L2TP Over IPsec Between Windows 2000/XP PC and PIX/ASA 7.2 Using Pre-shared Key Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to configure Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) over IP Security (IPsec) from remote Microsoft Windows 2000/2003 and XP clients to a PIX Security Appliance corporate office using pre-shared keys with Microsoft Windows 2003 Internet Authentication Service (IAS) RADIUS Server for user authentication. Refer to Microsoft - Checklist: Configuring IAS for dial-up and VPN access ![]() for further information on IAS.
for further information on IAS.
The primary benefit of configuring L2TP with IPsec in a remote access scenario is that remote users can access a VPN over a public IP network without a gateway or a dedicated line. This enables remote access from virtually any place with POTS. An additional benefit is that the only client requirement for VPN access is the use of Windows 2000 with Microsoft Dial-Up Networking (DUN). No additional client software, such as Cisco VPN Client software, is required.
This document also describes how to use the Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) in order to configure the PIX 500 Series Security Appliance for L2TP over IPsec.
Note: Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) over IPsec is supported on Cisco Secure PIX Firewall Software Release 6.x and later.
In order to configure L2TP Over IPsec between the PIX 6.x and Windows 2000, refer to Configuring L2TP Over IPsec Between PIX Firewall and Windows 2000 PC Using Certificates.
In order to configure L2TP over IPsec from remote Microsoft Windows 2000 and XP clients to a corporate site using an encrypted method, refer to Configuring L2TP over IPsec from a Windows 2000 or XP Client to a Cisco VPN 3000 Series Concentrator Using Pre-Shared Keys.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Before the secure tunnel establishment, IP connectivity needs to exist between the peers.
Make sure that UDP port 1701 is not blocked anywhere along the path of the connection.
Use only the default tunnel group and default group policy on the Cisco PIX/ASA. User-defined policies and groups do not work.
Note: The security appliance does not establish an L2TP/IPsec tunnel with Windows 2000 if either Cisco VPN Client 3.x or Cisco VPN 3000 Client 2.5 is installed. Disable the Cisco VPN service for Cisco VPN Client 3.x, or the ANetIKE service for Cisco VPN 3000 Client 2.5 from the Services panel in Windows 2000. In order to do this choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Services, restart the IPsec Policy Agent Service from the Services panel, and reboot the machine.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
PIX Security Appliance 515E with software version 7.2(1) or later
-
Adaptive Security Device Manager 5.2(1) or later
-
Microsoft Windows 2000 Server
-
Microsoft Windows XP Professional with SP2
-
Windows 2003 Server with IAS
Note: If you upgrade the PIX 6.3 to version 7.x, make sure that you have installed SP2 in Windows XP (L2TP Client).
Note: The information in the document is also valid for ASA security appliance.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Related Products
This configuration can also be used with Cisco ASA 5500 Series Security Appliance 7.2(1) or later.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
Complete these steps in order to configure L2TP over IPsec.
-
Configure IPsec transport mode in order to enable IPsec with L2TP.
Windows 2000 L2TP/IPsec client uses IPsec transport mode—Only the IP payload is encrypted, and the original IP headers are left intact. The advantages of this mode are that it adds only a few bytes to each packet and allows devices on the public network to see the final source and destination of the packet. Therefore, in order for Windows 2000 L2TP/IPsec clients to connect to the security appliance, you must configure IPsec transport mode for a transform (see step 2 in the ASDM configuration). With this capability (transport), you can enable special processing (for example, QoS) on the intermediate network based on the information in the IP header. However, the Layer 4 header is encrypted, which limits the examination of the packet. Unfortunately, the transmission of the IP header in clear text, transport mode allows an attacker to perform some traffic analysis.
-
Configure L2TP with a virtual private dial-up network (VPDN) group.
The configuration of L2TP with IPsec supports certificates that use the pre-shared keys or RSA signature methods, and the use of dynamic (as opposed to static) crypto maps. Pre-shared key is used as an authentication to establish the L2TP over IPsec tunnel.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to find more information on the commands used in this document.
Note: The IP addressing schemes used in this configuration are not legally routable on the Internet. They are RFC 1918 addresses which have been used in a lab environment.
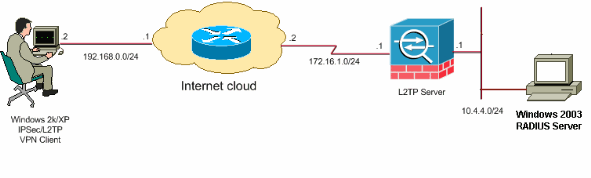
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Configurations
This document uses these configurations:
Windows L2TP/IPsec Client Configuration
Complete these steps in order to configure L2TP over IPsec on Windows 2000. For Windows XP skip steps 1 and 2 and start from step 3:
-
Add this registry value to your Windows 2000 machine:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Rasman\Parameters
-
Add this registry value to this key:
Value Name: ProhibitIpSec Data Type: REG_DWORD Value: 1
Note: In some cases (Windows XP Sp2), the addition of this key (Value: 1) appears to break the connection as it makes the XP box negotiate L2TP only rather than an L2TP with IPsec connection. It is mandatory to add an IPsec policy in conjunction with that registry key. If you receive an error 800 when you try to establish a connection, remove the key (Value: 1) in order to get the connection to work.
Note: You must restart Windows 2000/2003 or XP machine in order for the changes to take effect. By default the Windows client attempts to use IPsec with a Certificate Authority (CA). The configuration of this registry key prevents this from occurring. Now you can configure an IPsec policy on the Windows station to match the parameters that you want on the PIX/ASA. Refer to How to Configure a L2TP/IPSec Connection Using Pre-shared Key Authentication (Q240262)
 for a step-by-step configuration of the Windows IPsec policy.
for a step-by-step configuration of the Windows IPsec policy.Refer to Configure a Preshared Key for Use with Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol Connections in Windows XP (Q281555)\
 for more information.
for more information. -
Create your connection.
-
Under Network and Dial-up Connections, right-click on the connection and choose Properties.
Go to the Security tab and click Advanced. Choose the protocols as this image shows.
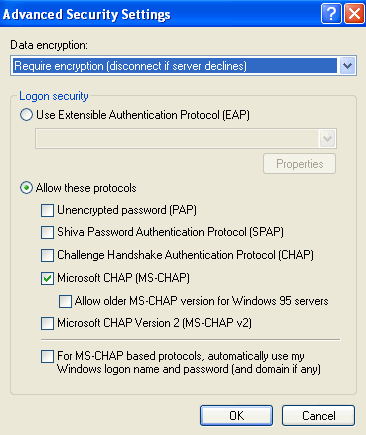
-
Note: This step is applicable only for Windows XP.
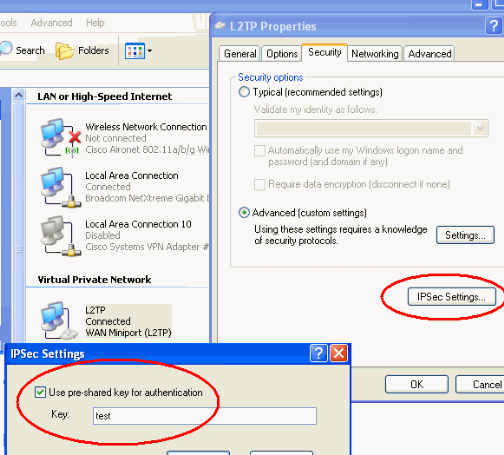
Click IPSec Settings, check Use pre-shared key for authentication and type in the pre-shared key in order to set the pre-shared key.
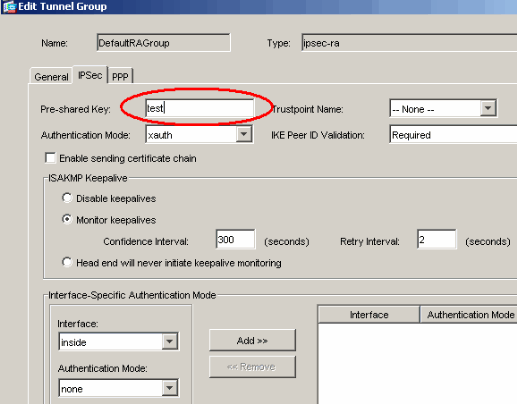
In this example, test is used as the pre-shared key.
L2TP Server in PIX Configuration
| PIX 7.2 |
|---|
pixfirewall#show run
PIX Version 7.2(1)
!
hostname pixfirewall
domain-name default.domain.invalid
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
names
!
!--- Configures the outside and inside interfaces.
interface Ethernet0
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet1
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 10.4.4.1 255.255.255.0
!
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
ftp mode passive
dns server-group DefaultDNS
domain-name default.domain.invalid
access-list nonat extended permit ip 10.4.4.0 255.255.255.0 10.4.5.0 255.255.255.0
nat (inside) 0 access-list nonat
pager lines 24
logging console debugging
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
!--- Creates a pool of addresses from which IP addresses are assigned !--- dynamically to the remote VPN Clients.
ip local pool clientVPNpool 10.4.5.10-10.4.5.20 mask 255.255.255.0
no failover
asdm image flash:/asdm-521.bin
no asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
!--- The global and nat command enable !--- the Port Address Translation (PAT) using an outside interface IP !--- address for all outgoing traffic.
global (outside) 1 interface
nat (inside) 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.2 1
timeout xlate 3:00:00
timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02
timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00
timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
!--- Create the AAA server group "vpn" and specify its protocol as RADIUS. !--- Specify the IAS server as a member of the "vpn" group and provide its !--- location and key.
aaa-server vpn protocol radius
aaa-server vpn host 10.4.4.2
key radiuskey
!--- Identifies the group policy as internal.
group-policy DefaultRAGroup internal
!--- Instructs the security appliance to send DNS and !--- WINS server IP addresses to the client.
group-policy DefaultRAGroup attributes
wins-server value 10.4.4.99
dns-server value 10.4.4.99
!--- Configures L2TP over IPsec as a valid VPN tunneling protocol for a group.
vpn-tunnel-protocol IPSec l2tp-ipsec
default-domain value cisco.com
!--- Configure usernames and passwords on the device !--- in addition to using AAA. !--- If the user is an L2TP client that uses Microsoft CHAP version 1 or !--- version 2, and the security appliance is configured !--- to authenticate against the local !--- database, you must include the mschap keyword. !--- For example, username <username> password <password> mschap.
username test password DLaUiAX3l78qgoB5c7iVNw== nt-encrypted
vpn-tunnel-protocol l2tp-ipsec
http server enable
http 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 inside
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart
!--- Identifies the IPsec encryption and hash algorithms !--- to be used by the transform set.
crypto ipsec transform-set TRANS_ESP_3DES_MD5 esp-3des esp-md5-hmac
!--- Since the Windows 2000 L2TP/IPsec client uses IPsec transport mode, !--- set the mode to transport. !--- The default is tunnel mode.
crypto ipsec transform-set TRANS_ESP_3DES_MD5 mode transport
!--- Specifies the transform sets to use in a dynamic crypto map entry.
crypto dynamic-map outside_dyn_map 20 set transform-set TRANS_ESP_3DES_MD5
!--- Requires a given crypto map entry to refer to a pre-existing !--- dynamic crypto map.
crypto map outside_map 20 ipsec-isakmp dynamic outside_dyn_map
!--- Applies a previously defined crypto map set to an outside interface.
crypto map outside_map interface outside
crypto isakmp enable outside
crypto isakmp nat-traversal 20
!--- Specifies the IKE Phase I policy parameters.
crypto isakmp policy 10
authentication pre-share
encryption 3des
hash md5
group 2
lifetime 86400
!--- Creates a tunnel group with the tunnel-group command, and specifies the local !--- address pool name used to allocate the IP address to the client. !--- Associate the AAA server group (VPN) with the tunnel group.
tunnel-group DefaultRAGroup general-attributes
address-pool clientVPNpool
authentication-server-group vpn
!--- Link the name of the group policy to the default tunnel !--- group from tunnel group general-attributes mode.
default-group-policy DefaultRAGroup
!--- Use the tunnel-group ipsec-attributes command !--- in order to enter the ipsec-attribute configuration mode. !--- Set the pre-shared key. !--- This key should be the same as the key configured on the Windows machine.
tunnel-group DefaultRAGroup ipsec-attributes
pre-shared-key *
!--- Configures the PPP authentication protocol with the authentication type !--- command from tunnel group ppp-attributes mode.
tunnel-group DefaultRAGroup ppp-attributes
no authentication chap
authentication ms-chap-v2
telnet timeout 5
ssh timeout 5
console timeout 0
!
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
!
!
policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map
parameters
message-length maximum 512
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect dns preset_dns_map
inspect ftp
inspect h323 h225
inspect h323 ras
inspect netbios
inspect rsh
inspect rtsp
inspect skinny
inspect esmtp
inspect sqlnet
inspect sunrpc
inspect tftp
inspect sip
inspect xdmcp
!
service-policy global_policy global
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:e1e0730fa260244caa2e2784f632accd
: end |
L2TP using ASDM Configuration
Complete these steps in order to configure the security appliance to accept L2TP over IPsec connections:
-
Add an IPsec transform set and specify IPsec to use transport mode rather than tunnel mode. In order to do this, choose Configuration > VPN > IPSec > Transform Sets and click Add. The Transform Sets pane displays.
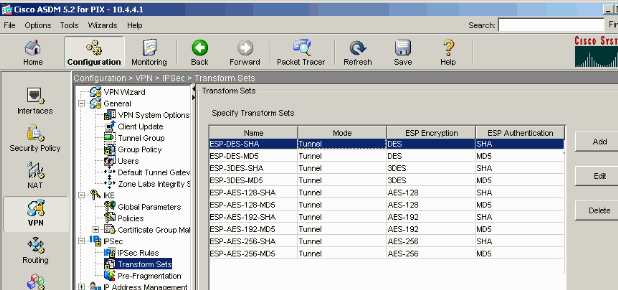
-
Complete these steps in order to add a transform set:
-
Enter a name for the transform set.
-
Choose the ESP Encryption and ESP Authentication methods.
-
Choose the mode as Transport.
-
Click OK.
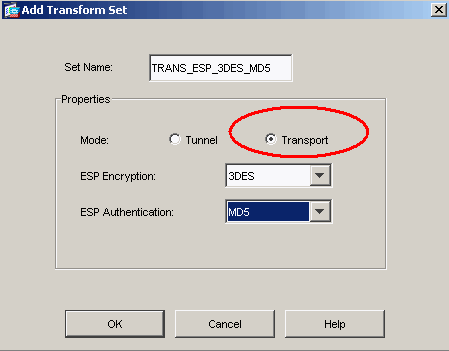
-
-
Complete these steps in order to configure a method of address assignment. This example uses IP address pools.
-
Choose Configuration > VPN > IP Address Management > IP Pools.
-
Click Add. The Add IP Pool dialog box appears.
-
Enter the name of the new IP address pool.
-
Enter the starting and ending IP addresses.
-
Enter the subnet mask and click OK.
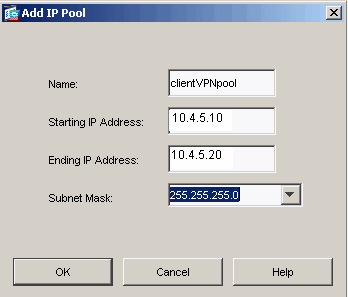
-
-
Choose Configuration > VPN > General > Group Policy in order to configure L2TP over IPsec as a valid VPN tunneling protocol for the group policy. The Group Policy pane displays.
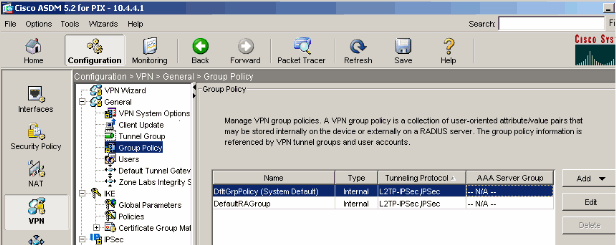
-
Select a group policy (DiffGrpPolicy) and click Edit.
The Edit Group Policy dialog displays. Check L2TP over IPSec in order to enable the protocol for the group policy and then click OK.
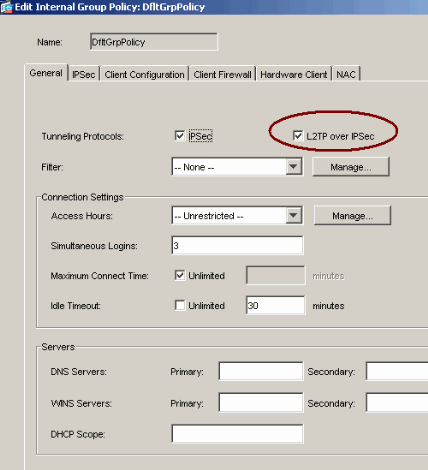
-
Complete these steps in order to assign the IP address pool to a tunnel group:
-
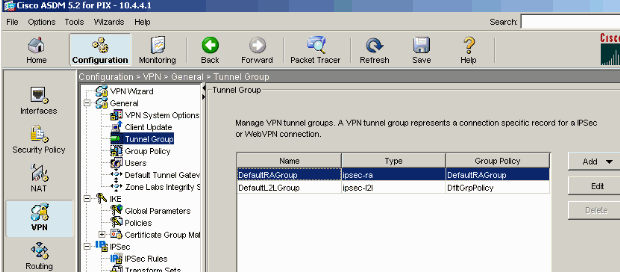
Choose Configuration > VPN > General > Tunnel Group.
-
After the Tunnel Group pane appears, select a tunnel group (DefaultRAGroup) in the table.
-
Click Edit.
-
-
Complete these steps when the Edit Tunnel Group window appears:
-
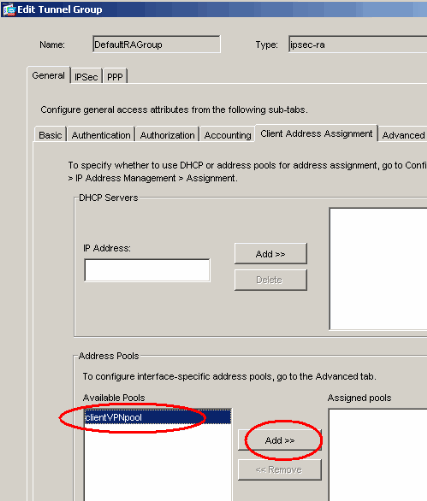
From the General tab, go to the Client Address Assignment tab.
-
In the Address Pools area, choose an address pool to assign to the tunnel group.
-
Click Add. The address pool appears in the Assigned Pools box.
-
-
In order to set the pre-shared key, go to the IPSec tab, enter your Pre-shared Key, and click OK.
-
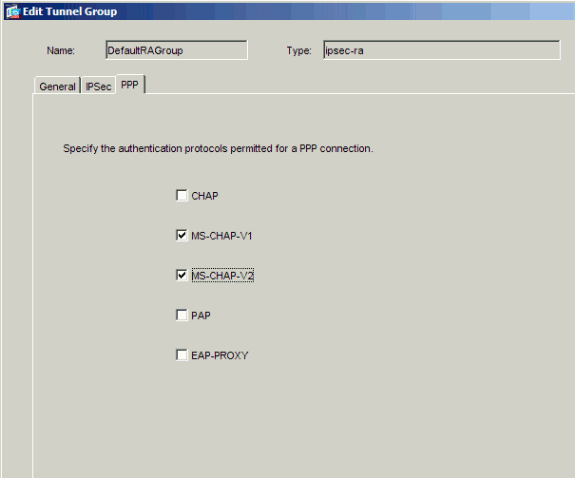
L2TP over IPsec uses PPP authentication protocols. Specify the protocols that are permitted for PPP connections on the PPP tab of the tunnel group. Select the MS-CHAP-V1 protocol for authentication.
-
Specify a method to authenticate users who attempt L2TP over IPsec connections.
You can configure the security appliance to use an authentication server or its own local database. In order to do this, go to the Authentication tab of the tunnel group. By default, the security appliance uses its local database. The Authentication Server Group drop-down list displays LOCAL. In order to use an authentication server, select one from the list.
Note: The security appliance only supports the PPP authentications PAP and Microsoft CHAP versions 1 and 2 on the local database. EAP and CHAP are performed by proxy authentication servers. Therefore, if a remote user belongs to a tunnel group configured with EAP or CHAP, and the security appliance is configured to use the local database, that user is not able to connect.
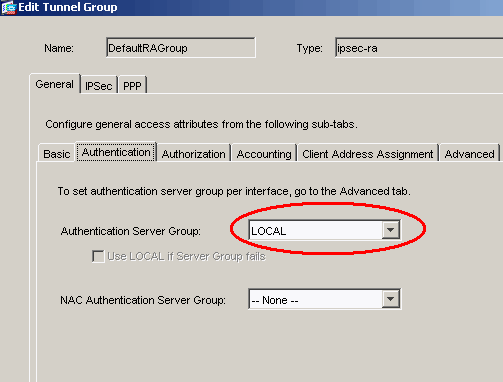
Note: Choose Configuration > VPN > General > Tunnel Group in order to go back to the tunnel group configuration so that you can link the group policy to the tunnel group and enable Tunnel Group Switching (optional). When the Tunnel Group pane appears, choose the tunnel group and click Edit.
Note: Tunnel Group Switching enables the security appliance to associate different users that establish L2TP over IPsec connections with different tunnel groups. Since each tunnel group has its own AAA server group and IP address pools, users can be authenticated through methods specific to their tunnel group. With this feature, instead of sending just a username, the user sends a username and a group name in the format username@group_name, where "@" represents a delimiter that you can configure, and the group name is the name of a tunnel group that is configured on the security appliance.
Note: Tunnel Group Switching is enabled by Strip Group processing, which enables the security appliance to select the tunnel group for user connections by obtaining the group name from the username presented by the VPN Client. The security appliance then sends only the user part of the username for authorization and authentication. Otherwise (if disabled), the security appliance sends the entire username, including the realm. In order to enable Tunnel Group Switching, check Strip the realm from username before passing it on to the AAA server, and check Strip the group from username before passing it on to the AAA server. Then click OK.
-
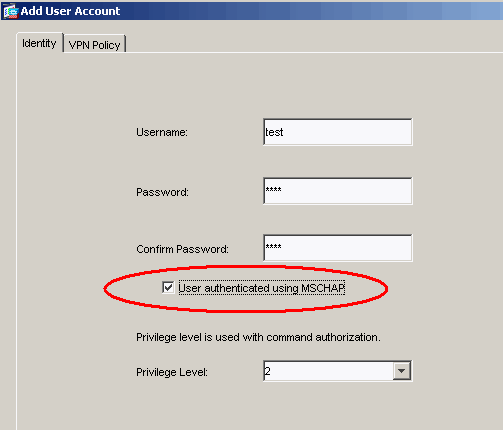
Complete these steps in order to create a user in the local database:
-
Choose Configuration >Properties > Device Administration > User Accounts.
