Ersatz des Compute-Servers UCS C240 M4 - vEPC
Download-Optionen
-
ePub (1.0 MB)
In verschiedenen Apps auf iPhone, iPad, Android, Sony Reader oder Windows Phone anzeigen
Inklusive Sprache
In dem Dokumentationssatz für dieses Produkt wird die Verwendung inklusiver Sprache angestrebt. Für die Zwecke dieses Dokumentationssatzes wird Sprache als „inklusiv“ verstanden, wenn sie keine Diskriminierung aufgrund von Alter, körperlicher und/oder geistiger Behinderung, Geschlechtszugehörigkeit und -identität, ethnischer Identität, sexueller Orientierung, sozioökonomischem Status und Intersektionalität impliziert. Dennoch können in der Dokumentation stilistische Abweichungen von diesem Bemühen auftreten, wenn Text verwendet wird, der in Benutzeroberflächen der Produktsoftware fest codiert ist, auf RFP-Dokumentation basiert oder von einem genannten Drittanbieterprodukt verwendet wird. Hier erfahren Sie mehr darüber, wie Cisco inklusive Sprache verwendet.
Informationen zu dieser Übersetzung
Cisco hat dieses Dokument maschinell übersetzen und von einem menschlichen Übersetzer editieren und korrigieren lassen, um unseren Benutzern auf der ganzen Welt Support-Inhalte in ihrer eigenen Sprache zu bieten. Bitte beachten Sie, dass selbst die beste maschinelle Übersetzung nicht so genau ist wie eine von einem professionellen Übersetzer angefertigte. Cisco Systems, Inc. übernimmt keine Haftung für die Richtigkeit dieser Übersetzungen und empfiehlt, immer das englische Originaldokument (siehe bereitgestellter Link) heranzuziehen.
Inhalt
Einführung
Dieses Dokument beschreibt die erforderlichen Schritte zum Ersetzen eines fehlerhaften Computing-Servers in einer Ultra-M-Konfiguration, die StarOS Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) hostet.
Hintergrundinformationen
Ultra-M ist eine vorkonfigurierte und validierte Kernlösung für virtualisierte mobile Pakete, die die Bereitstellung von VNFs vereinfacht. OpenStack ist der Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (VIM) für Ultra-M und besteht aus den folgenden Knotentypen:
- Computing
- Object Storage Disk - Computing (OSD - Computing)
- Controller
- OpenStack-Plattform - Director (OSPD)
Die High-Level-Architektur von Ultra-M und die beteiligten Komponenten sind in diesem Bild dargestellt:
 UltraM-Architektur
UltraM-Architektur
Dieses Dokument richtet sich an Mitarbeiter von Cisco, die mit der Cisco Ultra-M-Plattform vertraut sind. Es beschreibt die Schritte, die zum Zeitpunkt des Ersatzes des Compute-Servers auf der Ebene von OpenStack und StarOS VNF durchgeführt werden müssen.
Hinweis: Ultra M 5.1.x wird zur Definition der Verfahren in diesem Dokument berücksichtigt.
Abkürzungen
| VNF | Virtuelle Netzwerkfunktion |
| CF | Kontrollfunktion |
| SF | Servicefunktion |
| WSA | Elastic Service Controller |
| MOP | Verfahrensweise |
| OSD | Objektspeicherdatenträger |
| HDD | Festplattenlaufwerk |
| SSD | Solid-State-Laufwerk |
| VIM | Virtueller Infrastrukturmanager |
| VM | Virtuelles System |
| EM | Element Manager |
| USA | Ultra-Automatisierungsservices |
| UUID | Universell eindeutige IDentifier |
Workflow des MoP
 Workflow für den Austausch
Workflow für den Austausch
Voraussetzungen
Sicherung
Bevor Sie einen Compute-Knoten austauschen, ist es wichtig, den aktuellen Zustand Ihrer Red Hat OpenStack Platform-Umgebung zu überprüfen. Es wird empfohlen, den aktuellen Zustand zu überprüfen, um Komplikationen zu vermeiden, wenn der Computing-Ersetzungsprozess eingeschaltet ist. Sie kann durch diesen Austausch erreicht werden.
Im Falle einer Wiederherstellung empfiehlt Cisco, eine Sicherung der OSPD-Datenbank mithilfe der folgenden Schritte durchzuführen:
[root@director ~]# mysqldump --opt --all-databases > /root/undercloud-all-databases.sql
[root@director ~]# tar --xattrs -czf undercloud-backup-`date +%F`.tar.gz /root/undercloud-all-databases.sql
/etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf /var/lib/glance/images /srv/node /home/stack
tar: Removing leading `/' from member names
Dieser Prozess stellt sicher, dass ein Knoten ausgetauscht werden kann, ohne dass die Verfügbarkeit von Instanzen beeinträchtigt wird. Außerdem wird empfohlen, die StarOS-Konfiguration zu sichern, insbesondere wenn der auszutauschende Computing-Knoten als Host für die Control Function (CF) Virtual Machine (VM) fungiert.
Identifizieren der im Compute-Knoten gehosteten VMs
Identifizieren Sie die VMs, die auf dem Computing-Server gehostet werden. Es gibt zwei Möglichkeiten:
- Der Computing-Server enthält nur Service Function (SF) VM:
[stack@director ~]$ nova list --field name,host | grep compute-10
| 49ac5f22-469e-4b84-badc-031083db0533 | VNF2-DEPLOYM_s9_0_8bc6cc60-15d6-4ead-8b6a-10e75d0e134d |
pod1-compute-10.localdomain |
- Der Computing-Server enthält eine Kombination aus VMs:
[stack@director ~]$ nova list --field name,host | grep compute-8
| 507d67c2-1d00-4321-b9d1-da879af524f8 | VNF2-DEPLOYM_XXXX_0_c8d98f0f-d874-45d0-af75-88a2d6fa82ea | pod1-compute-8.localdomain |
| f9c0763a-4a4f-4bbd-af51-bc7545774be2 | VNF2-DEPLOYM_c1_0_df4be88d-b4bf-4456-945a-3812653ee229 | pod1-compute-8.localdomain |
| 75528898-ef4b-4d68-b05d-882014708694 | VNF2-ESC-ESC-0 | pod1-compute-8.localdomain |
| f5bd7b9c-476a-4679-83e5-303f0aae9309 | VNF2-UAS-uas-0 | pod1-compute-8.localdomain |
Hinweis: In der hier gezeigten Ausgabe entspricht die erste Spalte dem Universally Unique IDentifier (UUID), die zweite Spalte dem VM-Namen und die dritte Spalte dem Hostnamen, in dem das virtuelle System vorhanden ist. Die Parameter aus dieser Ausgabe werden in den nachfolgenden Abschnitten verwendet.
Graceful Power Aus
Fall 1. Computing-Knoten-Hosts nur SF VM
Migration der SF-Karte in den Standby-Status
- Melden Sie sich beim StarOS VNF an, und identifizieren Sie die Karte, die dem SF VM entspricht. Verwenden Sie die UUID der im Abschnitt "Identifizieren der im Compute-Knoten gehosteten VMs" angegebenen SF VM, und identifizieren Sie die Karte, die der UUID entspricht:
[local]VNF2# show card hardware
Tuesday might 08 16:49:42 UTC 2018
<snip>
Card 8:
Card Type : 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card
CPU Packages : 26 [#0, #1, #2, #3, #4, #5, #6, #7, #8, #9, #10, #11, #12, #13, #14, #15, #16, #17, #18, #19, #20, #21, #22, #23, #24, #25]
CPU Nodes : 2
CPU Cores/Threads : 26
Memory : 98304M (qvpc-di-large)
UUID/Serial Number : 49AC5F22-469E-4B84-BADC-031083DB0533
<snip>
- Überprüfen Sie den Status der Karte:
[local]VNF2# show card table
Tuesday might 08 16:52:53 UTC 2018
Slot Card Type Oper State SPOF Attach
----------- -------------------------------------- ------------- ---- ------
1: CFC Control Function Virtual Card Active No
2: CFC Control Function Virtual Card Standby -
3: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
4: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
5: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
6: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
7: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
8: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
9: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
10: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Standby -
- Wenn sich die Karte im aktiven Zustand befindet, verschieben Sie sie in den Standby-Status:
[local]VNF2# card migrate from 8 to 10
Herunterfahren der SF-VM von ESC
- Melden Sie sich beim ESC-Knoten an, der der VNF entspricht, und überprüfen Sie den Status der SF VM:
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ cd /opt/cisco/esc/esc-confd/esc-cli
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 esc-cli]$ ./esc_nc_cli get esc_datamodel | egrep --color "<state>|<vm_name>|<vm_id>|<deployment_name>"
<snip>
<state>SERVICE_ACTIVE_STATE</state>
<vm_name>VNF2-DEPLOYM_c1_0_df4be88d-b4bf-4456-945a-3812653ee229</vm_name>
<state>VM_ALIVE_STATE</state>
<vm_name> VNF2-DEPLOYM_s9_0_8bc6cc60-15d6-4ead-8b6a-10e75d0e134d</vm_name>
<state>VM_ALIVE_STATE</state>
<snip>
- Beenden Sie die SF VM mit dem VM-Namen. (VM-Name siehe Abschnitt " Identifizieren der im Compute-Knoten gehosteten VMs"):
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 esc-cli]$ ./esc_nc_cli vm-action STOP VNF2-DEPLOYM_s9_0_8bc6cc60-15d6-4ead-8b6a-10e75d0e134d
- Nach dem Beenden muss das virtuelle System in den SHUTOFF-Status wechseln:
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ cd /opt/cisco/esc/esc-confd/esc-cli
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 esc-cli]$ ./esc_nc_cli get esc_datamodel | egrep --color "<state>|<vm_name>|<vm_id>|<deployment_name>"
<snip>
<state>SERVICE_ACTIVE_STATE</state>
<vm_name>VNF2-DEPLOYM_c1_0_df4be88d-b4bf-4456-945a-3812653ee229</vm_name>
<state>VM_ALIVE_STATE</state>
<vm_name>VNF2-DEPLOYM_c3_0_3e0db133-c13b-4e3d-ac14-
<state>VM_ALIVE_STATE</state>
<vm_name>VNF2-DEPLOYM_s9_0_8bc6cc60-15d6-4ead-8b6a-10e75d0e134d</vm_name>
<state>VM_SHUTOFF_STATE</state>
<snip>
Entfernen des Computing-Knotens aus der Nova Aggregate-Liste
- Listen Sie die nova-Aggregate auf, und identifizieren Sie die Aggregate, die dem von ihm gehosteten VNF-Server entsprechen. In der Regel hat das Format <VNFNAME>-SERVICE<X>:
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-list
+----+-------------------+-------------------+
| Id | Name | Availability Zone |
+----+-------------------+-------------------+
| 29 | POD1-AUTOIT | mgmt |
| 57 | VNF1-SERVICE1 | - |
| 60 | VNF1-EM-MGMT1 | - |
| 63 | VNF1-CF-MGMT1 | - |
| 66 | VNF2-CF-MGMT2 | - |
| 69 | VNF2-EM-MGMT2 | - |
| 72 | VNF2-SERVICE2 | - |
| 75 | VNF3-CF-MGMT3 | - |
| 78 | VNF3-EM-MGMT3 | - |
| 81 | VNF3-SERVICE3 | - |
+----+-------------------+-------------------+
In diesem Fall gehört der zu ersetzende Computing-Server zu VNF2. Die entsprechende aggregierte Liste ist also VNF2-SERVICE2.
- Entfernen Sie den Computing-Knoten aus der angegebenen Aggregation (entfernen Sie ihn durch den Hostnamen, der im Abschnitt "Identifizieren der im Compute-Knoten gehosteten VMs" angegeben ist):
nova aggregate-remove-host
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-remove-host VNF2-SERVICE2 pod1-compute-10.localdomain
- Überprüfen Sie, ob der Computing-Knoten aus den Aggregaten entfernt wurde. Nun darf der Host nicht unter der Aggregatzuordnung aufgeführt werden:
nova aggregate-show
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-show VNF2-SERVICE2
Fall 2. Computing-Knoten-Hosts CF/ESC/EM/UAS
Migration der CF-Karte in den Standby-Status
- Melden Sie sich beim StarOS VNF an, und identifizieren Sie die Karte, die dem CF VM entspricht. Verwenden Sie die UUID des CF VM, die im Abschnitt "Identifizieren der im Compute-Knoten gehosteten VMs" angegeben ist, und suchen Sie die Karte, die der UUID entspricht:
[local]VNF2# show card hardware
Tuesday might 08 16:49:42 UTC 2018
<snip>
Card 2:
Card Type : Control Function Virtual Card
CPU Packages : 8 [#0, #1, #2, #3, #4, #5, #6, #7]
CPU Nodes : 1
CPU Cores/Threads : 8
Memory : 16384M (qvpc-di-large)
UUID/Serial Number : F9C0763A-4A4F-4BBD-AF51-BC7545774BE2
<snip>
- Überprüfen Sie den Status der Karte:
[local]VNF2# show card table
Tuesday might 08 16:52:53 UTC 2018
Slot Card Type Oper State SPOF Attach
----------- -------------------------------------- ------------- ---- ------
1: CFC Control Function Virtual Card Standby -
2: CFC Control Function Virtual Card Active No
3: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
4: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
5: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
6: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
7: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
8: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
9: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Active No
10: FC 4-Port Service Function Virtual Card Standby -
- Wenn sich die Karte im aktiven Zustand befindet, verschieben Sie sie in den Standby-Status:
[local]VNF2# card migrate from 2 to 1
Herunterfahren von CF und EM VM aus ESC
- Melden Sie sich beim ESC-Knoten an, der der VNF entspricht, und überprüfen Sie den Status der VMs:
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ cd /opt/cisco/esc/esc-confd/esc-cli
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 esc-cli]$ ./esc_nc_cli get esc_datamodel | egrep --color "<state>|<vm_name>|<vm_id>|<deployment_name>"
<snip>
<state>SERVICE_ACTIVE_STATE</state>
<vm_name>VNF2-DEPLOYM_c1_0_df4be88d-b4bf-4456-945a-3812653ee229</vm_name>
<state>VM_ALIVE_STATE</state>
<vm_name>VNF2-DEPLOYM_c3_0_3e0db133-c13b-4e3d-ac14-
<state>VM_ALIVE_STATE</state>
<deployment_name>VNF2-DEPLOYMENT-em</deployment_name>
<vm_id>507d67c2-1d00-4321-b9d1-da879af524f8</vm_id>
<vm_id>dc168a6a-4aeb-4e81-abd9-91d7568b5f7c</vm_id>
<vm_id>9ffec58b-4b9d-4072-b944-5413bf7fcf07</vm_id>
<state>SERVICE_ACTIVE_STATE</state>
<vm_name>VNF2-DEPLOYM_XXXX_0_c8d98f0f-d874-45d0-af75-88a2d6fa82ea</vm_name>
<state>VM_ALIVE_STATE</state>
<snip>
- Beenden Sie das CF- und EM VM einzeln mit dem VM-Namen. (VM-Name siehe Abschnitt "Identifizieren der im Compute-Knoten gehosteten VMs"):
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 esc-cli]$ ./esc_nc_cli vm-action STOP VNF2-DEPLOYM_c1_0_df4be88d-b4bf-4456-945a-3812653ee229
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 esc-cli]$ ./esc_nc_cli vm-action STOP VNF2-DEPLOYM_XXXX_0_c8d98f0f-d874-45d0-af75-88a2d6fa82ea
- Nach dem Anhalten müssen die VMs in den SHUTOFF-Status wechseln:
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ cd /opt/cisco/esc/esc-confd/esc-cli
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 esc-cli]$ ./esc_nc_cli get esc_datamodel | egrep --color "<state>|<vm_name>|<vm_id>|<deployment_name>"
<snip>
<state>SERVICE_ACTIVE_STATE</state>
<vm_name>VNF2-DEPLOYM_c1_0_df4be88d-b4bf-4456-945a-3812653ee229</vm_name>
<state>VM_SHUTOFF_STATE</state>
<vm_name>VNF2-DEPLOYM_c3_0_3e0db133-c13b-4e3d-ac14-
<state>VM_ALIVE_STATE</state>
<deployment_name>VNF2-DEPLOYMENT-em</deployment_name>
<vm_id>507d67c2-1d00-4321-b9d1-da879af524f8</vm_id>
<vm_id>dc168a6a-4aeb-4e81-abd9-91d7568b5f7c</vm_id>
<vm_id>9ffec58b-4b9d-4072-b944-5413bf7fcf07</vm_id>
<state>SERVICE_ACTIVE_STATE</state>
<vm_name>VNF2-DEPLOYM_XXXX_0_c8d98f0f-d874-45d0-af75-88a2d6fa82ea</vm_name>
VM_SHUTOFF_STATE
<snip>
Migration von ESC in den Standby-Modus
- Melden Sie sich beim im Computing-Knoten gehosteten ESC an, und prüfen Sie, ob er sich im Master-Status befindet. Wenn ja, schalten Sie den ESC in den Standby-Modus um:
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 esc-cli]$ escadm status
0 ESC status=0 ESC Master Healthy
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ sudo service keepalived stop
Stopping keepalived: [ OK ]
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ escadm status
1 ESC status=0 In SWITCHING_TO_STOP state. Please check status after a while.
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ sudo reboot
Broadcast message from admin@vnf1-esc-esc-0.novalocal
(/dev/pts/0) at 13:32 ...
The system is going down for reboot NOW!
Entfernen des Computing-Knotens aus der Nova Aggregate-Liste
- Listen Sie die nova-Aggregate auf, und identifizieren Sie die Aggregate, die dem von ihm gehosteten VNF-Server entsprechen. In der Regel sind dies die Formate <VNFNAME>-EM-MGMT<X> und <VNFNAME>-CF-MGMT<X>.
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-list
+----+-------------------+-------------------+
| Id | Name | Availability Zone |
+----+-------------------+-------------------+
| 29 | POD1-AUTOIT | mgmt |
| 57 | VNF1-SERVICE1 | - |
| 60 | VNF1-EM-MGMT1 | - |
| 63 | VNF1-CF-MGMT1 | - |
| 66 | VNF2-CF-MGMT2 | - |
| 69 | VNF2-EM-MGMT2 | - |
| 72 | VNF2-SERVICE2 | - |
| 75 | VNF3-CF-MGMT3 | - |
| 78 | VNF3-EM-MGMT3 | - |
| 81 | VNF3-SERVICE3 | - |
+----+-------------------+-------------------+
In unserem Fall gehört der Computing-Server zu VNF2. Die Aggregate, die also übereinstimmen, sind VNF2-CF-MGMT2 und VNF2-EM-MGMT2.
- Entfernen Sie den Computing-Knoten aus der angegebenen Aggregation:
nova aggregate-remove-host
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-remove-host VNF2-CF-MGMT2 pod1-compute-8.localdomain
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-remove-host VNF2-EM-MGMT2 pod1-compute-8.localdomain
- Überprüfen Sie, ob der Computing-Knoten aus den Aggregaten entfernt wurde. Stellen Sie nun sicher, dass der Host nicht unter den Aggregaten aufgeführt ist:
nova aggregate-show
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-show VNF2-CF-MGMT2
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-show VNF2-EM-MGMT2
Löschen von Computing-Knoten
Die in diesem Abschnitt beschriebenen Schritte sind unabhängig von den im Computing-Knoten gehosteten VMs häufig.
Computing-Knoten aus der Dienstliste löschen
- Löschen Sie den Computing-Service aus der Dienstliste:
[stack@director ~]$ source corerc
[stack@director ~]$ openstack compute service list | grep compute-8
| 404 | nova-compute | pod1-compute-8.localdomain | nova | enabled | up | 2018-05-08T18:40:56.000000 |
openstack compute service delete
[stack@director ~]$ openstack compute service delete 404
Neutrale Agenten löschen
- Löschen Sie den alten zugeordneten Neutron-Agent und den offenen Switch-Agent für den Computing-Server:
[stack@director ~]$ openstack network agent list | grep compute-8
| c3ee92ba-aa23-480c-ac81-d3d8d01dcc03 | Open vSwitch agent | pod1-compute-8.localdomain | None | False | UP | neutron-openvswitch-agent |
| ec19cb01-abbb-4773-8397-8739d9b0a349 | NIC Switch agent | pod1-compute-8.localdomain | None | False | UP | neutron-sriov-nic-agent |
openstack network agent delete
[stack@director ~]$ openstack network agent delete c3ee92ba-aa23-480c-ac81-d3d8d01dcc03
[stack@director ~]$ openstack network agent delete ec19cb01-abbb-4773-8397-8739d9b0a349
Aus der Ironischen Datenbank löschen
- Löschen Sie einen Knoten aus der ironischen Datenbank, und überprüfen Sie ihn:
[stack@director ~]$ source stackrc
nova show| grep hypervisor
[stack@director ~]$ nova show pod1-compute-10 | grep hypervisor
| OS-EXT-SRV-ATTR:hypervisor_hostname | 4ab21917-32fa-43a6-9260-02538b5c7a5a
ironic node-delete
[stack@director ~]$ ironic node-delete 4ab21917-32fa-43a6-9260-02538b5c7a5a
[stack@director ~]$ ironic node-list (node delete must not be listed now)
Löschen aus der Overcloud
- Erstellen Sie eine Skriptdatei mit dem Namen delete_node.sh, deren Inhalt wie gezeigt angezeigt wird. Stellen Sie sicher, dass die erwähnten Vorlagen mit den Vorlagen übereinstimmen, die im deploy.sh-Skript für die Stackbereitstellung verwendet wurden:
delete_node.sh
openstack overcloud node delete --templates -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/puppet-pacemaker.yaml -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/network-isolation.yaml -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/storage-environment.yaml -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/neutron-sriov.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/network.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/ceph.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/compute.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/layout.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/layout.yaml --stack
[stack@director ~]$ source stackrc
[stack@director ~]$ /bin/sh delete_node.sh
+ openstack overcloud node delete --templates -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/puppet-pacemaker.yaml -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/network-isolation.yaml -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/storage-environment.yaml -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/neutron-sriov.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/network.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/ceph.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/compute.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/layout.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/layout.yaml --stack pod1 49ac5f22-469e-4b84-badc-031083db0533
Deleting the following nodes from stack pod1:
- 49ac5f22-469e-4b84-badc-031083db0533
Started Mistral Workflow. Execution ID: 4ab4508a-c1d5-4e48-9b95-ad9a5baa20ae
real 0m52.078s
user 0m0.383s
sys 0m0.086s
- Warten Sie, bis der OpenStack-Stack-Vorgang in den VOLLSTÄNDIGEN Zustand wechselt:
[stack@director ~]$ openstack stack list
+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| ID | Stack Name | Stack Status | Creation Time | Updated Time |
+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| 5df68458-095d-43bd-a8c4-033e68ba79a0 | pod1 | UPDATE_COMPLETE | 2018-05-08T21:30:06Z | 2018-05-08T20:42:48Z |
+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+----------------------+----------------------+
Installation des neuen Computing-Knotens
- Die Schritte zur Installation eines neuen UCS C240 M4 Servers sowie die Schritte zur Ersteinrichtung können wie folgt aufgerufen werden:
Cisco UCS C240 M4 Serverinstallations- und Serviceleitfaden
- Legen Sie nach der Installation des Servers die Festplatten in die entsprechenden Steckplätze als alten Server ein
- Melden Sie sich mit der CIMC IP-Adresse beim Server an.
- Führen Sie ein BIOS-Upgrade durch, wenn die Firmware nicht der zuvor verwendeten empfohlenen Version entspricht. Schritte für ein BIOS-Upgrade finden Sie hier:
BIOS-Upgrade-Leitfaden für Rackmount-Server der Cisco UCS C-Serie
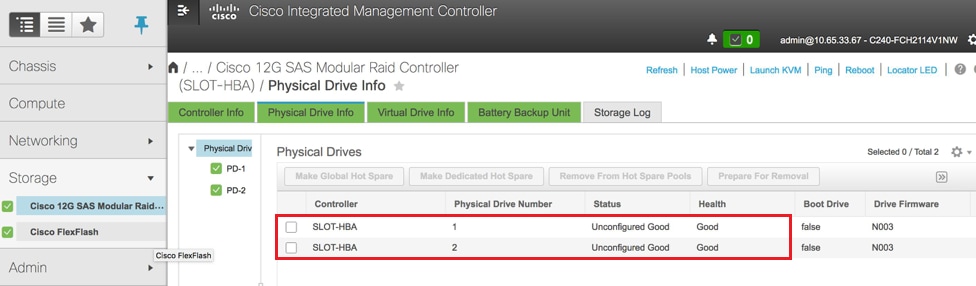
- Überprüfen Sie den Status physischer Laufwerke. Es muss "Unconfigured Good" (Nicht konfiguriert gut) lauten:
Speicher > Cisco 12-G-SAS-RAID-Controller (SLOT-HBA) > Informationen zum physischen Laufwerk
- Erstellen Sie eine virtuelle Festplatte von den physischen Laufwerken mit RAID Level 1:
Storage > Cisco 12G SAS Modular RAID Controller (SLOT-HBA) > Controller-Info > Virtuelles Laufwerk aus nicht verwendeten physischen Laufwerken erstellen
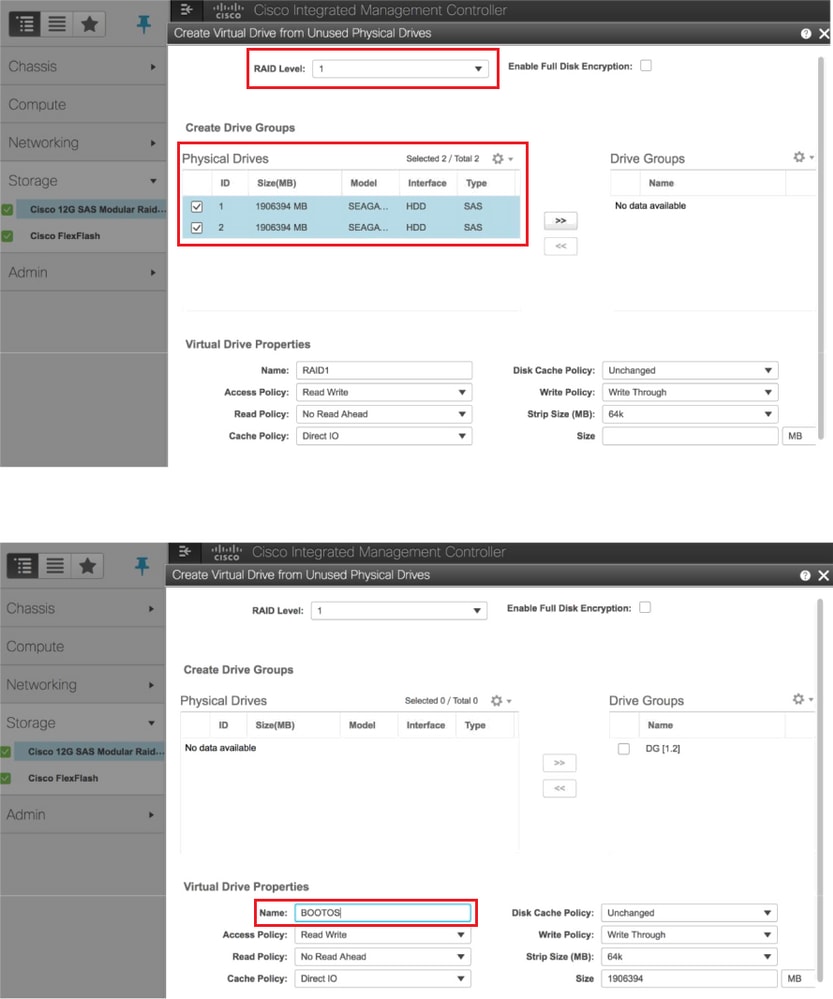
- Wählen Sie VD aus, und konfigurieren Sie "Als Startlaufwerk festlegen":

- IPMI over LAN aktivieren:
Admin > Kommunikationsdienste > Kommunikationsdienste

- Hyperthreading deaktivieren:
Computing > BIOS > BIOS konfigurieren > Erweitert > Prozessorkonfiguration

Hinweis: Das hier abgebildete Image und die in diesem Abschnitt beschriebenen Konfigurationsschritte beziehen sich auf die Firmware-Version 3.0(3e). Wenn Sie an anderen Versionen arbeiten, kann es zu geringfügigen Abweichungen kommen.
Hinzufügen des neuen Computing-Knotens zur Overcloud
Die in diesem Abschnitt beschriebenen Schritte sind unabhängig von der vom Computing-Knoten gehosteten VM identisch.
- Computing-Server mit einem anderen Index hinzufügen
Erstellen Sie eine Datei add_node.json, die nur die Details des neuen Computing-Servers enthält, der hinzugefügt werden soll. Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Indexnummer für den neuen Computing-Server noch nicht verwendet wurde. Erhöhen Sie in der Regel den nächsthöchsten Rechenwert.
Beispiel: Die höchste vorherige Version wurde deshalb für Computing-17 erstellt. Daher wurde Compute-18 für das 2-VNF-System erstellt.
Hinweis: Achten Sie auf das Json-Format.
[stack@director ~]$ cat add_node.json
{
"nodes":[
{
"mac":[
"<MAC_ADDRESS>"
],
"capabilities": "node:compute-18,boot_option:local",
"cpu":"24",
"memory":"256000",
"disk":"3000",
"arch":"x86_64",
"pm_type":"pxe_ipmitool",
"pm_user":"admin",
"pm_password":"<PASSWORD>",
"pm_addr":"192.100.0.5"
}
]
}
- Importieren Sie die json-Datei:
[stack@director ~]$ openstack baremetal import --json add_node.json
Started Mistral Workflow. Execution ID: 78f3b22c-5c11-4d08-a00f-8553b09f497d
Successfully registered node UUID 7eddfa87-6ae6-4308-b1d2-78c98689a56e
Started Mistral Workflow. Execution ID: 33a68c16-c6fd-4f2a-9df9-926545f2127e
Successfully set all nodes to available.
- Führen Sie eine Knotenintrospektion mithilfe der UUID aus, die im vorherigen Schritt angegeben wurde:
[stack@director ~]$ openstack baremetal node manage 7eddfa87-6ae6-4308-b1d2-78c98689a56e
[stack@director ~]$ ironic node-list |grep 7eddfa87
| 7eddfa87-6ae6-4308-b1d2-78c98689a56e | None | None | power off | manageable | False |
[stack@director ~]$ openstack overcloud node introspect 7eddfa87-6ae6-4308-b1d2-78c98689a56e --provide
Started Mistral Workflow. Execution ID: e320298a-6562-42e3-8ba6-5ce6d8524e5c
Waiting for introspection to finish...
Successfully introspected all nodes.
Introspection completed.
Started Mistral Workflow. Execution ID: c4a90d7b-ebf2-4fcb-96bf-e3168aa69dc9
Successfully set all nodes to available.
[stack@director ~]$ ironic node-list |grep available
| 7eddfa87-6ae6-4308-b1d2-78c98689a56e | None | None | power off | available | False |
- Führen Sie das Skript deploy.sh aus, das zuvor für die Bereitstellung des Stacks verwendet wurde, um den neuen Computing-Knoten dem Overcloud-Stack hinzuzufügen:
[stack@director ~]$ ./deploy.sh
++ openstack overcloud deploy --templates -r /home/stack/custom-templates/custom-roles.yaml -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/puppet-pacemaker.yaml -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/network-isolation.yaml -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/storage-environment.yaml -e /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/environments/neutron-sriov.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/network.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/ceph.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/compute.yaml -e /home/stack/custom-templates/layout.yaml --stack ADN-ultram --debug --log-file overcloudDeploy_11_06_17__16_39_26.log --ntp-server 172.24.167.109 --neutron-flat-networks phys_pcie1_0,phys_pcie1_1,phys_pcie4_0,phys_pcie4_1 --neutron-network-vlan-ranges datacentre:1001:1050 --neutron-disable-tunneling --verbose --timeout 180
…
Starting new HTTP connection (1): 192.200.0.1
"POST /v2/action_executions HTTP/1.1" 201 1695
HTTP POST http://192.200.0.1:8989/v2/action_executions 201
Overcloud Endpoint: http://10.1.2.5:5000/v2.0
Overcloud Deployed
clean_up DeployOvercloud:
END return value: 0
real 38m38.971s
user 0m3.605s
sys 0m0.466s
- Warten Sie, bis der Status des OpenStack-Stacks abgeschlossen ist:
[stack@director ~]$ openstack stack list
+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| ID | Stack Name | Stack Status | Creation Time | Updated Time |
+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| 5df68458-095d-43bd-a8c4-033e68ba79a0 | ADN-ultram | UPDATE_COMPLETE | 2017-11-02T21:30:06Z | 2017-11-06T21:40:58Z |
+--------------------------------------+------------+-----------------+----------------------+----------------------+
- Überprüfen Sie, ob sich der neue Rechenknoten im aktiven Zustand befindet:
[stack@director ~]$ source stackrc
[stack@director ~]$ nova list |grep compute-18
| 0f2d88cd-d2b9-4f28-b2ca-13e305ad49ea | pod1-compute-18 | ACTIVE | - | Running | ctlplane=192.200.0.117 |
[stack@director ~]$ source corerc
[stack@director ~]$ openstack hypervisor list |grep compute-18
| 63 | pod1-compute-18.localdomain |
Einstellungen für den Austausch nach dem Server
Nachdem Sie den Server zur Cloud hinzugefügt haben, verwenden Sie den unten stehenden Link, um die Einstellungen anzuwenden, die zuvor auf dem alten Server vorhanden waren:
Stellen Sie die VMs wieder her
Fall 1. Computing-Knoten-Hosts nur SF VM
Hinzufügen zur Nova Aggregate-Liste
- Fügen Sie den Computing-Knoten dem Aggregat-Host hinzu, und überprüfen Sie, ob der Host hinzugefügt wurde:
nova aggregate-add-host
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-add-host VNF2-SERVICE2 pod1-compute-18.localdomain
nova aggregate-show
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-show VNF2-SERVICE2
SF VM-Wiederherstellung vom ESC
- Die SF VM befindet sich in der nova-Liste im Fehlerzustand:
[stack@director ~]$ nova list |grep VNF2-DEPLOYM_s9_0_8bc6cc60-15d6-4ead-8b6a-10e75d0e134d
| 49ac5f22-469e-4b84-badc-031083db0533 | VNF2-DEPLOYM_s9_0_8bc6cc60-15d6-4ead-8b6a-10e75d0e134d | ERROR | - | NOSTATE |
- Stellen Sie die SF VM vom ESC wieder her:
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ sudo /opt/cisco/esc/esc-confd/esc-cli/esc_nc_cli recovery-vm-action DO VNF2-DEPLOYM_s9_0_8bc6cc60-15d6-4ead-8b6a-10e75d0e134d
[sudo] password for admin:
Recovery VM Action
/opt/cisco/esc/confd/bin/netconf-console --port=830 --host=127.0.0.1 --user=admin --privKeyFile=/root/.ssh/confd_id_dsa --privKeyType=dsa --rpc=/tmp/esc_nc_cli.ZpRCGiieuW
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="1">
<ok/>
</rpc-reply>
- Überwachen Sie yangesc.log:
admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ tail -f /var/log/esc/yangesc.log
…
14:59:50,112 07-Nov-2017 WARN Type: VM_RECOVERY_COMPLETE
14:59:50,112 07-Nov-2017 WARN Status: SUCCESS
14:59:50,112 07-Nov-2017 WARN Status Code: 200
14:59:50,112 07-Nov-2017 WARN Status Msg: Recovery: Successfully recovered VM [VNF2-DEPLOYM_s9_0_8bc6cc60-15d6-4ead-8b6a-10e75d0e134d].
- Stellen Sie sicher, dass die SF-Karte als Standby-SF im VNF verfügbar ist.
Fall 2. Computing-Knoten-Hosts CF, ESC, EM und UAS
Hinzufügen zur Nova Aggregate-Liste
Fügen Sie den Rechenknoten den Aggregat-Hosts hinzu, und überprüfen Sie, ob der Host hinzugefügt wurde. In diesem Fall muss der Computing-Knoten sowohl den CF- als auch den EM-Host-Aggregaten hinzugefügt werden.
nova aggregate-add-host
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-add-host VNF2-CF-MGMT2 pod1-compute-18.localdomain
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-add-host VNF2-EM-MGMT2 pod1-compute-18.localdomain
nova aggregate-show
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-show VNF2-CF-MGMT2
[stack@director ~]$ nova aggregate-show VNF2-EM-MGMT2
Recovery von UAS VM
- Überprüfen Sie den Status der UAS VM in der nova-Liste, und löschen Sie sie:
[stack@director ~]$ nova list | grep VNF2-UAS-uas-0
| 307a704c-a17c-4cdc-8e7a-3d6e7e4332fa | VNF2-UAS-uas-0 | ACTIVE | - | Running | VNF2-UAS-uas-orchestration=172.168.11.10; VNF2-UAS-uas-management=172.168.10.3
[stack@tb5-ospd ~]$ nova delete VNF2-UAS-uas-0
Request to delete server VNF2-UAS-uas-0 has been accepted.
- Um die autovnf-uas VM wiederherzustellen, führen Sie das uas-check-Skript aus, um den Status zu überprüfen. Sie muss einen Fehler melden. Führen Sie dann erneut mit —fix-Option aus, um das fehlende UAS VM neu zu erstellen:
[stack@director ~]$ cd /opt/cisco/usp/uas-installer/scripts/
[stack@director scripts]$ ./uas-check.py auto-vnf VNF2-UAS
2017-12-08 12:38:05,446 - INFO: Check of AutoVNF cluster started
2017-12-08 12:38:07,925 - INFO: Instance 'vnf1-UAS-uas-0' status is 'ERROR'
2017-12-08 12:38:07,925 - INFO: Check completed, AutoVNF cluster has recoverable errors
[stack@director scripts]$ ./uas-check.py auto-vnf VNF2-UAS --fix
2017-11-22 14:01:07,215 - INFO: Check of AutoVNF cluster started
2017-11-22 14:01:09,575 - INFO: Instance VNF2-UAS-uas-0' status is 'ERROR'
2017-11-22 14:01:09,575 - INFO: Check completed, AutoVNF cluster has recoverable errors
2017-11-22 14:01:09,778 - INFO: Removing instance VNF2-UAS-uas-0'
2017-11-22 14:01:13,568 - INFO: Removed instance VNF2-UAS-uas-0'
2017-11-22 14:01:13,568 - INFO: Creating instance VNF2-UAS-uas-0' and attaching volume ‘VNF2-UAS-uas-vol-0'
2017-11-22 14:01:49,525 - INFO: Created instance ‘VNF2-UAS-uas-0'
- Melden Sie sich bei autovnf-uas an. Warten Sie ein paar Minuten, und UAS muss wieder in den guten Zustand zurückkehren:
VNF2-autovnf-uas-0#show uas
uas version 1.0.1-1
uas state ha-active
uas ha-vip 172.17.181.101
INSTANCE IP STATE ROLE
-----------------------------------
172.17.180.6 alive CONFD-SLAVE
172.17.180.7 alive CONFD-MASTER
172.17.180.9 alive NA
Hinweis: Wenn uas-check.py —fix fehlschlägt, müssen Sie diese Datei möglicherweise kopieren und erneut ausführen.
[stack@director ~]$ mkdir –p /opt/cisco/usp/apps/auto-it/common/uas-deploy/
[stack@director ~]$ cp /opt/cisco/usp/uas-installer/common/uas-deploy/userdata-uas.txt /opt/cisco/usp/apps/auto-it/common/uas-deploy/
Wiederherstellung des ESC VM
- Überprüfen Sie den Status des ESC VM in der Nova-Liste, und löschen Sie ihn:
stack@director scripts]$ nova list |grep ESC-1
| c566efbf-1274-4588-a2d8-0682e17b0d41 | VNF2-ESC-ESC-1 | ACTIVE | - | Running | VNF2-UAS-uas-orchestration=172.168.11.14; VNF2-UAS-uas-management=172.168.10.4 |
[stack@director scripts]$ nova delete VNF2-ESC-ESC-1
Request to delete server VNF2-ESC-ESC-1 has been accepted.
