How OSPF Injects a Default Route into a Not So Stubby Area
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document shows how Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) injects a default route into a not so stubby area (NSSA). The area border router (ABR) for the NSSA does not, by default, originate a default route into the NSSA. You must use the area <x> nssa default-information originate command.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, see the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: To find additional information on the commands used in this document, use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) .
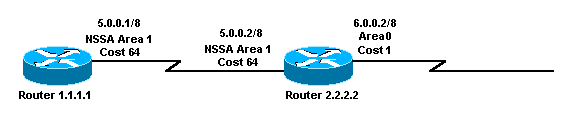
Network Diagram
This document uses the network setup shown in this diagram.
Configurations
This document uses the configurations shown here.
| Router 1.1.1.1 |
|---|
Current configuration: hostname r1.1.1.1 interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 interface Serial2/1/0 ip address 5.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 router ospf 2 network 5.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 1 area 1 nssa end |
| Router 2.2.2.2 |
|---|
Current configuration: hostname r2.2.2.2 interface Loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.0.0.0 interface Serial0/1/0 ip address 5.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 interface ATM1/0.20 ip address 6.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 router ospf 2 network 5.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 1 network 6.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0 area 1 nssa default-information originate end |
Verify
This section provides information you can use to confirm your configuration is working properly.
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
-
show ip ospf database —Displays a list of the Link State Advertisements (LSAs) and types them into a link state database. This list shows only the information in the LSA header.
-
show ip ospf database nssa-external —Displays information only about the NSSA external LSAs.
-
show ip route —Displays the current status of the routing table.
Examine the OSPF Database in a Not So Stubby Area
To see how the OSPF Database looks, use the show ip ospf database command.
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 600 0x80000001 0x9583 1
Summary Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
5.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 600 0x80000001 0x8E61
Router Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 864 0x8000005E 0xD350 2
2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 584 0x8000001E 0xF667 2
Summary Net Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
6.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 585 0x80000004 0xA87C
Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Tag
0.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 601 0x80000001 0xD0D8 0
The ABR for the NSSA originates a type 7 and an LSA with a link ID of 0.0.0.0. This is a result of the area 1 nssa default-information-originate command in its OSPF configuration.
r2.2.2.2#show ip ospf database nssa-external 0.0.0.0
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 2)
Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 1)
LS age: 650
Options: (No TOS-capability, No Type 7/5 translation, DC)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 0.0.0.0 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0xD0D8
Length: 36
Network Mask: /0
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
TOS: 0
Metric: 1
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
External Route Tag: 0
The ABR originates the 0.0.0.0 type 7 LSA, even though it does not have a default route.
r2.2.2.2#show ip route 0.0.0.0 % Network not in table r1.1.1.1#show ip route ospf O IA 6.0.0.0/8 [110/65] via 5.0.0.2, 00:00:18, Serial2/1/0 O*N2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 5.0.0.2, 00:00:18, Serial2/1/0
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
10-Aug-2005 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback