BGP Implementation Using 32-bit AS Number Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) using 32-bit AS number. In BGP, each routing domain is a single administrative domain and has a unique AS number assigned to it, and is operated within a uniform set of routing policies. It also maintains interdomain routing.
In this document, BGP peering is configured between 16-bit and 32-bit speaking BGP routers. The new 32-bit AS mode is compatible with the16-bit AS mode. The BGP peers which can operate in 32-bit mode respond positively to the new capability, and that session operates in new mode. On the other hand, the 32-bit BGP peers when communicating with the 16-bit BGP speakers, the 16-bit speaking routers ignore this new capability and operate their BGP session in 16-bit mode.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have basic knowledge of BGP.
Hardware and Software Versions
The configurations in this document are based on the Cisco 7200 Series Router with Cisco IOS® Software Release 15.0(1).
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Configure
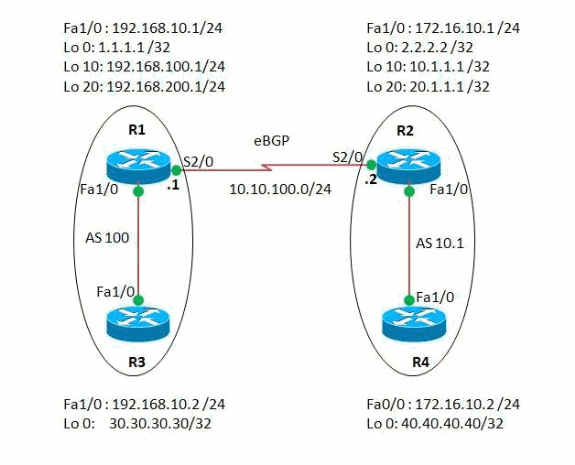
In this example, routers R1 and R3 are configured to be in AS 100 forming iBGP relationship using 16-bit AS mode. Routers R2 and R4 are configured in AS 10.1, and form iBGP peering using the 32-bit AS mode. The routers R1 and R2 run and IGP protocol, in this example OSPF between each other and also forms eBGP neighboring between them.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) in order to find more information on the commands used in this document.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Configurations
This document uses these configurations:
| Router R1 |
|---|
R1#show run Building configuration... ! version 15.0 ! hostname R1 ! ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback10 ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback20 ip address 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial2/0 ip address 10.10.100.1 255.255.255.0 serial restart-delay 0 ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.10.100.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! router bgp 100 !--- BGP is configured using 16-bit AS number no synchronization bgp router-id 10.10.10.10 bgp asnotation dot !--- This command change the default asplain notation to dot notation. !--- Note that without this command the AS number will treated as asplain notation i.e. 10.1 will be displayed as 655361 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.168.100.0 network 192.168.200.0 neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 10.1 !--- The AS number of the eBGP peer in 32-bit neighbor 2.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 255 neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 192.168.10.2 remote-as 100 neighbor 192.168.10.2 next-hop-self no auto-summary ! end |
| Router R2 |
|---|
R2#show run ! version 15.0 ! hostname R2 ! ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback10 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback20 ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial2/0 ip address 10.10.100.2 255.255.255.0 serial restart-delay 0 ! ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.10.100.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! router bgp 10.1 !--- BGP is configured using 32-bit AS number no synchronization bgp router-id 20.20.20.20 bgp asnotation dot bgp log-neighbor-changes network 10.1.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 network 20.1.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 1.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop 255 neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 172.16.10.2 remote-as 10.1 neighbor 172.16.10.2 next-hop-self no auto-summary ! end |
| Router R3 |
|---|
R3#show run Building configuration... ! version 15.0 ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 30.30.30.30 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! router bgp 100 no synchronization bgp router-id 3.3.3.3 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 30.30.30.30 mask 255.255.255.255 neighbor 192.168.10.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 192.168.10.1 next-hop-self no auto-summary !--- iBGP peering is formed between routers R1 and R3 using 16-bit AS number. ! end |
| Router R4 |
|---|
R4#show run Building configuration... ! version 15.0 ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 40.40.40.40 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 172.16.10.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! router bgp 10.1 no synchronization bgp router-id 4.4.4.4 bgp asnotation dot bgp log-neighbor-changes network 40.40.40.40 mask 255.255.255.255 neighbor 172.16.10.1 remote-as 10.1 no auto-summary ! end !--- iBGP peering is formed between routers R2 and R4 using 32-bit AS number. |
Verify
Use this section in order to confirm that your configuration works properly.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT in order to view an analysis of show command output.
Show Commands
In order to verify that BGP can support 32-bit ASN, use the show ip bgp neighbor command.
| show ip bgp neighbor |
|---|
In router R1
R1#show ip bgp neighbor 2.2.2.2
BGP neighbor is 2.2.2.2, remote AS 10.1, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 20.20.20.20
BGP state = Established, up for 03:28:22
Last read 00:00:41, last write 00:00:29, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Neighbor sessions:
1 active, is multisession capable
Neighbor capabilities:
Route refresh: advertised and received(new)
Four-octets ASN Capability: advertised and received
Address family IPv4 Unicast: advertised and received
Multisession Capability: advertised and received
Message statistics, state Established:
InQ depth is 0
OutQ depth is 0
Sent Rcvd
Opens: 1 1
Notifications: 0 0
Updates: 3 3
Keepalives: 229 230
Route Refresh: 0 0
Total: 233 234
!--- Output omitted---!
|
To show the entries in the BGP routing table, use the show ip bgp command.
| show ip bgp |
|---|
In router R1
R1#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 13, local router ID is 10.10.10.10
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.1.1.1/32 2.2.2.2 0 0 10.1 I
*> 20.1.1.1/32 2.2.2.2 0 0 10.1 I
*>i30.30.30.30/32 192.168.10.2 0 100 0 I
*> 40.40.40.40/32 2.2.2.2 0 10.1 I
*> 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 I
*> 192.168.200.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 I
!--- Note that the routes highlighted are received from the eBGP peer router R2 which is in 32-bit AS 10.1.
In router R3
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 11, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i10.1.1.1/32 192.168.10.1 0 100 0 655361 I
*>i20.1.1.1/32 192.168.10.1 0 100 0 655361 I
*> 30.30.30.30/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 I
*>i40.40.40.40/32 192.168.10.1 0 100 0 655361 I
*>i192.168.100.0 192.168.10.1 0 100 0 I
*>i192.168.200.0 192.168.10.1 0 100 0 I
!--- The router R3 does not have bgp asnotation dot configured in it. Therefore, the route received from the router in 32-bit AS AS 10.1 is displayed as 655361.
In router R4
R4#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 7, local router ID is 4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i10.1.1.1/32 172.16.10.1 0 100 0 I
*>i20.1.1.1/32 172.16.10.1 0 100 0 I
*>i30.30.30.30/32 172.16.10.1 0 100 0 100 I
*> 40.40.40.40/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 I
*>i192.168.100.0 172.16.10.1 0 100 0 100 I
*>i192.168.200.0 172.16.10.1 0 100 0 100 I
!--- The above output shows the entries in BGP routing table of router R4.
|
In order to verify reachability between routers, use the ping command.
| ping |
|---|
From router R3 R3#ping 40.40.40.40 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 40.40.40.40, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 68/101/148 msFrom router R4 R4#ping 30.30.30.30 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 30.30.30.30, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/89/112 ms !--- The above output shows that End to End connectivity is established between R3 and R4, where R3 is AS 100(16-bit AS) and router R4 is in AS 10.1(32-bit AS). |
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
25-Jun-2012 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback