Configuring Dialer Profiles to Bridge using ISDN
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration for bridging two different sites over ISDN using one B channel per site using dialer profiles.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Before you attempt this configuration, you need to gather this information from the ISDN service provider:
-
The ISDN switch type
-
ISDN Service Profile Identifiers (SPIDs) and Local Directory Numbers (LDNs), where applicable. In North America, SPIDS are required for all ISDN switch types except for 5ESS custom point-to-point. The LDN is the local seven-digit ISDN phone number (no area codes) of your router. LDNs are required for DMS-100.
You also need to gather this network information:
-
The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) hostname - You must assign a PPP client name to both devices.
-
The PPP authentication type - Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) authentication is preferred and is used in this example.
-
The PPP password - You must assign a PPP password to all locations.
-
IP address information - You must create an IP network design.
-
Phone numbers - ISDN phone numbers of both locations.
-
Username and passwords.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Background Information
Dialer profiles allow the configuration of physical interfaces to be separated from the logical configuration required for a call. With dialer profiles, the logical and physical configurations are dynamically bound on a per-call basis.
Note: You cannot bridge on one B channel and route on the other channel.
Configure
This section present information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: To find additional information on the commands used in this document, use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) .
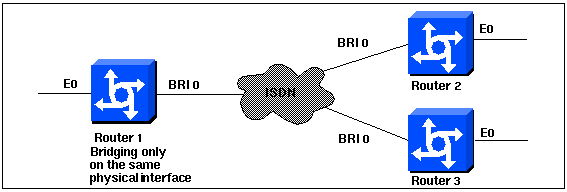
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Configurations
| Router 1 |
|---|
Current configuration: ! version 11.2 service udp-small-servers service tcp-small-servers ! hostname Router1 no ip routing ! enable password foo ! username Router2 password bar username Router3 password bar isdn switch-type basic-5ess ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 media-type 10BaseT bridge-group 1 ! interface BRI0 no ip address no ip mroute-cache encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache dialer pool-member 1 ppp authentication chap ! interface Dialer0 no ip address no ip mroute-cache encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache dialer remote-name Router2 dialer string 5552323 dialer pool 1 dialer-group 2 no fair-queue no cdp enable ppp authentication chap bridge-group 1 ! interface Dialer1 no ip address no ip mroute-cache encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache dialer remote-name Router3 dialer string 5553434 dialer pool 1 dialer-group 2 no cdp enable ppp authentication chap bridge-group 1 ! dialer-list 2 protocol bridge permit bridge 1 protocol ieee end |
| Router 2 |
|---|
Current configuration: ! version 11.2 service udp-small-servers service tcp-small-servers ! hostname Router2 no ip routing ! enable password foo ! username Router1 password bar isdn switch-type basic-5ess ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 no ip route-cache bridge-group 1 ! interface BRI0 no ip address encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache dialer pool-member 1 ! interface Dialer0 no ip address encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache dialer remote-name Router1 dialer string 5551212 dialer pool 1 dialer-group 2 no fair-queue no cdp enable ppp authentication chap bridge-group 1 ! dialer-list 2 protocol bridge permit bridge 1 protocol ieee ! end |
| Router 3 |
|---|
Current configuration: ! version 11.2 service udp-small-servers service tcp-small-servers ! hostname Router3 no ip routing ! username Router1 password bar isdn switch-type basic-5ess ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 10.1.1.3 255.255.255.0 no ip route-cache bridge-group 1 ! interface BRI0 no ip address encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache dialer pool-member 1 ppp authentication chap ! interface Dialer0 no ip address encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache dialer remote-name Router1 dialer string 5551212 dialer pool 1 dialer-group 2 no cdp enable ppp authentication chap bridge-group 1 ! dialer-list 2 protocol bridge permit bridge 1 protocol ieee ! end |
Verify
There is currently no verification procedure available for this configuration.
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
Troubleshooting Commands
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Before issuing debug commands, refer to Important Information on Debug Commands.
-
debug ppp authentication — To see if a client passes authentication. If you use a version prior to Cisco IOS® Software Release 11.2, use the debug ppp chap command instead.
-
debug ppp negotiation — To see if a client passes Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) negotiation; this is when you check for address negotiation.
-
debug ppp error — To display protocol errors and error statistics associated with PPP connection negotiation and operation.
-
debug isdn q931 — To check ISDN connections as users dial in, in order to see what is happening with the ISDN call (for example, if the connection is being dropped).
-
show isdn status — The status should be:
layer 1 = active layer 2 = MULTIPLE_FRAMES_ESTABLISHED
If Layer 1 is not active, then the wiring adapter or port may be bad or not plugged in. If Layer 2 is in a state of TEI_Assign, then the router is not talking to the switch.
-
show bridge — To view classes of entries in the bridge forwarding database.
-
show span — To display the spanning-tree topology known to the router.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
04-Feb-2010 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback