Client mode specifies that NAT or PAT be done so that the PCs and other hosts at the remote end of the VPN tunnel form a private network that do not use any IP addresses in the IP address space of the destination server. In Client mode, the outside interface of the Cisco VPN hardware client can be assigned an IP address by the remote server.
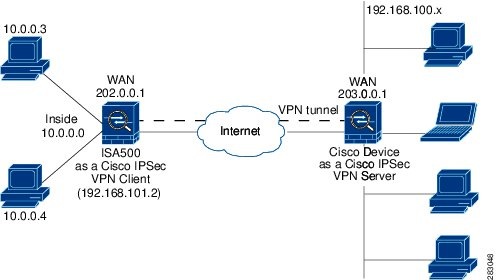
Figure 7 illustrates the client mode of operation. In this example, the security appliance provides access to two PCs, which have IP addresses in the 10.0.0.0 private network space. These PCs connect to the Ethernet interface on the security appliance, and the server assigns an IP address 192.168.101.2 to the security appliance. The security appliance performs NAT or PAT translation over the VPN tunnel so that the PCs can access the destination network. When accessing the remote network 192.168.100.x, the hosts 10.0.0.3 and 10.0.04 will be translated to 192.168.101.2, but hosts in the remote network 192.168.100.x cannot access the hosts 10.0.0.3 and 10.0.04.
Figure 8-5 IPsec VPN Client Connection
