Call Flow Debugging of an SSG Internet Gateway configured with DHCP Secure ARP, SSG Port-Bundle Host Key, SSG TCP Redirect, SESM, and SSG/DHCP Awareness
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
The focus of this document is an IOS Internet Gateway that runs SSG and DHCP with SESM for portal services.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
Technology and Feature Overview
Service Selection Gateway (SSG)
Service Selection Gateway (SSG) is a switching solution for service providers who offer intranet, extranet, and Internet connections to subscribers with broadband access technology, such as digital subscriber lines (DSL), cable modems, or wireless to allow simultaneous access to network services.
SSG works in conjunction with the Cisco Subscriber Edge Services Manager (SESM). Together with the SESM, SSG provides subscriber authentication, service selection, and service connection capabilities to subscribers of Internet services. Subscribers interact with an SESM web application using a standard Internet browser.
The SESM operates in two modes:
-
RADIUS mode—This mode obtains subscriber and service information from a RADIUS server. SESM in RADIUS mode is similar to the SSD.
-
LDAP mode—The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) mode provides access to an LDAP-compliant directory for subscriber and service profile information. This mode also has enhanced functionality for SESM web applications and uses a role-based access control (RBAC) model to manage subscriber access.
SSG Port Bundle Host Key
The SSG Port-Bundle Host Key feature enhances communication and functionality between SSG and SESM with a mechanism that uses the host source IP address and source port to identify and monitor subscribers.
With the SSG Port-Bundle Host Key feature, SSG performs port-address translation (PAT) and network-address translation (NAT) on the HTTP traffic between the subscriber and the SESM server. When a subscriber sends an HTTP packet to the SESM server, SSG creates a port map that changes the source IP address to a configured SSG source IP address and changes the source TCP port to a port allocated by SSG. SSG assigns a bundle of ports to each subscriber because one subscriber can have several simultaneous TCP sessions when it accesses a web page. The assigned host key, or combination of port-bundle and SSG source IP address, uniquely identifies each subscriber. The host key is carried in RADIUS packets sent between the SESM server and SSG in the Subscriber IP vendor-specific attribute (VSA). When the SESM server sends a reply to the subscriber, SSG translates the destination IP address and destination TCP port in accordance with the port map.
SSG TCP Redirection for Unauthenticated Users
Redirection for unauthenticated users redirects packets from a user if the user has not authorized with the service provider. When an unauthorized subscriber attempts to connect to a service on a TCP port (for example, to www.cisco.com), SSG TCP Redirect redirects the packet to the captive portal (SESM or a group of SESM devices). SESM issues a redirect to the browser to display the logon page. The subscriber logs in to SESM and is authenticated and authorized. SESM then presents the subscriber with a personalized home page, the service provider home page, or the original URL.
DHCP Secured IP Address Assignment
The DHCP Secure IP Address Assignment feature introduces the capability to secure ARP table entries to Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) leases in the DHCP database. This feature secures and synchronizes the MAC address of the client to the DHCP binding, preventing unauthorized clients or hackers from spoofing the DHCP server and taking over a DHCP lease of an authorized client. When this feature is enabled, and the DHCP server assigns an IP address to the DHCP client, the DHCP server adds a secure ARP entry to the ARP table with the assigned IP address and the MAC address of the client. This ARP entry cannot be updated by any other dynamic ARP packets, and this ARP entry exists in the ARP table for the configured lease time or as long as the lease is active. The secured ARP entry can be deleted only by an explicit termination message from the DHCP client or DHCP server when the DHCP binding expires. This feature can be configured for a new DHCP network or used to upgrade the security of a current network. The configuration of this feature does not interrupt service and is not visible to the DHCP client.
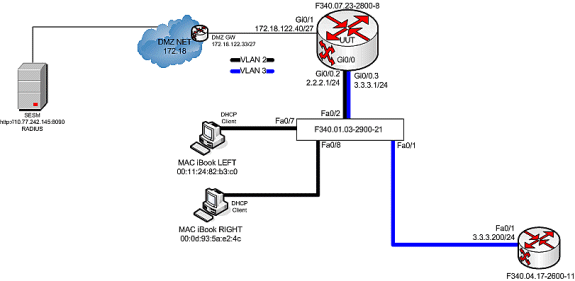
Testbed Diagram
Call Flow Debug
Complete these steps:
-
When MAC iBook LEFT first connects the Ethernet cable to this network, it leases IP address 2.2.2.5/29 from the IOS DHCP Server that runs on “F340.07.23-2800-8.”
debug ip dhcp server packet debug ssg dhcp events *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: DHCP-DISCOVER event received. SSG-dhcp awareness feature enabled *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: DHCPDISCOVER received from client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 on interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2. *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: Get pool name called for 0011.2482.b3c0. No hostobject *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN: Get pool class called, class name = Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: Sending DHCPOFFER to client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: creating ARP entry (2.2.2.5, 0011.2482.b3c0). *Oct 13 20:24:04.073: DHCPD: unicasting BOOTREPLY to client 0011.2482.b3c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: DHCPREQUEST received from client 0100.1124.82b3.c0. *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN:2.2.2.5: IP address notification received. *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: SSG-DHCP-EVN:2.2.2.5: HostObject not present *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: Can't find any hostname to update *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: Sending DHCPACK to client 0100.1124.82b3.c0 (2.2.2.5). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: creating ARP entry (2.2.2.5, 0011.2482.b3c0). *Oct 13 20:24:05.073: DHCPD: unicasting BOOTREPLY to client 0011.2482.b3c0 (2.2.2.5). F340.07.23-2800-8#show ip dhcp binding Bindings from all pools not associated with VRF: IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type Hardware address/ User name 2.2.2.5 0100.1124.82b3.c0 Oct 13 2008 08:37 PM Automatic -
After it successfully leases IP address 2.2.2.5, MAC iBook LEFT opens a web browser and points it to http://3.3.3.200, which is used to simulate protected resources tied to SSG Service “distlearn.” SSG Service “distlearn” is locally defined in the SSG Router “F340.07.23-2800-8”:
local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255"
In reality, http://3.3.3.200 is a Cisco IOS router configured for “ip http server” and listens on TCP 80, so it is basically a web server.
After the MAC iBook LEFT attempts to browse to http://3.3.3.200, since this connection is ingress on an interface configured with “ssg direction downlink,” the SSG router first checks for the existence of an active SSG Host Object for the source IP address of the HTTP request. Because this the first such request from IP address 2.2.2.5, an SSG Host Object does not exist, and a TCP redirect toward SESM is instantiated for host 2.2.2.5 through this configuration:
ssg tcp-redirect port-list ports port 80 port 8080 port 8090 port 443 All hosts with destination requests on these TCP Ports are candidates for redirection. server-group ssg_tr_unauth server 10.77.242.145 8090 10.77.242.145 is the SESM server and it’s listening for HTTP on TCP 8090. “server” MUST be in default network or open-garden. redirect port-list ports to ssg_tr_unauth redirect unauthenticated-user to ssg_tr_unauth If an SSG router receives a packets on an interface with “ssg direction downlink” configured, it first compares the Source IP address of the packet with the SSG Host Object Table. If an Active SSG Host Object matching the Source IP address of this packet is not found, AND the destination TCP Port of the packet matches “port-list ports”, and the destination IP address is NOT included as a part of “ssg default-network” OR SSG Open Garden, then the user will be redirected because his is unauthenticated [no Host Object] and his packet is destined for a TCP port in the “port-list ports”. The user will then be captivated until an SSG Host Object is created, or until a timeout which is configurable via “redirect captivate initial default group”. debug ssg tcp redirect debug ssg ctrl-event *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: SSG-TCP-REDIR:-Up: created new remap entry for unauthorised user at 2.2.2.5 *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: Redirect server set to 10.77.242.145,8090 *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: Initial src/dest port mapping 49273<->80 F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg tcp-redirect mappings Authenticated hosts: No TCP redirect mappings for authenticated users Unauthenticated hosts: Downlink Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 TCP remapping Host:2.2.2.5 to server:10.77.242.145 on port:8090 The initial HTTP request from 2.2.2.5 had a source TCP Port of 49273 and a destination IP address of 3.3.3.200 and TCP port of 80. Because of the SSG TCP Redirect, the destination IP header is overwritten with the socket of the SESM server 10.77.242.145:8090. If Port Bundle Host Key were NOT configured, the Source socket of 2.2.2.5:49273 would remain unchanged. However, in this case, Port Bundle Host Key is configured therefore the source address of this packet is ALSO changed based on this configuration: ssg port-map destination range 80 to 8100 ip 10.77.242.145 source ip 172.18.122.40 Any packets destined to SESM on TCP ports 80-8100 are subject to PBHK source NAT to IP socket 172.18.122.40, starting with a port of 64. *Oct 13 20:24:36.833: group:ssg_tr_unauth, web-proxy:0 *Oct 13 20:24:37.417: SSG-REDIR-EVT: -Down: TCP-FIN Rxd for user at 2.2.2.5, port 49273 *Oct 13 20:24:37.421: SSG-REDIR-EVT: -Up: TCP-FIN Rxd from user at 2.2.2.5, src port 49273 As a part of this SSG TCP Redirect, the original URL is preserved http://3.3.3.200 but the destination IP socket is rewritten to 10.77.242.145:8090. So, when the SESM receives this URL of http://3.3.3.200 on TCP port 8090, it sends an HTTP redirect back toward the client’s browser directing the client to the SESM login page, which is http://10.77.242.145:8080/home?CPURL=http%3A%2F%2F3.3.3. 200%2F&t=fma4443t. Notice the Browser Redirect points the Client Browser to TCP 8080 for captive portal. As such, the TCP session for the initial IOS SSG Redirect to 10.77.242.145:8090 is terminated. Also, notice SESM has captured the original URL of http://3.3.3.200 in the Redirect. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (4,&) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=4 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling account status query for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: No active HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64, Ack the query with Complete ID. *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Send cmd 4 to host S172.18.122.40:64. dst=10.77.242.145:51806 *Oct 13 20:24:38.049: SSG-CTL-EVN: Deleting SSGCommandContext ::~SSGCommandContext With Port Bundle Host Key configured, all HTTP communications between Client and SESM are subject to Port Bundling, which is effectively Source NAT for the TCP socket. Above, the “SSG-CTL-EVN” messages debug the communication between the SESM and the IOS SSG Router using a proprietary RADIUS-based protocol. When using Port Bundle Host Key, SESM always uses the Port Bundle to identify the host, which in this case is 172.18.122.40:64. You’ll see when SESM sends the HTTP redirect resulting in the Web browser connecting to 10.77.242.145:8090, SESM also queries SSG on the Control Channel for existence of Host Object for 172.18.122.40:64, which the SSG Router knows is actually 2.2.2.5. Since no Host Object is present, the SSG Router sends the SESM “No active HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64” This can be confirmed at this point like this: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host ### Total HostObject Count: 0At this point, the browser on MAC iBook Left looks like this when http://3.3.3.200 is entered:
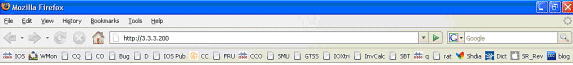
After the IOS SSG TCP and SESM HTTP redirects, the screen looks like this:
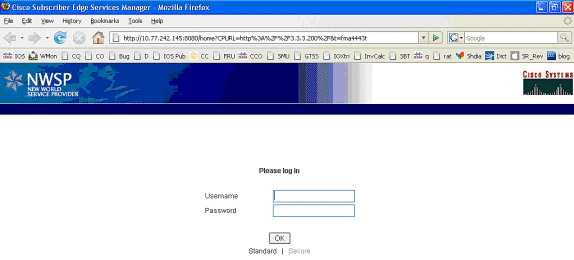
-
After the SSG TCP redirect to SESM and the subsequent HTTP redirect sent by SESM back to the browser of MAC iBook Left, MAC iBook Left enters user1 as the username and cisco as the password:
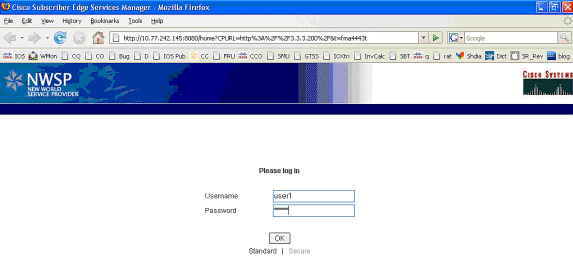
-
After the OK button is pushed, the SESM sends the SSG router these credentials through a proprietary RADIUS-based protocol.
*Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (1,user1) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=1 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling account logon for host 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: No auto-domain selected for user user1 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Authenticating user user1. *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: ssg_aaa_nasport_fixup function *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: slot=0, adapter=0, port=0, vlan-id=2, dot1q-tunnel-id=0, vpi=0, vci=0, type=10 *Oct 13 20:25:01.781: SSG-CTL-EVN: Deleting SSGCommandContext ::~SSGCommandContext
-
In turn, the SSG Router builds a RADIUS Access-Request Packet and sends it to RADIUS to authenticate user1:
*Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS(00000008): Send Access-Request to 10.77.242.145:1812 id 1645/11, len 88 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: authenticator F0 56 DD E6 7E 28 3D EF - BC B1 97 6A A9 4F F2 A6 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "user1" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: User-Password [2] 18 * *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 16 "0011.2482.b3c0" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15] *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 0 *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 9 "0/0/0/2" *Oct 13 20:25:01.785: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 172.18.122.40
-
RADIUS responds with an Access-Accept for user1, and an SSG Host Object is created in “F340.07.23-2800-8”:
*Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Received from id 1645/11 10.77.242.145:1812, Access-Accept, len 273 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: authenticator 52 7B 50 D7 F2 43 E6 FC - 7E 3B 22 A4 22 A7 8F A6 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Service-Type [6] 6 Framed [2] *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 23 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 17 "NInternet-Basic" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 13 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 7 "Niptv" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 14 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 8 "Ngames" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 18 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 12 "Ndistlearn" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 18 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 12 "Ncorporate" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 22 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 16 "Nhome_shopping" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 16 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 10 "Nbanking" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Vendor, Cisco [26] 16 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: ssg-account-info [250] 10 "Nvidconf" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "user1" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: Calling-Station-Id [31] 16 "0011.2482.b3c0" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15] *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 0 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 9 "0/0/0/2" *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 172.18.122.40 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS(00000008): eceived from id 1645/11 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 4 0 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating radius packet *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Response is good *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-EVN: HostObject::HostObject: size = 616 *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::Reset *Oct 13 20:25:02.081: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList NInternet-Basic *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Niptv *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ngames *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ndistlearn *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Ncorporate *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nhome_shopping *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nbanking *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: HostObject::InsertServiceList Nvidconf *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: DoAccountLogon: ProfileCache is Enabled *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Account logon is accepted [Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64, user1] *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Send cmd 1 to host S172.18.122.40:64. dst=10.77.242.145:51806 *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:02.085: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating HostObject for host 2.2.2.5 Finally, our SSG Host Object is created for 2.2.2.5. Notice that “user1” RADIUS profile is configured with many ssg-account-info VSA with “N” Attribute, which is an SSG code for Service to which the user is subscribed. Please note, this doesn’t mean “user1” has any Active services at this point, which can be confirmed with: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 1: 2.2.2.5 [Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64] ### Active HostObject Count: 1 F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 2.2.2.5 ------------------------ HostObject Content --- Activated: TRUE Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 User Name: user1 Host IP: 2.2.2.5 Host mac-address: 0011.2482.b3c0 Port Bundle: 172.18.122.40:64 Msg IP: 0.0.0.0 (0) Host DNS IP: 0.0.0.0 Host DHCP pool : Maximum Session Timeout: 64800 seconds Action on session timeout: Terminate Host Idle Timeout: 0 seconds User policing disabled User logged on since: *20:37:05.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:37:09.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 SMTP Forwarding: NO Initial TCP captivate: NO TCP Advertisement captivate: NO Default Service: NONE DNS Default Service: NONE Active Services: NONE AutoService: Internet-Basic; Subscribed Services: Internet-Basic; iptv; games; distlearn; corporate; home_shopping; banking; vidconf; Subscribed Service Groups: NONE
-
At this point, user1 is defined as an SSG Host Object but does not yet have access to any SSG Services. MAC iBook Left is presented with the Service Selection screen and clicks Distance Learning:
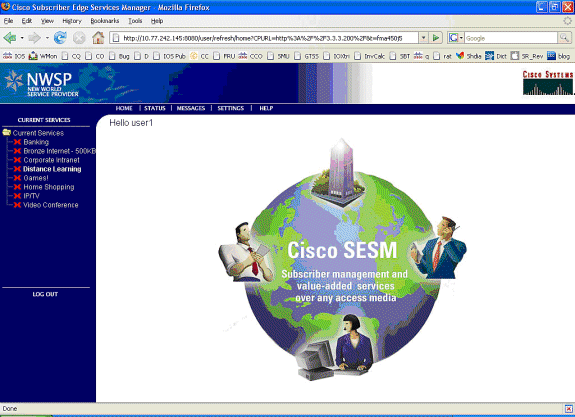
-
After Distance Learning is clicked, the SESM box communicates to the SSG Router with the control channel:
debug ssg ctrl-events *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Received cmd (11,distlearn) from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 SSG Router is receiving control channel command that SSG User 172.18.122.40:64 [maps to 2.2.2.5] wants to activate SSG Service ‘distlearn’. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add cmd=11 from Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 into SSG control cmd queue. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Dequeue cmd_ctx from the cmdQ and pass it to cmd handler *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Handling service logon for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Locating the HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating pseudo ServiceInfo for service: distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-EVN: ServiceInfo::ServiceInfo: size = 416 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: ServiceInfo: Init servQ and start new process for distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service(distlearn)::AddRef(): ref after = 1 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Got profile for distlearn locally Since “distlearn” is available from local configuration: local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255" ...we don’t need to make a AAA call to download SSG Service Information. However, please note that in most real-world SSG implementations, SSG Services are defined on the RADIUS AAA Server. *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Create a new service table for distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service bound on this interface are : distlearn *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service distlearn bound to interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3 firsthop 0.0.0.0 *Oct 13 20:25:38.029: Service Address List : *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: Addr:3.3.3.200 mask:255.255.255.255 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Add a new service distlearn to an existing table Here the SSG creates a Service Table for distlearn and binds it to an “ssg direction uplink” interface complete with the R attribute for the Service. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Locating the HostObject for Host-Key 172.18.122.40:64 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Checking connection activation for 172.18.122.40:64 to distlearn. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Creating ConnectionObject (172.18.122.40:64, distlearn) *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: ConnectionObject::ConnectionObject: size = 304 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service(distlearn)::AddRef(): ref after = 2 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Checking maximum service count. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: Opening connection for user user1 *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-EVN: Connection opened *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Service logon is accepted. *Oct 13 20:25:38.033: SSG-CTL-EVN: Activating the ConnectionObject. Once the Service is verified locally, SSG needs to build a “Connection” where a “Connection” is a tuple with: A. SSG Host Object B. SSG Service Name and Attributes C. SSG Downlink interface D. SSG Upstream interface A-D are used to create a pseudo hidden VRF service table for which traffic from this host can transit. See here: F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg connection 2.2.2.5 distlearn ------------------------ConnectionObject Content ---- User Name: user1 Owner Host: 2.2.2.5 Associated Service: distlearn Calling station id: 0011.2482.b3c0 Connection State: 0 (UP) Connection Started since: *20:40:21.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:41:04.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 Connection Traffic Statistics: Input Bytes = 420, Input packets = 5 Output Bytes = 420, Output packets = 5 Session policing disabled F340.07.23-2800-8#show ssg host 2.2.2.5 ------------------------ HostObject Content ----------- Activated: TRUE Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0.2 User Name: user1 Host IP: 2.2.2.5 Host mac-address: 0011.2482.b3c0 Port Bundle: 172.18.122.40:64 Msg IP: 0.0.0.0 (0) Host DNS IP: 0.0.0.0 Host DHCP pool : Maximum Session Timeout: 64800 seconds Action on session timeout: Terminate Host Idle Timeout: 0 seconds User policing disabled User logged on since: *20:37:05.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 User last activity at: *20:40:23.000 UTC Mon Oct 13 2008 SMTP Forwarding: NO Initial TCP captivate: NO TCP Advertisement captivate: NO Default Service: NONE DNS Default Service: NONE Active Services: distlearn; AutoService: Internet-Basic; Subscribed Services: Internet-Basic; iptv; games; distlearn; corporate; home_shopping; banking; vidconf; Subscribed Service Groups: NONE -
The SSG Connection is up, and the call flow is completed. MAC iBook Left can successfully browse to http://3.3.3.200:
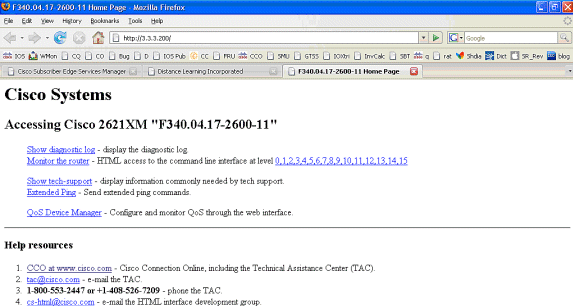
SSG Router Configuration Explanation with Feature Documents
version 12.4 service nagle no service pad service tcp-keepalives-in service tcp-keepalives-out service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname F340.07.23-2800-8 ! boot-start-marker boot system flash flash: c2800nm-adventerprisek9-mz.124-21.15 boot-end-marker ! logging buffered 1024000 debugging ! aaa new-model ! aaa authorization network default group radius ! aaa session-id common no ip source-route ! ip cef ip dhcp relay information trust-all ip dhcp use vrf connected ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.1 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.2 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.3 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.4 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.6 ip dhcp excluded-address 2.2.2.7 We are excluding 2.2.2.1-4 and 2.2.2.6-7 to ensure the only DHCP address that will be leased is 2.2.2.5/29. Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server ip dhcp pool dhcp_guest_v3501 network 2.2.2.0 255.255.255.248 default-router 2.2.2.1 dns-server 172.18.108.34 lease 0 4 update arp If an interface on this router is configured with an address in the 2.2.2.0/29 range, it will field DHCP request from host on that network and assign IP address 2.2.2.5, GW 2.2.2.1, and DNS Server 172.18.108.24. The lease time on the IP address will be 4 hours. Also, “update arp” will ensure ARP entries for IP addresses leased via DHCP will match the MAC entry in the DHCP Binding table. This will prevent SSG session hijacking in the event a static user re-uses a DHCP [or is given] leased address. Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Configuring DHCP Services for Accounting and Security ! no ip domain lookup ip auth-proxy max-nodata-conns 3 ip admission max-nodata-conns 3 ! voice-card 0 no dspfarm ! ssg enable Enables SSG subsystem. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg intercept dhcp Enables SSG/DHCP Awareness. In our example, this will result in an SSG Host object being destroyed when either of these occur: A. A DHCPRELEASE message is received for an IP address matching a currently Active SSG Host Object. B. A DHCP Lease expires for an IP address matching a currently Active SSG Host Object. Configuring SSG for On-Demand IP Address Renewal ssg default-network 10.77.242.145 255.255.255.255 All packets ingress to “ssg direction downlink” interfaces can access the “ssg default-network” regardless as to whether a Host or Connection Object exists. SSG allows all users, even unauthenticated users, to access the default network. Typically, SESM belongs to the default network. However, other types of servers, such as DNS/DHCP servers or TCP-Redirect servers, can also be part of the default network. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg service-password cisco If an SSG Service is not defined locally and we therefore need to make a RADIUS call when a user subscribes to an SSG Service, the password “cisco” is used in the RADIUS Access-Request for the Service. ssg radius-helper auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 ssg radius-helper key cisco Used to communicate with SESM on SSG Control Channel. SESM must also maintain a similar static configuration for each SSG Router it serves. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg auto-logoff arp match-mac-address interval 30 In the absence of user traffic, SSG will send an ARP Ping for all Active Host Objects and will invoke an AutoLogoff if either the host fails to reply or the MAC address of the host has changed. Configuring SSG to Log Off Subscribers ssg bind service distlearn GigabitEthernet0/0.3 SSG traffic is not routed using the Global routing table. Instead it’s routed from “ssg direction downstream” interface using the information in the mini-VRF seen in “show ssg connection”, which includes a manual binding of Service<-->”ssg direction uplink” interface. Hence, it is a requirement of SSG to manually bind services to interfaces or next-hop IP addresses. Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services ssg timeouts session 64800 Absolute timeout for SSG Host Object is 64800 seconds. Configuring SSG to Log Off Subscribers ssg port-map destination range 80 to 8100 ip 10.77.242.145 source ip 172.18.122.40 Port Bundle Host Key configuration. All traffic destined to 10.77.242.145 in the range of TCP 80 to 8100 will be Source NATed to 172.18.122.40. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks ssg tcp-redirect Enters SSG redirect sub-config. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers port-list ports port 80 port 8080 port 8090 port 443 Defines a list of destination TCP ports which are candidates for TCP redirection. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers server-group ssg_tr_unauth server 10.77.242.145 8090 Defines a redirect server list and defines the TCP port on which they’re listening for redirects. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers redirect port-list ports to ssg_tr_unauth redirect unauthenticated-user to ssg_tr_unauth If a Host Object does NOT exist and the traffic is ingress to an “ssg direction downlink” interface AND its destination port is in port-list ports, THEN redirect this traffic to “server-group ssg_tr_unauth”. Configuring SSG to Authenticate Web Logon Subscribers ssg service-search-order local remote Look for SSG Service defined in a local-profile in IOS configuration before making a AAA call to download Service information. Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services local-profile distlearn attribute 26 9 251 "R3.3.3.200;255.255.255.255" Local definition of SSG Service “distlearn” 26 9 251 is Vendor Specific, Cisco, SSG Service Info Attributes defined herein: R: Destination Network, Specifies IP routes belonging to this Service Configuring SSG for Subscriber Services RADIUS Profiles and Attributes for SSG interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0.2 description Guest Wireless Vlan encapsulation dot1Q 2 ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.248 no ip redirects no ip unreachables no ip mroute-cache ssg direction downlink All SSG Host Objects should be located on downlink direction. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks interface GigabitEthernet0/0.3 description Routed connection back to Blue encapsulation dot1Q 3 ip address 3.3.3.1 255.255.255.0 ssg direction uplink All SSG Services should be located on uplink direction. Implementing SSG: Initial Tasks interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 172.18.122.40 255.255.255.224 duplex auto speed auto ! ip forward-protocol nd ip route 10.77.242.144 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 10.77.242.145 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 157.157.157.0 255.255.255.0 3.3.3.5 ip route 172.18.108.34 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ip route 172.18.124.101 255.255.255.255 172.18.122.33 ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip radius source-interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ! radius-server host 10.77.242.145 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 timeout 5 retransmit 3 key 7 070C285F4D06 ! control-plane ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
Security and Session Reuse Considerations
When you use SSG and DHCP together, these scenarios can allow malicious users to reuse an authenticated SSG Host Object that allow unauthenticated access to secure resources:
-
If SSG/DHCP awareness is not configured with “ssg intercept dhcp,” a new DHCP user can lease a previously-leased IP address for which an SSG Host Object still exists. Since the first TCP request from this new user has a matching, although stale, SSG Host Object that matches the source IP address, this user is granted unauthenticated use of protected resources. This can be prevented with “ssg intercept dhcp,” which results in the removal of an SSG Host Object when either occurs:
-
DHCPRELEASE is received for an IP address that matches an Active Host Object.
-
The DHCP Lease expires for an IP address that matches an Active Host Object.
-
-
If a DHCP user socializes the leased IP address to a malicious user before a non-graceful DHCP logout, which is a DHCP logout for which a DHCPRELEASE is not sent, the malicious user can statically configure the machine with this IP address and reuse the SSG Host object whether or not “ssg intercept dhcp” is configured. This can be prevented with a combination of “ssg intercept dhcp” and “update arp” configured underneath the IOS DHCP Pool. The “update arp” ensures that the only IOS subsystem able to add or remove ARP entries is the DHCP server subsystem. With “update arp,” the IP-to-MAC DHCP binding always matches the IP-to-MAC binding in the ARP table. Even though the malicious user has a statically configured IP address that matches the SSG Host object, the traffic is not allowed to enter the SSG router. Because the MAC address does not match the MAC address of the current DHCP binding, the IOS DHCP server prevents the creation of an ARP entry.
-
When SSG and DHCP are configured together, “ssg intercept dhcp” and “update arp” prevent session reuse. The final non-security related challenge is to free the DHCP Lease and ARP entry when a DHCP Host performs a non-graceful logout. The configuration of “authorized arp” on the “ssg direction downlink” interface results in periodic ARP requests sent to all hosts to make sure they are still active. If no response is received from these periodic ARP messages, the DHCP binding is released, and the IOS DHCP subsystem purges the ARP entry.
interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 arp authorized arp probe interval 5 count 15
In this example, an ARP request is sent periodically to refresh all known ARP entries on Fa0/0 every 5s. After 15 failures, the DHCP binding is released, and the IOS DHCP subsystem purges the ARP entry.
In the context of SSG without “authorized arp,” if a DHCP host performs a non-graceful logout, the DHCP Lease and its associated SSG Host Object remain active until the lease for this DHCP address expires, but no session reuse occurs as long as “ssg intercept dhcp” is configured globally.
The “authorized arp” turns off dynamic ARP learning on the interface on which it is configured. The only ARP entries on the interface in question are those added by the IOS DHCP server after a lease is started. These ARP entries are then purged by IOS DHCP Server once the lease has terminated, either because of the receipt of a DHCP RELEASE, a lease expiration, or an ARP Probe failure because of a non-graceful DHCP logout.
Implementation Notes:
-
The “ssg auto-logoff arp” and “ssg auto-logoff icmp” are undesirable methods to prevent session reuse or resultant security issues. The “arp” and “icmp” variants of “ssg auto-logoff” only send an ARP or IMCP PING when traffic is not seen on the SSG connection within the configured “interval,” the lowest of which is 30 seconds. If DHCP leases a previously used IP address within 30 seconds, or a malicious user statically configures a currently-bound DHCP address within 30 seconds, the session is reused because SSG sees traffic on the connection object, and “ssg auto-logoff” does not invoke.
-
In all use cases, session reuse is not prevented if a malicious host performs a MAC address spoof.
Table 1 – Session Reuse and Security Considerations in SSG/DHCP Deployments
| Command | Function | Security Implications |
|---|---|---|
| ssg auto-logoff arp [match-mac-address] [interval seconds] ssg auto-logoff icmp [timeout milliseconds] [packets number] [interval seconds] | Removes SSG Host Object after failure of ARP or ICMP PING, which are only sent after no traffic is seen on the SSG connection within the “interval.” | Reuses session if DHCP leases a previously used IP address within 30 seconds, or a malicious user statically configures a currently-bound DHCP address within 30 seconds because SSG sees traffic on the connection object, and “ssg auto-logoff” does not invoke. |
| ssg intercept dhcp | Creates SSG/DHCP Awareness that allows the deletion of the SSG Host Object within these events: A DHCPRELEASE is received for an IP address that matches an Active Host Object. B. The DHCP Lease expires for an IP address that matches an Active Host Object. | Prevents DHCP users from the reuse of SSG sessions but does not prevent static users from spoofing DHCP addresses or the reuse of SSG sessions. |
| ip dhcp pool TEST update arp | Ensures that the only IOS subsystem capable of the addition or removal of ARP entries is the DHCP Server subsystem. | Prevents all session reuse when configured with “ssg intercept dhcp.” When configured without “ssg intercept dhcp,” if DHCP leases a previously used IP address, session reuse is still possible. |
| interface FastEthernet0/0 arp authorized | Sends periodic ARP requests to all hosts to make sure they are still active. Turns off dynamic ARP learning. | Allows DHCP binding and ARP entry deletion when a DHCP user performs a non-graceful logout. |
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
01-Dec-2008 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)





 Feedback
Feedback