Cisco HyperFlex Best Practices White Paper
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Best practices are a common way of helping customers gain the most effective use of a Cisco HyperFlex™ system. This document offers guidance on how to have an optimal HyperFlex deployment and can be applied to all HyperFlex clusters. All general best practices are for all HyperFlex clusters and include HyperFlex with VMware ESXi and Hyper-V Hypervisors, HyperFlex Edge, and a HyperFlex stretched cluster. For example, if you are looking for, HyperFlex Edge best practices, first read the common best practices and then jump to the section with the HyperFlex cluster you are looking for. If you are looking for settings outside of this best practices document, read the HyperFlex documentation on https://www.cisco.com.
The audience for this document includes HyperFlex administrators who already understand HyperFlex and have read the HyperFlex guides.
| Document summary |
Prepared for |
Prepared by |
| HyperFlex Best Practices for HX 4.0 |
Cisco Public |
Joost van der Made |
This document contains confidential material that is proprietary to Cisco. The materials, ideas, and concepts contained herein are to be used exclusively to assist in the configuration of Cisco software solutions.
All information in this document is provided in confidence and shall not be published or disclosed, wholly or in part, to any other party without Cisco’s written permission.
On the Cisco® website you can find documentation about Cisco HyperFlex (HX). Included in those documents are procedures to guide you in a correct HyperFlex configuration.
It is a best practice to read the documentation that applies to your procedure before you start with a HyperFlex cluster.
You can access the Cisco HyperFlex Guides online, which include:
● Configuration guides
● Admin guides
● End-user guides
● Install and upgrade guides
● Troubleshooting guides
● Technotes
Included in the HyperFlex Systems Documentation Roadmap are links to ordering guides, compatibility guides, hardware guides, network and external storage management guides, and more.
The Cisco HyperFlex Data Platform (HXDP) is evolving software with new releases coming every period. HyperFlex has long-lived and feature releases (Figure 1). Both types of releases have a specific cadence.
Long-lived releases, which are maintenance releases, include patch releases with bug fixes and a lifecycle of about 30 months. A long-lived release is targeted for stability.
Feature releases have a shorter lifecycle, of about nine months. These releases will be delivered when some significant changes are made in the software, such as new features. Patch releases can also be included in feature releases.
In the Cisco HyperFlex Software Release Model and Release Support Timeline document you will find updated information about the release models.
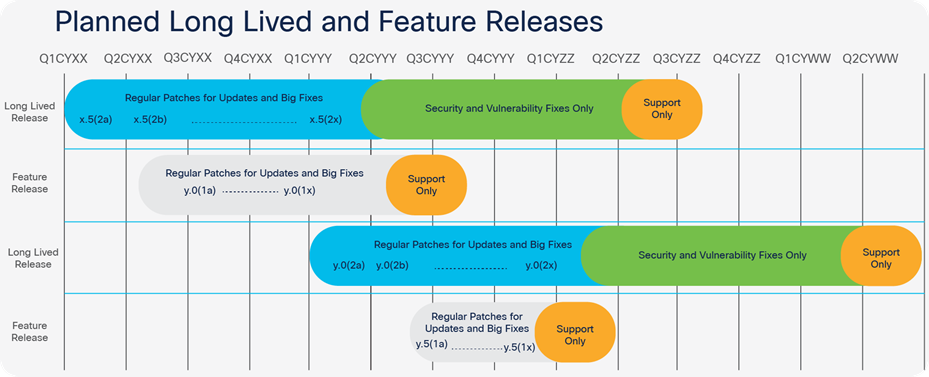
HXDP release support timeline
Before installing or upgrading a HyperFlex cluster, you should decide which release of the HyperFlex Data Platform (HXDP) is suitable for the cluster. Our Recommended Release document includes information about recommended HXDP versions, depending upon on the hypervisor, hardware, and features you use. The document also includes recommended releases of VMware ESXi and Cisco UCS® Manager and Cisco UCS server firmware to use.
The best practice is to upgrade Cisco UCS Manager and corresponding server firmware to the recommended release mentioned in the document.
When the recommended release is changed, it does not mean you will have to upgrade immediately. It is okay to stay on a long-lived release if you do not need the new features and/or need to add new hardware to the HyperFlex cluster.
Urgent notifications of issues will be communicated via Cisco Field Notices.
Cisco’s My Notifications allows a user to subscribe and receive important Cisco product and technology information. More information about this service can be found at My Notifications. To automatically receive emails with HX release notes updates, new software availability, recommended releases, known bugs, and field notices sign up at the Cisco Notifications portal.
You can sign up for every Cisco product to receive notifications. It is good to create two subscriptions: for software updates and known bugs combined, and for end-of-sale (EoS)/support announcements, field notices, and Cisco security advisories.
Figure 2 is a screenshot of how it looks if you want to receive daily emails of EoS/support announcements, field notices, and Cisco security advisories from the HyperFlex HX-Series (hardware) and HyperFlex HX Data Platform (software).

Set up notifications for Cisco HX products
The notification emails can have different content, depending on the chosen subscription. Figure 3 is an example of an email message that can be sent when there are updates regarding a bug.

My Notifications example email
Preinstallation considerations
HyperFlex can be installed via the HyperFlex installer or via Cisco Intersight™. When you install HX via the installer and claim it in Intersight, some features, such as upgrades, cannot be done in Intersight. However, when you install HX via Intersight, the upgrades feature is available.
When getting started with Intersight, check out the overview of the Cisco Intersight SaaS systems Management Platform and as well as available Intersight technical help.
In the preinstallation checklist for Cisco HX Data Platform make a note all information needed for a fresh installation and use this document with your installation documentation.
When you are rebuilding an existing HyperFlex cluster for a proof of concept or testing, use the Cleanup guide for a fresh installation.
Before installing HyperFlex on the nodes, design your logical and physical network topology.
● The network connection between the fabric interconnect and the northbound switch should be enough to support all network traffic. If redundant network connections do not have enough bandwidth, design your network to include more active connections to the switch.
● By configuring the Ethernet ports between the switch and fabric interconnect as a channel-group, even with only one connection, no downtime is needed to expand the number of links from the fabric interconnect to the switch.
● To get the most bandwidth and performance of the HyperFlex cluster, the fabric interconnect should be connected to an active/active redundant solution, like Cisco Nexus® switches with a virtual port channel (vPC) or a Cisco ACI® network.
● The connections from the fabric interconnect and the switch should be configured for port trunking. Even if only one VLAN should go over this connection, port trunking is still desired.
● The local Network Time Protocol (NTP) server and Dynamic Name Server (DNS) should be outside of the HyperFlex cluster and not be nested on the HyperFlex cluster. Nested solutions can cause challenges, which are easily preventable when those services are outside on a management network.
● VMware vCenter should be outside the cluster, preferably on a management network segment. Although a nested vCenter solution is supported, this is not a best practice solution because of the challenges you can face during a reboot of the system.
● Do not use VLAN 1 for the HyperFlex Management VLAN. The VMware network VLAN can be VLAN 1. Note: This is NOT a recommended solution for networking with Cisco UCS in general.
● For security reasons, keep the HyperFlex Data VLAN isolated in layer 2. This means this VLAN is a non-routable VLAN. For redundancy of the fabric interconnects, make sure the network switches connected to the fabric interconnects know this VLAN. The fabric interconnects is only capable of doing local switching. If traffic needs to go from the A side to the B side, the network switches must know this VLAN.
● For every HyperFlex cluster on your network, the HyperFlex storage VLAN must be unique, and thus different compared to other HyperFlex storage VLANs.
● To reduce typing mistakes, deploy a HyperFlex cluster with IP addresses instead of Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDN). This will also reduce the DNS dependency. Configuring a DNS server with the DNS names of the HyperFlex cluster is a method to remember the HX names easily for day-2 operations.
● During installation there is an option to have jumbo frames enabled. If you enable this feature and there is an error during installation, fix this error. The network should have end-to-end jumbo frames. If the network is not configured with jumbo frames, do not select this feature. When the do-not-fragment bit (DF) is enabled on a switch and you are trying to have jumbo frames going over the switch, the packets will be dropped. When no jumbo frames are selected, the default Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size of 1500 bytes will be chosen.
● Jumbo frames (MTU of 9000 bytes) are recommended by Cisco. They create less overhead and this will improve the performance.
Data is very important, and it should be highly available.
● Always use a replication factor (RF) of 3 for the production environment to achieve the highest level of fault tolerance. The RF is chosen during installation and you cannot change the RF afterwards. If you want to change the RF after installation, you will have to wipe and redeploy the whole HyperFlex cluster.
● Make sure there is enough capacity for better resiliency and performance. Do not size a HyperFlex cluster based only on storage. Consider the workload, CPU, and memory as well. The Hyperflex Sizer will apply the best practices for the sizing.
Every workload has unique characteristics. Make sure you understand the needs of the workload to get the best performance out of it.
● Always use the HyperFlex Sizer and HyperFlex Profiler for a good design and sizing for the current workload. The HyperFlex Sizer tool is developed and maintained to size any workload on the current version of HyperFlex with the currently available hardware.
● Use one or two extra nodes for enough performance capacity. If a failure or outage occurs, the current workload can still run with the same performance as without the outage.
● Do not size the HyperFlex cluster with the average of the current workload. Make sure it can handle the peaks of the applications. Think about the end of the month when there is more pressure on the systems to create reporting, etc.
● Applications today are time-sensitive so you will need to pay attention to latency in addition to Input/Output Operations Per Second (IOPS) and throughput.
A HyperFlex cluster can vary in size and is a scalable solution.
● Even though it is possible to fit all the workloads on one big HyperFlex cluster, smaller clusters have a better fault tolerance and the upgrade windows of those clusters are smaller. A HyperFlex cluster per workload is preferable.
● If you have different CPUs, VMware requires that Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC) mode be configured. The performance of the cluster will be degraded.
● When a HyperFlex cluster has more than eight nodes, logical availability zones (LAZ) are automatically created to make the fault domain smaller.
● Multiple HyperFlex clusters can be configured under the same fabric interconnect. For each HyperFlex installation make sure the name of the organization unit is different. This will create different organizations in Cisco UCS Manager.
During the HyperFlex installation, there are some checkboxes that you can select.
● To make sure there are no old partitions, select “Clear Partitions” to clean the disks.
● Only select the options VDI or VSI when installing HyperFlex on a hybrid system. If you are running mixed VDI and VSI workloads, do not select this option. Only select this optimization when running VDI desktops, and only on hybrid HX models. This option is only shown during the “I know what I am doing” installation workflow.
● Always run the hx_post_install script after a successful installation. It can be used to set up vMotion, to add VM VLANs, to create new certificates, to disable SSH ESXi warnings, and to add license keys to the HyperFlex cluster. This script is located on the HyperFlex Installer and on the HX Controller. The easiest way to access the controller is to SSH to the cluster IP address (CIP) and log in with admin account credentials.
HyperFlex uses Cisco Smart Licensing. Learn more about Smart Licensing. Before activating the licenses on the HyperFlex cluster, there is a 90-day evaluation license on the cluster.
A Smart Licensing account can contain multiple different HyperFlex licenses (Figure 4). If a created token is used at the HyperFlex cluster, this cluster will look for the licenses that it needs at that moment.
● Make sure the HyperFlex licenses are compliant. The best practice is to have all features and functions created at the HyperFlex cluster before registering the cluster. Of course, this must be done before the 90-day evaluation period of the HyperFlex cluster is completed.
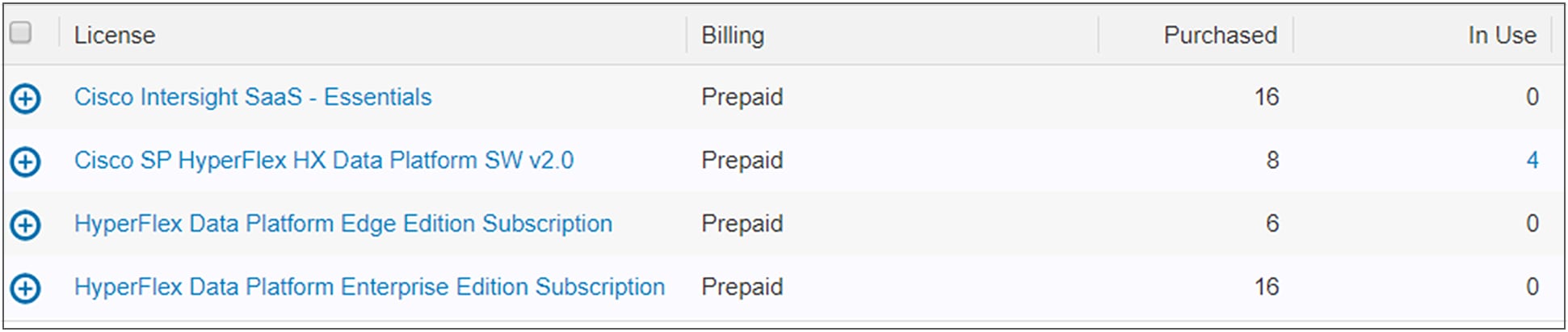
Available HyperFlex and Intersight licenses housed in the Smart Account
After installation some features can still be configured.
● When auto-support is enabled, the cluster will periodically send information about the environment for proactive support and product improvements. To improve future HXDP releases, enable this feature in HyperFlex. The communication will be done over a https connection.
● Receiving notifications gives insight in the HyperFlex cluster. To receive email notifications of the HyperFlex cluster, enable this feature via HyperFlex Connect. The subject should include a good description and the email body will include more information about the cluster health. You can use this email to trigger third-party monitoring tools and have the right action.
● Before putting the HyperFlex cluster in production, failover testing of the HX cluster and hardware should be completed. Also test the application to confirm the application can survive the failovers. It is good to test all kinds of failure scenarios to see if there are any weaknesses in the application. Some applications cannot handle vMotion well.
● Try to use as few datastores as possible. In most cases, one datastore on a regular cluster should be enough. Multiple datastores on a cluster don’t improve the performance. With a few datastores, there is not much management overhead. The deduplication opportunities for clones are better and the boot-up time is faster.
● Internal performance testing with VDI workloads has shown the best performance obtained with a datastore block size set to 4k. All other workloads should choose an 8k block size for VM datastores. This is the default value when creating a new datastore.
When using high-performance applications, the default Queue Depth (QD) of 1024 per datastore can be a bottleneck. This value cannot be changed; the solution for this application is to have multiple datastores for the application.
● HyperFlex is secure in many ways. Follow the HX Data Platform Security Hardening Guide and run the automated stig script for the best security posture.
● ESXi security patches may be applied at any time if they are in the same release family. This is described in the ESXi and HXDP Compatibility Guidelines.
Cisco UCS Manager and VMware vCenter
When HyperFlex is connected to fabric interconnects it will configure Cisco UCS Manager during installation. VMware vCenter is needed when vSphere is the hypervisor.
● Do not use HX host profiles or change any settings in UCS Manager or ESXi. Manually adjusting the profiles can result in a non-optimal functioning cluster.
● Do not change network interface card (NIC) ordering in vCenter. If this happens, it is possible the HyperFlex cluster will not function anymore.
● Use the VMware Paravirtual SCSI (PVSCSI) adapter when application drives need a significantly high amount of I/O throughput. Using this adapter for the VMs will result in greater throughput and lower CPU utilization. It can be used for the data disk and the boot disk. To apply this adapter to the VM, the SCSI controller should be set to VMware Paravirtual.
● To separate multiple clusters on the same fabric interconnect there must be unique VLANs and MAC pool addresses.
● Future growth considerations need to be considered. Via Intersight you can see the capacity runway of the HyperFlex cluster.
● It is good to run a health check from time to time to triage issues or identify potential issues. You can run a HyperFlex-Hypercheck GitHub script.
● In HXDP 4.0.2a there is a button called Test Upgrade Eligibility to verify your desired upgrade and test the system.
HyperFlex is very scalable. When expanding, know the possibilities and limitations of HyperFlex.
● Think about the future expansion and how this can be accomplished. HyperFlex clusters can be expanded by adding drives, HyperFlex nodes, or compute-only nodes. This depends on the HyperFlex configuration. These Release Notes offer possibilities of each HyperFlex configuration.
● When expanding the HyperFlex cluster with nodes or compute-only nodes, make sure the new nodes are closely matched to the HyperFlex capability. The same storage is mandatory. The best practices for CPU and memory are to have the same configuration as the HyperFlex nodes in the current cluster.
● There are several different ways to expand a cluster. If you want only extra storage, you can add drives to the existing HyperFlex nodes. Make sure the configuration won’t exceed the HyperFlex maximum scale limitations of the cluster. For limitations read the release notes. Pay attention to the HyperFlex drive compatibility when expanding the cluster.
● When adding drives to the nodes, put drives in the nodes at a reasonable pace without stopping. Use the order of putting one drive per node across all nodes until all drives are in the nodes.
● Example: Drive 1 in Node 1, Drive 2 in Node 2, Drive 3 in Node 3, Drive 4 in Node 1, Drive 5 in Node 2, Drive 6 in Node 3, etc. The newly added storage is usable immediately in the HyperFlex cluster. In Cisco UCS Manager, the new drives won’t be shown. To see the new drives in UCS Manager a re-acknowledgement is needed, which is disruptive.
● If you are extending the cluster with HyperFlex nodes only, pay attention for the HyperFlex drive compatibility and try to have the same amount of memory and the same CPU in the new HyperFlex nodes. When the HyperFlex cluster contains different types of CPU, VMware Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC) must be configured. There is a possibility the cluster will not perform at a maximum of the capacity. Enabling EVC is not a best practice.
It is a best practice to protect all production workloads with a backup solution. The use of a backup application is recommended to enable the ability to retain multiple recovery points for a VM based on business requirements. For additional information, see the Managing Virtual Machine Disaster Recovery section in the Cisco HyperFlex Data Platform Administration Guide.
A backup application should be used to protect VM data. Backup applications provide several critical benefits, including but not limited to:
● The ability to retain backup data on multiple media types
● The ability to retain multiple copies of important backup data
● The ability to protect application data and perform log management functions
HX Data Platform native snapshots can be configured to save versions of VMs registered to vCenter. If a VM is deleted from a disk, any native snapshots of the VM are also deleted and cannot be used to recover the VM. The use of a backup application is recommended to enable the ability to recover VMs that have been deleted from a disk. Refer to the Managing Native Snapshots chapter of the Cisco HyperFlex Data Platform Administration Guide for information about HX Data Platform native snapshots.
The HX Data Platform replication feature can be configured to replicate a local VM to a paired remote HyperFlex cluster. The replication feature retains the most recently replicated VM snapshot of VMs protected with the solution.
The HX Data Platform for Hyper-V does not provide native data protection or a disaster recovery capability. The use of a backup application is recommended to provide the required level of protection to enable recovery in the event of data loss or disaster based on business requirements.
A HyperFlex upgrade can be done in a number of different ways:
● Before upgrading, consult the Release Selection Guidelines and review the release notes for the desired target.
● Verify that the VMs’ backups are current. In case of a failure, a restore can be used to go to the previous state of the VMs.
● To keep the maintenance window small, an offline upgrade is advisable. Rolling online upgrades on large clusters will consume a lot of time.
● If DRS is not enabled in vCenter, you will have to manually vacate nodes.
● Understand the limitations on upgrading the environment non-disruptively.
● Make sure the application running on the HyperFlex cluster supports vMotion/DRS or is using an application level of high availability.
● HX takes care of everything except the application. However, remember that it is a rolling upgrade and plan for enough performance capacity and time to accomplish the upgrade.
● Run the HyperFlex-Hypercheck GitHub script created by the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) and triage issues before upgrades.
● When the cluster is running HXDP 4.0.2a or higher, there is a Test Upgrade Eligible button. It will verify if the software components are the correct ones. It is not mandatory to test before the upgrade via HX Connect. The tests are part of the upgrade process.
● Do not use VMware Upgrade Manager (VUM) of VMware Life Cycle Manager (vLCM) for upgrading the vSphere version and always use HyperFlex-customized ESXi upgrade bundles.
Remove ESXi Agent Manager for HyperFlex 4.0 and higher
With a fresh installation of HXDP 4.0.2+ the VMware ESXi Agent Manager (EAM) is no longer needed and will not be configured during the installation. When the HyperFlex cluster is upgraded from a previous HXDP version to a 4.0.2+ version, the EAM is still configured. It is good to remove the EAM Service in VMware. There are several ways to accomplish this without disrupting the HyperFlex cluster. Contact your local Cisco systems engineer for the procedure.
● Without VMware EAM there are no dependencies on EAM Service.
● On the compute-only nodes, no controller VM is needed anymore.
● Any known EAM issues do not impact HyperFlex clusters.
HyperFlex can be installed on different hypervisors. Microsoft Hyper-V is one of them.
For installation and deployment, all the general best practices apply to HyperFlex Hyper-V clusters. They can be found in HyperFlex documentation section on page 3 in this document.
● Each HX node dynamically maps the SMB namespace to the storage controller VM that resides locally on the node. Do not create a DNS entry for the SMB namespace. Deploy the HXDP Installer on the cluster management network. The installation is latency sensitive and this solution is the safest way to install HyperFlex Hyper-V.
● Verify that the installation ISO is with Windows UBR 1884 or above for Windows Server 2016 and UBR 107 or above for Windows Server 2019. The installer will not work with an earlier Windows ISO.
● Having the HX installer automatically configure the AD constraint delegation limits mistakes.
● Configure the Primary Domain Controller (PDC) of the Windows Active directory to sync with an external NTP source as described in Windows Time service tools and settings.
● To avoid a cyclic dependency, do not put the Windows AD Domain Controller on HX.
● Read the best practices regarding NTP, DNS services, and Windows updates from Microsoft Active Directory: Design Considerations and Best Practices.
● The installation and deployment of a HyperFlex Hyper-V cluster is Windows-specific. This setup uses different ports, described in the HX Data Platform Security Hardening Guide. Ports are outlined as follows:
◦ SMB over IP (Microsoft-DS): port 445 TCP, UDP
◦ Kerberos: port 88 TCP, UDP
◦ LDAP: port 389 UDP
◦ DNS: port 53 TCP, UDP
● Always run the Microsoft Cluster Configuration Validation Wizard (ClusPrep) whenever there is a change, update, or upgrade to the cluster. Remediate of any errors or warnings.
● Do not use HyperFlex SMB as a generic file share; it is designed and optimized for VM placement. Do not use the HyperFlex SMB share for user data.
● Because the HX filesystem is striped across all nodes there is no performance advantage for creating additional datastores. For ease of management create a single large datastore for VM placement.
● An upgrade requires a mandatory services engagement with Cisco Customer Experience.
● Use the Cluster-Aware Updating (CAU) feature of Windows to keep Windows up to date.
● Configure a file share witness service for Windows and do not install it on the HyperFlex cluster.
All the generic best practices apply to HyperFlex Edge. They can be found in HyperFlex documentation section on page 3 in this document.
● Read the Cisco HyperFlex Edge Deployment Guide and Preinstallation Checklist for Cisco HyperFlex Edge. Make sure you fill in the correct checklist. There is a checklist for the 2-node cluster and a document for the 3-node and 4-node cluster.
● When deploying HyperFlex Edge via Cisco Intersight, use the Deployment Guide for HX Edge with Intersight.
