Konfigurieren von Microsoft Windows XP iSCSI Host auf MDS/IPS-8
Inhalt
Einführung
Die iSCSI-Treiber von Cisco, die sich auf dem Server befinden, sind eine Schlüsselkomponente der iSCSI-Lösung. Diese iSCSI-Treiber fangen SCSI-Befehle ab, kapseln sie in IP-Pakete und leiten sie an Cisco SN 5420, Cisco SN 5428, Cisco SN 5428-2 oder Cisco MDS/IPS-8 um. Dieses Dokument enthält Beispielkonfigurationen für einen Host mit Microsoft Windows XP iSCSI zu MDS/IPS-8.
Voraussetzungen
Anforderungen
Stellen Sie vor dem Versuch dieser Konfiguration sicher, dass Sie die folgenden Anforderungen erfüllen:
-
Bevor Sie Ihre iSCSI-Konfiguration auf dem MDS 9000 erstellen, müssen Sie einen iSCSI-Treiber installieren, der mit Ihrem PC kompatibel ist, auf dem Microsoft Windows XP ausgeführt wird. Die aktuelle Version des Cisco iSCSI-Treibers für Windows 2000/XP/2003 finden Sie auf der Seite Cisco iSCSI Drivers (nur registrierte Kunden) unter Cisco.com. Der Name der Datei ist die Cisco iSCSI-Treiberversionsnummer für Win2k und ist in der Tabelle auf dieser Seite zu finden.
Verwendete Komponenten
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument basieren auf den folgenden Software- und Hardwareversionen:
-
PC mit Microsoft Windows XP und Cisco iSCSI-Treiber Version 3.1.2
-
Cisco MDS 9216 mit Softwareversion 1.1.2
canterbury# show module Mod Ports Module-Type Model Status --- ----- ------------------------------- ------------------ ------------ 1 16 1/2 Gbps FC/Supervisor DS-X9216-K9-SUP active * 2 8 IP Storage Module DS-X9308-SMIP ok Mod Sw Hw World-Wide-Name(s) (WWN) --- ----------- ------ -------------------------------------------------- 1 1.1(2) 1.0 20:01:00:0c:30:6c:24:40 to 20:10:00:0c:30:6c:24:40 2 1.1(2) 0.3 20:41:00:0c:30:6c:24:40 to 20:48:00:0c:30:6c:24:40 Mod MAC-Address(es) Serial-Num --- -------------------------------------- ---------- 1 00-0b-be-f8-7f-08 to 00-0b-be-f8-7f-0c JAB070804QK 2 00-05-30-00-ad-e2 to 00-05-30-00-ad-ee JAB070806SB * this terminal session canterbury# canterbury# show version Cisco Storage Area Networking Operating System (SAN-OS) Software TAC support: http://www.cisco.com/tac Copyright (c) 2002-2003 by Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. The copyright for certain works contained herein are owned by Andiamo Systems, Inc. and/or other third parties and are used and distributed under license. Software BIOS: version 1.0.7 loader: version 1.0(3a) kickstart: version 1.1(2) system: version 1.1(2) BIOS compile time: 03/20/03 kickstart image file is: bootflash:/k112 kickstart compile time: 7/13/2003 20:00:00 system image file is: bootflash:/s112 system compile time: 7/13/2003 20:00:00 Hardware RAM 963112 kB bootflash: 500736 blocks (block size 512b) slot0: 0 blocks (block size 512b) canterbury uptime is 6 days 1 hours 11 minute(s) 5 second(s) Last reset at 783455 usecs after Thu Aug 28 12:59:37 2003 Reason: Reset Requested by CLI command reload System version: 1.1(2) canterbury#
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument wurden von den Geräten in einer bestimmten Laborumgebung erstellt. Alle in diesem Dokument verwendeten Geräte haben mit einer leeren (Standard-)Konfiguration begonnen. Wenn Ihr Netzwerk in Betrieb ist, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die potenziellen Auswirkungen eines Befehls verstehen.
Konventionen
Der Begriff MDS 9000 bezieht sich auf alle Fibre Channel (FC)-Switches der MDS 9000-Familie (MDS 9506, MDS 9509 oder MDS 9216). IPS-Blade bezieht sich auf das IP Storage Services-Modul.
Weitere Informationen zu Dokumentkonventionen finden Sie in den Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Hintergrundtheorie
Das IP-Speichermodul bietet IP-Hosts Zugriff auf Fibre Channel (FC)-Speichergeräte. Das IP-Speichermodul ist DS-X9308-SMIP. Es bietet transparentes SCSI-Routing. IP-Hosts, die das iSCSI-Protokoll verwenden, können transparent auf SCSI (FCP)-Ziele im FC-Netzwerk zugreifen. Der IP-Host sendet in iSCSI Protocol Data Units (PDUs) eingekapselte SCSI-Befehle über eine TCP/IP-Verbindung an einen MDS 9000 IPS-Port. Auf dem IP-Speichermodul wird die Konnektivität in Form von Gigabit Ethernet (GE)-Schnittstellen bereitgestellt, die entsprechend konfiguriert sind. Mit dem IP-Speichermodul können Sie virtuelle iSCSI-Ziele erstellen und diesen physischen FC-Zielen zuordnen, die im FC-SAN verfügbar sind. Die FC-Ziele werden IP-Hosts so präsentiert, als wären die physischen Ziele lokal angefügt.
Jeder iSCSI-Host, der über das IP-Speichermodul Zugriff auf den Speicher benötigt, muss über einen kompatiblen iSCSI-Treiber verfügen. Mit dem iSCSI-Protokoll ermöglicht der iSCSI-Treiber einem iSCSI-Host die Übertragung von SCSI-Anfragen und -Antworten über ein IP-Netzwerk. Aus der Perspektive eines Host-Betriebssystems scheint der iSCSI-Treiber ein SCSI-Transporttreiber zu sein, ähnlich einem FC-Treiber für einen Peripheriekanal im Host. Aus Sicht des Speichergeräts erscheint jeder IP-Host als FC-Host.
Das Routing von SCSI vom IP-Host zum FC-Speichergerät besteht aus den folgenden Hauptmaßnahmen:
-
iSCSI-Anfragen und -Antworten werden über ein IP-Netzwerk zwischen Hosts und dem IP-Speichermodul übertragen.
-
Weiterleiten von SCSI-Anfragen und -Antworten zwischen Hosts in einem IP-Netzwerk und dem FC-Speichergerät (Konvertierung von iSCSI in FCP und umgekehrt). Dies wird vom IP-Speichermodul durchgeführt.
-
Übertragung von FCP-Anfragen oder -Antworten zwischen dem IP-Speichermodul und FC-Speichergeräten.
Das IP-Speichermodul importiert FC-Ziele nicht standardmäßig in iSCSI. Bevor das IP-Speichermodul iSCSI-Initiatoren FC-Ziele zur Verfügung stellt, muss entweder eine dynamische oder statische Zuordnung konfiguriert werden. Wenn beide konfiguriert sind, haben statisch zugeordnete FC-Ziele einen konfigurierten Namen. In dieser Konfiguration werden Beispiele für statische Zuordnung bereitgestellt.
Bei dynamischer Zuordnung wird jedes Mal, wenn der iSCSI-Host eine Verbindung zum IP-Speichermodul herstellt, ein neuer FC-N-Port erstellt, und die für diesen N-Port zugewiesenen nWWNs und pWWNs können unterschiedlich sein. Verwenden Sie die statische Zuordnungsmethode, wenn Sie bei jeder Verbindung mit dem IP-Speichermodul dieselben nWWNs und pWWNs für den iSCSI-Host erhalten müssen. Die statische Zuordnung kann auf dem IP-Speichermodul verwendet werden, um auf intelligente FC-Speicher-Arrays zuzugreifen, die über Zugriffskontrolle und LUN-Zuordnung (Logical Unit Number) bzw. Maskierung auf der Grundlage der pWWNs und/oder nWWNs des Initiators verfügen.
Sie können den Zugriff auf jedes statisch zugeordnete iSCSI-Ziel steuern, wenn Sie eine Liste der IP-Speicherports angeben, auf denen diese angekündigt werden, und eine Liste der iSCSI-Initiatorknotennamen angeben, die auf dieses Ziel zugreifen dürfen. FC Zoning-basierte Zugriffskontrolle und iSCSI-basierte Zugriffskontrolle sind die beiden Mechanismen, mit denen die Zugriffskontrolle für iSCSI bereitgestellt werden kann. Beide Methoden können gleichzeitig verwendet werden.
Die iSCSI-Erkennung tritt auf, wenn ein iSCSI-Host eine iSCSI-Erkennungssitzung erstellt und alle iSCSI-Ziele abfragt. Das IP-Speichermodul gibt nur die Liste der iSCSI-Ziele zurück, auf die der iSCSI-Host basierend auf den Zugriffskontrollrichtlinien zugreifen darf.
iSCSI-Sitzungen werden erstellt, wenn ein IP-Host eine iSCSI-Sitzung initiiert. Das IP-Speichermodul überprüft, ob das angegebene iSCSI-Ziel (in der Sitzungsanfrage) ein statisches zugeordnete Ziel ist. Wenn true, überprüft es, ob der iSCSI-Knotenname des IP-Hosts auf das Ziel zugreifen darf. Wenn der IP-Host keinen Zugriff hat, wird die Anmeldung abgelehnt.
Das IP-Speichermodul erstellt dann einen virtuellen FC-N-Port (der N-Port ist möglicherweise bereits vorhanden) für diesen IP-Host und führt eine FC-Namensserver-Abfrage für die FCID des FC-Ziel-pWWN durch, auf den der IP-Host zugreift. Er verwendet den pWWN des virtuellen N-Ports des IP-Hosts als Anforderer der Namenserver-Abfrage. Daher führt der Nameserver eine zonenerzwungene Abfrage für das pWWN aus und antwortet auf die Abfrage. Wenn die FCID vom Namensserver zurückgegeben wird, wird die iSCSI-Sitzung akzeptiert. Andernfalls wird die Anmeldeanforderung abgelehnt.
Konfigurieren
In diesem Abschnitt erhalten Sie Informationen zum Konfigurieren der in diesem Dokument beschriebenen Funktionen.
Hinweis: Weitere Informationen zu den in diesem Dokument verwendeten Befehlen finden Sie im Cisco MDS 9000 Family Command Reference, Release 1.2.1a and Cisco MDS 9000 Family Software Configuration Guide, Release 1.2.1a Configuration Guides.
Hinweis: Um weitere Informationen zu den in diesem Dokument verwendeten Befehlen zu erhalten, verwenden Sie das Command Lookup Tool (nur registrierte Kunden).
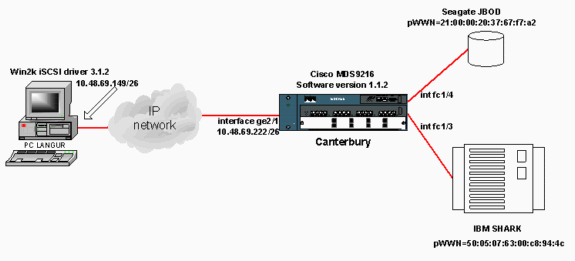
Netzwerkdiagramm
In diesem Dokument wird die folgende Netzwerkeinrichtung verwendet:
Konfigurationen
In diesem Dokument werden folgende Konfigurationen verwendet:
-
Canterbury (MDS 9216)
| Canterbury (MDS 9216) |
|---|
canterbury# sh run Building Configuration ... .... vsan database vsan 601 !--- VSAN 601 has been used for iSCSI targets. .... vsan database vsan 601 interface fc1/3 vsan 601 interface fc1/4 .... boot system bootflash:/s112 boot kickstart bootflash:/k112 ip domain-name cisco.com ip name-server 144.254.10.123 ip default-gateway 10.48.69.129 ip route 10.48.69.149 255.255.255.255 interface GigabitEthernet2/1 ip routing iscsi authentication none iscsi initiator ip-address 10.48.69.149 !--- Identifies the iSCSI initiator based on the IP address. !--- A virtual N port is created for each NIC or network interface. static pWWN 20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c !--- Defining the PC Langur`s pwwn above; this is necessary here since lunmasking is !--- enforced on the IBM Shark, but not on the JBOD. Therefore, pWWN must be statically !--- bound to the initiator to be able to access and manage disks on IBM Shark. vsan 601 !--- VSAN 601 has been used for iSCSI targets. !--- Targets by way of VSAN 601 are accessible by iSCSI initiators. The !--- targets are defined below. Create a static iSCSI virtual target !--- for Seagate JBOD. iscsi virtual-target name san-fc-jbod-1 pWWN 21:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2 advertise interface GigabitEthernet2/1 initiator ip address 10.48.69.149 permit !--- Create a static iSCSI virtual target for IBM Shark. iscsi virtual-target name shark-c8 pWWN 50:05:07:63:00:c8:94:4c advertise interface GigabitEthernet2/1 initiator ip address 10.48.69.149 permit ... !--- Here, the zone named 'Zone1' is used under VSAN 601 for connectivity. !--- Both initiator and targets are assigned as members of this zone. switchname canterbury zone name Zone1 vsan 601 member pWWN 50:05:07:63:00:c8:94:4c !--- This is IBM Shark. member pWWN 20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c !--- This is PC Langur. member pWWN 21:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2 !--- This is Seagate JBOD. member symbolic-nodename 10.48.69.149 !--- You have this entry since zone membership is based on pWWN (not on IP address). zoneset name ZoneSet1 vsan 601 member Zone1 zoneset activate name ZoneSet1 vsan 601 .... interface GigabitEthernet2/1 ip address 10.48.69.222 255.255.255.192 iscsi authentication none no shutdown .... interface fc1/3 no shutdown interface fc1/4 no shutdown ... interface mgmt0 ip address 10.48.69.156 255.255.255.192 interface iscsi2/1 no shutdown canterbury# |
Überprüfen
Dieser Abschnitt enthält Informationen, mit denen Sie bestätigen können, dass Ihre Konfiguration ordnungsgemäß funktioniert.
Bestimmte show-Befehle werden vom Output Interpreter Tool unterstützt (nur registrierte Kunden), mit dem Sie eine Analyse der show-Befehlsausgabe anzeigen können.
Gehen Sie auf dem PC zur Systemsteuerung und aktivieren Sie die folgenden Optionen:
-
Netzwerkverbindungen -> LAN-Verbindung -> TCP/IP-Eigenschaften
-
iSCSI Config -> Status des Ziels (Informationen zum Anzeigen einer Screenshot finden Sie im Abschnitt Displays vom PC dieses Dokuments).
Führen Sie auf dem MDS 9216 die folgenden Befehle aus, um die Konnektivität zu überprüfen:
-
Zonenstatus anzeigen - Zeigt Zoneninformationen an.
-
show zone active vsan 601: Anzeigebereiche, die zum angegebenen VSAN gehören.
-
show fcns database vsan 601 - Zeigt Informationen zum Namenserver für ein bestimmtes VSAN an.
-
show fcns database detail vsan 601 - Zeigt die lokalen Einträge für das angegebene VSAN an.
-
show flogi database vsan 601 - Zeigt Informationen zum FLOGI-Server für ein bestimmtes VSAN an.
-
show vsan mitgliedschaft - Zeigt Schnittstelleninformationen für verschiedene VSANs an.
-
show iscsi initiator - Zeigt Informationen zum iSCSI-Initiator an.
-
show iscsi initiator detail - Zeigt iSCSI-Initiatorinformationen genauer an.
-
show iscsi initiator iscsi-session detail - Zeigt detaillierte Informationen für die iSCSI-Initiatorsitzung an.
-
show iscsi initiator fcp-session detail - Zeigt detaillierte Informationen für die iSCSI-Initiator-FCP-Sitzung an.
-
show ips stats tcp interface gigabitethernet 2/1 detail - Zeigt TCP-Statistiken für eine bestimmte GE-Schnittstelle.
-
show iscsi virtual-target configured - zeigt virtuelle iSCSI-Ziele an, die auf dem MDS 9000 konfiguriert wurden.
-
show iscsi initiator configured (konfigurierter Initiator anzeigen) - zeigt iSCSI-Initiatoren an, die auf dem MDS 9000 konfiguriert wurden.
-
show ips arp interface gigabitethernet 2/1 - Zeigt IP-Speicher-ARP-Informationen für eine bestimmte GE-Schnittstelle an.
-
show scsi-target devices vsan 601 - Zeigt SCSI-Geräte für ein bestimmtes VSAN an (für die Zuordnung von FC-LUNs zu iSCSI-LUNs).
-
show int iscsi 2/1 - zeigt iSCSI-Schnittstellen an.
-
show iscsi stats iscsi 2/1 - Zeigt iSCSI-Statistiken an.
-
show int GigabitEthernet 2/1 - zeigt GE-Schnittstelle an.
-
show ip route - Zeigt Informationen zur IP-Route an.
-
show ips ip route interface gigabitethernet 2/1 - zeigt die Routing-Tabelle an.
Fehlerbehebung
Dieser Abschnitt enthält Informationen zur Fehlerbehebung in Ihrer Konfiguration.
Fehlerbehebungsverfahren
Dieser Abschnitt enthält Informationen zur Fehlerbehebung in Ihrer Konfiguration.
Hier einige relevante Informationen zur Fehlerbehebung für diese Konfiguration:
-
Displays von PC
-
Displays von Cisco MDS 9216 in Canterbury
-
Fabric Manager und Geräte-Manager werden angezeigt.
Displays von PC
Diese Bildschirmerfassung ist die iSCSI-Anzeige von PC Langur:
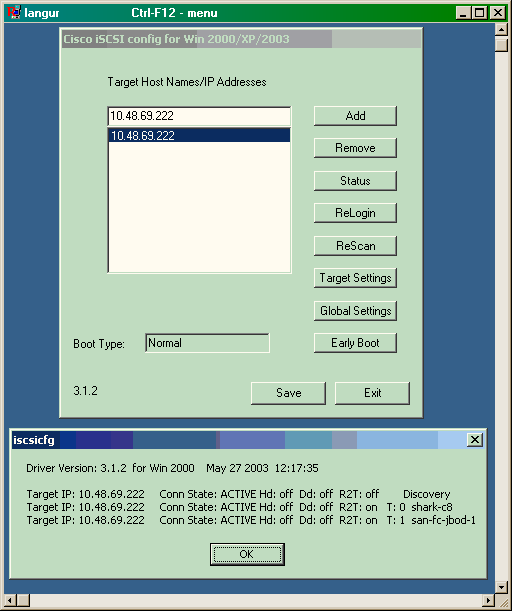
Um diese neuen Datenträger zu überprüfen, klicken Sie in der linken unteren Ecke des PCs auf Start. Wählen Sie folgende Optionen aus:
Arbeitsplatz -> Systemsteuerung -> Verwaltung -> Computerverwaltung
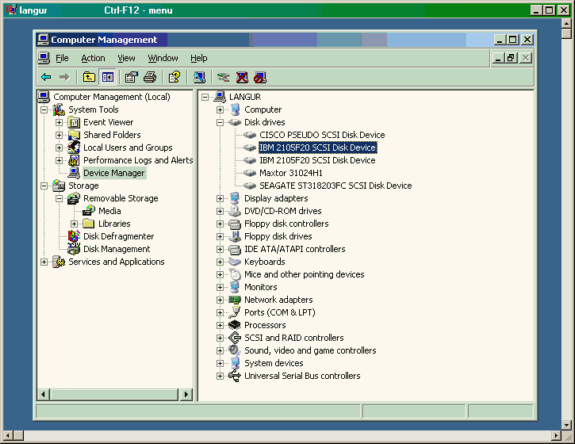
Wählen Sie unter Systemprogramme die Option Geräte-Manager aus. Klicken Sie auf der rechten Seite auf Laufwerke. Folgendes sollte angezeigt werden:
Um diese Festplatten zu verwalten, klicken Sie in der linken unteren Ecke des PCs auf Start. Wählen Sie folgende Optionen aus:
Arbeitsplatz -> Systemsteuerung -> Verwaltung -> Computerverwaltung
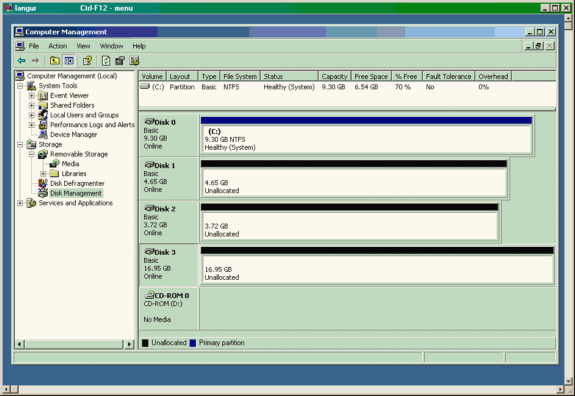
Klicken Sie unter Speicher auf Datenträgerverwaltung. Die Bildschirmaufnahme von PC Langur ist unten dargestellt. Beachten Sie, dass Disk1 und Disk2 von IBM Shark sind, und Disk3 ist die Seagate JBOD.
Displays von Canterbury (MDS 9216)
| Displays von Canterbury (MDS 9216) |
|---|
canterbury# show zone status
...
VSAN: 601 default-zone: deny distribute: active only Interop: Off
Full Zoning Database :
Zonesets:1 Zones:1 Aliases: 0
Active Zoning Database :
Name: ZoneSet1 Zonesets:1 Zones:1
Status: Activation completed at Wed Sep 10 09:25:45 2003
...
canterbury#
canterbury# show zone active vsan 601
zone name Zone1 vsan 601
symbolic-nodename 10.48.69.231
* fcid 0x020001 [pWWN 50:05:07:63:00:c8:94:4c]
* fcid 0x020005 [pWWN 20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c]
* fcid 0x0201e8 [pWWN 21:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2]
* fcid 0x020005 [symbolic-nodename 10.48.69.149]
canterbury#
canterbury# show fcns database vsan 601
VSAN 601:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
FCID TYPE pWWN (VENDOR) FC4-TYPE:FEATURE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
0x020001 N 50:05:07:63:00:c8:94:4c (IBM) scsi-fcp:target fc..
0x020005 N 20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c (Cisco) scsi-fcp:init isc..w
0x0201e8 NL 21:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2 (Seagate) scsi-fcp:target
Total number of entries = 3
canterbury#
canterbury# show fcns database detail vsan 601
------------------------
VSAN:601 FCID:0x020001
------------------------
port-wwn (vendor) :50:05:07:63:00:c8:94:4c (IBM)
node-wwn :50:05:07:63:00:c0:94:4c
class :2,3
node-ip-addr :0.0.0.0
ipa :ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
fc4-types:fc4_features:scsi-fcp:target fcsb2-ch-cu fcsb2-cu-ch
symbolic-port-name :
symbolic-node-name :
port-type :N
port-ip-addr :0.0.0.0
fabric-port-wwn :20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:40
hard-addr :0x000000
------------------------
VSAN:601 FCID:0x020005
------------------------
port-wwn (vendor) :20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c (Cisco)
node-wwn :21:00:00:0c:30:6c:24:42
class :2,3
node-ip-addr :10.48.69.149
ipa :ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
fc4-types:fc4_features:scsi-fcp:init iscsi-gw
symbolic-port-name :
symbolic-node-name :10.48.69.149
port-type :N
port-ip-addr :0.0.0.0
fabric-port-wwn :20:41:00:0c:30:6c:24:40
hard-addr :0x000000
------------------------
VSAN:601 FCID:0x0201e8
------------------------
port-wwn (vendor) :21:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2 (Seagate)
node-wwn :20:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2
class :3
node-ip-addr :0.0.0.0
ipa :ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
fc4-types:fc4_features:scsi-fcp:target
symbolic-port-name :
symbolic-node-name :
port-type :NL
port-ip-addr :0.0.0.0
fabric-port-wwn :20:04:00:0c:30:6c:24:40
hard-addr :0x000000
Total number of entries = 3
canterbury#
canterbury# show flogi database vsan 601
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
INTERFACE VSAN FCID PORT NAME NODE NAME
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
fc1/3 601 0x020001 50:05:07:63:00:c8:94:4c 50:05:07:63:00:c0:94:4c
fc1/4 601 0x0201e8 21:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2 20:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2
iscsi2/1 601 0x020005 20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c 21:00:00:0c:30:6c:24:42
Total number of flogi = 3.
canterbury#
canterbury# show vsan membership
...
vsan 601 interfaces:
fc1/3 fc1/4
...
canterbury#
canterbury# show iscsi initiator
...
iSCSI Node name is 10.48.69.149
iSCSI Initiator name: iqn.1987-05.com.cisco:02.e746244830dd.langur
iSCSI alias name: LANGUR
Node WWN is 21:00:00:0c:30:6c:24:42 (dynamic)
Member of vsans: 601
Number of Virtual n_ports: 1
Virtual Port WWN is 20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c (configured)
Interface iSCSI 2/1, Portal group tag: 0x80
VSAN ID 601, FCID 0x020005
canterbury#
canterbury# show iscsi initiator detail
...
iSCSI Node name is 10.48.69.149
iSCSI Initiator name: iqn.1987-05.com.cisco:02.e746244830dd.langur
iSCSI alias name: LANGUR
Node WWN is 21:00:00:0c:30:6c:24:42 (dynamic)
Member of vsans: 601
Number of Virtual n_ports: 1
Virtual Port WWN is 20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c (configured)
Interface iSCSI 2/1, Portal group tag is 0x80
VSAN ID 601, FCID 0x 20005
2 FC sessions, 2 iSCSI sessions
iSCSI session details
Target: shark-c8
Statistics:
PDU: Command: 45, Response: 45
Bytes: TX: 5968, RX: 0
Number of connection: 1
TCP parameters
Local 10.48.69.222:3260, Remote 10.48.69.149:2196
Path MTU: 1500 bytes
Retransmission timeout: 300 ms
Round trip time: Smoothed 219 ms, Variance: 15
Advertized window: Current: 61 KB, Maximum: 62 KB, Scale: 0
Peer receive window: Current: 63 KB, Maximum: 63 KB, Scale: 0
Congestion window: Current: 11 KB
Target: san-fc-jbod-1
Statistics:
PDU: Command: 26, Response: 26
Bytes: TX: 3168, RX: 0
Number of connection: 1
TCP parameters
Local 10.48.69.222:3260, Remote 10.48.69.149:3124
Path MTU: 1500 bytes
Retransmission timeout: 300 ms
Round trip time: Smoothed 219 ms, Variance: 15
Advertized window: Current: 61 KB, Maximum: 62 KB, Scale: 0
Peer receive window: Current: 63 KB, Maximum: 63 KB, Scale: 0
Congestion window: Current: 11 KB
FCP Session details
Target FCID: 0x020001 (S_ID of this session: 0x020005)
pWWN: 50:05:07:63:00:c8:94:4c, nWWN: 50:05:07:63:00:c0:94:4c
Session state: LOGGED_IN
1 iSCSI sessions share this FC session
Target: shark-c8
Negotiated parameters
RcvDataFieldSize 2048 our_RcvDataFieldSize 1392
MaxBurstSize 0, EMPD: FALSE
Random Relative Offset: FALSE, Sequence-in-order: Yes
Statistics:
PDU: Command: 0, Response: 45
Target FCID: 0x0201e8 (S_ID of this session: 0x020005)
pWWN: 21:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2, nWWN: 20:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2
Session state: LOGGED_IN
1 iSCSI sessions share this FC session
Target: san-fc-jbod-1
Negotiated parameters
RcvDataFieldSize 1392 our_RcvDataFieldSize 1392
MaxBurstSize 0, EMPD: FALSE
Random Relative Offset: FALSE, Sequence-in-order: Yes
Statistics:
PDU: Command: 0, Response: 26
canterbury# show iscsi initiator iscsi-session detail
iSCSI Node name is 10.48.69.149
iSCSI Initiator name: iqn.1987-05.com.cisco:02.e746244830dd.langur
iSCSI alias name: LANGUR
Node WWN is 21:00:00:0c:30:6c:24:42 (dynamic)
Member of vsans: 601
Number of Virtual n_ports: 1
Virtual Port WWN is 20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c (configured)
Interface iSCSI 2/1, Portal group tag is 0x80
VSAN ID 601, FCID 0x 20005
2 FC sessions, 2 iSCSI sessions
iSCSI session details
Target: shark-c8
Statistics:
PDU: Command: 45, Response: 45
Bytes: TX: 5968, RX: 0
Number of connection: 1
TCP parameters
Local 10.48.69.222:3260, Remote 10.48.69.149:2196
Path MTU: 1500 bytes
Retransmission timeout: 300 ms
Round trip time: Smoothed 217 ms, Variance: 14
Advertized window: Current: 62 KB, Maximum: 62 KB, Scale: 0
Peer receive window: Current: 63 KB, Maximum: 63 KB, Scale: 0
Congestion window: Current: 11 KB
Target: san-fc-jbod-1
Statistics:
PDU: Command: 26, Response: 26
Bytes: TX: 3168, RX: 0
Number of connection: 1
TCP parameters
Local 10.48.69.222:3260, Remote 10.48.69.149:3124
Path MTU: 1500 bytes
Retransmission timeout: 300 ms
Round trip time: Smoothed 217 ms, Variance: 14
Advertized window: Current: 61 KB, Maximum: 62 KB, Scale: 0
Peer receive window: Current: 63 KB, Maximum: 63 KB, Scale: 0
Congestion window: Current: 11 KB
canterbury#
canterbury# show iscsi initiator fcp-session detail
iSCSI Node name is 10.48.69.149
iSCSI Initiator name: iqn.1987-05.com.cisco:02.e746244830dd.langur
iSCSI alias name: LANGUR
Node WWN is 21:00:00:0c:30:6c:24:42 (dynamic)
Member of vsans: 601
Number of Virtual n_ports: 1
Virtual Port WWN is 20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c (configured)
Interface iSCSI 2/1, Portal group tag is 0x80
VSAN ID 601, FCID 0x 20005
2 FC sessions, 2 iSCSI sessions
FCP Session details
Target FCID: 0x020001 (S_ID of this session: 0x020005)
pWWN: 50:05:07:63:00:c8:94:4c, nWWN: 50:05:07:63:00:c0:94:4c
Session state: LOGGED_IN
1 iSCSI sessions share this FC session
Target: shark-c8
Negotiated parameters
RcvDataFieldSize 2048 our_RcvDataFieldSize 1392
MaxBurstSize 0, EMPD: FALSE
Random Relative Offset: FALSE, Sequence-in-order: Yes
Statistics:
PDU: Command: 0, Response: 45
Target FCID: 0x0201e8 (S_ID of this session: 0x020005)
pWWN: 21:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2, nWWN: 20:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2
Session state: LOGGED_IN
1 iSCSI sessions share this FC session
Target: san-fc-jbod-1
Negotiated parameters
RcvDataFieldSize 1392 our_RcvDataFieldSize 1392
MaxBurstSize 0, EMPD: FALSE
Random Relative Offset: FALSE, Sequence-in-order: Yes
Statistics:
PDU: Command: 0, Response: 26
canterbury#
canterbury# show ips stats tcp interface gigabitethernet 2/1 detail
TCP Statistics for port GigabitEthernet2/1
TCP send stats
241247690 segments, 176414627280 bytes
239428551 data, 1738205 ack only packets
42541 control (SYN/FIN/RST), 0 probes, 38280 window updates
498 segments retransmitted, 526612 bytes
464 retransmitted while on ethernet send queue, 111295209 packets split
2505024 delayed acks sent
TCP receive stats
34418285 segments, 8983771 data packets in sequence, 9282604852 bytes in s
equence
854523 predicted ack, 6126542 predicted data
0 bad checksum, 0 multi/broadcast, 0 bad offset
0 no memory drops, 0 short segments
1844 duplicate bytes, 77 duplicate packets
0 partial duplicate bytes, 0 partial duplicate packets
123700 out-of-order bytes, 2235 out-of-order packets
6 packet after window, 0 bytes after window
0 packets after close
28128679 acks, 173967225697 ack bytes, 0 ack toomuch, 75348 duplicate acks
0 ack packets left of snd_una, 12 non-4 byte aligned packets
18442549 window updates, 0 window probe
88637 pcb hash miss, 2150 no port, 14 bad SYN, 0 paws drops
TCP Connection Stats
26 attempts, 42272 accepts, 42274 established
42327 closed, 40043 drops, 24 conn drops
106 drop in retransmit timeout, 152 drop in keepalive timeout
0 drop in persist drops, 0 connections drained
TCP Miscellaneous Stats
9776335 segments timed, 9780142 rtt updated
402 retransmit timeout, 457 persist timeout
69188 keepalive timeout, 69015 keepalive probes
TCP SACK Stats
100 recovery episodes, 231520160 data packets, 330107461536 data bytes
396 data packets retransmitted, 482072 data bytes retransmitted
13 connections closed, 46 retransmit timeouts
TCP SYN Cache Stats
42281 entries, 42272 connections completed, 3 entries timed out
0 dropped due to overflow, 6 dropped due to RST
0 dropped due to ICMP unreach, 0 dropped due to bucket overflow
0 abort due to no memory, 43 duplicate SYN, 1833 no-route SYN drop
0 hash collisions, 0 retransmitted
TCP Active Connections
Local Address Remote Address State Send-Q Recv-Q
10.48.69.222:3260 10.48.69.149:1026 ESTABLISH 0 0
10.48.69.222:3260 10.48.69.149:2196 ESTABLISH 0 0
10.48.69.222:3260 10.48.69.149:3124 ESTABLISH 0 0
0.0.0.0:3260 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN 0 0
canterbury#
canterbury# show iscsi virtual-target configured
target: shark-c8
* Port WWN 50:05:07:63:00:c8:94:4c
!--- The asterisk (*) in front of the pWWN means !--- that you have both discovery and target sessions. If !--- you do not see this, it means that only a discovery !--- session exists.
Configured node
No. of advertised interface: 1
GigabitEthernet 2/1
No. of initiators permitted: 2
initiator 10.48.69.231/32 is permitted
initiator 10.48.69.149/32 is permitted
all initiator permit is disabled
target: san-fc-jbod-1
* Port WWN 21:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2
Configured node
No. of advertised interface: 1
GigabitEthernet 2/1
No. of initiators permitted: 2
initiator 10.48.69.232/32 is permitted
initiator 10.48.69.149/32 is permitted
all initiator permit is disabled
canterbury#
canterbury# show iscsi initiator configured
...
iSCSI Node name is 10.48.69.149
Member of vsans: 601
No. of pWWN: 1
Port WWN is 20:03:00:0c:30:6c:24:4c
canterbury#
canterbury# show ips arp interface gigabitethernet 2/1
Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface
Internet 10.48.69.149 3 0008.e21e.c7bc ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.200 0 0008.e21e.c7bc ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.201 4 0202.3d30.45c9 ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.206 9 0005.9ba6.95ff ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.209 6 0009.7c60.561f ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.229 4 0800.209e.edab ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.233 0 0010.4200.7d5b ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.235 0 0800.20b6.6559 ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.238 4 0030.6e1b.6f51 ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.239 1 0030.6e1c.a00b ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.248 7 0202.3d30.45f8 ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.48.69.252 1 0202.3d30.45fc ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
Internet 10.10.2.28 0 0202.3d0a.021c ARPA GigabitEthernet2/1
canterbury#
canterbury# show scsi-target devices vsan 601
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VSAN FCID pWWN VENDOR MODEL REV
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
601 0x020001 50:05:07:63:00:c8:94:4c IBM 2105F20 .114
601 0x0201e8 21:00:00:20:37:67:f7:a2 SEAGATE ST318203FC 0004
canterbury#
canterbury# show int iscsi 2/1
iscsi2/1 is up
Hardware is GigabitEthernet
Port WWN is 20:41:00:0c:30:6c:24:40
Admin port mode is ISCSI
Port mode is ISCSI
Speed is 1 Gbps
iSCSI initiator is identified by name
Number of iSCSI session: 3, Number of TCP connection: 3
Configured TCP parameters
Local Port is 3260
PMTU discover is enabled, reset timeout is 3600 sec
Keepalive-timeout is 60 sec
Minimum-retransmit-time is 300 ms
Max-retransmissions 4
Sack is enabled
Maximum allowed bandwidth is 500000 kbps
Minimum available bandwidth is 500000 kbps
Estimated round trip time is 10000 usec
5 minutes input rate 16 bits/sec, 2 bytes/sec, 0 frames/sec
5 minutes output rate 16 bits/sec, 2 bytes/sec, 0 frames/sec
iSCSI statistics
Input 76856 packets, 8696216 bytes
Command 13139 pdus, Data-out 85 pdus, 84292 bytes
Output 89876 packets, 6629892 bytes
Response 13132 pdus (with sense 16), R2T 25 pdus
Data-in 13072 pdus, 2125736 bytes
canterbury#
canterbury# show iscsi stats iscsi 2/1
iscsi2/1
5 minutes input rate 8 bits/sec, 1 bytes/sec, 0 frames/sec
5 minutes output rate 8 bits/sec, 1 bytes/sec, 0 frames/sec
iSCSI statistics
76857 packets input, 8696264 bytes
Command 13139 pdus, Data-out 85 pdus, 84292 bytes, 0 fragments
output 89877 packets, 6629940 bytes
Response 13132 pdus (with sense 16), R2T 25 pdus
Data-in 13072 pdus, 2125736 bytes
canterbury#
canterbury# show interface gigabitethernet 2/1
GigabitEthernet2/1 is up
Hardware is GigabitEthernet, address is 0005.3000.ade6
Internet address is 10.48.69.222/26
MTU 1500 bytes
Port mode is IPS
Speed is 1 Gbps
Beacon is turned off
Auto-Negotiation is turned on
iSCSI authentication: NONE
5 minutes input rate 464 bits/sec, 58 bytes/sec, 0 frames/sec
5 minutes output rate 64 bits/sec, 8 bytes/sec, 0 frames/sec
30544982 packets input, 9266250283 bytes
29435 multicast frames, 0 compressed
0 input errors, 0 frame, 0 overrun 0 fifo
233947842 packets output, 179379369852 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 fifo
0 carrier errors
canterbury#
canterbury# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static
Gateway of last resort is 10.48.69.129
S 10.48.69.149, gigabitethernet2-1
C 6.6.6.0/30 is directly connected, gigabitethernet2-6
C 5.5.5.0/30 is directly connected, gigabitethernet2-5
C 10.48.69.192/26 is directly connected, gigabitethernet2-1
C 10.48.69.128/26 is directly connected, mgmt0
canterbury#
canterbury# show ips ip route interface gigabitethernet 2/1
Codes: C - connected, S - static
No default gateway
S 10.48.69.149/32 via 0.0.0.0, GigabitEthernet2/1
C 10.48.69.192/26 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet2/1
canterbury# |
Fabric Manager und Geräte-Manager werden angezeigt.
Dieser Abschnitt enthält Screenshots von MDS Fabric Manager 1.1(2) und Device Manager 1.1.(2).
Topologiediagramm vom Fabric Manager
Diese Bildschirmerfassung ist das Topologiediagramm aus dem Fabric Manager:
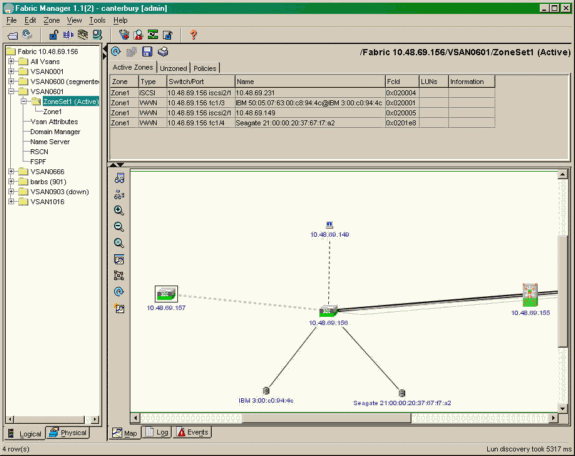
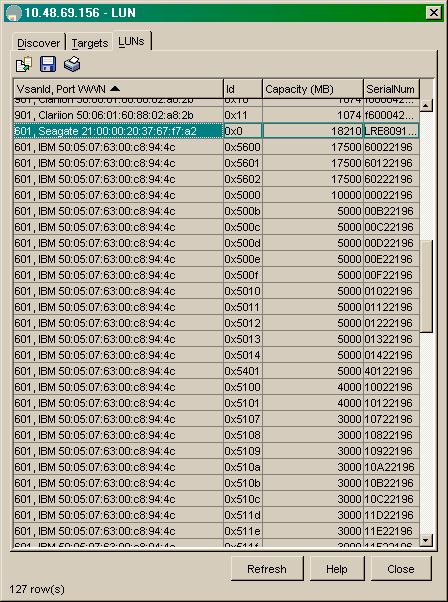
Wählen Sie FC-LUNs aus, um die pWWNs, LUN-IDs und die Kapazität Ihrer LUNs im Geräte-Manager anzuzeigen.
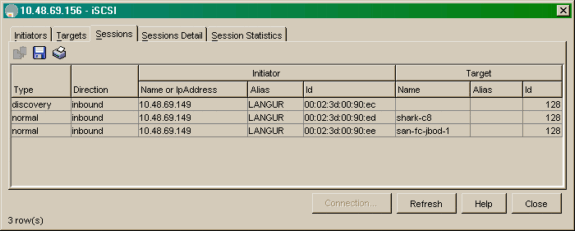
Wählen Sie IP-iSCSI aus, um die iSCSI-Sitzungen im Geräte-Manager anzuzeigen.
Zugehörige Informationen
- Cisco iSCSI-Software-Downloads (nur registrierte Kunden)
- iSCSI-Treiber für Windows 2000 - Häufig gestellte Fragen
- iSCSI-Treiber: Versionshinweise für Cisco iSCSI-Treiber für Microsoft Windows, Treiberversion 3.1.2
- Fehlerbehebung beim iSCSI-Treiber für Windows 2000
- Technischer Support - Cisco Systems
Cisco kontaktieren
- Eine Supportanfrage öffnen

- (Erfordert einen Cisco Servicevertrag)
 Feedback
Feedback