuration of the URL block buffer
For example:
hostname#show url-block url-block url-mempool 128 url-block url-size 4 url-block block 128In software version 7.2 and later, issue the show running-config url-block form of this command.
-
show url-block block statistics—Shows the URL block statistics
For example:
hostname#show url-block block statistics URL Pending Packet Buffer Stats with max block 128 ----------------------------------------------------- Cumulative number of packets held: 896 Maximum number of packets held (per URL): 3 Current number of packets held (global): 38 Packets dropped due to exceeding url-block buffer limit: 7546 HTTP server retransmission: 10 Number of packets released back to client: 0For software version 7.2, issue the show running-config url-block block statistics form of this command.
-
show url-cache stats—Shows how the cache is used
For example:
hostname#show url-cache stats URL Filter Cache Stats ---------------------- Size : 128KB Entries : 1724 In Use : 456 Lookups : 45 Hits : 8In software version 8.0, issue the show url-cache statistics form of this command.
-
show perfmon—Shows URL filtering performance statistics, along with other performance statistics. The filtering statistics are shown in the URL Access and URL Server Req rows.
For example:
hostname#show perfmon PERFMON STATS: Current Average Xlates 0/s 0/s Connections 0/s 2/s TCP Conns 0/s 2/s UDP Conns 0/s 0/s URL Access 0/s 2/s URL Server Req 0/s 3/s TCP Fixup 0/s 0/s TCPIntercept 0/s 0/s HTTP Fixup 0/s 3/s FTP Fixup 0/s 0/s AAA Authen 0/s 0/s AAA Author 0/s 0/s AAA Account 0/s 0/s
-
show filter—Shows the filtering configuration
For example:
hostname#show filter filter url http 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.255 172.30.21.99 255.255.255.255 allow proxy-block longurl-truncate cgi-truncate
In software version 7.2 and later, issue the show running-config filter form of this command.
Troubleshoot
This section provides information on how to troubleshoot your configuration.
Error: "%ASA-3-304009: Ran out of buffer blocks specified by url-block command"
Firewall runs out of URL cache that is meant to hold server replies when the firewall waits to get confirmation from the URL server.
Solution
The issue is basically related to a latency between the ASA and the Websense server. In order to resolve this issue try these workarounds.
-
Try to change the protocol that is used on the ASA to UDP in order to communicate with the Websense.
There is an issue with latency between the Websense server and the firewall, in which replies from the Websense server take a long time to return to the firewall, thus this causes the URL buffer to fill up while it waits for a response.
You can use UDP instead of TCP for the communication between the Websense server and the Firewall. This is because when you use TCP for URL filtering, for each new URL request, the ASA needs to establish a TCP connection with the Websense server. Since UDP is a connectionless protocol, the ASA is not forced to establish the connection to receive the response of the server. This should improve the performance of the server.
ASA(config)#url-server (inside) vendor websense host X.X.X.X timeout 30 protocol UDP version 4 connections 5
-
Make sure to increase the url-block block to the highest value possible, which is 128. This can be checked with the show url-block command.
If it shows 128, take Cisco bug ID CSCta27415 (registered customers only) enhancement into consideration.
Related Information
- Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliances Product Support
- Cisco PIX 500 Series Security Appliances Product Support
- Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager Product Support
- PIX/ASA: Establish and Troubleshoot Connectivity through the Cisco Security Appliance
- Troubleshoot Connections through the PIX and ASA
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
03-Jul-2007 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)











 Feedback
Feedback