Configuring VPN MPLS over POS, SRP and ATM on Cisco GSRs
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration for Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) virtual private network (VPN) over ATM, packet over SONET/SDH (POS), and spatial reuse protocol (SRP) on Cisco 12000 Gigabit Switch Routers (GSRs).
These acronyms are used in this document.
-
CE —Customer Edge router
-
PE—Provider Edge router
-
P—Provider core router
-
VRF—Virtual Routing and Forwarding
Prerequisites
Requirements
Before you attempt this configuration, ensure these requirements are met:
-
Basic knowledge of MPLS and the MPLS VPN feature.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
P and PE routers
-
Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.0(28)S on all routers
-
Cisco GSR 12000 series routers
-
-
CE routers
-
Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(28)S on all routers
-
Cisco 7200VXR routers
-
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Related Products
This configuration can also be used with these router platforms supported at the provider (P) core:
-
Cisco 7200
-
Cisco 7500
-
Cisco 7600
-
Cisco 8500
-
Cisco 10000
-
Cisco 10700
-
Cisco 12000
This configuration can also be used with these router platforms supported at the provider edge (PE):
-
Cisco 3600
-
Cisco 3700
-
Cisco 7200
-
Cisco 7500
-
Cisco 7600
-
Cisco 8500
-
Cisco 10000
-
Cisco 10700
-
Cisco 12000
Note: Cisco 3700/3600 routers do not have support for POS and SRP modules. Any platform below the 3600 does not support MPLS configuration.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Background Information
MPLS is made available to support multiple physical interfaces. These interfaces includes ATM, POS and SRP. These interfaces are typically used for backbone connections due to their high bandwidth support. The MPLS VPN feature allows service providers to interconnect multiple sites without the need for ATM, POS or SRP at the customer side.
There are two implementations of MPLS over ATM. One is the use of virtual path identifier (VPI) and virtual channel identified (VCI) as the label which is also known as "cell-based" MPLS over ATM. This implementation is documented under RFC 3035 ![]() . The second ATM implementation is the use of the MPLS "shim header" which is also known as packet-based MPLS over ATM. This shim header is inserted between the Layer 2 and Layer 3 headers. The format of the shim header is documented under RFC 3032
. The second ATM implementation is the use of the MPLS "shim header" which is also known as packet-based MPLS over ATM. This shim header is inserted between the Layer 2 and Layer 3 headers. The format of the shim header is documented under RFC 3032 ![]() . This sample configuration is based on the "shim header" implementation for the ATM interface.
. This sample configuration is based on the "shim header" implementation for the ATM interface.
Packet over Synchronous Optical Network/Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SONET/SDH), is a technology that places the IP layer directly above the SONET layer. It eliminates the overhead needed to run IP over ATM over SONET. POS supports multiple encapsulation format. These are PPP, HDLC and Frame Relay. The shim header is used to provide MPLS support. This sample configuration uses the default HDLC encapsulation on Cisco POS interfaces.
Spatial Reuse Protocol (SRP) is a Layer 2 technology that provides resiliency at the Layer 2 level. It also runs on top of SONET/SDH. MPLS support is provided by the shim header implementation.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: To find additional information on the commands used in this document, use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) .
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
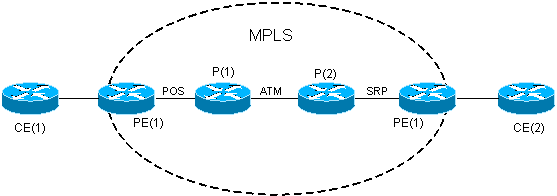
Configurations
This lists some considerations made on the sample configuration:
-
The MPLS VPN sample configuration service EIGRP routes from the CEs. Cisco bug ID CSCds09932 (registered customers only) has introduced EIGRP support for MPLS VPN with Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(22)S. This has been ported to Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2T via Cisco bug ID CSCdx26186 (registered customers only) starting on Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(15)T. The application of the same VRF to multiple EIGRP instances is not supported and can crash the router. A check on this issue was later integrated with Cisco bug ID CSCdz40426 (registered customers only) . Refer to MPLS VPN Support for EIGRP Between Provider Edge and Customer Edge to learn more about the MPLS VPN support for EIGRP.
-
The EIGRP autonomous system is the same on both CE routers. The BGP autonomous system is the same on both PE routers.
-
The MPLS backbone is based on POS, ATM and SRP interfaces and configured with Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and MP-BGP. The connection between PE and CE is Fast Ethernet.
This document uses these configurations:
| CE(1) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ip cef !--- CEF is not required on the CE because there is no MPLS configuration. !--- CEF is the fastest switching algorithm on Cisco routers !--- and it is best to leave it enabled. ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback1 ip address 11.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback2 ip address 11.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet2/0 ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.252 ! router eigrp 100 network 11.0.0.0 network 192.168.2.0 no auto-summary ! ip classless |
| PE(1) |
|---|
!
version 12.0
!
!--- CEF is enabled by default on GSR.
.
!
ip vrf Customer_A
rd 100:1
route-target export 100:1
route-target import 100:1
!--- Enables the VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) routing table.
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip vrf forwarding Customer_A
!--- Associates a VRF instance with an interface or subinterface.
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.252
!
interface POS4/0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
!--- Enables dynamic Label Switching of IPv4 packets on an interface. !--- At minimum, this is all you need to configure MPLS over POS. !--- Note the default encapsulation of POS interfaces is HDLC. !--- An mpls ip command can also be used instead of tag-switching ip.
crc 32
clock source internal
!
!
router eigrp 1
!
address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A
redistribute bgp 100 metric 10000 1 255 1 1500
network 192.168.2.0
no auto-summary
autonomous-system 100
!--- The autonomous-system 100 must match the AS used on the CE. !--- The bgp must be redistributed with metric. The default-metric !--- command can also be used.
exit-address-family
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
!
router bgp 100
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
!
address-family vpnv4
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 send-community both
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A
redistribute eigrp 100
!--- The EIGRP AS 100 must be redistributed to the BGP vrf instance.
no auto-summary
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
ip classless |
| P(1) |
|---|
!
version 12.0
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface POS2/0
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
!--- This enables MPLS over POS.
crc 32
!
!
interface ATM6/0
no ip address
!
interface ATM6/0.100 point-to-point
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
tag-switching ip
pvc 0/100
!
!--- This enables "packet-based" MPLS over ATM.
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.0.0.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
!
ip classless |
| P(2) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 ! interface ATM4/0 no ip address ! interface ATM4/0.100 point-to-point ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 tag-switching ip pvc 0/100 !--- This enables "packet-based" MPLS over ATM. ! ! interface SRP5/0 ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.252 no ip directed-broadcast tag-switching ip !--- This enables MPLS over SRP. ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.1.1.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.2.2.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! ip classless |
| PE(2) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ! ip vrf Customer_A rd 100:1 route-target export 100:1 route-target import 100:1 ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 ! interface SRP4/0 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.252 tag-switching ip !--- This enables MPLS over SRP. ! interface FastEthernet6/0 ip vrf forwarding Customer_A !--- Associates a VRF instance with an interface or subinterface. ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252 ! ! router eigrp 1 ! address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A redistribute bgp 100 metric 10000 1 255 1 1500 network 192.168.1.0 no auto-summary autonomous-system 100 exit-address-family !--- The autonomous-system 100 must match the AS used on the CE. !--- The bgp must be redistributed with metric. The default-metric !--- command can also be used. ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! router bgp 100 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A redistribute eigrp 100 !--- The EIGRP AS 100 must be redistributed to the BGP vrf instance. no auto-summary no synchronization exit-address-family ! ip classless |
| CE(2) |
|---|
! version 12.0 ! ip cef !--- CEF is not required on the CE because there is no MPLS configuration. !--- CEF is the fastest switching algorithm on Cisco routers so it is !--- best to leave it enabled. ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 22.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback1 ip address 22.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback2 ip address 22.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet2/0 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.252 ! ! router eigrp 100 network 22.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 no auto-summary ! |
Verify
This section provides information you can use to confirm your configuration is working properly.
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
-
show ip vrf—Verifies that the correct VRF exists.
-
show ip route vrf Customer_A—Verifies the routing information on the PE routers.
-
ping vrf Customer_A <ip address>—Verifies connectivity by sending ICMP packets.
-
traceroute vrf Customer_A <ip address>—Verifies the routing information on the PE routers.
-
show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A neighbors—Verifies the EIGRP neighbor inside the VRF instance.
-
show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A topology—Verifies EIGRP topology inside the VRF instance.
-
show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf Customer_A—Verifies the BGP table inside the VRF instance.
-
show ip cef vrf Customer_A <ip address> detail—Verifies the CEF table inside the VRF instance.
-
show tag-switching forwarding-table—Verifies if there is a route/tag for the destination prefix.
-
show ip route—Verifies that CEs exchange routes.
PE(1)
PE(1)#show ip vrf
Name Default RD Interfaces
Customer_A 100:1 FastEthernet0/0
PE(1)#show ip route vrf Customer_A
Routing Table: Customer_A
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is not set
22.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
B 22.3.1.0 [200/156160] via 4.4.4.4, 01:12:28
B 22.2.1.0 [200/156160] via 4.4.4.4, 01:12:28
B 22.1.1.0 [200/156160] via 4.4.4.4, 01:12:28
11.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 11.2.1.0 [90/156160] via 192.168.2.2, 01:12:50, FastEthernet0/0
D 11.3.1.0 [90/156160] via 192.168.2.2, 01:12:50, FastEthernet0/0
D 11.1.1.0 [90/156160] via 192.168.2.2, 01:12:50, FastEthernet0/0
192.168.1.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 192.168.1.0 [200/0] via 4.4.4.4, 01:16:14
192.168.2.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
PE(1)#ping vrf Customer_A 192.168.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
D-GSR-12012-2A#ping vrf Customer_A ip ?
WORD Ping destination address or hostname
<cr>
PE(1)#ping vrf Customer_A ip
Target IP address: 192.168.1.2
Repeat count [5]: 100
Datagram size [100]: 1500
Timeout in seconds [2]:
Extended commands [n]:
Sweep range of sizes [n]:
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 100, 1500-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (100/100), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
PE(1)#traceroute vrf Customer_A 192.168.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 192.168.1.2
1 10.0.0.2 [MPLS: Labels 18/28 Exp 0] 0 msec 0 msec 0 msec
2 10.1.1.2 [MPLS: Labels 19/28 Exp 0] 0 msec 0 msec 0 msec
3 192.168.1.1 4 msec 0 msec 0 msec
4 192.168.1.2 4 msec 0 msec *
PE(1)#show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 100
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq Type
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 192.168.2.2 Fa0/0 11 10:51:41 10 200 0 8
PE(1)#show ip eigrp vrf Customer_A topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS(100)/ID(192.168.2.1) Routing Table: Customer_A
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - Reply status
P 11.2.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via 192.168.2.2 (156160/128256), FastEthernet0/0
P 11.3.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via 192.168.2.2 (156160/128256), FastEthernet0/0
P 11.1.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via 192.168.2.2 (156160/128256), FastEthernet0/0
P 22.3.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via VPNv4 Sourced (156160/0)
P 22.2.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via VPNv4 Sourced (156160/0)
P 22.1.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 156160
via VPNv4 Sourced (156160/0)
P 192.168.1.0/30, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via VPNv4 Sourced (28160/0)
P 192.168.2.0/30, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via Connected, FastEthernet0/0
PE(1)#show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf Customer_A
BGP table version is 17, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 100:1 (default for vrf Customer_A)
*> 11.1.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 156160 32768 ?
*> 11.2.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 156160 32768 ?
*> 11.3.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 156160 32768 ?
*>i22.1.1.0/24 4.4.4.4 156160 100 0 ?
*>i22.2.1.0/24 4.4.4.4 156160 100 0 ?
*>i22.3.1.0/24 4.4.4.4 156160 100 0 ?
*>i192.168.1.0/30 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 ?
