NEAT Configuration Example with Cisco Identity Services Engine
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the configuration and behavior of Network Edge Authentication Topology (NEAT) in a simple scenario. NEAT utilizes the Client Information Signalling Protocol (CISP) in order to propagate client MAC addresses and VLAN information between supplicant and authenticator switches.
In this configuration example, both the authenticator switch (also called the authenticator) and supplicant switch (also called the supplicant) perform 802.1x authentication; the authenticator authenticates the supplicant, which, in turn, authenticates the testing PC.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of the IEEE 802.1x authentication standard.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- Two Cisco Catalyst 3560 Series switches with Cisco IOS® Software, Release 12.2(55)SE8; one switch acts as an authenticator, and the other acts as a supplicant.
- Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), Release 1.2.
- PC with Microsoft Windows XP, Service Pack 3.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Configure
This example covers sample configurations for the:
- Authenticator switch
- Supplicant switch
- Cisco ISE
The configurations are the minimum needed in order to perfom this lab exercise; they might not be optimal for or fulfill other needs.
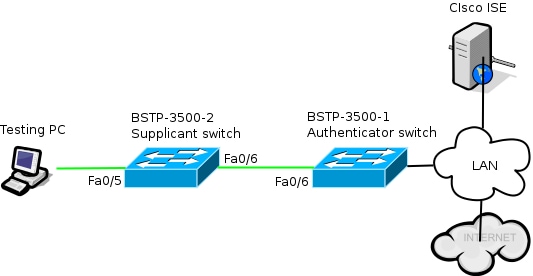
Network Diagram
This network diagram illustrates the connectivity used in this example. Black lines indicate logical or physical connectivity, and green lines indicate links authenticated through the use of 802.1x.
Authenticator Switch Configuration
The authenticator contains the basic elements needed for dot1x. In this example, commands that are specific to NEAT or CISP are bolded.
This is the basic authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) configuration:
aaa new-model
aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
aaa authorization network default group radius
aaa accounting dot1x default start-stop group radius
radius-server host 10.48.66.107 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key cisco
! Enable authenticator switch to authenticate the supplicant switch.
dot1x system-auth-control
! Enable CISP framework.
cisp enable
! configure uplink port as access and dot1x authentication.
interface FastEthernet0/6
switchport mode access
authentication port-control auto
dot1x pae authenticator
spanning-tree portfast
CISP is enabled globally, and the interconnecting port is configured in authenticator and access mode.
Supplicant Switch Configuration
Accurate supplicant configuration is crucial for the entire setup to work as expected. This example configuration contains a typical AAA and dot1x configuration.
This is the basic AAA configuration:
aaa new-model
aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
aaa authorization network default group radius
aaa accounting dot1x default start-stop group radius
radius-server host 10.48.66.107 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key cisco
! Enable supplicant switch to authenticate devices connected
dot1x system-auth-control
! Forces the switch to send only multicast EAPOL packets when it receives either
unicast or multicast packets, which allows NEAT to work on the supplicant
switch in all host modes.
dot1x supplicant force-multicast
! Enable CISP framework operation.
cisp enable
The supplicant should have configured credentials and should supply an Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) method to be used.
The supplicant can use EAP-Message Digest 5 (MD5) and EAP-Flexible Authentication via Secure Protocol (FAST) (among other EAP types) for authentication in case of CISP. In order to keep the ISE configuration to a minimum, this example uses EAP-MD5 for authentication of the supplicant to the authenticator. (The default would force use of EAP-FAST, which requires Protected Access Credential [PAC] provisioning; this document does not cover that scenario.)
! configure EAP mode used by supplicant switch to authenticate itself to
authenticator switch eap profile EAP_PRO
method md5
! Configure credentials use by supplicant switch during that authentication.
dot1x credentials CRED_PRO
username bsnsswitch
password 0 C1sco123
The connection of the supplicant to the authenticator is already configured to be a trunk port (in contrast to access port configuration on the authenticator). At this stage, this is expected; configuration will dynamically change when the ISE returns the correct attribute.
interface FastEthernet0/6
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport mode trunk
dot1x pae supplicant
dot1x credentials CRED_PRO
dot1x supplicant eap profile EAP_PRO
The port that connects to the Windows PC has a minimal configuration and is shown here for reference only.
interface FastEthernet0/5
switchport access vlan 200
switchport mode access
authentication port-control auto
dot1x pae authenticator
ISE Configuration
This procedure describes how to set up a basic ISE configuration.
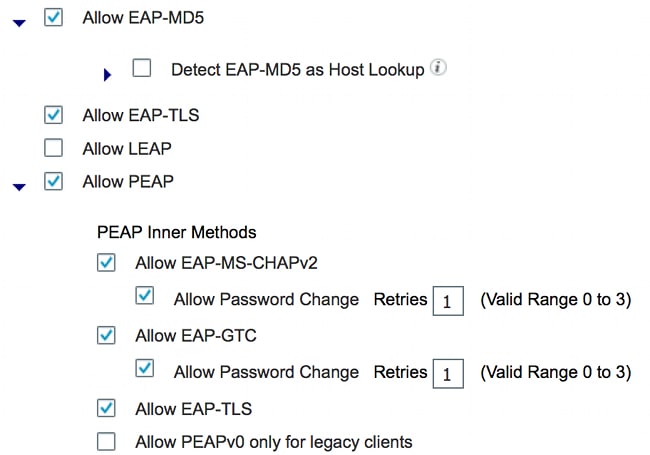
- Enable the required authentication protocols.
In this example, wired dot1x allows EAP-MD5 to authenticate the supplicant to the authenticator and allows Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP)-Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol Version 2 (MSCHAPv2) to authenticate the Windows PC to the supplicant.
Navigate to Policy > Results > Authentication > Allowed protocols, select the protocol service list used by wired dot1x, and ensure the protocols in this step are enabled.
- Create an authorization policy. Navigate to Policy > Results > Authorization > Authorization Policy, and create or update a policy so it contains NEAT as a returned attribute. This is an example of such a policy:
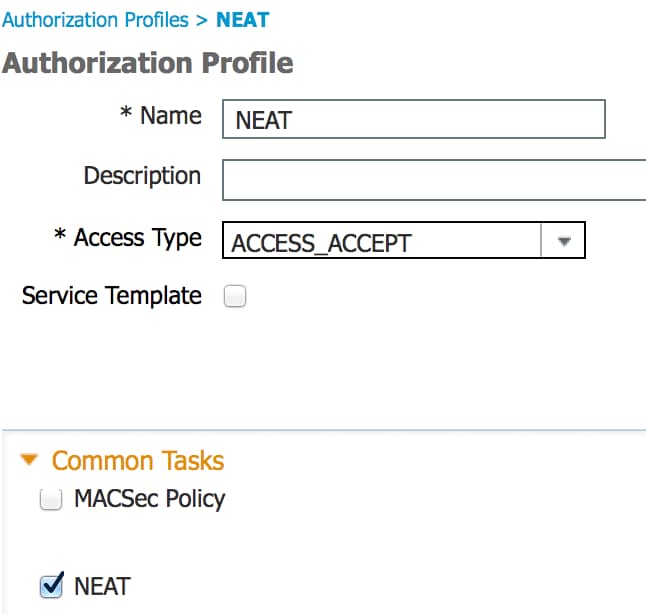
When the NEAT option is turned on, the ISE returns device-traffic-class=switch as part of authorization. This option is necessary in order to change the port mode of the authenticator from access to trunk. - Create an authorization rule to use this profile. Navigate to Policy > Authorization, and create or update a rule.
In this example, a special device group called Authenticator_switches is created, and all supplicants send a username that begins with bsnsswitch.

- Add the switches to the appropriate group. Navigate to Administration > Network Resources > Network Devices, and click Add.
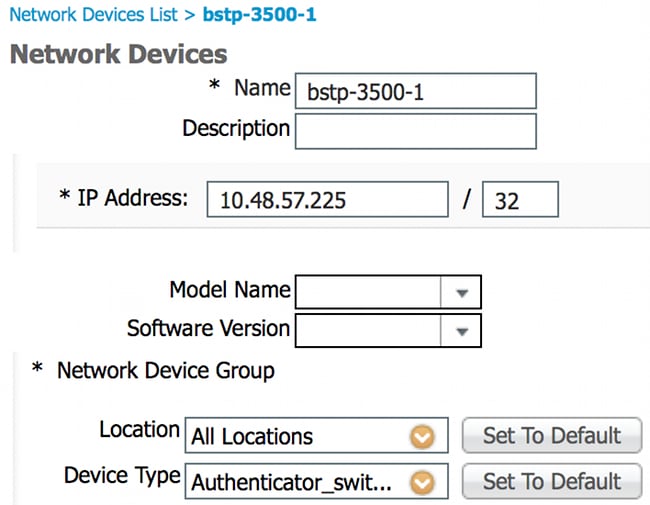
In this example, BSTP-3500-1 (the authenticator) is part of Authenticator_switches group; BSTP-3500-2 (the supplicant) does not need to be part of this group.
