ASA SNMP Feature Enhancement Implementation
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the new Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) features that are available for the Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) 5500-X Series Firewall in software Release 9.1.5 and Releases 9.2.(1) and later.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the Cisco ASA 5500-X Series Firewall that runs Cisco ASA® Software Release 9.1.5 and Releases 9.2.(1) and later.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
In ASA Versions 9.1.5 and 9.2.1, these SNMP enhancements are introduced:
- Support for 128 SNMP hosts is added.
- Support for cpmCPUTotal5minRev SNMP Object Identifiers (OIDs) is added.
- Support for 1,472-byte SNMP messages is added.
Support for 128 SNMP Hosts
This feature allows the ASA to support more than the current 32 SNMP hosts.
Purpose
Currently, the ASA has a hard limit of 32 SNMP hosts total. This includes hosts that can be configured for traps and for polling. The next sections describe the affects that this feature has on single and multi-context modes.
Single-Context Mode
- Allows a significantly higher number of entries (total hosts) to be configured, upwards of 4,096. However, out of these entries, only 128 can be used for traps.
- For polling configuration purposes, up to 4,096 polling hosts and 128 trap hosts are allowed to be configured. However, the actual number of servers that poll the system should be restricted to less than 128, as performance impacts from a higher number of hosts are unknown and not supported.
Multi-Context Mode
- For configuration purposes, up to 4,000 hosts per context are allowed and a system-wide limit of 64,000 total hosts is imposed.
- Out of the total configured hosts, only 128 (per context) can be used for traps, and the overall system limit for traps in multi-context mode is 32,000.
- Although you can configure up to 4,000 total hosts per context, the actual number of servers that poll any context should be limited to 128.
Description
You might prefer to monitor the network devices from a large pool of SNMP hosts. Ideally, you want the ability to specify an IP range and/or a subnet of the IP addresses that are allowed to monitor the network devices. The ASA currently does not provide that flexibility and limits the maximum SNMP hosts to 32.
The support for this feature involves two aspects:
- Provide the capability for the ASA to handle up to 128 SNMP hosts.
- Provide the required configuration commands so that you can configure a significantly higher number of hosts, as detailed in the previous section via a single command.
The current design on the ASA is such that individual hosts can be configured via the CLI. For this feature, these additional design requirements were considered:
- The introduction of the snmp-server host-group CLI command with snmp-server host CLI command retention.
- The ability for entries to come from both the snmp-server host-group and snmp-server host CLI commands.
- For SNMP Version 3, the introduction of the snmp-server userlist CLI command with snmp-server user CLI command retention.
- A configuration overlap must also be supported. For example, the multiple host-group commands can be given with hosts that overlap in the network objects. Similarly, you can specify a host with an IP address that overlaps with the current hosts or the host group. This provides a mechanism that can be used in order to overwrite the parameters for a few hosts in a group, without the need to reconfigure the complete group.
Some software restrictions and caveats that are associated with this feature are:
- As a part of the snmp-server host-group command, the default is poll if [trap|poll] is not specified. It is also important to note that for this command, both the traps and polling cannot be enabled for the same host group. If this is required, Cisco recommends that you use the snmp-server host command for the relevant hosts.
- You can specify network objects that overlap in different host-group commands. The values that are specified in the last host group takes effect for the common set of hosts in the different network objects.
Here is an example:
object network network1
range 64.103.236.40 64.103.236.50
object network network2
range 64.103.236.35 64.103.236.55
snmp-server host-group inside network1 poll version 3 user-list SNMP-List
snmp-server host-group inside network2 poll version 3 user-list SNMP-List
Enter the show snmp-server host command in order to view host entries:
asa(config)# show snmp-server host
host ip = 64.103.236.35, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.36, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.37, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.38, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.39, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.40, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.41, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.42, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.43, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.44, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.45, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.46, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.47, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.48, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.49, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.50, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.51, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.52, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.53, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.54, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.55, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
Here are some important notes about the use of this feature:
- If a host group or host that overlaps with other host groups is deleted, the hosts are set up again with the values that are used for the configured host groups.
- The values or parameters that are associated with the hosts are dependent upon the order that the commands are executed.
- The user list that is configured cannot be deleted if the list is used by a particular host group.
- The SNMP user cannot be deleted if the user is referred to in a particular user list.
- A network object cannot be deleted if it is used by the host-group CLI command.
Configure
Use the information that is described in this section in order to configure the ASA so that this new feature is implemented.
CLI Commands
For SNMP Version 3, the administrator can associate various users with a specified group of hosts. This is useful if the administrator wants a set of users to have the ability to access the ASA from a group of hosts. This CLI command is used in order to configure a user list for multiple users:
ASA(config)# [no] snmp-server user-list <list_name> username <user_name>
In order to associate the user list with a host group, enter this command into the CLI:
[no] snmp-server host-group <interface> <network-object> [trap|poll]
[community [enc_type] <text>] [version {1 | 2c | 3 [user name | user-list
<list-name>]}] [udp-port <port_number>]
With this single command, you can specify a network object in order to indicate the multiple hosts that should be added. With the network object, you can specify either a subnet mask or the range of IP addresses that should be added, with the use of a single command. All of the IP addresses that are listed as a part of the network object are added as SNMP host entries. Similarly, for each of the users that are specified in the user list, there is a separate SNMP host entry.
These commands are used in order to allow administrators to clear and view the new configuration options for the SNMP servers:
- clear configure snmp-server user-list
- clear configure snmp-server host-group
- show running-config snmp-server user-list
- show running-config snmp-server host-group
Example Configuration
Complete these steps in order to use the new SNMP group options and create an SNMP server host group for Version 2c polling:
- Create a network object:
asa(config)# object network network1
asa(config-network-object)# range 64.103.236.40 64.103.236.50 - Define the SNMP host group:
asa(config)#snmp-server host-group inside network1 poll community ***** version 2c
- Define the SNMP Version 3 group:
asa(config)#snmp-server group SNMPRW-GROUP v3 noauth
- Tie the groups to the users:
asa(config)#snmp-server user cisco1 SNMPRW-GROUP v3
asa(config)#snmp-server user-list SNMP-List username cisco1
asa(config)#snmp-server host-group inside network1 poll version 3 user-list SNMP-List
This image illustrates the changes that are made within the Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM):

Support for cpmCPUTotal5minRev SNMP OIDs
This feature allows the ASA to support cpmCPUTotal5minRev SNMP OIDs.
Purpose
This feature adds support for cpmCPUTotal5minRev and cpmCPUTotal1minRev OIDs on the ASA and deprecates the currently-supported OIDs cpmCPUTotal5min and cpmCPUTotal1min. The purpose of these OIDs is to monitor the CPU usage. The currently-supported OIDs range from 1 to 100, while the newly-supported OIDs range from 0 to 100. Hence, support was added for newer OIDs, as they cover a wider range.
It is important to note that since the deprecated OIDs (cpmCPUTotal5min and cpmCPUTotal1min) are no longer supported on the ASA, if the ASA is upgraded and the deprecated OIDs are polled, the ASA does not return any information for those OIDs. After an upgrade of the ASA, you are now required to monitor the cpmCPUTotal5minRev and cpmCPUTotal1minRev for CPU usage.
CLI Commands
There are no CLI changes introduced with this new feature.
New OIDs
These are the new OIDs that are added with this feature:
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7. cpmCPUTotal1minRev
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.8. cpmCPUTotal5minRev
Support for 1,472-Byte SNMP Messages
The ASA platforms limit the maximum packet size for SNMP requests to 512 bytes. When you perform a bulk query for a large number of MIB OIDs within a single SNMP request, the SNMP connection times-out and an error syslog is generated on the ASA. RFC3417 suggests that the maximum packet size for SNMP requests should be 1,472 bytes. This is the size of the SNMP payload for the packet. Additionally, the Ethernet Header and the IP Header Size must be added in order to compute the total size of the packet.
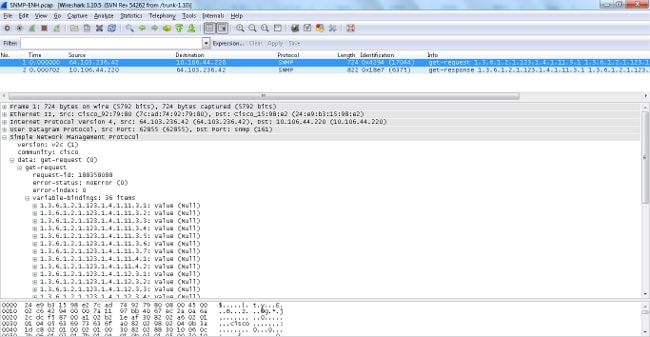

Troubleshoot
This section provides information that you can use in order to troubleshoot system issues on the ASA.
Show Commands
These show commands can be useful when attempts are made to troubleshoot issues on the ASA:
- asa# show run snmp-server host-group
snmp-server host-group inside network1 poll version 3 user-list SNMP-List - asa# show run snmp-server user-list
snmp-server user-list SNMP-List username cisco1 - asa# show snmp-server host
This CLI command displays the entries that are present in the SNMP server address table, which includes both the host and the host group configurations:
asa(config)#show run object network
object network network1
range 64.103.236.40 64.103.236.50
object network network2
range 64.103.236.35 64.103.236.55
object network network3
range 64.103.236.60 64.103.236.70
ciscoasa/admin(config)# show run snmp-server
snmp-server group cisco-group v3 noauth
snmp-server user user1 cisco-group v3
snmp-server user user2 cisco-group v3
snmp-server user user3 cisco-group v3
snmp-server user-list cisco username user1
snmp-server user-list cisco username user2
snmp-server user-list cisco username user3
snmp-server host-group management0/0 net2 poll version 3 user-list cisco
no snmp-server locationno snmp-server contact
ciscoasa/admin(config)# show snmp-server host
host ip = 64.103.236.35, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.36, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.37, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.38, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.39, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.40, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.41, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
host ip = 64.103.236.42, interface = inside poll version 3 cisco1
As shown, these commands show all of the hosts that are configured via the host-group command. You can use this command in order to verify whether all of the entries are available and also cross-verify the host groups that overlap.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback