SAFE Secure Cloud Architecture Guide
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
The Secure Cloud is a place in the network (PIN) where a company centralizes data and performs services for business. Cloud service providers host data center services in the Secure Cloud. This guide addresses Secure Cloud business flows and the security used to defend them. The focus of this guide in on the security controls necessary to provide “security FOR the cloud”.
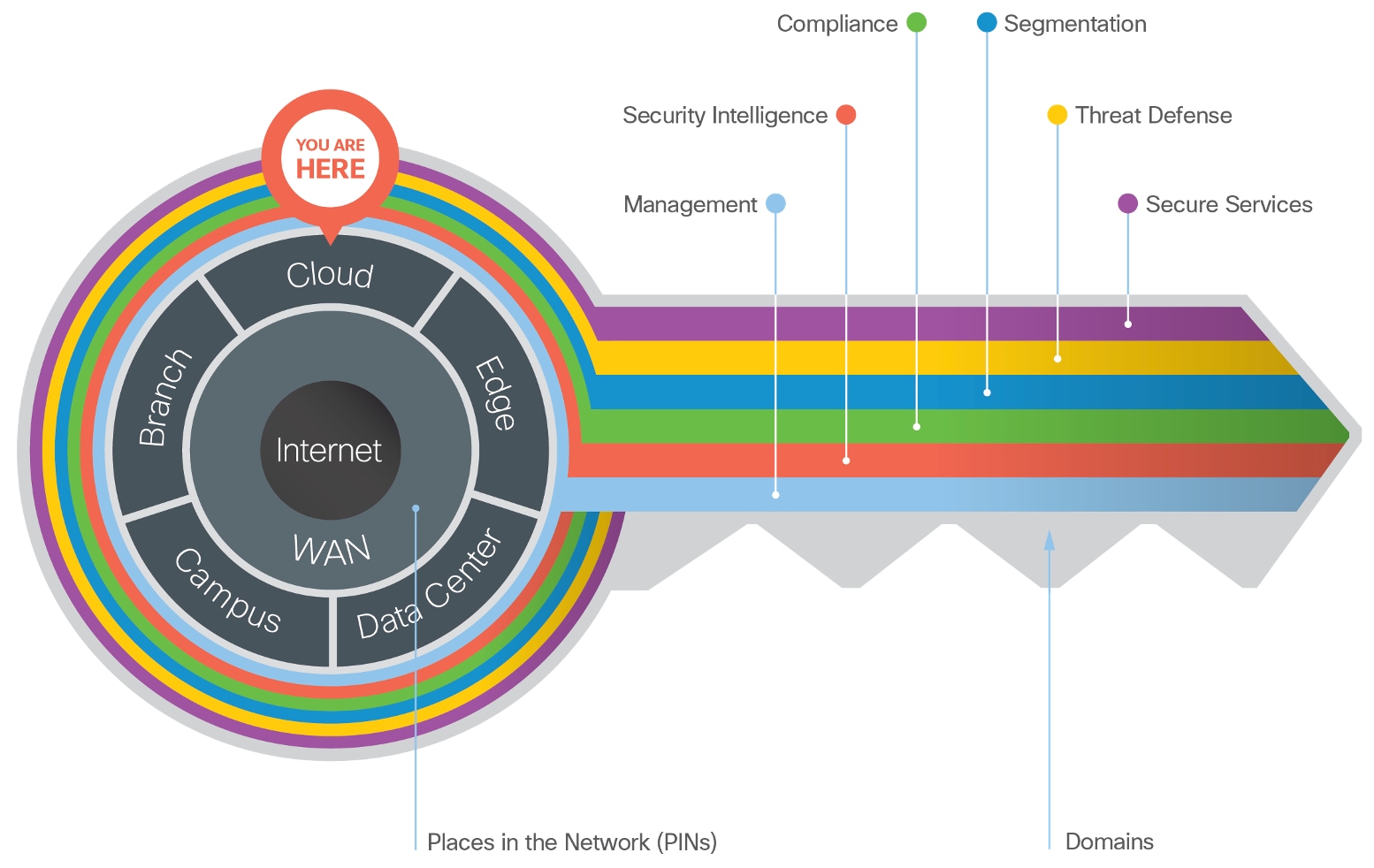
The Secure Cloud is one of the seven places in the network within SAFE. SAFE is a holistic approach in which Secure PINs model the physical infrastructure and Secure Domains represent the operational aspects of a network.
The Secure Cloud architecture guide provides:
● Business flows for the cloud
● Cloud threats and security capabilities
● Business flow security architecture
● Design examples and a suggested components
SAFE simplifies security by starting with business flows, then addressing their respective threats with corresponding security capabilities, architectures, and designs. SAFE provides guidance that is holistic and understandable.
The Internet is a collection of interconnected Information Technology (IT) and clouds. Terms of clouds varies by context, ownership and integration.
| Cloud Term |
Definition |
| Cloud |
Cloud computing enables convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. |
| Public Cloud |
A style of computing where scalable and elastic IT-enabled capabilities are provisioned services out of multiple, private cloud and public cloud availability zones. Workloads are not ported between these zones. |
| Private Cloud |
A style of computing where scalable and elastic IT-enabled capabilities are provisioned over IT infrastructure that is on-prem. |
| Hybrid Cloud |
A style of computing where scalable and elastic IT-enabled capabilities are provisioned services out of multiple, private and public cloud availability zones. Workloads are actively ported between these zones for reasons including cost, performance and availability. |
| Multicloud |
A style of computing where scalable and elastic IT-enabled capabilities are provisioned services out of multiple, private cloud and public cloud availability zones. Workloads are not ported between these zones. |
| Hybrid IT |
Hybrid IT is when an enterprise adds cloud-based services to complete their entire pool of IT resources. A hybrid IT model enables organizations to lease a portion of their required IT resources from a public/private cloud service provider. |
Cloud Service Providers (CSP) provide public cloud services. CSPs deliver a variety of cloud services that can provide business application delivery. The following table lists the cloud service types, definitions and the corresponding SAFE PIN Architecture Guide the cloud service is covered under.
| Cloud Service Type |
Definition |
SAFE PIN Architecture Guide |
| Software as a Service (SaaS) |
Software that is deployed over the internet. A provider licenses an application to customers either as a service on demand, through a subscription, in a “pay-as-you-go” model, or (increasingly) at no charge when there is opportunity to generate revenue from streams other than the user, such as from advertisement or user list sales. |
Secure Internet |
| Functions as a Service (FaaS) |
A cloud computing service that provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage application functionalities without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an application. Also referred to as Serverless. |
Secure Cloud |
| Platform as a Service (PaaS) |
A computing platform that allows the creation of web applications quickly and easily and without the complexity of buying and maintaining the software and infrastructure underneath it. |
Secure Cloud |
| Container as a Service (CaaS) |
A cloud service that allows software developers and IT departments to upload, organize, run, scale, manage and stop containers by using container-based virtualization. |
Secure Cloud |
| Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) |
A way of delivering Cloud Computing infrastructure – servers, storage, network and operating systems – as an on-demand service. Rather than purchasing servers, software, datacenter space or network equipment, clients instead buy those resources as a fully outsourced service on demand. |
Secure Cloud |
| On-Prem |
IT services are provisioned over private IT infrastructure for the dedicated use of a single organization. The customer owns all costs for hosting the applications in a location they own. |
Secure Data Center |
The customer selects the cloud service model which best serves the business need. The following figure represents the responsibility model between the Cloud Service Provider and the Customer.
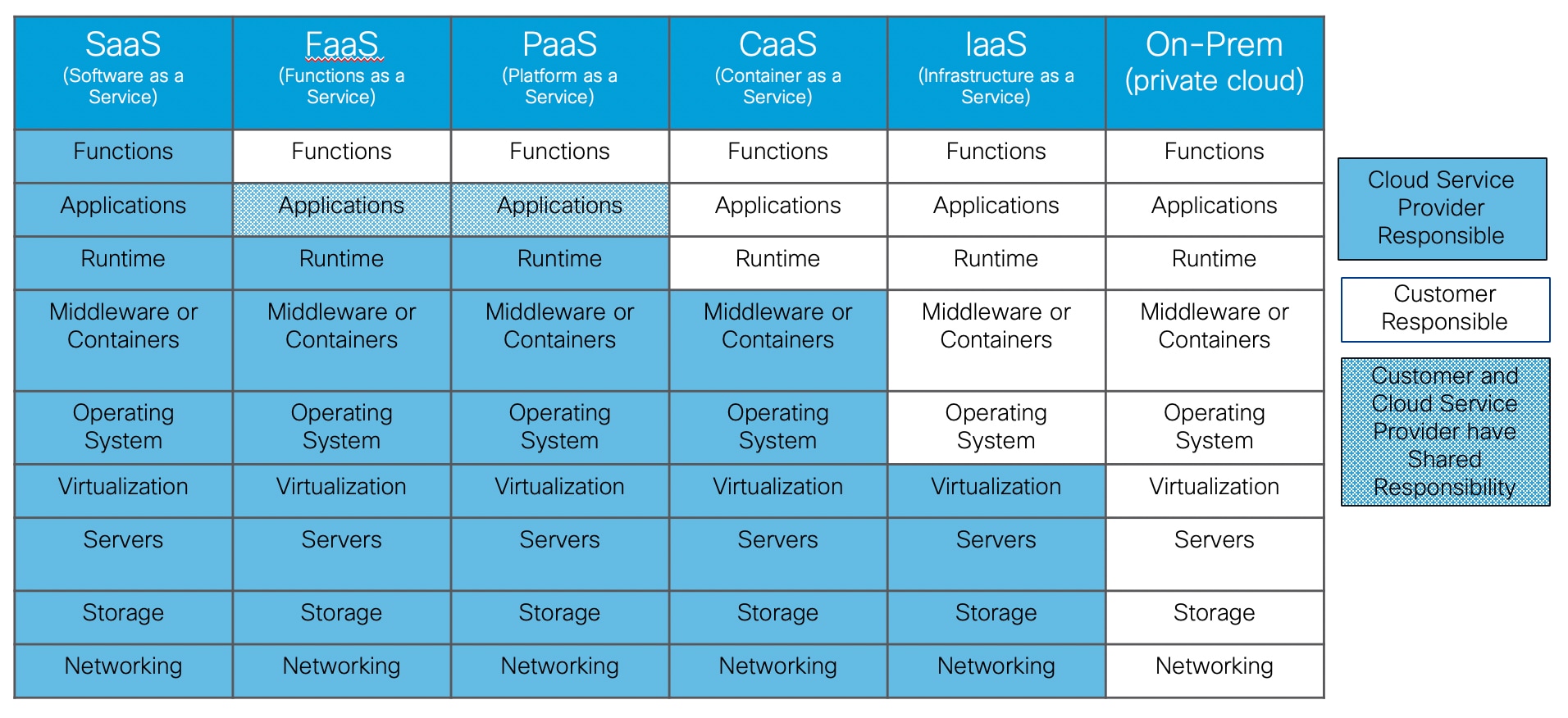
On the far left, the Software as a Service (SaaS) cloud service has the cloud service provider being responsible for all costs.
On the far right, the On-Prem cloud service (i.e. private cloud) is a traditional data center deployment where the customer is responsible for all costs.
The cloud services between them have varying ownership responsibility. A customer needs to evaluate the service level agreements for all cloud services under consideration.
Runtime is a responsibility highlighted because with an On-Prem or IaaS deployment the customer owns runtime even if the servers sit idle. In a PaaS or FaaS deployment, a customer would only pay for the runtime that they used.
The SAFE model is based on ten business flows as described in the SAFE Overview Guide. SAFE’s color-coded business flows illustrate the security needed for each role. These flows depict the attack surface, ensuring that controls are easily accounted for.
The Secure Cloud provides business services to the company’s users.
● Employees in the branch, campus, and remote locations require access to applications, collaboration services (voice, video, email), and the Internet
● Systems communicate east/west within the cloud service, as well as with other cloud services or on-premise data centers
The three business flows this architecture guide focuses on describing the capabilities required to secure the Secure Cloud PIN are depicted in Figure 4.
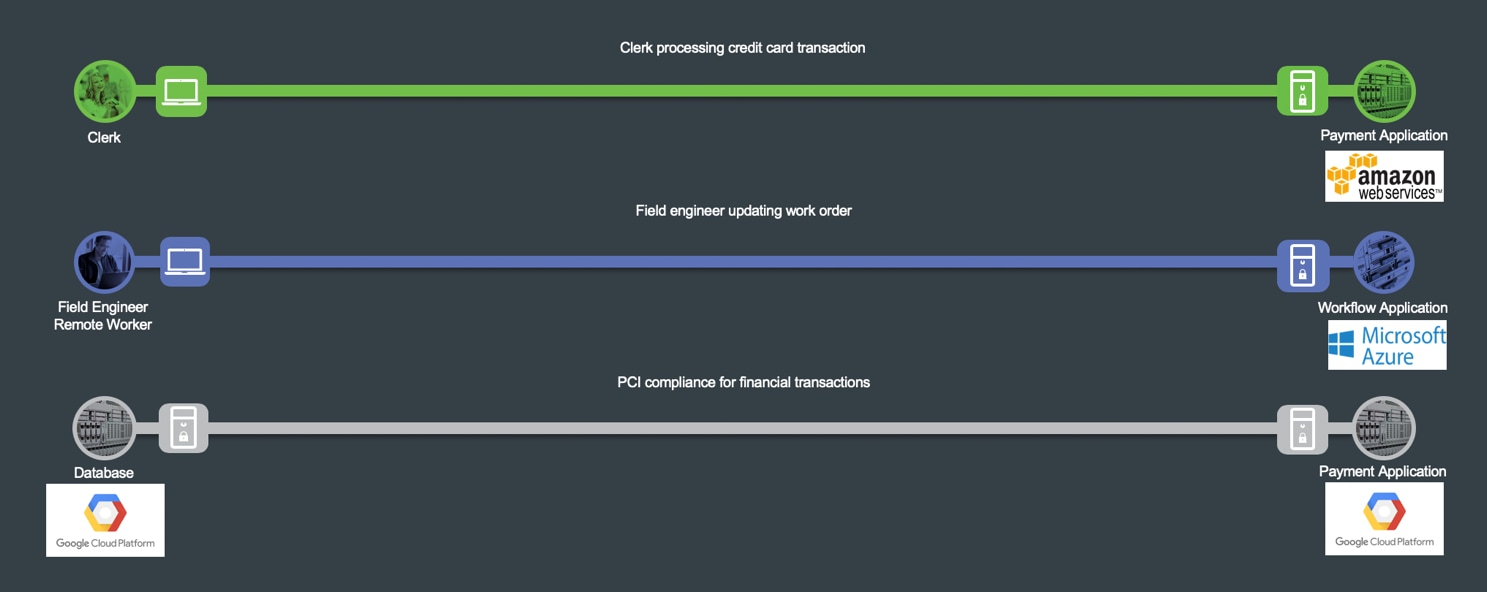
The green business flow is an example of a secure application, depicted by a clerk in the branch accessing a payment application hosted in the cloud (Amazon Web Services). The capabilities in the branch are documented in the Secure Branch architecture guide.