- Suchen Sie in AutoVNF-UAS die ESC-Bereitstellungstransaktion, und suchen Sie im Protokoll für die Transaktion die Befehlszeile boot_vm.py zum Erstellen der ESC-Instanz:
ubuntu@VNF2-uas-uas-0:~$ sudo -i
root@VNF2-uas-uas-0:~# confd_cli -u admin -C
Welcome to the ConfD CLI
admin connected from 127.0.0.1 using console on VNF2-uas-uas-0
VNF2-uas-uas-0#show transaction
TX ID TX TYPE DEPLOYMENT ID TIMESTAMP STATUS
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
35eefc4a-d4a9-11e7-bb72-fa163ef8df2b vnf-deployment VNF2-DEPLOYMENT 2017-11-29T02:01:27.750692-00:00 deployment-success
73d9c540-d4a8-11e7-bb72-fa163ef8df2b vnfm-deployment VNF2-ESC 2017-11-29T01:56:02.133663-00:00 deployment-success
VNF2-uas-uas-0#show logs 73d9c540-d4a8-11e7-bb72-fa163ef8df2b | display xml
<config xmlns="http://tail-f.com/ns/config/1.0">
<logs xmlns="http://www.cisco.com/usp/nfv/usp-autovnf-oper">
<tx-id>73d9c540-d4a8-11e7-bb72-fa163ef8df2b</tx-id>
<log>2017-11-29 01:56:02,142 - VNFM Deployment RPC triggered for deployment: VNF2-ESC, deactivate: 0
2017-11-29 01:56:02,179 - Notify deployment
..
2017-11-29 01:57:30,385 - Creating VNFM 'VNF2-ESC-ESC-1' with [python //opt/cisco/vnf-staging/bootvm.py VNF2-ESC-ESC-1 --flavor VNF2-ESC-ESC-flavor --image 3fe6b197-961b-4651-af22-dfd910436689 --net VNF2-UAS-uas-management --gateway_ip 172.168.10.1 --net VNF2-UAS-uas-orchestration --os_auth_url http://10.1.2.5:5000/v2.0 --os_tenant_name core --os_username ****** --os_password ****** --bs_os_auth_url http://10.1.2.5:5000/v2.0 --bs_os_tenant_name core --bs_os_username ****** --bs_os_password ****** --esc_ui_startup false --esc_params_file /tmp/esc_params.cfg --encrypt_key ****** --user_pass ****** --user_confd_pass ****** --kad_vif eth0 --kad_vip 172.168.10.7 --ipaddr 172.168.10.6 dhcp --ha_node_list 172.168.10.3 172.168.10.6 --file root:0755:/opt/cisco/esc/esc-scripts/esc_volume_em_staging.sh:/opt/cisco/usp/uas/autovnf/vnfms/esc-scripts/esc_volume_em_staging.sh --file root:0755:/opt/cisco/esc/esc-scripts/esc_vpc_chassis_id.py:/opt/cisco/usp/uas/autovnf/vnfms/esc-scripts/esc_vpc_chassis_id.py --file root:0755:/opt/cisco/esc/esc-scripts/esc-vpc-di-internal-keys.sh:/opt/cisco/usp/uas/autovnf/vnfms/esc-scripts/esc-vpc-di-internal-keys.sh
Speichern Sie die Zeile boot_vm.py in einer Shell-Skriptdatei (esc.sh), und aktualisieren Sie alle Zeilen mit dem Benutzernamen ****** und dem Kennwort **** mit den richtigen Informationen (in der Regel Kern/<PASSWORD>). Sie müssen auch die -encrypt_key-Option entfernen. Für user_pass und user_cond_pass müssen Sie das Format - Benutzername: Kennwort (Beispiel - admin:<PASSWORD>).
- Suchen Sie die URL zu bootvm.py aus running-config, und rufen Sie die Datei "bootvm.py" auf die virtuelle Plattform autovnf-uas. In diesem Fall ist 10.1.2.3 die IP-Adresse der Auto-IT-VM:
root@VNF2-uas-uas-0:~# confd_cli -u admin -C
Welcome to the ConfD CLI
admin connected from 127.0.0.1 using console on VNF2-uas-uas-0
VNF2-uas-uas-0#show running-config autovnf-vnfm:vnfm
…
configs bootvm
value http:// 10.1.2.3:80/bundles/5.1.7-2007/vnfm-bundle/bootvm-2_3_2_155.py
!
root@VNF2-uas-uas-0:~# wget http://10.1.2.3:80/bundles/5.1.7-2007/vnfm-bundle/bootvm-2_3_2_155.py
--2017-12-01 20:25:52-- http://10.1.2.3 /bundles/5.1.7-2007/vnfm-bundle/bootvm-2_3_2_155.py
Connecting to 10.1.2.3:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 127771 (125K) [text/x-python]
Saving to: ‘bootvm-2_3_2_155.py’
100%[=====================================================================================>] 127,771 --.-K/s in 0.001s
2017-12-01 20:25:52 (173 MB/s) - ‘bootvm-2_3_2_155.py’ saved [127771/127771]
- Erstellen Sie eine /tmp/esc_params.cfg-Datei:
root@VNF2-uas-uas-0:~# echo "openstack.endpoint=publicURL" > /tmp/esc_params.cfg
- Führen Sie ein Shell-Skript aus, um ESC vom UAS-Knoten bereitzustellen:
root@VNF2-uas-uas-0:~# /bin/sh esc.sh
+ python ./bootvm.py VNF2-ESC-ESC-1 --flavor VNF2-ESC-ESC-flavor --image 3fe6b197-961b-4651-af22-dfd910436689
--net VNF2-UAS-uas-management --gateway_ip 172.168.10.1 --net VNF2-UAS-uas-orchestration --os_auth_url
http://10.1.2.5:5000/v2.0 --os_tenant_name core --os_username core --os_password <PASSWORD> --bs_os_auth_url
http://10.1.2.5:5000/v2.0 --bs_os_tenant_name core --bs_os_username core --bs_os_password <PASSWORD>
--esc_ui_startup false --esc_params_file /tmp/esc_params.cfg --user_pass admin:<PASSWORD> --user_confd_pass
admin:<PASSWORD> --kad_vif eth0 --kad_vip 172.168.10.7 --ipaddr 172.168.10.6 dhcp --ha_node_list 172.168.10.3
172.168.10.6 --file root:0755:/opt/cisco/esc/esc-scripts/esc_volume_em_staging.sh:/opt/cisco/usp/uas/autovnf/vnfms/esc-scripts/esc_volume_em_staging.sh
--file root:0755:/opt/cisco/esc/esc-scripts/esc_vpc_chassis_id.py:/opt/cisco/usp/uas/autovnf/vnfms/esc-scripts/esc_vpc_chassis_id.py
--file root:0755:/opt/cisco/esc/esc-scripts/esc-vpc-di-internal-keys.sh:/opt/cisco/usp/uas/autovnf/vnfms/esc-scripts/esc-vpc-di-internal-keys.sh
- Melden Sie sich beim neuen ESC an, und überprüfen Sie den Backup-Zustand:
ubuntu@VNF2-uas-uas-0:~$ ssh admin@172.168.11.14
…
####################################################################
# ESC on VNF2-esc-esc-1.novalocal is in BACKUP state.
####################################################################
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-1 ~]$ escadm status
0 ESC status=0 ESC Backup Healthy
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-1 ~]$ health.sh
============== ESC HA (BACKUP) ===================================================
ESC HEALTH PASSED
FC- und EM-VMs vom ESC wiederherstellen
- Überprüfen Sie den Status der CF- und EM-VMs aus der Nova-Liste. Sie müssen sich im FEHLER-Status befinden.
[stack@director ~]$ source corerc
[stack@director ~]$ nova list --field name,host,status |grep -i err
| 507d67c2-1d00-4321-b9d1-da879af524f8 | VNF2-DEPLOYM_XXXX_0_c8d98f0f-d874-45d0-af75-88a2d6fa82ea | None | ERROR|
| f9c0763a-4a4f-4bbd-af51-bc7545774be2 | VNF2-DEPLOYM_c1_0_df4be88d-b4bf-4456-945a-3812653ee229 |None | ERROR
- Melden Sie sich bei ESC Master an, führen Sie "restore vm-action" für jedes betroffene EM und CF VM aus. Sei geduldig! Der WSA würde die Wiederherstellungsaktion planen und dies möglicherweise nicht für einige Minuten. Überwachen Sie yangesc.log:
sudo /opt/cisco/esc/esc-confd/esc-cli/esc_nc_cli recovery-vm-action DO
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ sudo /opt/cisco/esc/esc-confd/esc-cli/esc_nc_cli recovery-vm-action DO VNF2-DEPLOYMENT-_VNF2-D_0_a6843886-77b4-4f38-b941-74eb527113a8
[sudo] password for admin:
Recovery VM Action
/opt/cisco/esc/confd/bin/netconf-console --port=830 --host=127.0.0.1 --user=admin --privKeyFile=/root/.ssh/confd_id_dsa --privKeyType=dsa --rpc=/tmp/esc_nc_cli.ZpRCGiieuW
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="1">
<ok/>
</rpc-reply>
[admin@VNF2-esc-esc-0 ~]$ tail -f /var/log/esc/yangesc.log
…
14:59:50,112 07-Nov-2017 WARN Type: VM_RECOVERY_COMPLETE
14:59:50,112 07-Nov-2017 WARN Status: SUCCESS
14:59:50,112 07-Nov-2017 WARN Status Code: 200
14:59:50,112 07-Nov-2017 WARN Status Msg: Recovery: Successfully recovered VM [VNF2-DEPLOYMENT-_VNF2-D_0_a6843886-77b4-4f38-b941-74eb527113a8]
- Melden Sie sich beim neuen EM an, und prüfen Sie, ob der EM-Status aktiv ist:
ubuntu@VNF2vnfddeploymentem-1:~$ /opt/cisco/ncs/current/bin/ncs_cli -u admin -C
admin connected from 172.17.180.6 using ssh on VNF2vnfddeploymentem-1
admin@scm# show ems
EM VNFM
ID SLA SCM PROXY
---------------------
2 up up up
3 up up up
- Melden Sie sich beim StarOS VNF an, und überprüfen Sie, ob sich die CF-Karte im Standby-Modus befindet.
Handhabung von ESC-Wiederherstellungsfehlern
Falls ESC aufgrund eines unerwarteten Zustands nicht starten kann, empfiehlt Cisco, einen ESC-Switchover durch einen Neustart des Master-ESC durchzuführen. Der ESC-Switchover würde etwa eine Minute dauern. Führen Sie das Skript "health.sh" auf dem neuen Master-ESC aus, um zu überprüfen, ob der Status aktiv ist. Master-ESC zum Starten der VM und zum Beheben des VM-Status. Diese Wiederherstellungsaufgabe würde bis zu 5 Minuten in Anspruch nehmen.
Sie können /var/log/esc/yangesc.log und /var/log/esc/escmanager.log überwachen. Wenn Sie NICHT sehen, dass VM nach 5-7 Minuten wiederhergestellt wird, muss der Benutzer die manuelle Wiederherstellung der betroffenen VM(s) durchführen.
Aktualisierung der Konfiguration automatisch bereitstellen
Bearbeiten Sie in AutoDeploy VM die Datei autodeploy.cfg, und ersetzen Sie den alten Computing-Server durch den neuen. Dann laden Sie Ersetzen in cond_cli. Dieser Schritt ist für eine spätere erfolgreiche Deaktivierung der Bereitstellung erforderlich.
root@auto-deploy-iso-2007-uas-0:/home/ubuntu# confd_cli -u admin -C
Welcome to the ConfD CLI
admin connected from 127.0.0.1 using console on auto-deploy-iso-2007-uas-0
auto-deploy-iso-2007-uas-0#config
Entering configuration mode terminal
auto-deploy-iso-2007-uas-0(config)#load replace autodeploy.cfg
Loading. 14.63 KiB parsed in 0.42 sec (34.16 KiB/sec)
auto-deploy-iso-2007-uas-0(config)#commit
Commit complete.
auto-deploy-iso-2007-uas-0(config)#end
Starten Sie nach der Konfigurationsänderung die standardkonformen und automatischen Bereitstellungsdienste neu.
root@auto-deploy-iso-2007-uas-0:~# service uas-confd restart
uas-confd stop/waiting
uas-confd start/running, process 14078
root@auto-deploy-iso-2007-uas-0:~# service uas-confd status
uas-confd start/running, process 14078
root@auto-deploy-iso-2007-uas-0:~# service autodeploy restart
autodeploy stop/waiting
autodeploy start/running, process 14017
root@auto-deploy-iso-2007-uas-0:~# service autodeploy status
autodeploy start/running, process 14017
Aktivieren von Syslogs
Um die Syslogs für den UCS-Server, OpenStack-Komponenten und die wiederhergestellten VMs zu aktivieren, folgen Sie den Abschnitten
"Re-Enable syslog for UCS and OpenStack Components" und "Enable Syslog for the VNFs" finden Sie unter dem folgenden Link:
Zugehörige Informationen
- https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_openstack_platform/10/html/director_installation_and_usage/sect-Scaling_the_Overcloud - sect-Removing_Compute_Nodes
- https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_openstack_platform/10/html/director_installation_and_usage/sect-Scaling_the_Overcloud#sect-Adding_Compute_or_Ceph_Storage_Nodes
- Technischer Support und Dokumentation - Cisco Systems
Revisionsverlauf
| Überarbeitung | Veröffentlichungsdatum | Kommentare |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01-Jun-2018 |
Erstveröffentlichung |
Beiträge von Cisco Ingenieuren
- Partheeban RajagopalCisco Advanced Services
- Padmaraj RamanoudjamCisco Advanced Services
Cisco kontaktieren
- Eine Supportanfrage öffnen

- (Erfordert einen Cisco Servicevertrag)
 Feedback
Feedback