تصحيح أخطاء تدفق المكالمات لعبارة إنترنت SSG التي تم تكوينها باستخدام ARP الآمن ل DHCP، و SSG Port-Bundle Host Key، و SSG TCP Redirect، و SESM، و SSG/DHCP Awareness
المحتويات
المقدمة
بؤرة هذا المستند هي عبارة على الإنترنت IOS تشغل SSG و DHCP مع SESM لخدمات البوابة.
المتطلبات الأساسية
المتطلبات
لا توجد متطلبات خاصة لهذا المستند.
المكونات المستخدمة
لا يقتصر هذا المستند على إصدارات برامج ومكونات مادية معينة.
الاصطلاحات
راجع اصطلاحات تلميحات Cisco التقنية للحصول على مزيد من المعلومات حول اصطلاحات المستندات.
معلومات أساسية
نظرة عامة على التقنية والميزات
عبّارة تحديد الخدمة (SSG)
عبارة إختيار الخدمة (SSG) هي حل تحويل لمزودي الخدمة الذين يقدمون إتصالات الإنترنت والإكسترانت والإنترانت للمشتركين باستخدام تقنية الوصول إلى النطاق الترددي العريض، مثل خطوط المشترك الرقمي (DSL) أو أجهزة مودم الكبلات أو الشبكات اللاسلكية للسماح بالوصول المتزامن إلى خدمات الشبكة.
تعمل SSG بالاقتران مع مدير الخدمات لحافة المشترك (SESM) من Cisco. بجانب SESM، توفر SSG مصادقة المشترك، واختيار الخدمة، وقدرات اتصال الخدمة لمشتركي خدمات الإنترنت. يتفاعل المشتركون مع تطبيق ويب SESM باستخدام متصفح إنترنت قياسي.
تعمل SESM في وضعين:
-
وضع RADIUS—يحتوي هذا الوضع على معلومات المشترك والخدمة من خادم RADIUS. SESM في وضع RADIUS مماثل ل SSD.
-
وضع LDAP- يوفر وضع البروتوكول الخفيف للوصول إلى الدليل (LDAP) الوصول إلى دليل متوافق مع LDAP للحصول على معلومات المشترك وملف تعريف الخدمة. كما يعمل هذا الوضع على تحسين وظائف تطبيقات ويب SESM ويستخدم نموذج التحكم في الوصول (RBAC) القائم على الدور لإدارة وصول المشترك.
مفتاح مضيف حزمة منفذ SSG
تعمل ميزة "مفتاح مضيف حزمة منفذ SSG" على تحسين الاتصال والوظائف بين SSG و SESM باستخدام آلية تستخدم عنوان IP لمصدر المضيف ومنفذ المصدر للتعرف على المشتركين ومراقبتهم.
مع ال SSG أيسر-حزمة مضيف سمة، ينجز SSG أيسر-عنوان ترجمة (ضرب) وشبكة عنوان ترجمة (NAT) على ال HTTP حركة مرور بين المشترك وال SESM نادل. عندما يرسل مشترك حزمة HTTP إلى خادم SESM، SSG يخلق خريطة منفذ تقوم بتغيير عنوان IP للمصدر إلى عنوان IP لمصدر SSG تم تكوينه وتغير منفذ TCP للمصدر إلى منفذ مخصص من قبل SSG. تعين SSG مجموعة من المنافذ إلى كل مشترك لأن أحد المشتركين يمكن أن يكون له عدة جلسات TCP متزامنة عند دخوله إلى صفحة ويب. يعرف مفتاح المضيف المعين، أو مجموعة من عنوان IP لمصدر SSG وحزمة المنفذ، كل مشترك بشكل فريد. يتم نقل مفتاح المضيف في حزم RADIUS التي يتم إرسالها بين خادم SESM و SSG في السمة الخاصة ببائع IP الخاص بالمشترك (VSA). عندما يرسل خادم SESM ردا إلى المشترك، SSG يترجم الغاية عنوان IP وغاية TCP ميناء وفقا لخريطة المنفذ.
إعادة توجيه SSG TCP للمستخدمين غير المصدق عليهم
تقوم إعادة التوجيه للمستخدمين غير المصدق عليهم بإعادة توجيه الحزم من مستخدم ما إذا لم يكن المستخدم مخولا مع مزود الخدمة. عندما يحاول مشترك غير مصرح له الاتصال بخدمة على منفذ TCP (على سبيل المثال، إلى www.cisco.com)، تقوم إعادة توجيه SSG TCP بإعادة توجيه الحزمة إلى المدخل المقيد (SESM أو مجموعة من أجهزة SESM). يصدر SESM إعادة توجيه إلى المستعرض لعرض صفحة تسجيل الدخول. يقوم المشترك بتسجيل الدخول إلى SESM ويتم مصادقته وتكليفه. بعد ذلك، يعرض SESM المشترك بصفحة رئيسية مخصصة، أو الصفحة الرئيسية لمزود الخدمة، أو عنوان URL الأصلي.
تعيين عنوان IP الآمن ل DHCP
تقدم ميزة "تعيين عنوان IP الآمن ل DHCP" إمكانية تأمين إدخالات جدول ARP إلى عقود إيجار بروتوكول التكوين الديناميكي للمضيف (DHCP) في قاعدة بيانات DHCP. تؤمن هذه الميزة عنوان MAC الخاص بالعميل وتزامنه مع ربط DHCP، مما يمنع العملاء غير المصرح لهم أو المتسللين من انتحال خادم DHCP والاستيلاء على تأجير DHCP لعميل مفوض. عندما يتم تمكين هذه الميزة، ويقوم خادم DHCP بتعيين عنوان IP إلى عميل DHCP، يضيف خادم DHCP إدخال ARP الآمن إلى جدول ARP باستخدام عنوان IP المعين وعنوان MAC الخاص بالعميل. لا يمكن تحديث إدخال ARP هذا بواسطة أي حزم ARP ديناميكية أخرى، كما أن إدخال ARP هذا موجود في جدول ARP لوقت الإيجار الذي تم تكوينه أو طالما كان التأجير نشطا. لا يمكن حذف إدخال ARP الآمن إلا من خلال رسالة إنهاء صريحة من عميل DHCP أو خادم DHCP عند انتهاء صلاحية ربط DHCP. يمكن تكوين هذه الميزة لشبكة DHCP جديدة أو إستخدامها لترقية أمان شبكة حالية. لا يؤدي تكوين هذه الميزة إلى مقاطعة الخدمة ولا يظهر لعميل DHCP.
رسم بياني Testbed
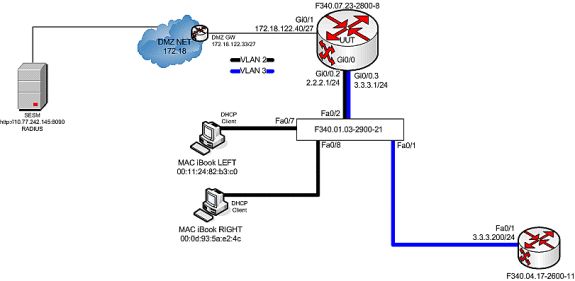
تصحيح أخطاء تدفق المكالمات
أكمل الخطوات التالية:
-
عندما يقوم مفتاح Mac Book الأيسر بتوصيل كبل الإيثرنت بهذه الشبكة أولا، فإنه يؤجر عنوان IP 2.2.2.5/29 من خادم IOS DHCP الذي يعمل على "F340.07.23-2800-8".
debug ip dhcp server packet debug ssg dhcp events *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: DHCP-DISCOVER event received. SSG-dhcp awareness feature enabled *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: DHCPDISCOVER received from client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 on interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2. *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: Get pool name called for 0011.2482.b3c0. No hostobject *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: Get pool class called, class name = Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: Sending DHCPOFFER to client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: creating ARP entry (2.2.2.5, 0011.2482.b3c0). *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: unicasting BOOTREPLY to client 0011.2482.b3c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: DHCPREQUEST received from client 0100.1124.82b3.c0. *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN:2.2.2.5: IP address notification received. *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN:2.2.2.5: HostObject not present *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: Can't find any hostname to update *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: Sending DHCPACK to client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: creating ARP entry (2.2.2.5, 0011.2482.b3c0). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: unicasting BOOTREPLY to client 0011.2482.b3c0 (2.2.2.5). F340.07.23-2800-8#show ip dhcp binding Bindings from all pools not associated with VRF: IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type Hardware address/ User name 2.2.2.5 0100.1124.82b3.c0 Oct 13 2008 08:37 PM Automatic -
بعد أن يقوم بتأجير عنوان IP 2.2.2.5 بنجاح، يفتح Mac iBook LEFT متصفح ويب ويرشده إلى http://3.3.3.200، والذي يستخدم لمحاكاة الموارد المحمية المرتبطة بخدمة SSG "distlearn". يتم تحديد خدمة SSG "distlearn" محليا في موجه SSG "F340.07.23-2800-8":
local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255"
في الواقع، http://3.3.3.200 هو موجه Cisco IOS تم تكوينه ل "ip http server" ويستمع إلى TCP 80، لذلك هو أساسا خادم ويب.
بعد أن يحاول Mac iBook LEFT الاستعراض إلى http://3.3.3.200، نظرا لأن هذا الاتصال هو مدخل على واجهة تم تكوينها باستخدام "إرتباط لأسفل لاتجاه SSG"، يتحقق موجه SSG أولا من وجود كائن مضيف SSG نشط لعنوان IP للمصدر الخاص بطلب HTTP. لأن هذا الطلب الأول من عنوان IP 2.2.2.5، لا يوجد كائن مضيف SSG، ويتم إنشاء مثيل لإعادة توجيه TCP نحو SESM للمضيف 2.2.2.5 من خلال هذا التكوين:
ssg tcp-redirect port-list ports port 80 port 8080 port 8090 port 443 All hosts with destination requests on these TCP Ports are candidates for redirection. server-group ssg_tr_unauth server 10.77.242.145 8090 10.77.242.145 is the SESM server and it’s listening for HTTP on TCP 8090. “server” MUST be in default network or open-garden. redirect port-list ports to ssg_tr_unauth redirect unauthenticated-user to ssg_tr_unauth If an SSG router receives a packets on an interface with “ssg direction downlink” configured, it first compares the Source IP address of the packet with the SSG Host Object Table. If an Active SSG Host Object matching the Source IP address of this packet is not found, AND the destination TCP Port of the packet matches “port-list ports”, and the destination IP address is NOT included as a part of “ssg default-network” OR SSG Open Garden, then the user will be redirected because his is unauthenticated [no Host Object] and his packet is destined for a TCP port in the “port-list ports”. The user will then be captivated until an SSG Host Object is created, or until a timeout which is configurable via “redirect captivate initial default group”. debug ssg tcp redirect debug ssg ctrl-event *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: SSG-TCP-REDIR:-Up: created new remap entry for unauthorised user at 2.2.2.5 *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: Redirect server set to 10.77.242.145,8090 *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: Initial src/dest port mapping 49273<->80 F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg tcp-redirect mappings Authenticated hosts: No TCP redirect mappings for authenticated users Unauthenticated hosts: Downlink Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 TCP remapping Host:2.2.2.5 to server:10.77.242.145 on port:8090 The initial HTTP request from 2.2.2.5 had a source TCP Port of 49273 and a destination IP address of 3.3.3.200 and TCP port of 80. Because of the SSG TCP Redirect, the destination IP header is overwritten with the socket of the SESM server 10.77.242.145:8090. If Port Bundle Host Key were NOT configured, the Source socket of 2.2.2.5:49273 would remain unchanged. However, in this case, Port Bundle Host Key is configured therefore the source address of this packet is ALSO changed based on this configuration: ssg port-map destination range 80 to 8100 ip 10.77.242.145 source ip 172.18.122.40 Any packets destined to SESM on TCP ports 80-8100 are subject to PBHK source NAT to IP socket 172.18.122.40, starting with a port of 64. *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: group:ssg_tr_unauth, web-proxy:0 *Oct 13 20:24:37.417: SSG-REDIR-EVT: -Down: TCP-FIN Rxd for user at 2.2.2.5, port 49273 *Oct 13 20:24:37.421: SSG-REDIR-EVT: -Up: TCP-FIN Rxd from user at 2.2.2.5, src port 49273 As a part of this SSG TCP Redirect, the original URL is preserved http://3.3.3.200 but the destination IP socket is rewritten to 10.77.242.145:8090. So, when the SESM receives this URL of http://3.3.3.200 on TCP port 8090, it sends an HTTP redirect back toward the client’s browser directing the client to the SESM login page, which is http://10.77.242.145:8080/home?CPURL=http%3A%2F%2F3.3.3. 200%2F&t=fma4443t. Notice the Browser Redirect points the Client Browser to TCP 8080 for captive portal. As such, the TCP session for the initial IOS SSG Redirect to 10.77.242.145:8090 is terminated. Also, notice SESM has captured the original URL of http://3.3.3.200 in the Redirect. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (4,&) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=4 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling account status query for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: No active HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64, Ack the query with Complete ID. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Send cmd 4 to host S172.18.122.40:64. dst=10.77.242.145:51806 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Deleting SSGCommandContext ::~SSGCommandContext With Port Bundle Host Key configured, all HTTP communications between Client and SESM are subject to Port Bundling, which is effectively Source NAT for the TCP socket. Above, the “SSG-CTL-EVN” messages debug the communication between the SESM and the IOS SSG Router using a proprietary RADIUS-based protocol. When using Port Bundle Host Key, SESM always uses the Port Bundle to identify the host, which in this case is 172.18.122.40:64. You’ll see when SESM sends the HTTP redirect resulting in the Web browser connecting to 10.77.242.145:8090, SESM also queries SSG on the Control Channel for existence of Host Object for 172.18.122.40:64, which the SSG Router knows is actually 2.2.2.5. Since no Host Object is present, the SSG Router sends the SESM “No active HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64” This can be confirmed at this point like this: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host ### Total HostObject Count: 0عند هذه النقطة، المتصفح الموجود على Mac iBook Left يبدو هكذا عند إدخال http://3.3.3.200:
بعد عمليات إعادة توجيه IOS SSG TCP و SESM HTTP، تبدو الشاشة كما يلي:
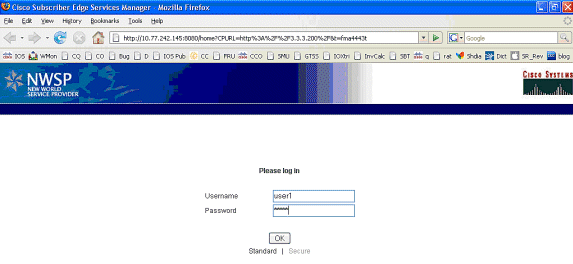
-
بعد إعادة توجيه SSG TCP إلى SESM وإعادة توجيه HTTP التالية التي تم إرسالها بواسطة SESM مرة أخرى إلى متصفح Mac IBook Left، يدخل Mac iBook User1 باسم المستخدم وCisco ككلمة مرور:
-
بعد الضغط على زر موافق، يرسل SESM موجه SSG بيانات الاعتماد هذه من خلال بروتوكول خاص يستند إلى RADIUS.
*Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (1,user1) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=1 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling account logon for host 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: No auto-domain selected for user user1 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Authenticating user user1. *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: ssg_aaa_nasport_fixup function *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: slot=0, adapter=0, port=0, vlan-id=2, dot1q-tunnel-id=0, vpi=0, vci=0, type=10 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Deleting SSGCommandContext ::~SSGCommandContext
-
وبدوره، يقوم موجه SSG ببناء حزمة طلب وصول RADIUS وإرسالها إلى RADIUS لمصادقة المستخدم 1:
*Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS(00000008): Send Access-Request to 10.77.242.145:1812 id 1645/11, len 88 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: authenticator F0 56 DD E6 7E 28 3D EF - BC B1 97 6A A9 4F F2 A6 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "user1" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: User-Password [2] 18 * *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 16 "0011.2482.b3c0" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15] *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 0 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 9 "0/0/0/2" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 172.18.122.40
-
يستجيب RADIUS مع قبول الوصول للمستخدم 1، ويتم إنشاء كائن مضيف SSG في "F340.07.23-2800-8":
*Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Received from id 1645/11 10.77.242.145:1812, Access-Accept, len 273 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: authenticator 52 7B 50 D7 F2 43 E6 FC - 7E 3B 22 A4 22 A7 8F A6 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Service-Type [6] 6 Framed [2] *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 23 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 17 "NInternet-Basic" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 13 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 7 "Niptv" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 14 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 8 "Ngames" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 18 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 12 "Ndistlearn" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 18 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 12 "Ncorporate" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 22 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 16 "Nhome_shopping" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 16 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 10 "Nbanking" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 16 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 10 "Nvidconf" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "user1" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 16 "0011.2482.b3c0" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15] *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 0 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 9 "0/0/0/2" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 172.18.122.40 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS(00000008): eceived from id 1645/11 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 4 0 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating radius packet *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Response is good *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-EVN: HostObject::HostObject: size = 616 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::Reset *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList NInternet-Basic *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Niptv *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ngames *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ndistlearn *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ncorporate *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nhome_shopping *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nbanking *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nvidconf *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: DoAccountLogon: ProfileCache is Enabled *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Account logon is accepted [Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64, user1] *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Send cmd 1 to host S172.18.122.40:64. dst=10.77.242.145:51806 *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating HostObject for host 2.2.2.5 Finally, our SSG Host Object is created for 2.2.2.5. Notice that “user1” RADIUS profile is configured with many ssg-account-info VSA with “N” Attribute, which is an SSG code for Service to which the user is subscribed. Please note, this doesn’t mean “user1” has any Active services at this point, which can be confirmed with: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 1: 2.2.2.5 [Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64] ### Active HostObject Count: 1 F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 2.2.2.5 ------------------------ HostObject Content --- Activated: TRUE Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 User Name: user1 Host IP: 2.2.2.5 Host mac-address: 0011.2482.b3c0 Port Bundle: 172.18.122.40:64 Msg IP: 0.0.0.0 (0) Host DNS IP: 0.0.0.0 Host DHCP pool : Maximum Session Timeout: 64800 seconds Action on session timeout: Terminate Host Idle Timeout: 0 seconds User policing disabled User logged on since: *20:37:05.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:37:09.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 SMTP Forwarding: NO Initial TCP captivate: NO TCP Advertisement captivate: NO Default Service: NONE DNS Default Service: NONE Active Services: NONE AutoService: Internet-Basic; Subscribed Services: Internet-Basic; iptv; games; distlearn; corporate; home_shopping; banking; vidconf; Subscribed Service Groups: NONE
-
عند هذه النقطة، يتم تحديد user1 ككائن مضيف SSG ولكن ليس لديه حق الوصول إلى أي خدمات SSG. يتم تقديم الكمبيوتر المحمول Mac IBook الأيسر مع شاشة تحديد الخدمة وينقر على التعلم عن بعد:
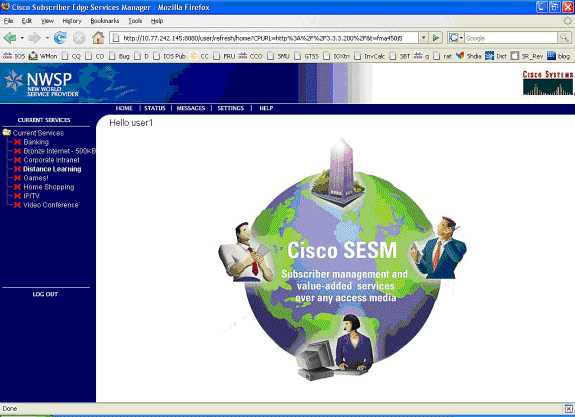
-
بعد النقر فوق التعلم عن بعد، يتصل مربع SESM بموجه SSG باستخدام قناة التحكم:
debug ssg ctrl-events *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (11,distlearn) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 SSG Router is receiving control channel command that SSG User 172.18.122.40:64 [maps to 2.2.2.5] wants to activate SSG Service ‘distlearn’. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=11 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling service logon for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Locating the HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating pseudo ServiceInfo for service: distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-EVN: ServiceInfo::ServiceInfo: size = 416 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: ServiceInfo: Init servQ and start new process for distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service(distlearn)::AddRef(): ref after = 1 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Got profile for distlearn locally Since “distlearn” is available from local configuration: local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255" ...we don’t need to make a AAA call to download SSG Service Information. However, please note that in most real-world SSG implementations, SSG Services are defined on the RADIUS AAA Server. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Create a new service table for distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service bound on this interface are : distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service distlearn bound to interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3 firsthop 0.0.0.0 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: Service Address List : *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: Addr:3.3.3.200 mask:255.255.255.255 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add a new service distlearn to an existing table Here the SSG creates a Service Table for distlearn and binds it to an “ssg direction uplink” interface complete with the R attribute for the Service. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Locating the HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Checking connection activation for 172.18.122.40:64 to distlearn. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating ConnectionObject (172.18.122.40:64, distlearn) *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: ConnectionObject::ConnectionObject: size = 304 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service(distlearn)::AddRef(): ref after = 2 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Checking maximum service count. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: Opening connection for user user1 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: Connection opened *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service logon is accepted. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating the ConnectionObject. Once the Service is verified locally, SSG needs to build a “Connection” where a “Connection” is a tuple with: A. SSG Host Object B. SSG Service Name and Attributes C. SSG Downlink interface D. SSG Upstream interface A-D are used to create a pseudo hidden VRF service table for which traffic from this host can transit. See here: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg connection 2.2.2.5 distlearn ------------------------ConnectionObject Content ---- User Name: user1 Owner Host: 2.2.2.5 Associated Service: distlearn Calling station id: 0011.2482.b3c0 Connection State: 0 (UP) Connection Started since: *20:40:21.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:41:04.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 Connection Traffic Statistics: Input Bytes = 420, Input packets = 5 Output Bytes = 420, Output packets = 5 Session policing disabled F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 2.2.2.5 ------------------------ HostObject Content ----------- Activated: TRUE Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 User Name: user1 Host IP: 2.2.2.5 Host mac-address: 0011.2482.b3c0 Port Bundle: 172.18.122.40:64 Msg IP: 0.0.0.0 (0) Host DNS IP: 0.0.0.0 Host DHCP pool : Maximum Session Timeout: 64800 seconds Action on session timeout: Terminate Host Idle Timeout: 0 seconds User policing disabled User logged on since: *20:37:05.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:40:23.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 SMTP Forwarding: NO Initial TCP captivate: NO TCP Advertisement captivate: NO Default Service: NONE DNS Default Service: NONE Active Services: distlearn; AutoService: Internet-Basic; Subscribed Services: Internet-Basic; iptv; games; distlearn; corporate; home_shopping; banking; vidconf; Subscribed Service Groups: NONE -
تم تشغيل اتصال SSG، وتم إكمال تدفق المكالمات. يمكن لصفحة Mac IBook اليسرى الاستعراض بنجاح إلى http://3.3.3.200:
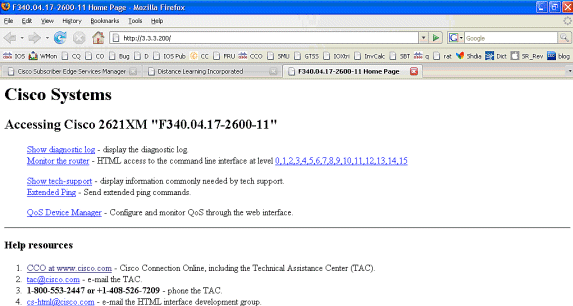
شرح تكوين موجه SSG مع مستندات الميزة
version 12.4 service nagle no service pad service tcp-keepalives-in service tcp-keepalives-out service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname F340.07.23-2800-8 ! boot-start-marker boot system flash flash: c2800nm-adventerprisek9-mz.124-21.15 boot-end-marker ! logging buffered 1024000 debugging ! aaa new-model ! aaa authorization network default group radius ! aaa session-id common no ip source-route ! ip cef ip dhcp relay information trust-all ip dhcp use vrf connected ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.1 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.2 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.3 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.4 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.6 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.7 We are excluding 2.2.2.1-4 and 2.2.2.6-7 to ensure the only DHCP address that will be leased is 2.2.2.5/29. Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server ip dhcp pool dhcp_guest_v3501 network 2.2.2.0 255.255.255.248 default-router 2.2.2.1 dns-server 172.18.108.34 lease 0 4 update arp If an interface on this router is configured with an address in the 2.2.2.0/29 range, it will field DHCP request from host on that network and assign IP address 2.2.2.5, GW 2.2.2.1, and DNS Server 172.18.108.24. The lease time on the IP address will be 4 hours. Also, “update arp” will ensure ARP entries for IP addresses leased via DHCP will match the MAC entry in the DHCP Binding table. This will prevent SSG session hijacking in the event a static user re-uses a DHCP [or is given] leased address. Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Configuring DHCP Services for Accounting and Security ! no ip domain lookup ip auth-proxy max-nodata-conns 3 ip admission max-nodata-conns 3 ! voice-card 0 no dspfarm ! ssg enable Enables SSG subsystem. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg intercept dhcp Enables SSG/DHCP Awareness. In our example, this will result in an SSG Host object being destroyed when either of these occur: A. A DHCPRELEASE message is received for an IP address matching a currently Active SSG Host Object. B. A DHCP Lease expires for an IP address matching a currently Active SSG Host Object. Configuring SSG for On-Demand IP Address Renewal ssg default-network 10.77.242.145 255.255.255.255 All packets ingress to “ssg direction downlink” interfaces can access the “ssg default-network” regardless as to whether a Host or Connection Object exists. SSG allows all users, even unauthenticated users, to access the default network. Typically, SESM belongs to the default network. However, other types of servers, such as DNS/DHCP servers or TCP-Redirect servers, can also be part of the default network. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg service-password cisco If an SSG Service is not defined locally and we therefore need to make a RADIUS call when a user subscribes to an SSG Service, the password “cisco” is used in the RADIUS Access-Request for the Service. ssg radius-helper auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 ssg radius-helper key cisco Used to communicate with SESM on SSG Control Channel. SESM must also maintain a similar static configuration for each SSG Router it serves. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg auto-logoff arp match-mac-address interval 30 In the absence of user traffic, SSG will send an ARP Ping for all Active Host Objects and will invoke an AutoLogoff if either the host fails to reply or the MAC address of the host has changed. Configuring SSG to Log Off Subscribers ssg bind service distlearn GigabitEthernet0/0.3 SSG traffic is not routed using the Global routing table. Instead it’s routed from “ssg direction downstream” interface using the information in the mini-VRF seen in “show ssg connection”, which includes a manual binding of Service<-->”ssg direction uplink” interface. Hence, it is a requirement of SSG to manually bind services to interfaces or next-hop IP addresses. Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services ssg timeouts session 64800 Absolute timeout for SSG Host Object is 64800 seconds. Configuring SSG to Log Off Subscribers ssg port-map destination range 80 to 8100 ip 10.77.242.145 source ip 172.18.122.40 Port Bundle Host Key configuration. All traffic destined to 10.77.242.145 in the range of TCP 80 to 8100 will be Source NATed to 172.18.122.40. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg tcp-redirect Enters SSG redirect sub-config. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers port-list ports port 80 port 8080 port 8090 port 443 Defines a list of destination TCP ports which are candidates for TCP redirection. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers server-group ssg_tr_unauth server 10.77.242.145 8090 Defines a redirect server list and defines the TCP port on which they’re listening for redirects. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers redirect port-list ports to ssg_tr_unauth redirect unauthenticated-user to ssg_tr_unauth If a Host Object does NOT exist and the traffic is ingress to an “ssg direction downlink” interface AND its destination port is in port-list ports, THEN redirect this traffic to “server-group ssg_tr_unauth”. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers ssg service-search-order local remote Look for SSG Service defined in a local-profile in IOS configuration before making a AAA call to download Service information. Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255" Local definition of SSG Service “distlearn” 26 9 251 is Vendor Specific, Cisco, SSG Service Info Attributes defined herein: R: Destination Network, Specifies IP routes belonging to this Service Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services RADIUS Profiles and Attributes for SSG interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2 description Guest Wireless Vlan encapsulation dot1Q 2 ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.248 no ip redirects no ip unreachables no ip mroute-cache ssg direction downlink All SSG Host Objects should be located on downlink direction. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3 description Routed connection back to Blue encapsulation dot1Q 3 ip address 3.3.3.1 255.255.255.0 ssg direction uplink All SSG Services should be located on uplink direction. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 172.18.122.40 255.255.255.224 duplex auto speed auto ! ip forward-protocol nd ip route 10.77.242.144 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 10.77.242.145 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 157.157.157.0 255.255.255.0 3.3.3.5 ip route 172.18.108.34 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 172.18.124.101 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip radius source-interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ! radius-server host 10.77.242.145 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 timeout 5 retransmit 3 key 7 070C285F4D06 ! control-plane ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
اعتبارات إعادة إستخدام الأمن والجلسة
عندما تستخدم SSG و DHCP معا، يمكن أن تسمح هذه السيناريوهات للمستخدمين الضارين بإعادة إستخدام كائن مضيف SSG مصدق الذي يسمح بالوصول غير المصدق إلى الموارد الآمنة:
-
إذا لم يتم تكوين وعي SSG/DHCP مع "ssg intercept dhcp"، يمكن لمستخدم DHCP جديد تأجير عنوان IP مستأجر مسبقا والذي لا يزال كائن مضيف SSG موجودا له. بما أن طلب TCP الأول من هذا المستخدم الجديد له مطابقة، على الرغم من أنه قديم، أو كائن مضيف SSG الذي يطابق عنوان IP للمصدر، فإن هذا المستخدم يتم منحه إستخداما غير مصدق عليه للموارد المحمية. ويمكن منع ذلك مع "ssg intercept dhcp"، والذي ينتج عنه إزالة كائن مضيف SSG عندما يحدث إما:
-
يتم تلقي DHCPprelease لعنوان IP يطابق كائن مضيف نشط.
-
ينتهي إيجار DHCP لعنوان IP الذي يطابق كائن مضيف نشط.
-
-
إذا قام مستخدم DHCP بإشراك عنوان IP المؤجر بشكل إجتماعي إلى مستخدم ضار قبل تسجيل خروج DHCP غير الجميل، وهو تسجيل خروج DHCP لم يتم إرسال DHCP له، فيمكن للمستخدم الضار تكوين الجهاز بشكل ثابت باستخدام عنوان IP هذا وإعادة إستخدام كائن مضيف SSG سواء تم تكوين "ssg intercept DHCP" أو لا. يمكن منع هذا الأمر باستخدام مجموعة من "ssg intercept dhcp" و"update arp" التي تم تكوينها أسفل تجمع IOS DHCP. يضمن "تحديث arp" أن نظام IOS الفرعي الوحيد القادر على إضافة إدخالات ARP أو إزالتها هو النظام الفرعي لخادم DHCP. مع "تحديث arp"، يتطابق ربط IP إلى MAC DHCP دائما مع ربط IP إلى MAC في جدول ARP. على الرغم من أن المستخدم الضار لديه عنوان IP تم تكوينه بشكل ثابت ويطابق كائن مضيف SSG، فإنه لا يسمح لحركة مرور البيانات بإدخال موجه SSG. لأن عنوان MAC لا يطابق عنوان MAC الخاص بربط DHCP الحالي، يمنع خادم IOS DHCP إنشاء إدخال ARP.
-
عند تكوين SSG و DHCP معا، تمنع "ssg intercept dhcp" و"update arp" إعادة إستخدام الجلسة. التحدي الأخير غير المرتبط بالأمان هو تحرير تأجير DHCP وإدخال ARP عندما يقوم مضيف DHCP بتنفيذ تسجيل خروج غير رائع. ينتج عن تكوين "ARP المعتمد" على واجهة "SSG direction downlink" طلبات ARP دورية مرسلة إلى جميع الأجهزة المضيفة للتأكد من أنها لا تزال نشطة. إذا لم يتم تلقي أي إستجابة من رسائل ARP الدورية هذه، يتم إصدار ربط DHCP، ويقوم النظام الفرعي IOS DHCP بإزالة إدخال ARP.
interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 arp authorized arp probe interval 5 count 15
في هذا المثال، يتم إرسال طلب ARP بشكل دوري لتحديث جميع إدخالات ARP المعروفة على Fa0/0 كل 5s. بعد 15 فشل، يتم إصدار ربط DHCP، ويزيل النظام الفرعي IOS DHCP إدخال ARP.
