Fehlerbehebung bei VXLAN mit mehreren Standorten und CloudSec in Square-Topologie
Download-Optionen
Inklusive Sprache
In dem Dokumentationssatz für dieses Produkt wird die Verwendung inklusiver Sprache angestrebt. Für die Zwecke dieses Dokumentationssatzes wird Sprache als „inklusiv“ verstanden, wenn sie keine Diskriminierung aufgrund von Alter, körperlicher und/oder geistiger Behinderung, Geschlechtszugehörigkeit und -identität, ethnischer Identität, sexueller Orientierung, sozioökonomischem Status und Intersektionalität impliziert. Dennoch können in der Dokumentation stilistische Abweichungen von diesem Bemühen auftreten, wenn Text verwendet wird, der in Benutzeroberflächen der Produktsoftware fest codiert ist, auf RFP-Dokumentation basiert oder von einem genannten Drittanbieterprodukt verwendet wird. Hier erfahren Sie mehr darüber, wie Cisco inklusive Sprache verwendet.
Informationen zu dieser Übersetzung
Cisco hat dieses Dokument maschinell übersetzen und von einem menschlichen Übersetzer editieren und korrigieren lassen, um unseren Benutzern auf der ganzen Welt Support-Inhalte in ihrer eigenen Sprache zu bieten. Bitte beachten Sie, dass selbst die beste maschinelle Übersetzung nicht so genau ist wie eine von einem professionellen Übersetzer angefertigte. Cisco Systems, Inc. übernimmt keine Haftung für die Richtigkeit dieser Übersetzungen und empfiehlt, immer das englische Originaldokument (siehe bereitgestellter Link) heranzuziehen.
Inhalt
Einleitung
In diesem Dokument werden die Konfiguration und Fehlerbehebung für mehrere VXLANs mit CloudSec zwischen in Vierkanttopologie verbundenen Grenz-Gateways beschrieben.
Voraussetzungen
Anforderungen
Cisco empfiehlt, dass Sie mit den folgenden Themen vertraut sind:
- Nexus NX-OS © Software.
- VXLAN-EVPN-Technologie.
- BGP- und OSPF-Routing-Protokolle.
Verwendete Komponenten
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument basieren auf den folgenden Software- und Hardwareversionen:
- Cisco Nexus 9000
- NX-OS-Version 10.3(4a):
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument beziehen sich auf Geräte in einer speziell eingerichteten Testumgebung. Alle Geräte, die in diesem Dokument benutzt wurden, begannen mit einer gelöschten (Nichterfüllungs) Konfiguration. Wenn Ihr Netzwerk in Betrieb ist, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die möglichen Auswirkungen aller Befehle kennen.
Konfigurieren
Netzwerkdiagramm
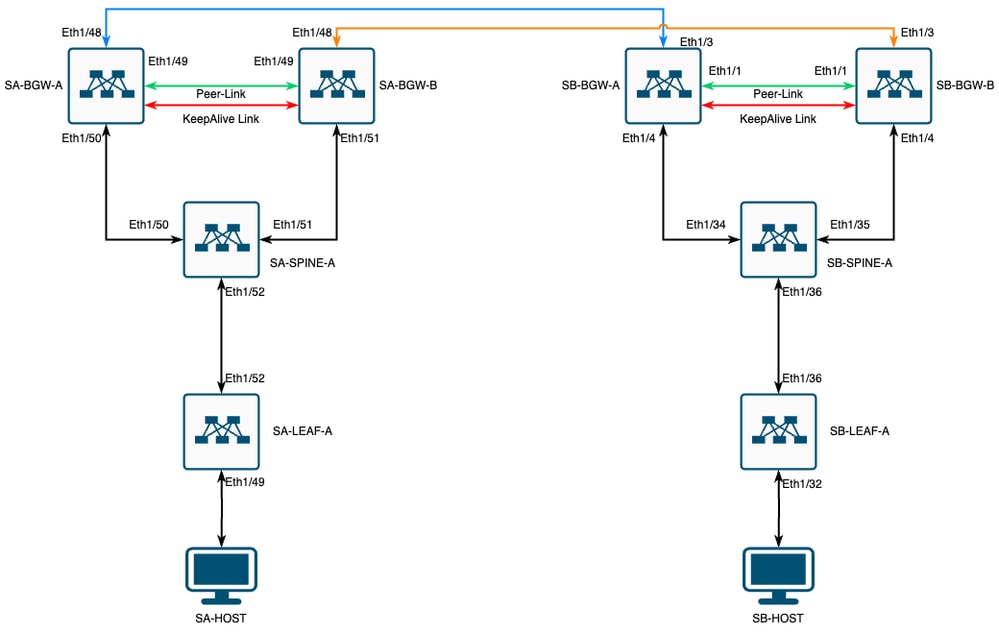 VXLAN MultiSite mit CloudSec in quadratischer Topologie
VXLAN MultiSite mit CloudSec in quadratischer Topologie
Einzelheiten der Topologie
- VXLAN-EVPN-Fabric mit zwei Standorten
- Beide Standorte sind mit vPC Border Gateways konfiguriert.
- Endpunkte werden in VLAN 1100 gehostet.
- Die Grenz-Gateways der einzelnen Standorte weisen über die SVI-Schnittstelle Vlan3600 eine IPv4-iBGP-Nachbarschaft zueinander auf.
- Grenz-Gateways an einem Standort haben eine eBGP-IPv4-Nachbarschaft und verfügen am anderen Standort nur über ein direkt verbundenes Grenz-Gateway.
- Die Grenz-Gateways von Standort A verfügen über eine eBGP L2VPN-EVPN-Nachbarschaft mit Grenz-Gateways von Standort B.
Adressierungsplan
Die IP-Adressen in der Tabelle werden während der Konfiguration verwendet:
| STANDORT A | STANDORT B | |||||||||||
| Geräterolle | Schnittstellen-ID | Physische Int-IP | RID-Schleife IP | NVE-Loop-IP | MSITE-VIP | Backup-SVI, IP | Schnittstellen-ID | Physische Int-IP | RID-Schleife IP | NVE-Loop-IP | MSITE-VIP | Backup-SVI, IP |
| BLATT | Eth1/52 | 192.168.1.1/30 | 192.168.2.1/32 | 192.168.3.1/32 | – | – | Eth1/36 | 192.168.11.1/30 | 192.168.12.1/32 | 192.168.13.1/32 | – | – |
| WIRBELSÄULE | Eth1/52 | 192.168.1.2/30 | – | Eth1/36 | 192.168.11.2/30 | – | ||||||
| Eth1/50 | 192.168.1.5/30 | 192.168.2.2/32 | – | – | – | Eth1/34 | 192.168.11.5/30 | 192.168.12.2/32 | – | – | – | |
| Eth1/51 | 192.168.1.9/30 | – | Eth1/35 | 192.168.11.9/30 | – | |||||||
| BGW-A | Eth1/51 | 192.168.1.6/30 | 192.168.2.3/32 | 192.168.3.2/32 | 192.168.100.1/32 | 192.168.4.1/30 | Eth1/4 | 192.168.11.6/30 | 192.168.12.3/32 | 192.168.13.2/32 | 192.168.200.1/32 | 192.168.14.1/30 |
| Eth1/48 | 10.12.10.1/30 | 192.168.3.254/32 | Eth1/3 | 10.12.10.2/30 | 192.168.13.254/32 | |||||||
| BGW-B | Eth1/51 | 192.168.1.10/30 | 192.168.2.4/32 | 192.168.3.3/32 | 192.168.100.1/32 | 192.168.4.2/30 | Eth1/4 | 192.168.11.10/30 | 192.168.12.4/32 | 192.168.13.3/32 | 192.168.200.1/32 | 192.168.14.2/30 |
| Eth1/48 | 10.12.10.5/30 | 192.168.3.254/32 | Eth1/3 | 10.12.10.6/30 | 192.168.13.254/32 |
Konfigurationen
- Beachten Sie, dass in diesem Leitfaden nur standortübergreifende Konfigurationen dargestellt werden. Die vollständige Konfiguration können Sie der offiziellen Dokumentation von Cisco für VXLAN Cisco Nexus Serie 9000 NX-OS VXLAN-Konfigurationsanleitung, Version 10.3(x), entnehmen.
Um CloudSec zu aktivieren, muss der dci-advertise-pip Befehl unter dem Border-Gateway "evpn multisite" konfiguriert werden:
| SA-BGW-A und SA-BGW-B | SB-BGW-A und SB-BGW-B |
|
|
BGP-Konfiguration
Diese Konfiguration ist standortspezifisch.
| SA-BGW-A und SA-BGW-B | SB-BGW-A und SB-BGW-B |
|
|
- Mit dem Befehl maximum-path können mehrere eBGP L2VPN-EVPN-Pfade vom Nachbarn empfangen werden.
- Der Befehl additional-path weist den BGP-Prozess an, anzukündigen, dass das Gerät zusätzliche Pfade senden/empfangen kann.
Für alle L3VNI-VRFs auf Grenz-Gateways muss Multipath ebenfalls konfiguriert werden:
| SA-BGW-A und SA-BGW-B | SB-BGW-A und SB-BGW-B |
|
|
Konfiguration der Tunnelverschlüsselung
Diese Konfiguration muss für alle Border Gateways identisch sein:
key chain CloudSec_Key_Chain1 tunnel-encryption key 1000 key-octet-string Cl0udSec! cryptographic-algorithm AES_128_CMAC feature tunnel-encryption tunnel-encryption must-secure-policy tunnel-encryption source-interface loopback0 tunnel-encryption policy CloudSec_Policy1Diese Konfiguration ist standortspezifisch. Der tunnel-encryption Befehl darf nur auf die Schnittstelle angewendet werden, die über den Befehl evpn multisite dci-trackingverfügt.
| SA-BGW-A und SA-BGW-B | SB-BGW-A und SB-BGW-B |
|
|
Nach der Aktivierung der Tunnelverschlüsselung werden dem lokalen Loopback weitere Attribute hinzugefügt, während Routen an den Nachbarn gemeldet werden. Allen eBGP-IPv4-Unicast-Nachbarn muss dieses Attribut angezeigt werden:
SA-BGW-A# show ip bgp 192.168.2.3 BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family IPv4 Unicast BGP routing table entry for 192.168.2.3/32, version 1320 Paths: (2 available, best #1) Flags: (0x000002) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in urib Multipath: eBGP iBGP Advertised path-id 1 Path type: local, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop AS-Path: NONE, path locally originated 0.0.0.0 (metric 0) from 0.0.0.0 (192.168.2.3) Origin IGP, MED not set, localpref 100, weight 32768 Tunnel Encapsulation attribute: Length 152 !---This is a new attribute Path type: redist, path is valid, not best reason: Locally originated, no labeled nexthop AS-Path: NONE, path locally originated 0.0.0.0 (metric 0) from 0.0.0.0 (192.168.2.3) Origin incomplete, MED 0, localpref 100, weight 32768 Path-id 1 advertised to peers: 10.12.10.2 192.168.4.2 SA-BGW-A# Für den Routing-Typ 2 gibt es auch ein neues Attribut:
SA-BGW-A# show bgp l2vpn evpn 00ea.bd27.86ef BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN Route Distinguisher: 65002:31100 BGP routing table entry for [2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[00ea.bd27.86ef]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216, version 7092 Paths: (2 available, best #2) Flags: (0x000202) (high32 00000000) on xmit-list, is not in l2rib/evpn, is not in HW Multipath: eBGP iBGP Path type: external, path is valid, not best reason: Router Id, multipath, no labeled nexthop Imported to 1 destination(s) Imported paths list: L2-31100 AS-Path: 65002 , path sourced external to AS 192.168.13.3 (metric 0) from 192.168.12.4 (192.168.12.4) Origin IGP, MED 2000, localpref 100, weight 0 Received label 31100 Received path-id 1 Extcommunity: RT:65001:31100 ENCAP:8 ESI: 0300.0000.00fd.ea00.0309 Advertised path-id 1 Path type: external, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop Imported to 1 destination(s) Imported paths list: L2-31100 AS-Path: 65002 , path sourced external to AS 192.168.13.2 (metric 0) from 192.168.12.3 (192.168.12.3) Origin IGP, MED 2000, localpref 100, weight 0 Received label 31100 Received path-id 1 Extcommunity: RT:65001:31100 ENCAP:8 ESI: 0300.0000.00fd.ea00.0309 Path-id 1 not advertised to any peer Route Distinguisher: 192.168.2.3:33867 (L2VNI 31100) BGP routing table entry for [2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[00ea.bd27.86ef]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216, version 7112 Paths: (2 available, best #1) Flags: (0x000212) (high32 0x000400) on xmit-list, is in l2rib/evpn, is not in HW Multipath: eBGP iBGP Advertised path-id 1 Path type: external, path is valid, is best path, no labeled nexthop, in rib Imported from 65002:31100:[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[00ea.bd27.86ef]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216 AS-Path: 65002 , path sourced external to AS 192.168.13.2 (metric 0) from 192.168.12.3 (192.168.12.3) Origin IGP, MED 2000, localpref 100, weight 0 Received label 31100 Received path-id 1 Extcommunity: RT:65001:31100 ENCAP:8 ESI: 0300.0000.00fd.ea00.0309 Path type: external, path is valid, not best reason: Router Id, multipath, no labeled nexthop, in rib Imported from 65002:31100:[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[00ea.bd27.86ef]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216 AS-Path: 65002 , path sourced external to AS 192.168.13.3 (metric 0) from 192.168.12.4 (192.168.12.4) Origin IGP, MED 2000, localpref 100, weight 0 Received label 31100 Received path-id 1 Extcommunity: RT:65001:31100 ENCAP:8 ESI: 0300.0000.00fd.ea00.0309 !---Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI) is also new attribute Path-id 1 (dual) advertised to peers: 192.168.2.2 SA-BGW-A# Überprüfung
ÜberprüfungVor dem Aktivieren von CloudSec sollten Sie überprüfen, ob das Setup ohne CloudSec ordnungsgemäß funktioniert:
SA-BGW-A(config)# show clock Warning: No NTP peer/server configured. Time may be out of sync. 10:02:01.016 UTC Fri Jul 19 2024 Time source is NTP SA-BGW-A(config)# show tunnel-encryption session Tunnel-Encryption Peer Policy Keychain RxStatus TxStatus ------------------------ ---------------------------------------- ---------------------------------------- ----------------- ----------------- =============================================== SA-HOST-A# show clock Warning: No NTP peer/server configured. Time may be out of sync. 10:02:21.592 UTC Fri Jul 19 2024 Time source is NTP SA-HOST-A# ping 10.100.20.10 count unlimited interval 1 PING 10.100.20.10 (10.100.20.10): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=0 ttl=254 time=1.583 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=254 time=10.407 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=2 ttl=254 time=1.37 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=3 ttl=254 time=1.489 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=4 ttl=254 time=6.685 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=5 ttl=254 time=1.547 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=6 ttl=254 time=1.859 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=7 ttl=254 time=5.219 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=8 ttl=254 time=1.337 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=9 ttl=254 time=3.528 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=10 ttl=254 time=4.057 msNach der CloudSec-Konfiguration muss auch der Endpunkt auf der SA erfolgreich einen Ping an den Endpunkt auf Standort B senden. In einigen Fällen kann der Ping-Test jedoch erfolglos sein. Es hängt davon ab, welcher Cloudsec-Peer vom lokalen Gerät zum Senden von Cloudsec-verschlüsseltem Datenverkehr ausgewählt wurde.
SA-HOST-A# ping 10.100.20.10 PING 10.100.20.10 (10.100.20.10): 56 data bytes Request 0 timed out Request 1 timed out Request 2 timed out Request 3 timed out Request 4 timed out --- 10.100.20.10 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100.00% packet loss SA-HOST-A# Fehlerbehebung
FehlerbehebungÜberprüfen Sie die lokale ARP-Tabelle auf dem Quellendpunkt:
SA-HOST-A# ping 10.100.20.10 count unlimited interval 1 Request 352 timed out Request 353 timed out Request 354 timed out 356 packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100.00% packet loss SA-HOST-A# clear ip arp delete-force SA-HOST-A# show ip arp Flags: * - Adjacencies learnt on non-active FHRP router + - Adjacencies synced via CFSoE # - Adjacencies Throttled for Glean CP - Added via L2RIB, Control plane Adjacencies PS - Added via L2RIB, Peer Sync RO - Re-Originated Peer Sync Entry D - Static Adjacencies attached to down interface IP ARP Table for context default Total number of entries: 1 Address Age MAC Address Interface Flags 10.100.20.10 00:00:02 00ea.bd27.86ef Vlan1100 SA-HOST-A# Diese Ausgabe bestätigt, dass der BUM-Datenverkehr weitergeleitet wird und die Kontrollebene funktioniert. Der nächste Schritt ist die Überprüfung des Tunnel-Verschlüsselungsstatus:
SA-BGW-A# show tunnel-encryption session Tunnel-Encryption Peer Policy Keychain RxStatus TxStatus ------------------------ ---------------------------------------- ---------------------------------------- ----------------- ----------------- 192.168.13.2 CloudSec_Policy1 CloudSec_Key_Chain1 Secure (AN: 0) Secure (AN: 0) 192.168.13.3 CloudSec_Policy1 CloudSec_Key_Chain1 Secure (AN: 0) Secure (AN: 0) SA-BGW-A# Diese Ausgabe zeigt, dass die CloudSec-Sitzung eingerichtet ist. Als Nächstes können Sie unbegrenzte Pings auf SA-HOST-A ausführen:
SA-HOST-A# ping 10.100.20.10 count unlimited interval 1Von diesem Punkt an müssen Sie Geräte an Standort A überprüfen und feststellen, ob der Datenverkehr diese Geräte erreicht. Sie können diese Aufgabe mit ELAM auf allen Geräten entlang des Pfads am Standort A durchführen. Wenn Sie in-select den Standardwert 6 bis 9 ändern, können Sie die Übereinstimmung anhand der inneren Header festlegen. Weitere Informationen zu ELAM finden Sie unter diesem Link: Nexus 9000 Cloud Scale ASIC (Tahoe) NX-OS ELAM.
ELAM auf SA-LEAF-A
ELAM auf SA-LEAF-AIm Produktionsnetzwerk sind mehr als ein SPINE-Gerät vorhanden. Um zu verstehen, an welches Spine der Datenverkehr gesendet wurde, müssen Sie zuerst ein ELAM auf LEAF starten. Trotz der in-select 9 Verwendung muss auf dem mit der Quelle verbundenen LEAF der äußere IPv4-Header verwendet werden, da der Datenverkehr, der diesen LEAF erreicht hat, nicht VXLAN-verschlüsselt ist. In realen Netzwerken kann es schwierig sein, das von Ihnen erzeugte Paket genau zu erfassen. In solchen Fällen können Sie Ping mit einer bestimmten Länge ausführen und den Pkt-len-Header verwenden, um Ihr Paket zu identifizieren. Standardmäßig hat ein icmp-Paket eine Länge von 64 Byte. Plus 20 Byte IP-Header, was zusammenfassend 84 Byte PKT Len ergab:
SA-LEAF-A# debug platform internal tah elam SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam)# trigger init in-select 9 Slot 1: param values: start asic 0, start slice 0, lu-a2d 1, in-select 9, out-select 0 SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set outer ipv4 src_ip 10.100.10.10 dst_ip 10.100.20.10 SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 SUGARBOWL ELAM REPORT SUMMARY slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 ============================ Incoming Interface: Eth1/49 Src Idx : 0xc1, Src BD : 1100 Outgoing Interface Info: dmod 1, dpid 64 !---Note dpid value Dst Idx : 0xcd, Dst BD : 1100 Packet Type: IPv4 Outer Dst IPv4 address: 10.100.20.10 Outer Src IPv4 address: 10.100.10.10 Ver = 4, DSCP = 0, Don't Fragment = 0 Proto = 1, TTL = 255, More Fragments = 0 Hdr len = 20, Pkt len = 84, Checksum = 0xb4ae !---64 byte + 20 byte IP header Pkt len = 84 Inner Payload Type: CE L4 Protocol : 1 L4 info not available Drop Info: ---------- LUA: LUB: LUC: LUD: Final Drops: SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show system internal ethpm info all | i i "dpid=64" !---Put dpid value here IF_STATIC_INFO: port_name=Ethernet1/52,if_index:0x1a006600,ltl=5940,slot=0, nxos_port=204,dmod=1,dpid=64,unit=0,queue=65535,xbar_unitbmp=0x0,ns_pid=255,slice_num=1,port_on_slice=24,src_id=48 SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show cdp neighbors interface ethernet 1/52 Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device, s - Supports-STP-Dispute Device-ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID SA-SPINE-A(FDO242210CS) Eth1/52 130 R S s N9K-C93240YC-FX2 Eth1/52 Total entries displayed: 1 SA-LEAF-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# An dieser Ausgabe können Sie sehen, dass der Datenverkehr SA-LEAF-A erreicht und über die Schnittstelle Ethernet1/52 weitergeleitet wird, die von der Topologie aus mit SA-SPINE-A verbunden ist.
ELAM auf SA-SPINE-A
ELAM auf SA-SPINE-AAuf SPINE wird der Pkt-Len-Wert größer sein, da der 50-Byte-VXLAN-Header ebenfalls hinzugefügt wurde. Standardmäßig kann SPINE auf internen Headern ohne vxlan-parse oder feature nv overlay nicht übereinstimmen. Daher müssen Sie den vxlan-parse enable Befehl auf SPINE verwenden:
SA-SPINE-A(config-if)# debug platform internal tah elam SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam)# trigger init in-select 9 Slot 1: param values: start asic 0, start slice 0, lu-a2d 1, in-select 9, out-select 0 SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam)# vxlan-parse enable SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set inner ipv4 src_ip 10.100.10.10 dst_ip 10.100.20.10 SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 HEAVENLY ELAM REPORT SUMMARY slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 ============================ Incoming Interface: Eth1/52 Src Idx : 0xcd, Src BD : 4153 Outgoing Interface Info: dmod 1, dpid 72 Dst Idx : 0xc5, Dst BD : 4151 Packet Type: IPv4 Outer Dst IPv4 address: 192.168.100.1 Outer Src IPv4 address: 192.168.3.1 Ver = 4, DSCP = 0, Don't Fragment = 0 Proto = 17, TTL = 255, More Fragments = 0 Hdr len = 20, Pkt len = 134, Checksum = 0x7d69 !---84 bytes + 50 bytes VXLAN header Pkt len = 134 Inner Payload Type: IPv4 Inner Dst IPv4 address: 10.100.20.10 Inner Src IPv4 address: 10.100.10.10 L4 Protocol : 17 L4 info not available Drop Info: ---------- LUA: LUB: LUC: LUD: Final Drops: SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show system internal ethpm info all | i i "dpid=72" IF_STATIC_INFO: port_name=Ethernet1/50,if_index:0x1a006200,ltl=5948,slot=0, nxos_port=196,dmod=1,dpid=72,unit=0,queue=65535,xbar_unitbmp=0x0,ns_pid=255,slice_num=1,port_on_slice=0,src_id=0 SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show cdp neighbors interface ethernet 1/50 Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device, s - Supports-STP-Dispute Device-ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID SA-BGW-A(FDO242210CX) Eth1/50 169 R S s N9K-C93240YC-FX2 Eth1/50 Total entries displayed: 1 SA-SPINE-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# SA-SPINE-A sendet den Datenverkehr je nach Ausgabe an SA-BGW-A.
ELAM auf SA-BGW-A
ELAM auf SA-BGW-ASA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set inner ipv4 src_ip 10.100.10.10 dst_ip 10.100.20.10 SA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 HEAVENLY ELAM REPORT SUMMARY slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 ============================ Incoming Interface: Eth1/50 Src Idx : 0xc5, Src BD : 1100 Outgoing Interface Info: dmod 1, dpid 48 Dst Idx : 0xbd, Dst BD : 1100 Packet Type: IPv4 Outer Dst IPv4 address: 192.168.100.1 Outer Src IPv4 address: 192.168.3.1 Ver = 4, DSCP = 0, Don't Fragment = 0 Proto = 17, TTL = 254, More Fragments = 0 Hdr len = 20, Pkt len = 134, Checksum = 0x7e69 Inner Payload Type: IPv4 Inner Dst IPv4 address: 10.100.20.10 Inner Src IPv4 address: 10.100.10.10 L4 Protocol : 17 L4 info not available Drop Info: ---------- LUA: LUB: LUC: LUD: Final Drops: SA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show system internal ethpm info all | i i "dpid=48" IF_STATIC_INFO: port_name=Ethernet1/48,if_index:0x1a005e00,ltl=5956,slot=0, nxos_port=188,dmod=1,dpid=48,unit=0,queue=65535,xbar_unitbmp=0x0,ns_pid=255,slice_num=0,port_on_slice=48,src_id=96 SA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show cdp neighbors interface ethernet 1/48 Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device, s - Supports-STP-Dispute Device-ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID SB-BGW-A(FDO2452070B) Eth1/48 122 R S s N9K-C93216TC-FX2 Eth1/3 Total entries displayed: 1 SA-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# Laut Ausgabe von SA-BGW-A wurde der Datenverkehr über Ethernet 1/48 an SB-BGW-A weitergeleitet. Im nächsten Schritt überprüfen Sie SB-BGW-A:
SB-BGW-A# debug platform internal tah elam SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam)# trigger init in-select 9 Slot 1: param values: start asic 0, start slice 0, lu-a2d 1, in-select 9, out-select 0 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set inner ipv4 src_ip 10.100.10.10 dst_ip 10.100.20.10 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 !---Reset the previous filter and start again just in case if packet was not captured. SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# reset SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set inner ipv4 src_ip 10.100.10.10 dst_ip 10.100.20.10 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# Laut Ausgabe von SB-BGW-A wurde ELAM nicht einmal ausgelöst. Das bedeutet, dass entweder der SB-BGW-B die Pakete empfängt und sie nicht richtig entschlüsseln und analysieren kann oder gar nicht. Um zu verstehen, was mit dem Cloudsec-Datenverkehr passiert ist, können Sie erneut ein ELAM auf SB-BGW-A ausführen. Der Triggerfilter muss jedoch auf die äußere IP-Adresse gesetzt werden, die für Cloudsec verwendet wird, da der innere Header des verschlüsselten Cloudsec-Datenpakets nicht sichtbar ist. Aus der vorherigen Ausgabe wissen Sie, dass der SA-BGW-A den Datenverkehr behandelt hat, was bedeutet, dass SA-BGW-A den Datenverkehr mit Cloudsec verschlüsselt. Sie können also NVE IP von SA-BGW-A als Triggerfilter für ELAM verwenden. Die Länge der VXLAN-verschlüsselten ICMP-Pakete der vorherigen Ausgänge beträgt 134 Byte. Plus 32 Byte CloudSec-Header in der Zusammenfassung ergibt 166 Byte:
SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# reset SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# set outer ipv4 src_ip 192.168.3.2 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# start SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# report ELAM not triggered yet on slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 0 HEAVENLY ELAM REPORT SUMMARY slot - 1, asic - 0, slice - 1 ============================ Incoming Interface: Eth1/3 Src Idx : 0x9, Src BD : 4108 Outgoing Interface Info: dmod 1, dpid 130 Dst Idx : 0xd, Dst BD : 4109 Packet Type: IPv4 Outer Dst IPv4 address: 192.168.13.3 !---NVE IP address of SB-BGW-B Outer Src IPv4 address: 192.168.3.2 Ver = 4, DSCP = 0, Don't Fragment = 0 Proto = 17, TTL = 254, More Fragments = 0 Hdr len = 20, Pkt len = 166, Checksum = 0xd546 !---134 byte VXLAN packet + 32 byte cloudsec header Pkt len = 166 Inner Payload Type: CE L4 Protocol : 17 L4 info not available Drop Info: ---------- LUA: LUB: LUC: LUD: Final Drops: !---To reach SB-BGW-B NVE IP traffic was sent out of Ethernet1/4 which is connected to SB-SPINE-A SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show system internal ethpm info all | i i "dpid=130" IF_STATIC_INFO: port_name=Ethernet1/4,if_index:0x1a000600,ltl=6132,slot=0, nxos_port=12,dmod=1,dpid=130,unit=0,queue=65535,xbar_unitbmp=0x0,ns_pid=255,slice_num=1,port_on_slice=58,src_id=116
SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show cdp neighbors interface ethernet 1/4 Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device, s - Supports-STP-Dispute Device-ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID SB-SPINE-A(FDO22302CJ0) Eth1/4 131 R S s N9K-C9236C Eth1/34 Total entries displayed: 1 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show ip route 192.168.13.3 IP Route Table for VRF "default" '*' denotes best ucast next-hop '**' denotes best mcast next-hop '[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric] '%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string> 192.168.13.3/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 192.168.11.5, Eth1/4, [110/6], 00:56:13, ospf-UNDERLAY, intra via 192.168.14.2, [200/0], 01:13:46, bgp-65002, internal, tag 65002 !---The device still have a route for SB-BGW-B NVE IP via SVI
SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show ip route 192.168.14.2 IP Route Table for VRF "default" '*' denotes best ucast next-hop '**' denotes best mcast next-hop '[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric] '%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string> 192.168.14.2/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 192.168.14.2, Vlan3600, [250/0], 01:15:05, am SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show ip arp 192.168.14.2 Flags: * - Adjacencies learnt on non-active FHRP router + - Adjacencies synced via CFSoE # - Adjacencies Throttled for Glean CP - Added via L2RIB, Control plane Adjacencies PS - Added via L2RIB, Peer Sync RO - Re-Originated Peer Sync Entry D - Static Adjacencies attached to down interface IP ARP Table Total number of entries: 1 Address Age MAC Address Interface Flags 192.168.14.2 00:00:13 ecce.1324.c803 Vlan3600 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show mac address-table address ecce.1324.c803 Legend: * - primary entry, G - Gateway MAC, (R) - Routed MAC, O - Overlay MAC age - seconds since last seen,+ - primary entry using vPC Peer-Link, (T) - True, (F) - False, C - ControlPlane MAC, ~ - vsan, (NA)- Not Applicable VLAN MAC Address Type age Secure NTFY Ports ---------+-----------------+--------+---------+------+----+------------------ G 3600 ecce.1324.c803 static - F F vPC Peer-Link(R) SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# Aus dieser Ausgabe können Sie sehen, dass der CloudSec-Datenverkehr basierend auf der Routing-Tabelle über die Schnittstelle Ethernet1/4 an den SB-BGW-B weitergeleitet wird. Gemäß Cisco Nexus Serie 9000 NX-OS VXLAN Configuration Guide, Release 10.3(x) Richtlinien und Einschränkungen:
-
CloudSec-Datenverkehr, der für den Switch bestimmt ist, muss über die DCI-Uplinks in den Switch gelangen.
Laut dem Abschnitt zur Unterstützung von CloudSec durch vPC Border Gateway im selben Leitfaden sind die BGP-Pfadattribute beider vPC BGWs identisch, wenn der vPC BGW die PIP-Adresse des vPC BGWs erlernt und auf der DCI-Seite ankündigt. Daher können die zwischengeschalteten DCI-Knoten den Pfad vom vPC-BGW wählen, der nicht die PIP-Adresse besitzt. In diesem Szenario wird die MCT-Verbindung für verschlüsselten Datenverkehr vom Remote-Standort verwendet. In diesem Fall wird jedoch die Schnittstelle zum SPINE verwendet. Dennoch verfügen die BGWs über eine OSPF-Adjacency über die BackUp-SVI.
SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show ip ospf neighbors OSPF Process ID UNDERLAY VRF default Total number of neighbors: 2 Neighbor ID Pri State Up Time Address Interface 192.168.12.4 1 FULL/ - 01:33:11 192.168.14.2 Vlan3600 192.168.12.2 1 FULL/ - 01:33:12 192.168.11.5 Eth1/4 SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)#Grund des Problems und Behebung
Grund des Problems und BehebungDer Grund hierfür sind die OSPF-Kosten der SVI-Schnittstelle. Standardmäßig beträgt die Referenzbandbreite für automatische Kosten in NX-OS 40 G. SVI-Schnittstellen haben eine Bandbreite von 1 Gbit/s, während die physische Schnittstelle eine Bandbreite von 10 Gbit/s aufweist:
SB-BGW-A(TAH-elam-insel9)# show ip ospf interface brief OSPF Process ID UNDERLAY VRF default Total number of interface: 5 Interface ID Area Cost State Neighbors Status Vlan3600 3 0.0.0.0 40 P2P 1 up <Output omitted> Eth1/4 5 0.0.0.0 1 P2P 1 up In diesem Fall kann das Problem durch eine administrative Änderung der Kosten für SVI gelöst werden. Die Feinabstimmung muss an allen Border Gateways erfolgen.
SB-BGW-A(config)# int vlan 3600 SB-BGW-A(config-if)# ip ospf cost 1 SB-BGW-A(config-if)# sh ip route 192.168.13.3 IP Route Table for VRF "default" '*' denotes best ucast next-hop '**' denotes best mcast next-hop '[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric] '%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string> 192.168.13.3/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 192.168.14.2, Vlan3600, [110/2], 00:00:08, ospf-UNDERLAY, intra via 192.168.14.2, [200/0], 01:34:07, bgp-65002, internal, tag 65002 SB-BGW-A(config-if)#
!---The ping is started to work immediately
Request 1204 timed out Request 1205 timed out Request 1206 timed out 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1207 ttl=254 time=1.476 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1208 ttl=254 time=5.371 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1209 ttl=254 time=5.972 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1210 ttl=254 time=1.466 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1211 ttl=254 time=2.972 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1212 ttl=254 time=4.582 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1213 ttl=254 time=1.434 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1214 ttl=254 time=4.486 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1215 ttl=254 time=2.743 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1216 ttl=254 time=1.469 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1217 ttl=254 time=7.322 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1218 ttl=254 time=1.532 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1219 ttl=254 time=1.438 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1220 ttl=254 time=7.122 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1221 ttl=254 time=1.344 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1222 ttl=254 time=1.63 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1223 ttl=254 time=6.133 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1224 ttl=254 time=1.455 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1225 ttl=254 time=3.221 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1226 ttl=254 time=4.435 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1227 ttl=254 time=1.463 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1228 ttl=254 time=5.14 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1229 ttl=254 time=2.796 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1230 ttl=254 time=1.49 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1231 ttl=254 time=6.707 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1232 ttl=254 time=1.447 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1233 ttl=254 time=1.285 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1234 ttl=254 time=7.097 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1235 ttl=254 time=1.295 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1236 ttl=254 time=0.916 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1237 ttl=254 time=6.24 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1238 ttl=254 time=1.439 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1239 ttl=254 time=2.739 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1240 ttl=254 time=4.477 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1241 ttl=254 time=1.431 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1242 ttl=254 time=5.372 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1243 ttl=254 time=3.119 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1244 ttl=254 time=1.504 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1245 ttl=254 time=6.909 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1246 ttl=254 time=1.498 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1247 ttl=254 time=1.454 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1248 ttl=254 time=6.701 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1249 ttl=254 time=1.441 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1250 ttl=254 time=1.888 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1251 ttl=254 time=6.052 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1252 ttl=254 time=1.469 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1253 ttl=254 time=3.61 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1254 ttl=254 time=4.213 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1255 ttl=254 time=1.276 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1256 ttl=254 time=5.712 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1257 ttl=254 time=2.299 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1258 ttl=254 time=1.417 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1259 ttl=254 time=7.159 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1260 ttl=254 time=1.538 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1261 ttl=254 time=1.629 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1262 ttl=254 time=7.892 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1263 ttl=254 time=1.495 ms 64 bytes from 10.100.20.10: icmp_seq=1264 ttl=254 time=2.792 ms ^C --- 10.100.20.10 ping statistics --- 1265 packets transmitted, 58 packets received, 95.42% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 0.916/3.31/7.892 ms SA-HOST-A# Revisionsverlauf
| Überarbeitung | Veröffentlichungsdatum | Kommentare |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
29-Jul-2024 |
Erstveröffentlichung |
Beiträge von Cisco Ingenieuren
- Chingiz KhalafovTechnischer Berater
Cisco kontaktieren
- Eine Supportanfrage öffnen

- (Erfordert einen Cisco Servicevertrag)
 Feedback
Feedback