-
Click Add.
If the user is an L2TP client that uses Microsoft CHAP version 1 or 2, and the security appliance is configured to authenticate against the local database, you must check User Authenticated using MSCHAP in order to enable the MSCHAP.
-
Click OK.
-
-
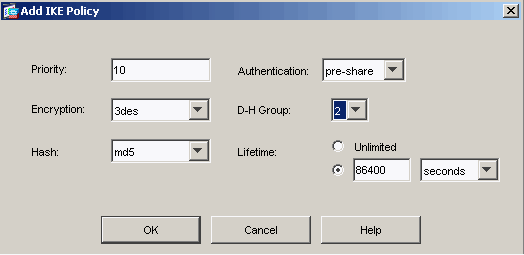
Choose Configuration > VPN > IKE > Policies and click Add in order to create an IKE policy for Phase I. Click OK to continue.
-
(Optional) If you expect multiple L2TP clients behind a NAT device to attempt L2TP over IPsec connections to the security appliance, you must enable NAT traversal so that ESP packets can pass through one or more NAT devices. Complete these steps in order to do this:
-
Choose Configuration > VPN > IKE > Global Parameters.
-
Ensure that ISAKMP is enabled on an interface.
-
Check Enable IPSec over NAT-T.
-
Click OK.
-
Microsoft Windows 2003 Server with IAS Configuration
Complete these steps in order to configure the Microsoft Windows 2003 server with IAS.
Note: These steps assume that IAS is already installed on the local machine. If not, add this through Control Panel > Add/Remove Programs.
-
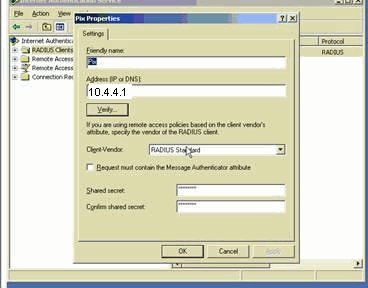
Choose Administrative Tools > Internet Authentication Service and right-click on RADIUS Client in order to add a new RADIUS client. After you type the client information, click OK.
This example shows a client named "Pix" with an IP address of 10.4.4.1. Client-Vendor is set to RADIUS Standard, and the shared secret is radiuskey.
-
Choose Remote Access Policies, right-click on Connections to Other Access Servers, and select Properties.
-
Ensure that the option for Grant Remote Access Permissions is selected.
-
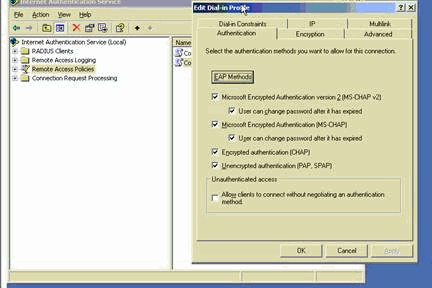
Click Edit Profile and check these settings:
-
On the Authentication tab, check Unencrypted authentication (PAP, SPAP).
-
On the Encryption tab, ensure that the option for No Encryption is selected.
Click OK when you are finished.
-
-
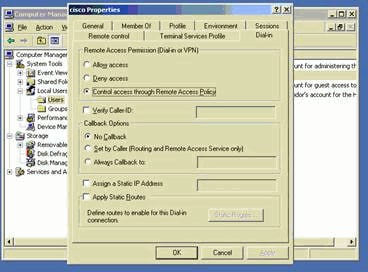
Choose Administrative Tools > Computer Management > System Tools > Local Users and Groups, right-click on Users and select New Users in order to add a user into the local computer account.
-
Add a user with Cisco password password1 and check this profile information:
-
On the General tab, ensure that the option for Password Never Expired is selected instead of the option for User Must Change Password.
-
On the Dial-in tab, select the option for Allow access (or leave the default setting of Control access through Remote Access Policy).
Click OK when you are finished.
-
Extended Authentication for L2TP over IPSec using Active Directory
Use this configuration on the ASA in order to allow the authentication for the L2tp connection to take place from the Active Directory:
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)# tunnel-group DefaultRAGroup ppp-attributes ciscoasa(config-ppp)# authentication pap
Also, on the L2tp client, go to Advanced Security Settings (Custom) and choose only the option for Unencrypted password (PAP).
Verify
This section provides information you can use to confirm your configuration is working properly.
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool ![]() (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
(registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
-
show crypto ipsec sa—Shows all current IKE security associations (SAs) at a peer.
pixfirewall#show crypto ipsec sa interface: outside Crypto map tag: outside_dyn_map, seq num: 20, local addr: 172.16.1.1 access-list 105 permit ip host 172.16.1.1 host 192.168.0.2 local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (172.16.1.1/255.255.255.255/17/0) remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (192.168.0.2/255.255.255.255/17/1701) current_peer: 192.168.0.2, username: test dynamic allocated peer ip: 10.4.5.15 #pkts encaps: 23, #pkts encrypt: 23, #pkts digest: 23 #pkts decaps: 93, #pkts decrypt: 93, #pkts verify: 93 #pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0 #pkts not compressed: 23, #pkts comp failed: 0, #pkts decomp failed: 0 #post-frag successes: 0, #post-frag failures: 0, #fragments created: 0 #PMTUs sent: 0, #PMTUs rcvd: 0, #decapsulated frgs needing reassembly: 0 #send errors: 0, #recv errors: 0 local crypto endpt.: 172.16.1.1, remote crypto endpt.: 192.168.0.2 path mtu 1500, ipsec overhead 58, media mtu 1500 current outbound spi: C16F05B8 inbound esp sas: spi: 0xEC06344D (3959829581) transform: esp-3des esp-md5-hmac in use settings ={RA, Transport, } slot: 0, conn_id: 3, crypto-map: outside_dyn_map sa timing: remaining key lifetime (sec): 3335 IV size: 8 bytes replay detection support: Y outbound esp sas: spi: 0xC16F05B8 (3245278648) transform: esp-3des esp-md5-hmac in use settings ={RA, Transport, } slot: 0, conn_id: 3, crypto-map: outside_dyn_map sa timing: remaining key lifetime (sec): 3335 IV size: 8 bytes replay detection support: Y -
show crypto isakmp sa—Shows all current IKE SAs at a peer.
pixfirewall#show crypto isakmp sa Active SA: 1 Rekey SA: 0 (A tunnel will report 1 Active and 1 Rekey SA during rekey) Total IKE SA: 1 1 IKE Peer: 192.168.0.2 Type : user Role : responder Rekey : no State : MM_ACTIVE -
show vpn-sessiondb—Includes protocol filters that you can use in order to view detailed information about L2TP over IPsec connections. The full command from global configuration mode is show vpn-sessoindb detailed remote filter protocol l2tpOverIpsec.
This example shows the details of a single L2TP over IPsec connection:
pixfirewall#show vpn-sessiondb detail remote filter protocol L2TPOverIPSec Session Type: Remote Detailed Username : test Index : 1 Assigned IP : 10.4.5.15 Public IP : 192.168.0.2 Protocol : L2TPOverIPSec Encryption : 3DES Hashing : MD5 Bytes Tx : 1336 Bytes Rx : 14605 Client Type : Client Ver : Group Policy : DefaultRAGroup Tunnel Group : DefaultRAGroup Login Time : 18:06:08 UTC Fri Jan 1 1993 Duration : 0h:04m:25s Filter Name : NAC Result : N/A Posture Token: IKE Sessions: 1 IPSec Sessions: 1 L2TPOverIPSec Sessions: 1 IKE: Session ID : 1 UDP Src Port : 500 UDP Dst Port : 500 IKE Neg Mode : Main Auth Mode : preSharedKeys Encryption : 3DES Hashing : MD5 Rekey Int (T): 28800 Seconds Rekey Left(T): 28536 Seconds D/H Group : 2 IPSec: Session ID : 2 Local Addr : 172.16.1.1/255.255.255.255/17/1701 Remote Addr : 192.168.0.2/255.255.255.255/17/1701 Encryption : 3DES Hashing : MD5 Encapsulation: Transport Rekey Int (T): 3600 Seconds Rekey Left(T): 3333 Seconds Idle Time Out: 30 Minutes Idle TO Left : 30 Minutes Bytes Tx : 1336 Bytes Rx : 14922 Pkts Tx : 25 Pkts Rx : 156 L2TPOverIPSec: Session ID : 3 Username : test Assigned IP : 10.4.5.15 Encryption : none Auth Mode : msCHAPV1 Idle Time Out: 30 Minutes Idle TO Left : 30 Minutes Bytes Tx : 378 Bytes Rx : 13431 Pkts Tx : 16 Pkts Rx : 146
Troubleshoot
This section provides information to troubleshoot your configuration. Sample debug output is also shown.
Troubleshooting Commands
Certain commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) , which allows you to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands and IP Security Troubleshooting - Understanding and Using debug Commands before you use debug commands.
-
debug crypto ipsec 7—Displays the IPsec negotiations of Phase 2.
-
debug crypto isakmp 7—Displays the ISAKMP negotiations of Phase 1.
Sample debug Output
PIX Firewall
PIX#debug crypto isakmp 7
pixfirewall# Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE_DECODE RECEIVED Mess
age (msgid=0) with payloads : HDR + SA (1) + VENDOR (13) + VENDOR (13) + VENDOR
(13) + NONE (0) total length : 256
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, processing SA payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, Oakley proposal is acceptable
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, processing VID payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, processing VID payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, Received Fragmentation VID
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, processing VID payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, Received NAT-Traversal ver 02 V
ID
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, processing IKE SA payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE SA Proposal # 1, Transform
# 2 acceptable Matches global IKE entry # 2
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, constructing ISAKMP SA payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, constructing Fragmentation VID
+ extended capabilities payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE_DECODE SENDING Message (msgid=0)
with payloads : HDR + SA (1) + VENDOR (13) + NONE (0) total length : 104
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE_DECODE RECEIVED Message (msgid=0)
with payloads : HDR + KE (4) + NONCE (10) + NONE (0) total length : 184
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, processing ke payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, processing ISA_KE payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, processing nonce payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, constructing ke payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, constructing nonce payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, constructing Cisco Unity VID pa
yload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, constructing xauth V6 VID paylo
ad
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, Send IOS VID
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, Constructing ASA spoofing IOS V
endor ID payload (version: 1.0.0, capabilities: 20000001)
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, constructing VID payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: IP = 192.168.0.2, Send Altiga/Cisco VPN3000/Cisco
ASA GW VID
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, Connection landed on tunnel_group Def
aultRAGroup
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Generat
ing keys for Responder...
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE_DECODE SENDING Message (msgid=0)
with payloads : HDR + KE (4) + NONCE (10) + VENDOR (13) + VENDOR (13) + VENDOR (
13) + VENDOR (13) + NONE (0) total length : 256
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE_DECODE RECEIVED Message (msgid=0)
with payloads : HDR + ID (5) + HASH (8) + NONE (0) total length : 60
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, process
ing ID payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, process
ing hash payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Computi
ng hash for ISAKMP
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, Connection landed on tunnel_group Def
aultRAGroup
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Freeing previ
ously allocated memory for authorization-dn-attributes
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, constru
cting ID payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, constru
cting hash payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Computi
ng hash for ISAKMP
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, constru
cting dpd vid payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE_DECODE SENDING Message (msgid=0)
with payloads : HDR + ID (5) + HASH (8) + VENDOR (13) + NONE (0) total length :
80
!--- Phase 1 completed succesfully.
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, PHASE 1 COMPL
ETED
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, Keep-alive type for this connection:
None
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, Keep-alives configured on but peer do
es not support keep-alives (type = None)
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Startin
g P1 rekey timer: 21600 seconds.
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE_DECODE RECEIVED Message (msgid=e1
b84b0) with payloads : HDR + HASH (8) + SA (1) + NONCE (10) + ID (5) + ID (5) +
NONE (0) total length : 164
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, process
ing hash payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, process
ing SA payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, process
ing nonce payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, process
ing ID payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Received remo
te Proxy Host data in ID Payload: Address 192.168.0.2, Protocol 17, Port 1701
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, process
ing ID payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Received loca
l Proxy Host data in ID Payload: Address 172.16.1.1, Protocol 17, Port 1701
!--- PIX identifies the L2TP/IPsec session.
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, L2TP/IPSec se
ssion detected.
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, QM IsRekeyed
old sa not found by addr
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE Remote Pe
er configured for crypto map: outside_dyn_map
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, process
ing IPSec SA payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, IPSec S
A Proposal # 1, Transform # 1 acceptable Matches global IPSec SA entry # 20
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE: requesti
ng SPI!
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE got
SPI from key engine: SPI = 0xce9f6e19
!--- Constructs Quick mode in Phase 2.
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, oakley
constucting quick mode
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, constru
cting blank hash payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, constru
cting IPSec SA payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, constru
cting IPSec nonce payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, constru
cting proxy ID
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Transmi
tting Proxy Id:
Remote host: 192.168.0.2 Protocol 17 Port 1701
Local host: 172.16.1.1 Protocol 17 Port 1701
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, constru
cting qm hash payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE_DECODE SENDING Message (msgid=e1b
84b0) with payloads : HDR + HASH (8) + SA (1) + NONCE (10) + ID (5) + ID (5) + N
ONE (0) total length : 144
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE_DECODE RECEIVED Message (msgid=e1
b84b0) with payloads : HDR + HASH (8) + NONE (0) total length : 48
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, process
ing hash payload
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, loading
all IPSEC SAs
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Generat
ing Quick Mode Key!
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Generat
ing Quick Mode Key!
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Security nego
tiation complete for User () Responder, Inbound SPI = 0xce9f6e19, Outbound SPI
= 0xd08f711b
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, IKE got
a KEY_ADD msg for SA: SPI = 0xd08f711b
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Pitcher
: received KEY_UPDATE, spi 0xce9f6e19
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1 DEBUG]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, Startin
g P2 rekey timer: 3059 seconds.
!--- Phase 2 completes succesfully.
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: Group = DefaultRAGroup, IP = 192.168.0.2, PHASE 2 COMPL
ETED (msgid=0e1b84b0)
Jan 02 18:26:44 [IKEv1]: IKEQM_Active() Add L2TP classification rules: ip <192.1
68.0.2> mask <0xFFFFFFFF> port <1701>
PIX#debug crypto ipsec 7
pixfirewall# IPSEC: Deleted inbound decrypt rule, SPI 0x71933D09
Rule ID: 0x028D78D8
IPSEC: Deleted inbound permit rule, SPI 0x71933D09
Rule ID: 0x02831838
IPSEC: Deleted inbound tunnel flow rule, SPI 0x71933D09
Rule ID: 0x029134D8
IPSEC: Deleted inbound VPN context, SPI 0x71933D09
VPN handle: 0x0048B284
IPSEC: Deleted outbound encrypt rule, SPI 0xAF4DA5FA
Rule ID: 0x028DAC90
IPSEC: Deleted outbound permit rule, SPI 0xAF4DA5FA
Rule ID: 0x02912AF8
IPSEC: Deleted outbound VPN context, SPI 0xAF4DA5FA
VPN handle: 0x0048468C
IPSEC: New embryonic SA created @ 0x01BFCF80,
SCB: 0x01C262D0,
Direction: inbound
SPI : 0x45C3306F
Session ID: 0x0000000C
VPIF num : 0x00000001
Tunnel type: ra
Protocol : esp
Lifetime : 240 seconds
IPSEC: New embryonic SA created @ 0x0283A3A8,
SCB: 0x028D1B38,
Direction: outbound
SPI : 0x370E8DD1
Session ID: 0x0000000C
VPIF num : 0x00000001
Tunnel type: ra
Protocol : esp
Lifetime : 240 seconds
IPSEC: Completed host OBSA update, SPI 0x370E8DD1
IPSEC: Creating outbound VPN context, SPI 0x370E8DD1
Flags: 0x00000205
SA : 0x0283A3A8
SPI : 0x370E8DD1
MTU : 1500 bytes
VCID : 0x00000000
Peer : 0x00000000
SCB : 0x028D1B38
Channel: 0x01693F08
IPSEC: Completed outbound VPN context, SPI 0x370E8DD1
VPN handle: 0x0048C164
IPSEC: New outbound encrypt rule, SPI 0x370E8DD1
Src addr: 172.16.1.1
Src mask: 255.255.255.255
Dst addr: 192.168.0.2
Dst mask: 255.255.255.255
Src ports
Upper: 1701
Lower: 1701
Op : equal
Dst ports
Upper: 1701
Lower: 1701
Op : equal
Protocol: 17
Use protocol: true
SPI: 0x00000000
Use SPI: false
IPSEC: Completed outbound encrypt rule, SPI 0x370E8DD1
Rule ID: 0x02826540
IPSEC: New outbound permit rule, SPI 0x370E8DD1
Src addr: 172.16.1.1
Src mask: 255.255.255.255
Dst addr: 192.168.0.2
Dst mask: 255.255.255.255
Src ports
Upper: 0
Lower: 0
Op : ignore
Dst ports
Upper: 0
Lower: 0
Op : ignore
Protocol: 50
Use protocol: true
SPI: 0x370E8DD1
Use SPI: true
IPSEC: Completed outbound permit rule, SPI 0x370E8DD1
Rule ID: 0x028D78D8
IPSEC: Completed host IBSA update, SPI 0x45C3306F
IPSEC: Creating inbound VPN context, SPI 0x45C3306F
Flags: 0x00000206
SA : 0x01BFCF80
SPI : 0x45C3306F
MTU : 0 bytes
VCID : 0x00000000
Peer : 0x0048C164
SCB : 0x01C262D0
Channel: 0x01693F08
IPSEC: Completed inbound VPN context, SPI 0x45C3306F
VPN handle: 0x0049107C
IPSEC: Updating outbound VPN context 0x0048C164, SPI 0x370E8DD1
Flags: 0x00000205
SA : 0x0283A3A8
SPI : 0x370E8DD1
MTU : 1500 bytes
VCID : 0x00000000
Peer : 0x0049107C
SCB : 0x028D1B38
Channel: 0x01693F08
IPSEC: Completed outbound VPN context, SPI 0x370E8DD1
VPN handle: 0x0048C164
IPSEC: Completed outbound inner rule, SPI 0x370E8DD1
Rule ID: 0x02826540
IPSEC: Completed outbound outer SPD rule, SPI 0x370E8DD1
Rule ID: 0x028D78D8
IPSEC: New inbound tunnel flow rule, SPI 0x45C3306F
Src addr: 192.168.0.2
Src mask: 255.255.255.255
Dst addr: 172.16.1.1
Dst mask: 255.255.255.255
Src ports
Upper: 1701
Lower: 1701
Op : equal
Dst ports
Upper: 1701
Lower: 1701
Op : equal
Protocol: 17
Use protocol: true
SPI: 0x00000000
Use SPI: false
IPSEC: Completed inbound tunnel flow rule, SPI 0x45C3306F
Rule ID: 0x02831838
IPSEC: New inbound decrypt rule, SPI 0x45C3306F
Src addr: 192.168.0.2
Src mask: 255.255.255.255
Dst addr: 172.16.1.1
Dst mask: 255.255.255.255
Src ports
Upper: 0
Lower: 0
Op : ignore
Dst ports
Upper: 0
Lower: 0
Op : ignore
Protocol: 50
Use protocol: true
SPI: 0x45C3306F
Use SPI: true
IPSEC: Completed inbound decrypt rule, SPI 0x45C3306F
Rule ID: 0x028DAC90
IPSEC: New inbound permit rule, SPI 0x45C3306F
Src addr: 192.168.0.2
Src mask: 255.255.255.255
Dst addr: 172.16.1.1
Dst mask: 255.255.255.255
Src ports
Upper: 0
Lower: 0
Op : ignore
Dst ports
Upper: 0
Lower: 0
Op : ignore
Protocol: 50
Use protocol: true
SPI: 0x45C3306F
Use SPI: true
IPSEC: Completed inbound permit rule, SPI 0x45C3306F
Rule ID: 0x02912E50
Troubleshoot using ASDM
You can use ASDM in order to enable logging and to view the logs.
-
Choose Configuration > Properties > Logging > Logging Setup, select Enable Logging and click Apply in order to enable logging.
-
Choose Monitoring > Logging > Log Buffer > On Logging Level, select Logging Buffer, and click View in order to view the logs.
Problem: Frequent Disconnects
Idle / Session Timeout
If the idle timeout is set to 30 minutes (default), it means that it drops the tunnel after no traffic passes through it for 30 minutes. The VPN client gets disconnected after 30 minutes regardless of the setting of idle timeout and encounters the PEER_DELETE-IKE_DELETE_UNSPECIFIED error message.
Configure idle timeout and session timeout as none in order to make the tunnel always be up and so that the tunnel is never dropped.
Enter the vpn-idle-timeout command in group-policy configuration mode or in username configuration mode in order to configure the user timeout period:
hostname(config)#group-policy DfltGrpPolicy attributes hostname(config-group-policy)#vpn-idle-timeout none
Configure a maximum amount of time for VPN connections with the vpn-session-timeout command in group-policy configuration mode or in username configuration mode:
hostname(config)#group-policy DfltGrpPolicy attributes hostname(config-group-policy)#vpn-session-timeout none
Troubleshoot Windows Vista
Simultaneous User
Windows Vista L2TP/IPsec introduced some architectural changes that prohibited more than one simultaneous user from being connected to a head-end PIX/ASA. This behavior does not occur on Windows 2K/XP. Cisco has implemented a workaround for this change as of Release 7.2(3) and greater.
Vista PC Not Able to Connect
If the Windows Vista computer is not able to connect the L2TP server, then verify that you have configured ONLY mschap-v2 under the ppp-attributes on the DefaultRAGroup.
Related Information
- Most Common L2L and Remote Access IPSec VPN Troubleshooting Solutions
- Cisco PIX 500 Series Security Appliances
- Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliances
- Cisco PIX Firewall Software Product Support
- Cisco Secure PIX Firewall Command References
- RADIUS Support Page
- IPSec Negotiation/IKE Protocols Support Page
- Requests for Comments (RFCs)

- Layer Two Tunnel Protocol (L2TP)
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)

















 Feedback
Feedback