● Select the network topology where there is a fit between the top-of-rack switches and the workload running on HX Edge. Different speed and media types are possible to physically connect the HyperFlex node to the network switch.
● Intersight has the ability to manage multiple HX Edge clusters via one dashboard. If the HX Edge nodes are connected to the Internet, use Intersight for the installation. This is mandatory for a 2-node HX Edge cluster. Policies and HyperFlex profiles can be created in advance in Intersight for rapid cluster installation via cloning of the profiles and polices or via Intersight APIs.
● For a 2-node cluster a witness is needed to have a quorum. Intersight provides an invisible cloud witness for 2-node deployments.
● Cisco Intersight offers full lifecycle management for HyperFlex Edge. Firmware, the Hypervisor, and the HyperFlex Data Platform can easily be upgraded with one button in Intersight.
● Do not overburden HX Edge deployments. They are targeted for a specific ROBO profile (Figure 5). Use the HyperFlex Sizer Tool and choose the workload type to be HX Edge (ROBO) to create workloads for HX Edge.

HyperFlex Sizer tool with HX Edge (ROBO) workload
All the generic best practices apply to HyperFlex stretched clusters. They can be found in HyperFlex documentation section on page 3 in this document.
The Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform Stretched Cluster white paper includes guidelines regarding HyperFlex stretched clusters. This document is a good starting point to read before installing a HyperFlex stretched cluster.
● A stretched cluster requires two pairs of fabric interconnects (FI)—one pair of FIs on each site. These four FIs should be from the same type. Do not mix different types of FIs from the same series.
● Use the HyperFlex sizing tool when creating a design for a HX stretched cluster. This tool will take the RF 2+2 into account.
● All of the workload running on a HyperFlex stretched cluster should be able to run on one site only. The maximum capacity of the HyperFlex cluster is 50 percent. In case of a disaster at one data center, all the workloads can still be running on the other data center. A HyperFlex stretched cluster is an enterprise solution. All other scenarios are not supported.
● If there is a firewall between the two data centers where the HyperFlex stretched cluster is configured, make sure the correct ports are opened on the firewalls. Use the HX Data Platform Security Hardening Guide for the ports and directions of the traffic.
● If encryption is needed on the HyperFlex stretched cluster, third-party software can be used.
● To establish a quorum, a witness server is needed. Put the witness server at a third site with low latency.
● When upgrading a HyperFlex stretched cluster, the witness must also be upgraded. This procedure will be done after the HXDP upgrade of the cluster.
● Intersight Invisible Witness is different from HyperFlex Stretched Cluster Witness. At this moment a separate witness VM should be running on a third site.
● When expanding the HyperFlex stretched cluster, update the sites to the desired version first, and then expand the cluster symmetrically. At both data centers there should be an equal number of HyperFlex nodes and/or compute nodes.
● VMWare DRS and high availability should be turned on in vCenter.
● Adjust the VMware high-availability cluster settings and follow the steps provided in the HyperFlex Stretched Cluster white paper.
● VXLAN and VMware NSX with a HyperFlex stretched cluster is not supported. Overlay Transport Virtualization (OTV) is supported and documented in the HyperFlex Stretched Cluster white paper.
● The link from the data centers to the witness should not exceed 100 msec.
● Create two datastores, each with their own affinity to one data center side.
● Survivability while maintaining online status requires a majority zookeeper quorum and more than 50 percent of the nodes. The witness counts as an active zookeeper node.
● After a site failure the VMs should be manually migrated back to the correct data center.
● When the cluster is healthy again, double-check the VM placement and verify in vCenter if they are running in the expected data center. If not, adjust vCenter and the affinity rules.
For additional information, see the following resources:
● Cisco HyperFlex Software Release Model and Release support timeline
● Recommended Release document
● Preinstallation checklist for Cisco HX Data Platform
● Bill of materials compatibility
● HX Data Platform Security Hardening Guide
● ESXi and HXDP compatibility guidelines
● Windows Time service tools and settings
● Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform Stretched Cluster white paper