Configure Model-driven Telemetry on Cisco IOS-XE Devices with YANG Suite
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to configure model-driven telemetry on Cisco IOS®-XE devices with the use of YANG Suite to perform sample Telemetry Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs).
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Knowledge of YANG is needed to understand the data that is required when using telemetry.
- Knowledge of NETCONF operations, such as get, get-config, edit-config.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- CSR1000V with Cisco IOS XE 17.3.3
- Cisco YANG Suite version 2.8
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Related Products
This document can also be used with these hardware and software versions: Cisco IOS XE devices, including Cisco Catalyst 9000 switches, Cisco ASR 1000, ISR 4000 and CSR 1000 routers.
Background Information
YANG Suite needs to be installed. For more information on YANG Suite installation visit the documentation or the Github repository.
NETCONF-YANG must be configured and running on the device, even if NETCONF is not used. For more information on NETCONF configuration visit the documentation.
A device profile, a YANG repository and a YANG module set associated to the device of interest must exist in YANG Suite. For more information on how to create a device profile, a YANG repository and a YANG module set visit the YANG Suite documentation under Managing Device Profiles.
Information About Model-Driven Telemetry
Telemetry is an automated communication process by which measurements and other data are collected at remote or inaccessible points and transmitted to the receiving equipment for monitoring. Model-driven telemetry provides a mechanism to stream YANG-modeled data to a data collector.
Applications can subscribe to specific data items they need with the use of standards-based YANG data models over NETCONF, RESTCONF, or gRPC Network Management Interface (gNMI) protocols. Subscriptions can also be created with the command line (CLI).
Structured data is published at a defined cadence (periodically), or on-change, based upon the subscription criteria and data type.
Telemetry Roles
In systems that use telemetry, different roles are involved. In this document these telemetry roles are described:
- Publisher: Network element that sends the telemetry data.
- Receiver: Receives the telemetry data. This is also called the collector.
- Controller: Network element that creates subscriptions but does not receive the telemetry data. The telemetry data associated with the subscriptions, it creates goes to receivers. This is also called the management agent or management entity.
- Subscriber: Network element that creates subscriptions. Technically, while this does not have to be the receiver too, in this document, both are the same.
Subscription Overview
Subscriptions are items that create associations between telemetry roles, and define the data that is sent between them.
Two types of subscriptions are used in telemetry on Cisco IOS XE systems: dynamic and configured subscriptions.
Dynamic subscriptions are created by clients (the subscriber) that connect into the publisher, they are considered dial-in. Configured subscriptions cause the publisher to initiate connections to receivers, and as a result, they are considered dial-out.
Subscription Identifiers
Subscriptions are identified by a 32-bit positive integer value. The IDs for configured subscriptions is set by the controller, and for dynamic subscriptions is set by the publisher.
Data Source Specification
Sources of telemetry data in a subscription are specified by the use of a stream and a filter. The term stream refers to a related set of events. RFC 5277 defines an event stream as a set of event notifications that match some forwarding criteria.
Cisco IOS XE supports two streams: yang-push and yang-notif-native.
Normally, the set of events from a stream are filtered. Different filter types are used for different stream types.
This document uses yang-push as the stream type and leverages XPath filters.
Configure
Configure a Periodic Dynamic Subscription with YANG Suite
Dynamic subscriptions are created by subscribers who connect to the publisher and call for subscription creation using a mechanism within that connection, usually, an RPC. The lifetime of the subscription is limited to the lifetime of the connection between the subscriber and the publisher, and telemetry data is sent only to that subscriber. These subscriptions do not persist if either the publisher or the subscriber is rebooted. You can create dynamic subscriptions by using the in-band <establish-subscription> RPC. The <establish-subscription> RPC is sent from an IETF telemetry subscriber to the network device. The stream, xpath-filter, and period fields in the RPC are mandatory.
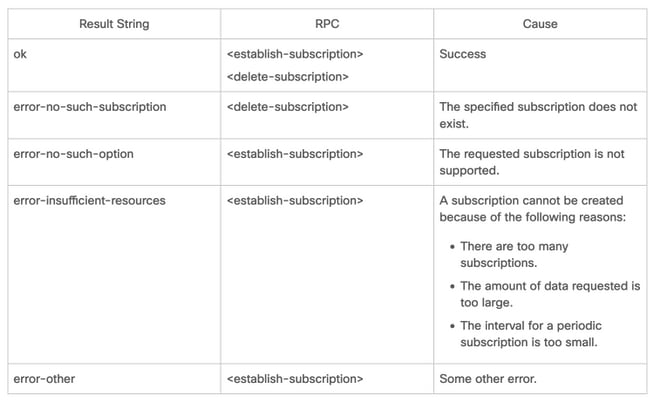
When an RPC is sent, the RPC reply from a publisher contains a message with an element that contains a result string.
This table displays the response and reason for the response in an <rpc-reply> message:
You can send an RPC from YANG Suite to configure a periodic subscription.
Steps to Obtain the XPath Filter
To obtain the XPath filter you can leverage YANG Suite once you define the data that you need to stream. In this example, memory statistics information is the data to stream.
Step 1. In YANG Suit under Protocols > NETCONF, select the YANG set associated to the device in use. In this example the YANG Set is called CSR1000V.
Step 2. Load the YANG module that contains the data of interest. In this example it is Cisco-IOS-XE-memory-oper.
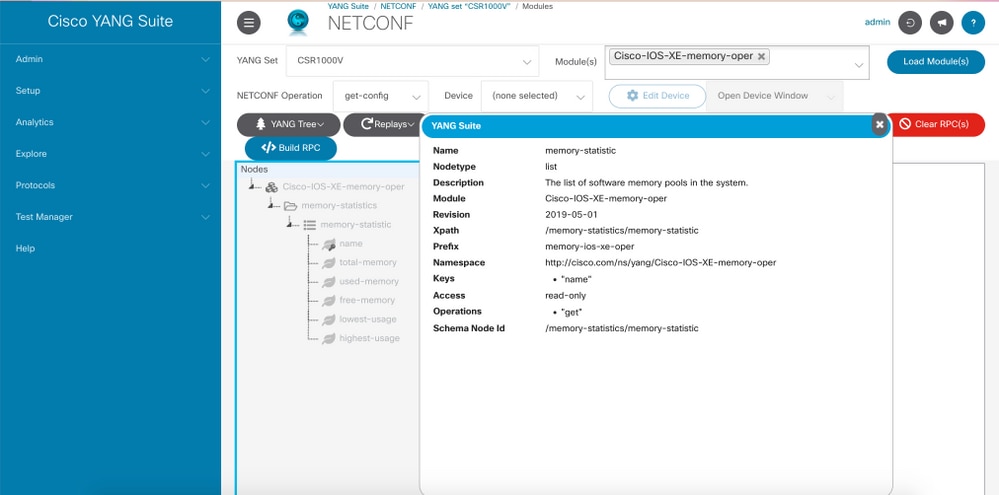
Step 3. In the YANG tree find the node you want to obtain the XPath filter for, in this example is memory-statistic, right click on it and select Properties.
Step 4. In the pop-up window that appears there are 2 properties that together define the XPath filter. Those values are Xpath and Prefix.
Steps to Create a Periodic NETCONF Dynamic Subscription
To create a periodic NETCONF dynamic subscription, you need to use the IETF-event-notification YANG module.
Step 1. In YANG Suit under Protocols > NETCONF, select the YANG set associated to the device in use. In this example the YANG Set is called CSR1000V.
Step 2. Load the IETF-event-notifications YANG Module.
Step 3. The NETCONF operation must be Other RPC.
Step 4. In the Device dropdown menu, select the device of interest, then click Open device window in a new window or in a new tab.
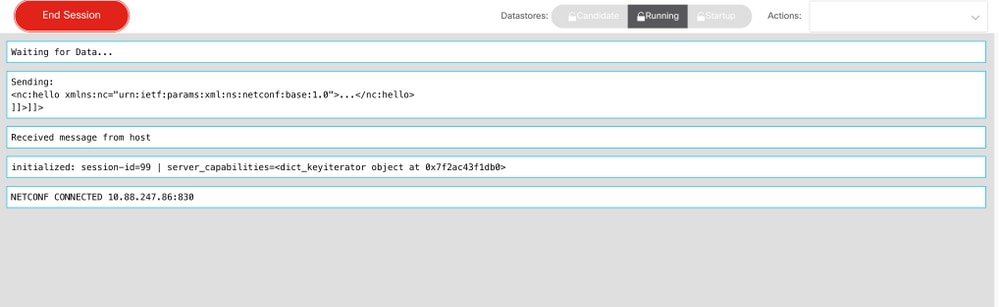
Step 5. In the separate window that opens, click Start Session in order to establish an active NETCONF session with the device. This is an example of an established NETCONF session window.
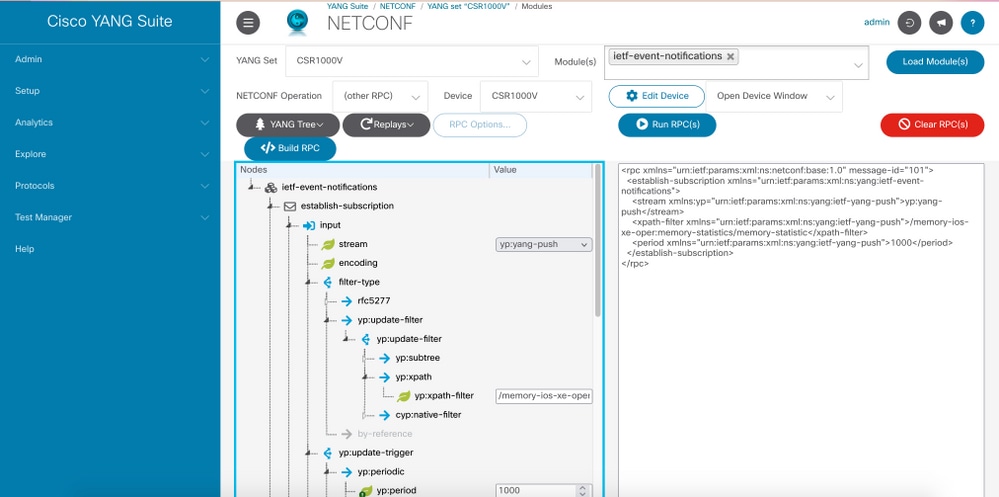
Step 6. Return to the previous window. In the nodes under ietf-event-notification tree, expand the establish-subscription node and choose input.
Step 7. You need to define stream, filter and update-trigger values.
stream: yang-push.
filter: xpath-filter
The XPath filter must have this format:
/prefix:xpath
In this example, with the use of the parameters obtained in Steps to Obtain the XPath Filter section.
/memory-ios-xe-oper:memory-statistics/memory-statistic
Tip: Pay attention to the position of the "/" in the XPath filter
Step 8. The update-trigger is a value in centiseconds (1/100 of a second). A period of 1000 results in getting updates every 10 seconds.
Step 9. Once stream, filter and update-trigger values have been provided, click Build RPC and an RPC like the one shown in this image is going to appear.
Step 10. You can now click Run RPC and create a periodic NETCONF Dial-In subscription.
Step 11. RPC messages appear now in the window where the NETCONF Session was established.
This image is an example of the RPC sent and the RPC-reply received with an OK message this means that the subscription was successful.
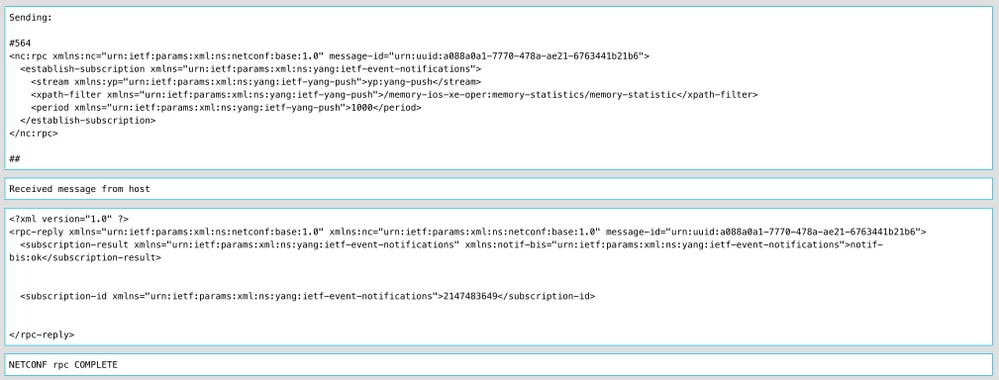
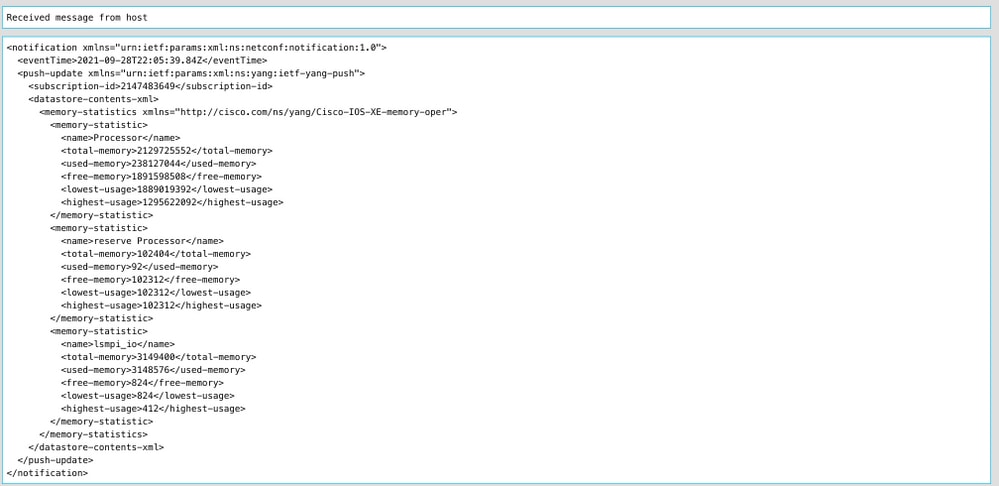
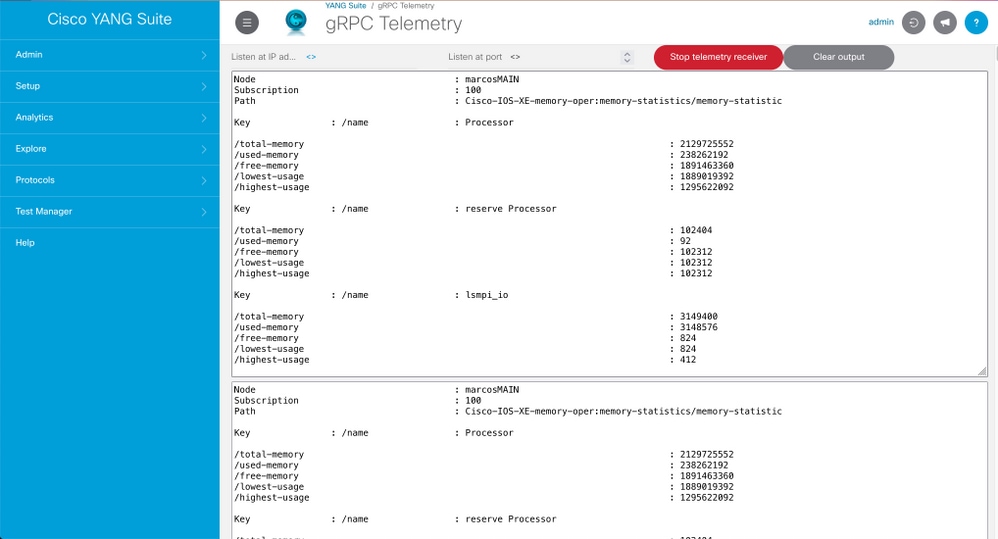
This image is an example of the memory statistics data that is received every 10 seconds.
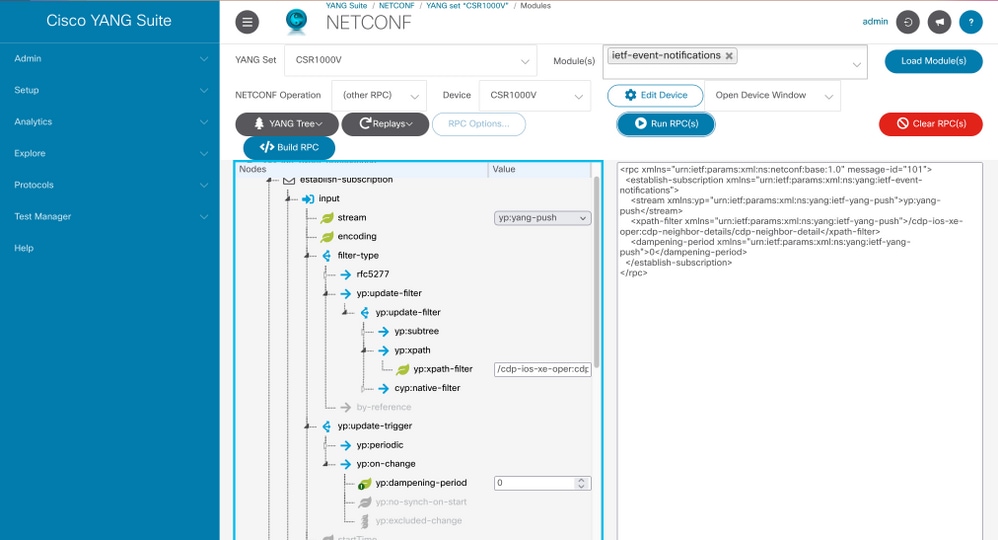
Configure an On-Change Dynamic Subscription with YANG Suite
All the steps indicated in the Configure a Periodic subscription with YANG Suite section apply to this section, the only difference is in the update-trigger value where you must define a dampening-period with a value of 0, no other value is possible.
This is an example of an RPC to establish an on-change subscription for CDP neighbors data.
Configure a Periodic Configured Subscription with YANG Suite
Configured subscriptions are created by management operations on the publisher by controllers, and explicitly include the specification of the receiver of the telemetry data defined by a subscription. These subscriptions persist across reboots of the publisher as they become part of the configuration of the device.
Configured dial-out subscriptions are configured on the device with any of these methods:
- Using configuration CLIs to change to device configuration through console/VTY.
- Using NETCONF/RESTCONF to configure the desired subscription.
This document does not cover how to configure a dial-out subscription with the CLI, instead it shows how to send a NETCONF RPC message from YANG Suite to configure a dial-out subscription.
For configured subscriptions the gRPC protocol is available and can only be used with the yang-push stream. Only Key-value Google Protocol Buffers (kvGPB) encoding is supported with the gRPC transport protocol.
You can use YANG Suite as a receiver to test sample dial-out subscriptions.
To create a periodic configured subscription, you need to use the Cisco-IOS-XE-mdt-cfg YANG module.
Step 1. In YANG Suite, under Protocols > gRPC Telemetry, enter IP address and port, and then click Start telemetry receiver for YANG Suite to start listening at the indicated IP address and port.
Note: If gRPC Telemetry option is not available, plugin can be installed through the Admin > Manage plugins page in YANG Suite
Step 2. Under Protocols > NETCONF, select the YANG set associated to the device in use. In this example the YANG Set is called CSR1000V.
Step 3. Load the Cisco-IOS-XE-mdt-cfg YANG module.
Step 4. The NETCONF operation must be edit-config.
Step 5. Choose the device of interest.
Step 6. Under the Cisco-IOS-XE-mdt-cfg tree these values need to be defined in the mdt-subscription node: subscription-id, stream, encoding, period and xpath-filter. And also, the information about the receiver: IP address, port and protocol.
Step 7. These values are used for this example:
subscription-id: 100
stream: yang-push
encoding: encode-kvgpb
period: 1000
xpath filter: /memory-ios-xe-oper:memory-statistics/memory-statistic
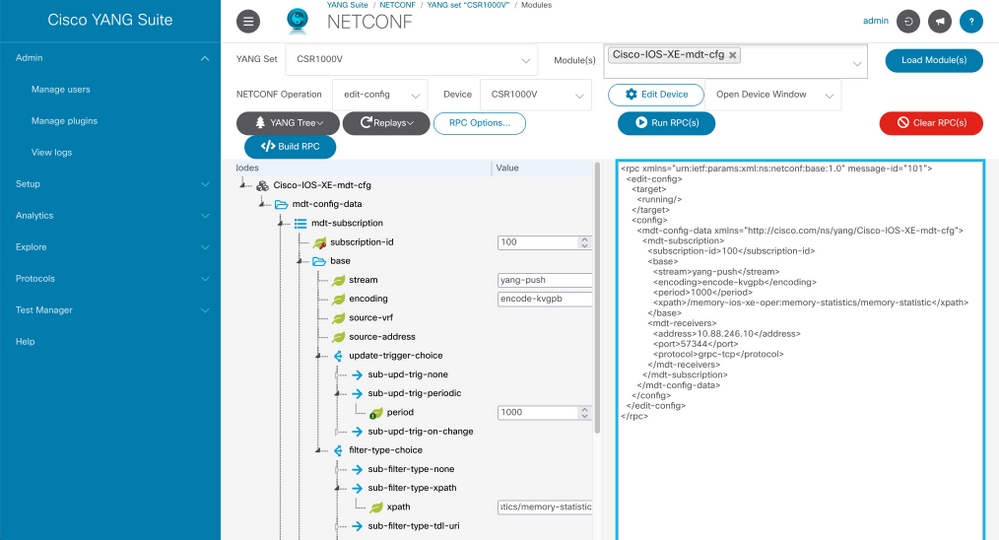
Information about the receiver needs to defined
address: <IP addresss>
port: <port>
protocol: grpc-tcp
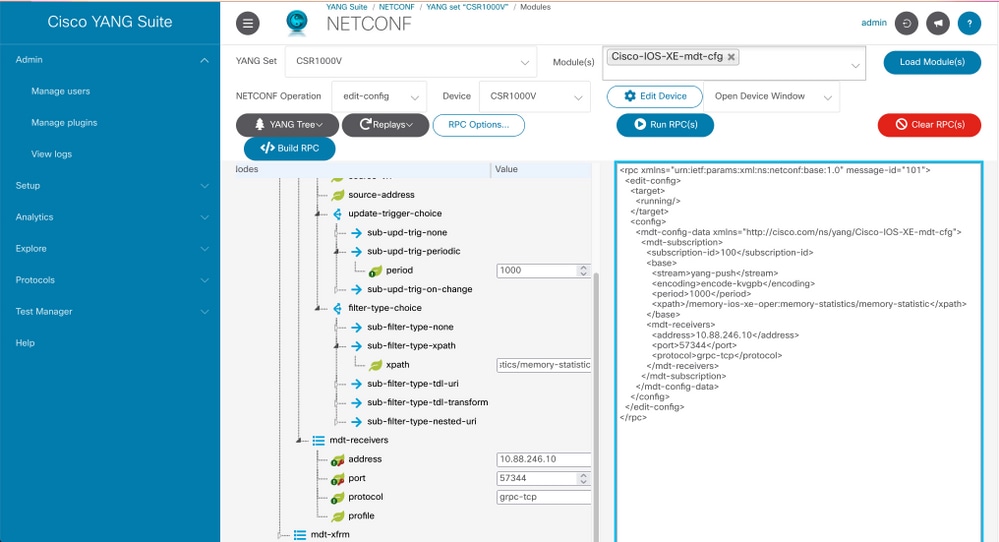
Step 8. Click Build RPC button.
Step 9. Click Run RPC.
Step 10. If successful, then under Protocols > gRPC Telemetry, information is now received.
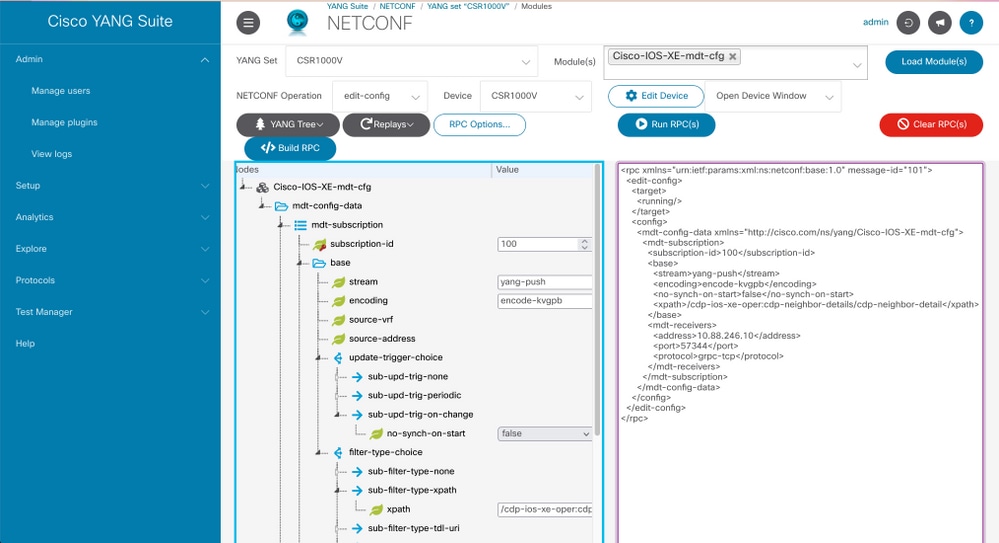
Configure an On-Change Configured Subscription with YANG Suite
To configure an On-Change dial-out subscription the same process described under Configure a Periodic Configured Subscription with YANG Suite section is followed, the only value that changes is the no-sync-on-start leaf that must be set to false.
This image is an example RPC for an on-change configured subscription.
Verify
Use this section in order to confirm that your configuration works properly.
Display information about telemetry subscriptions on a Cisco IOS XE with show telemetry ietf subscription all.
Device#show telemetry ietf subscription all Telemetry subscription brief ID Type State Filter type -------------------------------------------------------- 100 Configured Valid xpath 2147483651 Dynamic Valid xpath
List details about a subscription with show telemetry ietf <subscriptionID> detail.
Device#show telemetry ietf 100 detail
Telemetry subscription detail:
Subscription ID: 2147483651
Type: Dynamic
State: Valid
Stream: yang-push
Filter:
Filter type: xpath
XPath: /memory-ios-xe-oper:memory-statistics/memory-statistic
Update policy:
Update Trigger: periodic
Period: 10000
Encoding: encode-xml
Source VRF:
Source Address:
Notes:
Receivers:
Address Port Protocol Protocol Profile
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10.88.246.10 57344 netconf
Verify the status of the connection to the receiver with show telemetry internal connection.
Device# show telemetry internal connection
Telemetry connection
Peer Address Port VRF Source Address Transport State Profile
--------------- ----- --- --------------- ---------- ------------- -------------
10.88.246.10 57344 0 10.88.246.2 grpc-tcp Active
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use in order to troubleshoot your configuration.
Scenario 1. If the state of the telemetry subscription is valid and you do not receive streams in the receiver.
Verify status of the connection to the receiver.
Device#show telemetry internal connection
Telemetry connection
Peer Address Port VRF Source Address Transport State Profile
--------------- ----- --- --------------- ---------- ------------- -------------
10.88.246.10 57350 0 10.88.247.86 grpc-tcp Connecting
If state is Connecting, ensure the correct connectivity between the publisher and the receiver.
Device# ping <Receiver IPAddress>
Ensure that the port in use is open.
Device# telnet <Receiver IPAddress> <PORT>
Trying 10.88.246.10, 57350 ...
% Connection refused by remote host
In this example, the port is not open/reachable. Verify there isn't a firewall that can block the port and ensure that port specified is the correct one.
In devices that use VRFs, you need to specify the source VRF/source address in the RPC for configured subscriptions. This image shows an RPC where the source VRF is specified.
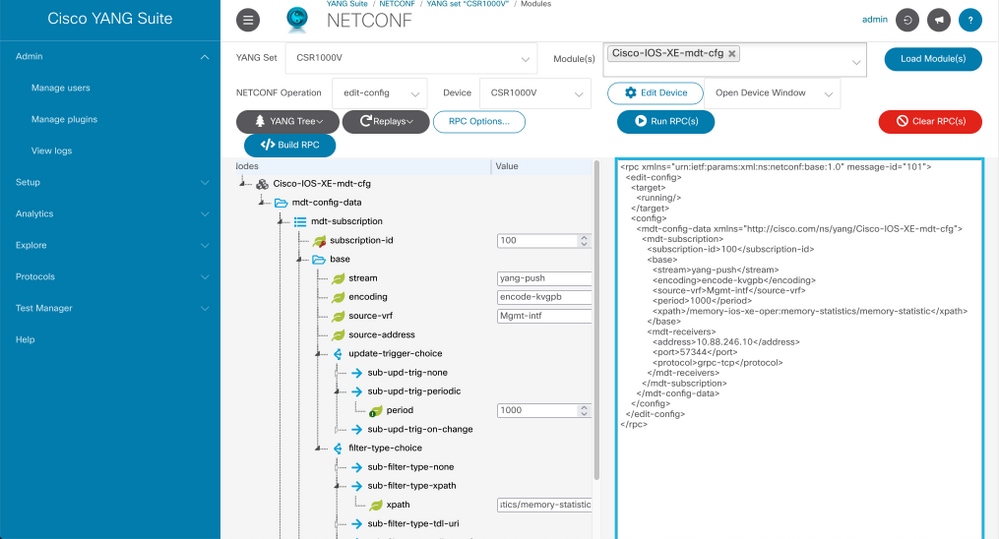
Scenario 2. If the state of the telemetry subscription is invalid.
Device# show telemetry ietf subscription all
Telemetry subscription brief
ID Type State Filter type
--------------------------------------------------------
200 Configured Invalid xpath
Verify subscription details.
Device# show telemetry ietf subscription 200 detail
Telemetry subscription detail:
Subscription ID: 200
Type: Configured
State: Invalid
Stream: yang-push
Filter:
Filter type: xpath
XPath: /memory-ios-xe-oper:/memory-statistics/memory-statistic
Update policy:
Update Trigger: periodic
Period: 1000
Encoding: encode-kvgpb
Source VRF:
Source Address:
Notes: XPath parse error 'Invalid expression: offset(21)' 58.
Receivers:
Address Port Protocol Protocol Profile
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10.88.247.89 57344 grpc-tcp
Notice the syntax of the XPath filter, it has an extra "/" after the ":", the correct XPath filter is:
/memory-ios-xe-oper:memory-statistics/memory-statistic
Any syntax error such as missing letters or extra characters in the XPath filter can lead to an invalid subscription.
If you need support for YANG Suite tool, contact the support mailer or the support forum.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
30-Sep-2021 |
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Marcos SanchezCisco TAC Engineer
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback