Router mit drei Schnittstellen ohne NAT-Konfiguration der Cisco IOS Firewall
Inhalt
Einführung
Dieses Dokument enthält ein Beispiel für eine typische Konfiguration für ein kleines Unternehmen, das mit dem Internet verbunden ist und seine eigenen Server betreibt. Die Verbindung zum Internet erfolgt über eine serielle Leitung. Ethernet 0 ist mit dem internen Netzwerk (einem einzigen LAN) verbunden. Ethernet 1 ist mit einem DMZ-Netzwerk verbunden, das über einen Knoten verfügt, der für die Bereitstellung von Services für die Außenwelt verwendet wird. Der ISP hat dem Unternehmen den Netzwerkblock 192.168.27.0/24 zugewiesen. Diese wird gleichmäßig zwischen der DMZ und dem internen LAN mit der Subnetzmaske 255.255.255.128 aufgeteilt. Grundlegende Richtlinien sind:
-
Erlauben Sie Benutzern im internen Netzwerk, eine Verbindung zu einem beliebigen Dienst im öffentlichen Internet herzustellen.
-
Jeder Benutzer im Internet kann eine Verbindung zu den WWW-, FTP- und SMTP-Diensten (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) auf dem DMZ-Server herstellen und DNS-Abfragen (Domain Name System) durchführen. Dies ermöglicht es externen Personen, Webseiten des Unternehmens anzuzeigen, Dateien abzurufen, die das Unternehmen für den externen Gebrauch veröffentlicht hat, und E-Mails an das Unternehmen zu senden.
-
Lassen Sie internen Benutzern zu, sich mit dem POP-Service auf dem DMZ-Server (zum Abholen ihrer E-Mail) und Telnet-Verbindung (zum Verwalten) zu verbinden.
-
Die DMZ darf keine Verbindungen herstellen, weder zum privaten Netzwerk noch zum Internet.
-
Überprüfen Sie alle Verbindungen, die über die Firewall zu einem SYSLOG-Server im privaten Netz führen. Systeme im internen Netzwerk verwenden den DNS-Server in der DMZ. Eingabe-Zugriffslisten werden an allen Schnittstellen verwendet, um Spoofing zu verhindern. Mithilfe von Zugriffslisten für die Ausgabe wird gesteuert, welcher Datenverkehr an eine beliebige Schnittstelle gesendet werden kann.
Informationen zur Konfiguration eines Zwei-Schnittstellen-Routers ohne NAT mithilfe der Cisco IOS-Firewall-Konfiguration finden Sie unter Zwei-Schnittstellen-Router ohne NAT unter Verwendung der Cisco IOS® Firewall.
Unter Konfiguration der NAT-Cisco IOS-Firewall mit Zweischnittstelle-Router können Sie einen Zwei-Schnittstellen-Router mit NAT mithilfe einer Cisco IOS-Firewall konfigurieren.
Voraussetzungen
Anforderungen
Für dieses Dokument bestehen keine speziellen Anforderungen.
Verwendete Komponenten
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument basieren auf den Versionen Software und Hardware:
-
Cisco IOS Softwareversion 12.2(15)T13 mit Firewall-Feature-Set
-
Cisco 7204 VXR-Router
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument wurden von den Geräten in einer bestimmten Laborumgebung erstellt. Alle in diesem Dokument verwendeten Geräte haben mit einer leeren (Standard-)Konfiguration begonnen. Wenn Ihr Netzwerk in Betrieb ist, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die potenziellen Auswirkungen eines Befehls verstehen.
Konventionen
Weitere Informationen zu Dokumentkonventionen finden Sie in den Cisco Technical Tips Conventions (Technische Tipps zu Konventionen von Cisco).
Konfigurieren
In diesem Abschnitt erhalten Sie Informationen zum Konfigurieren der in diesem Dokument beschriebenen Funktionen.
Hinweis: Verwenden Sie das Command Lookup Tool (nur registrierte Kunden), um weitere Informationen zu den in diesem Abschnitt verwendeten Befehlen zu erhalten.
Netzwerkdiagramm
In diesem Dokument wird die folgende Netzwerkeinrichtung verwendet:
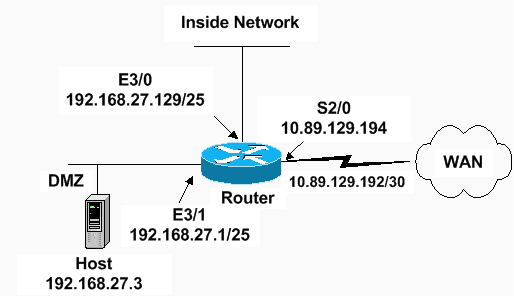
Konfigurationen
In diesem Dokument wird diese Konfiguration verwendet.
| 7204 VXR-Router |
|---|
version 12.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname Router ! logging queue-limit 100 enable secret 5 <something> ! ip subnet-zero ip cef no ip domain lookup ! ip inspect audit-trail ! !--- Sets the length of time a TCP session !--- is still managed after no activity. ! ip inspect tcp idle-time 14400 ! !--- Sets the length of time a UDP session !--- is still managed after no activity. ! ip inspect udp idle-time 1800 ! !--- Sets the length of time a DNS name lookup session !--- is still managed after no activity. ! ip inspect dns-timeout 7 ! !--- Sets up inspection list "standard" !--- to be used for inspection of inbound Ethernet 0 !--- and inbound serial (applied to both interfaces). ! ip inspect name standard cuseeme ip inspect name standard ftp ip inspect name standard h323 ip inspect name standard http ip inspect name standard rcmd ip inspect name standard realaudio ip inspect name standard smtp ip inspect name standard sqlnet ip inspect name standard streamworks ip inspect name standard tcp ip inspect name standard tftp ip inspect name standard udp ip inspect name standard vdolive ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 ! no voice hpi capture buffer no voice hpi capture destination ! mta receive maximum-recipients 0 ! interface ethernet 3/0 ip address 192.168.27.129 255.255.255.128 ! !--- Apply the access list to allow all legitimate !--- traffic from the inside network and prevent spoofing. ! ip access-group 101 in ! !--- Apply inspection list "standard" for inspection !--- of inbound Ethernet traffic. This inspection opens !--- temporary entries on access lists 111 and 121. ! ip inspect standard in duplex full interface ethernet 3/1 ip address 192.168.27.1 255.255.255.128 ! !--- Apply the access list to permit DMZ traffic (except spoofing) !--- on the DMZ interface inbound. The DMZ is not permitted to initiate !--- any outbound traffic except Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). ! ip access-group 111 in ! !--- Apply inspection list "standard" for inspection of outbound !--- traffic from e1. This adds temporary entries on access list 111 !--- to allow return traffic, and protects servers in DMZ from !--- distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. ip inspect standard out duplex full ! interface serial 2/0 ip address 10.89.129.194 255.255.255.252 !--- Apply the access list to allow legitimate traffic. ! ip access-group 121 in serial restart_delay 0 ! ip classless no ip http-server !--- A syslog server is located at this address. logging 192.168.27.131 !--- This command enables the logging of session !--- information (addresses and bytes). !--- Access list 20 is used to control which !--- network management stations can access via SNMP. ! access-list 20 permit 192.168.27.5 ! !--- Use an access list to allow all legitimate traffic from !--- the inside network and prevent spoofing. The inside !--- network can only connect to the Telnet and POP3 !--- service of 192.168.27.3 on DMZ, and can ping (ICMP) to the DMZ. !--- Additional entries can be added to permit SMTP, WWW, and !--- so forth, if necessary. In addition, the inside network can !--- connect to any service on the Internet. ! access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.27.128 0.0.0.127 host 192.168.27.3 eq pop3 access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.27.128 0.0.0.127 host 192.168.27.3 eq telnet access-list 101 permit icmp 192.168.27.128 0.0.0.127 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.127 access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.27.128 0.0.0.127 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.127 access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.27.128 0.0.0.127 any access-list 101 deny ip any any ! ! !--- The access list permits ping (ICMP) from the DMZ and denies all !--- traffic initiated from the DMZ. Inspection opens !--- temporary entries to this list. ! access-list 111 permit icmp 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.127 any access-list 111 deny ip any any ! ! ! !--- Access list 121 allows anyone on the Internet to connect to !--- WWW, FTP, DNS, and SMTP services on the DMZ host. It also !--- allows some ICMP traffic. access-list 121 permit udp any host 192.168.27.3 eq domain access-list 121 permit tcp any host 192.168.27.3 eq domain access-list 121 permit tcp any host 192.168.27.3 eq www access-list 121 permit tcp any host 192.168.27.3 eq ftp access-list 121 permit tcp any host 192.168.27.3 eq smtp access-list 121 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 administratively-prohibited access-list 121 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 echo access-list 121 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 echo-reply access-list 121 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 packet-too-big access-list 121 permit icmp any 192.169.27.0 0.0.0.255 time-exceeded access-list 121 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 traceroute access-list 121 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 unreachable access-list 121 deny ip any any ! !--- Apply access list 20 for SNMP process. ! snmp-server community secret RO 20 snmp-server enable traps tty ! call rsvp-sync ! mgcp profile default ! dial-peer cor custom ! gatekeeper shutdown ! line con 0 exec-timeout 5 0 password 7 14191D1815023F2036 login local line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 5 0 password 7 14191D1815023F2036 login local length 35 end |
Überprüfen
In diesem Abschnitt überprüfen Sie, ob Ihre Konfiguration ordnungsgemäß funktioniert.
Das Output Interpreter Tool (nur registrierte Kunden) (OIT) unterstützt bestimmte show-Befehle. Verwenden Sie das OIT, um eine Analyse der Ausgabe des Befehls show anzuzeigen.
-
show access-list - Überprüft die richtige Konfiguration der in der aktuellen Konfiguration konfigurierten Zugriffslisten.
Router#show access-list Standard IP access list 20 10 permit 192.168.27.5 Extended IP access list 101 10 permit tcp 192.168.27.128 0.0.0.127 host 192.168.27.3 eq pop3 20 permit tcp 192.168.27.128 0.0.0.127 host 192.168.27.3 eq telnet 30 permit icmp 192.168.27.128 0.0.0.127 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.127 40 deny ip 192.168.27.128 0.0.0.127 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.127 50 permit ip 192.168.27.128 0.0.0.127 any 60 deny ip any any Extended IP access list 111 10 permit icmp 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.127 any 20 deny ip any any (9 matches) Extended IP access list 121 10 permit udp any host 192.168.27.3 eq domain 20 permit tcp any host 192.168.27.3 eq domain 30 permit tcp any host 192.168.27.3 eq www 40 permit tcp any host 192.168.27.3 eq ftp 50 permit tcp any host 192.168.27.3 eq smtp 60 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 administratively-prohibited 70 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 echo 80 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 echo-reply 90 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 packet-too-big 100 permit icmp any 192.169.27.0 0.0.0.255 time-exceeded 110 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 traceroute 120 permit icmp any 192.168.27.0 0.0.0.255 unreachable 130 deny ip any any (4866 matches) Router# -
show ip audit all - Verifiziert die Konfiguration der Protokollbefehle.
Router#show ip audit all Event notification through syslog is enabled Event notification through Net Director is disabled Default action(s) for info signatures is alarm Default action(s) for attack signatures is alarm Default threshold of recipients for spam signature is 250 PostOffice:HostID:0 OrgID:0 Msg dropped:0 :Curr Event Buf Size:0 Configured:100 Post Office is not enabled - No connections are active Router# -
show ip inspect all (Alle anzeigen) - Verifiziert die Konfiguration der Cisco IOS Firewall Inspection-Regeln pro Schnittstelle.
Router#show ip inspect all Session audit trail is enabled Session alert is enabled one-minute (sampling period) thresholds are [400:500] connections max-incomplete sessions thresholds are [400:500] max-incomplete tcp connections per host is 50. Block-time 0 minute. tcp synwait-time is 30 sec -- tcp finwait-time is 5 sec tcp idle-time is 14400 sec -- udp idle-time is 1800 sec dns-timeout is 7 sec Inspection Rule Configuration Inspection name standard cuseeme alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 ftp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 h323 alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 http alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 rcmd alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 realaudio alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 smtp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 sqlnet alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 streamworks alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 1800 tcp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 tftp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 1800 udp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 1800 vdolive alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 Interface Configuration Interface Ethernet3/0 Inbound inspection rule is standard cuseeme alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 ftp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 h323 alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 http alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 rcmd alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 realaudio alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 smtp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 sqlnet alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 streamworks alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 1800 tcp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 tftp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 1800 udp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 1800 vdolive alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 Outgoing inspection rule is not set Inbound access list is 101 Outgoing access list is not set Interface Ethernet3/1 Inbound inspection rule is not set Outgoing inspection rule is standard cuseeme alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 ftp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 h323 alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 http alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 rcmd alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 realaudio alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 smtp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 sqlnet alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 streamworks alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 1800 tcp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 tftp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 1800 udp alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 1800 vdolive alert is on audit-trail is on timeout 14400 Inbound access list is 111 Outgoing access list is not set Router#
Fehlerbehebung
Wenn Sie den IOS-Firewall-Router konfiguriert haben und die Verbindungen nicht funktionieren, stellen Sie sicher, dass die Überprüfung mit dem Befehl ip inspect (name defined) in oder out auf der Schnittstelle aktiviert ist. In dieser Konfiguration wird ip inspect standard in für das SchnittstellenEthernet 3/0 und ip inspect standard out für das SchnittstellenEthernet 3/1 angewendet.
Weitere Informationen zur Fehlerbehebung finden Sie unter Fehlerbehebung bei Cisco IOS Firewall-Konfigurationen.
Zugehörige Informationen
Revisionsverlauf
| Überarbeitung | Veröffentlichungsdatum | Kommentare |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
20-Feb-2007 |
Erstveröffentlichung |
Cisco kontaktieren
- Eine Supportanfrage öffnen

- (Erfordert einen Cisco Servicevertrag)
 Feedback
Feedback