The blue business flow is an engineer connected directly to the Internet accessing a secure workflow application hosted in the cloud (Microsoft Azure).
Lastly, the gray business flow represents the east-west traffic between a database server and a payment application hosted in Google Cloud Platform. The business requires visibility and control capabilities for the traffic between the hosted applications.
Functional Controls are common security considerations that are derived from the technical aspects of the business flows.
| Cloud Term |
Definition |
| Secure Applications |
Applications require sufficient security controls for protection. |
| Secure Remote Access |
Secure remote access for employees and third-party partners that are external to the company network. |
| Secure East/West Traffic |
Data moves securely; internally, externally, or to third-party resources. |

Cloud security is simplified by grouping capabilities into three groups which align to the functional controls: Foundational, Business, and Access. Each flow requires the access and foundational groups. Business activity risks require appropriate capabilities to control or mitigate them.
For more information regarding capability groups and functional controls, refer to the SAFE overview guide.
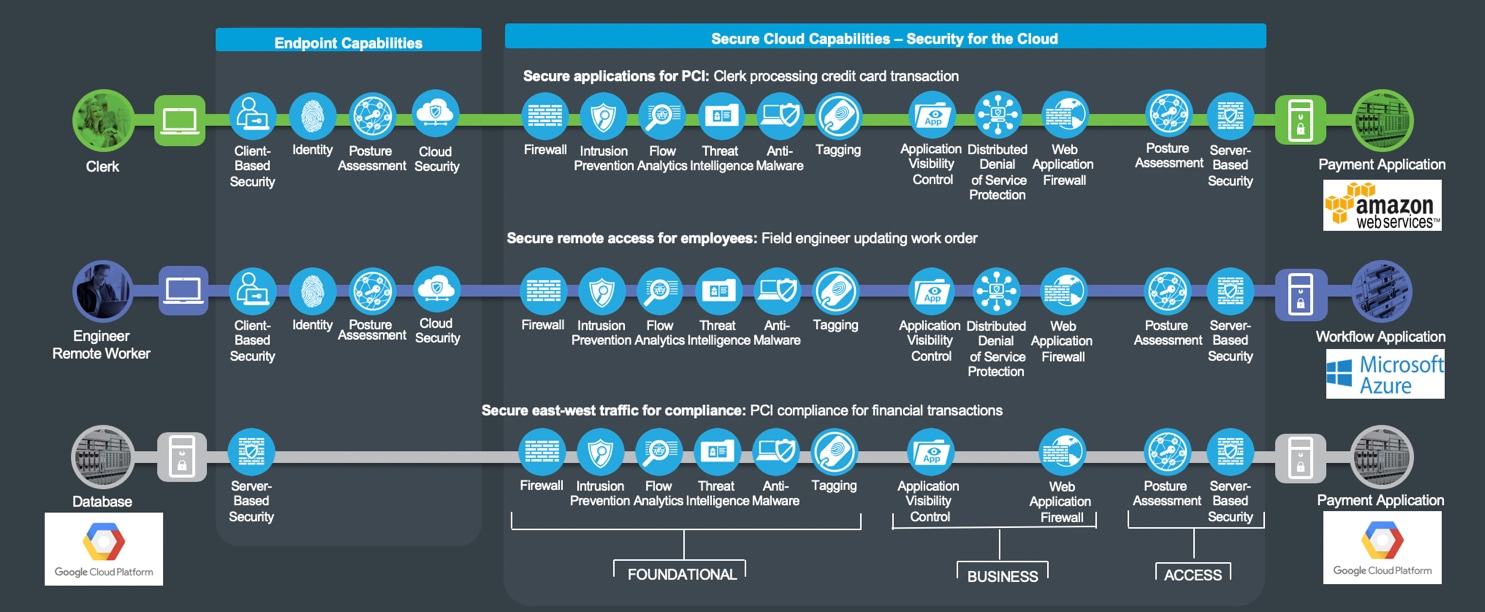
Secure Cloud threats and capabilities are defined in the following sections.
Cloud services contain the majority of business information assets and intellectual property. These are the primary goals of targeted attacks and require the highest level of investment to secure. The cloud assets have four primary threats:
Data extraction (data loss)
The unauthorized ex-filtration or theft of a company’s intellectual property, innovation, and proprietary company data.
Unauthorized network access
Unauthorized access gives attackers the potential to cause damage, such as deleting sensitive files from a host, planting a virus, and hindering network performance with a flood of illegitimate packets.
Malware propagation
Assets in the data center are targets for east/west contamination between servers, and north/south from employees, partners, or customer devices on the network. Applications that process credit card transactions and Internet of Things devices are the most prevalent targets.
Botnet cultivation
The resources of a server farm are a valuable target for botnet cultivation. Botnets are networks made up of remote controlled computers, or “bots.” They are used to steal data, send spam, or perform other attacks.

The defense is explained throughout the rest of the document.
The attack surface of the cloud is defined by the business flows, and includes the people and the technology present. The security capabilities that are needed to respond to the threats are mapped in Figure 7. The placement of these capabilities is discussed in the architecture section.
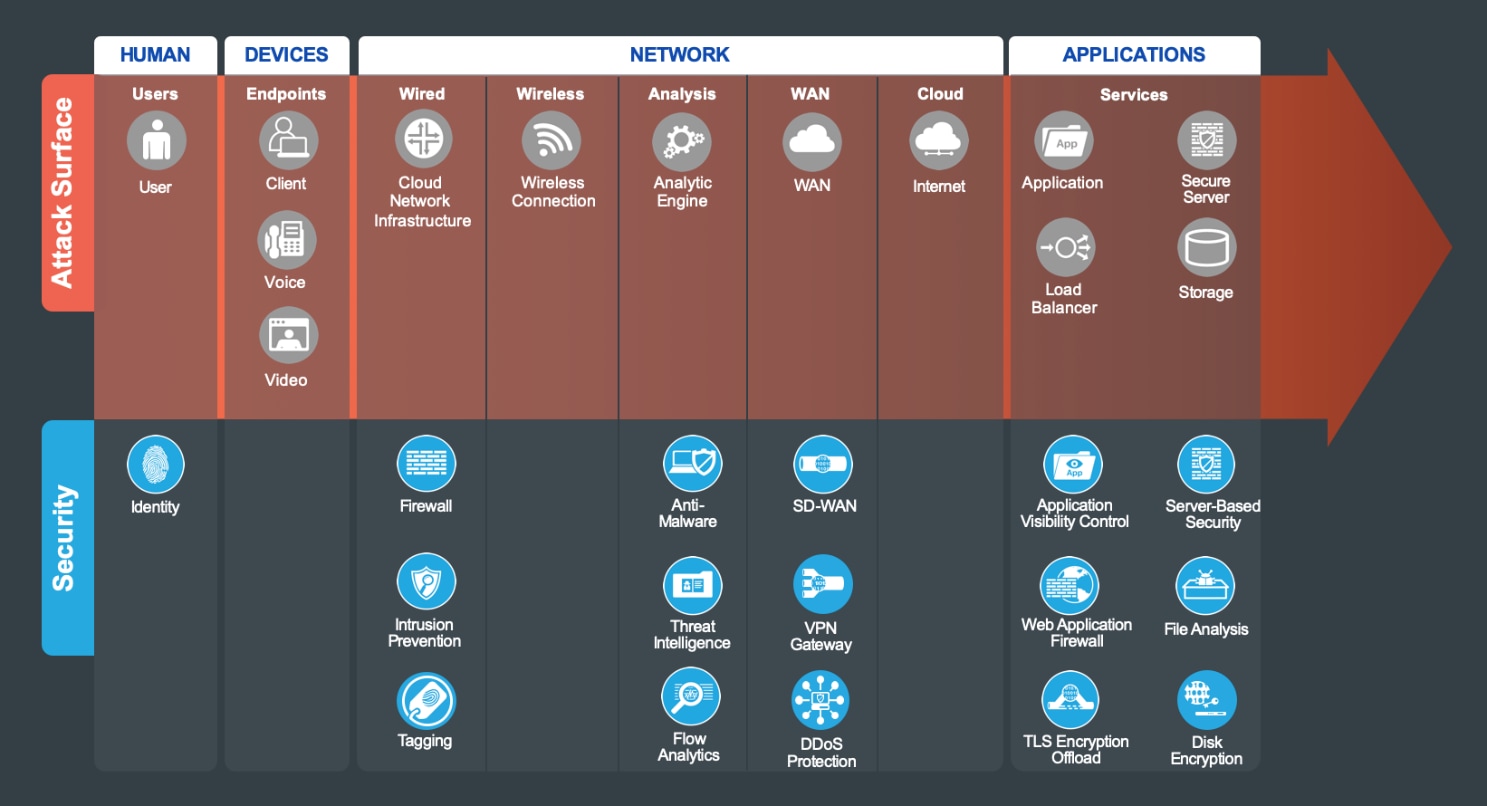
The suggested products that implement these capabilities can be found in Appendix B.

Users: Employees, third parties, customers, and administrators.
| Security Capability |
Threat |
||
|
|
Identity: Identity-based access. |
|
Attackers or disgruntled admins accessing restricted information resources. |
Network Attack Surface - Cloud Network Infrastructure

Routing and switching capabilities required to host business services in the cloud.
| Security Capability |
Threat |
||
|
|
Firewall: Stateful filtering and protocol inspection between segments in the virtual private cloud. |
|
Unauthorized access and malformed packets between and within application in the cloud. |
|
|
Intrusion Prevention: Blocking of attacks by signatures and anomaly analysis. |
|
Attacks using worms, viruses, or other techniques. |
|
|
Tagging: Software-based segmentation using native cloud capabilities |
|
Unauthorized access and malicious traffic between segments. |
Network Attack Surface - Analysis

| Security Capability |
Threat |
||
|
|
Anti-Malware: Identify, block, and analyze malicious files and transmissions. |
|
Malware distribution across networks or between servers and devices. |
|
|
Threat Intelligence: Contextual knowledge of existing and emerging hazards. |
|
Zero-day malware and attacks. |
|
|
Flow Analytics: Network traffic metadata identifying security incidents. |
|
Traffic, telemetry, and data exfiltration from successful attacks. |

| Security Capability |
Threat |
||
|
|
Virtual Private Network (VPN) or SD-WAN: Encrypted communication tunnels. |
|
Easily collecting information and identities. |
|
|
VPN Gateway or Concentrator: Encrypted remote access. |
|
Exposed services and data theft. |
|
|
DDoS Protection: Protection against scaled attack forms. |
|
Massively scaled attacks that overwhelm services. |
Applications Attack Surface - Applications

Management, servers, database, load balancer.
| Security Capability |
Threat |
||
|
|
Application Visibility Control: Inspects network communications. |
|
Unauthorized access and malformed packets connecting to services. |
|
|
Web Application Firewall: Advanced application inspection and monitoring. |
|
Attacks against poorly developed applications and website vulnerabilities. |
|
|
File Analysis: Inspects and analyzes suspicious files. |
|
Zero-day malware and attacks. |
|
|
TLS Encryption Offload: Accelerated encryption of data services. |
|
Theft of unencrypted traffic. |
Applications Attack Surface - Storage

Cloud Storage
| Security Capability |
Threat |
||
|
|
Disk Encryption: Encryption of data at rest. |
|
Theft of unencrypted data.
|
Applications Attack Surface - Servers

| Security Capability |
Threat |
||
|
|
Server-based Security: Security software for servers with the following capabilities: |
|
Viruses or malware compromising systems. |
|
|
Anti-Malware: Identify, block, and analyze malicious files and transmissions. |
|
Malware distribution across servers. |
|
|
Cloud Security: Security services from the cloud |
|
Redirection of session to malicious website. |
|
|
Flow Analytics: Network traffic metadata identifying security incidents. |
|
Traffic, telemetry, and data exfiltration from successful attacks. |
|
|
Application Dependency Mapping: |
|
Exploiting a misconfigured firewall policy. |
|
|
Vulnerability Assessment and Software Inventory: |
|
Exploiting unpatched or outdated applications. |
|
|
Process Anomaly Detection & Forensics: |
|
Exploiting privileged access to run shell code. |
|
|
Tagging: Grouping for Software Defined Policy |
|
Unauthorized access and malicious traffic between segments. |
|
|
Policy Generation, Audit, and Change Management: |
|
Targeted attacks taking advantage of known vulnerabilities. |
|
|
Host-based Firewall: Provides micro-segmentation and policy enforcement. |
|
Unauthorized access and malformed packets connecting to server. |
|
|
Disk Encryption: Protect information at rest. |
|
Unauthorized access to system-stored data. |

Management, Control, and Monitoring
| Security Capability |
Threat |
||
|
|
Analysis/Correlation: Security event management of real-time information. |
|
Diverse and polymorphic attacks. |
|
|
Anomaly Detection: Identification of infected hosts scanning for other vulnerable hosts. |
|
Malware distribution across services. |
|
|
Identity/Authorization: Centralized identity and administration policy. |
|
Viruses compromising systems. |
|
|
Logging/Reporting: Centralized event information collection. |
|
Redirection of session to malicious website. |
|
|
Monitoring: Network traffic inspection. |
|
Unauthorized access and malformed packets connecting to server. |
|
|
Policy/Configuration: Unified infrastructure management and compliance verification. |
|
Targeted attacks taking advantage of known vulnerabilities.. |
|
|
Vulnerability Management: Continuous scanning, patching, and reporting of infrastructure. |
|
Unauthorized access to system-stored data. |
SAFE underscores the challenges of securing the business. It enhances traditional network diagrams to include a security-centric view of the company business. The Secure Cloud architecture is a logical grouping of security and network technology that supports business use cases.
SAFE business flow security architecture depicts a security focus. A SAFE logical architecture can have many different physical designs.
The Secure Cloud architecture has the following characteristics:
● Visibility with centralized management, analytics, and shared services
● A core connecting distribution and application-centric layers
● Software-defined network segmentation
● Software-defined application segmentation
● Virtual servers requiring secure network access connectivity
Humans and devices are part of the attack surface, but are not part of the architecture within the secure cloud.
The Secure Cloud attack surface (Figure 7) consists of Humans, Devices, Network, and Applications. A successful breach gives an attacker the “keys to the kingdom.”
Security includes these considerations:
● Human administrators can be located anywhere
● Network security is required for applications hosted in public cloud
● Applications and data contain vital company information
● Application orchestration centralizes control of security, network, and server elements into a single critical target
The sections below discuss the security capability that defends the threats associated with each part of the attack surface.
Typically, humans are administrators for the secure data center, secure cloud and public SaaS applications.
No amount of technology can prevent successful attacks if the administrators themselves are compromised. Administrators that are disgruntled (fired, demoted, bullied, ideology), compromised (blackmail, threats, bribery), or have had their credentials stolen (phishing, key logger, password reuse) are the single biggest risk in the security of a company.
Administrators have a higher level of access than normal users which requires additional controls:
● Multi-factor authentication
● Limited access to job function
● Logging of administrator changes
● Dedicated, restricted workstations
● Removal of old administrator accounts
The primary security capability is Identity. One of the primary threats is “Unauthorized Network Access”. A strong Identity solution is required to mitigate against this threat.
The administrator’s device (i.e. laptop, tablet) is used to access tools that administrators use to control and monitor systems that maintain and secure the business applications whether they are secure data center, secure cloud or public SaaS applications. Administrators connect to centralized management systems using secure connectivity with strong encryption (SSH, TLS, VPN) and multi-factor authentication from a variety of devices.
The primary security capabilities are Client-Based Security and Posture Assessment for the device. Client-Based Security includes VPN client, Anti-Malware and Secure Internet Gateway capabilities.
The network is located in a virtual private cloud hosted by a cloud service provider. The foundational capabilities: Firewall, Intrusion Prevention and Tagging are required for protecting the application in the cloud. The cloud service providers offer default firewall capabilities for the various cloud service types they offer. For IaaS deployments, a virtual firewall with L4-L7 firewall protection capabilities with integrated intrusion prevention in the same virtual machine is recommended. The tagging capability will vary by cloud service and could include: VLANs, VXLANs or Security Group Tags (TrustSec).
The foundational capabilities include Anti-Malware, Threat Intelligence and Flow Analytics. One of the primary threats is “Malware propagation” and anti-malware detection of network traffic is required. To mitigate against this threat, the anti-malware solution should operate in-line with the traffic.
Threat Intelligence is recommended for all solution components and should source to a common intelligence feed to stay current with cyber threats. Analysis of the traffic is key to visibility, you can’t protect yourself unless you can see it. A Cloud Analytics Platform is recommended to analyze the traffic to and within the virtual private cloud hosting the applications, and can aggregate different CSPs analytics as well as on-prem data centers.
The servers are the endpoints in the cloud that host web services, applications, and databases. The access capabilities to secure them are Server-Based Security and Posture Assessment. Server-Based Security requires Anti-Malware, Host Based Firewall, Posture Assessment and Patching, Cloud Security, and Disk Encryption.
To secure access to applications beyond foundational and access capabilities, business capabilities must be deployed to manage business risks introduced by the business practice. The primary security capabilities Application Visibility Control, Web Application Firewall, TLS Offload and File Analysis.
Cisco’s Secure Cloud architecture defend the business against corresponding threats using an architectural approach that overcomes the limitations of a point product offering.
SAFE is Cisco’s security reference architecture that simplifies the security challenges of today and prepares for the threats of tomorrow.
This Appendix includes some proposed design examples for Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
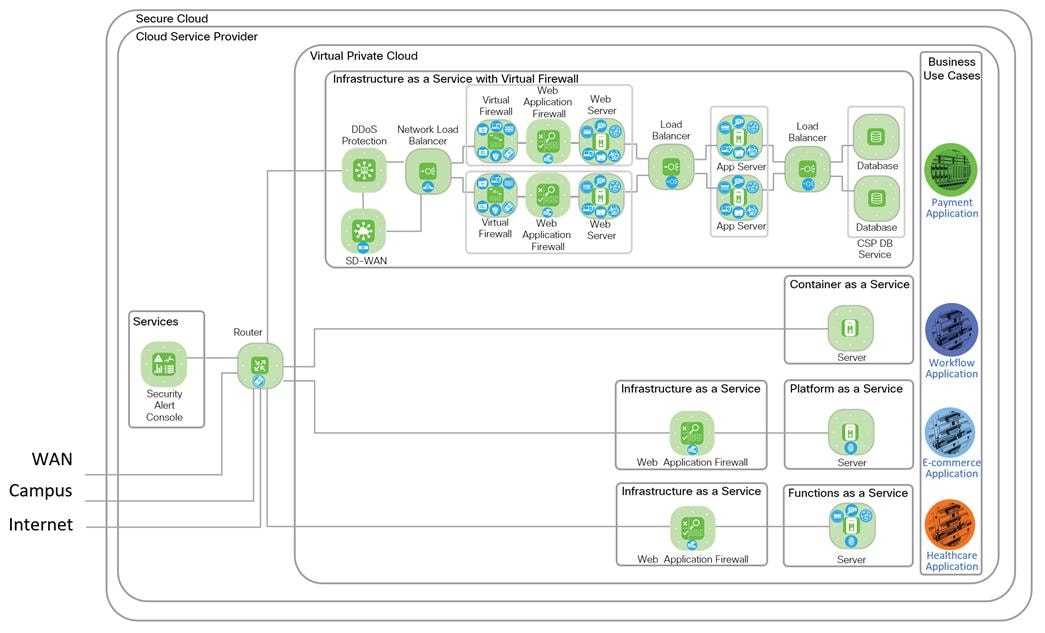
IaaS Design with 3-Tier Web Application
IaaS with Virtual Firewall Design with 3-Tier Web Application
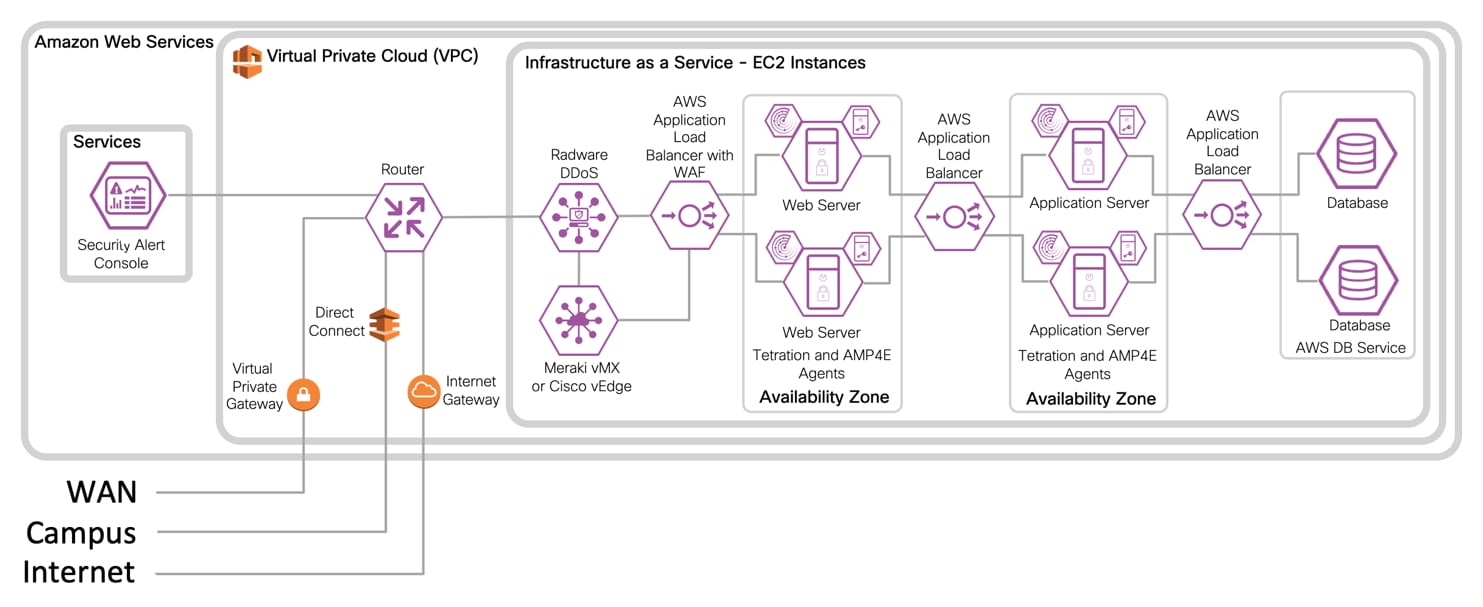
IaaS Design with 3-Tier Web Application
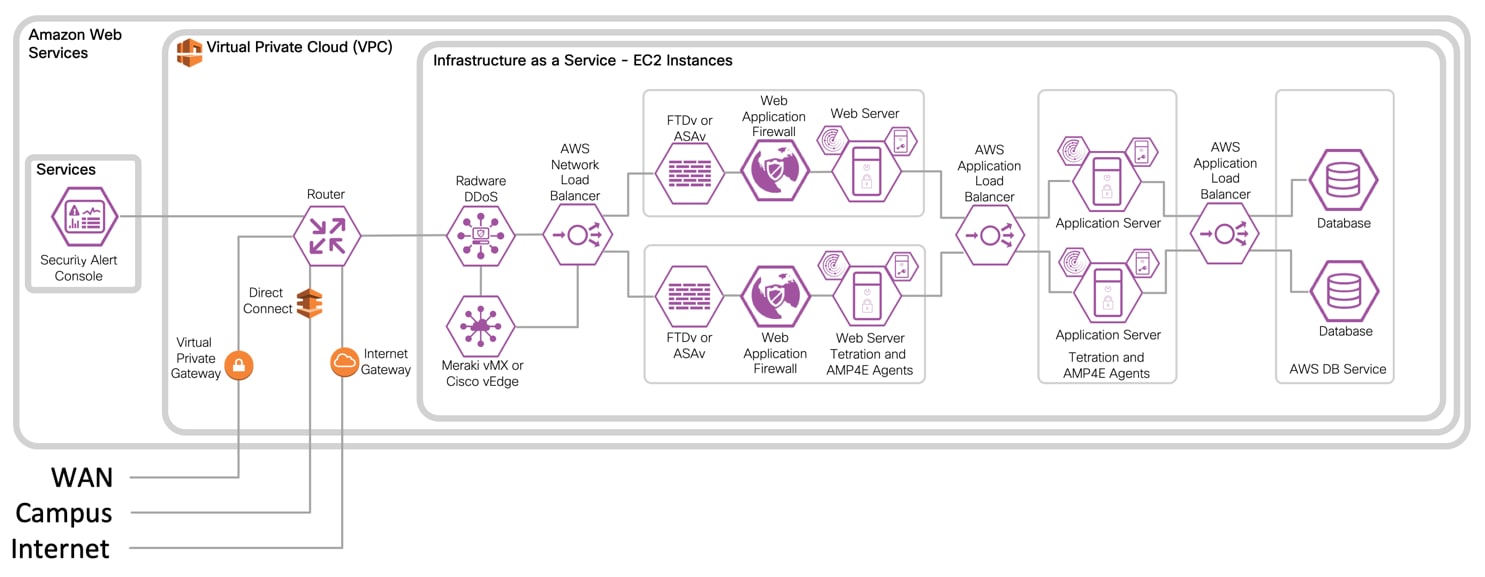
IaaS with Virtual Firewall Design with 3-Tier Web Application
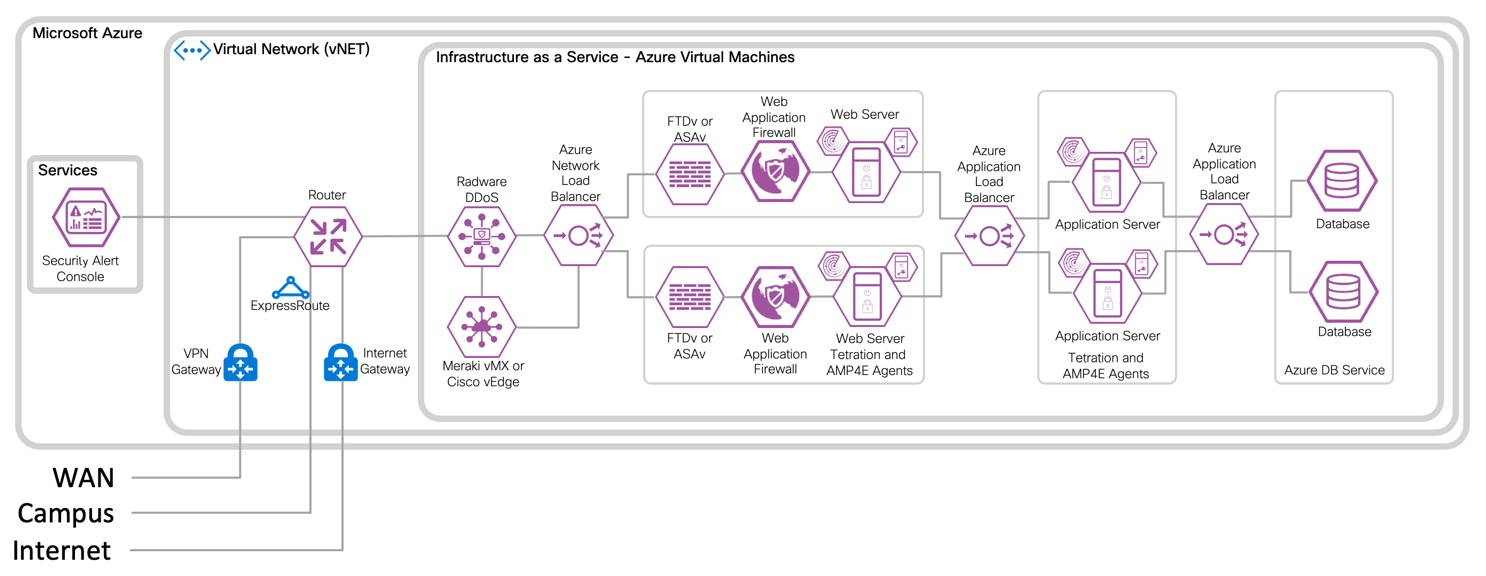
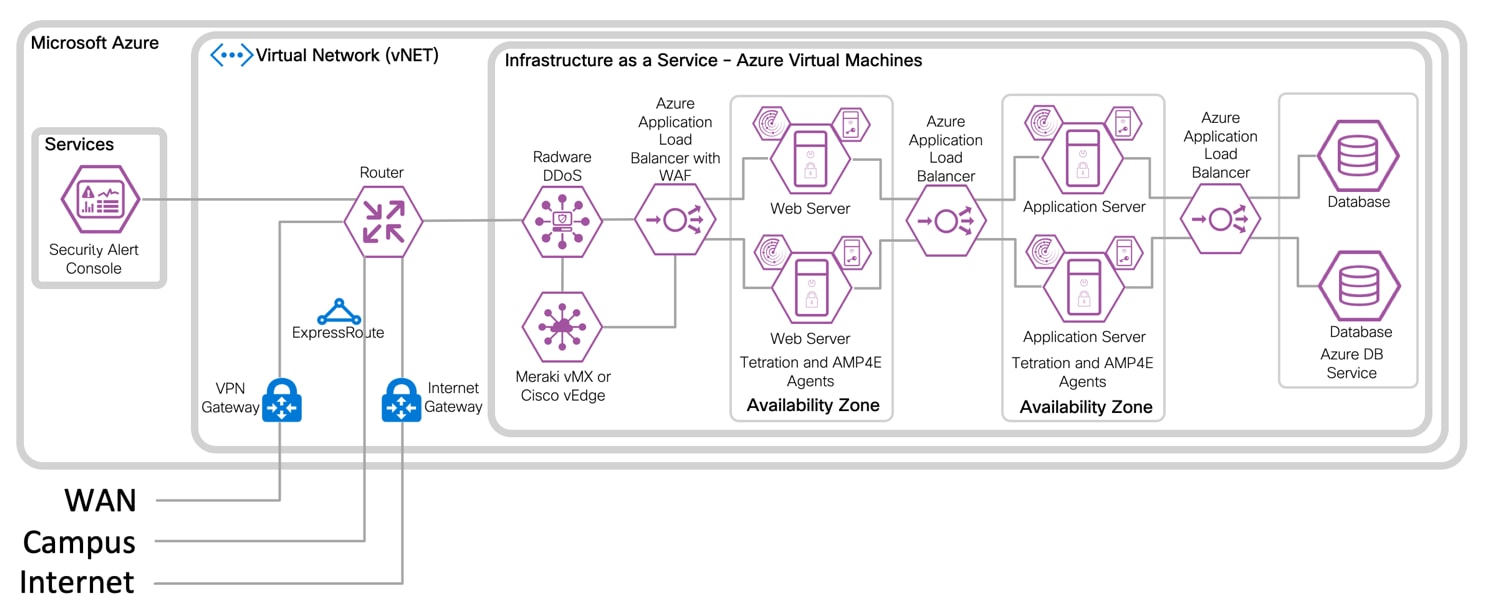
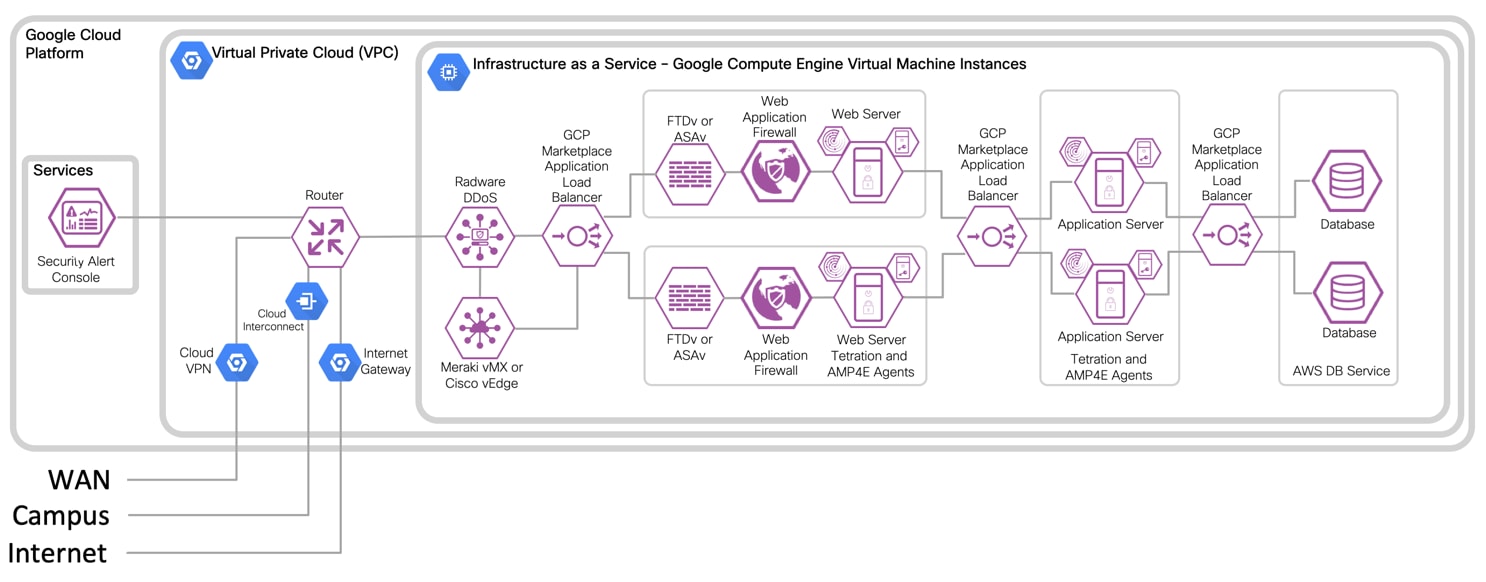
IaaS Design with 3-Tier Web Application
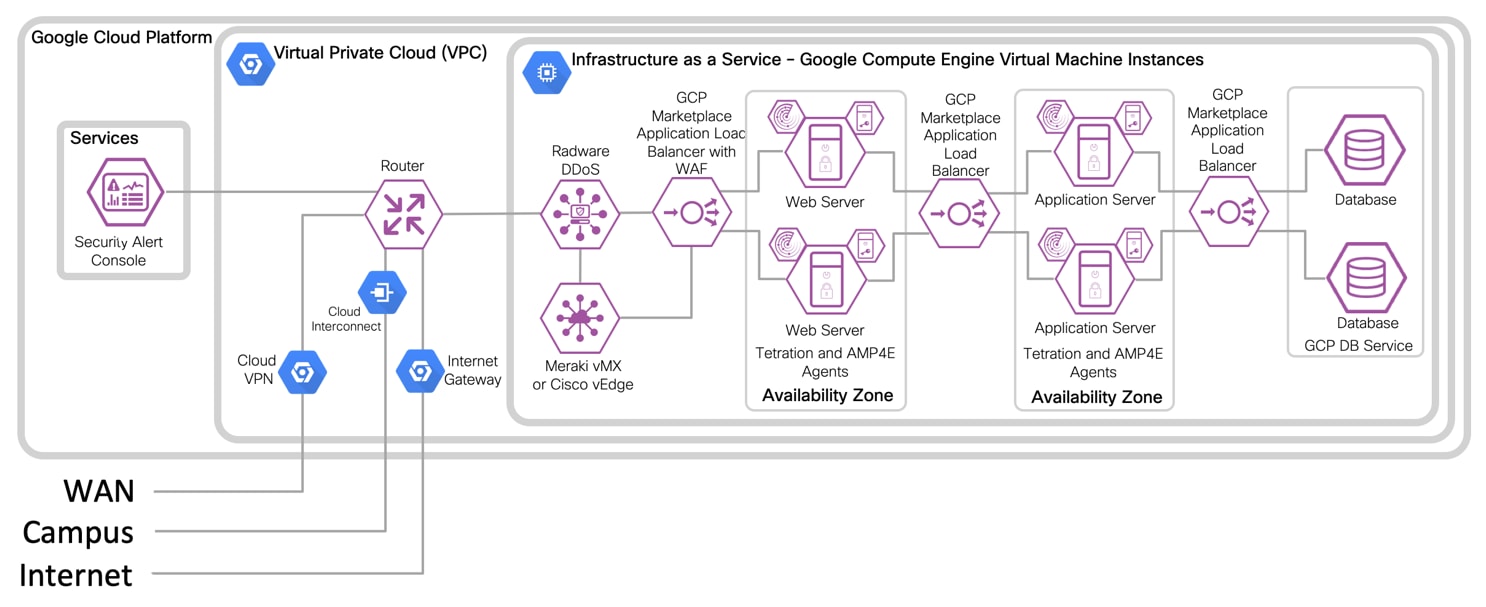
IaaS with Virtual Firewall Design with 3-Tier Web Application
Appendix B - Suggested Components
| Secure Cloud Attack Surface |
Security Capability |
Suggested Cisco Components |
||
| Human |
Users |
|
Identity |
Cisco Secure Access by Duo Cisco Meraki Mobile Device Management |
| Devices |
Endpoints |
|
Client-based Security |
Cisco Secure Client Cisco Secure Endpoint Cisco Umbrella |
|
|
Posture Assessment |
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) Cisco Meraki Mobile Device Management Cisco Secure Access by Duo Cisco Secure Client |
||
| Network |
Cloud Network Infrastructure |
|
Firewall |
Cisco Secure Firewall Cloud Native Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense Virtual (FTDv) Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance Virtual (ASAv) Cisco Cloud Services Router (CSR) |
|
|
Intrusion Prevention System |
Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense Virtual Cisco Secure IPS Virtual |
||
|
|
Tagging |
VLANs/VXLANs TrustSec SGT ACI |
||
| Analysis |
|
Anti-Malware |
Cisco Secure Endpoint |
|
|
|
Threat Intelligence |
Talos Threat Intelligence |
||
|
|
Flow Analytics |
Cisco Secure Cloud Analytics |
||
| WAN |
|
Virtual Private Network (VPN) or Software Defined WAN (SD-WAN) |
Cisco Secure Firewall Cloud Native Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense Virtual Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance Virtual (ASAv) Cisco Meraki Virtual MX Cisco vEdge (Viptela) Cisco Cloud Services Router |
|
|
|
VPN Gateway or Concentrator |
Cisco Secure Firewall Cloud Native Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense Virtual Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance Virtual Cisco Meraki Virtual MX |
||
|
|
DDoS Protection |
Cisco Secure DDoS |
||
| Applications |
Application |
|
Application Visibility Control |
Cisco Secure Workload Cisco Secure Firewall Cloud Native Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense Virtual Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance Virtual Cisco Meraki Virtual MX |
|
|
Web Application Firewall |
Cisco Secure WAF |
||
|
|
File Analysis |
Cisco Secure Malware Analytics |
||
|
|
TLS Encryption Offload |
Cisco Secure Application Delivery Controller (ADC) |
||
| Storage |
|
Disk Encryption |
Cloud Storage Provider |
|
| Server-Based Security |
|
Anti-Malware |
Cisco Secure Endpoint |
|
|
|
Cloud Security |
Cisco Umbrella |
||
|
|
Flow Analytics |
Cisco Secure Cloud Analytics Cisco Secure Workload |
||
|
|
Application Dependency Mapping |
Cisco Secure Workload |
||
|
|
Vulnerability Assessment and Software Inventory |
Cisco Secure Workload |
||
If you have feedback on this design guide or any of the Cisco Security design guides, please send an email to ask-security-cvd@cisco.com.
For more information on SAFE, see www.cisco.com/go/SAFE.