Cisco Optical Network Controller (CONC) Data Sheet
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
The Cisco® Optical Network Controller (CONC) provides an SDN-compliant domain controller for Cisco optical networks. Using an industry-standard OIF transport API (T-API) interface over RESTCONF, CONC gives a Hierarchical Controller (HCO) or orchestrator abstracted visibility and control for Cisco optical networks.
CONC is a hybrid optical domain controller with centralized PCE (path computation engine) and distributed APC (automatic power control). It has a Web UI with multiple applications providing full CRUD (create, read, update, and delete) services and NMS (Network Management System).
CONC design is based on microservices to enable scaling and alignment with Cisco automation products and platforms.
● Cisco Site Manager 7.11.2 and 24.1.1—NCS 1010, NCS 1014
CONC is built to address several challenges in network management:
● Controller, NMS, and EMS functions
● Integration into an SDN management environment including abstraction of vendor details
● Integration with Cisco automation software products like HCO, COSM, and CONP
● Support for current and future network topologies, including routed optical networking
● Centralized software control of the Cisco optical network, including movement of distributed-PCE network functions to a centralized-PCE
● Web UI with applications like inventory, topology, service manager, service assurance, etc.
● Single sign-on for seamless node (site) manager cross-launch
Cisco Optical Network Controller architecture
Cisco Optical Network Controller was designed to align with an ACTN (abstraction and control of traffic-engineered networks) standard architecture. CONC acts as a Provisioning Network Controller (PNC) in an ACTN as shown in the following figure.
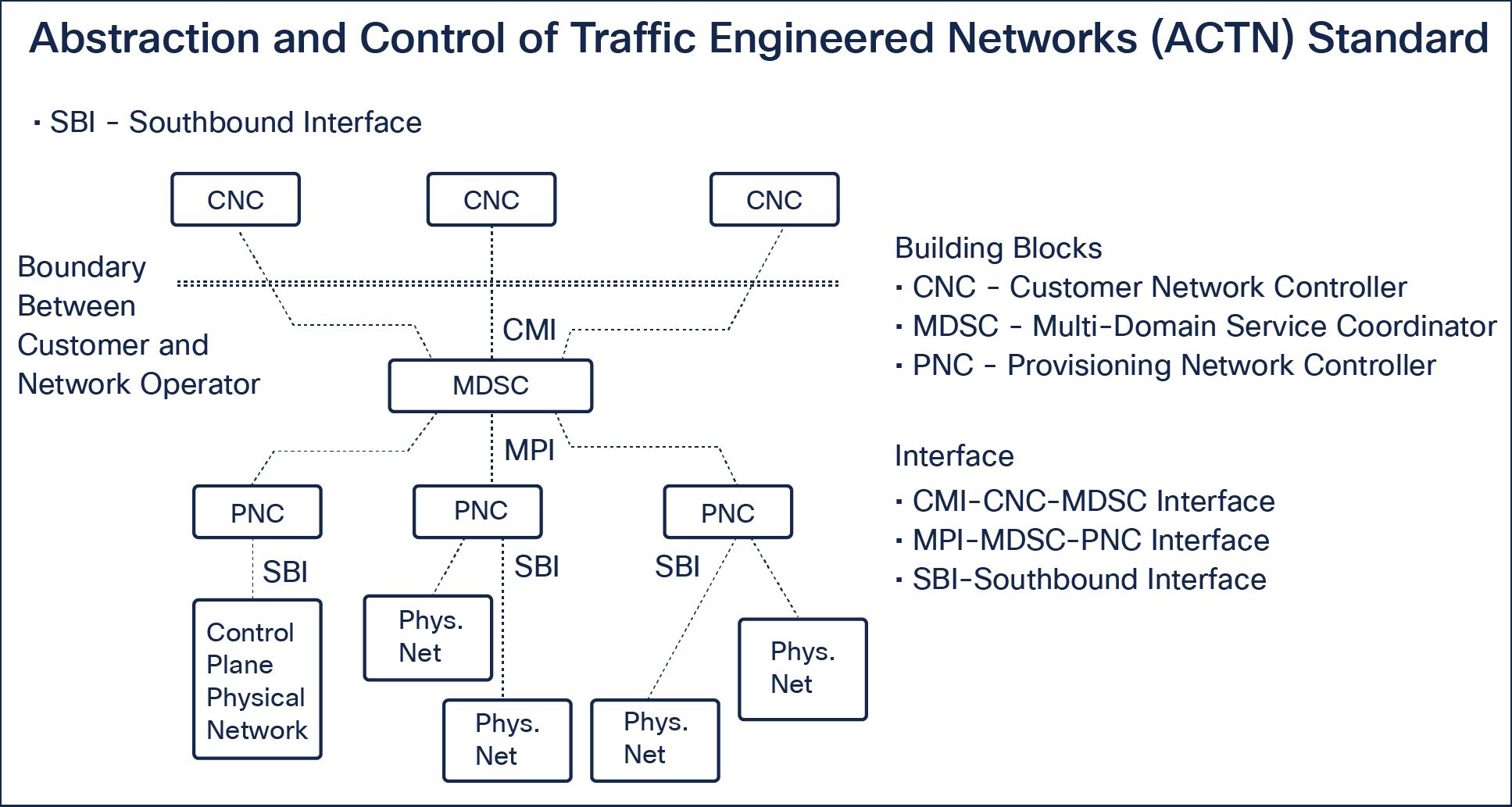
ACTN standard architecture
The following figure shows the CONC architecture. The northbound interface allows CONC to interact with any OSS solution while the southbound allows the monitoring and configuring of Cisco NCS 2000 and NCS 1000 optical devices. Additionally, the Crosswork framework on which CONC exists today provides functions including user management, logging and monitoring, and the common Kafka bus as well as the underlying platform for High Availability (HA) and scale.

Cisco Optical Network Controller high-level architecture
The functions that are created as parts of CONC include the centralized optical path computation element (O-PCE), which is the key to determining optically valid paths in a Cisco optical network. Additional CONC functions include device onboarding, topology, inventory, collector services (to gather information from the network), deployer services (to push information into the network), and capacity to add future applications.
Some architectural advantages of CONC are as follows:
● Components are designed as microservices and run as docker containers
● Being packaged as Docker images and launched in K8s pods
● Being designed to work in a distributed compute environment (future)
The next figure shows the overall architecture for Cisco’s management and automation offering. It is key to understand that CONC is built for and intended to be integrated within larger SDN OSS management frameworks.
1. In the RON use case (but also applicable outside RON), CONC is integrated with the Crosswork Hierarchical Controller (HCO). In this case, HCO is acting as the hierarchical controller providing visibility to the entire network and using the TAPI interface to manage optical devices using CONC as the optical domain controller (understanding the optical inventory and topology, provisioning optical services).
2. Cisco Optical Site Manager (COSM) interacts with CONC where COSM provides detailed node-level management for the Cisco NCS 1000 product line.
3. Given that CONC provides an industry-standard TAPI interface over RESTCONF, an HCO or orchestration system can use the topology/inventory and service-provisioning functions as well. To support third-party products, CONC has been integrated with Cisco Hierarchical Controller (now HCO, formerly Sedona NetFusion). This proves the ability for an OEM product to integrate to CONC over the TAPI interface.
4. ZTP provisioning of the optical devices can also be done by customers who prefer this option.
5. The CONP optical network planner tool can provide the necessary configuration files (NETCONF-YANG, JSON) that can be consumed by the CONC controller and or COSM. The data is then utilized to bulk configure NCS 1000 devices in the optical network according to the planning data.
6. EPNM is an optional software that can be added to provide software image management, PM history, and SNMP NBI as an intermediate step until CONC supports it.

Overall architecture for management and automation
Nodes application
Nodes (enrollment) app provides:
● COSM enrolment for NCS 1000 sites (nodes)
● Future SVO enrolment for NCS 2000 sites (nodes)
● Add/edit lat/long values
● Resync a specific site or multiple selected sites
● Periodic network sync
● Cross-launch a specific node functional view
● Bulk enrollment—import from excel file
● Export to an Excel file

Inventory application
The Inventory application provides the following information: node name, admin state, equipment type, equipment state, actual equipment type, serial number, product ID, hardware part number, CLEI code, version ID, hardware rev, software rev, boot ROM rev, manufacturing date, manufacturing id, and site location.
This is represented in a tree view (hierarchical view) when browsed “manually” by the user or in flat view as a reply to a user search.
Search supports the two types of searches: (1) Quick search—This is a free text search (minimum 3 characters are required) or (2) a Custom search—Search will be based on the column’s names and string entered in the text box.
The user can add/remove columns and filter the data.
The user can export a tree table or a flat tabled after a search or the entire network inventory data.

Topology application
The topology application provides:
● Sites and links assembling the topology
● Expandable/collapsible legend
● Per site alarm popovers: On hovering each site, highest severity current and alarm summary
● Site search flies into the site’s location
● Link info (free text user subscription)
● Cross-launch to COSM for deep-dive site info
● Resync a site with an indicator
● OTS/OMS toggle
● A light/dark mode toggle

Alarm application
The alarm application provides:
● Up to 72 weeks of current and history alarms
● Site/chassis/card/port/pluggable—fetched from COSM, stored in CONC DB + updates notified by COSM
● Service-level alarms
● List of current alarms; alarm history (selected range date/time)
● Search/filter/sort add/remove columns
● Alarm acknowledgement
● User notes
● Cross-launch relevant alarms to COSM
● Show alarm severity in the topology/show in site (COSM)
● Auto filter alarms to other apps (topology, service assurance, service manager)
● Alarms exportable to XSLX file, saved in the local user storage
● User could cross-launch each alarm to the relevant COSM view


Service manager application
The service manager application provides:
● A list of discovered/provisioned services—search/sort/filter add/remove columns
● A list of circuits filtered by topology selection—link (all the circuits running through that link), site (all the circuits running through that site), multiple links/sites
● List fields are service name; source and destination endpoints; tag (customer name); type (NC/trail); profile (unprotected/etc.); rate; central-freq + BW; related services (trail over NC)
● The list is exportable to XSLX.
● Provisioning OCH-NC with OSNR sigma threshold, admin state, wavelength central-freq/blank, app. code, single/multicarrier, endpoint selection from map and inventory (plus drop-down list); PCE criteria—hop, cost, OSNR, distance/latency; path disjoint; node/link ERO/XRO, allow regen
● Discovering OCH-NC/trail
● Provisioning OCH-trail—same as OCH-NC + discovered trunk app. code and wavelength configuration
● Error messages in case of PCE failure (e.g., spectrum not available) and in case of execution (e.g., device disconnected)
● Service edit—edit service name
● Service delete


Service assurance application
The service assurance application provides:
● Service data path visualization: TXP/MXP, PSM (future), MD/BRK/CCOFS, OLT, OLA, ports, links (client DSR, trunks, OCH, OTS)
● Service name; tag (customer) name; rate; cent freq + bandwidth; opp state, admin state, components ID (COSM/SVO-chassis-slot-port)
● Alarm severity visualization plus alarm app filter
● User could cross-launch each component to the relevant COSM NFV
● Exportable to XSLX file, saved in the local user storage
● OCH-NC, OCH-trail

Audit logs application
The audit logs application provides logs related to admin, system, and microservices logs, either with text logs or Graphana.
Workspace application
The workspace application provides ways to accomplish different day-to-day workflows; a workspace consists of multiple applications that interact with each other within the same view.
A few of the common workflows have been predefined (e.g., circuit provisioning, circuit monitoring, network monitoring). We are looking to add a user-defined workspace in a later release.
For a given predefined workspace, the user can resize and position different applications to be in a favorite order and save it for the next launch. Clicking on one application will result in updates on the other applications.
For example, in the following screenshot, a user clicks on service (circuit) from the service manager (top-left window). Then this circuit will be highlighted in the topology app (top-right window), will be fetched to the service assurance app (bottom-right window), and will filter the relevant alarms in the alarm app (bottom-left window).

CONC TAPI interface
CONC’s NorthBound Interface (NBI) is based on the ONF-standard TAPI model and is accessible via RESTCONF. Within the TAPI model, CONC 3.1 has implemented the following:
● Service-interface-point
◦ List all the interfaces available for client signal connection and possible termination point of service creation
● Topology-context
◦ Include topological information of all network nodes with their owned Network-Edge-Point (NEP)
◦ Include topological link that connects nodes in the network at their NEP
● Connectivity-context
◦ Include connection-service (circuits) present in the network
◦ Include connections that compose all connection-service
◦ Allow for creation and deletion of connection-service
● Physical-context
◦ Provide the inventory information off all network nodes including the hierarchical rack, shelf, slot, etc., relationship
CONC 3.1 supports two network-provisioning models through TAPI (HCO UI):
1. Provisioning wavelength service path (OCH) for router-based ZR+ optics
◦ Used when CONC controls the OLS network (ROADMs, amps, DWDM filters) but DCO (digital coherent optic) is in the router
◦ CONC determines if the DCO service can be carried, and then sets it up (if feasible) and returns values for to HCO
◦ HCO does settings on router (through CNC IP controller)
2. Provisioning service path with NCS 2000 and NCS 1000 (or third-party DWDM system)
◦ Used when values are already known for a service riding the optical network (e.g., when NCS 1004 is used or alien transceiver spec imported from CONC)
◦ CONC determines if that wavelength service can be carried and then sets it up (if feasible)
◦ User does settings on TXP

CONC 2.x (or later release) service provisioning with router-based ZR+ optics workflow

CONC 2.x (or later release) service provisioning with NCS 1000 or third-party DWDM
CONC is deployed in VMware with the following requirements:
1. VMware data center requirements:
a. vSphere server and client of version 7.0
b. ESXi version of 6.7.0/7.0
c. Requires two networks for deployment:
i. Control plane → private network
ii. VM management → northbound network
d. Can be deployed in a different ESXi host, but it needs 10G network between them.
2. Following sizing rules apply for CONC3.1:
High availability requires three VMs: active, standby, and arbitrator
Non-high availability requires a single active VM
Table 1. CONC Sizing Rule
| Deployment > |
S (up to 500 NEs) |
XS (up to 100 NEs) |
||||
| VM | |
CPU cores |
RAM (GB) |
SSD storage (TB) |
CPU cores |
RAM (GB) |
SSD storage (TB) |
| Active |
24 |
96 |
1 |
12 |
48 |
0.5 |
| Standby |
24 |
96 |
1 |
12 |
48 |
0.5 |
| Arbitrator |
24 |
96 |
1 |
12 |
48 |
0.5 |
3. PIDs for Cisco servers:
◦ UCSC-C220-M5SX (rack server)
◦ UCSB-B200-M5 (blade server)
Appendix 1: Supported equipment
NCS1010-SA
NCS1K-BRK-SA
NCS1014
NCS1010-AC-PSU
NCS1010-DC-PSU
NCS1010-FAN
NCS1K14-FAN
NCS1010-FTF
NCS1K14-BLANK
NCS1K-CNTLR2
NCS1010-CNTLR-K9
NCS1010-CTLR-2-K9
NCS1K14-CNTLR-K9
NCS1K14-CCMD-16-C
NCS1K14-2.4T-L-K9
NCS1K14-2.4T-K9
NCS1K14-2.4T-X-K9
NCS1K14-2.4TXL-K9
NCS1K14-2.4TX-FB2C
NCS1K14-2.4TX-LC1C
NCS1K14-2.4TX-LC2C
NCS1K14-2.4TX-FB1C
NCS1K-ILA-2R-C
NCS1K-ILA-C
NCS1K-ILA-R-C
NCS1K-OLT-C
NCS1K-OLT-R-C
NCS1K-E-ILA-R-C
NCS1K-E-ILA-2R-C
NCS1K-E-ILA-R-C-2
NCS1K-E-OLT-C
NCS1K-E-OLT-R-C
NCS1K-BRK-8
NCS1K-BRK-24
NCS1K-MD-32E-C
NCS1K-MD-32O-C
NCS1K-MD-32E-L
NCS1K-MD-32O-L
Find warranty information on Cisco.com at the Product Warranties page.
To place an order, visit the Cisco Ordering Home Page and refer to Table 3. To download software, visit the Cisco Software Center.
Table 2. Ordering information for Cisco Optical Network Controller
| Part number |
Description |
| S-OAS-CONC3.1-SW |
CONC3.1 software image |
| CONC-RTM-ESS-SM |
Essential CONC subscription for small device with support |
| CONC-RTM-SPC-SM |
Spectrum CONC subscription for small device with support |
| CONC-RTM-API-SM |
API CONC subscription for small device with support |
| CONC-RTM-ESS-LG |
Essential CONC subscription for large device with support |
| CONC-RTM-SPC-LG |
Spectrum CONC subscription for large device with support |
| CONC-RTM-API-LG |
API CONC subscription for large device with support |
● CONC licenses have two types of devices.
◦ Small: 1010 (future: 1001, 2002, 1012)
◦ Large: 1014 (future: 1004, 2006, 2015, 1020)
● Please refer to the diagram above describing the features/functions available per package.
◦ ESS (Essential) level is mandatory and has to be ordered for all the devices managed by CONC
◦ SPC (Spectrum) is optional. An SPC package requires ESS first. Thus, both ESS and SPC would be ordered for the relevant devices.
◦ API is optional. An API package requires ESS first. Thus, both ESS and API would be ordered for the relevant devices.
◦ The following combinations are legit: ESS, ESS+SPC, ESS+API, and A full blown of ESS+SPC+API.
● CONC licenses are subscription based, with 36- to 60-month terms, which include:
◦ SW upgrades to latest current CONC release (excluding labor)
◦ CONC CX support during the subscription term
Cisco services for migrating converged IP + optical solutions
Services from Cisco and our partners help you get the most value from your investments in the Cisco converged IP + optical solution, quickly and cost-effectively. We can help you design, implement, and validate your solution to speed migration and cutover. Coordinate every step through to interworking, strengthen your team, and make the most of tomorrow’s opportunities. Learn more at www.cisco.com/go/spservices.
Cisco environmental sustainability
Information about Cisco’s environmental sustainability policies and initiatives for our products, solutions, operations, and extended operations or supply chain is provided in the “Environment Sustainability” section of Cisco’s Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) report.
Reference links to information about key environmental sustainability topics (mentioned in the “Environment Sustainability” section of the CSR report) are provided in the following table:
| Sustainability topic |
Reference |
| Information on product material content laws and regulations |
|
| Information on electronic waste laws and regulations, including products, batteries, and packaging |
Cisco makes the packaging data available for informational purposes only. It may not reflect the most current legal developments, and Cisco does not represent, warrant, or guarantee that it is complete, accurate, or up to date. This information is subject to change without notice.
Flexible payment solutions to help you achieve your objectives
Cisco Capital® makes it easier to get the right technology to achieve your objectives, enable business transformation, and help you stay competitive. We can help you reduce the total cost of ownership, conserve capital, and accelerate growth. In more than 100 countries, our flexible payment solutions can help you acquire hardware, software, services, and complementary third-party equipment in easy, predictable payments. Learn more.
For more information about the Cisco Optical Network Controller, visit www.cisco.com/go/ncs4000 or contact your local Cisco account representative.
| New or revised topic |
Described in |
Date |
| CONC2.0 features |
CONC datasheet |
November 1, 2022 |
| CONC PIDs |
CONC datasheet |
December 9, 2023 |
| CONC3.1 applications and features |
CONC datasheet |