Configure Clientless SSL VPN (WebVPN) on the ASA
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes configuration of the Cisco ASA 5500 Series to allow Clientless SSL VPN access to internal network resources.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration:
- SSL-enabled browser
- ASA with Version 7.1 or higher
- X.509 certificate issued to the ASA domain name
- TCP port 443, which must not be blocked along the path from the client to the ASA
The full list of requirements can be found in Supported VPN Platforms, Cisco ASA 5500 Series.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- ASA Version 9.4(1)
- Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) Version 7.4(2)
- ASA 5515-X
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
This document describes configuration for the Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) 5500 Series to allow Clientless Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN access to internal network resources.
Clientless SSL Virtual Private Network (WebVPN) allows for limited, but valuable, secure access to the corporate network from any location.
Users can achieve secure browser-based access to corporate resources at any time.
No additional client is needed in order to gain access to internal resources.
The access is provided through a Hypertext Transfer Protocol over SSL connection.
Clientless SSL VPN provides secure and easy access to a broad range of web resources and both web-enabled and legacy applications from almost any computer that can reach Hypertext Transfer Protocol Internet (HTTP) sites.
This includes:
- Internal websites
- Microsoft SharePoint 2003, 2007, and 2010
- Microsoft Outlook Web Access 2003, 2007, and 2013
- Microsoft Outlook Web App 2010
- Domino Web Access (DWA) 8.5 and 8.5.1
- Citrix Metaframe Presentation Server 4.x
- Citrix XenApp Version 5 to 6.5
- Citrix XenDesktop Version 5 to 5.6, and 7.5
- VMware View 4
A list of supported software can be found in Supported VPN Platforms, Cisco ASA 5500 Series.
Clientless VPN Support Matrix
|
Windows |
Windows/Mac |
Mac |
||||
|
Features/Technology/Applications |
MS Edge |
IE |
Firefox |
Chrome |
Safari |
Comments |
|
RDP plug-in |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
POST plug-in |
N |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
End of support for Java 8 |
|
ICA plug-in |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
N |
End of support for Java 8 |
|
VNC plug-in |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
N |
End of support for Java 8 |
|
SSH/TELNET plug-in |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
N |
End of support for Java 8 |
|
FTP/CIFS plug-in |
N |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
End of support for Java 8 |
|
Java Web Folder |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
N |
End of support for Java 8 |
|
Smart Tunnel |
N |
Y |
N* |
N |
N |
* Not supported on Mac 10.14+ |
|
Port-forwarding |
N |
Y |
N* |
N |
N |
* Not supported on Mac 10.14+ |
|
AnyConnect WebLaunch |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
Service Workers support |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
GBP (client-side rewriter) |
N |
N |
Y |
Y |
N* |
Feature introduced from ASA 9.9.2+ ; *Supports only Safari 11.1+ |
|
OWA |
N |
N* |
N* |
N* |
N* |
* 2013 only supported 2013 EOS April 2023. |
|
SharePoint |
N |
N* |
N* |
N* |
N* |
* 2013 only supported. 2013 EOS April 2023. |
|
Office365 |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
Citrix XenApp and XenDesktop 7.6 |
N |
Y |
N* |
Y |
N |
* HTML5 Receiver supported |
|
Citrix XenApp and XenDesktop 7.15 |
N |
Y |
Y |
Y |
N |
|
|
Citrix HTML5 Receiver |
N |
N* |
N* |
N* |
N |
* Works only HTML5 Receiver Version 1.7 with StoreFront 3.0 |
|
Citrix NetScaler Gateway and Load Balancer |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
Content Security Policy |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
Not supported, as there is no possibility to process it properly |
|
Blob API |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
Fetch API |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
Spaces between chunk-size |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
ASA does not expect spaces in chunk-size and is not able to put chunks together |
|
SVG <use> |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
Stack size limitation (ASA < 9.9.2) |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
Server-side rewrite mechanism has a limited amount of stack memory for file rewrite. If a file is too large or complicated, it is corrupted. Majority of recent applications have such limitations |
|
Stack size limitation (ASA > 9.9.2) |
N |
N |
Y |
Y |
N |
|
|
Application with Oracle Forms |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
|
|
Applications with Angular Framework |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
Most of the applications with these Angular features are not supported: |
|
Flash content with ActionScript2 and ActionScript3 |
N |
N |
N |
N |
N |
|
Configure
This article describes the configuration process for both the ASDM and the CLI. Use either of the tools in order to configure the WebVPN, but some of the configuration steps can only be achieved with the ASDM.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to obtain more information about the commands used in this section.
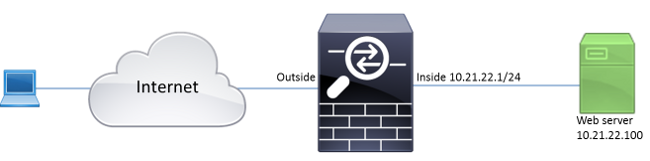
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Background Information
WebVPN uses the SSL protocol in order to secure the data transferred between the client and the server.
When the browser initiates a connection to the ASA, the ASA presents its certificate to authenticate itself to the browser.
To ensure that the connection between the client and the ASA is secure, provide the ASA with the certificate that is signed by the Certificate Authority that the client already trusts.
Otherwise the client does not have the means to verify authenticity of the ASA which results in the possibility of the man-in-the-middle attack and poor user experience, because the browser produces a warning that the connection is not trusted.
Note: By default, the ASA generates a self-signed X.509 certificate upon startup. This certificate is used in order to serve client connections by default. It is not recommended to use this certificate because its authenticity cannot be verified by the browser. Furthermore, this certificate is regenerated upon each reboot so it changes after each reboot.
Certificate installation is out of the scope of this document.
Configuration
Configure the WebVPN on the ASA with five major steps:
- Configure the certificate that is used by the ASA.
- Enable the WebVPN on an ASA interface.
- Create a list of servers and/or Uniform Resource Locator (URL) for WebVPN access.
- Create a group policy for WebVPN users.
- Apply the new group policy to a Tunnel Group.
Note: In ASA releases later than Release 9.4, the algorithm used to choose SSL ciphers has been changed (see Release Notes for the Cisco ASA Series, 9.4(x)).If only elliptic curve-capable clients are used, then it is safe to use elliptic curve private key for the certificate. Otherwise the custom cipher suite is to be used in order to avoid a ASA present a self-signed temporary certificate. You can configure the ASA to use only RSA-based ciphers with the ssl cipher tlsv1.2 custom "AES256-SHA:AES128-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DES-CBC3-SHA:DES-CBC-SHA:RC4-SHA:RC4-MD5" command.
- Option 1 - Import the certificate with the pkcs12 file.
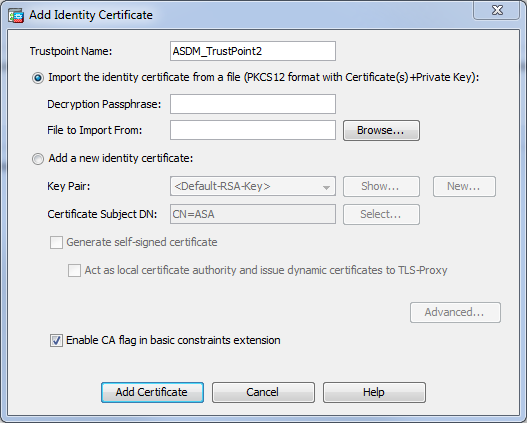
Choose Configuration > Firewall > Advanced > Certificate Management > Identity Certificates > Add. You can install it with the pkcs12 file or paste the contents in the Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) format.
CLI:
ASA(config)# crypto ca import TrustPoint-name pkcs12 "password"
Enter the base 64 encoded pkcs12.
End with the word "quit" on a line by itself:
MIIJUQIBAzCCCRcGCSqGSIb3DQEHAaCCCQgEggkEMIIJADCCBf8GCSqGSIb3DQEH
BqCCBfAwggXsAgEAMIIF5QYJKoZIhvcNAQcBMBwGCiqGSIb3DQEMAQYwDgQI8F3N
+vkvjUgCAggAgIIFuHFrV6enVflNv3sBByB/yZswhELY5KpeALbXhfrFDpLNncAB
z3xMfg6JkLYR6Fag1KjShg+o4qkDh8r9y9GQpaBt8x3Ozo0JJxSAafmTWqDOEOS/
7mHsaKMoao+pv2LqKTWh0O7No4Ycx75Y5sOhyuQGPhLJRdionbi1s1ioe4Dplx1b
--- output ommited ---
Enter the base 64 encoded pkcs12.
End with the word "quit" on a line by itself:
MIIJUQIBAzCCCRcGCSqGSIb3DQEHAaCCCQgEggkEMIIJADCCBf8GCSqGSIb3DQEH
BqCCBfAwggXsAgEAMIIF5QYJKoZIhvcNAQcBMBwGCiqGSIb3DQEMAQYwDgQI8F3N
+vkvjUgCAggAgIIFuHFrV6enVflNv3sBByB/yZswhELY5KpeALbXhfrFDpLNncAB
z3xMfg6JkLYR6Fag1KjShg+o4qkDh8r9y9GQpaBt8x3Ozo0JJxSAafmTWqDOEOS/
7mHsaKMoao+pv2LqKTWh0O7No4Ycx75Y5sOhyuQGPhLJRdionbi1s1ioe4Dplx1b
quit
INFO: Import PKCS12 operation completed successfullyOption 2 - Create a self-signed certificate.
Choose Configuration > Firewall > Advanced > Certificate Management > Identity Certificates > Add.
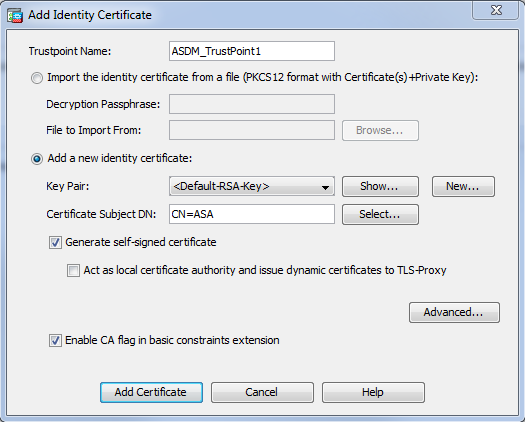
Click the Add a new identity certificate radio button. Check the Generate self-signed certificate check box. Choose a Common Name (CN) that matches domain name of the ASA.
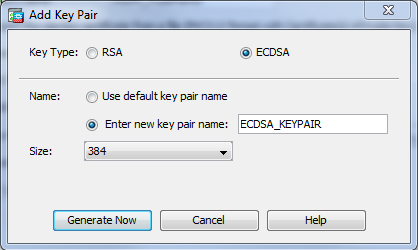
Click New in order to create the keypair for the certificate. Choose the Key Type, Name, and Size.
CLI:
ASA(config)# crypto key generate ecdsa label ECDSA_KEYPAIR noconfirm
ASA(config)# crypto ca trustpoint TrustPoint1
ASA(config-ca-trustpoint)# revocation-check none
ASA(config-ca-trustpoint)# id-usage ssl-ipsec
ASA(config-ca-trustpoint)# no fqdn
ASA(config-ca-trustpoint)# subject-name CN=ASA
ASA(config-ca-trustpoint)# enrollment self
ASA(config-ca-trustpoint)# keypair ECDSA_KEYPAIR
ASA(config-ca-trustpoint)# exit
ASA(config)# crypto ca enroll TrustPoint1 noconfirm - Choose the certificate to be used to serve WebVPN connections.
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Advanced > SSL Settings. From the Certificates menu, choose the trustpoint associated with the desired certificate for the outside interface. Click apply.
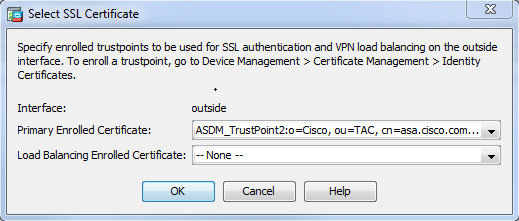
Equivalent CLI configuration:
ASA(config)# ssl trust-point <trustpoint-name> outside
- (Optional) Enable Domain Name Server (DNS) lookups.