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly. This section describes two behaviors:
- Authentication between switches
- Authentication between the Windows PC and the supplicant
It also explains three additional situations:
- Removal of an authenticated client from the network
- Removal of a supplicant
- Ports without dot1x on a supplicant
Supplicant Switch Authentication to Authenticator Switch
In this example, the supplicant authenticates to the authenticator. The steps in the process are:
- The supplicant is configured and plugged into port fastethernet0/6. The dot1x exchange causes the supplicant to use EAP in order to send a pre-configured username and password to the authenticator.
- The authenticator performs a RADIUS exchange and provides credentials for ISE validation.
- If the credentials are correct, the ISE returns attributes required by NEAT (device-traffic-class=switch), and the authenticator changes its switchport mode from access to trunk.
This example shows the exchange of CISP information between switches:
bstp-3500-1#debug cisp all
Oct 15 13:51:03.672: %AUTHMGR-5-START: Starting 'dot1x' for client
(001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID 0A3039E10000000600757ABB
Oct 15 13:51:03.723: %DOT1X-5-SUCCESS: Authentication successful for client
(001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID
Oct 15 13:51:03.723: %AUTHMGR-7-RESULT: Authentication result 'success' from
'dot1x' for client (001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID
0A3039E10000000600757ABB
Oct 15 13:51:03.723: Applying command... 'no switchport access vlan 1' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.739: Applying command... 'no switchport nonegotiate' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.748: Applying command... 'switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q'
at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.756: Applying command... 'switchport mode trunk' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.756: Applying command... 'switchport trunk native vlan 1' at
Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:03.764: Applying command... 'spanning-tree portfast trunk' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: %AUTHMGR-5-SUCCESS: Authorization succeeded for client
(001b.0d55.2187) on Interface Fa0/6 AuditSessionID 0A3039E10000000600757ABB
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Received action Run Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Start in
state Not Running
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator state changed to Waiting
link UP
Oct 15 13:51:04.805: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 13:51:05.669: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/6, changed state to
up
Oct 15 13:51:06.793: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Received action Run Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:06.793: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Start in
state Waiting link UP (no-op)
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
FastEthernet0/6, changed state to up
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Link UP in
state Waiting link UP
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator state changed to Idle
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT: Received action Start Tick Timer
Oct 15 13:51:07.799: CISP-EVENT: Started CISP tick timer
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:12.942: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:18.084: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x20 Length:0x0018
Type:HELLO
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposing CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:23.226: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'hello' timer (5s)
Oct 15 13:51:28.377: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): 'hello' timer expired
Oct 15 13:51:28.377: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Timeout in
state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:29.400: CISP-EVENT: Stopped CISP tick timer
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x22 Length:0x001C
Type:REGISTRATION
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: Payload: 0200E84B
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Receive
Packet in state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Proposed CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Negotiated CISP version: 1
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 59467
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x22 Length:0x001C
Type:REGISTRATION
Oct 15 13:51:36.707: Payload: 01000000
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x23 Length:0x003A
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: Payload: 010011020009001B0D5521C10300050 ...
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Receive
Packet in state Idle
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client 001b.0d55.21c1 (vlan: 200)
to authenticator list
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about new
downstream client 001b.0d55.21c1 (vlan: 200)
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client info at Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
to authenticator list
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about new
downstream client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client info at Authenticator
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 13:51:36.724: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x23 Length:0x0018
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Once authentication and authorization succeed, the CISP exchange occurs. Each exchange has a REQUEST, which is sent by the supplicant, and a RESPONSE, which serves as a reply and acknowledgment from the authenticator.
Two distinct exchanges are performed: REGISTRATION and ADD_CLIENT. During the REGISTRATION exchange, the supplicant informs the authenticator that it is CISP-capable, and the authenticator then acknowledges this message. The ADD_CLIENT exchange is used to inform the authenticator about devices connected to the supplicant's local port. As with REGISTRATION, ADD-CLIENT is initiated on the supplicant and acknowledged by the authenticator.
Enter these show commands in order to verify the communication, roles, and addresses:
bstp-3500-1#show cisp clients
Authenticator Client Table:
---------------------------
MAC Address VLAN Interface
---------------------------------
001b.0d55.21c1 200 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c0 1 Fa0/6
bstp-3500-1#show cisp registrations
Interface(s) with CISP registered user(s):
------------------------------------------
Fa0/6
Auth Mgr (Authenticator)
In this example, the role of Authenticator is correctly assigned to the correct interface (fa0/6), and two MAC addresses are registered. The MAC addresses are the supplicant on port fa0/6 on VLAN1 and on VLAN200.
Verification of dot1x authentication sessions can now be performed. The fa0/6 port on the upstream switch is already authenticated. This is the dot1x exchange that is triggered when BSTP-3500-2 (the supplicant) is plugged in:
bstp-3500-1#show authentication sessions
Interface MAC Address Method Domain Status Session ID
Fa0/6 001b.0d55.2187 dot1x DATA Authz Success 0A3039E10000000700FB3259
As expected at this stage, there are no sessions on the supplicant:
bstp-3500-2#show authentication sessions
No Auth Manager contexts currently exist
Windows PC Authentication to Supplicant Switch
In this example, the Windows PC authenticates to the supplicant. The steps in the process are:
- The Windows PC is plugged into FastEthernet 0/5 port on BSTP-3500-2 (the supplicant).
- The supplicant performs authentication and authorization with the ISE.
- The supplicant informs the authenticator that a new client is connected on the port.
This is the communication from the supplicant:
Oct 15 14:19:37.207: %AUTHMGR-5-START: Starting 'dot1x' for client
(c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID 0A3039E200000013008F77FA
Oct 15 14:19:37.325: %DOT1X-5-SUCCESS: Authentication successful for client
(c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID
Oct 15 14:19:37.325: %AUTHMGR-7-RESULT: Authentication result 'success' from
'dot1x' for client (c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID
0A3039E200000013008F77FA
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Received action Add Client
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Adding client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
to supplicant list
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant received event Add Client in
state Idle
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
to the ADD list
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Adding client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
to ADD CLIENT req
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x24 Length:0x0029
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: Payload: 010011020009C46413B429C30300050 ...
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Started 'retransmit' timer (30s)
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT: Started CISP tick timer
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant state changed to Request
Oct 15 14:19:37.341: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x24 Length:0x0018
Type:ADD_CLIENT
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant received event Receive Packet
in state Request
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Stopped 'retransmit' timer
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): All Clients implicitly ACKed
Oct 15 14:19:37.350: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Supplicant state changed to Idle
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: %AUTHMGR-5-SUCCESS: Authorization succeeded for client
(c464.13b4.29c3) on Interface Fa0/5 AuditSessionID 0A3039E200000013008F77FA
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Received action Run Authenticator
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Authenticator received event Start in
state Not Running
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Authenticator state changed to Waiting
link UP
Oct 15 14:19:38.356: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/5): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 14:19:38.373: CISP-EVENT: Stopped CISP tick timer
Oct 15 14:19:39.162: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/5, changed state to
up
An ADD_CLIENT exchange occurs, but no REGISTRATION exchange is needed.
In order to verify behavior on the supplicant, enter the show cisp registrations command:
bstp-3500-2#show cisp registrations
Interface(s) with CISP registered user(s):
------------------------------------------
Fa0/5
Auth Mgr (Authenticator)
Fa0/6
802.1x Sup (Supplicant)
The supplicant has the role of a supplicant towards the authenticator (fa0/6 interface) and the role of an authenticator towards the Windows PC (fa0/5 interface).
In order to verify behavior on the authenticator, enter the show cisp clients command:
bstp-3500-1#show cisp clients
Authenticator Client Table:
---------------------------
MAC Address VLAN Interface
---------------------------------
001b.0d55.21c1 200 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c0 1 Fa0/6
c464.13b4.29c3 200 Fa0/6
A new MAC address appears on the authenticator under VLAN 200. It is the MAC address that was observed in AAA requests on the supplicant.
Authentication sessions should indicate that the same device is connected on fa0/5 port of supplicant:
bstp-3500-2#show authentication sessions
Interface MAC Address Method Domain Status Session ID
Fa0/5 c464.13b4.29c3 dot1x DATA Authz Success 0A3039E20000001501018B58
Removal of Authenticated Client from Network
When a client is removed (for example, if a port is shut down), the authenticator is notified through the DELETE_CLIENT exchange.
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-RXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:REQUEST ID:0x25 Length:0x0029
Type:DELETE_CLIENT
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: Payload: 010011020009C46413B429C30300050 ...
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Receive
Packet in state Idle
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Removing client c464.13b4.29c3
(vlan: 200) from authenticator list
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about
deletion of downstream client c464.13b4.29c3 (vlan: 200)
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Transmitting a CISP Packet
Oct 15 15:54:05.415: CISP-TXPAK (Fa0/6): Code:RESPONSE ID:0x25 Length:0x0018
Type:DELETE_CLIENT
Removal of Supplicant Switch
When a supplicant is unplugged or removed, the authenticator introduces the original configuration back to the port in order to avoid security concerns.
Oct 15 15:57:31.257: Applying command... 'no switchport nonegotiate' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.273: Applying command... 'switchport mode access' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.273: Applying command... 'no switchport trunk encapsulation
dot1q' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.290: Applying command... 'no switchport trunk native vlan 1' at
Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.299: Applying command... 'no spanning-tree portfast trunk' at
Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.307: Applying command... 'switchport access vlan 1' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:31.315: Applying command... 'spanning-tree portfast' at Fa0/6
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
FastEthernet0/6, changed state to down
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator received event Link DOWN
in state Idle
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Removing client 001b.0d55.21c1
(vlan: 200) from authenticator list
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about
deletion of downstream client 001b.0d55.21c1 (vlan: 200)
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Removing client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
from authenticator list
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Notifying interest parties about
deletion of downstream client 001b.0d55.21c0 (vlan: 1)
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Authenticator state changed to Not
Running
Oct 15 15:57:32.247: CISP-EVENT (Fa0/6): Sync supp_id: 0
Oct 15 15:57:33.262: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/6, changed state
to down
At the same time, the supplicant removes clients that represent the supplicant from the CISP table and deactivates CISP on that interface.
Ports Without dot1x on Supplicant Switch
CISP information that is propagated from the supplicant to the authenticator serves only as another layer of enforcement. The supplicant informs the authenticator about all of the allowed MAC addresses that are connected to it.
A scenario that is typically misunderstood is this: if a device is plugged on a port that does not have dot1x enabled, the MAC address is learned and propagated to the upstream switch through CISP.
The authenticator allows communication that comes from all clients learned through CISP.
In essence, it is the role of supplicant to restrict access of devices, through dot1x or other methods, and to propagate MAC address and VLAN information to the authenticator. The authenticator acts as an enforcer of information provided in those updates.
As an example, a new VLAN (VLAN300) was created on both switches, and a device was plugged into port fa0/4 on the supplicant. Port fa0/4 is a simple access port that is not configured for dot1x.
This output from the supplicant shows a new registered port:
bstp-3500-2#show cisp registrations
Interface(s) with CISP registered user(s):
------------------------------------------
Fa0/4
Fa0/5
Auth Mgr (Authenticator)
Fa0/6
802.1x Sup (Supplicant)
On the authenticator, a new MAC address is visible on VLAN 300.
bstp-3500-1#show cisp clients
Authenticator Client Table:
---------------------------
MAC Address VLAN Interface
---------------------------------
001b.0d55.21c1 200 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c0 1 Fa0/6
001b.0d55.21c2 300 Fa0/6
c464.13b4.29c3 200 Fa0/6
68ef.bdc7.13ff 300 Fa0/6
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
These commands help you troubleshoot NEAT and CISP; this document includes examples for most of them:
- debug cisp all - shows the exchange of CISP information between switches.
- show cisp summary - displays a summary of the CISP interface status on the switch.
- show cisp registrations - indicates the interfaces that participate in CISP exchanges, the roles of those interfaces, and whether the interfaces are part of NEAT.
- show cisp clients - displays a table of known client MAC addresses and their location (VLAN and interface). This is useful mainly from the authenticator.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
18-Oct-2013 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)




 Feedback
Feedback