DOCSIS CPE Configurator Shared Secret Troubleshooting
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document explains how the Cisco Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) Configurator handles shared-secret keys.
Cable shared-secret is one mechanism that can be used to reduce theft of service by non-subscribers. It works by using a single shared-secret key configured in both the Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) and the DOCSIS config file that is sent down to cable modems prior to them coming online. If this feature is configured, the cable modem cannot complete registration to the CMTS without the key.
The first step in troubleshooting installations with cable shared-secret (particularly new installations) involves visually verifying that the cable shared-secret configured on the CMTS matches the one in the DOCSIS configuration file.
Before You Begin
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, see the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Prerequisites
The reader must have basic understanding of DOCSIS.
Components Used
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS® Software Release 11.3 XA.
Problem
To visually verify the cable shared-secret on the CMTS, check the configuration with the show run command, as shown in this example.
Router#show running-config interface Cable3/0 Building configuration... interface Cable3/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 no keepalive cable shared-secret SECRET-PASSWORD-TO-SHARE cable map-advance static cable downstream annex B cable downstream modulation 64qam cable downstream interleave-depth 32 cable downstream frequency 583250000 cable upstream 0 frequency 28000000 cable upstream 0 power-level 0 no cable upstream 0 shutdown cable dhcp-giaddr policy cable helper-address 192.168.101.3 !
When the Cisco DOCSIS CPE Configurator is used to open and view the DOCSIS config file in question, however, the cable shared-secret (called CMTS Authentication by the Configurator) does not appear, as shown in this graphic.
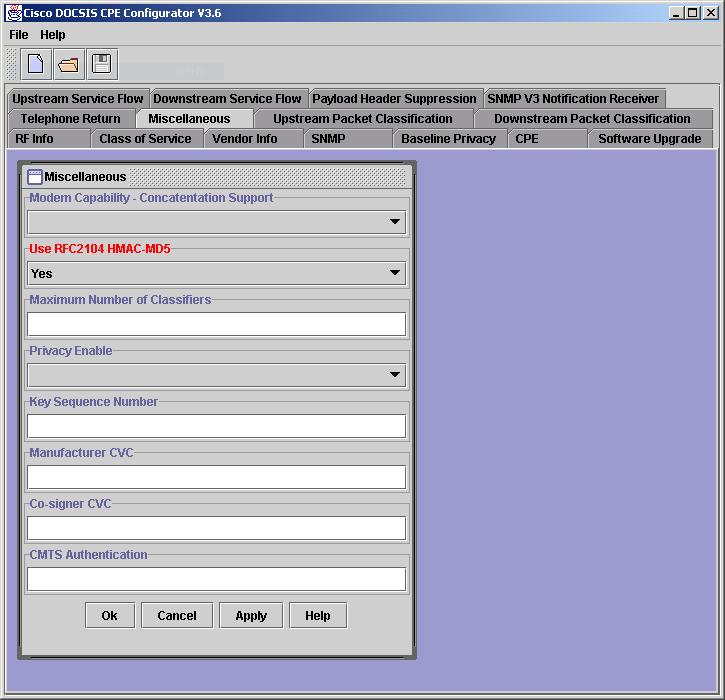
Explanation
By design, the Cisco DOCSIS CPE Configurator does not display the value of the CMTS Authentication field when a file is opened (for security purposes). When a new file is created or an existing one is updated to include the CMTS Authentication feature, however, the value can be seen as long as that Configurator session is open and active. Once the Configurator session on a given file ends (Configurator is closed or a different file opened), the CMTS Authentication value cannot be seen again.
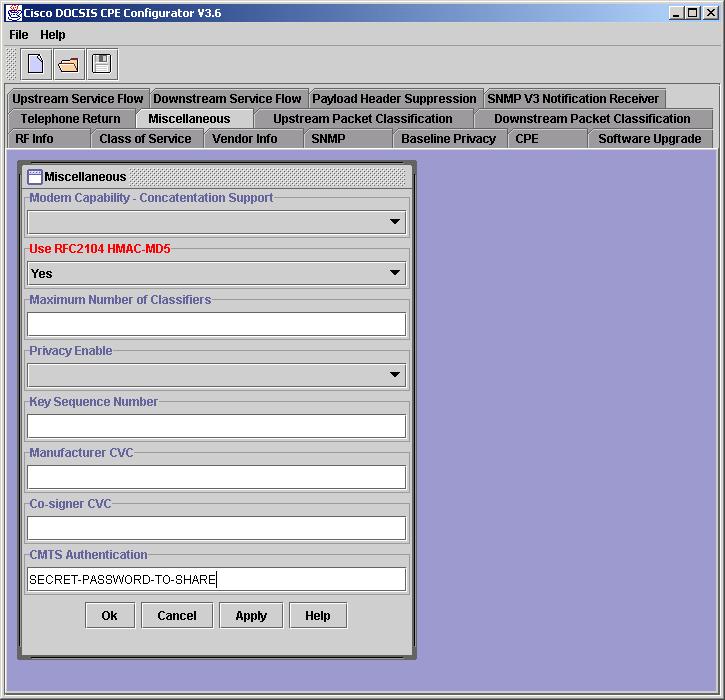
Note: Use caution when you overwrite existing files with the Cisco DOCSIS CPE Configurator. The CMTS Authentication value can be corrupted by overwriting an existing file. When possible, add CMTS Authentication to an existing file, then save to a new filename. When reuse of the same filename is required, save the updated file to a different filename and end the Configurator session (exit the Configurator or open a new file). You can issue command-line interface (CLI) commands or use GUI tools to change the filename to the desired, pre-existing one. In DOS, use the rename or copy commands; in UNIX, use the mv command; or inWindows Explorer, right-click the file and choose Rename.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
23-Aug-2006 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback