Introduction
This document describes how the IPv6 Link-Local address works within a network.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the Cisco 3700 series router with Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.4 (15)T1.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
A Link-Local address is an IPv6 unicast address that can be automatically configured on any interface that uses the Link-Local prefix FE80::/10 (1111 1110 10) and the interface identifier in the modified EUI-64 format. Link-Local addresses are not necessarily bound to the MAC address, although it is common to configure Link-Local addresses using the EUI-64 method (where the MAC address is embedded into the IPv6 address), Link-Local addresses can also be manually configured in the FE80::/10 format with the ipv6 address <address> link-local command.

Note: For more information about the EUI-64 Format Interface Identifiers, visit IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture RFC4291
Link-Local addresses in IPv6 are used only on a specific physical link, meaning a local network connection between devices. These addresses are crucial for tasks like automatic address configuration and for the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), which helps devices on the same link find and communicate with each other. Link-Local addresses allow communication between neighboring nodes without needing a globally unique address. Importantly, IPv6 routers do not forward data with Link-Local addresses beyond the local network. All IPv6-enabled interfaces automatically have a Link-Local unicast address.
Configuration
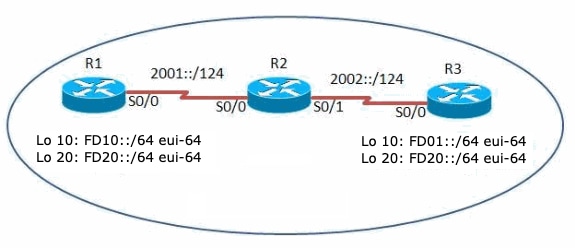
For this example, the routers R1, R2 and R3 are connected via serial interface and have the IPv6 addresses configured as mentioned in the network diagram. Loopback addresses are configured on the routers R1 and R3, and the routers use OSPFv3 to communicate with each other. This example uses the ping command to demonstrate the connectivity between the routers with Link-Local addresses. The routers R1 and R3 can ping each other with the IPv6 local unicast address, but not with their Link-Local address. However, router R2 is directly connected to R1 and R3 hence it can communicate with both the routers with their Link-Local address, because Link-Local addresses are used only within that local network specific to the physical interface.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Configurations Used
This document uses these configurations:
-
Router R1
-
Router R2
-
Router R3
This video demonstrates the key difference between the IPv6 Link-Local Address and global unicast address in Cisco IOS routers:
| Router R1 |
hostname R1
!
ipv6 cef
!
ipv6 unicast-routing
!
interface Loopback10
no ip address
ipv6 address FD10::/64 eui-64
!--- Assigned a IPv6 unicast address in EUI-64 format.
ipv6 ospf 1 area 1
!--- Enables OSPFv3 on the interface and associates the interface looback10 to area 1.
!
interface Loopback20
no ip address
ipv6 address FD20::/64 eui-64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 2
!--- Associates the Interface loopback20 to area 2.
!
interface Serial0/0
no ip address
ipv6 address 2001::1/124
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
!--- Associates the Interface serial0/0 to area 0.
clock rate 2000000
!
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 10.1.1.1
!--- Router R1 uses 10.1.1.1 as router id.
log-adjacency-changes
!
end
|
| Router R2 |
Router R3 |
hostname R2
!
ipv6 cef
!
ipv6 unicast-routing
!
!
!
interface Serial0/0
no ip address
ipv6 address 2001::2/124
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
clock rate 2000000
!
!
interface Serial0/1
no ip address
ipv6 address 2002::1/124
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
clock rate 2000000
!
!
!
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 10.2.2.2
log-adjacency-changes
!
end
|
hostname R3
!
ipv6 cef
!
ipv6 unicast-routing
!
!
!
interface Loopback10
no ip address
ipv6 address FD01::/64 eui-64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 1
!
!
interface Loopback20
no ip address
ipv6 address FD20::/64 eui-64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 2
!
!
interface Serial0/0
no ip address
ipv6 address FE80::AB8 link-local
ipv6 address 2002::2/124
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
clock rate 2000000
!
!
!
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 10.3.3.3
log-adjacency-changes
!
end
|
Verification
Verify OSPF Configuration
To verify the OSPF has been configured properly, use the show ipv6 route ospf command in routers R1 and R3.
| show ipv6 route ospf |
Router R1
R1#show ipv6 route ospf
IPv6 Routing Table - 10 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, R - RIP, B - BGP
U - Per-user Static route, M - MIPv6
I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary
O - OSPF intra, OI - OSPF inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
OI FD01::C002:1DFF:FEE0:0/128 [110/128]
via FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0, Serial0/0
O 2002::/124 [110/128]
via FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0, Serial0/0
OI FD20::C002:1DFF:FEE0:0/128 [110/128]
via FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0, Serial0/0
Router R3
R3#show ipv6 route ospf
IPv6 Routing Table - 10 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, R - RIP, B - BGP
U - Per-user Static route, M - MIPv6
I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary
O - OSPF intra, OI - OSPF inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
O 2001::/124 [110/128]
via FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0, Serial0/0
OI FD10::C000:1DFF:FEE0:0/128 [110/128]
via FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0, Serial0/0
OI FD20::C000:1DFF:FEE0:0/128 [110/128]
via FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0, Serial0/0
|
Verify Link-Local Address Reachability
The routers can ping each other with the global unicast address. If the routers use the Link-Local address only, the directly connected networks can communicate. For example, R1 can ping R3 with global unicast address but the two routers cannot communicate with Link-Local addresses. This is shown with the ping and debug ipv6 icmp commands in router R1 and R3.
Ping Link-Local Address From Remote Network
When the router R1 tries to communicate with router R3 with the link local address, the router R1 returns with an ICMP time-out message that indicates the Link-Local address is locally specific and cannot communicate to Link-Local addresses that are outside the directly connected network.
| Ping R3's Link-Local Address from router R1 |
In Router R1
R1#ping FE80::AB8
Output Interface: serial0/0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FE80::AB8, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of FE80::C000:1DFF:FEE0:0
.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
!--- Pinging Link-Local Address of router R3.
!--- The ping is unsuccessful and the ICMP packet cannot reach the destination through serial0/0.
!--- This timeout indicates that R1 has not received any replies from the router R3.
|
Ping Link-Local Address From Directly Connected Network
For router R2, the routers R1 and R3 are directly connected and can ping the Link-Local address of both router R1 and R2 when they communicate the related interface that is connected to the router. The output is shown here:
| Ping R1 Link-Local Addresses from router R2 |
In Router R2
R2#ping FE80::C000:1DFF:FEE0:0
Output Interface: serial0/0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FE80::C000:1DFF:FEE0:0, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/19/56 ms
!--- Pinging Link-Local Address of router R1, R2 connects to R1 via serial0/0.
Debug Output from R1
R1#
*Mar 1 03:59:53.367: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 03:59:53.371: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 03:59:53.423: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 03:59:53.427: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 03:59:53.463: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 03:59:53.463: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 03:59:53.467: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 03:59:53.467: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 03:59:53.471: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 03:59:53.471: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
!--- The debug output shows that the router R2 can ping router R1's Link-Local address.
|
| Ping R3 Link-Local Addresses from router R2 |
In Router R2
R2#ping FE80::AB8
Output Interface: serial0/1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FE80::AB8, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/18/60 ms
!--- Note that, to ping the Link-Local address, output interface is needed. In our case, R2 connects to R3 throught serial0/1.
Debug Output from R3
R3#
*Mar 1 04:12:11.518: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 04:12:11.522: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 04:12:11.594: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 04:12:11.598: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 04:12:11.618: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 04:12:11.618: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 04:12:11.622: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 04:12:11.622: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 04:12:11.626: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 04:12:11.630: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
!--- The debug output shows that the router R2 can ping router R3's Link-Local address.
|
The Link-Local address is specific only to that local network. The routers can have the same Link-Local address and still the directly connected network can communicate with each other without any conflict. This is not the same in case of global unicast address. The global unicast address that are routable must be unique in a network. The show ipv6 interface brief command shows the information about Link-Local address on the interface.
| show ipv6 interface brief |
In Router R1
R1#show ipv6 interface brief
Serial0/0 [up/up]
FE80::AB8
2001::1
Loopback10 [up/up]
FE80::C000:1DFF:FEE0:0
FD10::C000:1DFF:FEE0:0
Loopback20 [up/up]
FE80::C000:1DFF:FEE0:0
FD20::C000:1DFF:FEE0:0
In Router R3
R3#show ipv6 interface brief
Serial0/0 [up/up]
FE80::AB8
2002::2
Loopback10 [up/up]
FE80::C002:1DFF:FEE0:0
FD01::C002:1DFF:FEE0:0
Loopback20 [up/up]
FE80::C002:1DFF:FEE0:0
FD20::C002:1DFF:FEE0:0
!--- Shows that R1 and R3's serial interface has same Link-Local address FE80::AB8.
|
In this example, R1 and R3 are assigned with the same Link-Local address and R2 can still reach both the routers when they specify the related output interface.
| Ping R1 and R3's Link-local address from R2 |
Ping R1 Link-Local Address from R2
R2#ping FE80::AB8
Output Interface: serial0/0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FE80::AB8, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/26/92 ms
!--- R2 is connected to R1 through serial0/0.
Debug Output from R1
R1#
*Mar 1 19:51:31.855: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:51:31.859: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:51:31.915: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:51:31.919: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:51:31.947: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:51:31.947: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:51:31.955: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:51:31.955: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:51:31.955: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:51:31.955: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
Ping R3 Link-Local Address from R2
R2#ping FE80::AB8
Output Interface: serial0/1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FE80::AB8, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/28/76 ms
!--- R2 is connected to R1 through serial0/1.
Debug Output from R3
R3#
*Mar 1 19:53:38.815: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:53:38.819: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:53:38.911: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:53:38.915: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:53:38.923: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:53:38.927: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:53:38.955: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:53:38.955: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:53:38.963: ICMPv6: Received echo request from FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
*Mar 1 19:53:38.963: ICMPv6: Sending echo reply to FE80::C001:1DFF:FEE0:0
|
Note: The R2 can ping the Link-Local address of R1 and R3 only because they are directly connected. R2 cannot ping the Link-Local address of the loopback interfaces in routers R1 and R3 as they are not directly connected. Ping works on Link-Local addresses only in case of directly connected networks.
Note: Traceroutes do not work in case of Link-Local addresses and return with the "% No valid source address for destination"error message. This is because IPv6 routers must not forward packets that have Link-Local source or destination addresses to other links.
Related Information



 Feedback
Feedback