WebVPN server acts as a proxy for client connections. It means that the ASA creates connections to the resources on behalf of the client. If the clients require connections to the resources that use domain names, then the ASA needs to perform the DNS lookup.
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > DNS.
Configure at least one DNS server and enable DNS lookups on the interface that faces the DNS server.
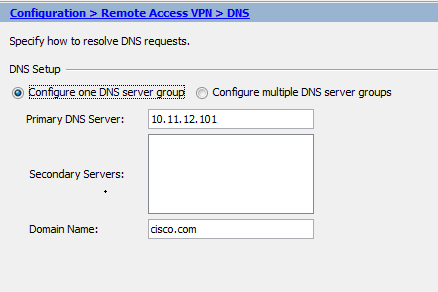
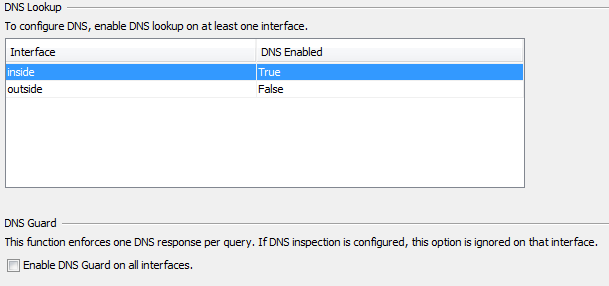
CLI:
ASA(config)# dns domain-lookup inside
ASA(config)# dns server-group DefaultDNS
ASA(config-dns-server-group)# name-server 10.11.12.101 - (Optional) Create Group Policy for WEBVPN connections.
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Clientless SSL VPN Access > Group Policies > Add Internal Group Policy.
Under General Options change the Tunelling Protocols value to "Clientless SSL VPN".
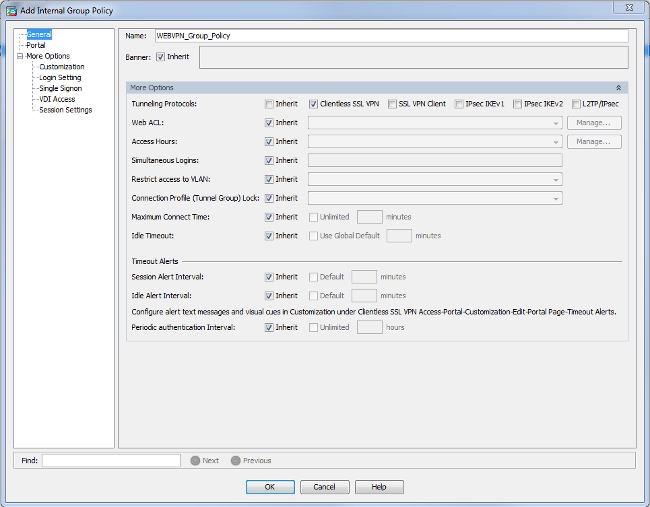
CLI:
ASA(config)# group-policy WEBVPN_Group_Policy internal
ASA(config)# group-policy WEBVPN_Group_Policy attributes
ASA(config-group-policy)# vpn-tunnel-protocol ssl-clientless - Configure the Connection Profile.
In ASDM, choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Clientless SSL VPN Access > Connection Profiles.
By default, the WebVPN connections use DefaultWEBVPNGroup profile. You can create additional profiles.
Note: There are various ways to assign users to other profiles.
- Users can manually select the connection profile from the drop-down list or with a specific URL. See ASA 8.x: Allow Users to Select a Group at WebVPN Login via Group-Alias and Group-URL Method.
- When you use an LDAP server, you can assign the user profile based on the attributes received from the LDAP server, see ASA Use of LDAP Attribute Maps Configuration Example.Edit the DefaultWEBVPNGroup profile and choose the WEBVPN_Group_Policy under Default Group Policy.
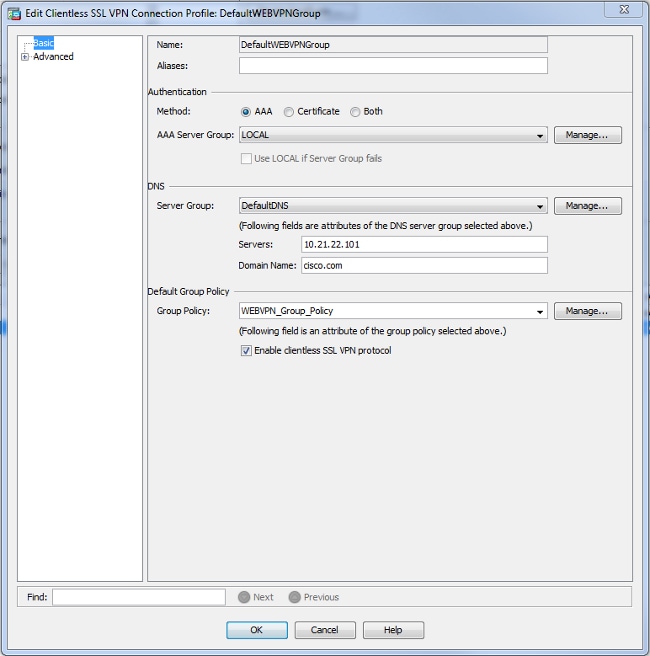
CLI:
ASA(config)# tunnel-group DefaultWEBVPNGroup general-attributes
ASA(config-tunnel-general)# default-group-policy WEBVPN_Group_Policy - In order to enable the WebVPN on the outside interface, choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Clientless SSL VPN Access > Connection Profiles.
Check the Allow Access checkbox next to the outside interface.
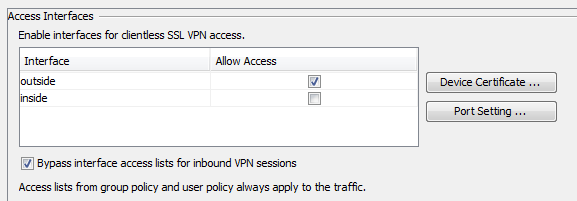
CLI:
ASA(config)# webvpn
ASA(config-webvpn)# enable outside - (Optional) Create bookmarks for content.
Bookmarks allow the user to browse the internal resource URLs.
In order to create a bookmark, choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Clientless SSL VPN Access > Portal > Bookmarks > Add.

Choose Add in order to add a specific bookmark.
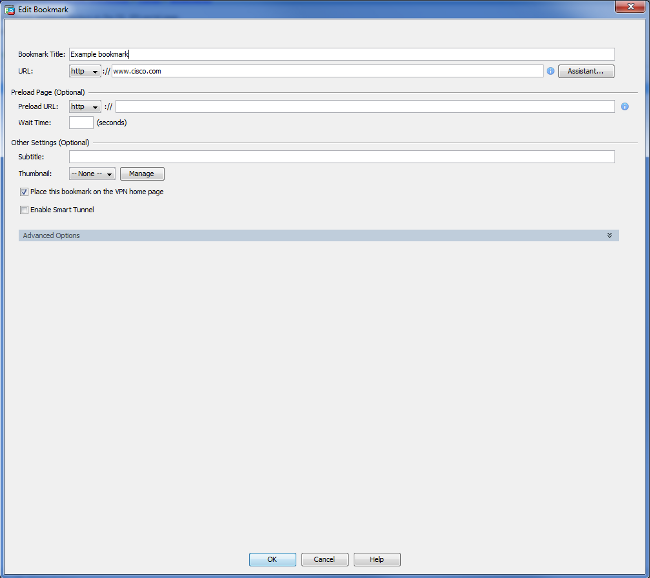
CLI:
It is impossible to create bookmarks via the CLI because they are created as XML files.
- (Optional) Assign bookmarks to a specific group policy.
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Clientless SSL VPN Access > Group Policies > Edit > Portal > Bookmark List.
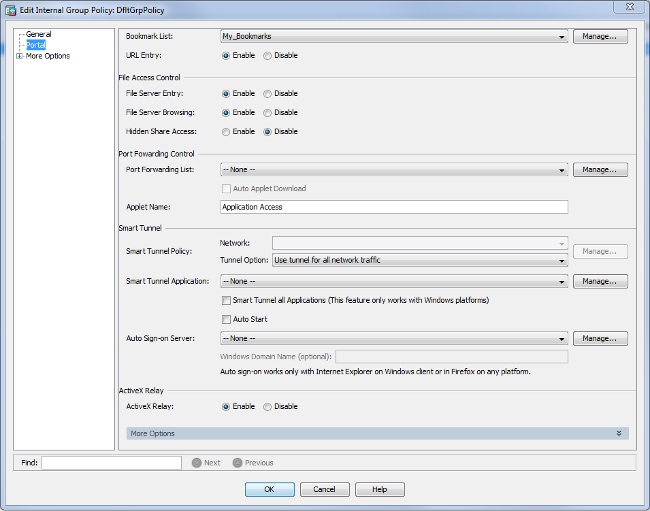
CLI:
ASA(config)# group-policy DfltGrpPolicy attributes
ASA(config-group-policy)# webvpn
ASA(config-group-webvpn)# url-list value My_Bookmarks
Verify
Once the WebVPN has been configured, use the address https://<FQDN of the ASA> in the browser.
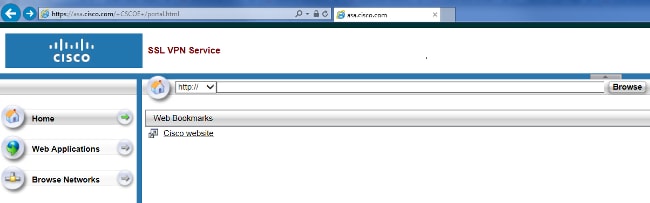
After login, you are able to see the address bar used to navigate to websites and the bookmarks.
Troubleshoot
Procedures Used to Troubleshoot
To troubleshoot your configuration:
In ASDM, choose Monitoring > Logging > Real-time Log Viewer > View. When a client connects to the ASA, note the establishment of TLS session, selection of group policy, and successful authentication of the user.
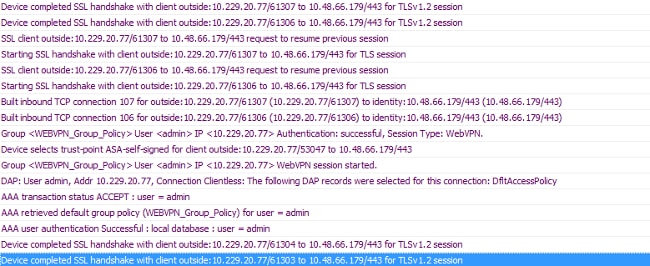
CLI:
ASA(config)# logging buffered debugging
ASA(config)# show logging
In ASDM, choose Monitoring > VPN > VPN Statistics > Sessions > Filter by: Clientless SSL VPN. Look for the new WebVPN session. Be sure to choose the WebVPN filter and click Filter. If a problem occurs, temporarily bypass the ASA device to ensure that clients can access the desired network resources. Review the configuration steps listed in this document.
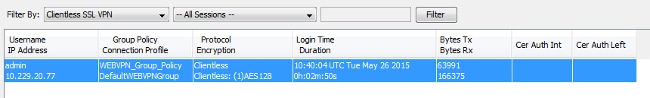
CLI:
ASA(config)# show vpn-sessiondb webvpn
Session Type: WebVPN
Username : admin Index : 3
Public IP : 10.229.20.77
Protocol : Clientless
License : AnyConnect Premium
Encryption : Clientless: (1)AES128 Hashing : Clientless: (1)SHA256
Bytes Tx : 72214 Bytes Rx : 270241
Group Policy : WEBVPN_Group_Policy Tunnel Group : DefaultWEBVPNGroup
Login Time : 10:40:04 UTC Tue May 26 2015
Duration : 0h:05m:21s
Inactivity : 0h:00m:00s
VLAN Mapping : N/A VLAN : none
Audt Sess ID : 0a1516010000300055644d84
Security Grp : none
Commands Used to Troubleshoot
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
-
show webvpn - There are many show commands associated with WebVPN. In order to see the use of show commands in detail, see the command reference section of the Cisco Security Appliance.
-
debug webvpn - The use of debug commands can adversely impact the ASA. In order to see the use of debug commands in more detail, see the command reference section of the Cisco Security Appliance.
Common Problems
User Cannot Log In
Problem
The message "Clientless (browser) SSL VPN access is not allowed." appears in the browser after an unsuccessful login attempt. The AnyConnect Premium license is not installed on the ASA or it is not in use as shown by "Premium AnyConnect license is not enabled on the ASA."
Solution
Enable the Premium AnyConnect license with these commands:
ASA(config)# webvpn
ASA(config-webvpn)# no anyconnect-essentials
Problem
The message "Login failed" appears in the browser after an unsuccessful login attempt. The AnyConnect license limit has been exceeded.
Solution
Look for this message in the logs:
%ASA-4-716023: Group <DfltGrpPolicy> User <cisco> IP <192.168.1.100>
Session could not be established: session limit of 2 reached.
Also, verify your license limit:
ASA(config)# show version | include Premium
AnyConnect Premium Peers : 2 perpetual
Problem
The message "AnyConnect is not enabled on the VPN server" appears in the browser after an unsuccessful login attempt. Clientless VPN protocol is not enabled in the group-policy.
Solution
Look for this message in the logs:
%ASA-6-716002: Group <DfltGrpPolicy> User <cisco> IP <192.168.1.100>
WebVPN session terminated: Client type not supported.
Make sure that Clientless VPN protocol is enabled for the desired group-policy:
ASA(config)# show run all group-policy | include vpn-tunnel-protocol
vpn-tunnel-protocol ikev1 ikev2 l2tp-ipsec ssl-clientless
Unable to Connect More Than Three WebVPN Users to the ASA
Problem
Only three WebVPN clients can connect to the ASA. The connection for the fourth client fails.
Solution
In most cases, this issue is related to a simultaneous login parameter within the group policy. Use this illustration in order to configure the desired number of simultaneous logins. In this example, the desired value is 20.
ASA(config)# group-policy Cisco attributes
ASA(config-group-policy)# vpn-simultaneous-logins 20
WebVPN Clients Cannot Hit Bookmarks and is Grayed Out
Problem
If these bookmarks were configured for users to sign in to the clientless VPN, but on the home screen under "Web Applications" they show up as grayed out, how can I enable these HTTP links so that the users are able to click them and go into the particular URL?
Solution
Verify that the ASA can resolve the websites through DNS. Try to ping the websites by name. If the ASA cannot resolve the name, the link is grayed out. If the DNS servers are internal to your network, configure the DNS domain-lookup private interface.
Citrix Connection Through WebVPN
Problem
The error message "the ica client received a corrupt ica file." occurs for Citrix over WebVPN.
Solution
If you use the secure gateway mode for Citrix connection through WebVPN, the ICA file can corrupt. Because the ASA is not compatible with this mode of operation, create a new ICA file in the Direct Mode (non-secure mode).
How to Avoid the Need for a Second Authentication for the Users
Problem
When you access CIFS links on the clientless WebVPN portal, you are prompted for credentials after you click the bookmark. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is used in order to authenticate both the resources and the users already have entered LDAP credentials to log in to the VPN session.
Solution
You can use the auto-signon feature in this case. Under the specific group-policy used and under its WebVPN attributes, configure this:
ASA(config)# group-policy WEBVPN_Group_Policy attributes
ASA(config-group-policy)# webvpn
ASA(config-group-webvpn)# auto-signon allow uri cifs://X.X.X.X/* auth-type all
where X.X.X.X=IP of the CIFS server and *=rest of the path to reach the share file/folder in question.
An example configuration snippet is shown here:
ASA(config)# group-policy ExamplePolicy attributes
ASA(config-group-policy)# webvpn
ASA(config-group-webvpn)# auto-signon allow uri
https://*.example..com/* auth-type all
For more information about this, see Configure SSO with HTTP Basic or NTLM Authentication.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
05-Jan-2016 |
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Jan KrupaCisco TAC Engineer
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback