Konfigurieren der Standardroute im EIGRP
Download-Optionen
-
ePub (103.2 KB)
In verschiedenen Apps auf iPhone, iPad, Android, Sony Reader oder Windows Phone anzeigen
Inklusive Sprache
In dem Dokumentationssatz für dieses Produkt wird die Verwendung inklusiver Sprache angestrebt. Für die Zwecke dieses Dokumentationssatzes wird Sprache als „inklusiv“ verstanden, wenn sie keine Diskriminierung aufgrund von Alter, körperlicher und/oder geistiger Behinderung, Geschlechtszugehörigkeit und -identität, ethnischer Identität, sexueller Orientierung, sozioökonomischem Status und Intersektionalität impliziert. Dennoch können in der Dokumentation stilistische Abweichungen von diesem Bemühen auftreten, wenn Text verwendet wird, der in Benutzeroberflächen der Produktsoftware fest codiert ist, auf RFP-Dokumentation basiert oder von einem genannten Drittanbieterprodukt verwendet wird. Hier erfahren Sie mehr darüber, wie Cisco inklusive Sprache verwendet.
Informationen zu dieser Übersetzung
Cisco hat dieses Dokument maschinell übersetzen und von einem menschlichen Übersetzer editieren und korrigieren lassen, um unseren Benutzern auf der ganzen Welt Support-Inhalte in ihrer eigenen Sprache zu bieten. Bitte beachten Sie, dass selbst die beste maschinelle Übersetzung nicht so genau ist wie eine von einem professionellen Übersetzer angefertigte. Cisco Systems, Inc. übernimmt keine Haftung für die Richtigkeit dieser Übersetzungen und empfiehlt, immer das englische Originaldokument (siehe bereitgestellter Link) heranzuziehen.
Inhalt
Einführung
In diesen Dokumenten wird beschrieben, wie Standardrouten im Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) konfiguriert werden.
Voraussetzungen
Anforderungen
Cisco empfiehlt, EIGRP kennen zu lernen.
Verwendete Komponenten
Dieses Dokument ist nicht auf bestimmte Software- und Hardwareversionen beschränkt.
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument wurden von den Geräten in einer bestimmten Laborumgebung erstellt. Alle in diesem Dokument verwendeten Geräte haben mit einer leeren (Standard-)Konfiguration begonnen. Wenn Ihr Netzwerk in Betrieb ist, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die potenziellen Auswirkungen eines Befehls verstehen.
Konfigurieren
Diese Methoden sind verfügbar, um die Standardroute in EIGRP anzukündigen, die in diesem Artikel erläutert wird:
1. Standard-Routing und Neuverteilung verwenden
2. Summary-Adresse verwenden
Netzwerkdiagramm
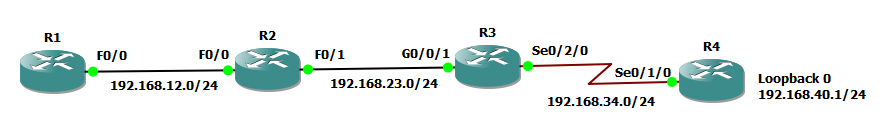
Konfiguration
Hier werden die Router R1, R2 und R3 mit EIGRP konfiguriert, und zwischen R3 und R4 wird kein EIGRP ausgeführt.
R1
!
router eigrp 1 network 192.168.12.0
!
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
D 192.168.23.0/24 [90/30720] via 192.168.12.2, 00:10:27, FastEthernet0/0
R2
! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.12.0 network 192.168.23.0
!
R2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
R3
! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.23.0
!
R3#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
D 192.168.12.0/24
[90/28416] via 192.168.23.2, 00:05:16, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
192.168.23.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
L 192.168.23.3/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
192.168.34.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.34.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/2/0
L 192.168.34.3/32 is directly connected, Serial0/2/0
Methode 1. Standard-Routing und -Neuverteilung verwenden
Diese Methode beschreibt, wie die Standardroute in EIGRP mithilfe der statischen Standardroute angekündigt wird:
R3(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.34.4
R3#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.34.4 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.34.4
D 192.168.12.0/24
[90/28416] via 192.168.23.2, 00:59:18, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
192.168.23.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
L 192.168.23.3/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
192.168.34.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.34.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/2/0
L 192.168.34.3/32 is directly connected, Serial0/2/0
Hinweis: In dieser Situation kann eine Netzwerk-Anweisung nicht innerhalb von EIGRP verwendet werden, um 0.0.0.0 anzukündigen, da sie nicht direkt verbunden ist.
Die Neuverteilung der statischen Route erfolgt unter EIGRP, wie hier gezeigt:
R3(config)#router eigrp 1 R3(config-router)#redistribute static metric 100000 1000 255 1 1500
Überprüfen
In diesem Abschnitt überprüfen Sie, ob Ihre Konfiguration ordnungsgemäß funktioniert.
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.12.2 to network 0.0.0.0
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
D 192.168.23.0/24 [90/30720] via 192.168.12.2, 00:14:01, FastEthernet0/0
D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/286720] via 192.168.12.2, 00:00:39, FastEthernet0/0
R2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.23.3 to network 0.0.0.0
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/284160] via 192.168.23.3, 00:04:44, FastEthernet0/1
Methode 2. Summary-Adresse verwenden
Diese Methode verwendet die Summierungsregel für EIGRP, wie im Bild gezeigt.
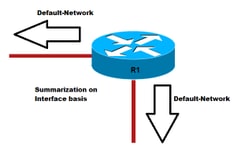
!
R3(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0/1 R3(config-if)#ip summary-address eigrp 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
!
Überprüfen
In diesem Abschnitt überprüfen Sie, ob Ihre Konfiguration ordnungsgemäß funktioniert.
R3#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is 0.0.0.0 to network 0.0.0.0
D* 0.0.0.0/0 is a summary, 00:00:06, Null0
D 192.168.12.0/24
[90/28416] via 192.168.23.2, 00:15:54, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
192.168.23.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
L 192.168.23.3/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
192.168.34.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.34.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/2/0
L 192.168.34.3/32 is directly connected, Serial0/2/0
Die Routing-Tabelle R1 und R2 zeigt nun eine vom EIGRP erhaltene Standardroute:
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.12.2 to network 0.0.0.0
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
D 192.168.23.0/24 [90/30720] via 192.168.12.2, 00:17:50, FastEthernet0/0
D* 0.0.0.0/0 [90/30976] via 192.168.12.2, 00:01:30, FastEthernet0/0
R2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.23.3 to network 0.0.0.0
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
D* 0.0.0.0/0 [90/28416] via 192.168.23.3, 00:03:50, FastEthernet0/1
Fehlerbehebung
Für diese Konfiguration sind derzeit keine spezifischen Informationen zur Fehlerbehebung verfügbar.
Beiträge von Cisco Ingenieuren
- Pravin KumarCisco TAC-Techniker
- Gaurav MahajanCisco TAC-Techniker
Cisco kontaktieren
- Eine Supportanfrage öffnen

- (Erfordert einen Cisco Servicevertrag)
 Feedback
Feedback