في سياق SSG بدون "ARP المعتمد"، إذا قام مضيف DHCP بتنفيذ تسجيل دخول غير سار، يظل إيجار DHCP وكائن مضيف SSG المرتبط به نشطا حتى ينتهي عقد إستئجار عنوان DHCP هذا، ولكن لا تحدث إعادة إستخدام الجلسة طالما تم تكوين "ssg intercept dhcp" بشكل عام.
يوقف "ARP المعتمد" تعلم ARP الديناميكي على الواجهة التي تم تكوينه عليها. إدخالات ARP الوحيدة على الواجهة المعنية هي تلك التي تمت إضافتها بواسطة خادم IOS DHCP بعد بدء عقد الإيجار. بعد ذلك يتم إزالة إدخالات ARP هذه بواسطة خادم IOS DHCP بمجرد إنهاء التأجير، إما بسبب إستلام إصدار DHCP، أو انتهاء صلاحية التأجير، أو فشل تحقيق ARP بسبب تسجيل خروج DHCP غير لطيف.
ملاحظات التنفيذ:
-
يعد "ssg auto-logoff arp" و"ssg auto-logoff icmp" طريقتين غير مرغوب فيهما لمنع إعادة إستخدام جلسة العمل أو مشاكل الأمان الناتجة. لا يرسل متغيرات "arp" و"icmp" ل "ssg auto-logoff" سوى إختبار اتصال ARP أو IMCP عندما لا ترى حركة مرور على اتصال SSG داخل "interval" الذي تم تكوينه، والذي يكون أقل منه 30 ثانية. إذا قام بروتوكول DHCP باستئجار عنوان IP تم إستخدامه مسبقا في غضون 30 ثانية، أو قام مستخدم ضار بتكوين عنوان DHCP مرتبط حاليا بشكل ثابت في غضون 30 ثانية، فسيتم إعادة إستخدام الجلسة لأن SSG يرى حركة مرور البيانات على كائن الاتصال، ولا يتم إستدعاء "ssg auto-loexit".
-
في جميع حالات الاستخدام، لا يتم منع إعادة إستخدام الجلسة إذا قام مضيف ضار بتنفيذ خاصية عنوان MAC.
الجدول 1 - إعادة إستخدام الجلسة واعتبارات الأمان في عمليات نشر SSG/DHCP
| دالة | الآثار الأمنية | |
|---|---|---|
| SSG Auto-Log arp [match-mac-address] [ثوان الفاصل] SSG Auto-LogICMP [المهلة المللي ثانية] [رقم الحزم] [ثوان الفاصل] | يحذف كائن مضيف SSG بعد فشل ARP أو ICMP ping، والذي يتم إرساله فقط بعد عدم ظهور حركة مرور على اتصال SSG ضمن "الفاصل الزمني". | يعيد إستخدام الجلسة إذا كان DHCP يستأجر عنوان IP مستخدم سابقا في غضون 30 ثانية، أو كان مستخدم ضار يقوم بتكوين عنوان DHCP مرتبط حاليا بشكل ثابت في غضون 30 ثانية لأن SSG يرى حركة مرور البيانات على كائن الاتصال، ولا يتم إستدعاء "ssg auto-loexit". |
| اعتراض ssg ل dhcp | يخلق وعي SSG/DHCP الذي يسمح بحذف كائن مضيف SSG ضمن هذه الأحداث: يتم تلقي DHCPRELEASE لعنوان IP الذي يطابق كائن مضيف نشط. ب. تنتهي صلاحية تأجير DHCP لعنوان IP الذي يطابق كائن مضيف نشط. | يمنع مستخدمي DHCP من إعادة إستخدام جلسات SSG ولكنه لا يمنع المستخدمين الثابتين من انتحال عناوين DHCP أو إعادة إستخدام جلسات SSG. |
| ip dhcp بركة تحديث إختبار arp | يضمن أن نظام IOS الفرعي الوحيد القادر على إضافة أو إزالة إدخالات ARP هو النظام الفرعي لخادم DHCP. | يمنع كل جلسة إعادة إستخدام عندما يشكل مع "ssg intercept dhcp." عندما يتم تكوينها دون "ssg intercept dhcp"، إذا كان DHCP يؤجر عنوان IP مستخدم مسبقا، فإن إعادة إستخدام الجلسة ما تزال ممكنة. |
| قارن FastEthernet0/0 arp معتمد | يرسل طلبات ARP الدورية إلى جميع الأجهزة المضيفة للتأكد من أنها لا تزال نشطة. يوقف تعلم ARP الديناميكي. | يسمح ب DHCP ملزم و ARP مدخل حذف عندما يقوم مستخدم DHCP بتنفيذ تسجيل خروج غير لطيف. |
معلومات ذات صلة
محفوظات المراجعة
| المراجعة | تاريخ النشر | التعليقات |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01-Dec-2008 |
الإصدار الأولي |
 التعليقات
التعليقات