Introduction
This document describes how to clear the replication in Hyperflex.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends knowledge in these topics:
- Unified Computing System Manager (UCSM)
- HyperFlex
- vCenter
- Networking
- DNS
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- HyperFlex Connect 5.0.2d
- Hyperflex Stretch Cluster
- Hyperflex Standard Cluster
- UCSM 4.2(1l)
- vCenter 7.0 U3
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Replication configuration can be cleared if necessary, clusters can be paired with new targets, to do that, the current replication configuration needs to be cleared from the cluster.
Additional Background Information
- For clearing the data protection, you must unprotect all the VMs. Then, remove them from the protection groups.
- Protection Groups can remain on the cluster if no VMs belong to them.
- Ensure dependencies from replication pairs are removed in both types of clusters, local and remote.
- Administrator access for both clusters is required for this operation.
Procedure
Step 1. Log into the Hyperflex system as administrator and go to the Replication option in the left action pane:
 Replication Option
Replication Option
Step 2. To unprotect the VMs, navigate to Local VMs > All Protected VMs. Pick the check box to select all VMs. Then click Unprotect.
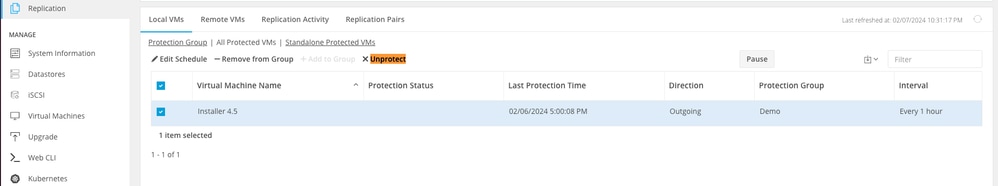 Unprotect VMs
Unprotect VMs
Step 3. Remove the VMs from the protection group, navigate to Local VMs > All Protected VMs. Pick the check box to select all VMs.Then click Remove from Group.
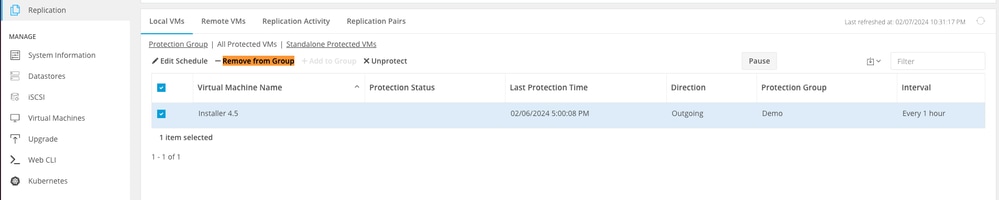 Remove VMs from Protection Groups
Remove VMs from Protection Groups
A prompt ask you if you want to unprotect the VMs. Click Unprotect.
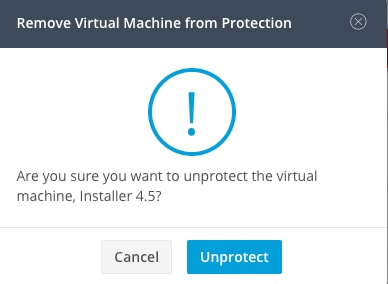 Uprotect Confirmation
Uprotect Confirmation
Once unprotected, the VMs no longer appear in the list.
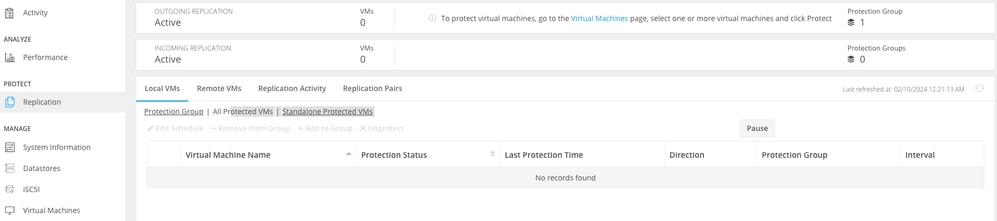 VM Protection Clear
VM Protection Clear
Unprotected VM behaviors
- If you want to unprotect the VM you are required to have connectivity between the clusters through the eth2.
-
When the VM is not removed from the protection, use ping to test connectivity, and check if the eth2 is running. If there is no connectivity and the eth2is not running,open a case with TAC.
It is a best practice to delete the protection groups if no VMs belong to them. This is not required.
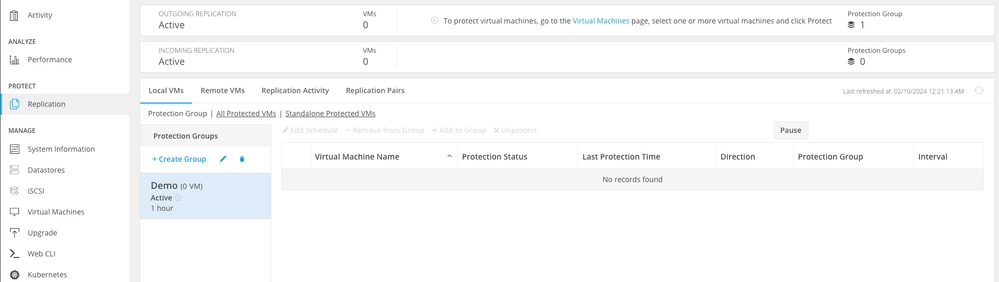 Delete Protection Groups
Delete Protection Groups
A prompt ask you if you want to delete the protection group. Click Delete:
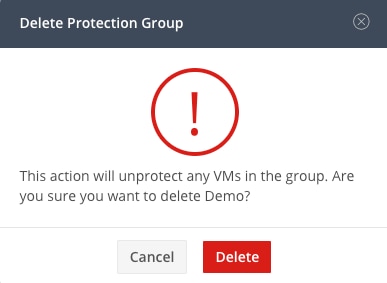 Protection Group Deletion Confirmation
Protection Group Deletion Confirmation
Step 4. Remove datastore mapping and select
 Remove Datastore Dependencies
Remove Datastore Dependencies
You are prompted to select which datastores to unmapped. Select the remote and choose the Do not map this datastore option for each of the mapped datastores. Then click on Map Datastore.
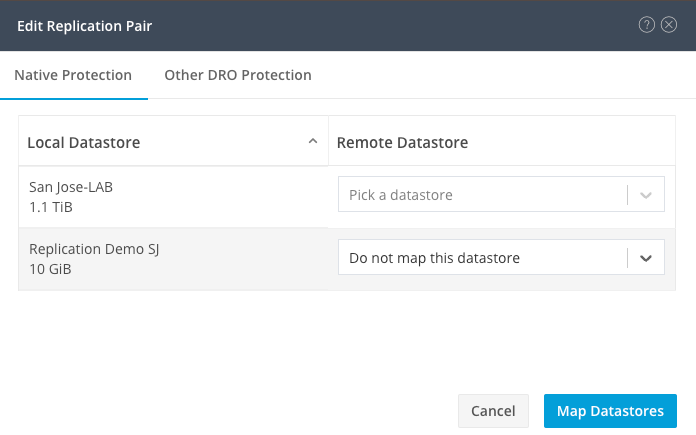 Unmap Datastores
Unmap Datastores

Note: Once the datastores are unmapped, the HX connect needs to be refreshed to proceed with the replication pair deletion.
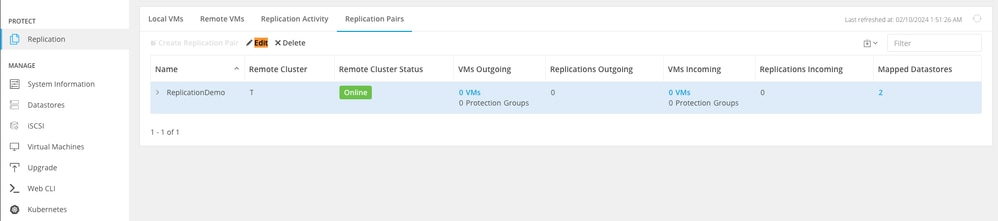
Step 5. Delete the replication pairs the local and remote clusters. Select .
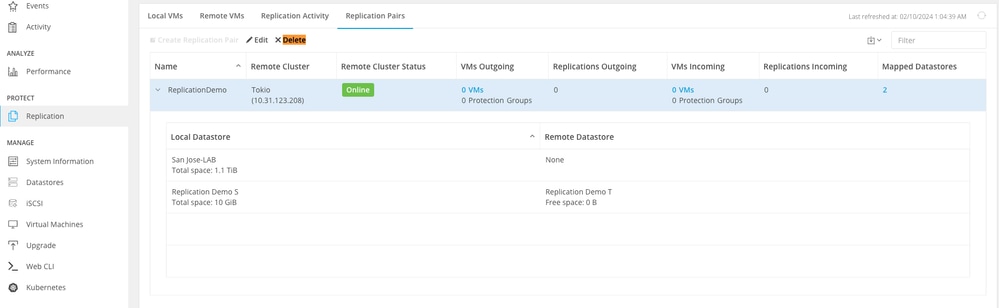 Delete Pairs
Delete Pairs
You need remote cluster Admin credentials to remove the pair. Enter the credentials and click on Delete
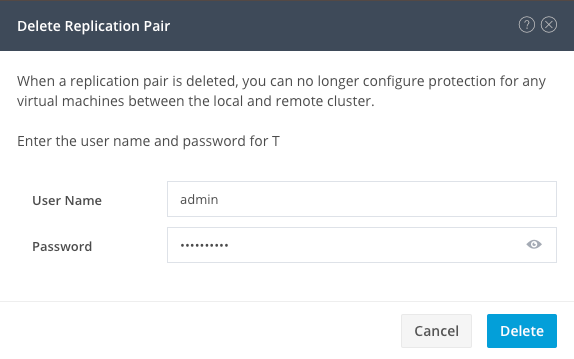 Peer Deletion Confirmation
Peer Deletion Confirmation
Behavior of Replication Pair
- When a replication pair is deleted, you can no longer configure protection for any virtual machines between the local and remote cluster.
- This action clears the protection in both clusters
- A replication network test is done when the replication pair is attempted to be done or modified.
- A replication network test is also done when the datastores are attempted to be unmapped.
- If the replication test does not pass, the changes are not allowed. Refer to the Troubleshoot session in this document to check connectivity if necessary.
- For further assistance regarding the eth2 connectivity, open a case with TAC.
Step 6. To clear the replication network, use the command:
stcli drnetwork cleanup
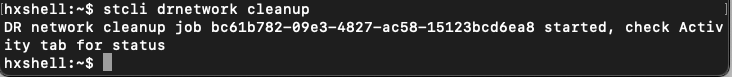 CleanUp Local
CleanUp Local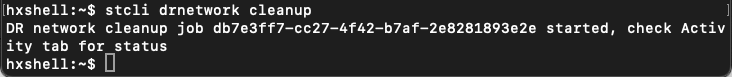 CleanUp Remote
CleanUp Remote

Note: Ensure the stcli drnetwork cleanup command is executed in both local and remote clusters.
Data replication network clean up can be monitored in the Activity tab in HX connect
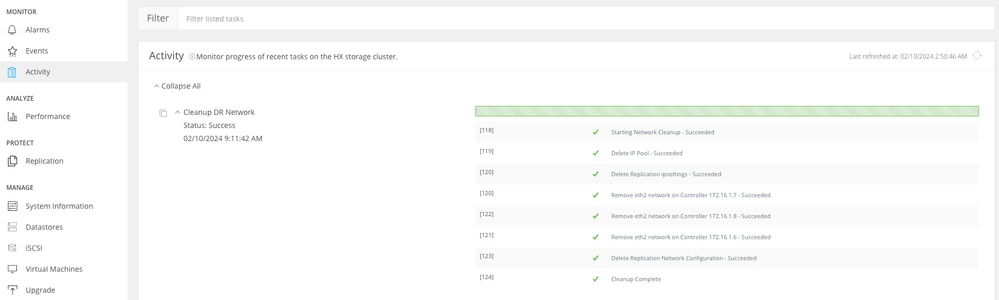 Monitor Data Replication Network CleanUp
Monitor Data Replication Network CleanUp
Refresh HX connect data replication network configuration appears unconfigured and ready to be configured again if required.
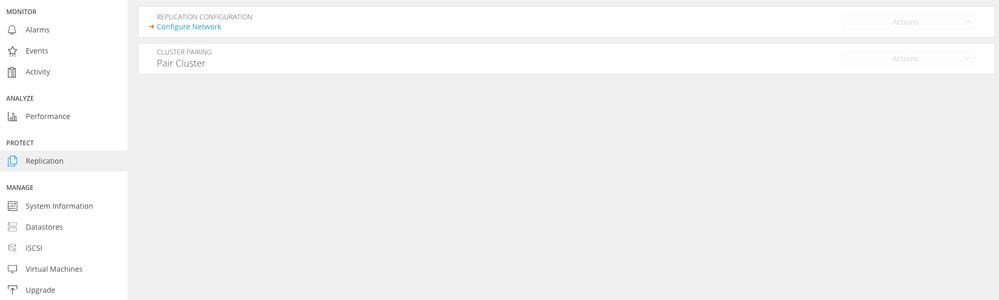 Data Replication Network Cleared
Data Replication Network Cleared
Troubleshoot
Verify VMs Protection
Ensure no VMs are being protected. To check this use the command:
stcli dp vm list --brief
Example with a protected VM:
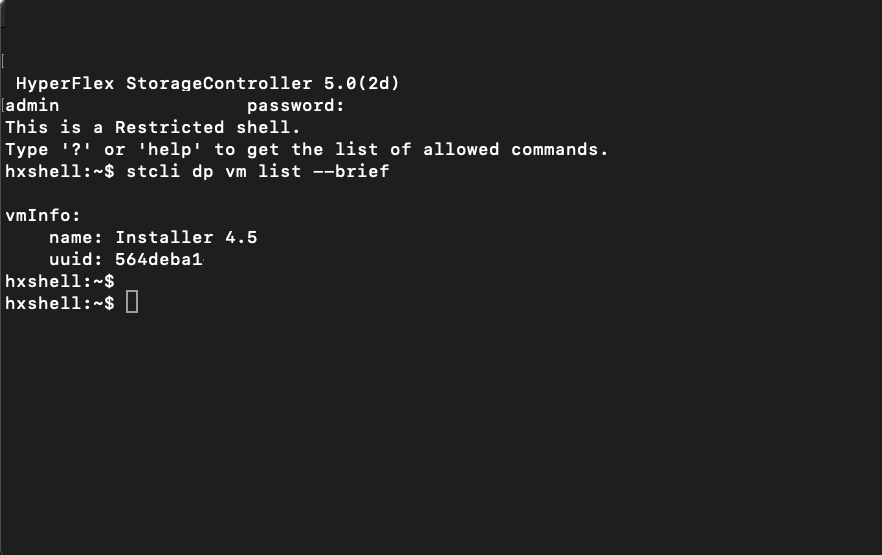 How to List Protected VMs
How to List Protected VMs
Example with no VM protected
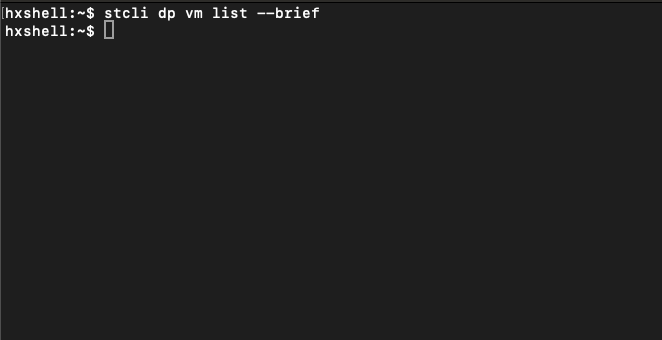 No VM Protected
No VM Protected

Note: Ensure no VMs are protected. The next image shows an example of the VM protection.
Check Data Protection Peer List
The Peer List can be checked. To ensure no entries appear when the replication is cleared, use the command:
stcli dp peer list
Example for data protection peer configured:
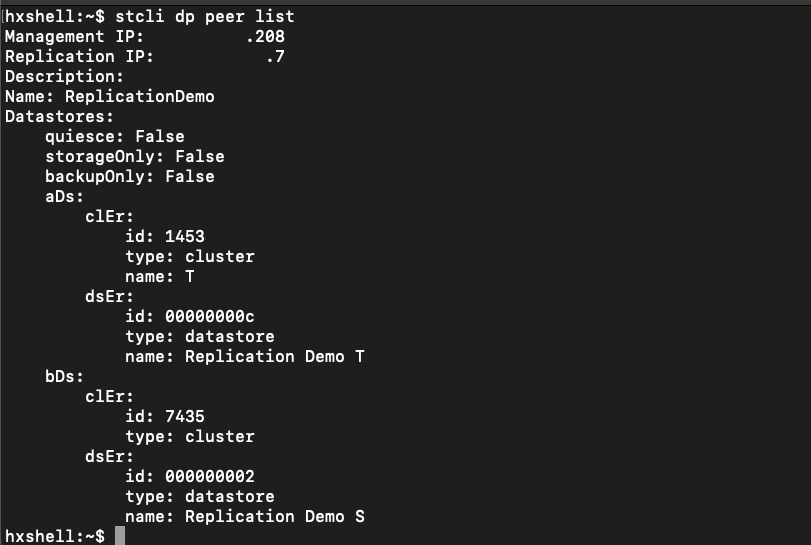 How to Check Peer List
How to Check Peer List
This is an example for the cleared data protection peer:
 Peer Cleared Example
Peer Cleared Example
Delete Manually the Peer When Necessary
In case the remote peer is permanently unavailable, or not available for a long period of time, this command is for clearing the peer relation:
stcli dp peer forget --name <pair-name>
Example of the peer forget command:
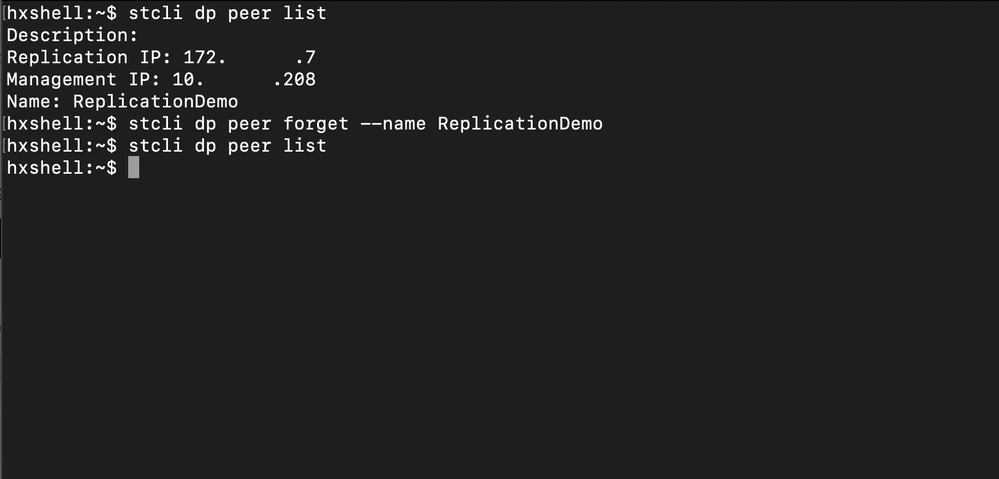 Replication Peer Forget Command
Replication Peer Forget Command
Take into account
- The cluster pairing is cleared from the HX connect as shown in the procedure in this document
- If this command is issued by mistake in one of the clusters when they still have connectivity with each other, ensure it is executed in the other peer as well.
- The command only clears the peer details on the cluster where it is executed.
Common Issues
Dependencies issues
Ensure VM protection is removed along with datastore mapping.
When trying to delete a replication pair without removing the VM Protection/Datastore Mapping, a pop up window appears indicating the dependencies must be cleared.
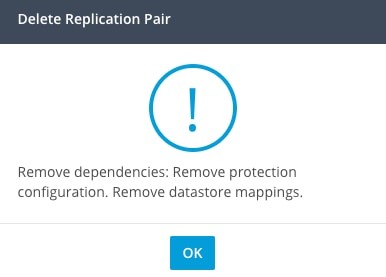 Peer Deletion Error
Peer Deletion Error

Note: It is expected this operation cannot be completed if communication issues are present between the cluster on the eth2 network.
Connectivity Issues
Connectivity issues can lead to difficulties with the clean up proccess because each of the storage controller virtual machines from each cluster are in active communication with their peers through the eth2. If at least one controller virtual machine does not response through the eth2 network, it can cause the replication and cleanup activities to fail.
- Verify the eth2 is present. Use the ifconfig command on eachstorage Controller virtual machines to confirm the eth2 appears up, if not up TAC intervention is needed.
- Use ping to test connectivity between the eth2 interfaces for each storage controller virtual machines.
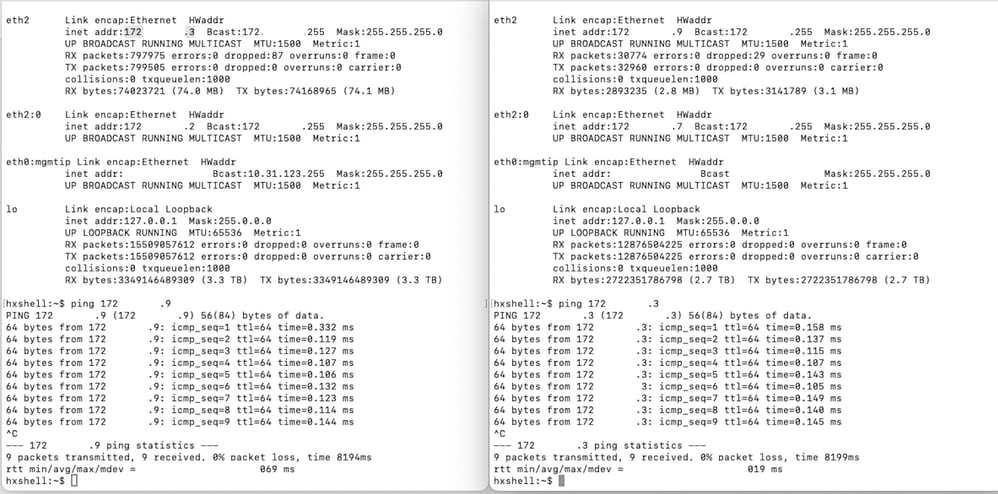 Eth2 Ping Test Example
Eth2 Ping Test Example
- Ensure the Replication VLAN in both clusters match.
- Ensure the replication VLAN is properly configured in all the paths between the clusters.
- Ensure the MTU matches in both clusters local and remote for the replication network
- Use the Test Remote Replication Network Option to verify connectivity. Select Replication, in the cluster pairing, select Actions > Test Remote Replication Network:
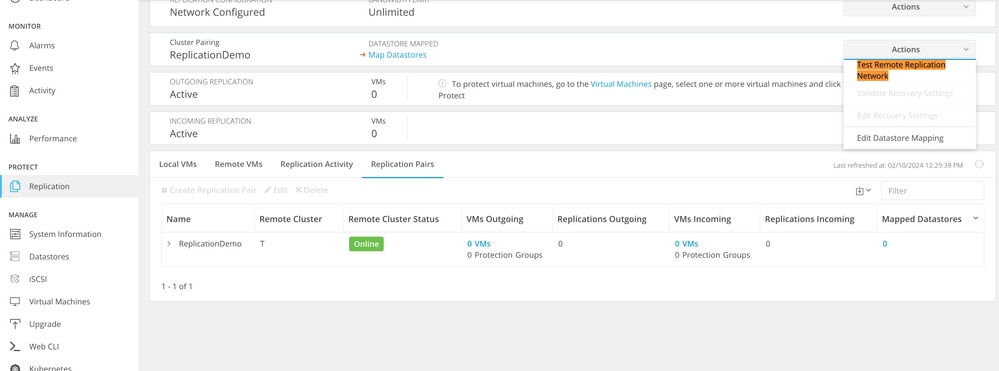 Test Remote Replication Network
Test Remote Replication Network
- Monitor this operation in the Activity tab.
Example of a successful test:
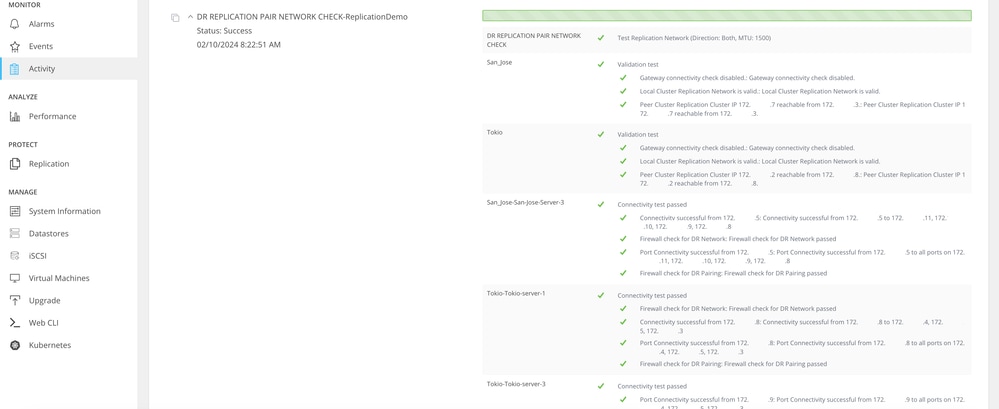 Successful Test Example
Successful Test Example
Example of a failed test:
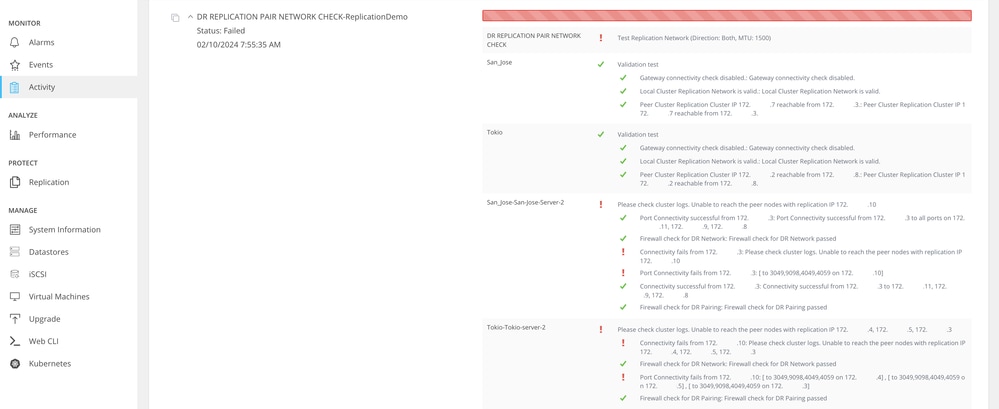 Unsuccessful Test
Unsuccessful Test
Related Information



























 Feedback
Feedback