*> 192.168.2.0/30 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
PE(1)#show ip cef vrf Customer_A
Prefix Next Hop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 drop Null0 (default route handler entry)
0.0.0.0/32 receive
11.1.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
11.2.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
11.3.1.0/24 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
22.1.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
22.2.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
22.3.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
192.168.1.0/30 10.0.0.2 POS4/0
192.168.2.0/30 attached FastEthernet0/0
192.168.2.0/32 receive
192.168.2.1/32 receive
192.168.2.2/32 192.168.2.2 FastEthernet0/0
192.168.2.3/32 receive
224.0.0.0/4 drop
224.0.0.0/24 receive
255.255.255.255/32 receive
PE(1)#show ip cef vrf Customer_A 11.1.1.0 detail
11.1.1.0/24, version 16, epoch 0, cached adjacency 192.168.2.2
0 packets, 0 bytes
tag information set, all rewrites owned
local tag: 27
via 192.168.2.2, FastEthernet0/0, 0 dependencies
next hop 192.168.2.2, FastEthernet0/0
valid cached adjacency
tag rewrite with Fa0/0, 192.168.2.2, tags imposed {}
PE(1)#show tag-switching forwarding-table
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface
16 Pop tag 2.2.2.2/32 0 PO4/0 point2point
17 17 3.3.3.3/32 0 PO4/0 point2point
18 18 4.4.4.4/32 0 PO4/0 point2point
19 19 10.2.2.0/30 0 PO4/0 point2point
20 Pop tag 10.1.1.0/30 0 PO4/0 point2point
22 Untagged 11.2.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
26 Untagged 11.3.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
27 Untagged 11.1.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
28 Aggregate 192.168.2.0/30[V] 255132
PE(1)#show tag-switching forwarding-table vrf Customer_A
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface
22 Untagged 11.2.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
26 Untagged 11.3.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
27 Untagged 11.1.1.0/24[V] 0 Fa0/0 192.168.2.2
28 Aggregate 192.168.2.0/30[V] 255132
P(1)
P(1)A#show tag-switching forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface 16 Pop tag 1.1.1.1/32 260843 PO2/0 point2point 17 Pop tag 3.3.3.3/32 0 AT6/0.100 point2point 18 19 4.4.4.4/32 269131 AT6/0.100 point2point 19 Pop tag 10.2.2.0/30 0 AT6/0.100 point2point
P(2)
P(2)#show tag-switching forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface 16 Pop tag 10.0.0.0/30 0 AT4/0.100 point2point 17 Pop tag 2.2.2.2/32 0 AT4/0.100 point2point 18 16 1.1.1.1/32 269930 AT4/0.100 point2point 19 Pop tag 4.4.4.4/32 276490 SR5/0 10.2.2.2
PE(2)
PE(2)#show tag-switching forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface 16 18 1.1.1.1/32 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 17 17 2.2.2.2/32 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 18 Pop tag 3.3.3.3/32 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 19 16 10.0.0.0/30 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 20 Pop tag 10.1.1.0/30 0 SR4/0 10.2.2.1 25 Untagged 22.1.1.0/24[V] 2280 Fa6/0 192.168.1.2 26 Untagged 22.2.1.0/24[V] 570 Fa6/0 192.168.1.2 27 Untagged 22.3.1.0/24[V] 570 Fa6/0 192.168.1.2 28 Aggregate 192.168.1.0/30[V] 251808
CE(1)
CE(1)#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is not set
22.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 22.3.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:45, FastEthernet2/0
D 22.2.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:45, FastEthernet2/0
D 22.1.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:45, FastEthernet2/0
11.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 11.2.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback1
C 11.3.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback2
C 11.1.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
192.168.1.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.1.0 [90/30720] via 192.168.2.1, 00:35:46, FastEthernet2/0
192.168.2.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0
CE(1)#ping 22.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 22.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
CE(2)
D-R7206-5A#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is not set
22.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 22.3.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback2
C 22.2.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback1
C 22.1.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
11.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 11.2.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:32, FastEthernet2/0
D 11.3.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:32, FastEthernet2/0
D 11.1.1.0 [90/158720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:32, FastEthernet2/0
192.168.1.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0
192.168.2.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.2.0 [90/30720] via 192.168.1.1, 00:36:33, FastEthernet2/0
CE(2)#ping 11.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 11.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
05-Jun-2005 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback