How OSPF Propagates External Routes into Multiple Areas
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document shows how Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) propagates external routes into multiple network areas.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, see the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: To find additional information on the commands used in this document, use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) .
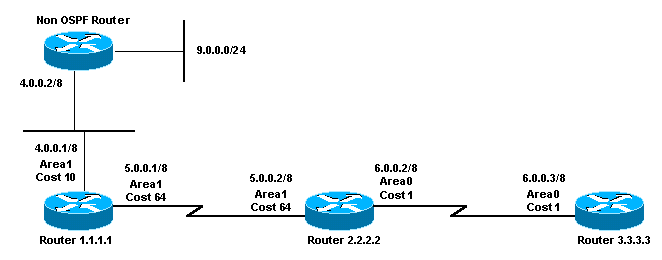
Network Diagram
This document uses the network setup shown in this diagram.
Configurations
This document uses the configurations shown here.
| Router 1.1.1.1 |
|---|
Current configuration: hostname r1.1.1.1 interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 interface Serial2/1/0 ip address 5.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 interface Ethernet2/0/0 ip address 4.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 router ospf 4 redistribute static metric 5 metric-type 1 network 5.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 1 network 4.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 1 ip route 9.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 4.0.0.2 end |
| Router 2.2.2.2 |
|---|
Current configuration: hostname r2.2.2.2 interface Loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.0.0.0 interface Serial0/1/0 ip address 5.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 interface ATM1/0.20 ip address 6.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 router ospf 2 network 5.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 1 network 6.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0 end |
| Router 3.3.3.3 |
|---|
Current configuration: hostname r3.3.3.3 interface Loopback0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.0.0.0 interface ATM2/0.20 point-to-point ip address 6.0.0.3 255.0.0.0 router ospf 2 network 6.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0 end |
Verify
This section provides information you can use to confirm your configuration is working properly.
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
-
show ip ospf database —Displays a list of the Link State Advertisements (LSAs) and types them into a link state database. This list shows only the information in the LSA header.
-
show ip ospf database [router] [link-state-id]—Displays a list of all of a router's LSAs in the database. LSAs are produced by every router. These fundamental LSAs list all of the routers' links, or interfaces, along with the states and outgoing costs of the links. They are flooded only within the area in which they originate.
-
show ip ospf database summary <link-state id> —Displays the area border router (ABR) summary links.
-
show ip ospf database external—Displays information only about the external LSAs.
-
show ip ospf database asbr-summary—Displays information only about the autonomous system boundary router summary LSAs.
Examine the OSPF Database
This output shows how the OSPF database looks given this network environment, using the show ip ospf database command.
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 93 0x80000020 0xCD0B 2
3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 1225 0x8000000D 0x9057 2
Summary Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
4.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 73 0x80000001 0xFFE6
5.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 1651 0x80000006 0x8466
Summary ASB Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
1.1.1.1 2.2.2.2 74 0x80000001 0x935C
Router Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 89 0x80000011 0xFF59 3
2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 88 0x80000033 0x2130 2
Summary Net Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
6.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 94 0x8000001F 0xCC43
Type-5 AS External Link States
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Tag
9.0.0.0 1.1.1.1 135 0x80000001 0x3AE8 0
To advertise external routes into OSPF, the autonomous system boundary router (ASBR) creates (type 5) external LSAs.
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database external 9.0.0.0
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Type-5 AS External Link States
Routing Bit Set on this LSA
LS age: 286
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 9.0.0.0 (External Network Number )
!--- 9.0.0.0/8 is advertised by the !--- ASBR (Router 1.1.1.1).
Advertising Router: 1.1.1.1
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0x3AE8
Length: 36
Network Mask: /8
Metric Type: 1 (Comparable directly to link state metric)
TOS: 0
Metric: 5
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
!--- Forwarding address is not specified since there !--- are no OSPF neighbors on Router 1.1.1.1's Ethernet. !--- When the forward address is 0.0.0.0, this means that !--- the traffic for this network is to be sent to the !--- advertising router (1.1.1.1).
External Route Tag: 0
To advertise reachability of an ASBR into other areas, the ABR creates (type 4) ASBR-summary LSAs.
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database asbr-summary 1.1.1.1
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Summary ASB Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 266
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Summary Links(AS Boundary Router)
Link State ID: 1.1.1.1 (AS Boundary Router address)
!--- ABR (Router 2.2.2.2) is advertising that it knows how !--- to reach the ASBR (Router 1.1.1.1).
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0x935C
Length: 28
Network Mask: /0
TOS: 0 Metric: 64
!--- The ABR's cost to reach the ASBR.
The ABR (Router 2.2.2.2) has installed an external route learned from the ASBR (Router 1.1.1.1) and flooded the external LSA from area 1 into area 0. (External LSAs are flooded unaltered into all areas.) However, the ASBR is not in area 0. Routers in area 0 do not know how to reach the ASBR. This is why the ABR creates an ASBR-summary LSA and advertises reachability for Router 1.1.1.1 into area 0.
Note: This next set of output is presented only to give more details about the OSPF database in this example setup. If you are familiar with this information, skip to the Calculate the Shortest Path section.
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database router 1.1.1.1
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Router Link States (Area 1)
Routing Bit Set on this LSA
LS age: 109
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 1.1.1.1
!--- For router links, Link State Id is always the !--- same as the Advertising Router.
Advertising Router: 1.1.1.1
!--- This is the router ID of the router that created !--- this LSA.
LS Seq Number: 80000011
Checksum: 0xFF59
Length: 60
AS Boundary Router
!--- Bit E in the router LSA indicates that this !--- router originates external LSAs.
Number of Links: 3
!--- There are three links in area 1.
Link connected to: a Stub Network
!--- This line represents the Ethernet segment !--- 4.0.0.0/8.
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 4.0.0.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.0.0.0
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 10
!--- OSPF cost of the Ethernet segment.
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
!--- This line shows that Router 1.1.1.1 is a !--- neighbor with Router 2.2.2.2.
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 2.2.2.2
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 5.0.0.1
!--- The interface address that connects to !--- Router 2.2.2.2 is 5.0.0.1.
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 64
!--- OSPF cost of the link connecting the two routers.
Link connected to: a Stub Network
!--- This line represents the serial link 5.0.0.0/8.
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 5.0.0.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.0.0.0
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 64
!--- OSPF cost of the serial link.
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database router 2.2.2.2
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Router Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 135
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 2.2.2.2
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000020
Checksum: 0xCD0B
Length: 48
Area Border Router
Number of Links: 2
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 3.3.3.3
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 6.0.0.2
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 6.0.0.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.0.0.0
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Router Link States (Area 1)
LS age: 130
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 2.2.2.2
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000033
Checksum: 0x2130
Length: 48
Area Border Router
Number of Links: 2
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 1.1.1.1
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 5.0.0.2
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 64
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 5.0.0.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.0.0.0
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 64
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database router 3.3.3.3
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Router Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 1280
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 3.3.3.3
Advertising Router: 3.3.3.3
LS Seq Number: 8000000D
Checksum: 0x9057
Length: 48
Number of Links: 2
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 2.2.2.2
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 6.0.0.3
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 6.0.0.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.0.0.0
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
To advertise routes from one area into another, the ABR creates (type 3) summary LSAs.
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database summary 4.0.0.0
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Summary Net Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 184
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Summary Links(Network)
Link State ID: 4.0.0.0 (summary Network Number)
!--- 4.0.0.0/8 is advertised into area 0 by !--- the ABR (Router 2.2.2.2).
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0xFFE6
Length: 28
Network Mask: /8
TOS: 0 Metric: 74
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database summary 5.0.0.0
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Summary Net Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 1768
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Summary Links(Network)
Link State ID: 5.0.0.0 (summary Network Number)
!--- 5.0.0.0/8 is advertised into area 0 by !--- the ABR (Router 2.2.2.2).
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000006
Checksum: 0x8466
Length: 28
Network Mask: /8
TOS: 0 Metric: 64
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database summary 6.0.0.0
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Summary Net Link States (Area 1)
LS age: 216
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Summary Links(Network)
Link State ID: 6.0.0.0
!--- 6.0.0.0/8 is advertised into area 1 by the ABR(2.2.2.2).
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 8000001F
Checksum: 0xCC43
Length: 28
Network Mask: /8
TOS: 0 Metric: 1
Calculate the Shortest Path
This section calculates the shortest path from the perspective of Router 3.3.3.3.
Router 3.3.3.3 looks in its own LSA and sees that Router 2.2.2.2 is a neighbor. It then looks at Router 2.2.2.2's LSA to verify that Router 2.2.2.2 sees Router 3.3.3.3 as a neighbor. If both routers see each other as neighbors, then they are considered reachable.
Each router also checks its local neighbor table (which you can see using the show ip ospf neighbor command) to verify that its and the neighbor's interfaces are on a common IP subnet.
Note: This check is not performed on an unnumbered interface.
If the interfaces are on a common subnet, the routers install routes for any stub networks listed in their neighbor's router LSA. In this example, 60.0.0.0/8 is the only stub network listed in Router 2.2.2.2's LSA in area 0, to which Router 3.3.3.3 is already directly connected.
After examining all the reachable router LSAs in area 0, Router 3.3.3.3 looks at summary LSAs in the database. It finds summary LSAs for 4.0.0.0/8 and 5.0.0.0/8. If Router 3.3.3.3 knows how to reach the advertising router that created the summary LSA, it installs the route in its routing table. In our example, the advertising router is Router 2.2.2.2, which Router 3.3.3.3 knows how to reach. It installs routes for 4.0.0.0/8 and 5.0.0.0/8 in its routing table. The metric for these routes is the metric to reach the advertising router plus the metric of the summary LSA. The metric of the summary LSA is calculated from the cost to reach the intra- or inter-area route for which the summary LSA is generated.
After calculating all the internal OSPF routes (intra- and inter-area), Router 3.3.3.3 examines the external LSAs. It first examines the external LSA 9.0.0.0/8 created by the ASBR 1.1.1.1,and then calculates how to reach the ASBR. Router 3.3.3.3 examines the ASBR-summary LSA for Router 1.1.1.1, created by the ABR (Router 2.2.2.2). After doing so, Router 3.3.3.3 knows that the ASBR is reachable through the ABR. Therefore, Router 3.3.3.3 installs a route for 9.0.0.0/8 its routing table. In our example, it's an E1 route, so the metric for is Router 3.3.3.3's metric to reach the ABR, plus the ABR's metric to reach the ASBR, plus the metric of the external LSA.
This output shows the OSPF routes in the routing table of each router described.
r3.3.3.3# show ip route ospf O IA 4.0.0.0/8 [110/75] via 6.0.0.2, 00:07:59, ATM2/0.20 O IA 5.0.0.0/8 [110/65] via 6.0.0.2, 00:07:59, ATM2/0.20 O E1 9.0.0.0/8 [110/70] via 6.0.0.2, 00:07:59, ATM2/0.20 r2.2.2.2#show ip route ospf O 4.0.0.0/8 [110/74] via 5.0.0.1, 00:06:55, Serial0/1/0 O E1 9.0.0.0/8 [110/69] via 5.0.0.1, 00:06:55, Serial0/1/0 r1.1.1.1#show ip route 9.0.0.0 Routing entry for 9.0.0.0/8 Known via "static", distance 1, metric 0 Redistributing via ospf 4 Advertised by ospf 4 metric 5 metric-type 1 Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 4.0.0.2 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
10-Aug-2005 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback