Introduction
This document describes the Cisco AnyConnect Mobility Client captive portal detection feature and the requirements for it to function correctly.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software versions:
- AnyConnect Version 4.7
- Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) Version 9.10
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Many wireless hotspots at hotels, restaurants, airports, and other public places use captive portals in order to block user access to the internet. They redirect HTTP requests to their own websites that require users to enter their credentials or acknowledge terms and conditions of the hotspot host.
Overview
Many facilities that offer Wi-Fi and wired access, such as airports, coffee shops, and hotels, require users to pay before they obtain access, agree to abide by an acceptable use policy, or both. These facilities use a technique called captive portal in order to prevent applications from access until users open a browser and accept the conditions for access.
Captive Portal Remediation Requirements
Support for both captive portal detection and remediation requires one of these licenses:
- AnyConnect Premium (Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN Edition)
- Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility
You can use a Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility license in order to provide support for captive portal detection and remediation in combination with either an AnyConnect Essentials or an AnyConnect Premium license.
Note: Captive portal detection and remediation is supported on the Microsoft Windows and Macintosh OS X operating systems supported by the release of AnyConnect that is in use.
Note: Always-ON VPN does not support connecting through a proxy
Captive Portal Hotspot Detection
AnyConnect displays the "Unable to contact VPN server" error message on the GUI if it cannot connect, regardless of the cause. The VPN server specifies the secure gateway. If Always-on is enabled and a captive portal is not present, the client continues to attempt to connect to the VPN and updates the status message accordingly.
If the Always-on VPN is enabled, the connect failure policy is closed, captive portal remediation is disabled, and AnyConnect detects the presence of a captive portal, then the AnyConnect GUI displays this message once per connection and once per reconnect:
The service provider in your current location is restricting access to the internet.
The AnyConnect protection settings must be lowered for you to log on with the service
provider. Your current enterprise security policy does not allow this.
If AnyConnect detects the presence of a captive portal and the AnyConnect configuration differs from that previously described, the AnyConnect GUI displays this message once per connection and once per reconnect:
The service provider in your current location is restricting access to the internet.
You need to log on with the service provider before you can establish a VPN session.
You can try this by visiting any website with your browser.
Caution: Captive portal detection is enabled by default and is not configurable. AnyConnect does not modify any browser configuration settings during captive portal detection.
Captive Portal Hotspot Remediation
Captive portal remediation is the process where you satisfy the requirements of a captive portal hotspot in order to obtain network access.
AnyConnect does not remediate the captive portal; it relies on the end user to perform the remediation.
In order to perform the captive portal remediation, the end user meets the requirements of the hotspot provider. These requirements can include payment of a fee to access the network, a signature on an acceptable use policy, both, or some other requirement that is defined by the provider.
Captive portal remediation must be explicitly allowed in an AnyConnect VPN Client profile if AnyConnect Always-on is enabled and the Connect failure policy is set to Closed. If Always-on is enabled and the Connect Failure policy is set to Open, you do not need to explicitly allow captive portal remediation in an AnyConnect VPN Client profile because the user is not restricted from network access.
False Captive Portal Detection
AnyConnect can falsely assume it is in a captive portal in these situations:
- If AnyConnect attempts to contact an ASA with a certificate that contains an incorrect server name (CN), then the AnyConnect client treats it as a captive portal environment.
In order to prevent this issue, make sure the ASA certificate is properly configured. The CN value in the certificate must match the name of the ASA server in the VPN client profile.
- If there is another device on the network before the ASA that responds when the user attempts to contact an ASA by the blockage of HTTPS access to the ASA, then the AnyConnect client treats it as a captive portal environment. This situation can occur when a user is on an internal network and connects through a firewall in order to connect to the ASA.
If you must restrict access to the ASA from inside the corporation, configure your firewall such that HTTP and HTTPS traffic to the ASA address does not return an HTTP status. HTTP/HTTPS access to the ASA is either allowed or completely blocked (also known as black-holed) in order to ensure the HTTP/HTTPS requests sent to the ASA do not return an unexpected response.
AnyConnect Behavior
This section describes how the AnyConnect behaves.
- AnyConnect tries an HTTPS probe to the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) defined in the XML profile.
- If there is a certificate error (not trusted/wrong FQDN), then AnyConnect tries an HTTP probe to the FQDN defined in the XML profile. If there is any other response than an HTTP 302, then it functions as if it is behind a captive portal.
Captive Portal Incorrectly Detected with IKEv2
When you attempt an Internet Key Exchange Version 2 (IKEv2) connection to an ASA with SSL authentication disabled, which runs the Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) portal on port 443, the HTTPS probe performed for captive portal detection results in a redirect to the ASDM portal (/admin/public/index.html). Since this is not expected by the client, it appears as a captive portal redirect, and the connection attempt is prevented because it appears that captive portal remediation is required.
Workarounds
If you encounter this issue, these are some possible workarounds:
- Remove HTTP commands on that interface so the ASA does not listen to HTTP connections on the interface.
- Remove the SSL trustpoint on the interface.
- Enable IKEV2 client-services.
- Enable WebVPN on the interface.
Caution: The same problem exists for Cisco IOS® routers. If ip http server is enabled on Cisco IOS, which is required if the same box is used as the PKI Server, AnyConnect falsely detects captive portal. The workaround is to use ip http access-class in order to stop responses to AnyConnect HTTP requests, instead of a request for authentication.
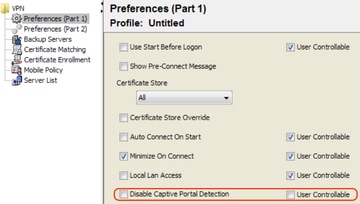
Disable the Captive Portal Feature
It is possible to disable the captive portal feature in AnyConnect client version 4.2.00096 and later. The administrator can determine if the option can be user configurable or disabled. This option is available under the Preferences (Part 1) section in the profile editor. The administrator can select Disable Captive Portal Detection or User Controllable as shown in this profile editor screen capture:
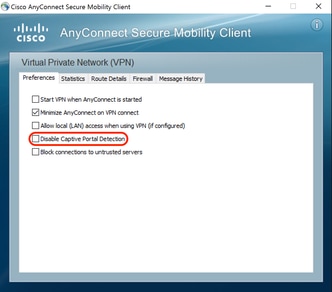
If User controllable is checked, the checkbox appears on the Preferences tab of the AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client UI as shown here:



 Feedback
Feedback