Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Service Insertion FAQ
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
● Next-generation firewall embedded within the SD-WAN routers.
● Security Service Edge (SSE) integrations with Cisco and third-party vendors – Cisco Umbrella®, Zscaler, Netskope, etc.
● Automated service insertion (new): Customers will also have a choice of inserting Cisco® or third-party physical or virtual services.
● Simplified IT: Simplify configuration and management of service chains across the network.
● Reduced operations: Reduce operation cycles via automated service insertion and visibility of one or more services on any router located anywhere.
● Enhanced security: Bring your own service and enhance network security posture with consistent policy across multicloud and on-premises environments.
● On-demand services insertion: Automation to easily insert services into the Catalyst SD-WAN fabric.
● Intent-based automation: Orchestration workflows capture and execute on the service insertion intent to build and attach the service chain.
● Service Chaining: Chain up to four different services without the need to manually stitch them together.
● Any service: Bring any Cisco or third-party services to be inserted.
● Any location: Services can be located anywhere – on-premises, in colocation facilities, or in the cloud.
● Any form factor: Services can be virtual or physical in nature. Similarly, the SD-WAN router acting as the service chain hub can have a virtual or physical form factor.
● Flexible traffic selection for service application: Use control policy, data policy, and/or interface ACL to match traffic and steer it towards a service chain.
● Define once, deploy multiple times: Different service chain definitions and configurations can be created and used repeatedly to deploy the appropriate service chain at the desired location at the desired time.
● Service chaining for inter- and intra-VPN, transit, branch-to-branch, branch-to-internet, branch-to-cloud, and cloud-to-cloud traffic.
● Automatic forwarding through all services in a chain.
● Multiple ways to attach services: IPv4, IPv6, dual-stack, and tunneled.
● Built-in load balancing and high availability across instances of a single service.
● Path preference and symmetric routing.
● Advanced service tracking.
● Ability to share a service chain across multiple user VPNs.
● Powerful traffic steering methods that use control policy, data policy, and interface Access Control Lists (ACLs) and all supported match conditions.
● Fail-open, fail-close behavior: configurable option to block or allow traffic, in case of service failure.
● Special features for security services: To- and from-service transports, trusted and untrusted postures, firewall between devices.
● Serviceability: Periodic, on-demand, and state notifications.
● Orchestration via Catalyst SD-WAN Manager: Workflow-based service chaining, traffic policy configuration.
● Service chain definition: Ordered sequence of services defined by the operator.
● Service chain instance: An actual instance of the services defined in the service chain definition. Services in the chain can be physical or virtual.
● Service chain policy: Traffic policy to identify what types of traffic are to be subjected to what specific service chains.
● Service chain hub: A Catalyst SD-WAN router where the service chain is attached. The hub forwards traffic toward a service chain based on the service chain policy and then sends it onward to the destination.
● Service chain advertisement: An advertisement from a service chain hub that identifies which particular service chain is reachable through it.
● Native support for multiple services in a chain.
● Selective service chaining using a rich set of match criteria in data, control, and interface ACL policies.
● The ability to attach to services in multiple ways (IPv4, IPv6, dual stack, and tunneling).
● A rich set of high-availability and load-balancing features.
● Advanced tracking of the chain.
● Deployment anywhere (on-premises, in the cloud, in a colocation facility).
1. Define the service chain: Define the services in the chain and their sequence.
2. Attach it to the hub router: Configure the service chain parameters and attach it to the desired Catalyst SD-WAN router (service chain hub). Service chain reachability is thus advertised by the hub to the Catalyst SD-WAN controller.
3. Define the service chain policy: Define the policy to match traffic or routes and apply it to all traffic origin sites.
Once the above steps are completed, traffic is steered through the service chain hub and associated service chain in accordance with the service chain policy.
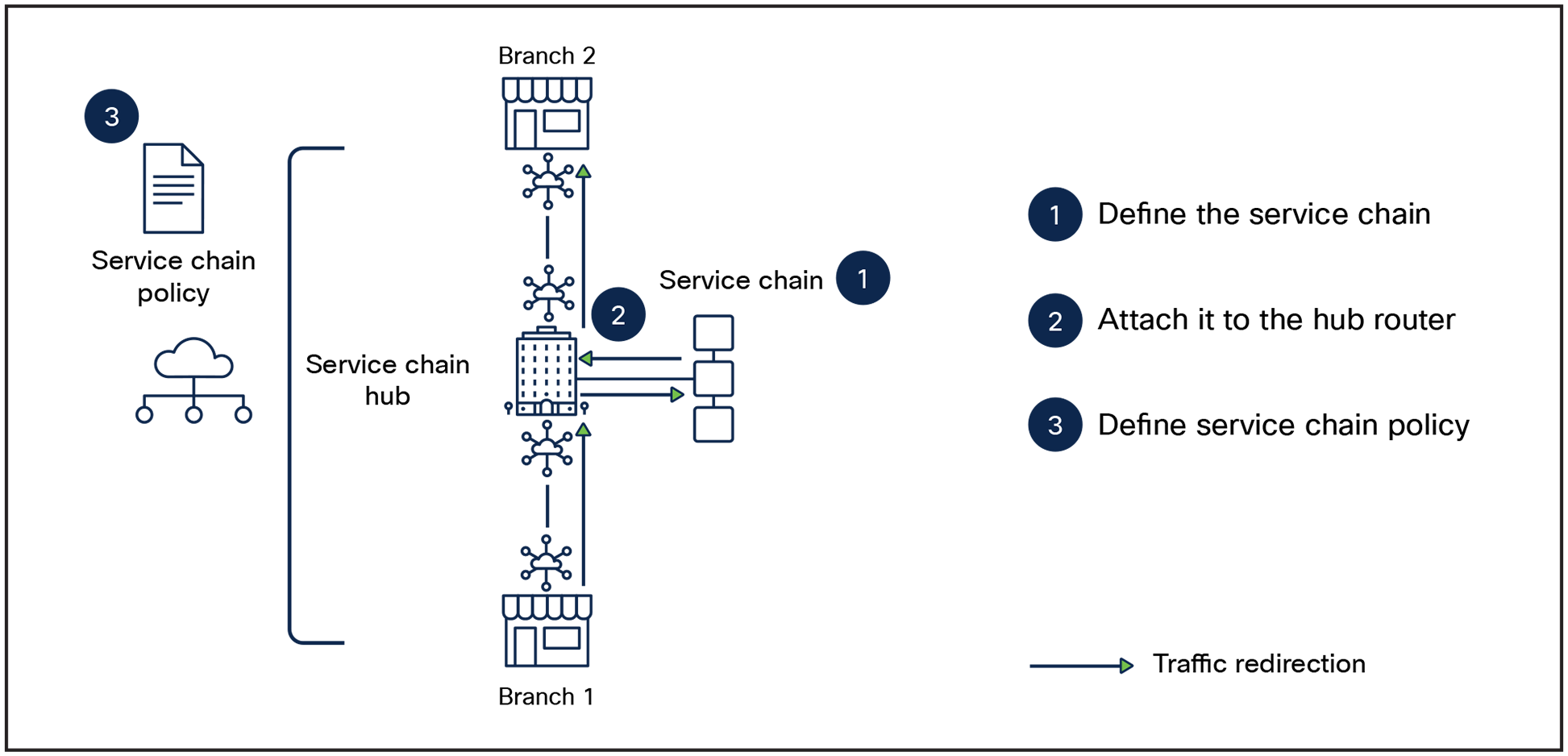
Steps for service insertion
For more information on license types, please refer to the Cisco DNA Software for SD-WAN Feature Matrix.