TL1 Session Setup on ONS 15454 and ONS 15327
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes three options to set up a Transaction Language 1 (TL1) session on a Cisco ONS 15454 or ONS 15327. The period for which a user is logged into the node for a ONS 15454 or ONS 15327 is called a session.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Readers of this document should have knowledge of these topics:
-
Cisco ONS 15454
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco ONS 15454 version 4 - all.
-
Cisco ONS 15454 version 3 - 3.3.0 and later.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Background Information
You can open a TL1 session on a ONS 15454 and ONS 15327 with the help of these three options:
-
Cisco Transport Controller (CTC)
-
Telnet
-
Craft interface
The TL1 password (PID) is masked when you access a TL1 session through any of these options. When you log out of any of these options, the session is closed. The ONS 15454 and ONS 15327 allow a maximum of 20 concurrent TL1 sessions (19 telnet sessions and one craft session) with any one or a combination of these options.
TL1 Session Through CTC
To open a TL1 session through the CTC, complete these steps:
-
Start Netscape or Internet Explorer from the PC with TCP/IP connection to the ONS 15454 or ONS 15327.
-
Enter the IP address of the node for ONS 15454 or ONS 15327 in the Netscape or Internet Explorer Web address (URL) field.
-
Log into the CTC.
-
Click Tools > Open TL1 Connection as shown in figure 1.
Figure 1 – Open TL1 Connection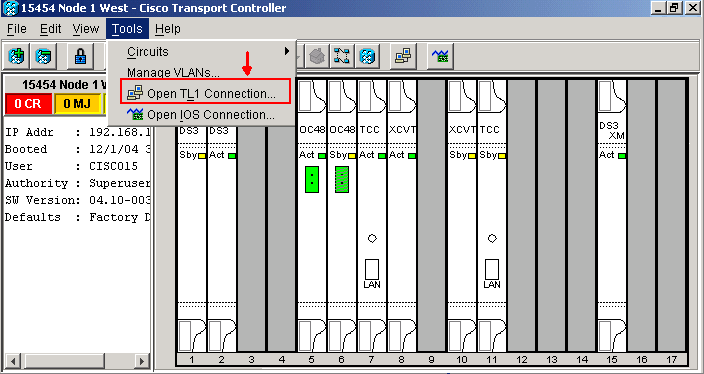
-
Select the node from the Select Node dialog box. Then click OK as shown in figure 2.
Figure 2 – Select Node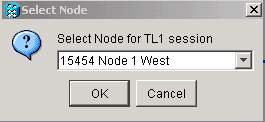
-
A TL1 interface window is displayed, as shown in figure 3. There are three sub-windows in the TL1 interface window: Request history, Message log, and TL1 request.
Type commands in the TL1 request window. Responses appear in the Message log window. The Request history window allows you to retrieve previous commands. To do so, just click on them.
Figure 3 – TL1 Interface Window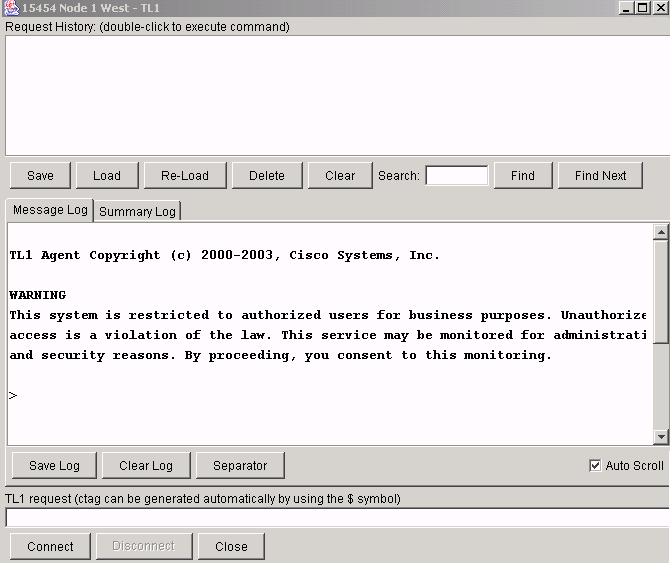
-
Type the activate user command in the TL1 request window to open a TL1 session:
ACT-user::<User ID>:<ctag>:<password>;
TL1 Session Through Telnet Over LAN
There are three available ports to access TL1 commands in a telnet session over a LAN connection. They are 2361, 3082 and 3083 as shown in figure 4. Port number 3082 is a raw TCP/IP port. It does not echo and it does not prompt the user. Port number 3083 is a telnet port that uses the telnet protocol and associated telnet escape sequences. Port number 2361 is supported for backward compatibility with earlier releases, and has the same behavior as Port 3083 (telnet port). Complete these steps:
-
Select Start > Run.
-
Enter cmd in the Run prompt box, and click OK.
-
At the DOS command prompt type:
telnet <node ip address or node name> <port number> and press Enter.
-
Type the activate user command to open a TL1 session:
ACT-user::<User ID>:<ctag>:<password>;
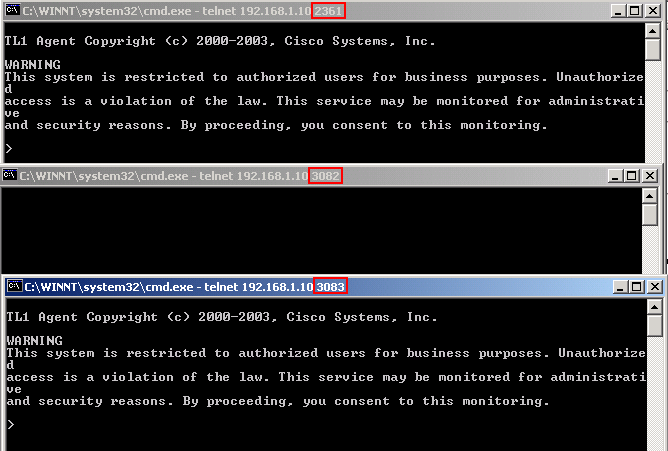
TL1 Session Through Craft Port
Instead of a browser, use a nine-pin craft port (RS-232 port), which is available on TCC/TCC2/TCC+ or XTC to access the ONS 15454 or ONS 15327. The craft port supports VT100 emulation such that TL1 commands can be entered directly without a browser. Complete these steps:
-
Connect the serial cable to the craft port on the active TCC/TCC+/TCC2 or XTC card.
-
Start HyperTerminal on the PC.
-
Select the correct COM port in the Connect using field from the drop-down list, as shown in figure 5.
Figure 5 – Select the Correct COM Port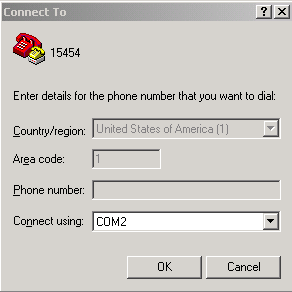
-
Set the bits per second to 9600, data bits to 8, parity to none, stop bits to 1 and flow control to none, as shown in figure 6.
Figure 6 – COM Port Settings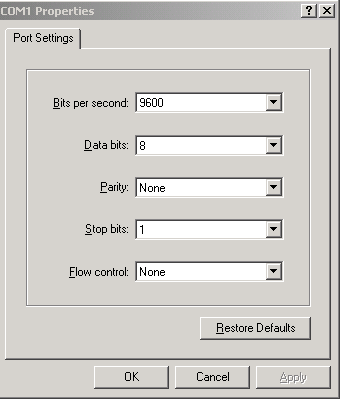
-
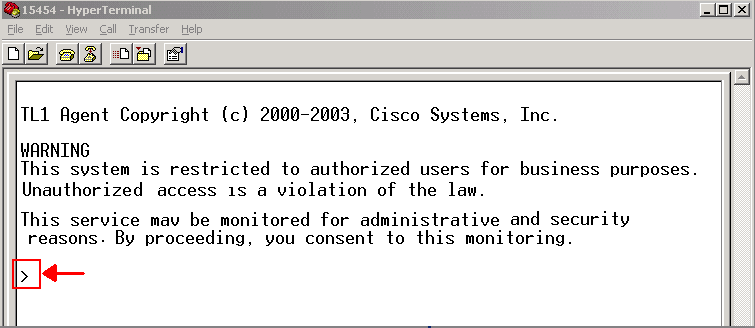
Press the ENTER key. The a > prompt appears, as shown in figure 7.
-
Type the activate user command to open a TL1 session:
ACT-user::<User ID>:<ctag>:<password>;
Related Information
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)





 Feedback
Feedback