Sample Extension for Provisioning Additional Operating System Types
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
Cisco Intelligent Automation for Cloud (IAC) supports adding a mechanism to use external Operating Systems (OSes) using Cisco Process Orchestrator Extension Points. It is configured via modifications to the standards table in Cisco Cloud Portal to allow access to those Extension Points. Note that no changes to Process Orchestrator workflows are needed for these modifications.
Before You Begin
Requirements
Before starting the configuration procedure, please ensure that you have:
-
Valid login credentials for Cisco Process Orchestrator with adequate permissions to edit processes. This includes the knowledge and understanding to operate Process Orchestrator.
-
Valid login credentials for Cisco Cloud Portal with adequate permissions to edit Service tables. This includes the knowledge and understanding to operate Cloud Portal.
-
Downloaded the TAP named IAC_OS_Extension_Point_Examples.tap.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the hardware and software versions supported in Cisco Intelligent Automation for Cloud 3.x (any version).
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Configuration Steps in Cloud Portal
In order to add to the supported Operating Systems (OSes) for any server provisioning within Cloud Portal, you may first have to modify the standards tables for OS Types and OS Systems to add needed OS types and OSes to the list.
NOTE: The Cloud Portal service Order a Physical Server requires no customization of Process Orchestrator workflows.
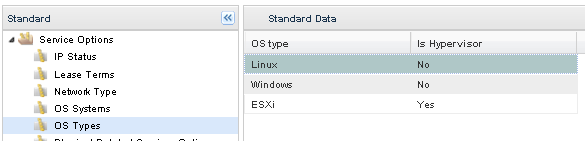
Modify Standard Table: OS Types
Most OSes are of one of the following: Windows, Linux, or ESXi. If you need to add another OS type, it must be added to the OS Types standards table.
Standards Table: OS Types
-
In Cloud Portal, go to Service Item Manager > Manage Standards > Service Options > OS Types.
-
If the correct OS Type does not exist, click Add New and enter information specific to the new operating system. Click Save to keep your changes. For example, to add an OS Type for Solaris, enter UNIX as an OS Type and No in the Is Hypervisor field.
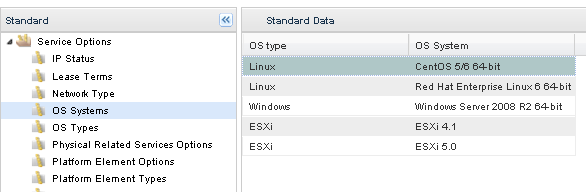
Modify Standard Table: OS Systems
After verifying that your OS Type exists in the OS Types standard table, you will need to add the specific OS System to the OS Systems table.
Standards Table: OS Systems
-
In Cloud Portal, go to Service Item Manager > Manage Standards > Service Options > OS Systems.
-
Click Add New and enter information specific to the new operating system. Click Save to keep your changes. For example, to add an OS System for Ubuntu 12.04 x64, enter Linux as the OS Type and Ubuntu 12.04 x64 as the OS System.
Configuration Steps in Process Orchestrator
The following Process Orchestrator extension points are described in this document:
-
Create Virtual Machine >> Other - Ubuntu and Windows 7
-
Customize Virtual Machine >> Other - UNIX
Extending Process Orchestrator Processes Using Extension Points
IAC features editable processes called Extension Points that are integrated into the content, allowing the ability to extend its functionality. The TAP named IAC_OS_Extension_Point_Examples.tap contains both Extension Point examples mentioned above. They are identified by the presence of '>>' within the name of those processes. To use these Extension Points, create child processes that contain custom workflows and insert them into the Extension Point. Below is an illustrated example of how to do this. Cisco does not recommend adding anything other than child processes directly to the workflow of an Extension Point.
Install the Extension Points in Process Orchestrator as follows:
-
In the Process Orchestrator console, go to Administration > Automation Packs > Import (right mouse), and import the automation pack into Process Orchestrator.
-
Edit the relevant extension point process (for example, Create Virtual Server >> User Defined).
-
Find the desired child process by selecting Processes from the Toolbox on the left of the Process Orchestrator console, and drag the child process into the workflow.
-
Click Save and close the edit window.
Modify Extension Point: Create Virtual Machine >> Other - Ubuntu and Windows 7
To support additional operating systems for the Order a Virtual Machine and Install OS service, you will need to modify this extension point. Any VMWare supported OS can be used when utilizing this service. However, OS customizations are only "officially" supported for built-in standard OSes. To extend customization support for additional OS types, open the Create Virtual Machine Other process (Note: For context see the parent process: Create Virtual Server). You can use the existing workflow in Create Virtual Server as a guideline for constructing your own workflow to support additional OSes.
Modify Extension Point: Customize Virtual Machine >> Other - UNIX
To support additional operating systems for the Order a Virtual Machine from Template service, you will need to modify this extension point. Any VMWare supported OS can be used when utilizing this service. However, OS customizations are only "officially" supported for built-in standard OSes. To extend customization support for additional OS types, open the Customize Virtual Machine Other process (Note: For context see the parent process: Customize Virtual Server). You can use the existing workflow in Customize Virtual Server as a guideline for constructing your own workflow to support additional OS customizations.
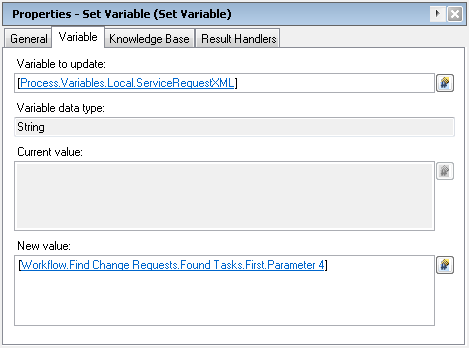
Every Cloud Portal service issues a request to Process Orchestrator with a set of instructions and data called the Service Request XML. The Service Request XML becomes a parameter of the Change Request that is created each time Process Orchestrator instantiates a request from the Cloud Portal. To access this data, you will need to reference Parameter 4 of the Change Request.
A Service Target is also instantiated for each Cloud Portal request. The Service Target contains a collection of Extended Target Properties that are unique to each instance and are used throughout a service request to store different kinds of data. The Cloud Portal Service Request Handler instantiates the Service Target and sets it as the affected target of the Change Request.
Once a Change Request is created, a process is triggered to service that request and uses the Service Target as its process target, as do all of its children (including its Extension Points). Because of this, you can get to the Change Request via the Service Target. You have access to the Service Target because it is the process target of the Extension Point. The activity you will need to use is a Find Change Requests. On the Search Criteria tab, the activity will ask you how far back in time you would like to look for Change Requests that were created, what state to filter by, and criteria for your search. For Search tasks created within the past:, any sensible answer is fine. Clicking the seconds link will allow you to change the interval to minutes, hours, or days. The safer choice, however, would probably be to set it for a longer period of time as opposed to a shorter one. You want to search for tasks that are in a state of Not Completed and then you will need to add some criteria. Click Add and use the following criteria: [Change Request.Affected Target.Name] equals [Process.Target.Name]
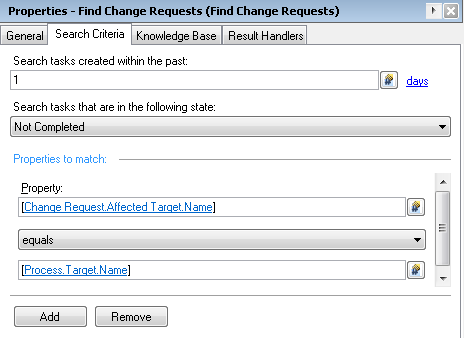
You can then reference the Service Request XML by Parameter 4 of the results of that activity.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
17-Feb-2013 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback