Introduction
This document describes how to configure Network Address Translation (NAT) server load balancing TCP traffic on Cisco IOS® routers.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions. This document applies to all Cisco routers and switches that run Cisco IOS.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Purpose
Users that access the local server from outside Internet will access the server using a single URL or IP address, however the NAT device is used to load share the user traffic to multiple identical servers with mirrored content.
Description
Outside users A and B access the contents of the Web server with the outside visible IP address 172.16.2.3 (Virtual IP address of the servers). The NAT router translates the traffic destined for 172.16.1.3 to the inside IP addresses 10.1.1.1, 10.1.1.2 and 10.1.1.3 in a round robin fashion and forwards it to the respective server. Each new session initiated from the outside user is translated to the next physical server IP address.
Configure
Network Diagram
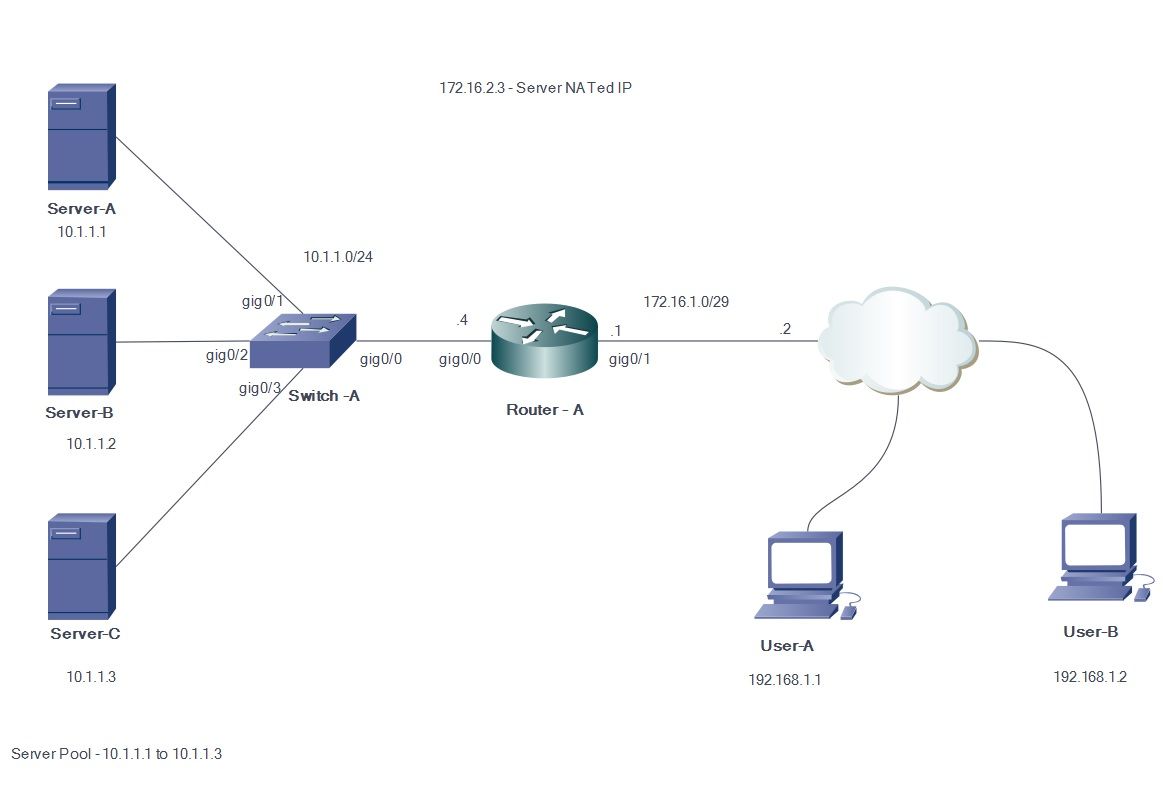
Steps
- User-A initiates a TCP connection with virtual server IP address 172.16.2.3.
- The NAT router, upon receiving the connection request, creates a NAT translation entry which allocates the next available real server IP address (for example, 10.1.1.1).
- The NAT router replaces the destination IP address with the allocated real IP address and forwards the packet.
- The server receives the packet and replies back to the source.
- The NAT router receives the packet returned from the server and performs the NAT table lookup. The router then translates the source address to the virtual server IP address (172.16.2.3) and forwards the packet.
- User-B initiates a TCP session with server virtual IP address 172.16.2.3. Upon receiving the connection request, the NAT router translates this to the next available real server IP address (for example, 10.1.1.2) and then forwards the packet to the server.
Since static NAT is bidirectional in the other direction, the destination of the packet will be translated. When doing this form of NAT, it is triggered by sending TCP packets. Sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) might not trigger the NAT translation.
Non-TCP traffic is directed to the first address in the pool.
Unlike static inside source NAT and static inside source PAT, the router does not respond to ARP inquiries about the global address, unless that address is not assigned to its interface.Therefore, it might be necessary to add it to an interface like the secondary. It is not possible to redirect ports with this method of translation (for example, 80 and 1087). The ports must match.
Note: The NAT pool IP address need not be same as the external interface IP address. In order to illustrate the same, the example uses an IP address from a different block 172.16.2.x than the actual interface IP subnet 172.16.1.x.
- Define a pool of addresses that contain the addresses of the real servers.
ip nat pool NATPOOL 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.3 prefix-length 24 type rotary
- Define an access-list that permits the address of the virtual-server.
access-list 1 permit host 172.16.2.3
- Enable a dynamic translation of inside destination addresses.
ip nat inside destination list <ACL name> pool <Pool Name>
ip nat inside destination list 1 pool NATPOOL
- Define NAT inside and outside interfaces.
Interface gig0/0
ip address 10.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
Ip nat inside
Interface gig0/1
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.248
Ip nat outside
IP addresses 10.1.1.1, 10.1.1.2 and 10.1.1.3 will now be handed out in a rotary fashion when someone tries to access IP address 172.16.2.3
Verify
In order to verify this, initiatie multiple TCP sessions from outside hosts to the virtual IP address. Debug IP NAT translation/show ip nat translation output can be used for verification.
Router#
Router#
*Jul 24 13:27:41.193: NAT*: s=192.168.1.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.3 [22864]
*Jul 24 13:27:41.196: NAT*: s=10.1.1.3->172.16.2.3, d=192.168.1.1 [18226]
Router#
*Jul 24 13:27:44.329: NAT*: s=192.168.2.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.1 [35533]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.331: NAT*: s=10.1.1.1->172.16.2.3, d=192.168.2.1 [14573]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.332: NAT*: s=192.168.2.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.1 [35534]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.332: NAT*: s=192.168.2.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.1 [35535]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.332: NAT*: s=192.168.2.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.1 [35536]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.333: NAT*: s=10.1.1.1->172.16.2.3, d=192.168.2.1 [14574]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.365: NAT*: s=10.1.1.1->172.16.2.3, d=192.168.2.1 [14575]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.365: NAT*: s=10.1.1.1->172.16.2.3, d=192.168.2.1 [14576]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.368: NAT*: s=192.168.2.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.1 [35537]
Router#
*Jul 24 13:27:44.369: NAT*: s=192.168.2.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.1 [35538]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.369: NAT*: s=192.168.2.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.1 [35539]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.369: NAT*: s=192.168.2.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.1 [35540]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.371: NAT*: s=10.1.1.1->172.16.2.3, d=192.168.2.1 [14577]
*Jul 24 13:27:44.574: NAT*: s=10.1.1.1->172.16.2.3, d=192.168.2.1 [14578]
Router#
*Jul 24 13:27:46.474: NAT*: s=10.1.1.1->172.16.2.3, d=192.168.2.1 [14579]
*Jul 24 13:27:46.478: NAT*: s=192.168.2.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.1 [35541]
*Jul 24 13:27:46.478: NAT*: s=192.168.2.1, d=172.16.2.3->10.1.1.1 [35542]
*Jul 24 13:27:46.479: NAT*: s=10.1.1.1->172.16.2.3, d=192.168.2.1 [14580]
Router#sh ip nat tr
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
tcp 172.16.2.3:23 10.1.1.1:23 192.168.2.1:49703 192.168.2.1:49703
tcp 172.16.2.3:23 10.1.1.2:23 192.168.2.1:50421 192.168.2.1:50421
tcp 172.16.2.3:80 10.1.1.3:80 192.168.1.1:26621 192.168.1.1:26621
Router#
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration.
Limitations
- It cannot detect whether an internal server in the group fails. This means that the Cisco IOS always will forward traffic to servers in the group, regardless of their operational status.
- It cannot determine actual loads of the internal servers, so it cannot perform load balancing efficiently.