Introduction
This document describes how to troubleshoot or debug IOX applications which encounters issue in getting started or stops unexpectedly.
Background Information
When you develope IOX applications, the best approach is to develope it on another platform and/or sandbox. Once your desired IOX application is tested and ready, it can be packaged and deployed on an IOX-enable device. In some cases, that deployment doesn't work as expected, the application might stop unexpectedly or may not even start.
The default behavior for and IOX VM/container/application is to stop as soon as the target command has terminated. This makes it difficult to troubleshoot if something unexpected happens as all non-persistent information will be disappeared. Another consequence is that it is very time consuming when you want to play/experiment with the capabilities of IOX applications. Starting another app/target/command/script would require you to at least change the package.yaml, build the new package, deactivate your current application, upgrade with the new package, re-activate the application and start it.
Basic Information on IOX Application Termination
Local Manager and IOX client do not provide a lot of information on the reason why applications/containers/VMs have stopped. Fortunately, the watchDog.log keeps track of this and also provides you with the last exit/return code of the application. Although this might not always help you, in a lot of cases it leads you to the reason you are looking for.
To fetch the watchDog.log with IOX client:
[jedepuyd@db ~]$ ioxclient app logs tail iox_docker_test watchDog.log 10
Currently active profile : default
Command Name: application-logs-tail
App/Service : iox_docker_test, Logfile : watchDog.log, viewing last 10 lines
APP END TIME:1498207460
Time taken by App : 0 minutes and 0 seconds.
Got the ip address - 10.197.215.227 for interface eth0
All interfaces got the ips
APP START TIME:1498207536
App iox_docker_test started with PID : 11
Monitoring this process now
App iox_docker_test completed with exit code: 127
APP END TIME:1498207536
Time taken by App : 0 minutes and 0 seconds.
To fetch the log using Local Manager:
- Log in to Local Manager.
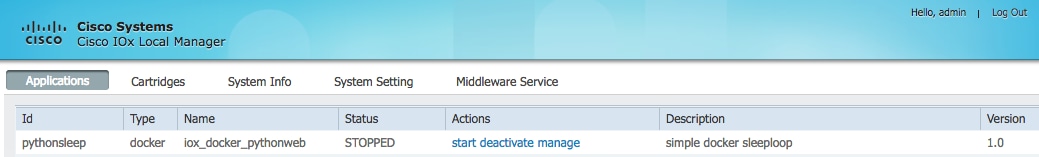
- As shown in the image, click on start deactivate manage for the relevant application
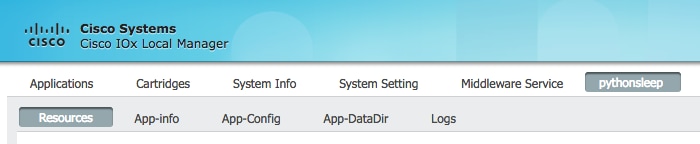
- Select Logs tab, as shown in the image:
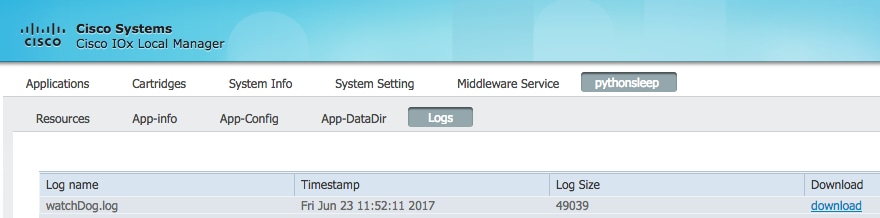
- Download the watchDog.log
For example, this application is terminated unexpectedly and you see this in the watchDog.log
APP START TIME:1498207536
App iox_docker_test started with PID : 11
Monitoring this process now
App iox_docker_test completed with exit code: 127
APP END TIME:1498207536
As you can see in the above log snippet, the exit code was 127. This is a reserved return code and it means: command not found, which indicates a faulty command is specified as a target or the script which is started tries to call a faulty command.
Most common reserved exit codes:
| RC |
Meaning |
Comment |
| 1 |
Catchall for general errors |
Miscellaneous errors, such as "divide by zero" and other impermissible operations |
| 2 |
Misuse of shell builtins |
Missing keyword or command, or permission problem (and diff return code on a failed binary file comparison). |
| 126 |
Command could not be executed |
Permission problem or command is not an executable |
| 127 |
Command not found |
Possible problem with $PATH or a typo |
| 128 |
Invalid argument to exit (RC>255) |
exit takes only integer args in the range 0 - 255 |
| 128+n |
Fatal error signal "n" |
exit code returns 137 (128 + 9) -> app error signal was 9 |
| 130 |
Terminated by Ctrl+c |
Control-C is fatal error signal 2, (130 = 128 + 2, see above) |
| 255 |
Exit status out of range (RC>255) |
exit takes only integer args in the range 0 - 255 |
More information on this can be found here: http://tldp.org/LDP/abs/html/exitcodes.html
Preventing IOX Containers from Stopping on Application/Target Termination
The above topic provides information on how to troubleshoot a failing application but it doesn't prevent the IOX application from stopping. This means that most likely valuable information related to troubleshooting has disappeared as all non-persistent data no longer exists.
As mentioned above, another use case is to play with the capabilities of the started IOX-application or to be flexible with commands and arguments.
To prevent IOX applications from terminating on application end, you can pass the -debug on to the activate command:
[jedepuyd@db ~]$ ioxclient app activate -debug on testdebug
Currently active profile : default
Command Name: application-activate
App testdebug is Activated
[jedepuyd@db ~]$ ioxclient app start testdebug
Currently active profile : default
Command Name: application-start
App testdebug is Started
[jedepuyd@db ~]$ ioxclient app console testdebug
Currently active profile : default
Command Name: application-console
Console setup is complete..
Running command : [ssh -p 2222 -i testdebug.pem appconsole@10.48.43.197]
/ #
In the above example, after activating and starting with the -debug on flag, you can access the container even if the application is terminated. You can launch other commands here and can freely experiment with the application in the environment where your application runs. This saves a lot of time in solving application issues or getting the right target and arguments set.
